Biology B4: PHOTOSYNTHESIS/RESPIRATION
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
photosynthesis, respiration, metabolism
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What is photosynthesis?
The endothermic process by which plants absorb energy from light in order to convert water and carbon dioxide into oxygen and glucose.
Symbol equation for photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
How are plants adapted for photosynthesis?
Several chloroplasts/chlorophyll
Wide surface area
Thin leaves
Stomata/air spaces in leaf
How does chlorophyll aid with photosynthesis?
Green pigment for increased absorption of light, many layered palisade cells contain many chloroplasts, maximum light energy is absorbed.
How does a wide surface area aid with photosynthesis?
Maximises light intake and diffusion of carbon dioxide particles into the leaf.
How do thin leaves aid with photosynthesis?
Minimises diffusion distance for both carbon dioxide intake and oxygen release.
How does stomata aid with photosynthesis?
Small holes in the lower epidermis for efficient gas exchange - CO2 diffuses into leaf, oxygen diffuses out of leaf
What are the LIMITING FACTORS that affect rate of photosynthesis?
Temperature
Light Intensity
Carbon Dioxide (and Chlorophyll)
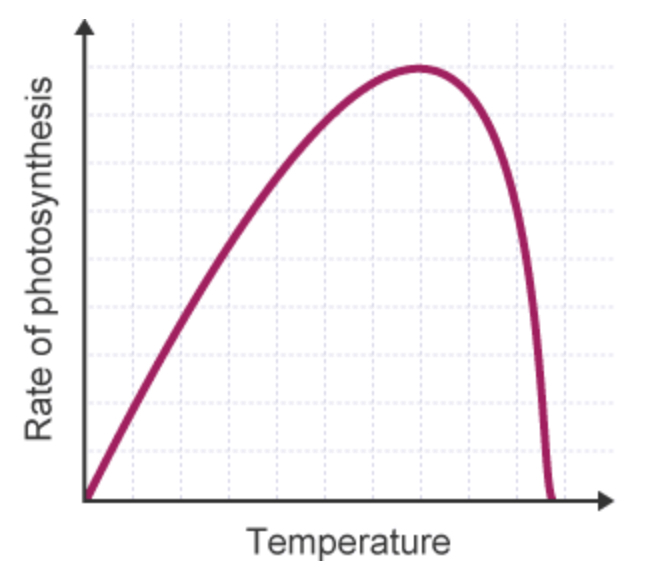
How is TEMPERATURE a limiting factor of photosynthesis?
LOW temperature environment: then there is INSUFFICIENT energy for a HIGHER rate of photosynthesis - LESS COLLISIONS between enzymes and substrates
TOO HIGH temperatures: DENATURED enzymes, rate of reaction FALLS
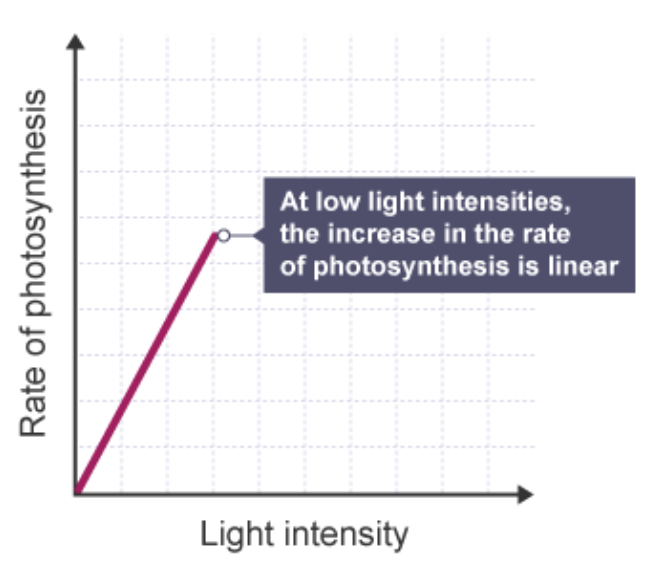
How is LIGHT a limiting factor of photosynthesis?
Light = ENERGY source for photosynthesis: As intensity increases, rate INCREASES until OTHER FACTORS are limiting - therefore rate doesn’t change, graph LEVELS OFF (plateau)
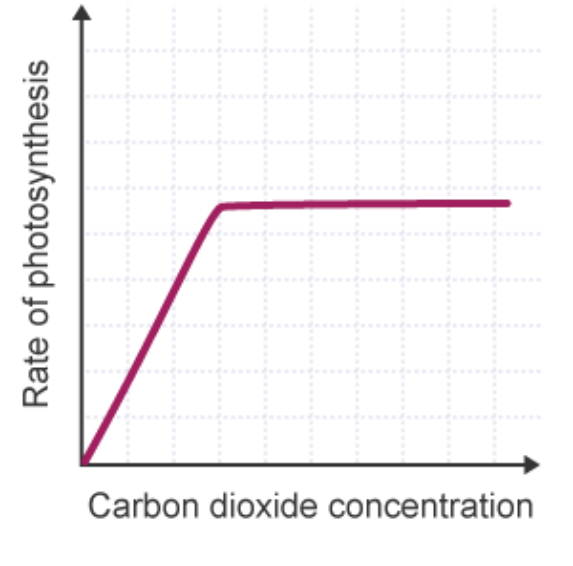
How is CO2 CONCENTRATION a limiting factor of photosynthesis?
Carbon Dioxide = REACTANT of photosynthesis: higher quantities = INCREASED rate until other factor becomes limiting, graph plateaus.
Why may industries not always maximise rate of photosynthesis?
In industry, photosynthesis at the highest possible rate is not always COST EFFECTIVE
What is the inverse square law? (HIGHER ONLY)
As the distance increases, light energy DECREASES
As plant is moved further away, it will receive less light due to light spreading out, less CONCENTRATION reaching leaf. 1/d squared
REQUIRED PRACTICAL - photosynthesis
Place stem of POND WEED into a water filled test tube
Add a FIXED CONCENTRATION of SODIUM CARBONATE (adds CO2 to water)
Place pond weed a FIXED DISTANCE from the light (10cm)
Count the number of bubbles produced in 1MIN using STOPCLOCK (or use GAS SYRINGE to improve ACCURACY)
Repeat at 20, 30, 40 and 50cm
Repeat steps 3-5 THREE TIMES to IDENTIFY ANOMALIES/ CALCULATE MEAN to plot in results table
Plot LINE GRAPH as data is CONTINUOUS.
What are the uses of glucose in plants?
Making STARCH
Respiration
Making CELLULOSE for CELL WALLS
Making AMINO ACIDS
Effects of NITRATE DEFICIENCY in plants
Less AMINO ACIDS made → less PROTEINS → STUNTED GROWTH
Effects of MAGNESIUM DEFICIENCY in plants
Less CHLOROPHYLL made → less LIGHT ABSORBED → less PHOTOSYNTHESIS → less GLUCOSE → less RESPIRATION → less ENERGY → less PROTEINS made → STUNTED GROWTH
What is AEROBIC respiration?
Exothermic reaction (opposite to photosynthesis) that releases ENERGY, using GLUCOSE and OXYGEN to produce CARBON DIOXIDE and WATER
Symbol equation for AEROBIC respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ENERGY (ATP)
Uses for AEROBIC RESPIRATION
To RELEASE ENERGY FOR:
CONVERTING SMALLER molecules into LARGER (bond forming)
CONVERTING LARGER molecules into SMALLER (bond breaking)
Muscle CONTRACTION (movement)
PROTEIN synthesis
Controlling BODY TEMPERATURE
ACTIVE TRANSPORT
What is ANAEROBIC respiration?
Form of respiration that DOES NOT require oxygen, therefore producing LESS energy than aerobic
Anaerobic respiration in ANIMALS
Glucose (C6H12O6) → LACTIC ACID (2C3H6O3)
Anaerobic respiration in PLANTS/YEAST
Glucose (C6H12O6) → ethanol (2C2H5OH) + carbon dioxide (2CO2)
Used in YEAST to make alcohol and bread (FERMENTATION)
Oxygen debt (HIGHER ONLY)
The amount of EXTRA OXYGEN the body needs after exercise to react with and BREAK DOWN lactic acid to remove it from cells
How is OXYGEN DEPT paid? (HIGHER ONLY)
Lactic acid is transported through BLOODSTREAM to the LIVER, where lactic acid is OXIDISED into CO2 and WATER or converted into glucose (then GLYCOGEN)
What is the body’s response to exercise?
Increased MUSCLE CONTRACTION → increased MOVEMENT → more ENERGY REQUIRED → more RESPIRATION (more OXYGEN required) → increased BREATHING RATE → increased HEART RATE to DISTRIBUTE REACTANTS from bloodstream, remove CO2 more QUICKLY
What is the body’s response to VIGOROUS exercise?
INSUFFICIENT oxygen supply → ANAEROBIC respiration → less ENERGY for muscle contraction → buildup of LACTIC ACID → MUSCLE FATIGUE + OXYGEN DEBT
Effect of an INCREASED HEART RATE
Allows more blood carrying GLUCOSE + OXYGEN to get to MUSCLE CELLS for AEROBIC RESPIRATION
SIMILARITIES of aerobic and anaerobic respiration
both use GLUCOSE as a reactant
both PRODUCE ENERGY
both are EXOTHERMIC REACTIONS
DIFFERENCES of aerobic and anaerobic respiration
Aerobic takes place in MITOCHONDRIA whereas anaerobic doesn’t (usually in CYTOPLASM)
Aerobic in the PRESENCE of oxygen, anaerobic in the ABSENCE of oxygen
Unlike aerobic, anaerobic causes MUSCLE FATIGUE, therefore only taking place for SHORT PERIODS OF TIME in an EMERGENCY
What is metabolism?
The sum of ALL the reactions that occur in a LIVING organism.
Metabolism includes…
Converting GLUCOSE into starch, glycogen and cellulose
Making LIPIDS
Making AMINO ACIDS
RESPIRATION
Making UREA from EXCESS proteins
What factors affect metabolism?
AGE - the older you get, the SLOWER your metabolism
GENES - some people INHERIT a slower metabolism than usual and put on weight easier
TEMPERATURE - ENZYME action
BODY COMPOSITION (proportion of MUSCLE:FAT)
SEX - MEN have a HIGHER metabolism than women