reflex arcs
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
reflex arc
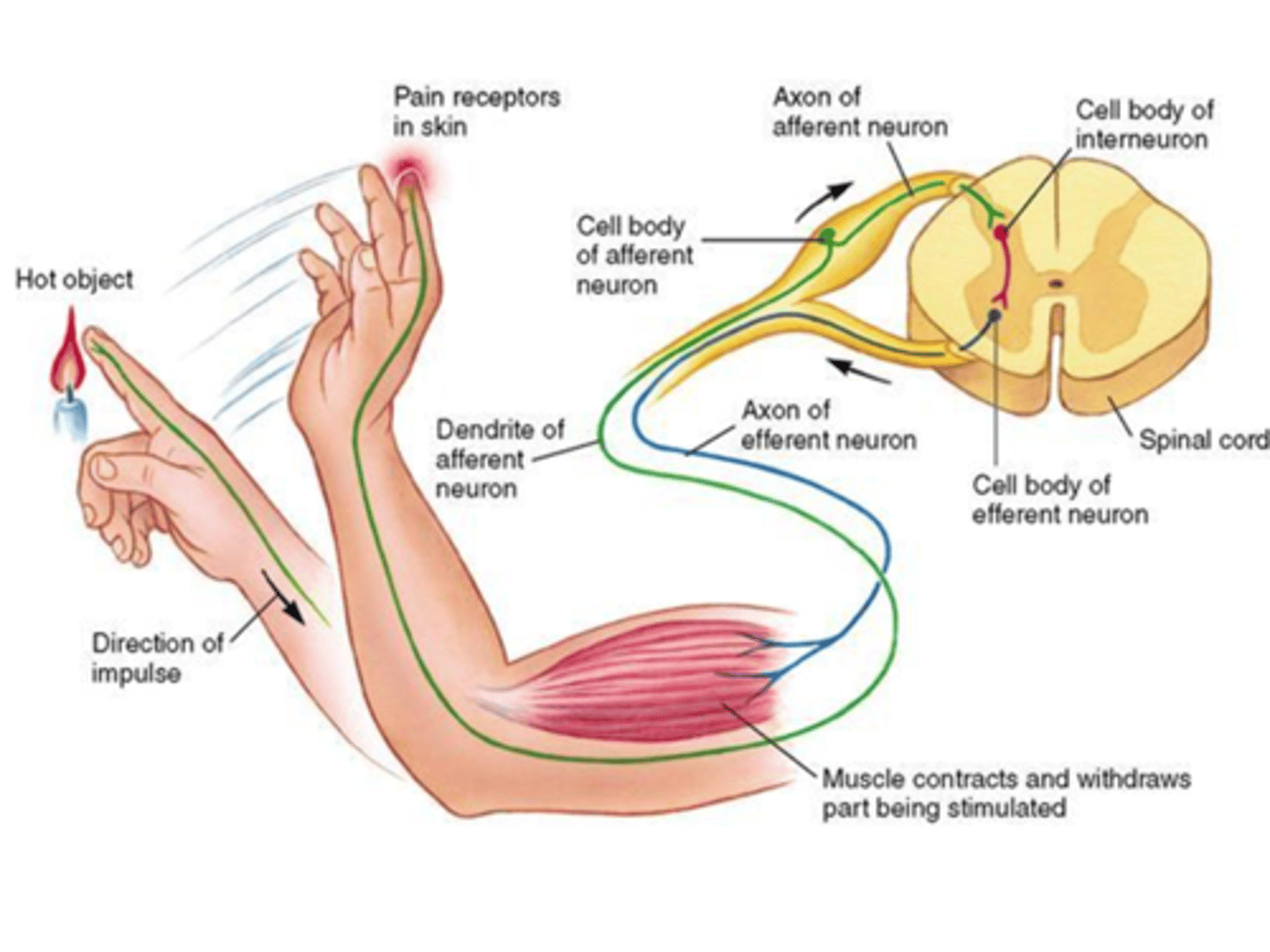
A reflex arc is the communication of this information from the initial stimulus to the final response. This happens in five stages:
1.Receptorthe dendrites of the sensory neuron are the receptors, when it receives a stimulus, such as pain, light or heat it responds by triggering a nerve impulse.
●
2)Sensory neuron (afferent)the impulse travels along to the axon terminal of the sensory neuron; these are in the white matter of the spinal cord or brain stem.
3. Integrating centreregions of grey matter within the CNS, this can be a single synapse between sensory and motor neurons or there can be more than one
●
4. Motor neuron (efferent)impulses pass from the integrating centre out of the CNS along the motor neuron to the effector
●
5. Effector
the part of the body that responds to the motor nerve impulse, a muscle or a gland
reflex arc in action
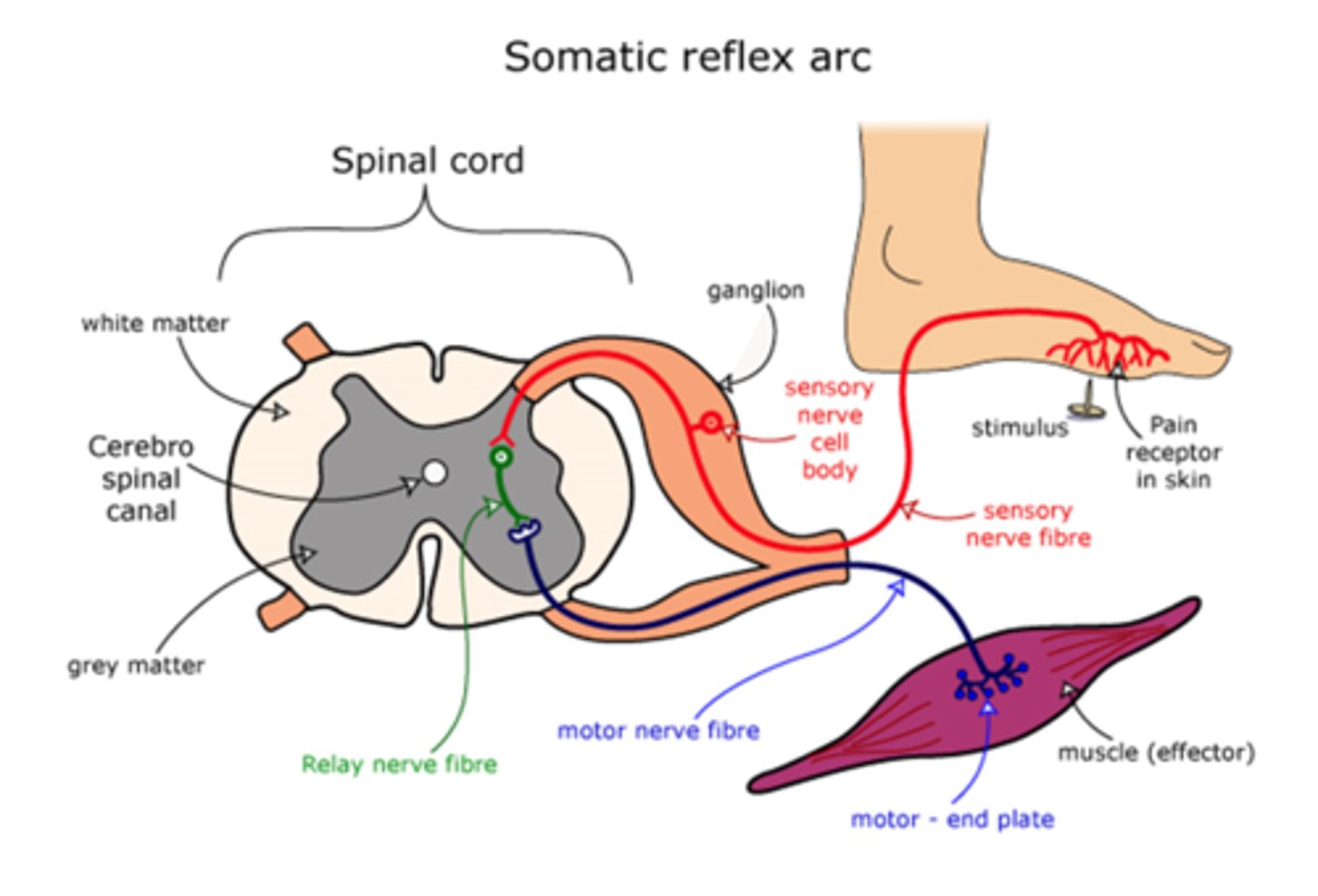
Reflex Terminology
Monosynaptic reflex arc – a pathway with only one synapse in the CNS.
Polysynaptic reflex arc – a pathway with more than two types of neuron and more than one CNS synapse.
Ipsilateral reflex arc – sensory impulses enter the spinal cord on the same side as motor impulses leave it.
Contralateral reflex arc – sensory impulses enter one side of the spinal cord and motor impulses exit on the opposite side.
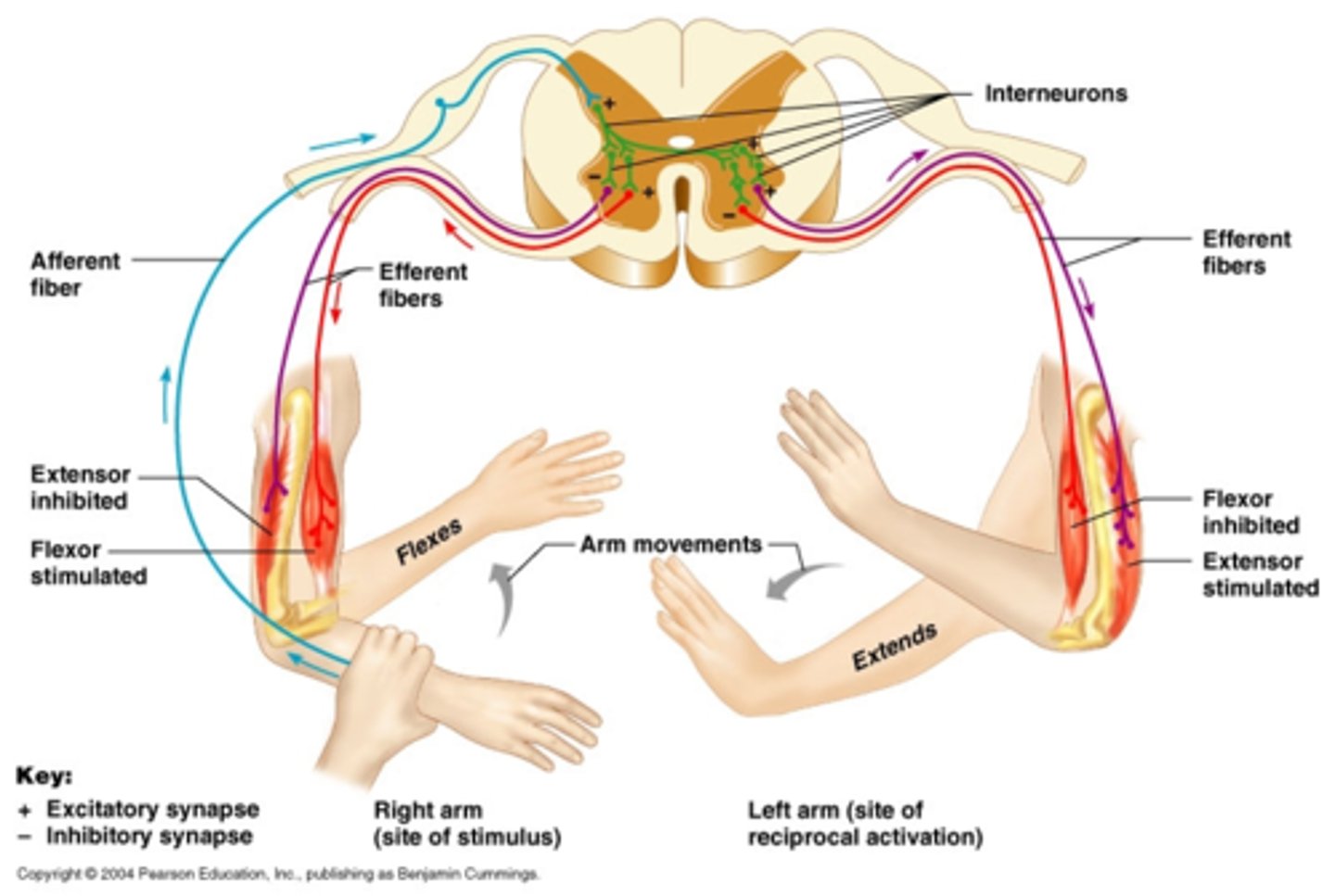
Reciprocal innervation – if a stimulus causes the flexor muscle of a limb to contract, it may also cause the extensor muscle of the same limb to relax, and also extend the opposite limb to maintain balance.
Intersegmental reflex arc – sensory impulses from one neuron go up and down the spinal cord and activate association neurons in different segments of the spinal cord.
pic
pic
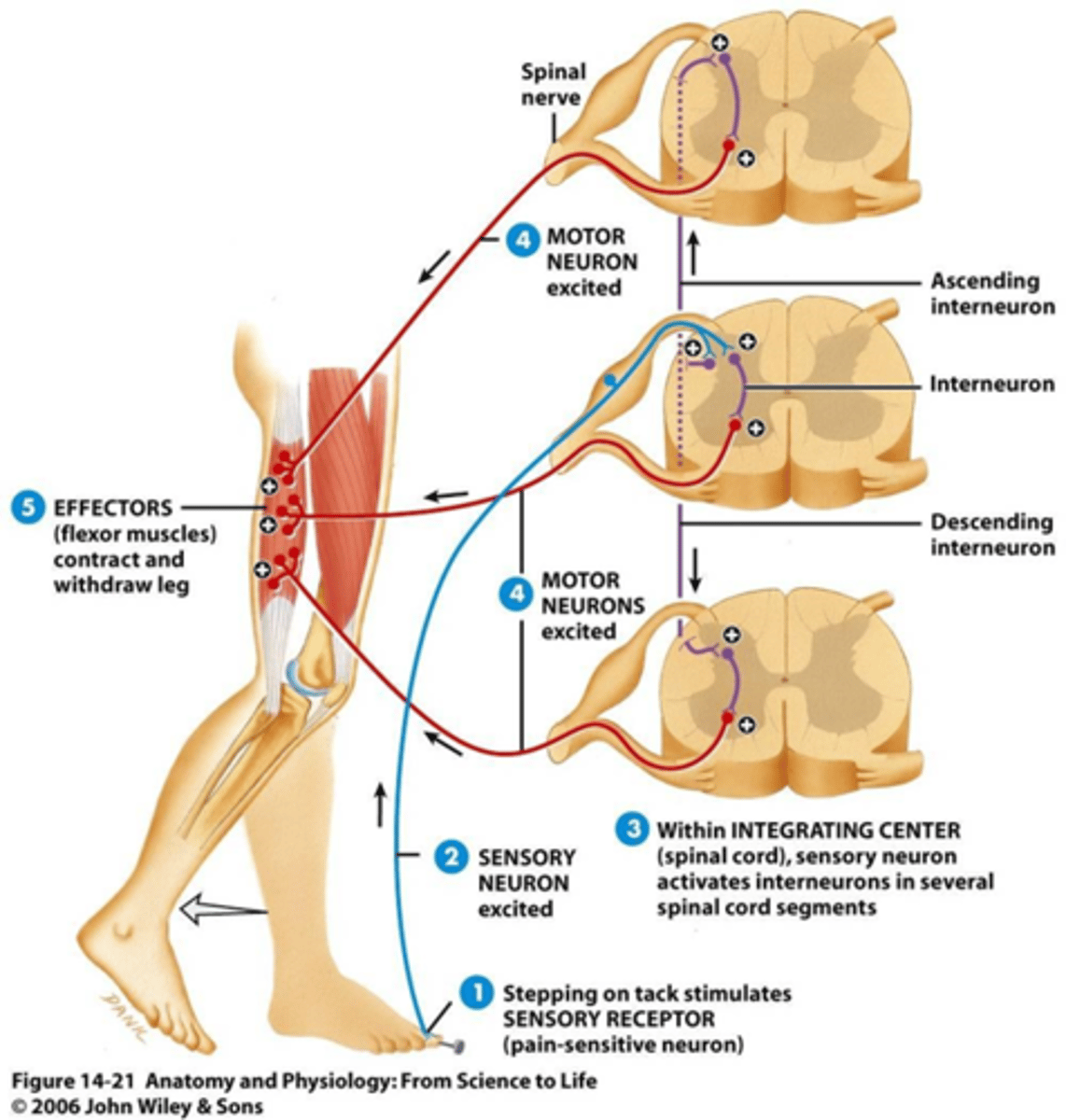
4 Somatic Reflexes
1.The Flexor Reflex (Withdrawal)
●
2.The Stretch Reflex (Patellar)
●
3.The Tendon Reflex
●
4.The Crossed Extensor Reflex
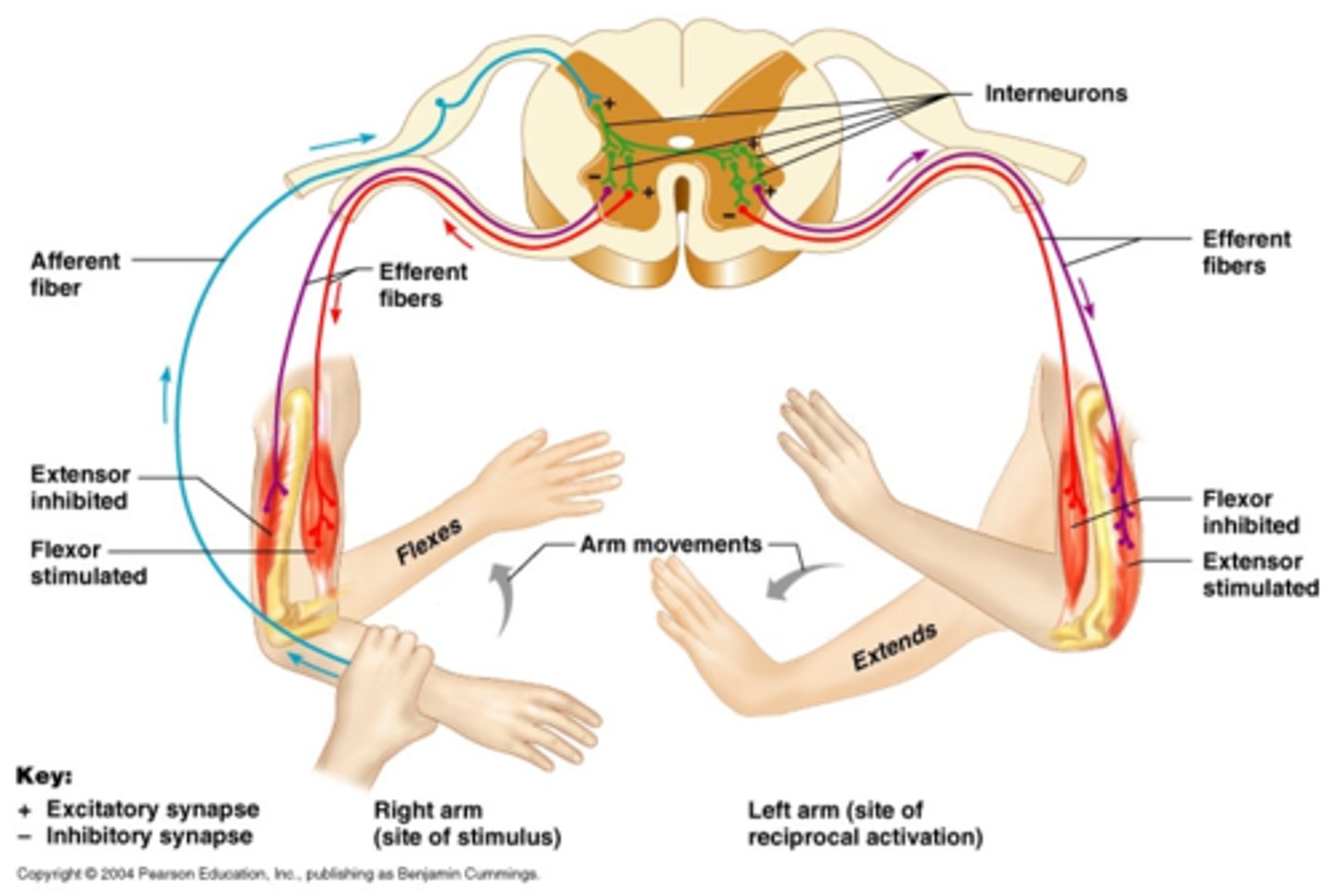
Flexor Reflex - 1
The Flexor reflex is used to withdraw a limb from danger
It is polysynaptic and ipsilateral and involves reciprocal innervation of different muscle pairs
One reflex arc causes contraction of the flexor muscle
At the same time, there is a polysynaptic reflex to the extensor (antagonistic) muscle causing it to relax
In the case of the arm, when the biceps contract the triceps will relax.
Flexor Reflex - 2
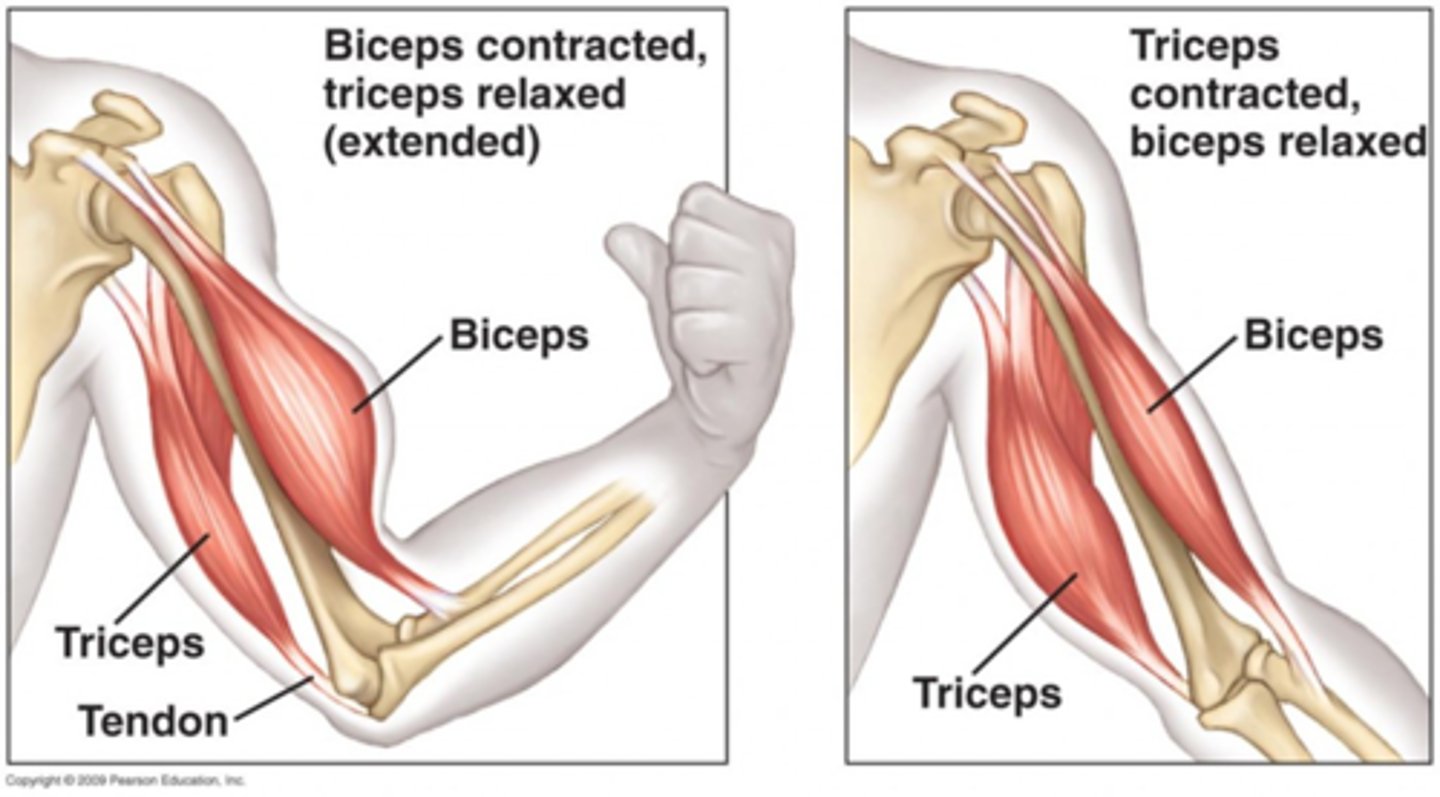
Flexor Reflex - 3
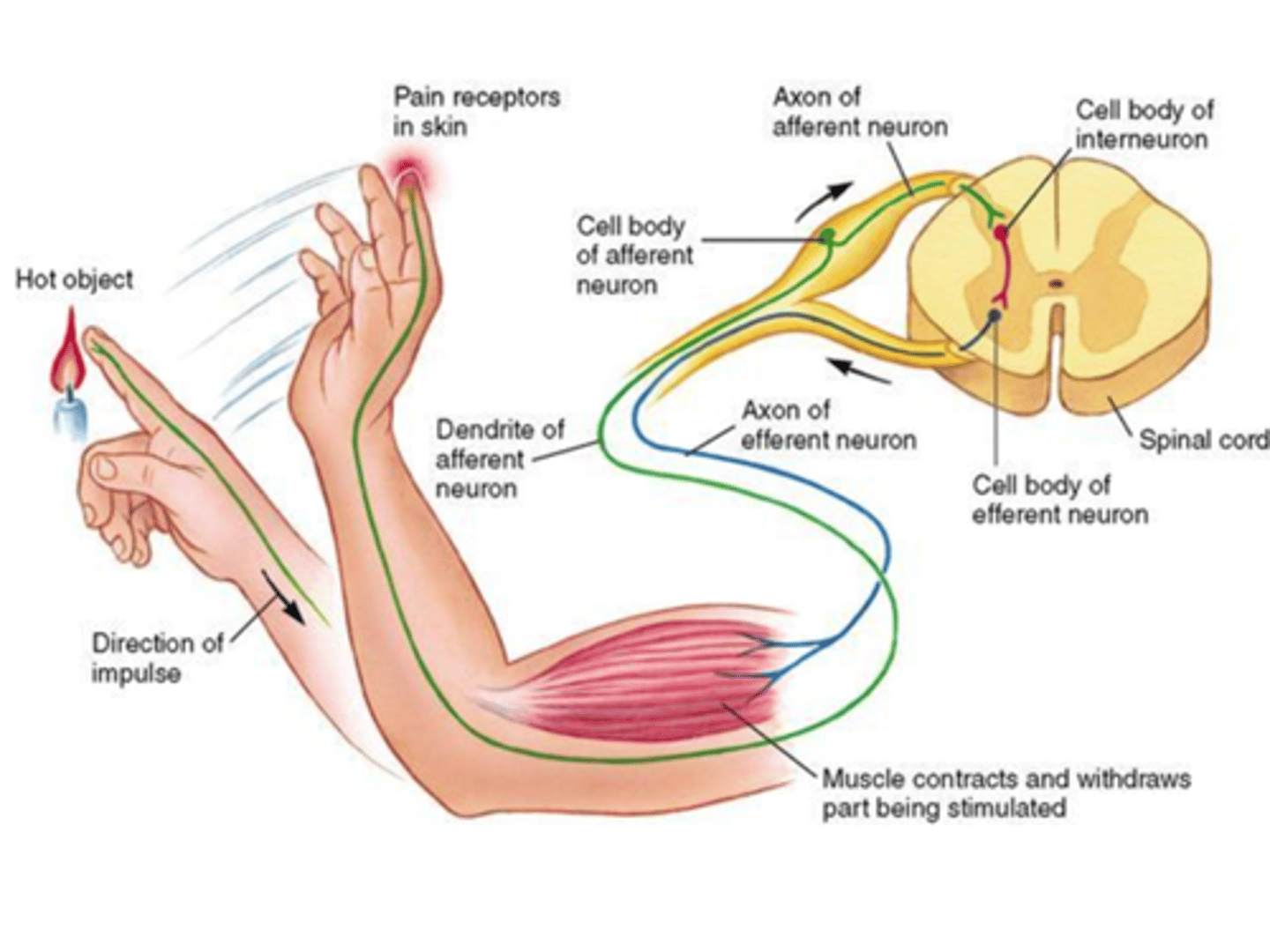
Stretch Reflex - 1
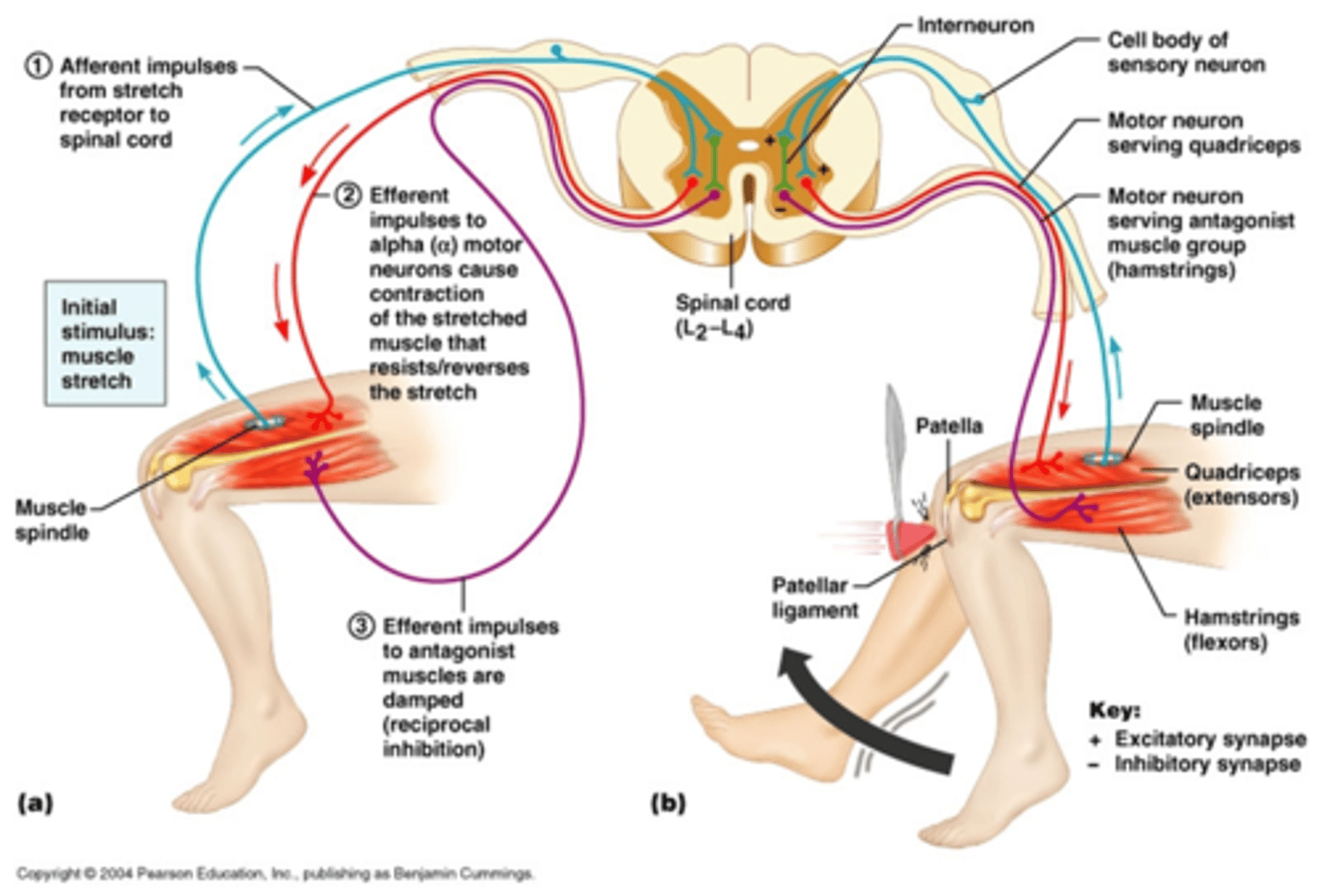
The stretch reflex responds to stretching of the muscle (also called Deep tendon reflex)
It is detected by receptors in the muscle called muscle spindles
It is monosynaptic and ipsilateral and helps regulate muscle length
Eg Lean to one side - postural muscles connected to vertebral column will stretch - in response the stretch reflex will be initiated to counteract and restore balance
Stretch Reflex - 2
The Tendon Reflex - 1
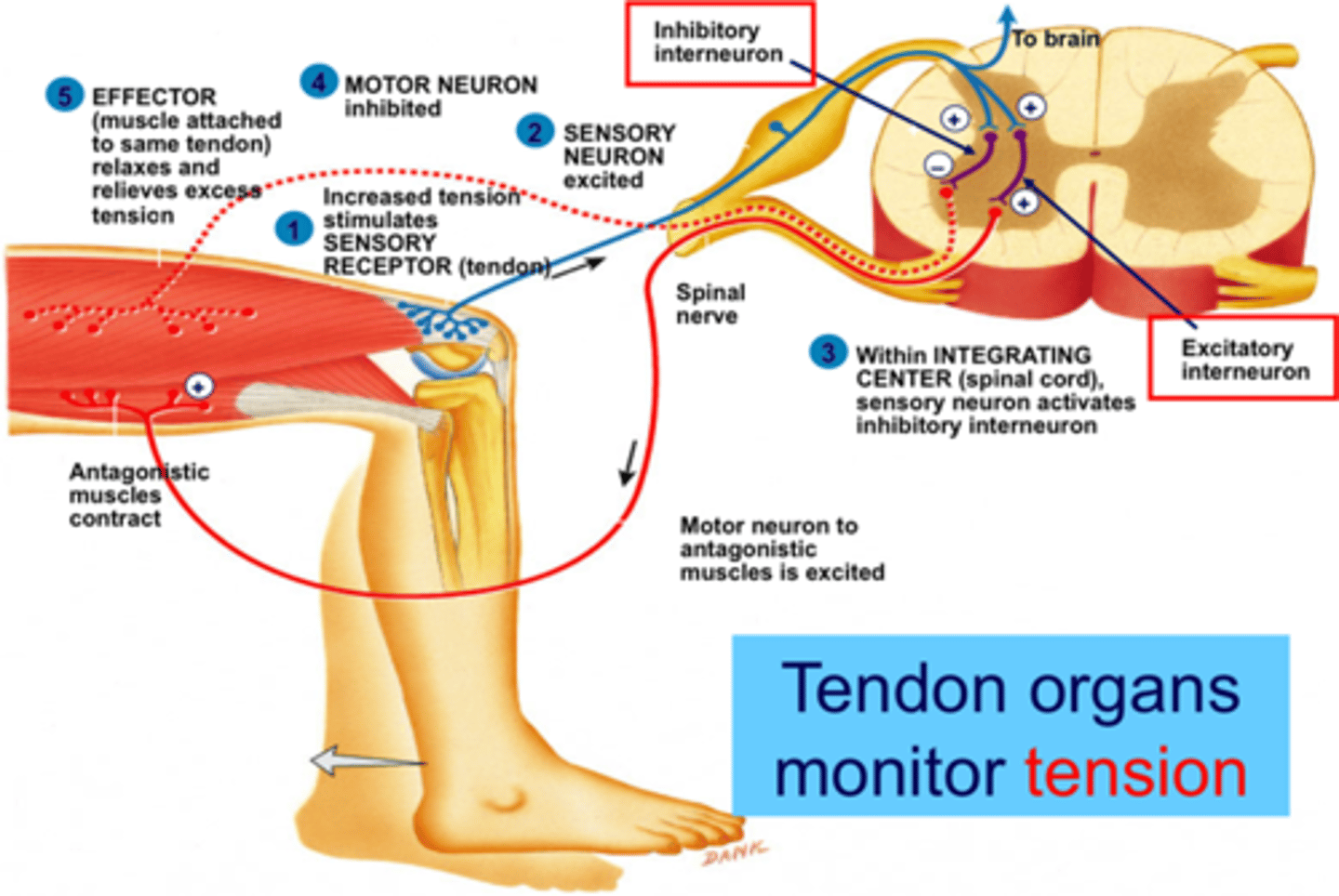
Also called the Golgi Tendon Reflex.
This is the inverse of the stretch reflex.
In the tendon reflex, an increase in the tension of a tendon stimulates the tendon organ, which causes an impulse to go from the sensory neuron, through the integrating centre where it synapse with an inhibitory association neuron, and inhibits the motor neuron leading to the muscle, causing it to relax.
This mechanism, like most reflexes is protective and protects the muscle from damage due to excessive tension.
The Tendon Reflex - 3
The Crossed Extensor Reflex - 1
The crossed extensor reflex extends the opposite limb to prevent the individual losing balance when the limb experiencing pain is quickly withdrawn.
This reflex is polysynaptic, contralateral and can be intersegmental.
The Crossed Extensor Reflex - 2
Autonomic/Visceral Reflexes
}Autonomic reflexes are responses that occur when nerve impulses pass through an autonomic reflex arc
}
}They follow the same basic pattern of transmission as somatic reflexes - receptor, sensory neuron, integrating centre, motor neuron and effector
}
}The integrating centre is located in the lower parts of the brain (hypothalamus or medulla) or even in the spinal cord
}
}Effectors will be smooth or cardiac muscle
Examples of Autonomic Reflexes
}Gastrocolic Reflex
}increase in motility of the colon in response to stretch in the stomach and byproducts of digestion in the small intestine
}
}Baroreceptor Reflex
}Maintains blood pressure at a steady state in the body
}
}Pupillary Light Reflex
}Constriction of the pupil in response to bright light