Local Anesthetics- Pharmacology- Exam 2
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Ester Local Anesthetics Drugs
Procaine
Benzocaine
Cocaine
Amide Local Anesthetics
Articaine
Lidocaine
Bupivacaine
Ropivacaine
What are drugs that produce transient and reversible loss of sensation of feeling in a limited area of the body without loss of consciousness
Local Anesthetics
-Delivered directly to the target tissue
Are Local Anesthetics vasoconstrictors or vasodilaots
Some have additional vasoconstrictor activity (Cocaine)
Others cause vasodilation and get combined with a vasoconstrictor to keep it localized
What only diminishes or terminates the effect of the anesthetic
Systemic circulation
Recovery is spontaneous with few side effects compared to general anesthetics
LA MOA
Prevent the generation and conduction of nerve impulses by blocking NA channels
-Blocks Voltage-gated NA channels from the Inside of nerve cell
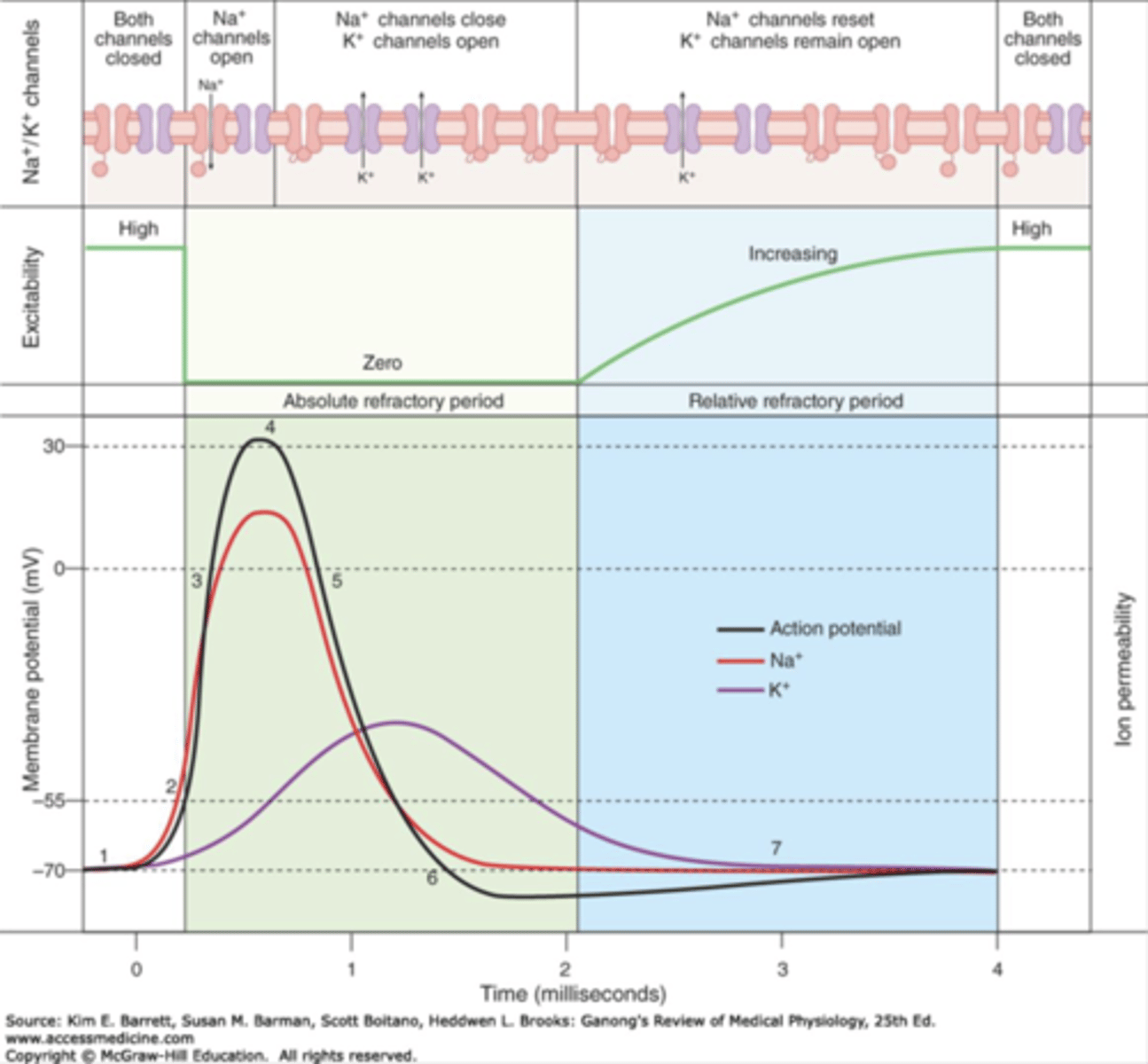
Action Potential Mechanism
1) Resting membrane potentiaal ~ -70mV
2) Excitation causes Na INflux in a depolarizing current till AP threshold is reached
3) Maximal depolarization
4) Na conductance decreases & K Increases
5) Movement of K+ out of cell repolarizes the cell
Charge of LA
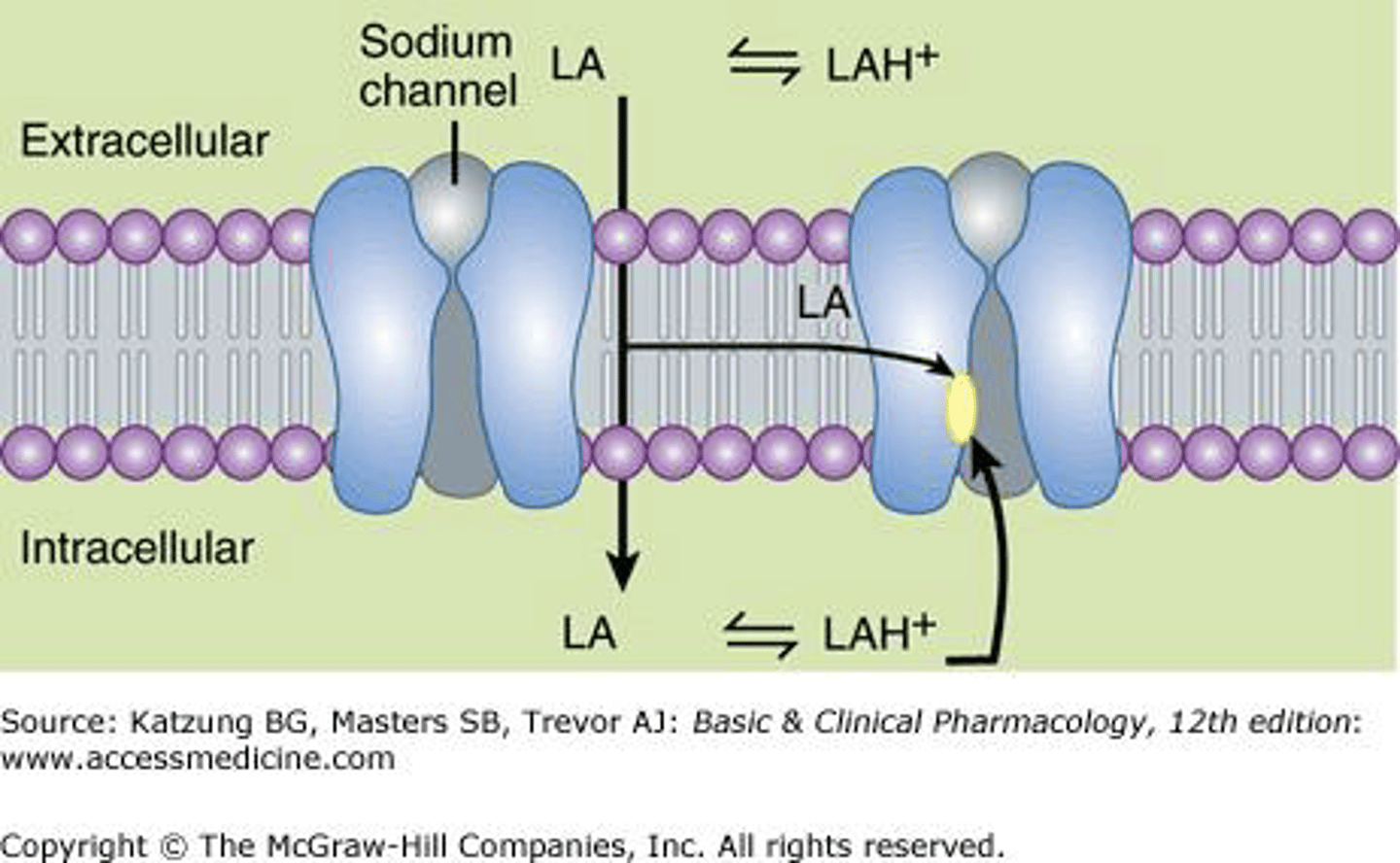
Exist as both nonionized base (high pKA) and cationic form
Injected as a charged hydrochloride salt (water-soluble ionized form)
- non-ionized base crosses sheath/membrane
Re-equilibration at the internal pH of the axon results in the cationic form being quantitatively the principal form of anesthetic on the internal surface of the membrane
Cationic form enters NA+ channel from internal surface to block NA movement
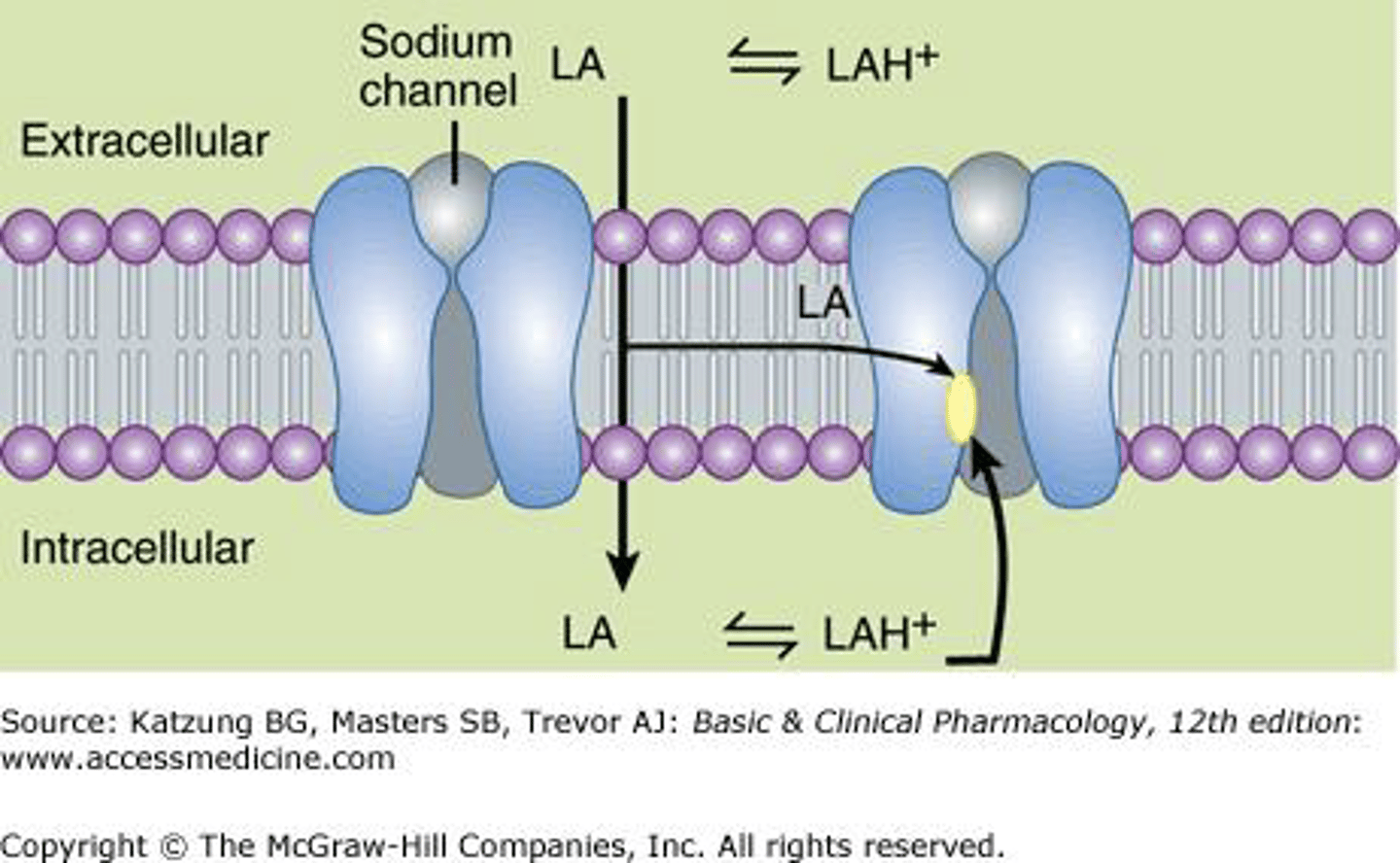
What form of the LA enters the NA+ channel from the internal surface to block NA+ movement
Cationic form
LA binds to the inner domain of Na channel to prolong _____________ state
Inactive state
Works better on nerves that fire rapidly (pain fibers)
Slows recovery time of 10-100X
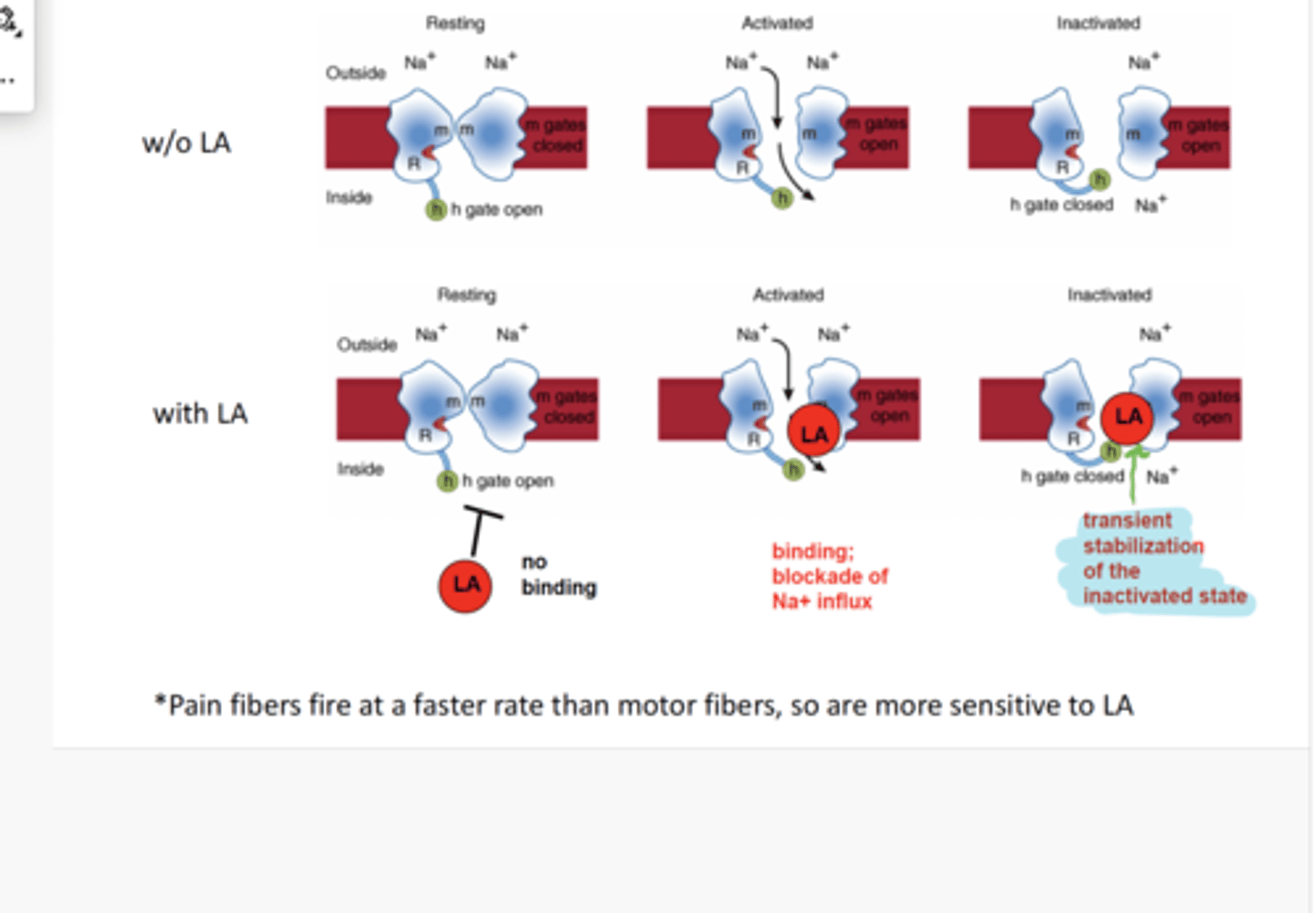
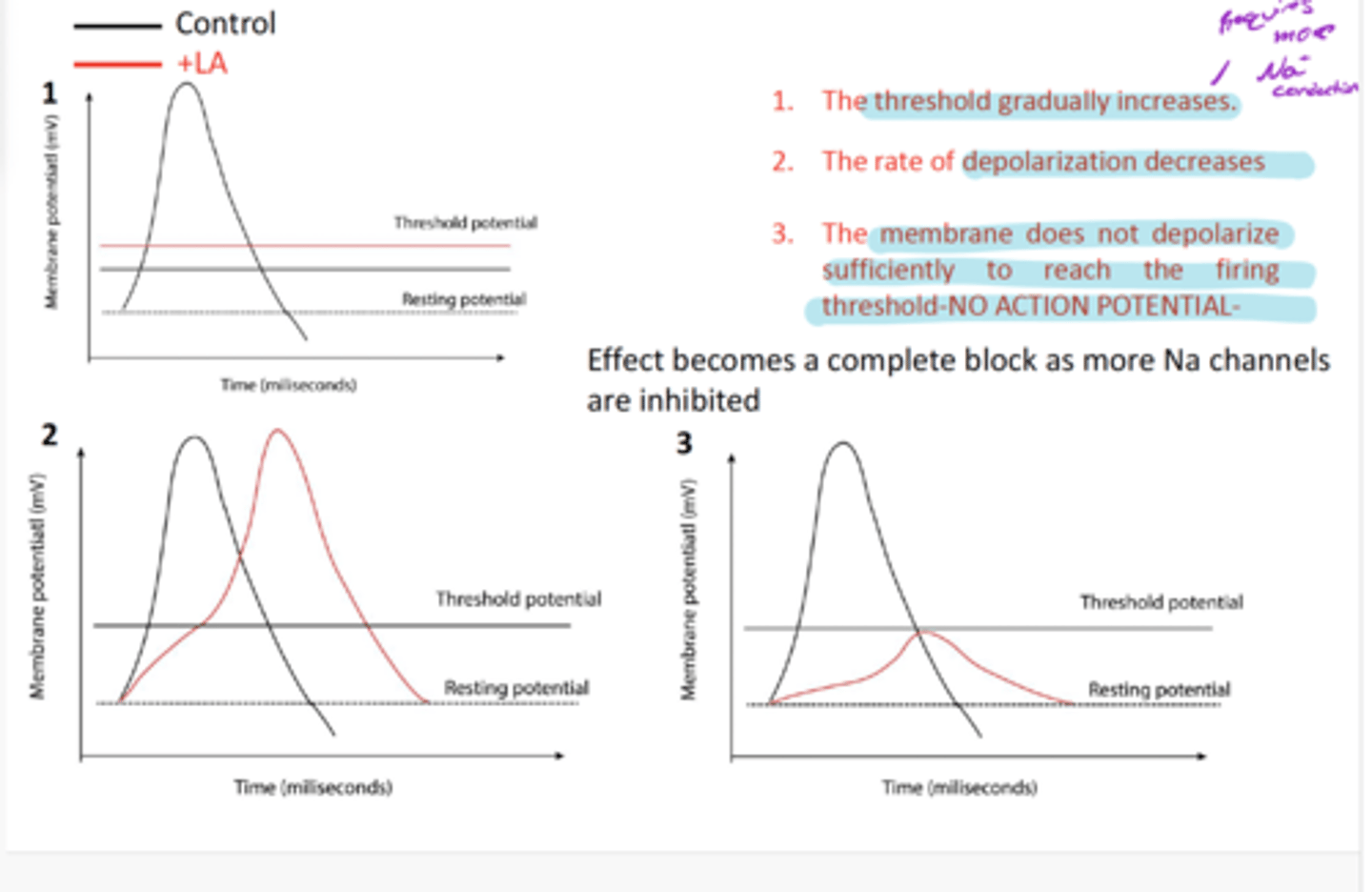
How LA changes nerve impulses
1) Threshold gradually increases (requires more Na+ conduction)
2) The rate of depolarization decreases
3) Membrane does not depolarize sufficiently to reach the firing threshold- NO AP
Becomes a complete block as more Na channels are inhibited
Variable Affecting LA action
Differential Sensitivity of nerve fibers
Physiochemical properties of drug
pH
Biotransformation (drug metabolism)
Effect of Vasoconstrictors
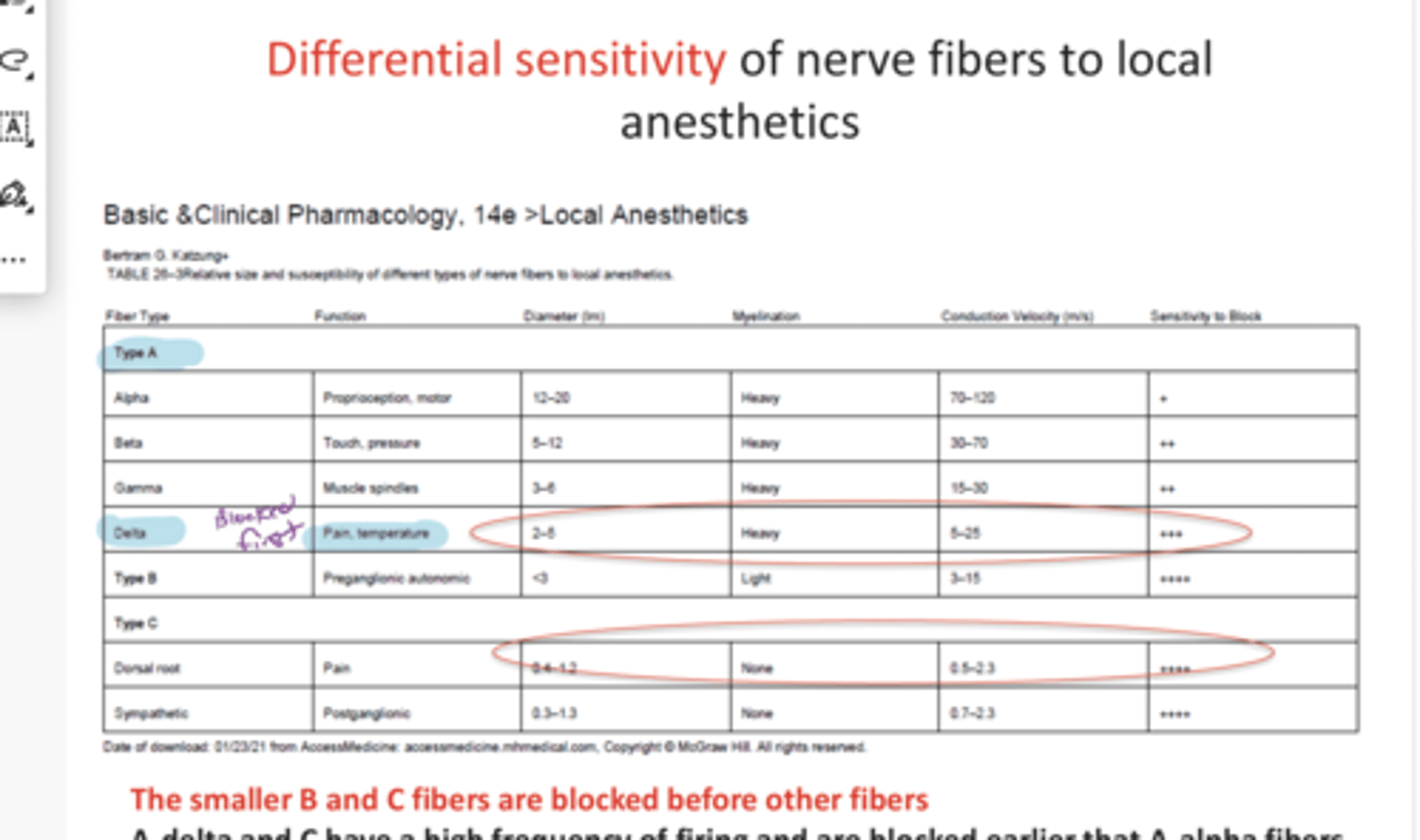
Differential Sensitivity of Nerve Fibers
Preferential block of small diameter fibers- usually propagate a signal over short distance
Myelinated nerves take 2-3 nodes of Ranvier to block
Rapid-firing pain fibers are blocked early
Preganglionic B fibers are blocked before the smaller un-myelinated C fibers that transmit pain signals, but together these are blocked earlier than other nerve fibers
Do myelinated of non-myelinated nerves block earlier
Myelinated nerves blocked early
How nodes of Ranvier does a LA need to bind to cause LA
2-3 nodes of Ranvier to block
-thinner nerve fibers have more nodes per unit length -> LA have more access -> more effective
The smaller ___ and __ fibers are blocked before other fibers
B & C
A-delta and C fibers have a high frequency of firing and are blocked before A-a fibers
Pain>Temp>Touch>Pressure>Motor
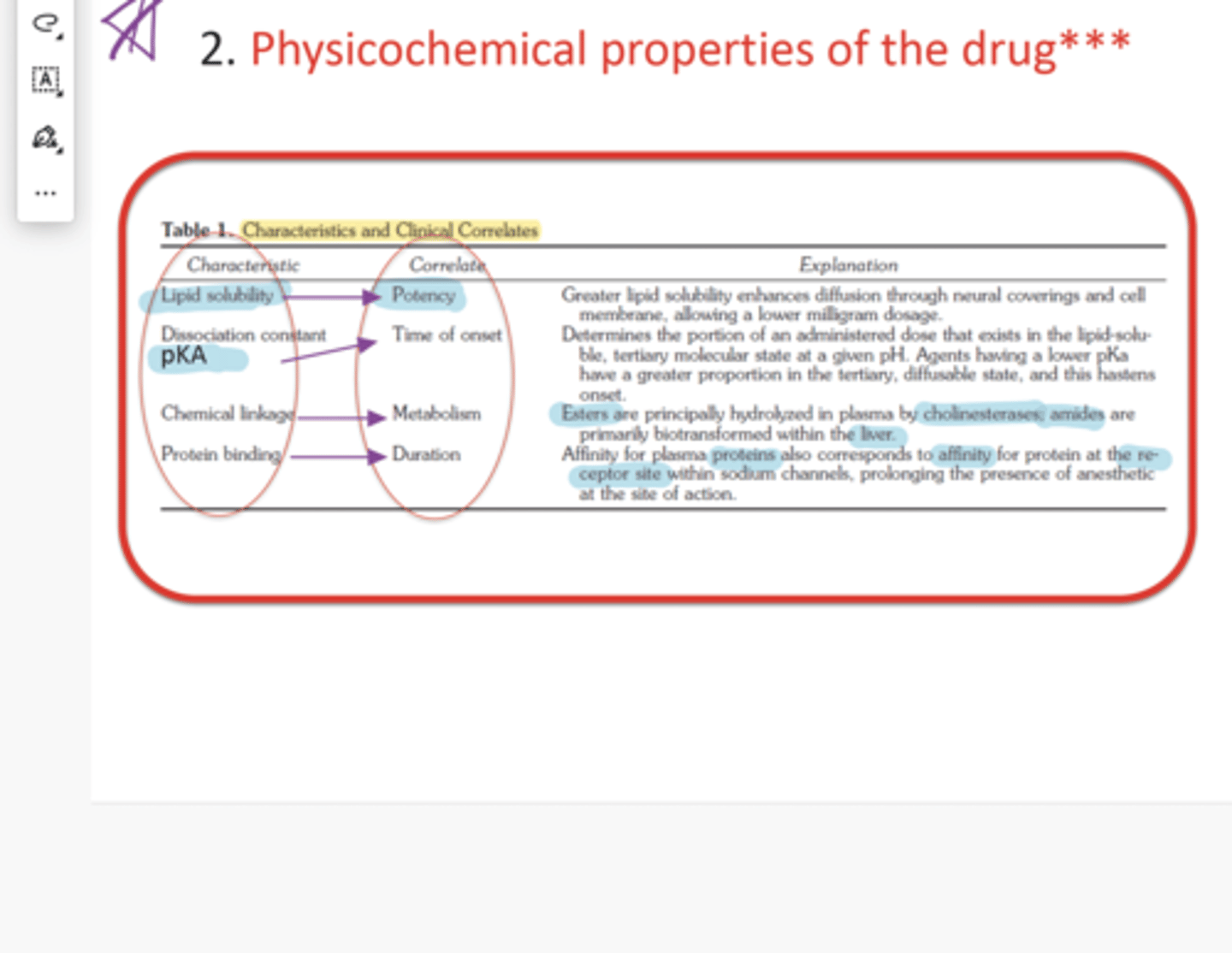
The lipid solubility of LA correlates with what physiochemical property
Potency
-Greater lipid solubility enhances diffusion through neural coverings and cell membrane, allowing a lower mg dose
pKA/Dissociation Constant of LA correlates with what physiochemical property
Time of onset
-Determines dose that exists in lipid-soluble, tertiary molecule state at given pH
-Agents with lower pKA have greater proportion in the tertiary, diffusible state, and hastens onset
Chemical Linkage of LA correlates with what physiochemical property
Metabolism
-Esters are hydrolyzed by cholinesterases; amines biotransformed in liver
The protein binding of LA correlates with the physiochemical property
Duration
-Plasma Protein affinity corresponds with receptor site affinity within Na channels
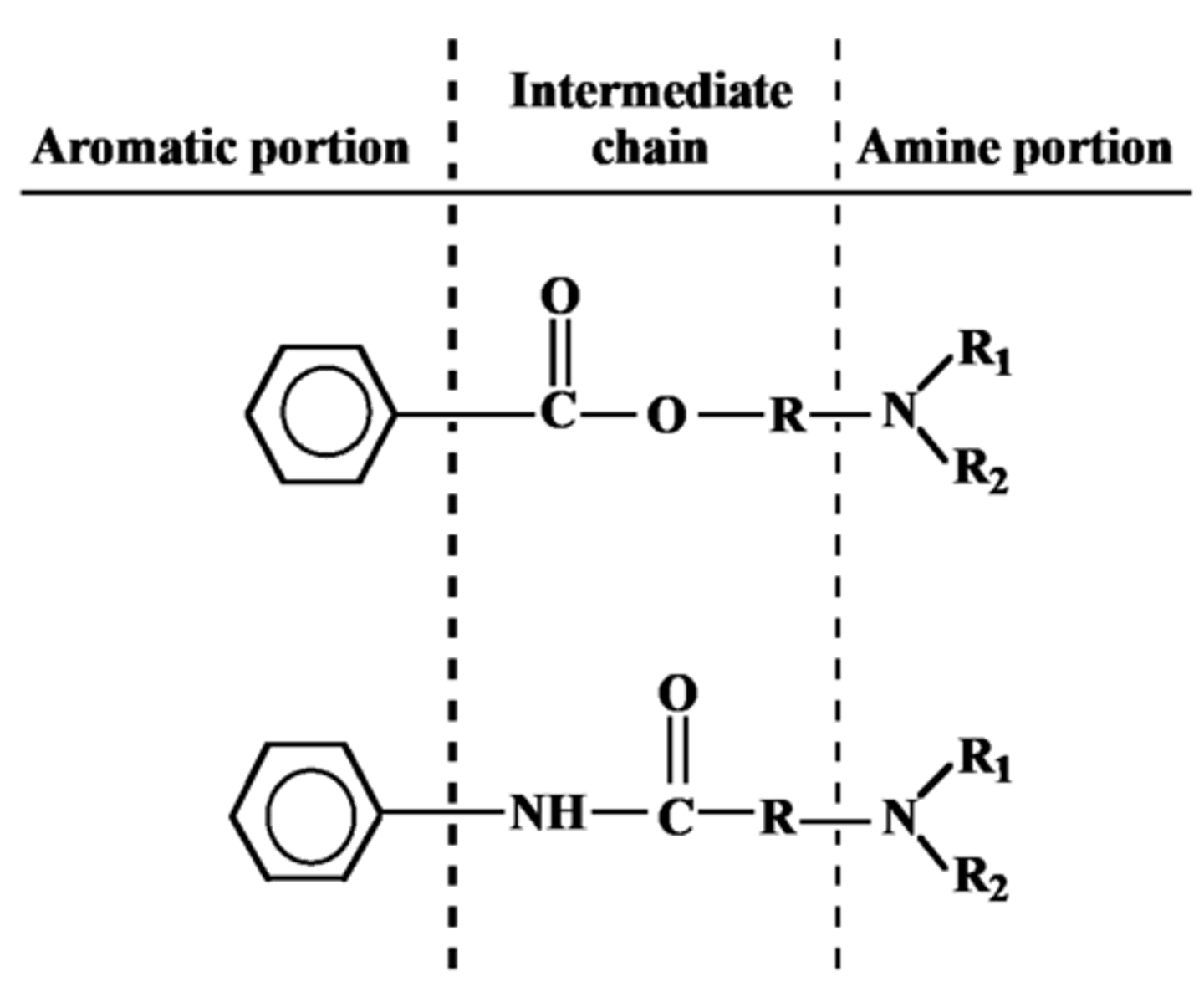
General Structure of LA
Aromatic Portion
Intermediate chain
Amine Portion
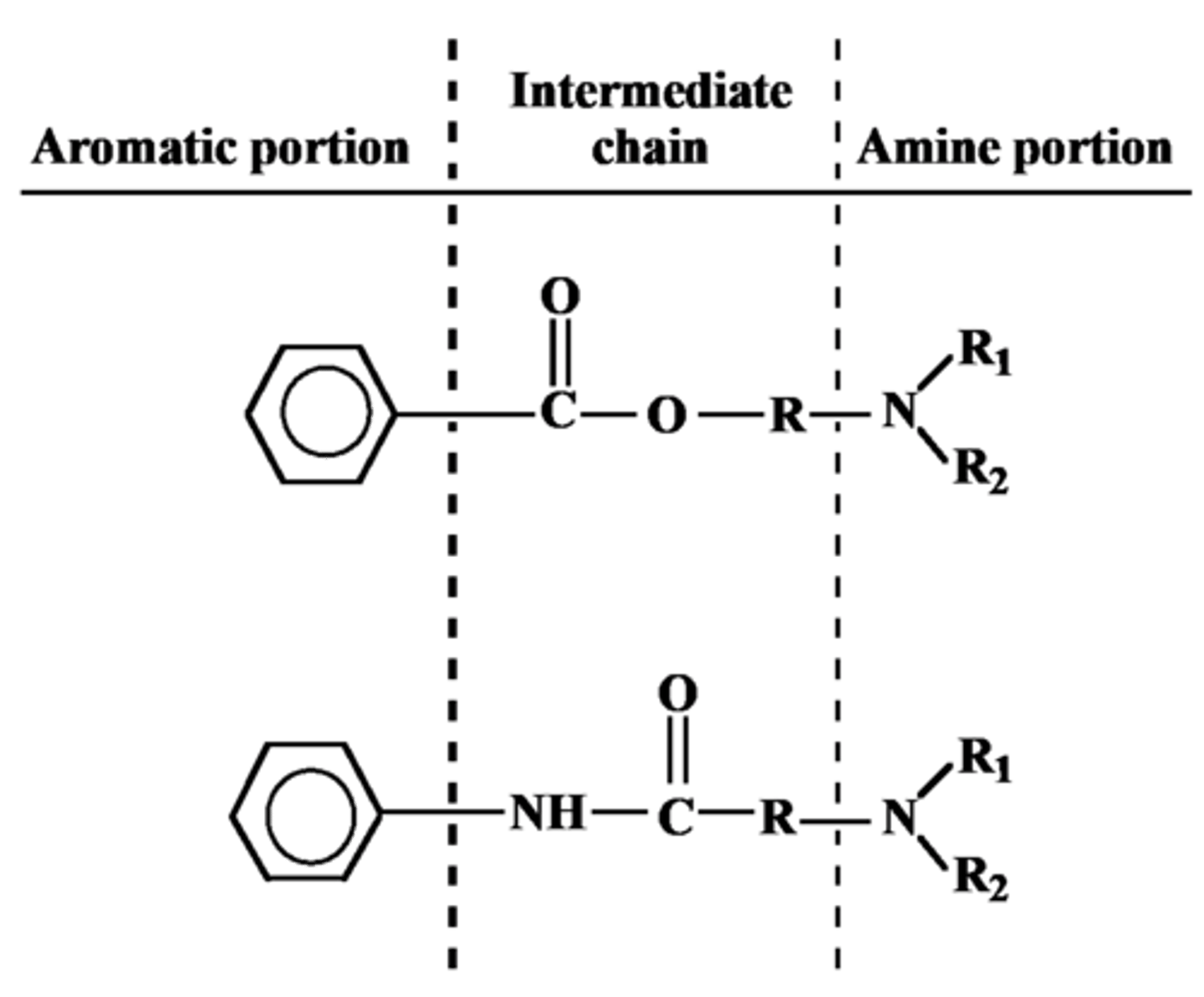
How doses the Aromatic portion of LA affect drug activity
Provides lipophilicity
How does Intermediate linkage of LA affect drug activity
Determines route of metabolism and allergy potential
How are Esters metabolized (What reaction)
Hydrolysis
-shorter half life than amindes
How does the Amine portion of LA affect drug action
Provides water solubility
Compounds lacking amine portion= water-insoluble (topical use)
When administered, usually in the ionized state to increase the aqueous solubility
Is Procaine an ester or amine
Ester
What LA is a natural alkaloid that can be classified as an ester and is used for ENT surgery
Cocaine
What LA ester lacks hydrophilic component (insoluble) and is used topically
Benzocaine
-used to numb gum before anesthetic injection with swab held between cheek and gum)
Easy way to tell if a LA is an ester
Rule of i
Lidocaine
ArtiIcaine
BupiIvacaine
LA are weak base or acid
Weak Base (depending upon pH)
Describe a LA when pH is higher than pKa and with pH is lower than pKA
pH> pKa:
Uncharged free base (unionized- crosses membrane)
pH
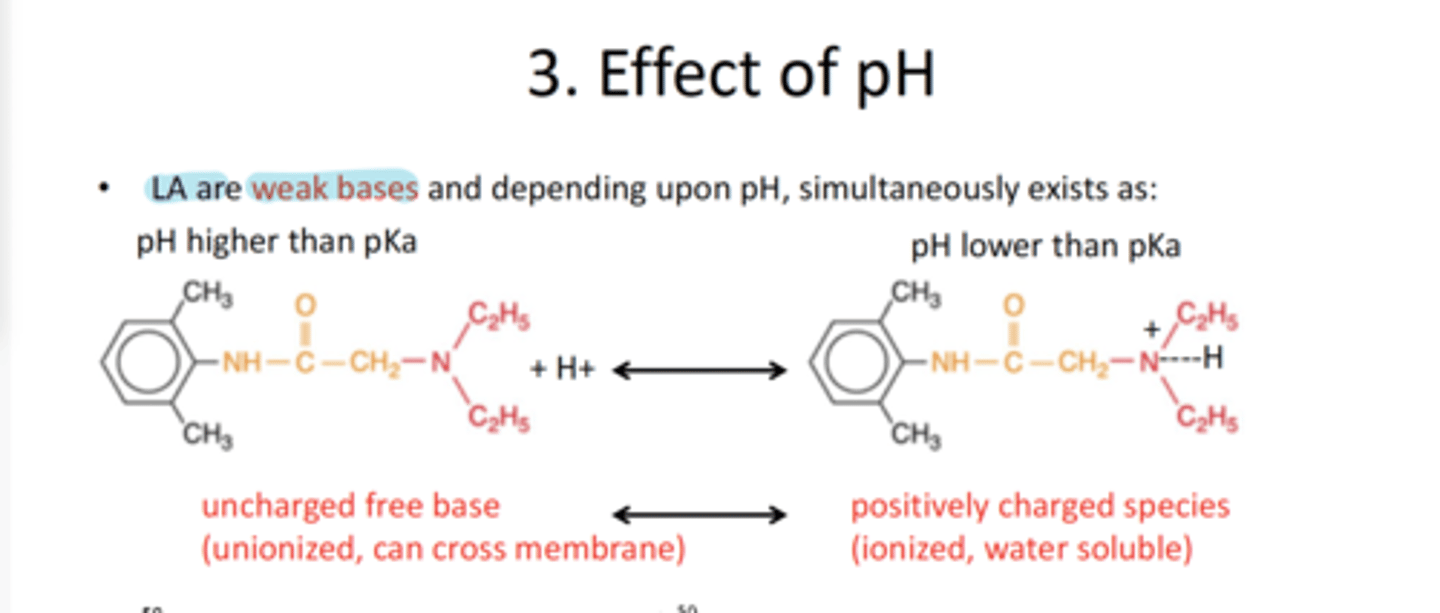
When pH is lowered how does LA become more ionized or nonionized
Ionized (Weak base protonated -> BH+)
Inflammation drops pH-> harder to anesthetize
How does the concentration of LA necessary for nerve block change when pH decreases
Will need to Increase LA concentration
-Higher amount of ionized drug
What can be added to LA to raise pH and shorten the onset of drug action
Bicarbonate
-pKa affects onset: closer to physiological pH, faster onset
The biotransformation of LA depends on what
Dosage
Delivery method
Local blood flow- vasoconstrictors
Systemic absorption terminates the effect
- potential to be toxic
LA like any drug undergoes what type of metabolism
Biphasic
Phase I: Formation of Reactive Intermediate
Phase I: Formation of Water soluble metabolite
Phase I reactions
Functionalization Reaction
Oxidation, Reduction, Hydrolysis
CP450, Esterases
Phase II Reaction
Conjugation with a polar group
Glucuronidation, GSH Conjugation, Acetylation
transferases
Ester LA are hydrolyzed in plasma by what enzyme
Pseudocholinesterase
Patients with atypical enzyme can experience prolonged effects or toxicity
What type of LA is associated with Allergic phenomena
Ester type
Attributable to formation of p-aminobenzoic acid
Amide LA is metabolized primarily where and how
Liver by cytochrome P450
Depends on
-Enzyme activity
-Hepatic blood flow
-Plasma protein level
Variability in Biotransformation
Enzyme differences (CYP450)
Age (elderly heterogeneous due to different rates of deterioration of enzyme and elimination systems)
Gender
Pathology
Enzyme inhibition
Severe liver disease can make it harder to metabolize what kind of LA
Amides
Effect of Vasoconstrictors in LA
Adding vasoconstrictor can prolong/retain and increase depth of anesthesia
-Epinephrine
Duration of LA action is proportional to what
Time of contact with nerve fiber
LA has Vasodilation properties which can limite duration
Clinical use of Topical Anesthesia
Direct application of aqueous solutions of local anesthetic salts to mucous membrane of nose, mouth, tracheobronchial tree, genitourinary tract
Does not exend to submucosal structures
Infiltration Anesthesia
Injection of LA directly into tissue to be incised (may have epi)
Nerve block anesthesia
an injection made into a nerve to block the conduction of impulses between the nerve and the CNS
Intravenous regional anesthesia
insertion of IV cannula into the extremity on which the procedure is to be performed and a tourniquet applied to interrupt blood circulation; then a large volume of local anesthetic injected into a peripheral vein, anesthetizing the extremity.
Spinal Anesthesia
regional anesthesia produced by injecting medication into the subarachnoid space
Epidural Anesthesia
regional anesthesia produced by injecting medication into the epidural space of the lumbar or sacral region of the spine
What is the choice of short-acting LA
Procaine
Cholorprocaine
What is the choice of LA for intermediate use
Lidocaine
Articaine
Mepivacaine
Prilocaine
What is the choice of Long-acting LA
Bupivacaine
Ropivacaine
Tetracaine
Levobupivacaine
What LA has a fast onset and an intermediate duration-suitable for use in dental procedures
Articaine
Undesired effects of LA
Local Anesthetic Systemic Toxicity
-Unintentional IV injections
Effects from Local Anesthetic Systemic Toxicity
Restlessness and tremors, Sensory Disturbances -> Unconsciousness -> Convulsions-> Respiratory Failure-> CVS Depression
Treated with
Benzodiazepines, O2, Supportive care
Excess systemic absorption can lead to what affects on BP
Decrease in BP (LA are Vasodilators)
Effects on Myocardium from LA
Decreases in:
Excitability
Conduction rate
Contraction force
Lidocaine and procainamide can be used as
Antiarrhythmic
Highly lipid soluble, highly protein-bound LA have greater _________toxicity
Cardiotoxicity
Bupivacaine
Etidocaine
LA Brain Toxicities
CNS toxicity linked to Twik-related acid-sensitive K+ channel (TASK)
Induces membrane depolarization (increased excitability)
Initial: agitation, confusion, dizziness, drowsiness, perioral numbness
Progressing to seizures, Respiratory arrest, coma
Caring for LA Brin Toxicity
Airway management
Cardia-epi
Seizures: benzodiazepines
Lipid emulsion therapy- lipids soak up lipid-soluble LA
Allergic Reaction to LA
Likely due to preservatives (Methylparaben or antioxidants)
Ask about epi or PABA sensitivity
Rarely due to LA
Allergic dermatitis/bronchospasms
More common with esters