Exam 2 : MKT 3343- ANDERSON TXST
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
what is derived demand?
the demand for industrial products and services that is driven by, or derived from, the demand for consumer products and services.
JCPenney example- derived demand
answer choice... pick it
Business marketing
involves the marketing of goods and services to companies, governments, or not-for-profit organizations for use in the creation of goods and services that they can produce and market to others. also known as business to business marketing
Organizational buyers
manufacturers, wholesalers, retailers, and government agencies that buy goods and services for their own use or for resale.
What are the types of organizational buyers?
industrial, reseller and government agency.
What are the 7 buying criteria?
price, technical ability, warranty/claim policies, quality specifications, deleivery schedules, past performance and production facilities/capacity
Supplier development
the deliberate effort by organizational buyers to build relationships that shape suppliers' products, services, and capabilities to fit a buyer's needs and those of its customers.
Reciprocity
an industrial buying practice in which two organizations agree to purchase each other's products and services.
Buying centers
Everyone in an organization who is part of overall purchase decision
Types of buying centers
users, influencers, buyers, deciders and gatekeepers
Types of buying situations
New buy, straight rebuy and modified rebuy
5 trends of global marketing ( ch.6 ppt)
decline of economic protectionism, the rise of economic integration, global competition, networked global marketplace, economic espionage
Protectionism
the practice of shielding one or more industries within a country's economy from foreign competition through the use of tariffs or quotas
Tariffs
government taxes on products or services entering a country.
Quota
a restriction placed on the amount of a product allowed to enter or leave a country.
What is the goal of protectionism?
to decrease world trade
Types of global firms
international, multinational and transnational
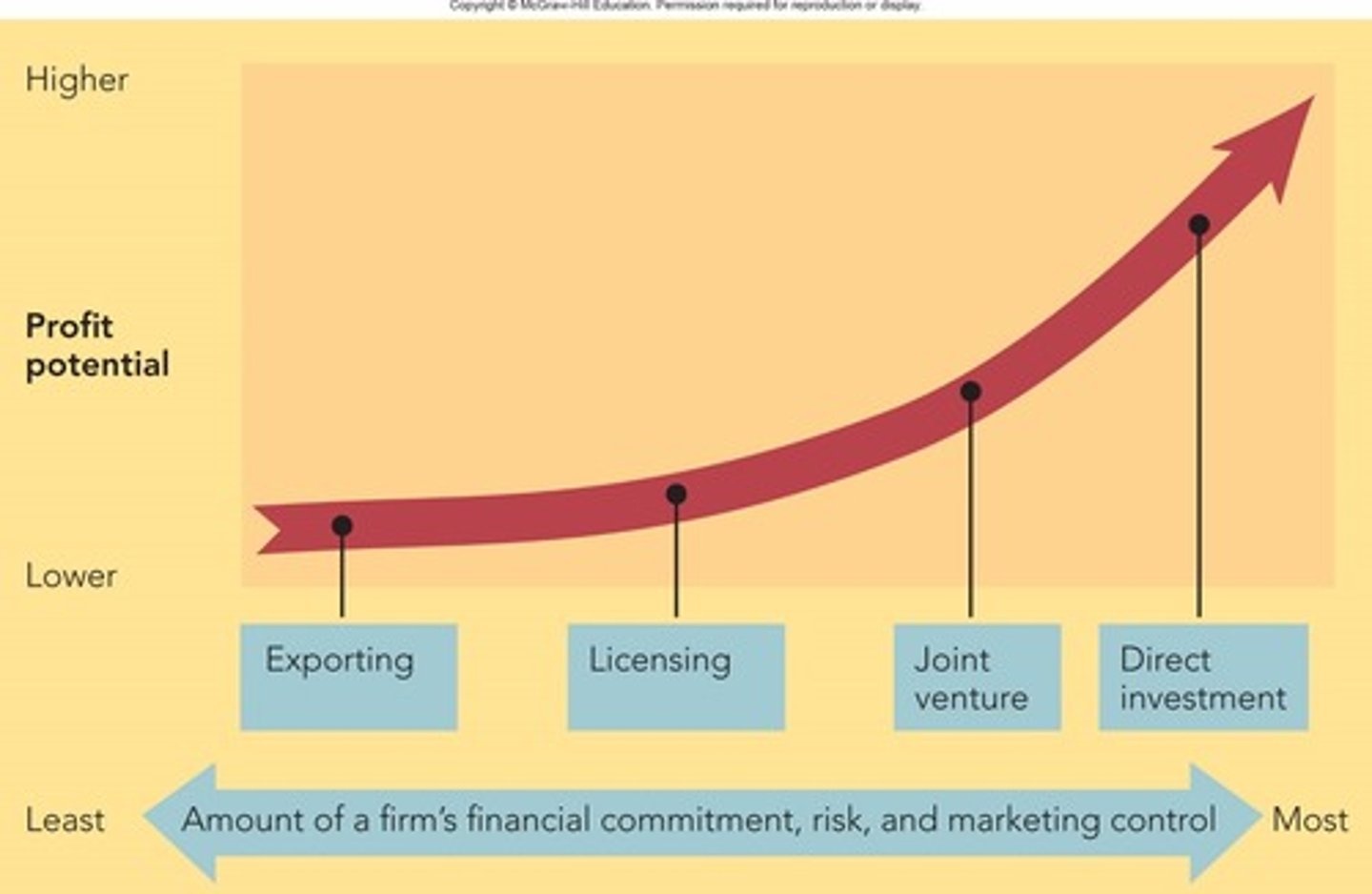
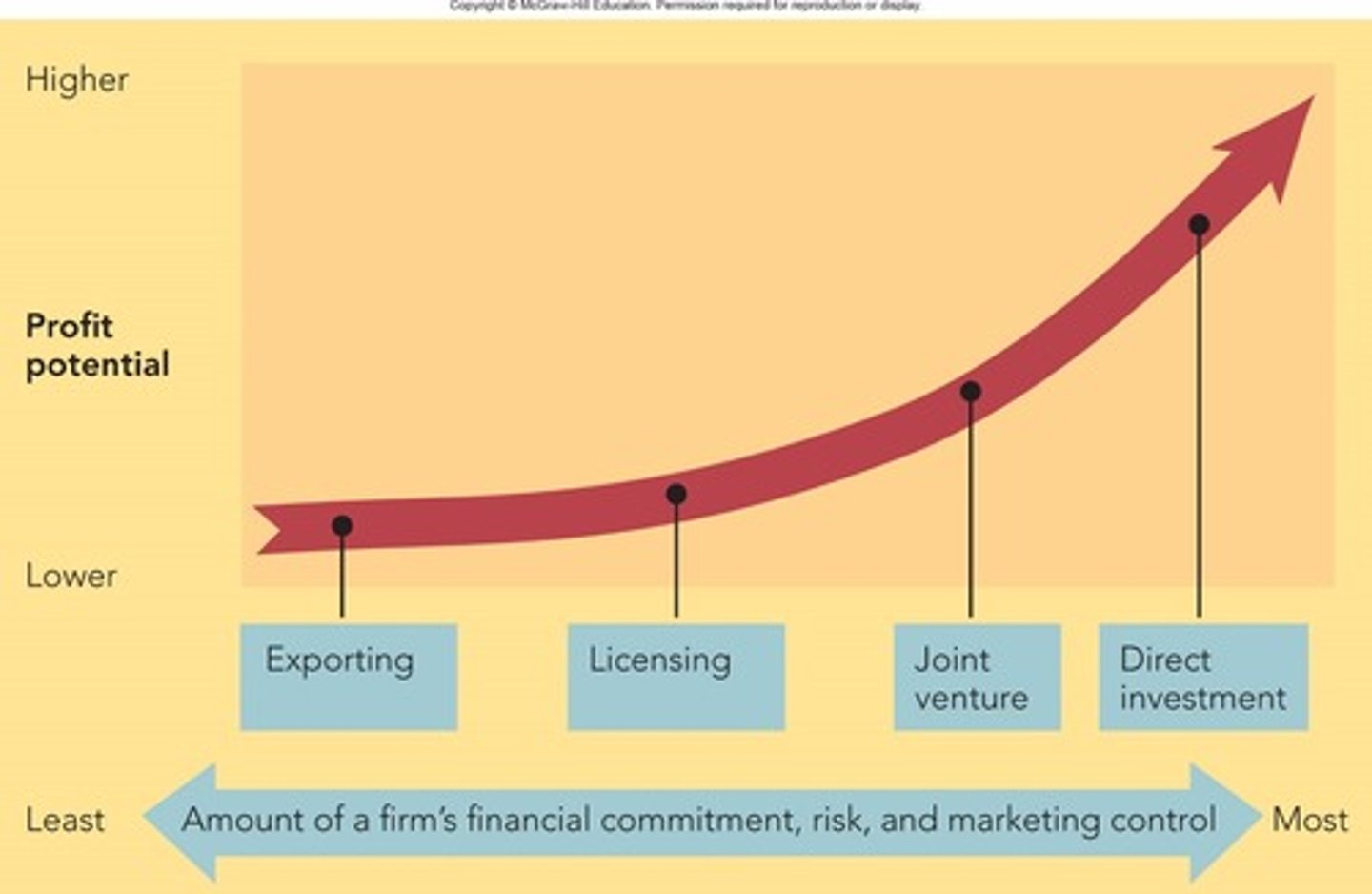
Who has the highest profit potential?
direct investment
Licensing
a company offers the right to use their intellectual property (e.g., trademark, patent) in return for a royalty or fee.
Exporting
is a global market-entry strategy in which a company produces products in one country and sells them in another country
Indirect exporting
occurs when a firm sells its domestically-produced goods in a foreign country through an intermediary
Direct exporting
requires no intermediary
Joint-venture
is a business arrangement in which two or more parties agree to pool their resources for the purpose of accomplishing a specific task.
Direct investment
is a global market-entry strategy that entails a domestic firm actually investing in and owning a foreign subsidiary or division.
Product extension
Selling virtually the same product in other countries is a product extension strategy. It works well when and where consumers share the same desires, needs, and uses for the product.
Product adaptation
Changing a product in some way to make it more appropriate for a country's climate or consumer preferences is a product adaptation strategy.
Cross-cultural analysis
involves the study of similarities and differences among consumers in two or more nations or societies.
5 steps for marketing research
define the problem, develop research plan, collect relevant info, develop findings, take marketing action
What occurs at step 1- define the problem?
set objectives and identify possible marketing action
Primary data
the facts and figures that are newly collected for the project.
Internal and external secondary data
comes from within a company (sales figures), outside the organization ( US census)
Open-ended questions
allow respondents to express opinions, ideas, or behaviors in their own words without being forced to choose among alternatives that have been predetermined by a marketing researcher.
closed-ended/ fixed alternative
require respondents to select one or more response options from a set of predetermined choices.
Dichotomous questions
only allows 1 of 2 answers for response
semantic differential scale
a five-point scale in which the opposite ends have one- or two-word adjectives that have opposite meanings.
Likert scale
in which the respondent indicates the extent to which he or she agrees or disagrees with a statement.
ex- counseling questionnaires
what is sampling?
getting opinion/facts of part of a group/population to apply to bigger scale
1 product multiple segments
When an organization produces only a single product or service and attempts to sell it to two or more market segments
ex- magazines
Multiple products multiple segments
common in the automobile industry where automakers produce different lines of cars, trucks, and SUV's...each targeted to a different market.
Market segmentation
involves aggregating prospective buyers into groups, or segments, that (1) have common needs and (2) will respond similarly to a marketing action.
tiffany/walmart strategy
Two-tier (or more) marketing strategy
offering different variations of the same basic offering to high-end and low-end segments/price
Cannibalization
the new products or new chain simply stealing customers and sales from the older, existing ones
Product differentiation
a marketing strategy that involves a firm using different marketing mix actions to help consumers perceive the product as being different and better than competing products.
Synergy
the increased customer value achieved through performing organizational functions such as
marketing or manufacturing more efficiently
Geographic segmentation
occurs when a business divides its market based on geography; city, state, region, etc.
Demographic segmentation
market segmentation according to age, rage, religion, gender, family size, income, and education
Psychological segmentation
segmentation based on lifestyle. People of similar lifestyles tend to live near one another, have similar interests, and buy similar offerings
Behavioral segmentation
Usage/Volume, Benefits, Loyalty, Price Sensitivity and status
Product positioning
is the place a product occupies in consumers' minds based on important attributes relative to competitive products.
what is organizational buying?
is the decision-making process by which formal organizations establish the need for purchased products and services and identify, evaluate, and choose among alternative brands and suppliers.
what type of organizational buyer is TXST?
government angency
what is a new buy?
1st time buyer
what is a straight rebuy?
purchasing a product w/o looking at other suppliers
what is a modified rebuy?
users, influencers or deciders want to change product specifications, price, delivery, etc.
types of marketing strategies
home strategy, multidomestic and global
List from least to greatest alternative marketing strategies amount of financial investment and risk (Figure 6-3)
exporting, licensing, joint venture and direct investment
semiotics
examines the correspondence between symbols and their role in the assignment of meaning for people. ex- thumbs up meaning in other countries
cultural symbols
are things that represent ideas and concepts. ex- empire state buliding
values
are a society's personally or socially preferable modes of conduct or states of existence that tend to persist over time. ex- McDonalds in India not selling beef
customs
are traditional practices followed by a social group or people.
back translation
to prevent unintended meanings
what occurs at step 2- develop a research plan?
specify constraints, what data is needed, how to collect data
what occurs at step 3- collecting relevant info?
obtaining primary and/or secondary data
what occurs at step 4- develop findings?
analyze data and present findings
what occurs in the final step of the marketing research process?
take marketing action and evaluate results
secondary data
are the facts and figures that have already been recorded prior to the project at hand
product repositioning
involves changing the place a product occupies in a consumer's mind relative to competitive products.