216 lec 13 Angular movement
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
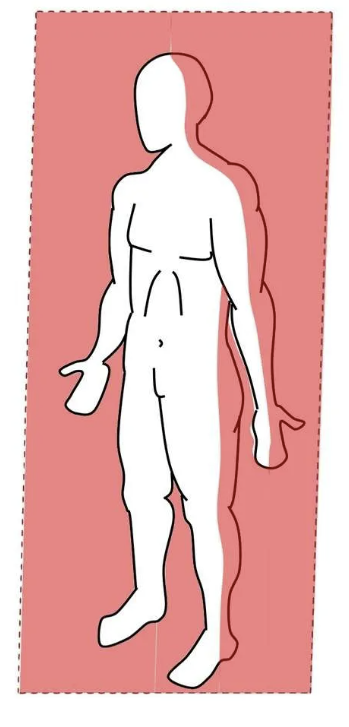
what plane? what type of rotation? what axis?
Frontal plane
Roll
Anterioposterior axis
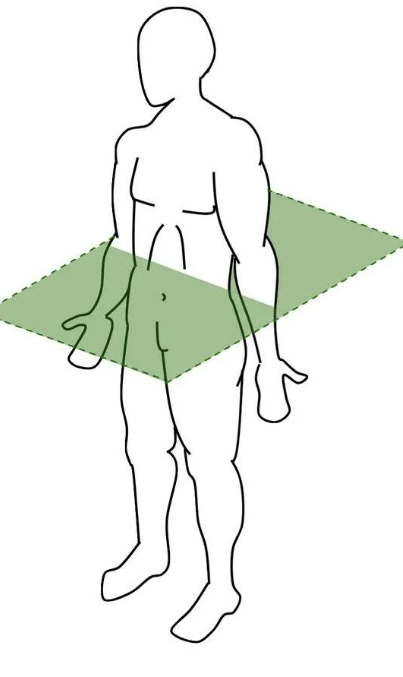
what plane? what type of rotation? what axis?
Transverse plane
Yaw
Longitudinal axis
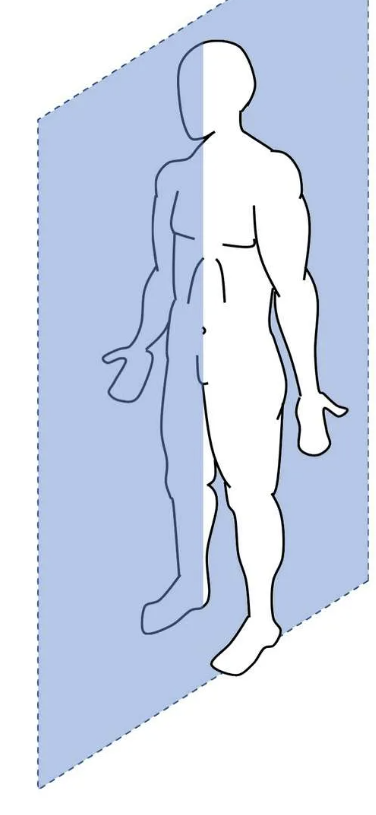
what plane? what type of rotation? what axis?
Sagittarius plane
Pitch
Mediolateral axis
flexion, extension, hyperextension are___ rotations that occur on ___ plane along the ___ axis
Pitch
Sagittal
Mediolateral
elevation and depression occurs on ____ plane
frontal plane
Abduction, adduction, lateral flexion are rotations that occur on plane along the __ axis
frontal
Roll
Anterioposterior
internal and external rotation, supination and pronation are ___rotations that occur on plane along the _ axis
Yaw
Transverse
Longitudinal
how do we measure angular movement in human body
connect center of rotation of 3 joints with 2 longitudinal segments >> identify joint angle
define relative angles
the angle at a joint
relative angle can either be ___ or ___
internal (angle on the inside of joint)
external (angle on the exterior surface of the joint
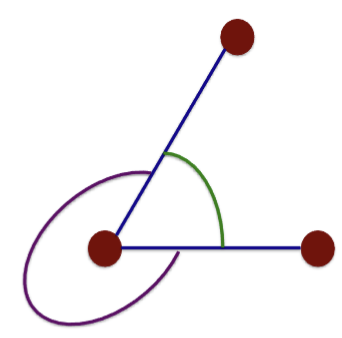
define absolute angle
space btw a body segment with respect to fixed line of reference
absolute angle measure the line’s position in space relative to ___ and ___
x-axis
y-axis
what is absolute angle good for
comparing angles of different things
whats degree
an arbitrary unit of measuring angles that simply divide a circle into 360 pieces
whats revolution
1 full turn around the circle
whats radian
a ratio btw the angle in a circle and the length of the arc
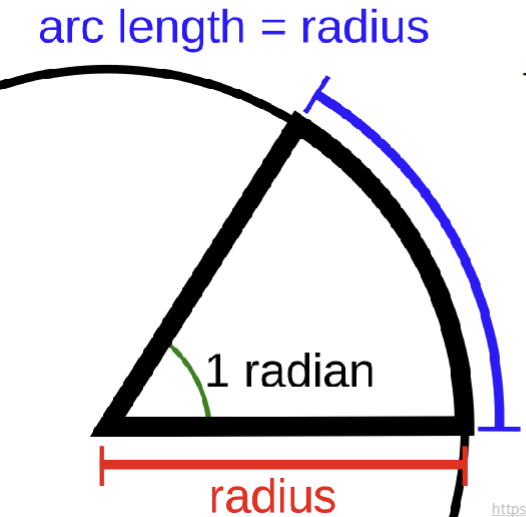
if the radius of a circle and the length of arc are equivalent, the angle must equal to ___ degree aka__
57.3 degree
1 radian
1 revolution = how much radian?
2 pie
to measure angles of static things or pictures, we use___
Basic goniometer
to measure angle of things during movement/dynamic, we use___
electrogoniometer
goniometers are widely used to assess___
range of motion
is the axis of rotation of a joint fixed? so what?
not fixed
we do not know the precise location of rotation. so we use estimate axis of rotation (aka Instant center)
angular distance (phi) vs displacement (theta)
BOTH describe object’s position in space
scalar VS vector (direction)
total amount of rotation VS change in angular position
angular speed (sigma) vs angular velocity (w-omega)
BOTH describe temporal pattern of movement
scalar VS vector
change in angular distance VS change in angular displacement over change in time
dynamic motion is characterized by a ____
change in angular velocity, aka angular acceleration
angular acceleration (change in angular velocity) is produced by ___
Torque
what does the sign in front of angular displacement n velocity mean
direction of rotation (clockwise or counter-clockwise)
what does the sign in front of angular acceleration mean
direction of torque
angular velocity is becoming more + or more -
linear vs angular kinemaitcs
describe change in position in space
describe change in rotations in space