MTE2201 Module 5 - Chain and Step Growth Polymerisation
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
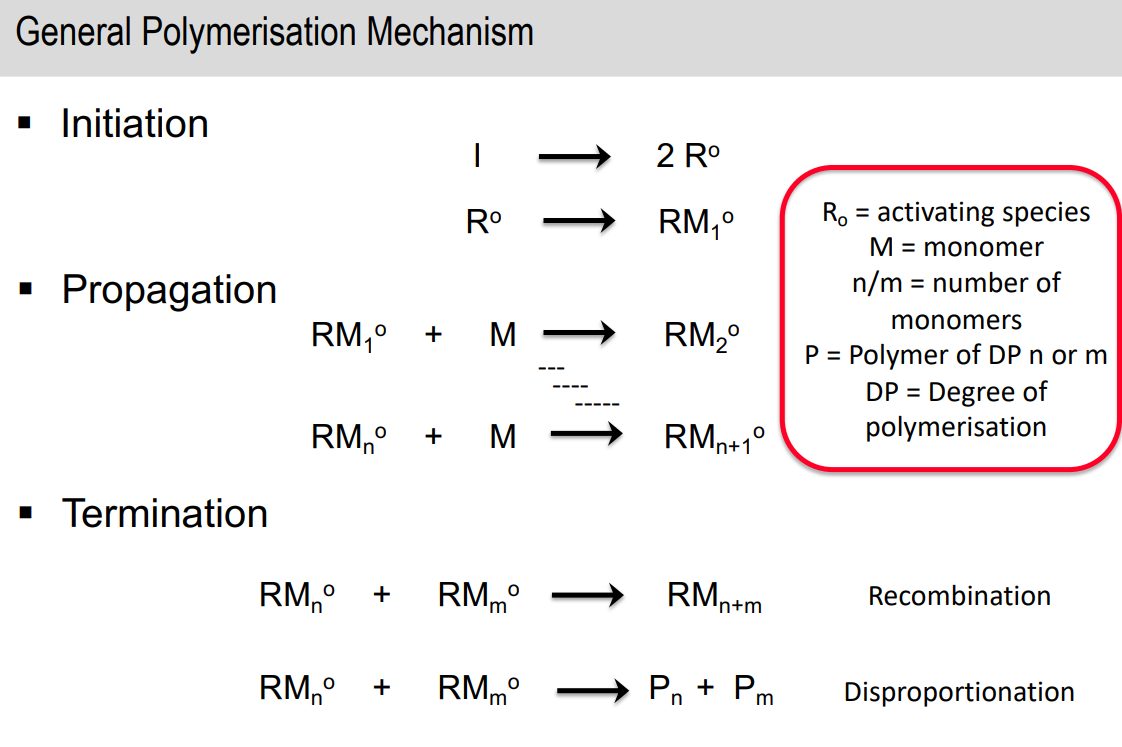
General chain growth polymerisation mechanism
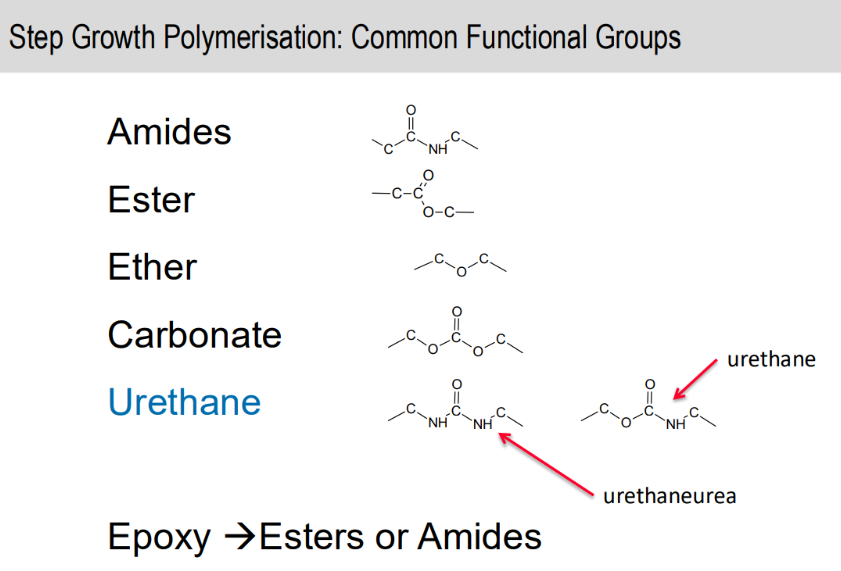
Common functional groups of step growth polymerisation
Discuss 3 methods of creating radicals
UV initiator – A weak covalent bond in a suitable compound is cleaved as it absorbs light, forming 2 radical fragments. Good for applications like 3D printing, where initiation needs to happen in specific areas only.
Redox initiator – An electron is transferred from a reactant in a redox reaction, forming a radical which can initiate polymerisation. Useful when the reaction system is aqueous or when polymerisation needs to occur at around room temps or lower.
Peroxide initiator– A peroxide decomposes into 2 fragments upon heating, breaking the O-O bond, in which one electron from the covalent bond goes to each fragment’s oxygen atom. Cost effective and good for when higher temps can be applied.
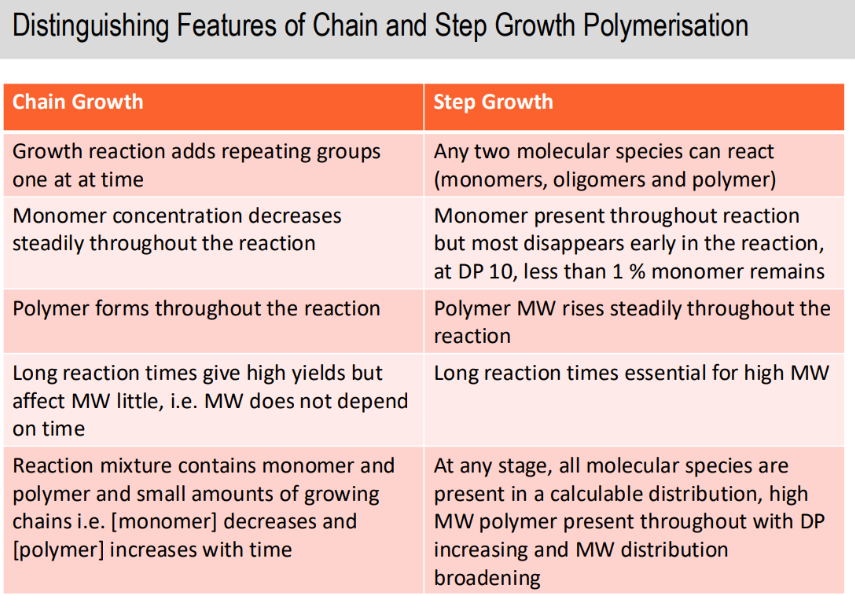
Difference between chain and step growth % conversion over time
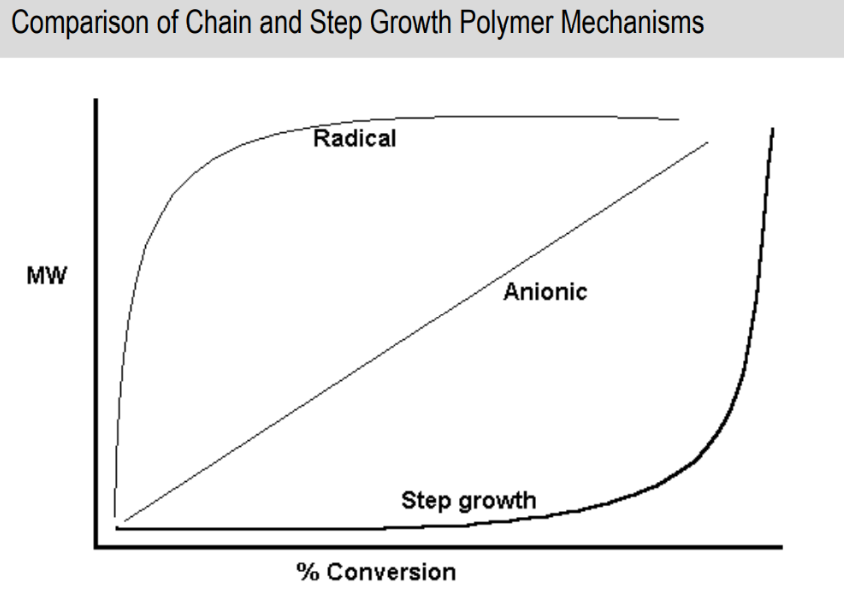
Differences between chain and step growth
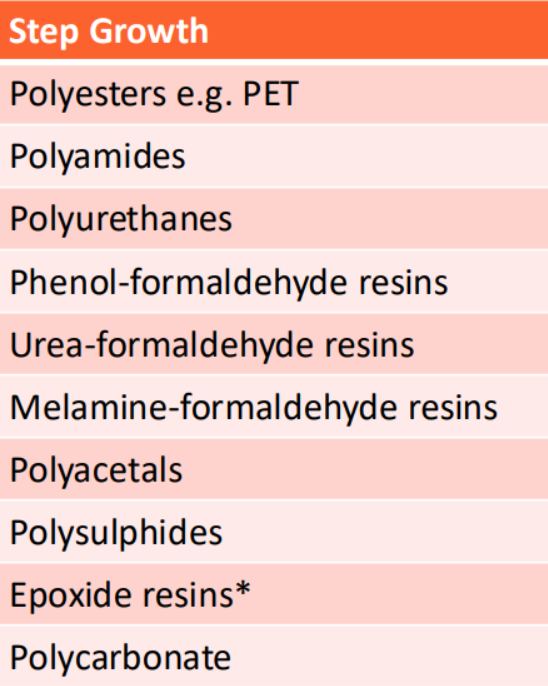
Classes of step growth polymers
Requirements for polymers achieving high molecular weights in step growth

Polyaddition reactions and examples that undergo this reaction
Step polymerisations where there is no elimination of another molecule, (like h2o).
This includes polyurethanes and epoxy resins
Define chain growth polymerisation
chain reactions where the propagation steps occur by reaction between monomer(s) and active site(s) on the polymer chains with regeneration of the active site(s) at each step
Cationic and anionic polymerisation process
a type of chain growth polymerization in which a cationic initiator transfers a proton to a monomer which then becomes reactive toward chain growth.
same idea with anionic, just with an electron

Chain growth kinetics: rate of propagation equations
M is monomer concentration, M* is concentration of all chain radicals
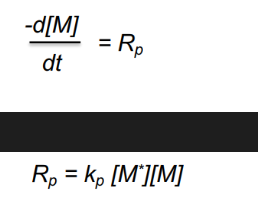
Chain growth kinetics: concentration of radicals equation
Ri and Rt are rates of initiation
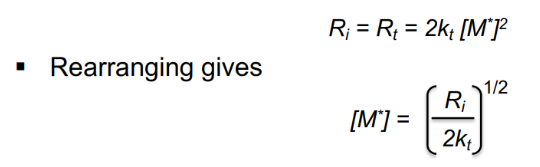
Thermodynamics of chain growth
Entropic changes (delta S) in chain polymerization are always negative
For spontaneous polymerisation to occur, gibbs free energy must be released (G<0)
rate of reaction for step growth
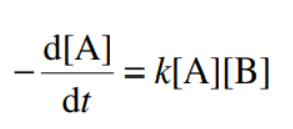
Extent of reaction and degree of polymerisation equation
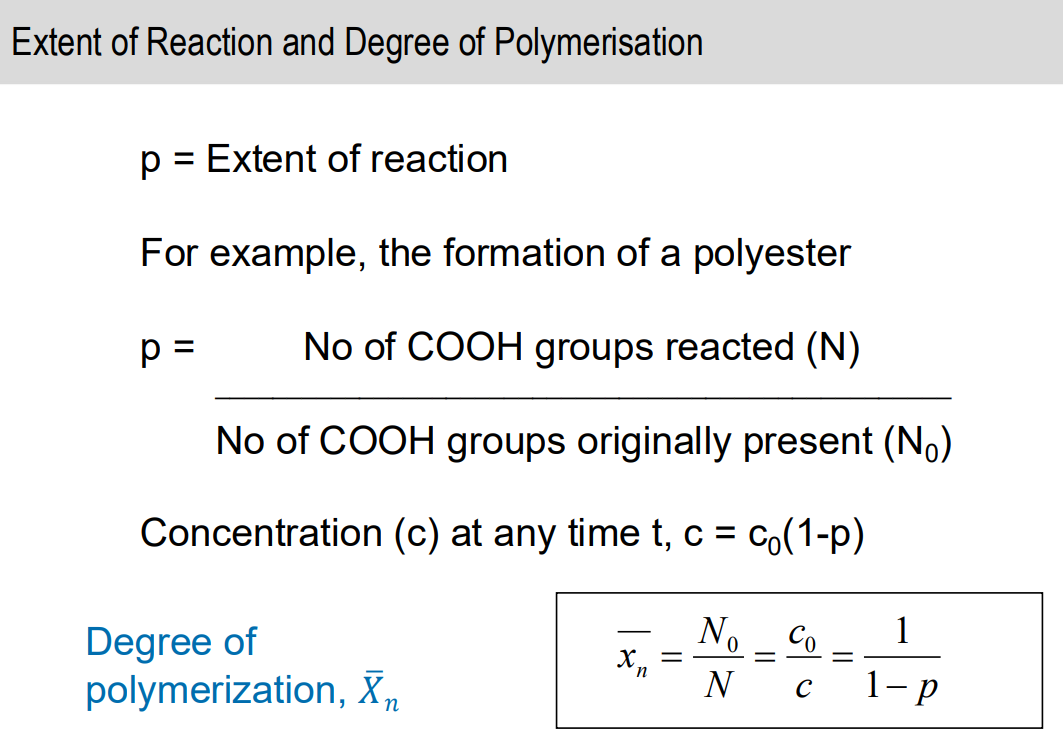
Non acid catalysed reaction
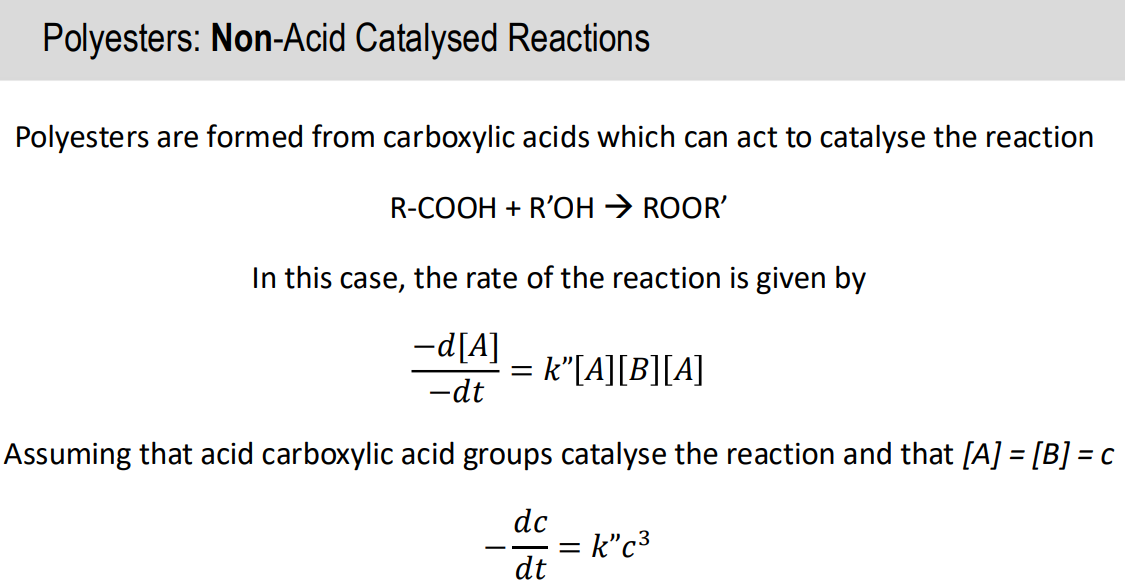
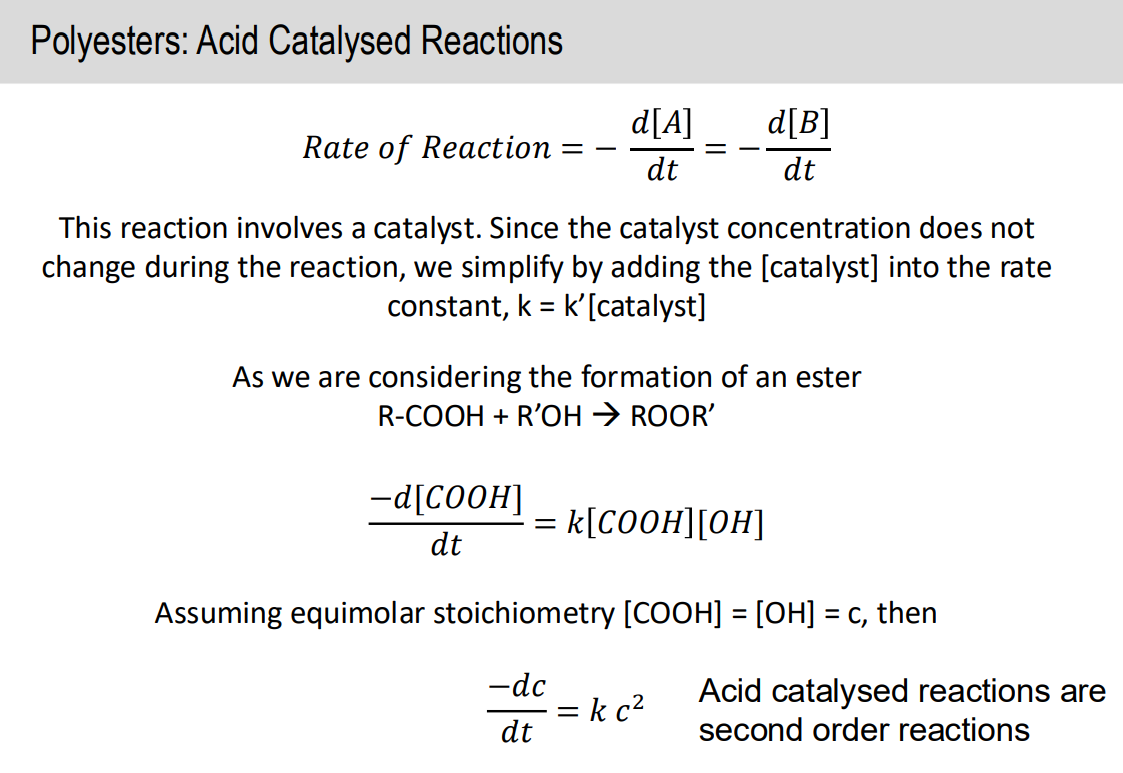
Acid catalysed reaction
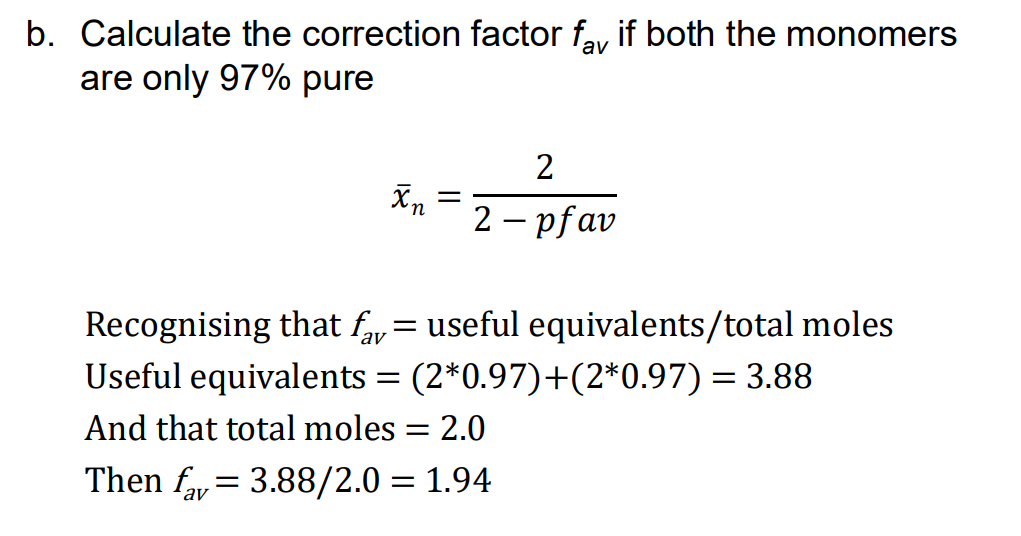
average functionality correction factor
0.97 is multiplied by 2 cause of 2 functional groups in a molecule