Ethics and Outsourcing
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
Outsourcing
obtaining goods or service from an outside or foreign supplier, especially in place of an internal source.
Can apply to specific functions within a supply chain (micro-level), or gradual outsourcing entire industry (as in, with global trade).
Why do companies outsource?
Reduction in costs:
Lower costs of labor and materials
Lower taxation
Less regulatory compliance costs
Access to resources and energy
Lower transaction costs
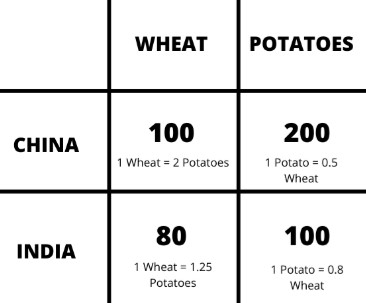
Trade and Efficiency – Comparative Advantage/Absolute Advantage
China has an absolute advantage in both wheat and potatoes
But, since India has a comparative advantage in producing wheat (costs less in opportunity cost), and China has a comparative advantage in potatoes, both countries should specialize
Efficiencies Counterargument
Cost-cutting leads to a “race to the bottom,” where suppliers neglect
Employees, the environment, and quality to produce at the lowest cost
Over time, ethical failures lead to loss in institutional trust
Distrust in capitalism
Distrust in certain supply chains
Outsourcing leads to loss in U.S. jobs
Increase in job retraining would be needed to retool shift in industries
In order to produce sustainably, outsourcing companies must increase monitoring costs
Commoditization, over time, leads to “fast food” approach where customers no longer are willing to pay higher prices for goods
Rights/Virtues based arguments
Global trade tends to lead to spread in education, human rights, and democracy, as
spread of technology and cultures introduce concepts to citizens of cultures with more heavy control
Increased trade leads to job and economic stimulation in impoverished economies
Combining resources leads to new discoveries
Focuses on global citizenship – less wars, etc. because we become interconnected
Virtue-Based - Counterarguments
Workers overseas are underpaid and overworked; foreign governments cede their power to foreign corporations
In reality, some parties prosper while others are hurt. Wage gaps have widened over the years as globalization occurs
Expansion of supply/consumption leads us to environmental overburdening