4.1 Joints and Motion Study Guide- HBS
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
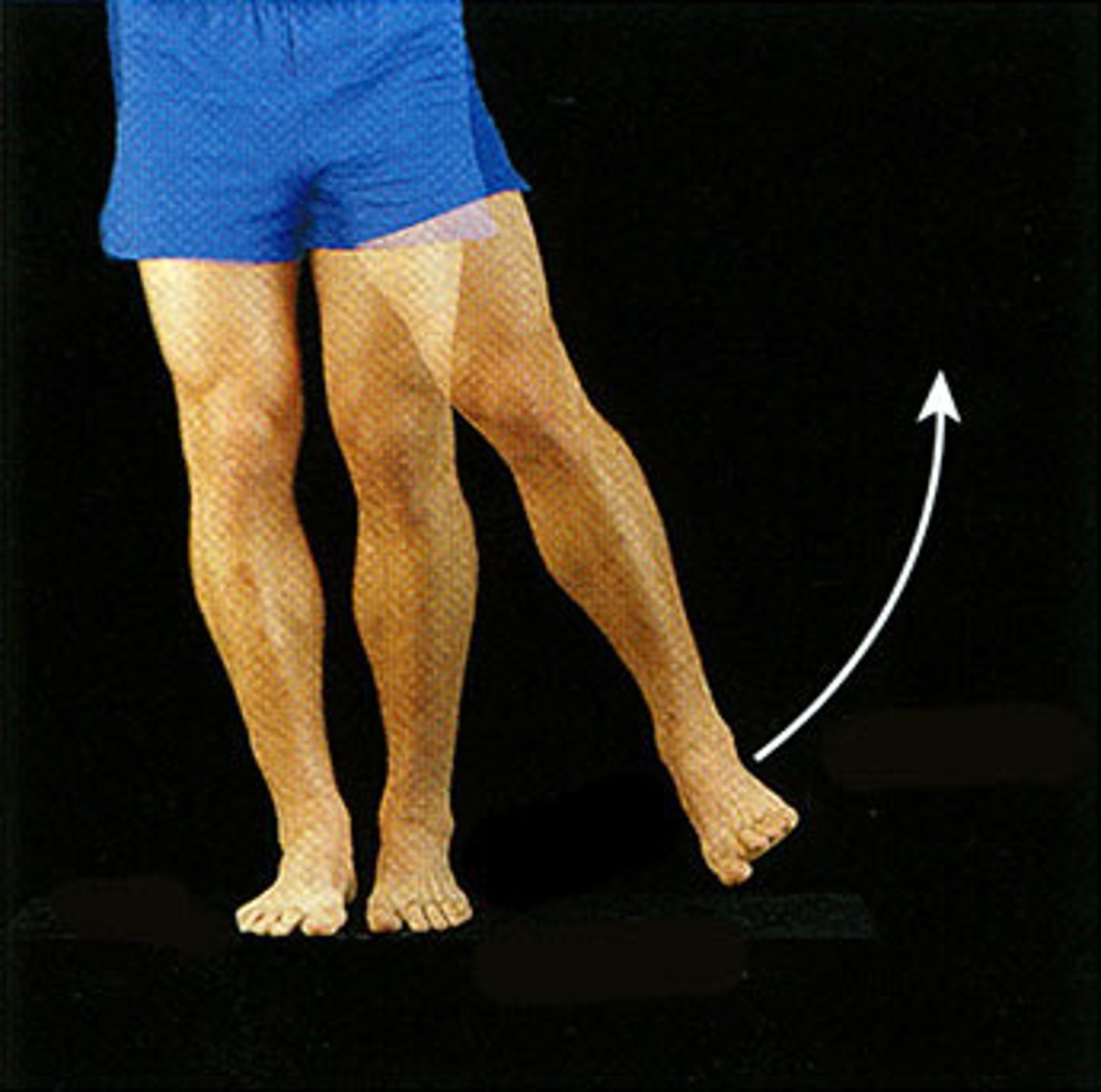
Abduction
Movement away from the midline of the body
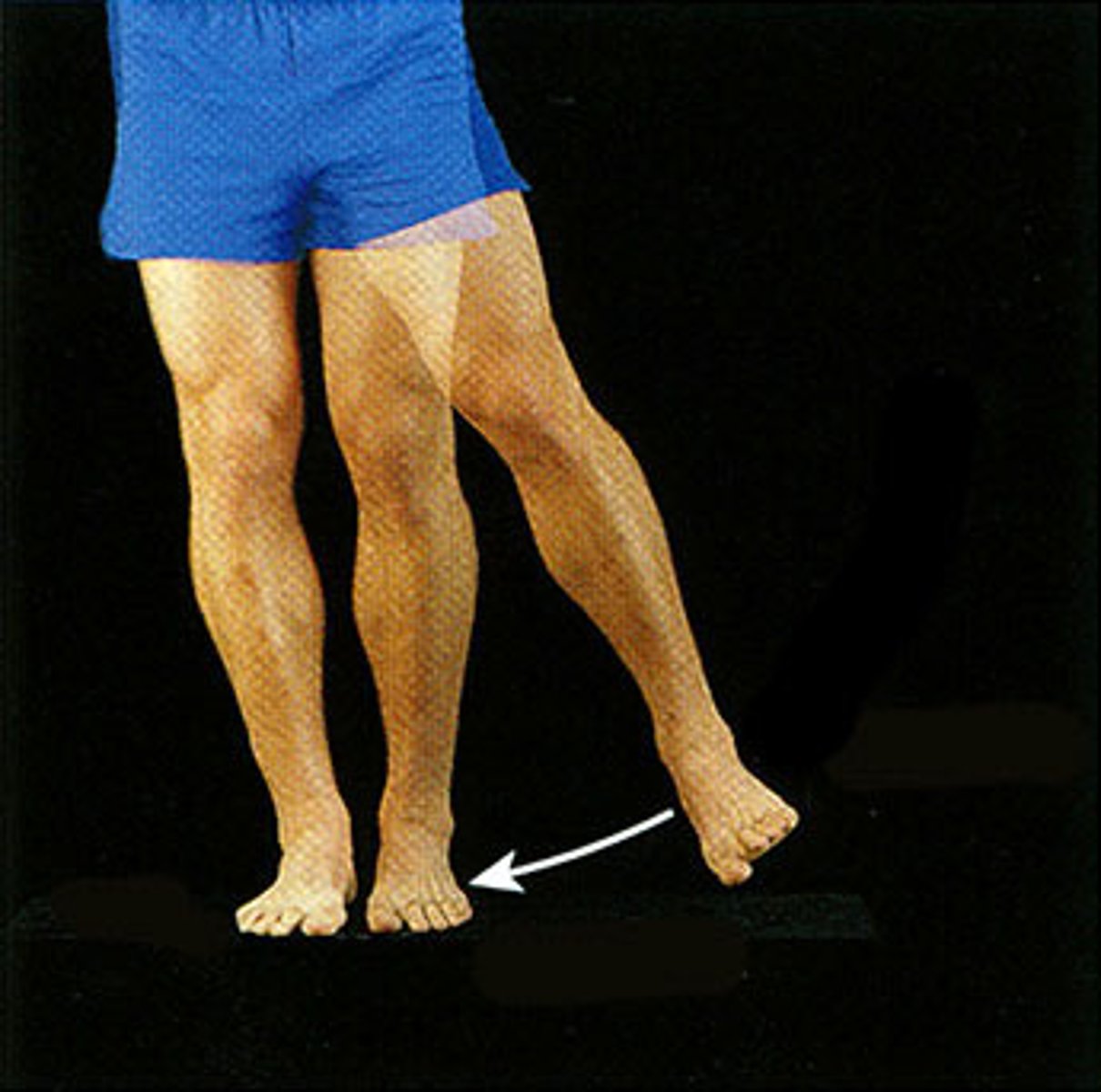
Adduction
Movement toward the midline off the body
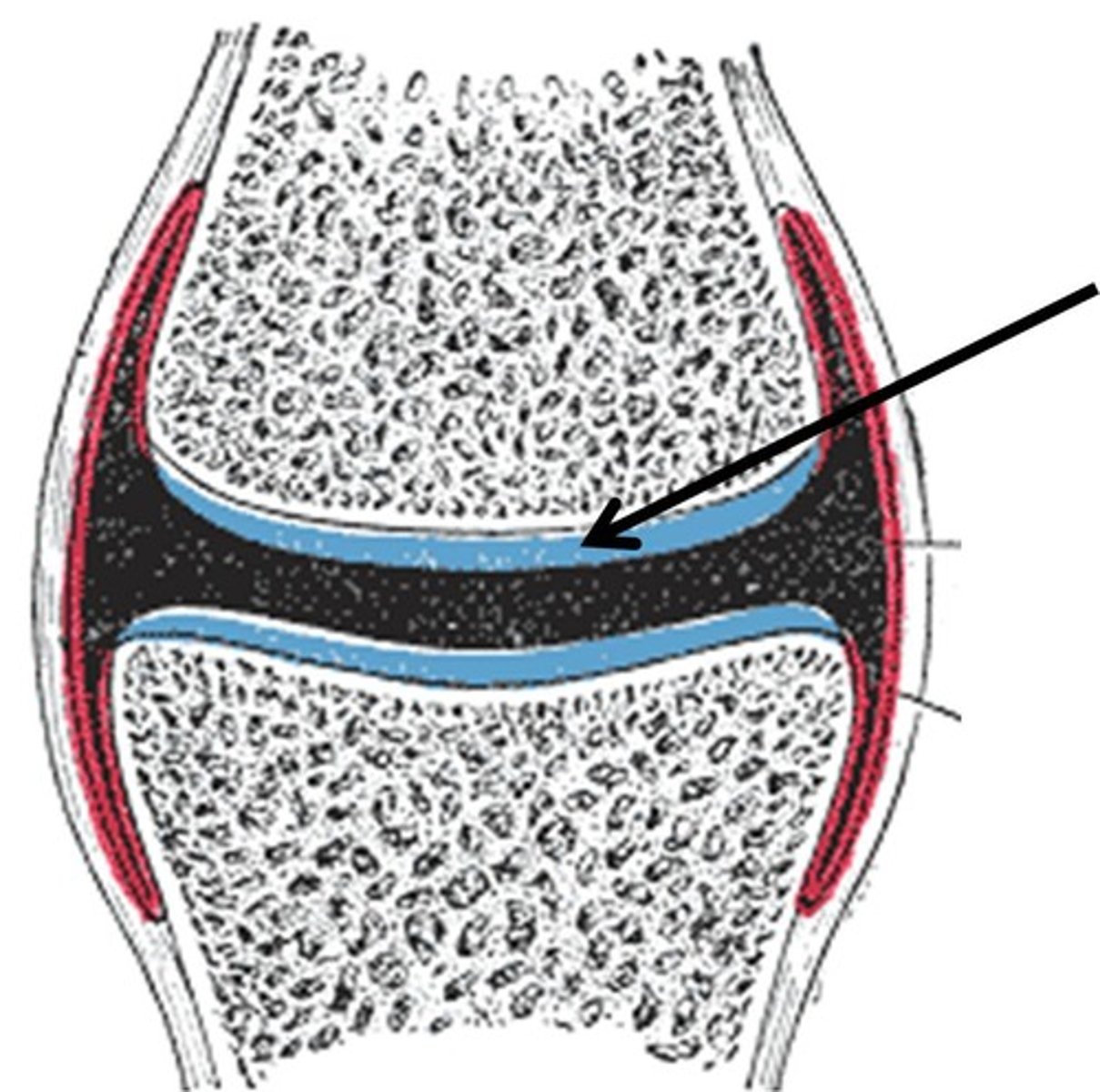
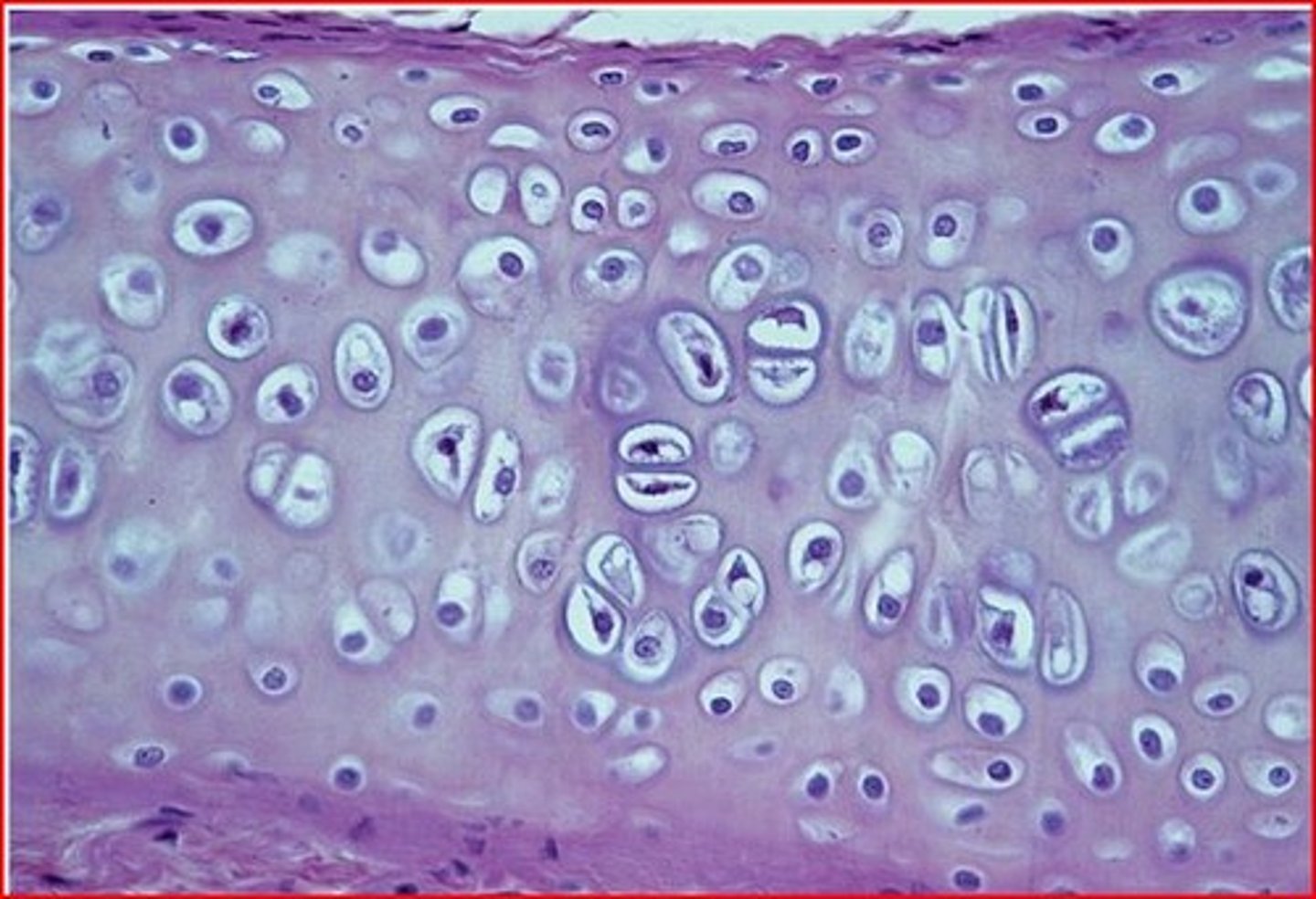
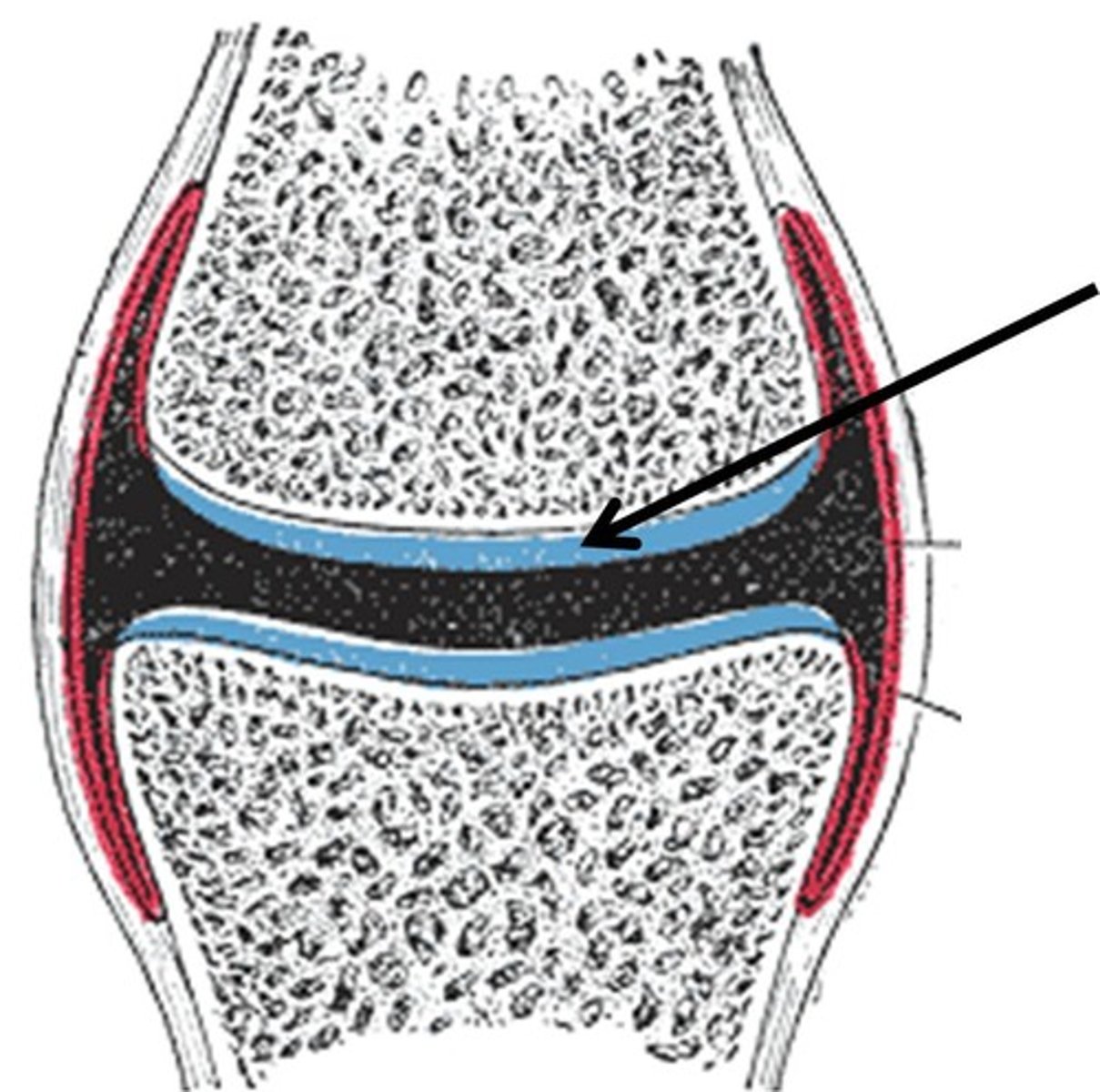
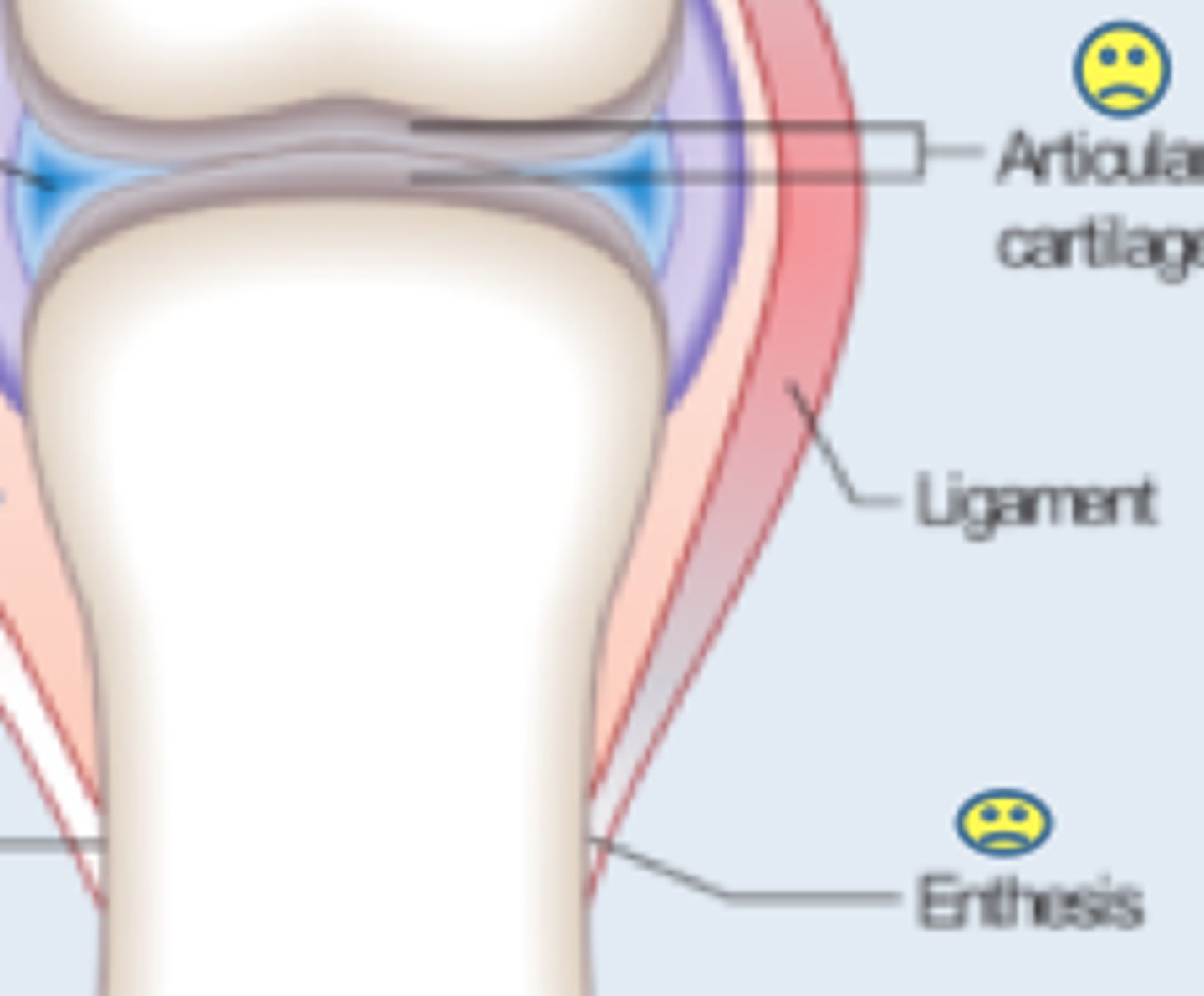
Articular cartilage
Hyaline cartilage attached to articular bone surfaces
Articulation
The action or manner in which the parts come together at a joint
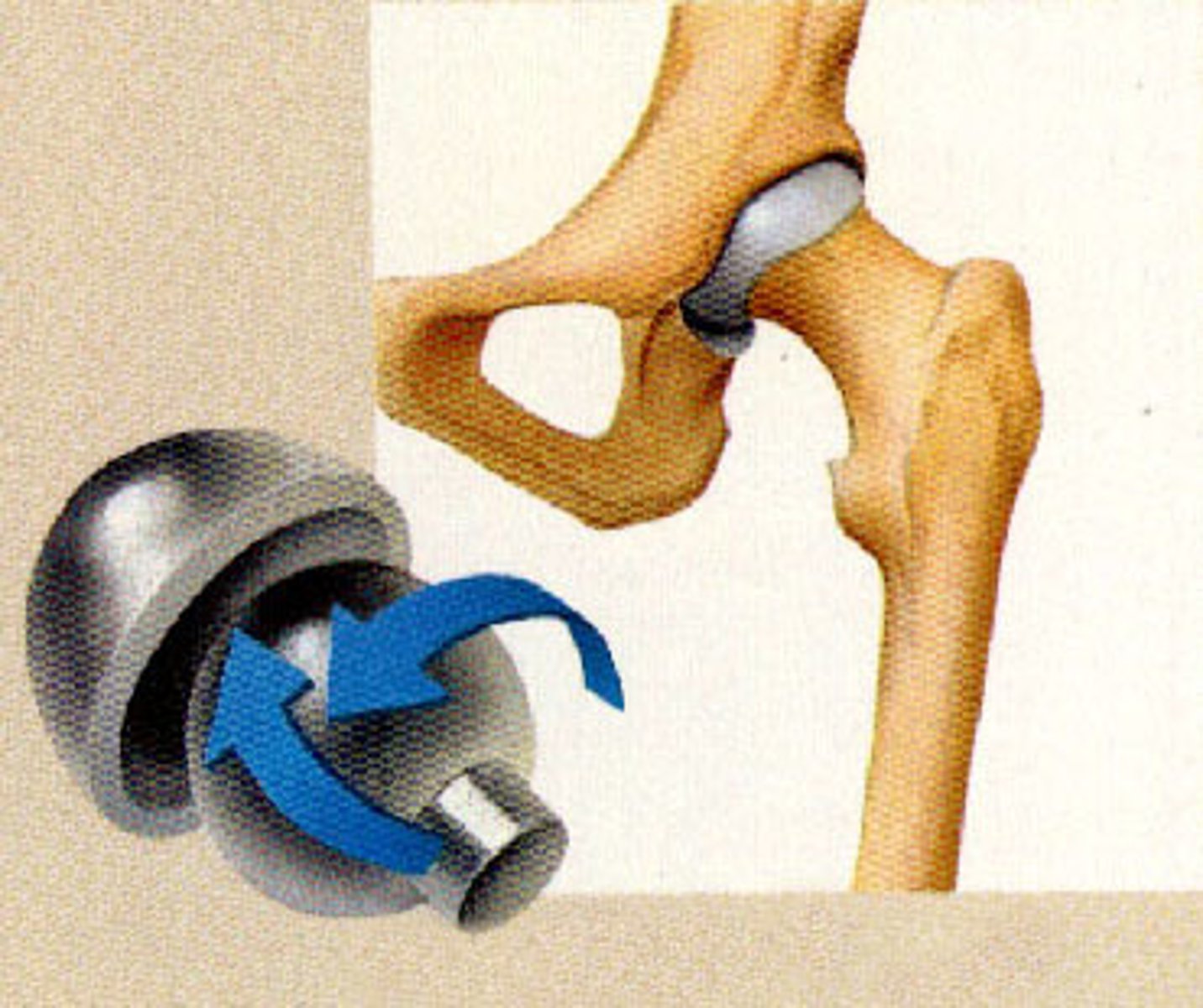
Ball-and-socket joint
An articulation (as the hip joint) in which the rounded head of one bone fits into a cuplike cavity of the other and admits movement in any direction
Cartilage
Cushions and protects bones and is usually translucent somewhat elastic tissue that composes most of the skeleton of vertebrate embryos and except for a small number of structures (as some joints, respiratory passages, and the external ear) is replaced by bone during ossification in the higher vertebrates.
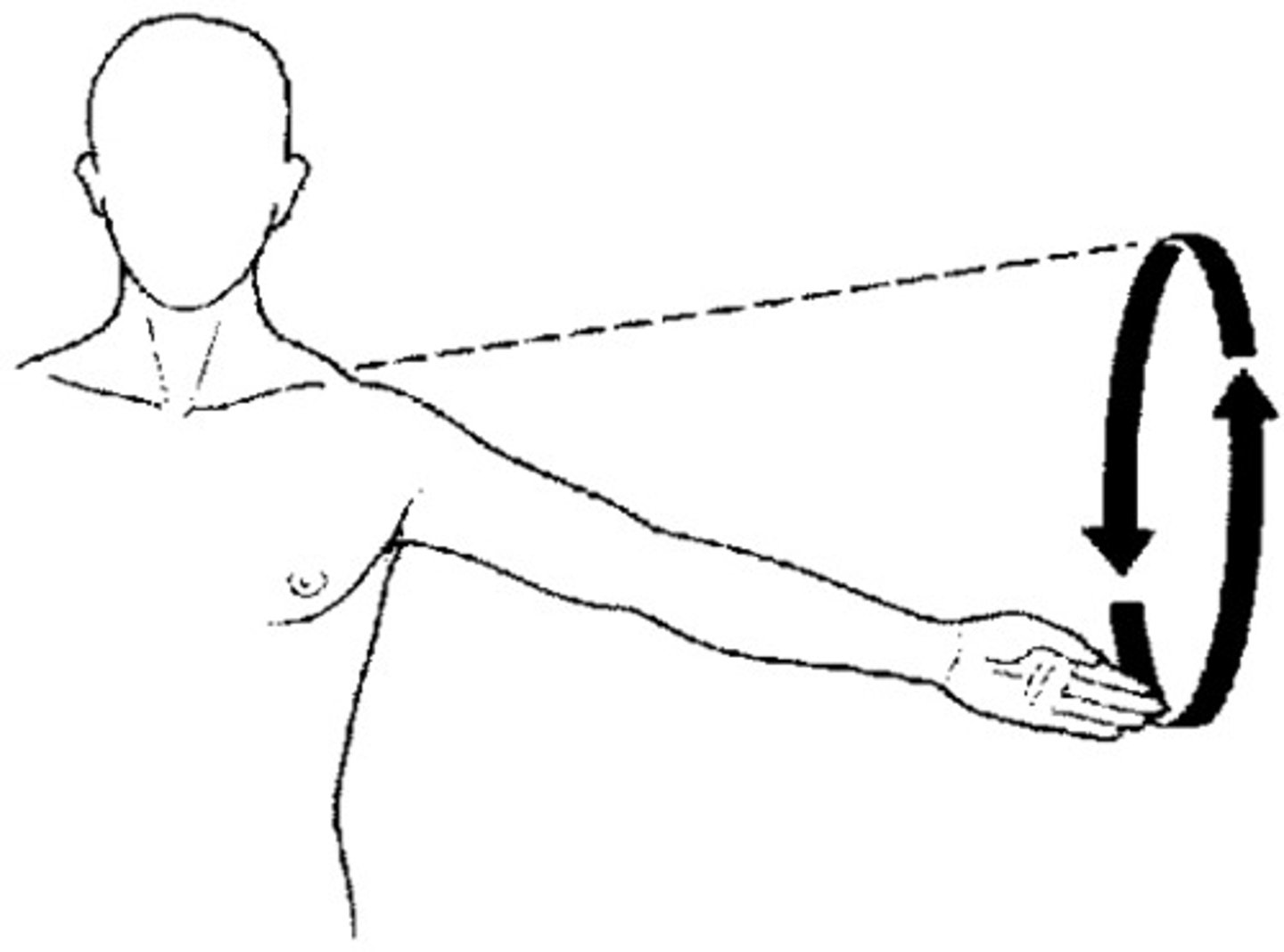
Circumduction
A movement at a synovial joint in which the distal end of the bone moves in a circle while the proximal end remains relatively stable
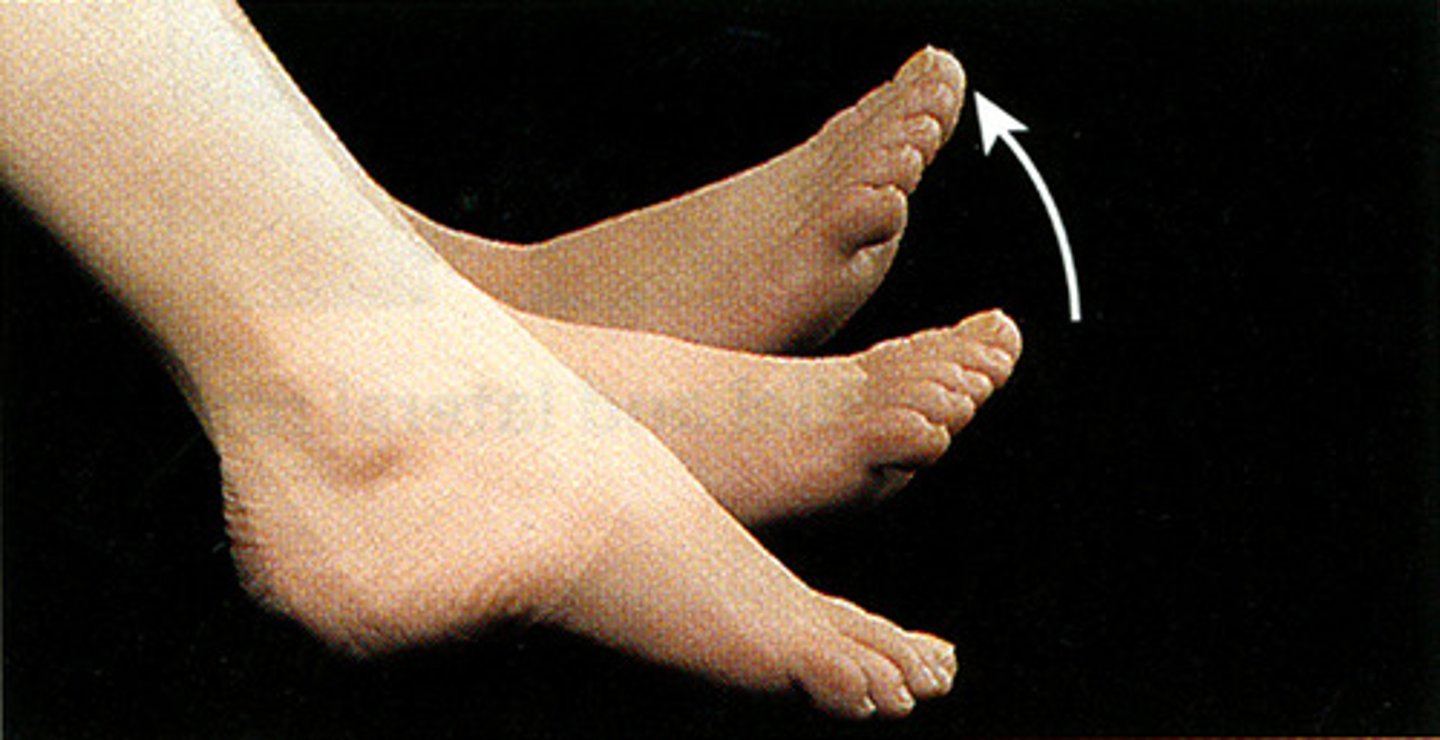
Dorsiflexion
Bending the foot in the direction of the dorsum (upper surface)
Extension
An unbending movement around a joint in a limb (as the knee or elbow) that increases the angle between the bones of the limb at the joint
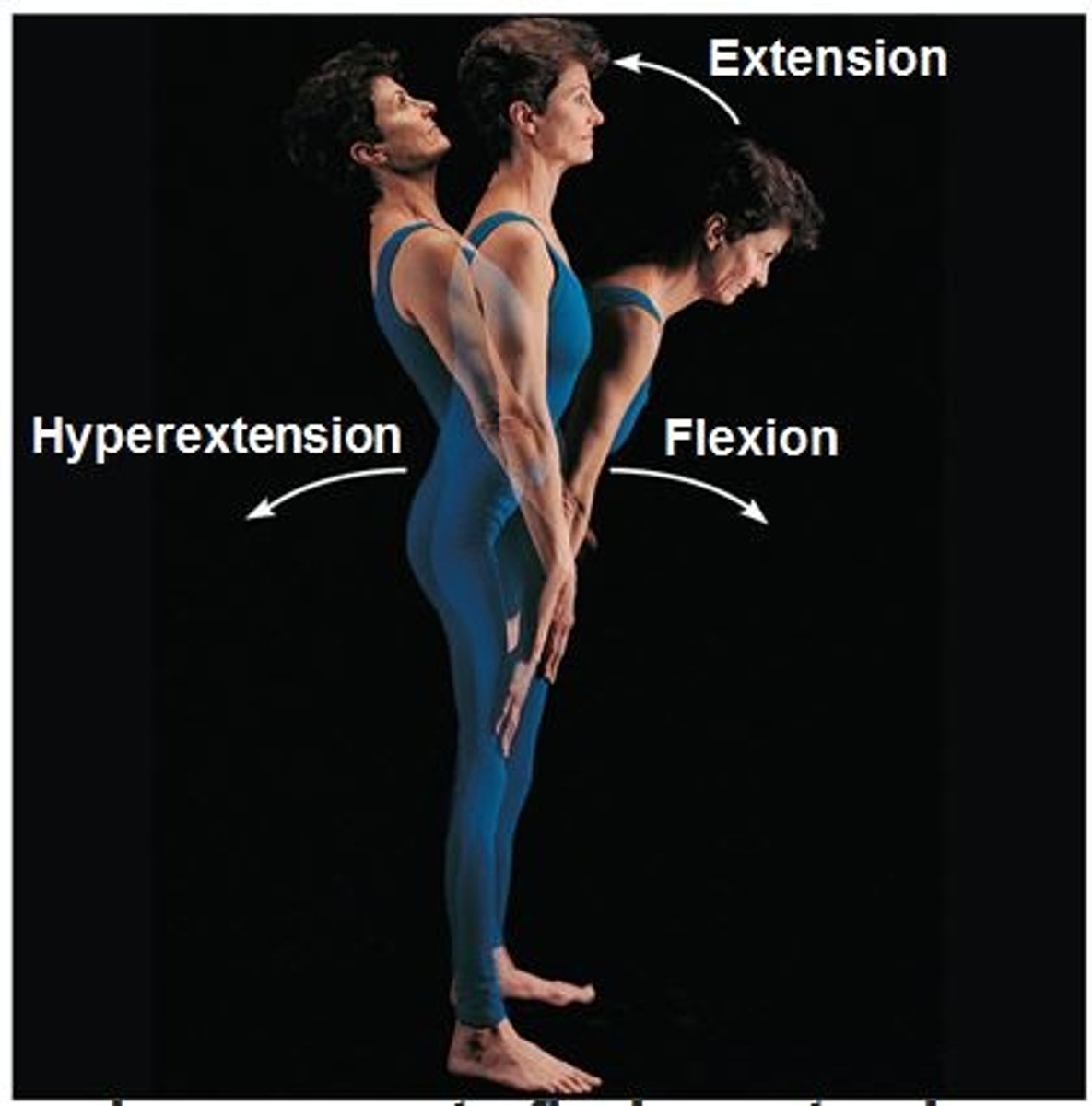
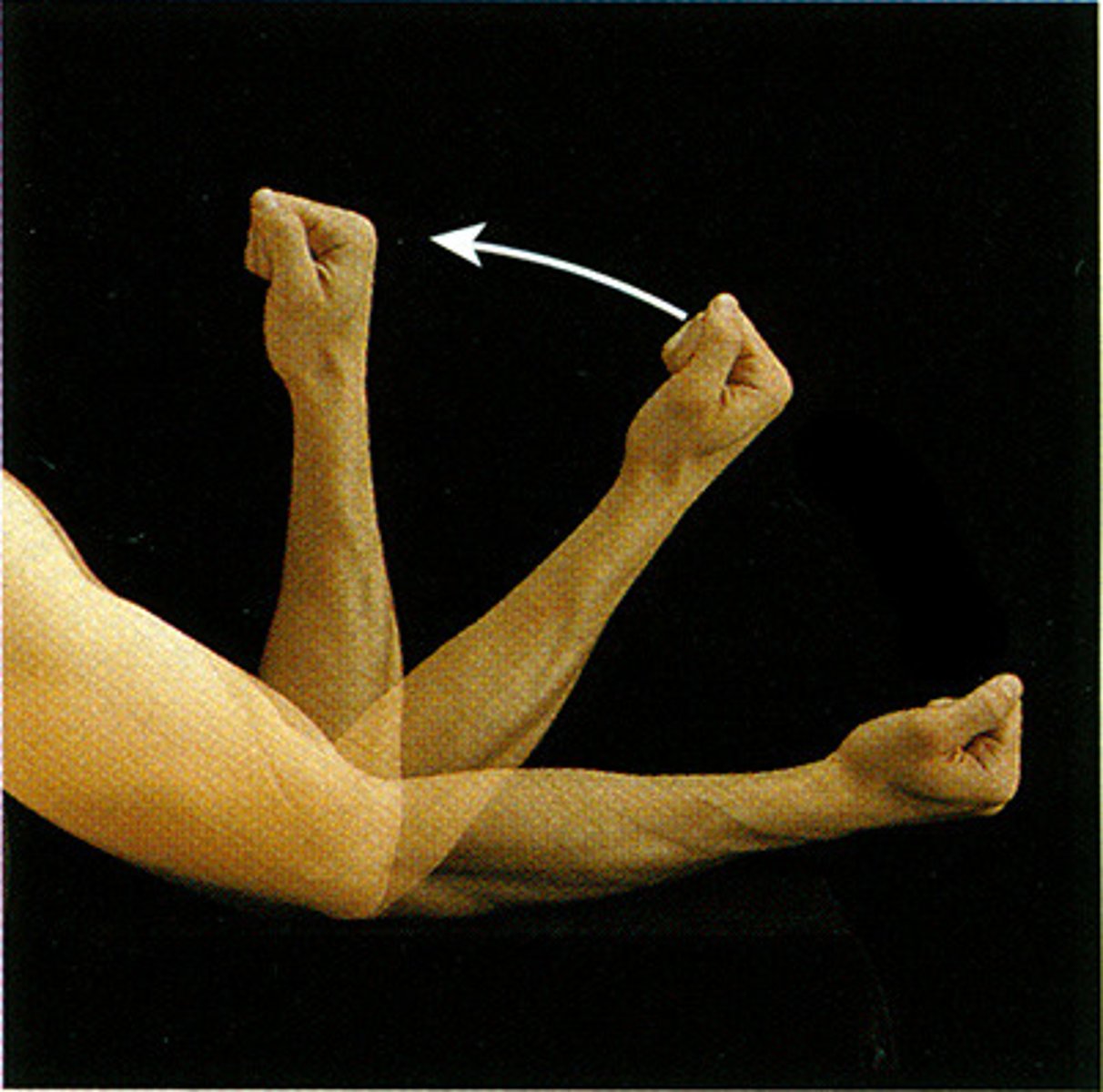
Flexion
A bending movement around a joint in a limb (as the knee or elbow) that decreases the angle between the bones of the limb at the joint
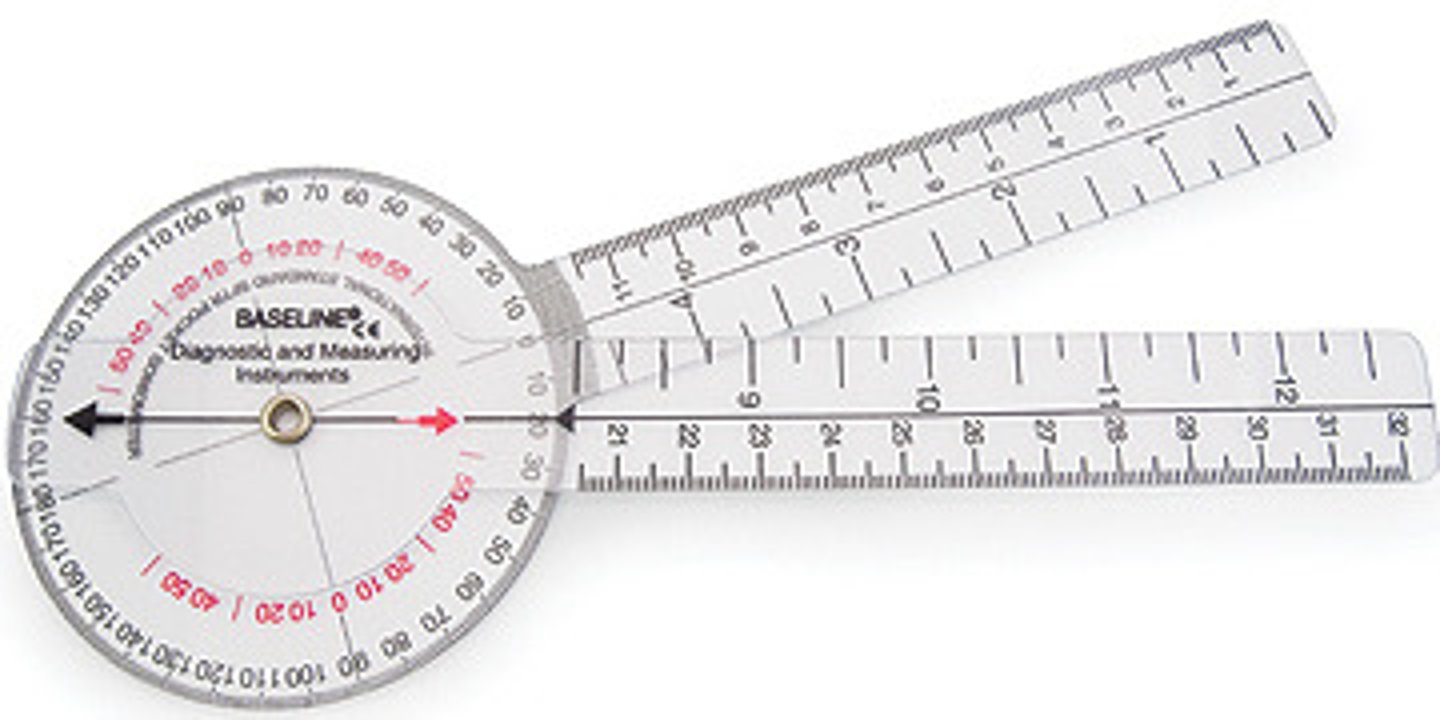
Goniometer
An instrument for measuring angles (as of a joint or the skull)
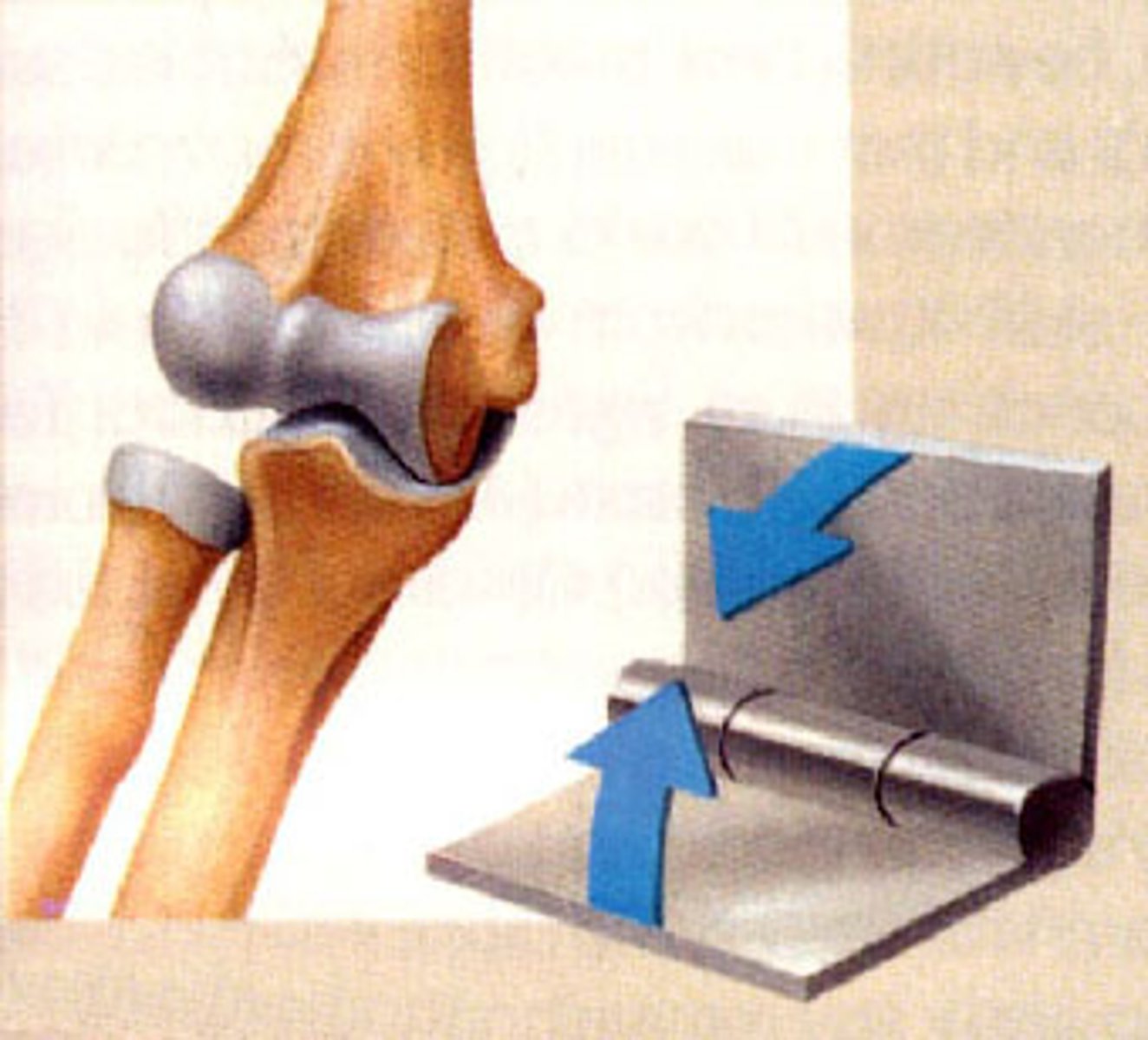
Hinge joint
Joint between bones (as at the elbow or knee) that permits motion in only one plane
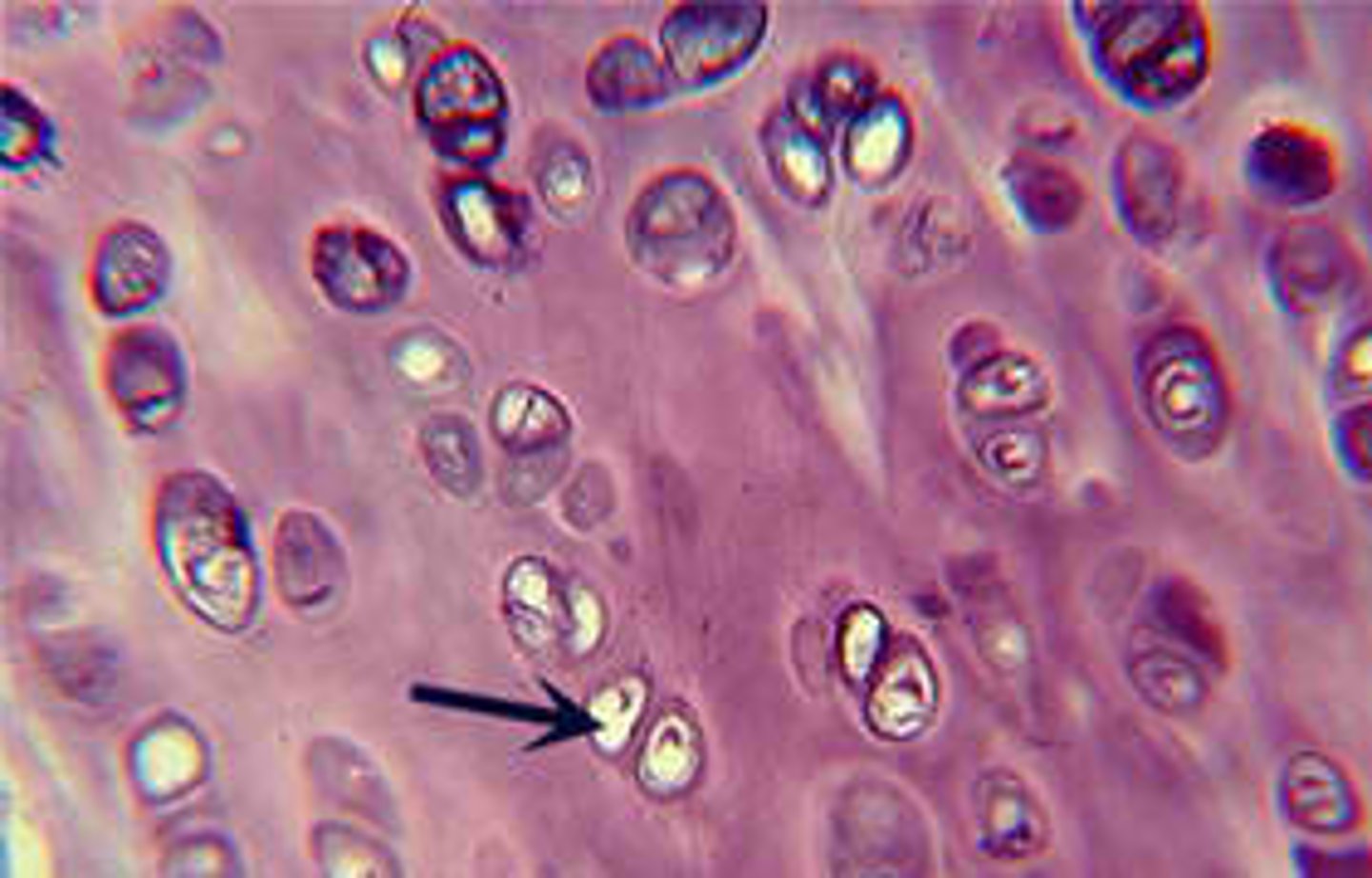
Hyaline cartilage
Translucent bluish white cartilage consisting of cells embedded in an apparently homogeneous matrix, present in joints and respiratory passages, and forming most of the fetal skeleton
Joint
The point of contact between elements of an animal skeleton whether movable or rigidly fixed together with the surrounding and supporting parts (as membranes, tendons, or ligaments)
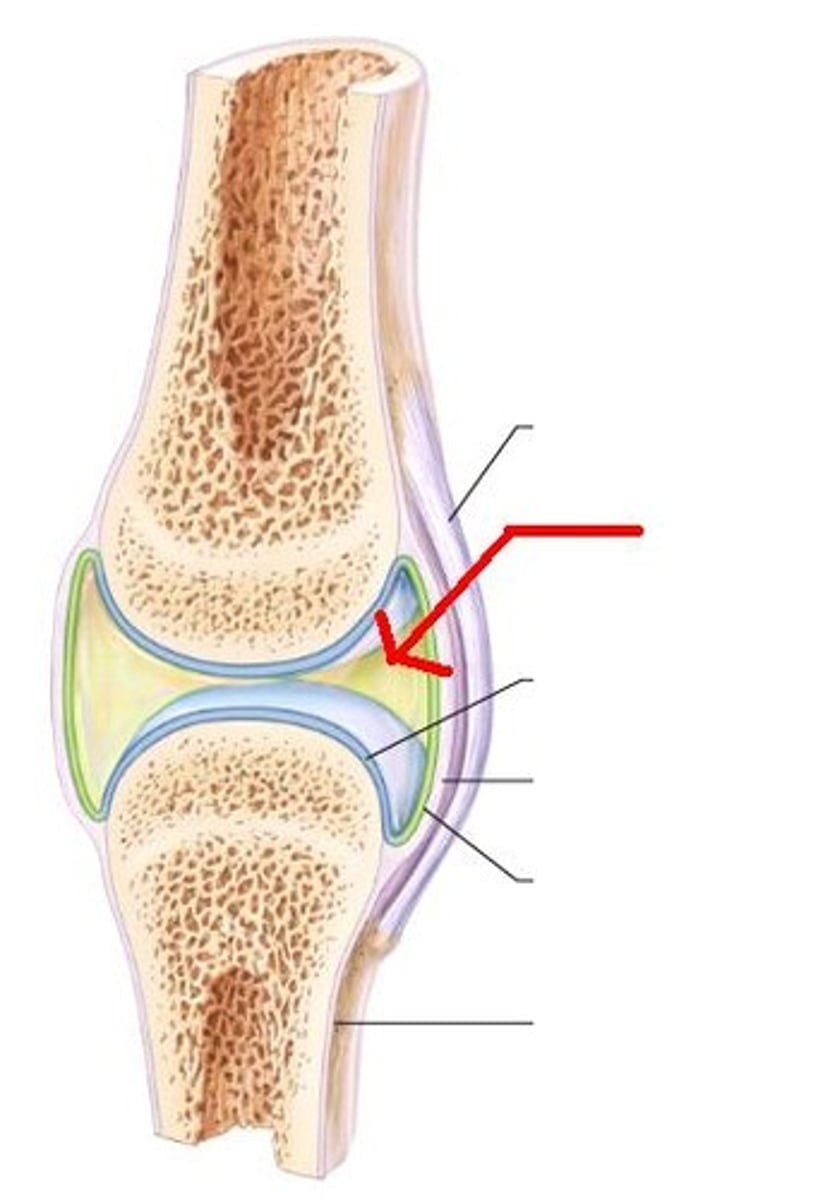
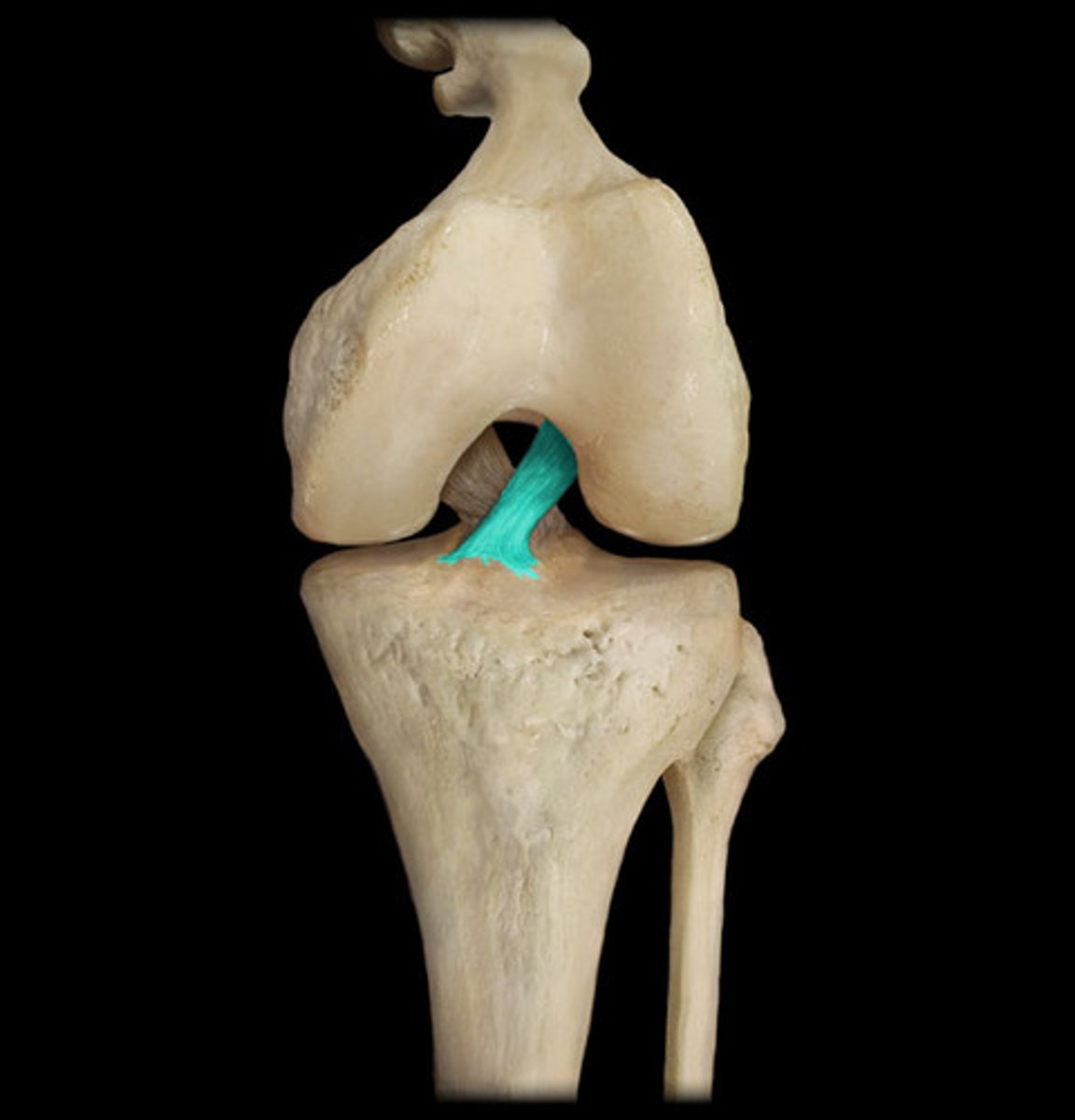
Ligament
Dense regular connective tissue that attaches bone to bone
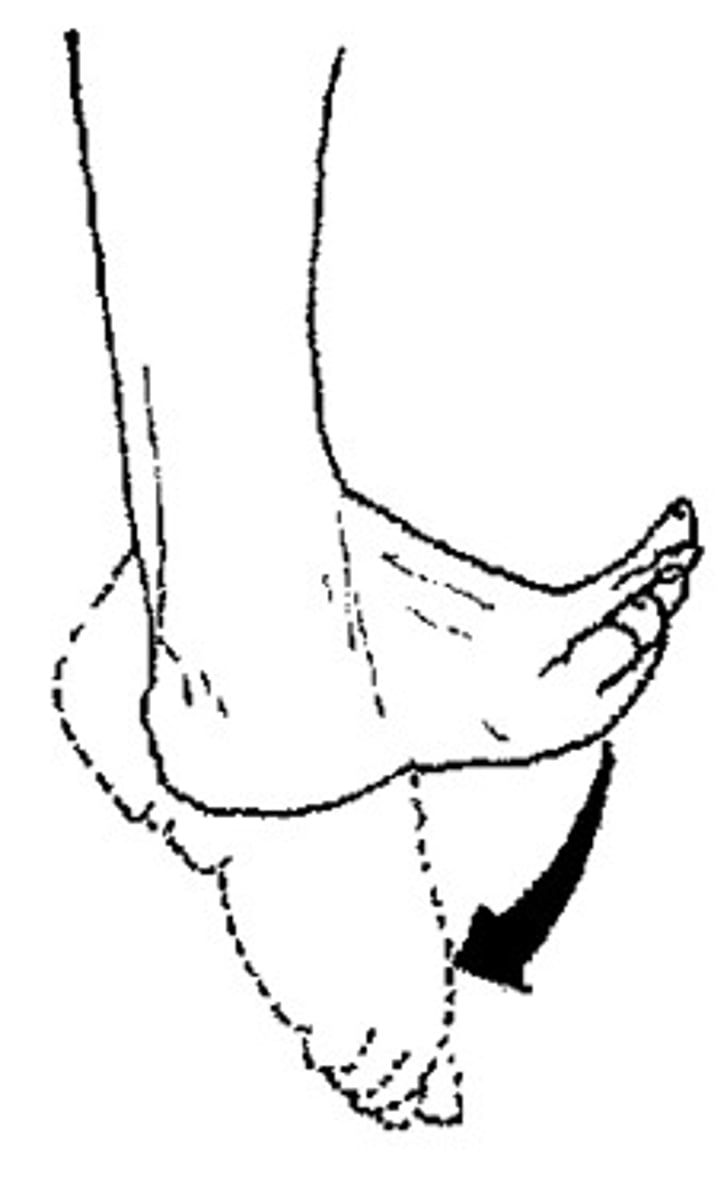
Plantar flexion
Bending the foot in the direction of the plantar surface (sole)
Range of Motion
The range through which a joint can be moved
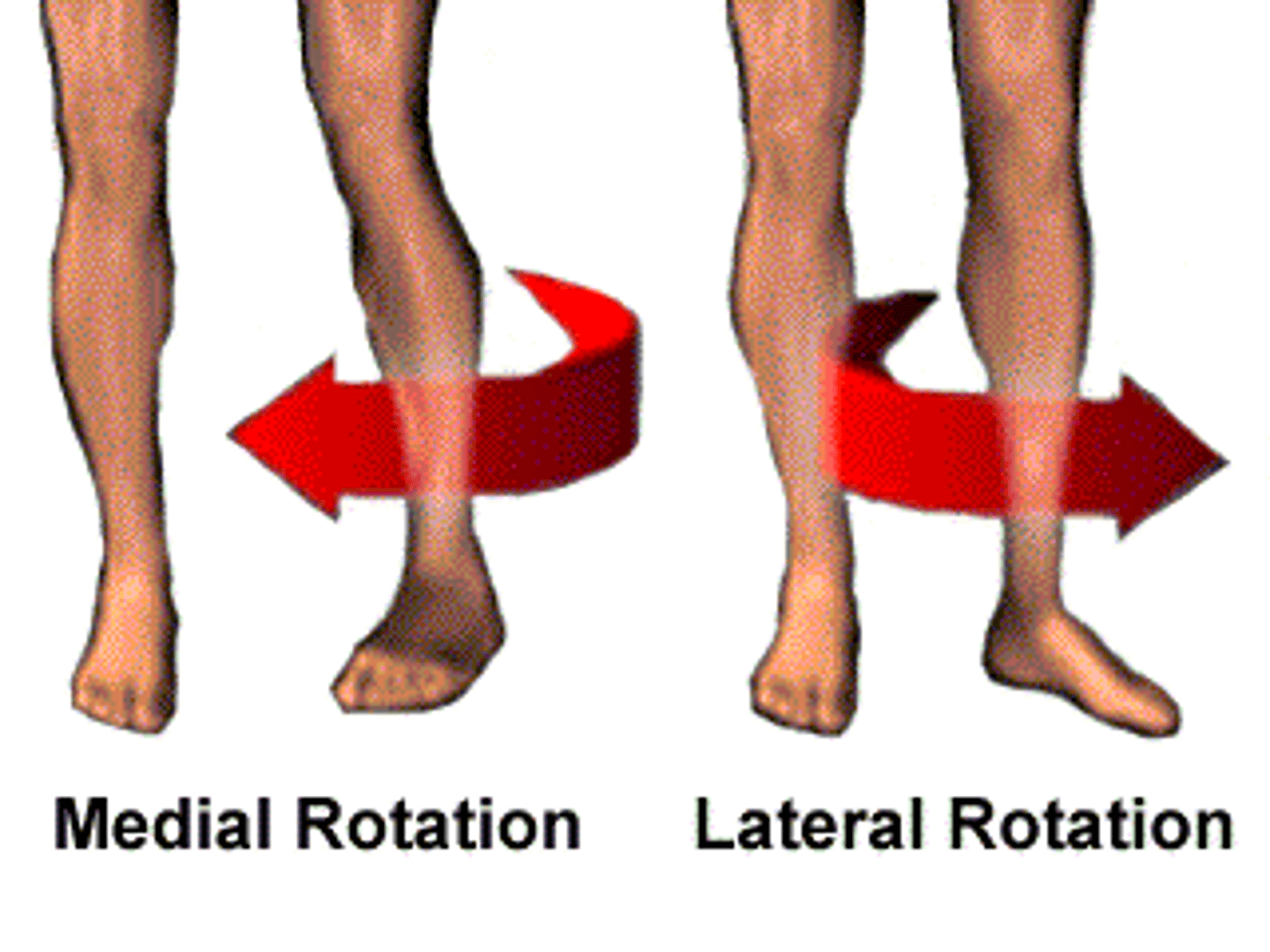
Rotation
Moving a bone around its own axis, with no other movement
Synovial cavity
The space between the articulating bones of a synovial joint, filled with synovial fluid. Also called a joint cavity.
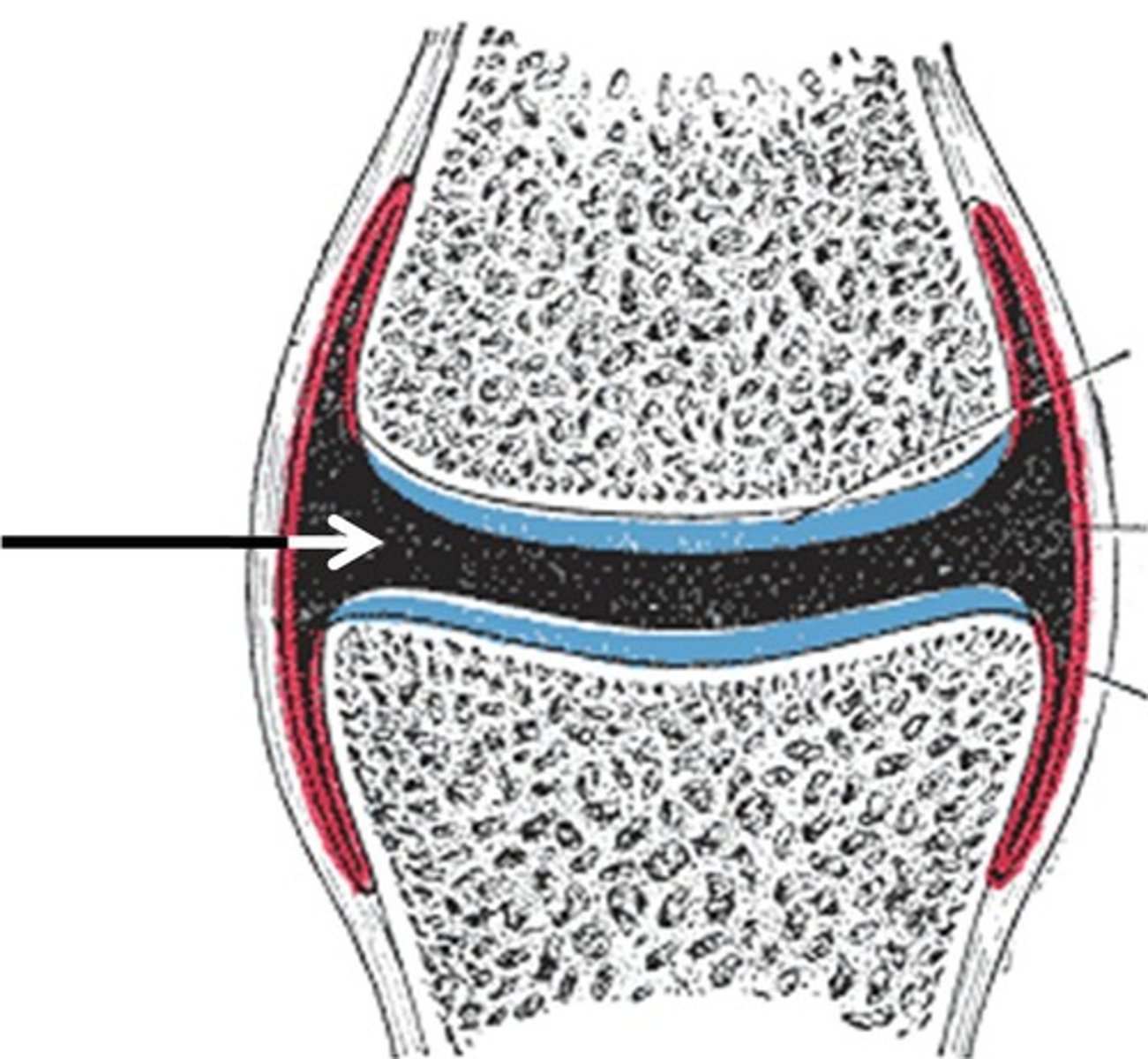
Synovial fluid
Secretion of synovial membranes that lubricates joints and nourishes articular cartilage
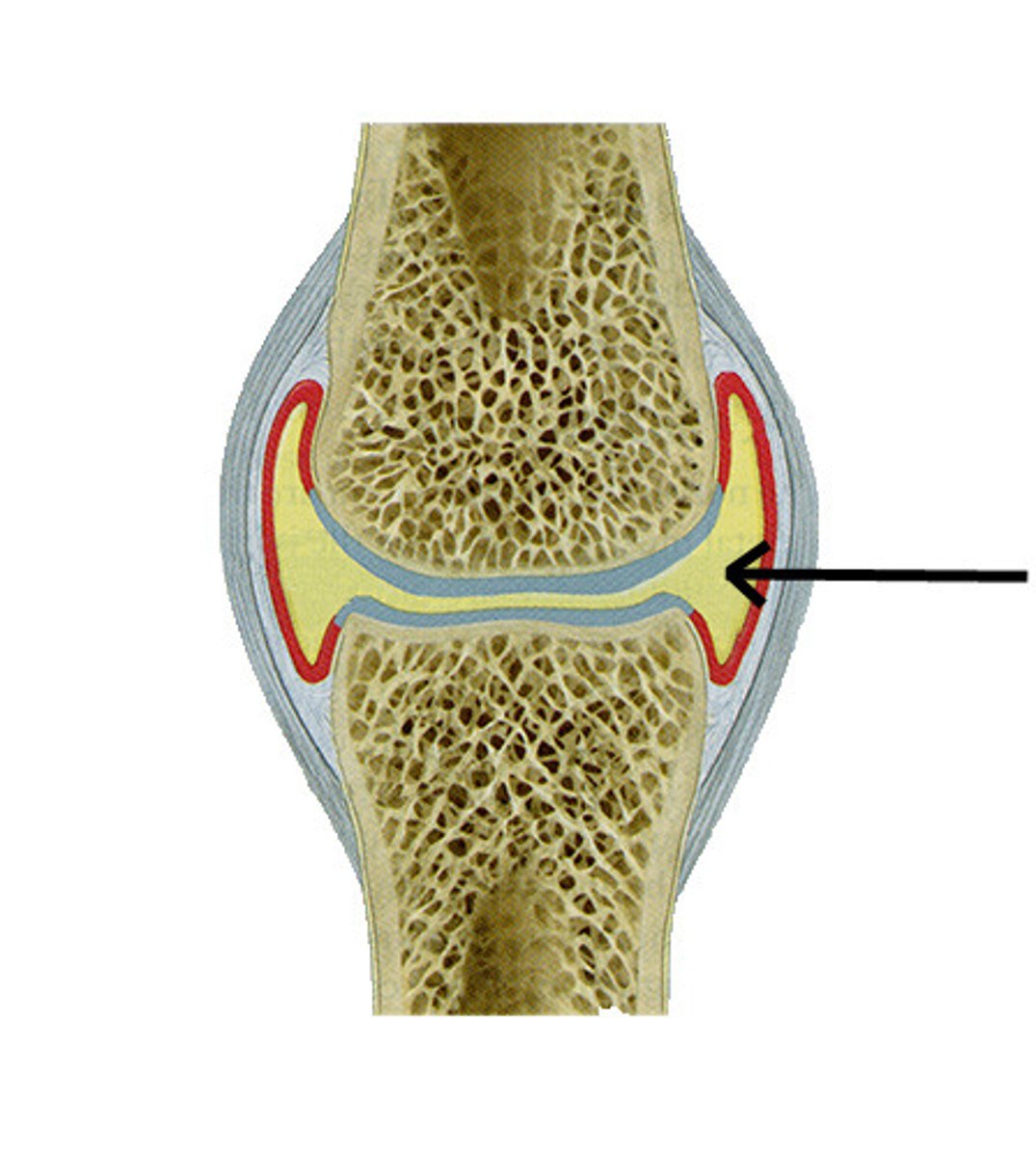
Synovial joint
A fully moveable joint in which the synovial (joint) cavity is present between the two articulating bones
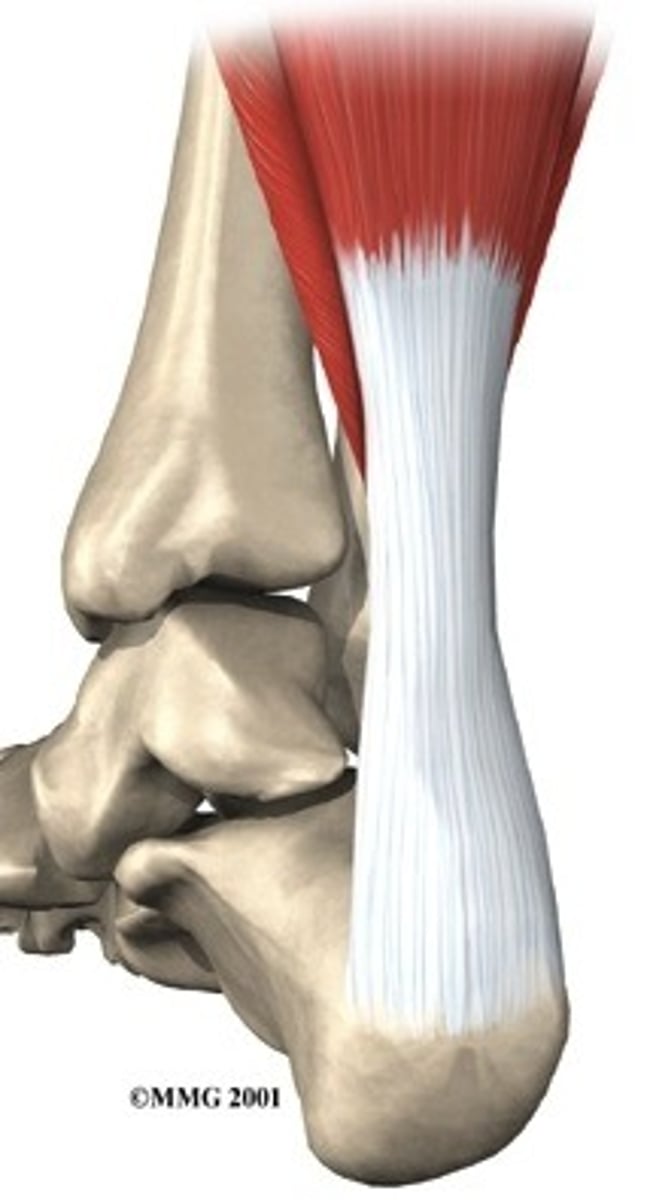
Tendon
A white fibrous cord of dense regular connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone
Smooth muscle
A tissue specialized for contraction, composed of smooth muscle fibers (cells), located in the walls of hollow internal organs, and innervated by the autonomic motor neurons
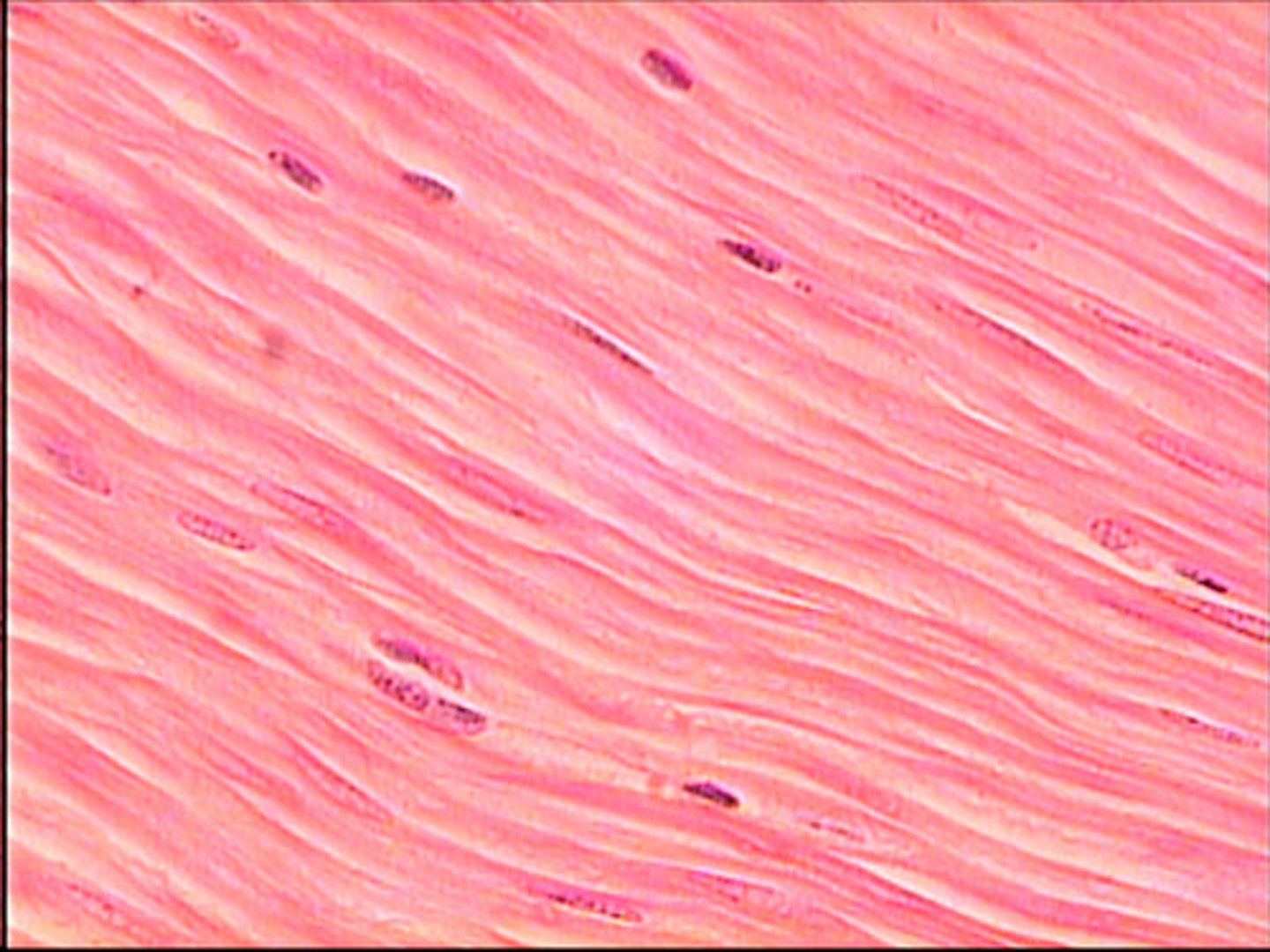
Striation
Any of the alternate dark and light cross bands of a myofibril of striated muscle
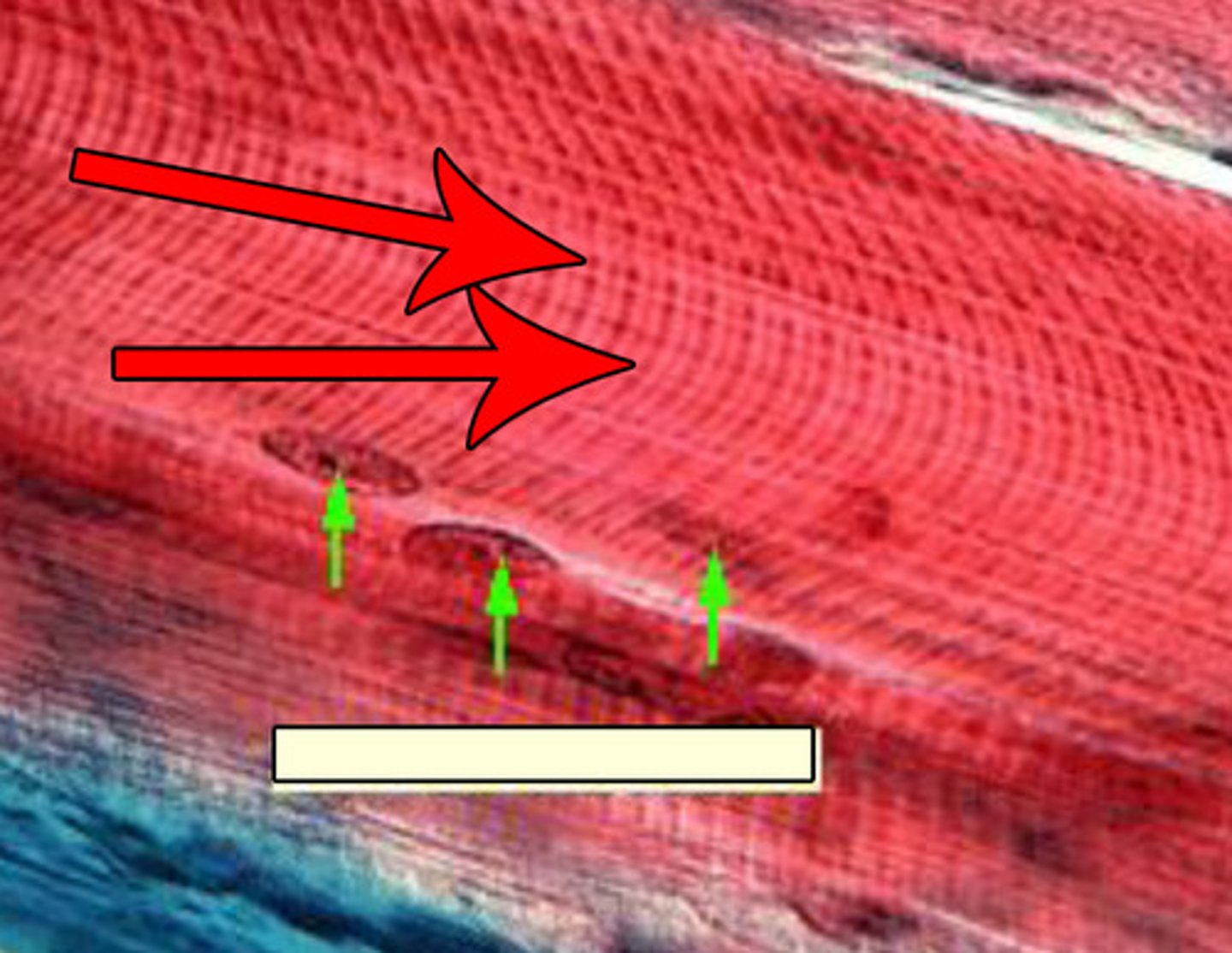
Skeletal muscle
An organ specialized for contraction, composed of striated muscle fibers (cells), supported by connective tissue, attached to bone by a tendon or aponeurosis, and stimulated by somatic motor neurons

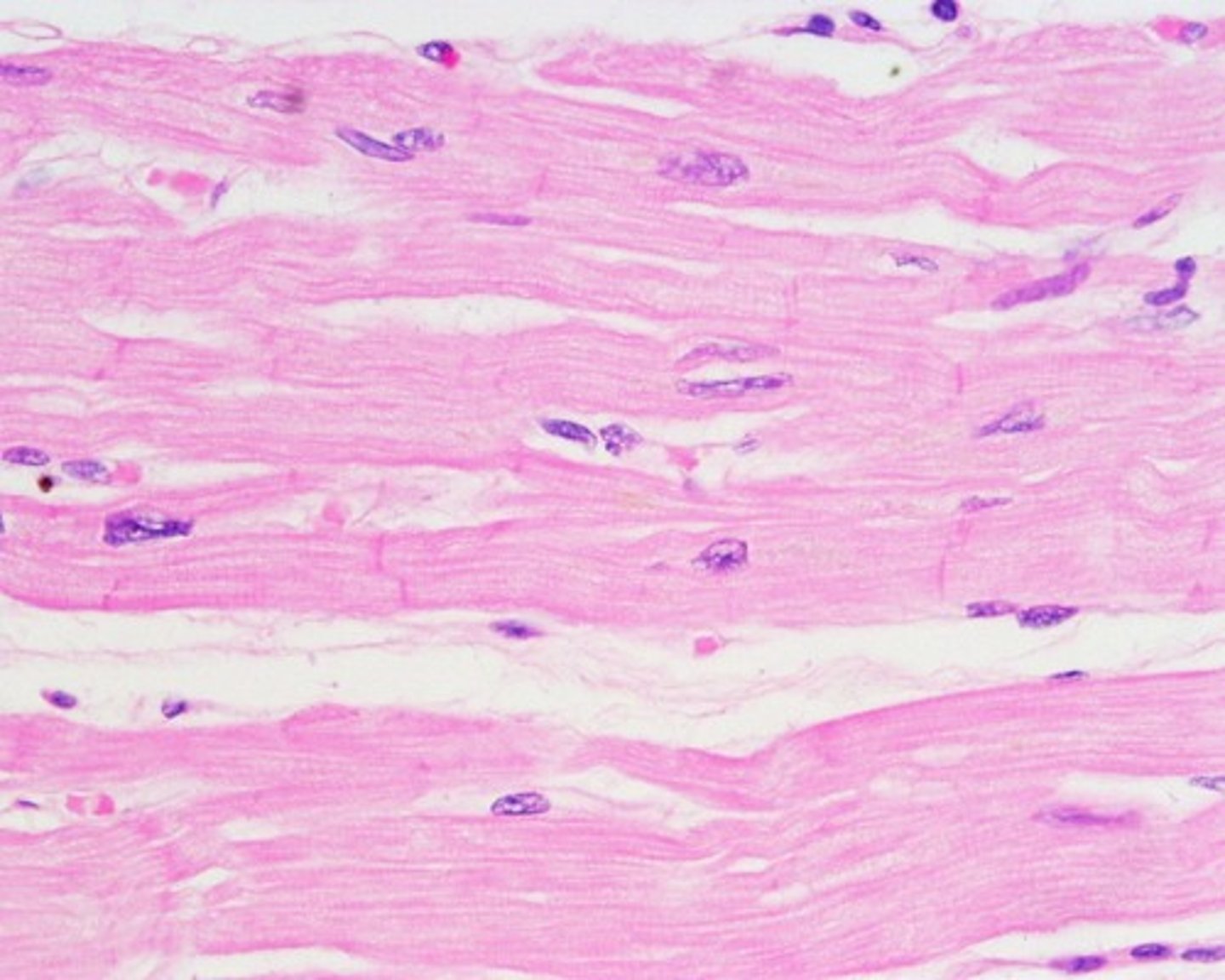
Cardiac muscle
Striated muscle fibers (cells) that form the wall of the heart; stimulated by the intrinsic conduction system and autonomic motor neurons
Muscle
An organ composed of one of the three types of muscular tissue (skeletal, cardiac, and smooth), specialized for contraction to produce voluntary and involuntary movements of parts of the body
Origin
The attachment of a muscle tendon to a stationary bone or the end opposite the insertion
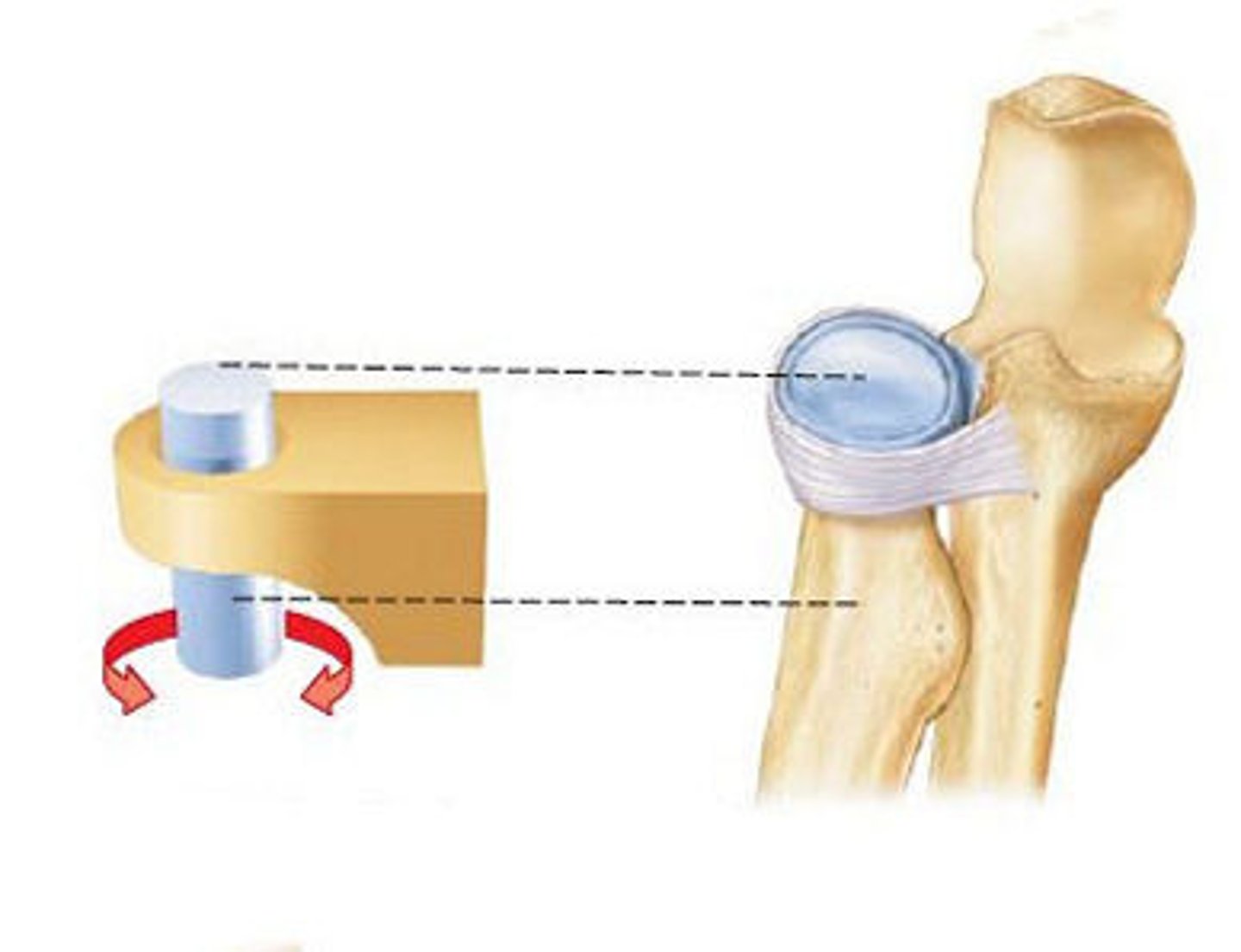
Pivot Joint
is a type of synovial joint. In pivot joints, the axis of a convex articular surface is parallel with the longitudinal axis of the bone.
Articular Cartilage
Enthesis
Bursa
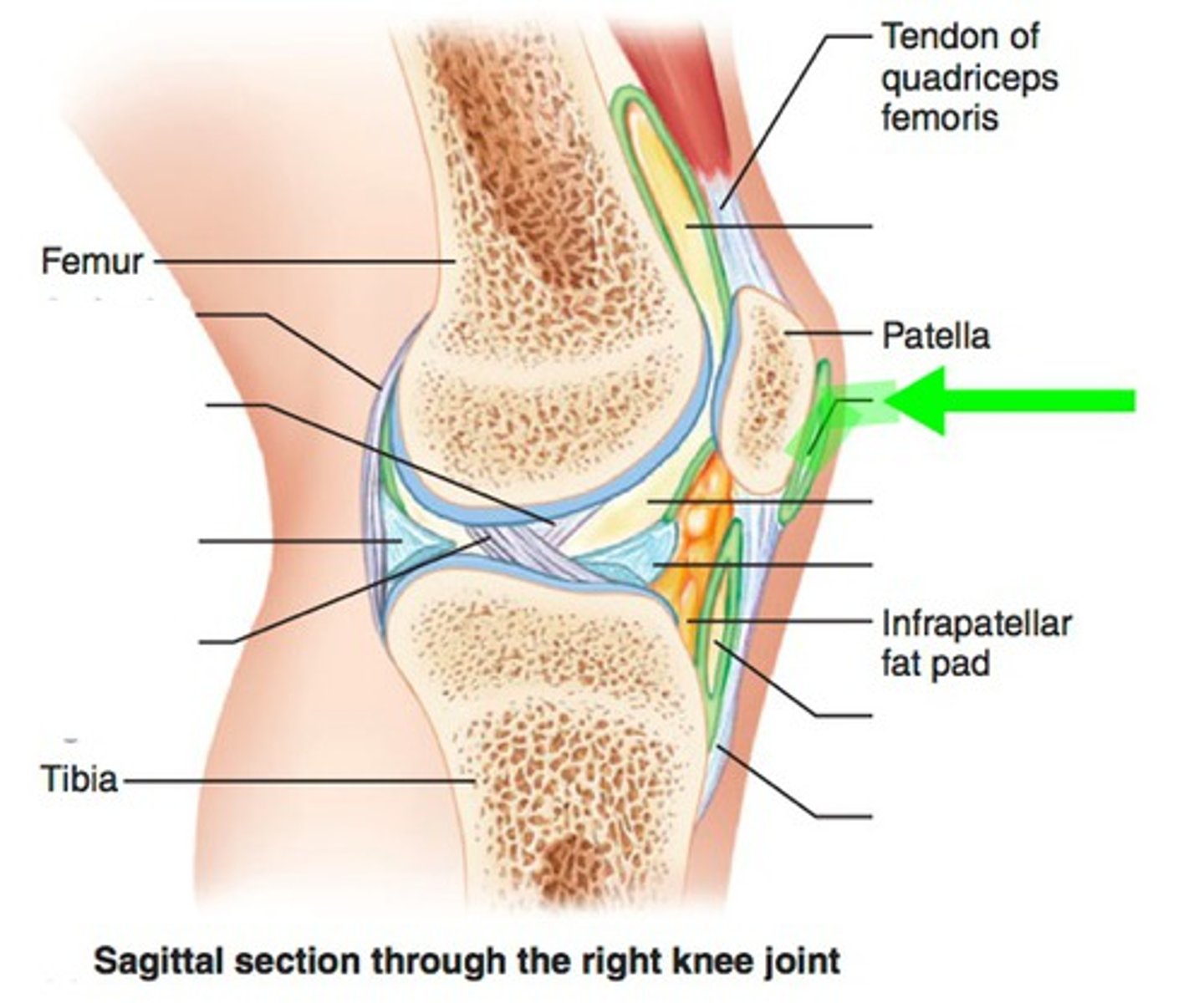
Articulation
Where parts come together at the joint
Fiborus joints
Joints that do not move
Cartilaginous joints
Joints that move a little and is linked by cartilage
Bones
This gives our bodies support and give our body shape. This needs muscles in order to move though.
Rule #1
Muscles must have at least two attachments and must cross at least one joint
Rule #2
Muscles always "pull" shorter
Rule #3
The attachment that moves is known as the insertion and the attachment that remains stationary is known as the origin
Rule #4
Muscles that decrease the angle between ventral surfaces of the body are known as flexors. Muscles that increase the angle between ventral surfaces of the body are known as extensors
Rule #5
Muscles work in opposing pairs
Rule #6
Muscle striations point to the attachments and show the direction of pull