Bacteria
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
How are bacteria classified?
1. metabolism
2. ability to produce endospores
3. motility
4. shape
What are resistant bodies that bacteria release when their environment becomes difficult to live in?
endospores
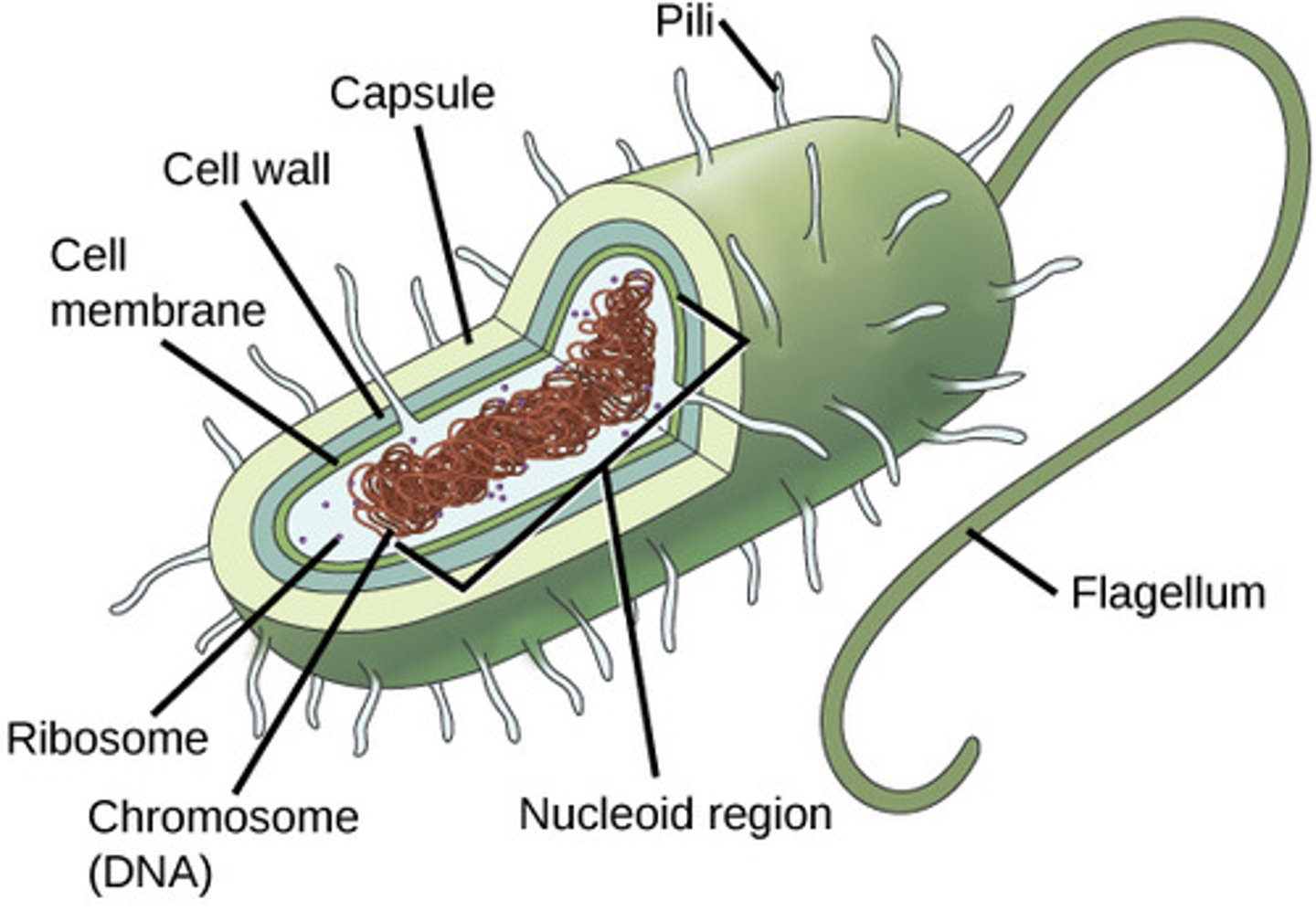
What do endospores contain?
1. DNA
2. small amount of cytoplasm
What are the bacterial means of motility?
1. flagella
2. corkscrew motion
3. gliding through slime material
Which bacterial shape is spherical?
cocci
Which bacterial shape is rod-shaped?
bacilli
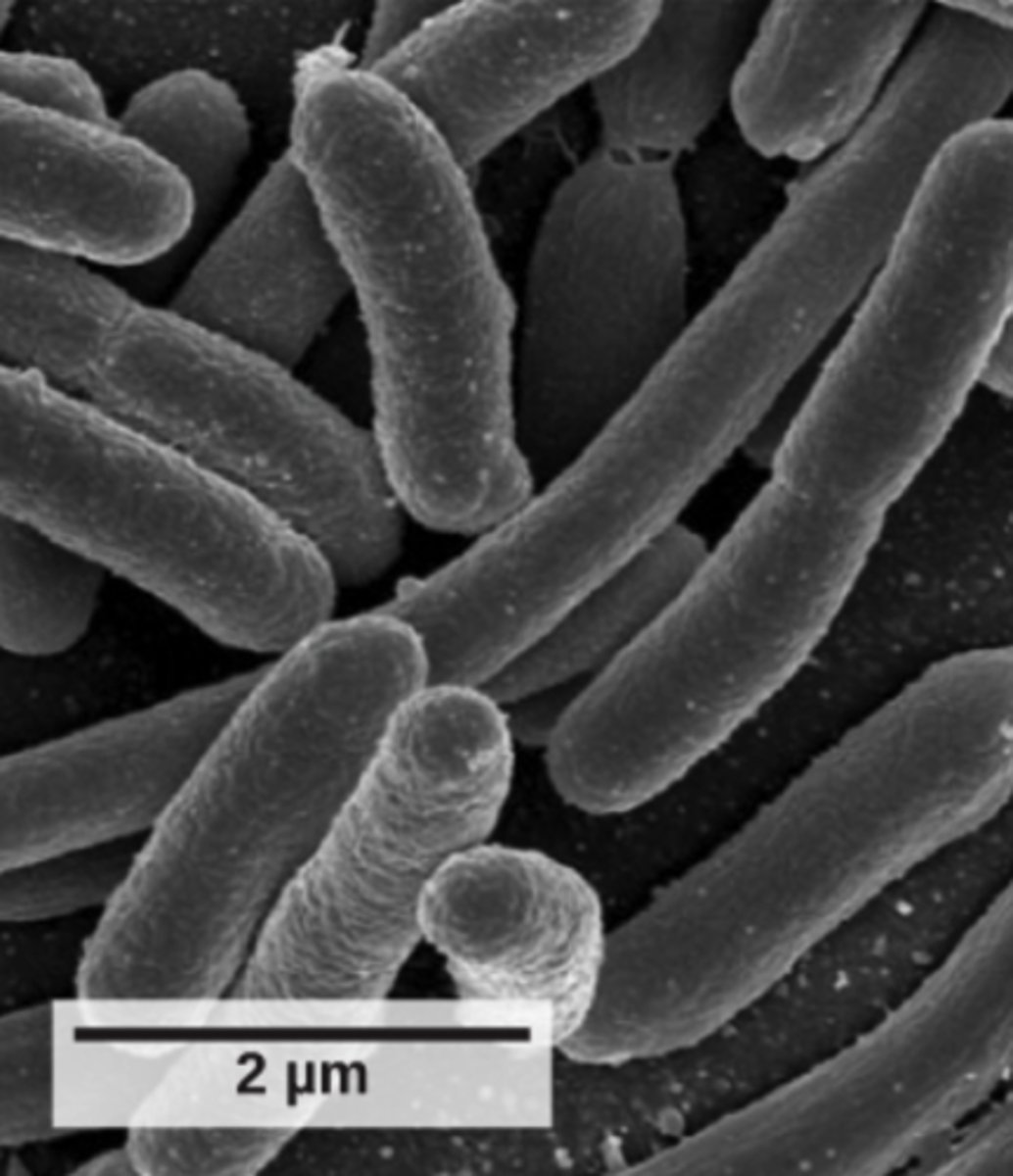
Which bacterial shape is spiral?
spirilla/spirochete

Which bacteria have thick peptidoglycan cell walls?
gram-positive
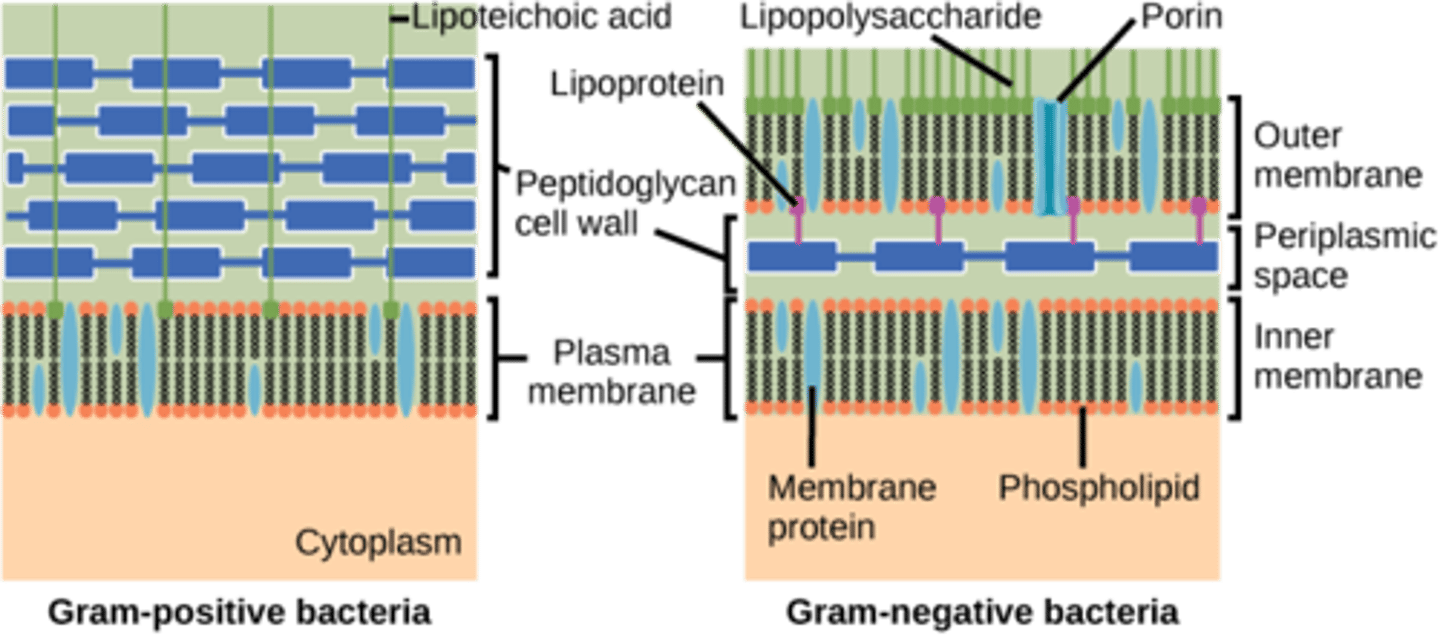
Which bacteria have thin peptidoglycan covered with lipopolysaccharides?
gram-negative
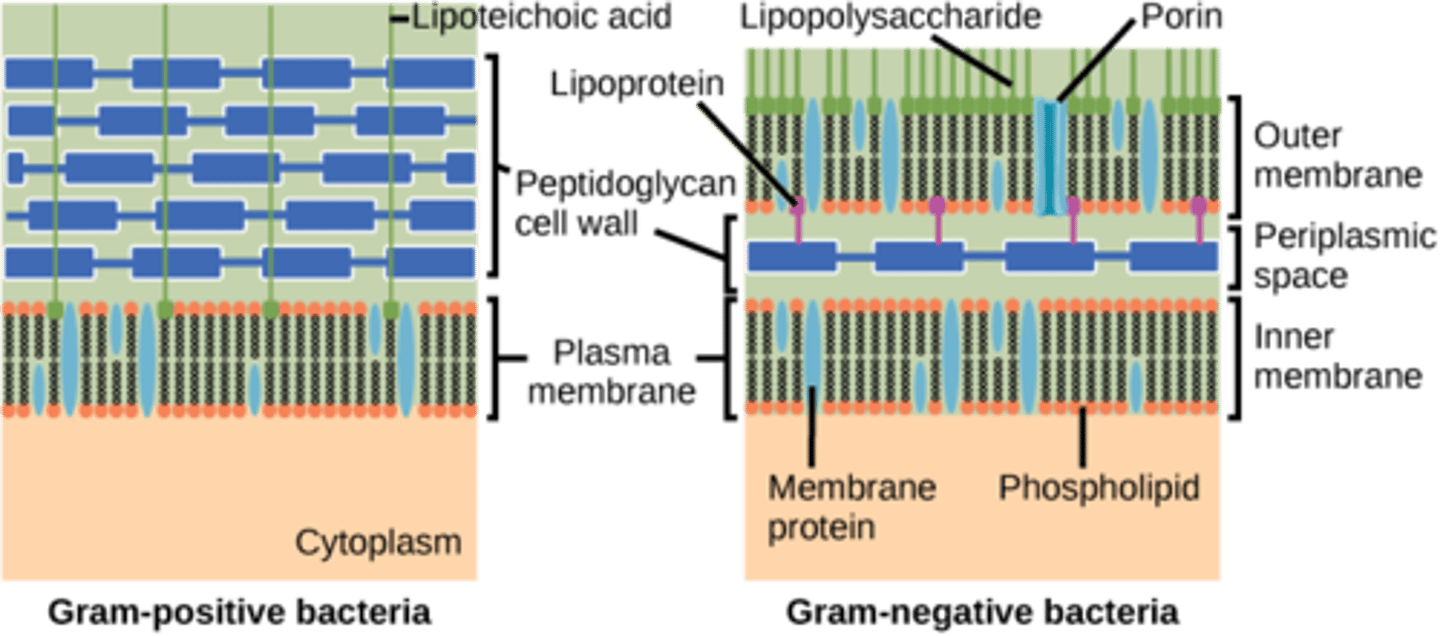
What special sugars does peptidoglycan contain?
amino sugars
What molecules are used as recognition and binding sites by bacterial viruses that cause infections?
teichoic acids
Where are teichoic acids found?
cell wall
On which bacteria are teichoic acids only found?
gram positive
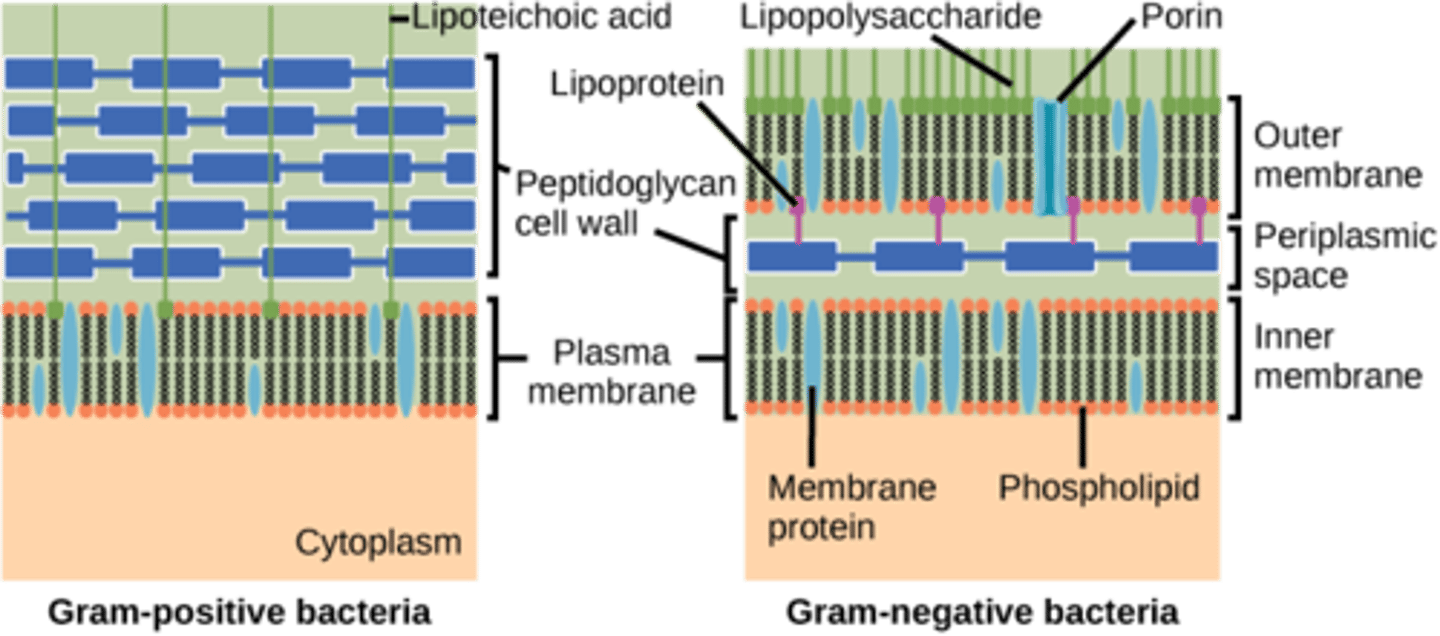
How are the teichoic acids attached to the peptidoglycan layer?
covalent bonds
Which bacteria are photosynthetic and contain an accessory pigment called phycobilins?
cyanobacteria
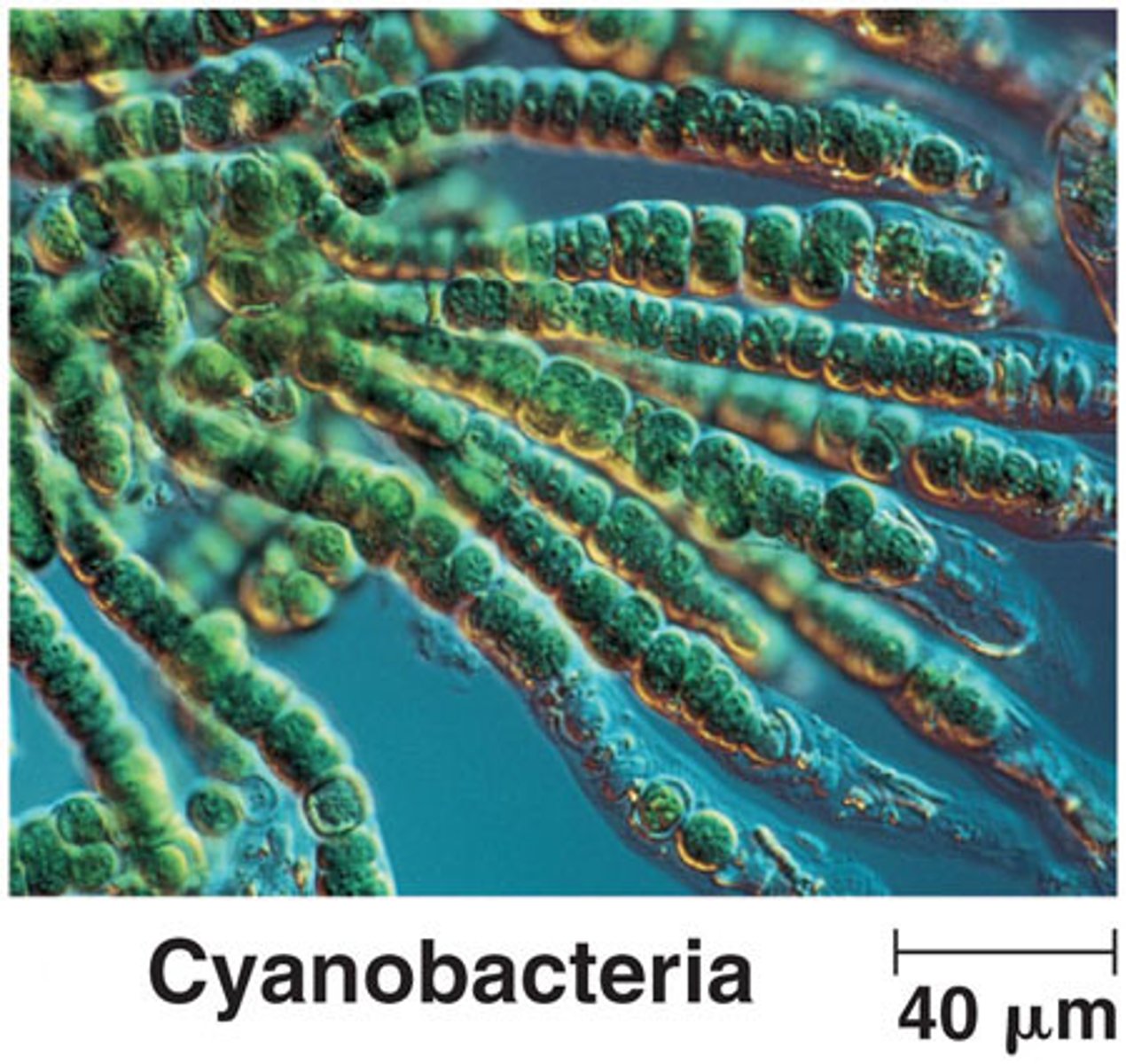
What specialized cells do cyanobacteria contain that produce nitrogen-fixing enzymes?
heterocysts
The nitrogen-fixing enzymes produced by heterocysts convert fixed inorganic nitrogen gas into NH3 that can be used to make what?
amino acids and nucleotides
What is the common name for cyanobacteria?
blue-green algae
(Note: not related to
eukaryotic algae groups)
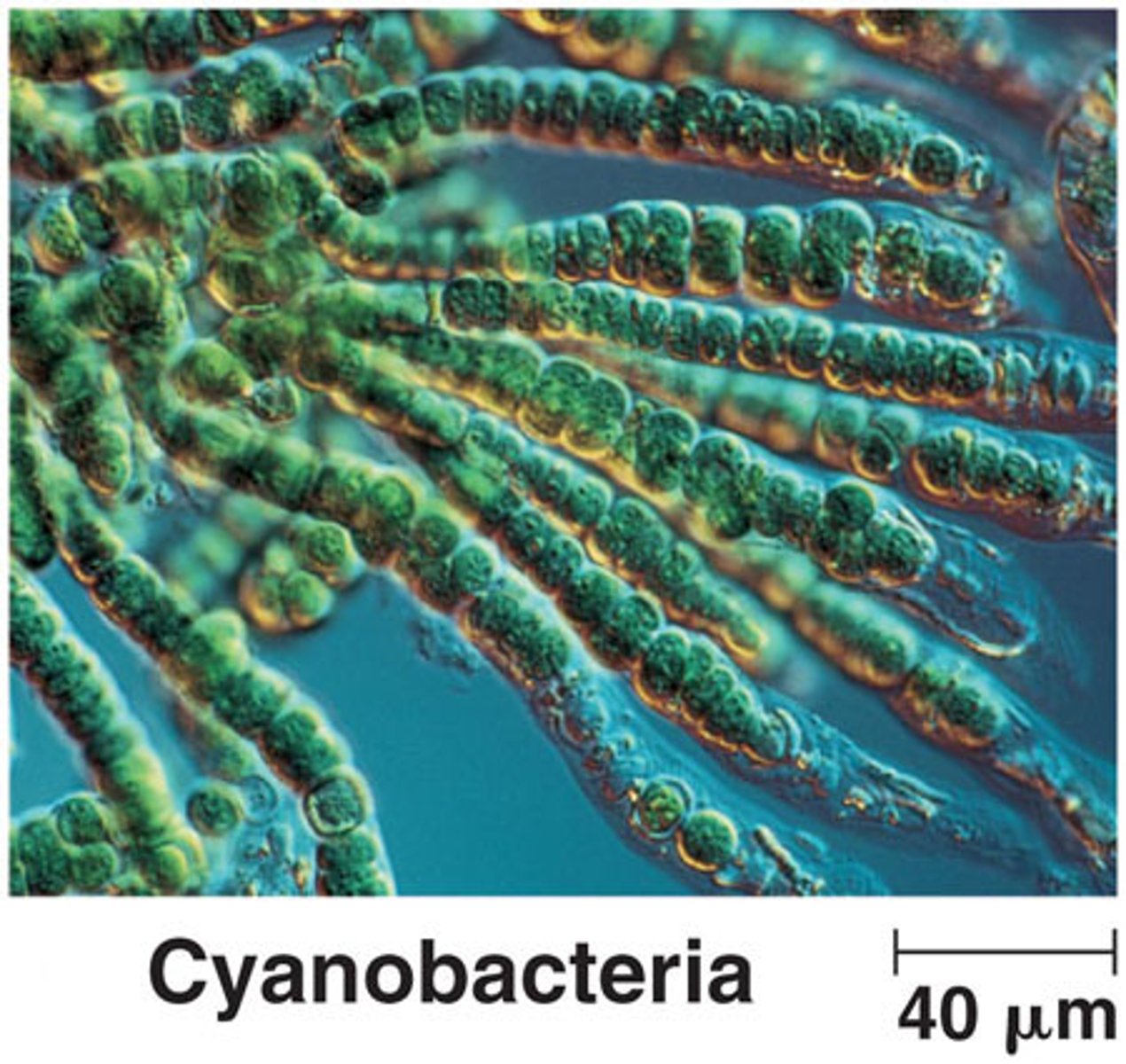
Of what organisms are the oldest known fossils?
cyanobacteria
Which bacterial group contains nitrifying bacteria, which are able to convert ammonia to nitrate with autotrophic metabolism?
chemosynthetic
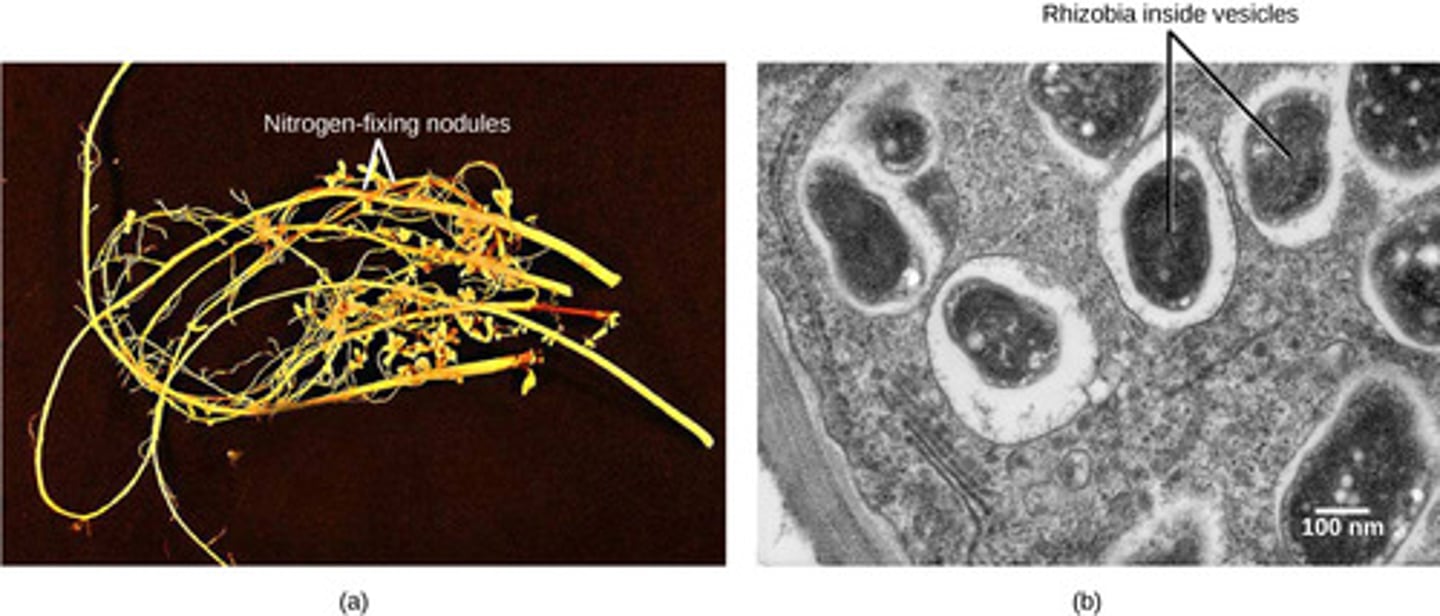
Which bacteria are heterotrophs that fix N2?
nitrogen-fixing
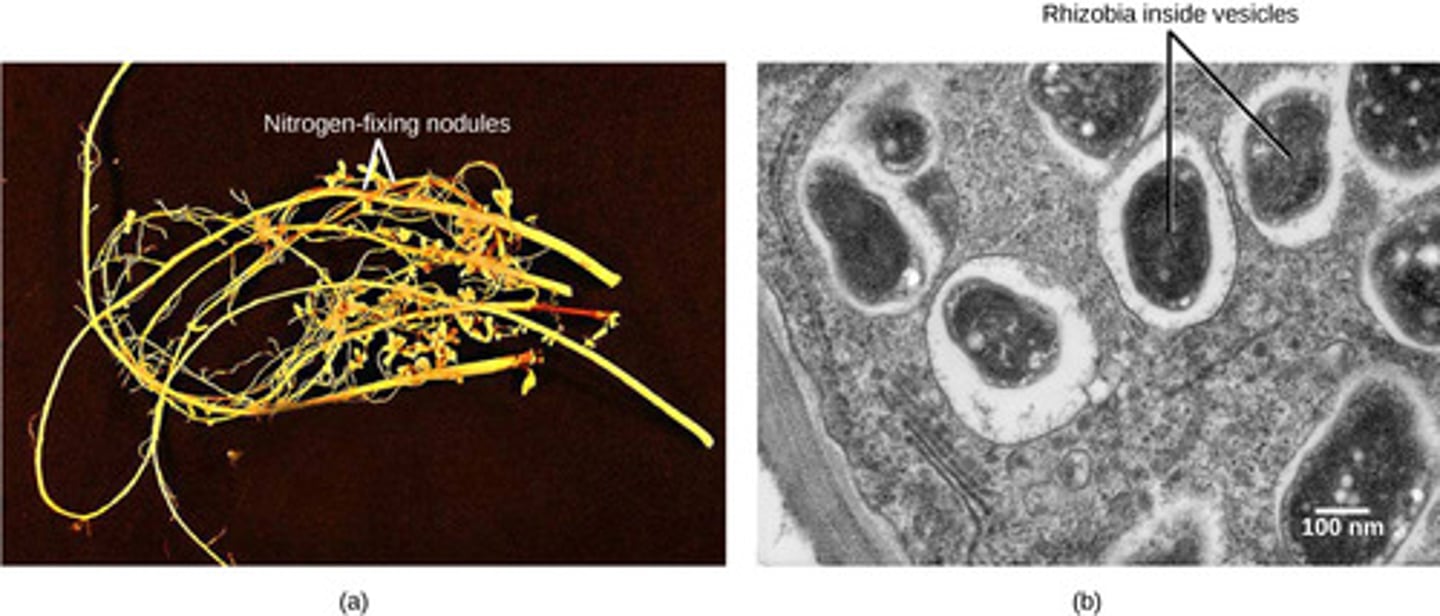
Where do nitrogen-fixing bacteria live?
nodules of plants
(Note: a form of mutualism)
Which bacterial group contains coiled bacteria that move with a corkscrew motion via internal flagella between cell wall layers?
Spirochetes
