Database Management Hell
1/85
Earn XP
Description and Tags
UGHHHHHHhHhh i just need to pass
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
database
a collection of data in a structured format. modern databases are invariably stored on computers.
database management system (DBMS)
software that reads and writes data in a database. ensures that data is secure, internally consistent, and available at all times. large & complex.
query
a request to retrieve or change data in a database.
data
numeric, textual, visual, or audio information that describes real-world systems.
format
data may be produced as numbers, text, images, audio, or video.
query language
a specialized programming language, designed specifically for database systems. they read and write data efficiently.
transaction
a group of queries that must be either completed or rejected as a whole.
architecture
describes the internal components and the relationships between components in a database system.
log
a file containing a complete record of all inserts, updates, and deletes processed by the database.
data dictionary/glossary
documents additional detail in text format. includes names, synonyms, and descriptions of entities, relationships, and attributes.
relational database
stores data in tables, columns, and rows, similar to a spreadsheet.
SQL
Structured Query Language and includes statements that read and write data, create and delete tables, and administer the database system.
CRUD operations
four common queries: Create, Read, Update, and Delete data
SQL statement
a complete, executable database command.
INSERT INTO table
VALUES (new values)
adds a new row
SELECT column
FROM table
WHERE column <=> value
retrieves based on your set parameters
UPDATE table
SET column <=> new value
WHERE column <=> row
change something based on parameters
CREATE TABLE table (
column datatype,
column datatype,
);
creates a new table by specifying the table and column names.
data type
indicates the format of column values. numeric, textual, or complex.
INT
stores integer values.
DECIMAL
stores fractional numeric values.
VARCHAR
stores textual values.
DATE
stores year, month, and day.
VARCHAR(10)
indicates ten characters size.
DECIMAL(10, 3)
indicates ten significant digits, including three after the decimal point.
database design
a specification of database objects such as tables, columns, data types, and indexes.
Conceptual design
Logical design
Physical design
conceptual design (aka analysis/modeling)
phase that specifies database requirements without regard to a specific database system.
conceptual design steps
Discover entities, relationships, and attributes
Determine cardinality
Distinguish strong and weak entities
Create supertype and subtype entities
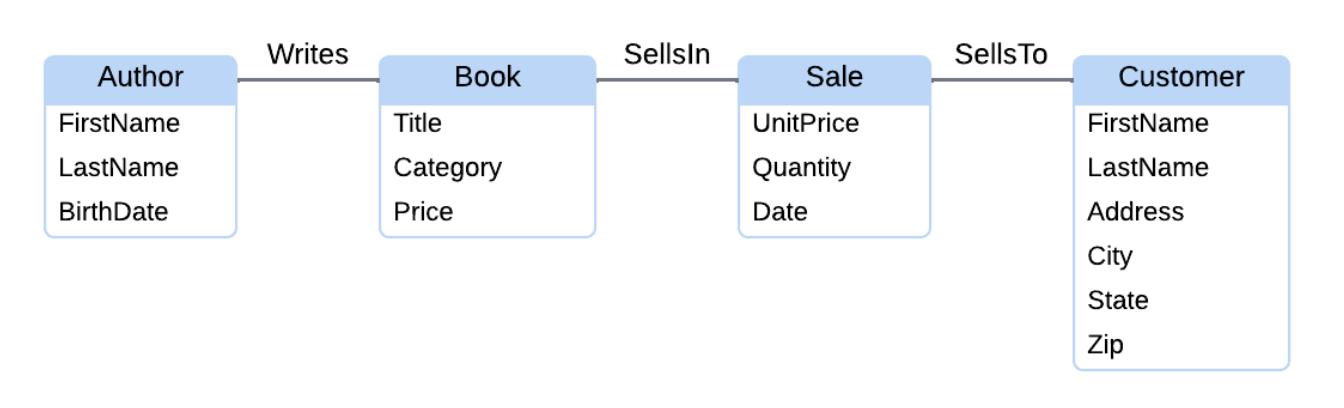
ER diagrams
entities, relationships, and attributes are depicted in a diagram.
ER diagram format
Rectangles with round corners represent entities. Entity names appear at the top of rectangles.
Lines between rectangles represent relationships.
Text inside rectangles and below entity names represent attributes.
logical design
phase that implements database requirements in a specific database system.
key
a column used to identify individual rows of a table. created with CREATE TABLE statements
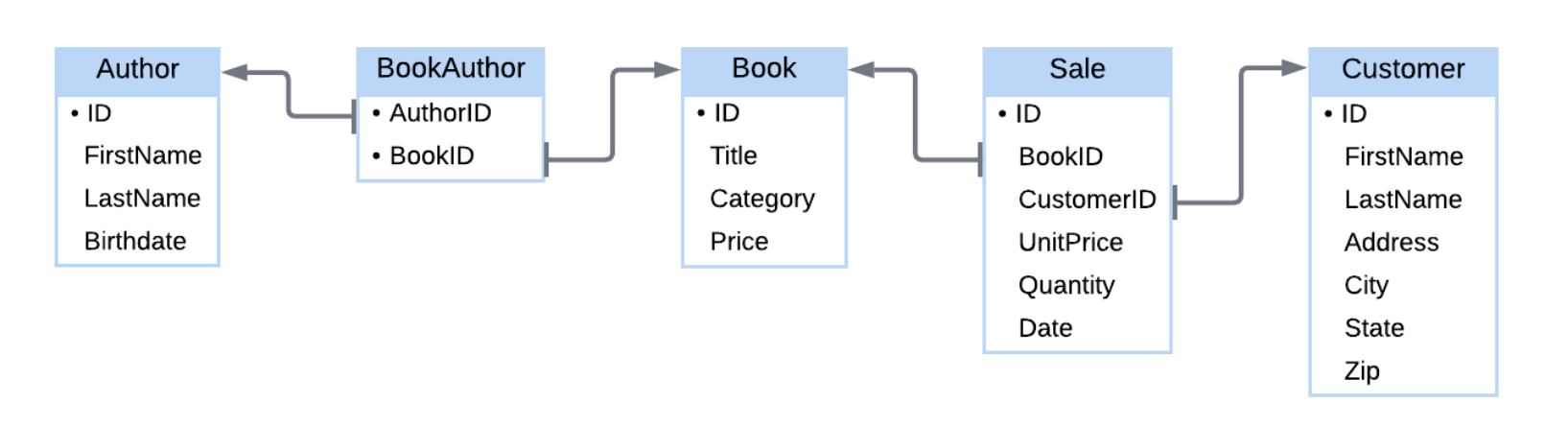
table diagram
ER diagrams but more detailed.
table diagram format
Rectangles with square corners represent tables. Table names appear at the top of rectangles.
Text within rectangles and below table names represents columns.
Bullets (●) indicate key columns.
Arrows between tables indicate columns that refer to keys. The tail of the arrow is aligned with the column and the arrow points to the table containing the key.
physical design
phase that adds indexes and specifies how tables are organized on storage media.
data independence
principle where physical design affects query processing speed but never affects the query result.
API (application programming interface)
a library of procedures or classes that links a host programming language to a database. host language calls library procedures, which handle details such as connecting to the database, executing queries, and returning results.
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS name;
creates database only if it doesn’t exist (duh)
stored procedure
a named collection of one or more SQL statements that are pre-compiled and stored within the database. a single stored procedure can perform a defined set of operations.
schema
a logical container or namespace within a database used to organize and group related database objects.
entity-relationship model
a high-level representation of data requirements, ignoring implementation details.
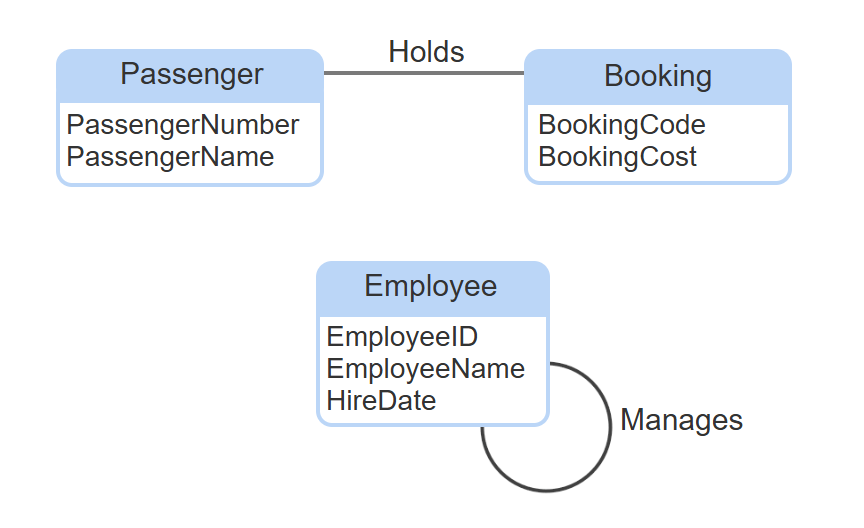
entity
a person, place, product, concept, or activity. usually nouns, but not all nouns are entities.
relationship
a statement about two entities. usually verbs.
attribute
a descriptive property of an entity used in both entity-relationship and relational models. in the relational model, attribute is a formal term for column. usually nouns that denote specific data, such as names.
type
a set in entity-relationship modeling, ex. set of employees
instance
an individual thing in entity-relationship modeling. ex: the employee Sam Snead.
cardinality
refers to maxima and minima of relationships and attributes.
relationship maximum
the greatest number of instances of one entity that can relate to a single instance of another entity.
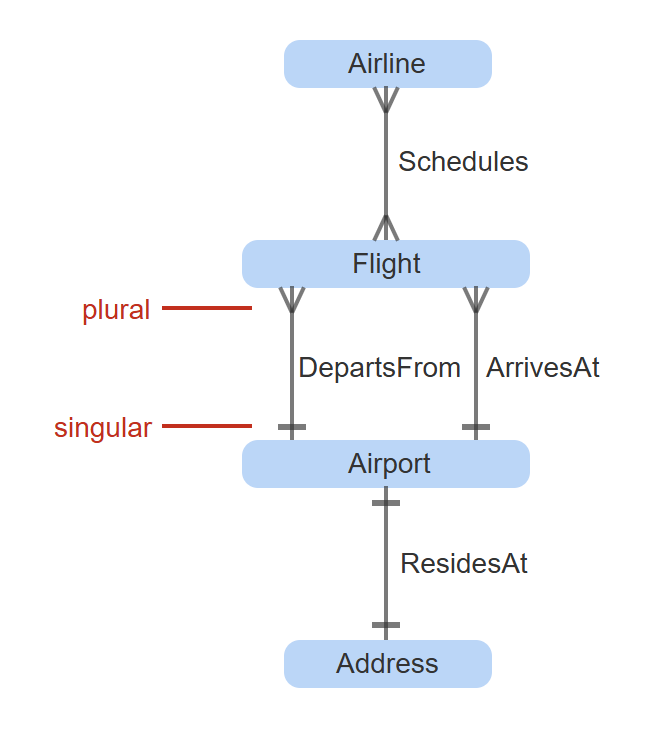
singular entity
when the maximum is one
plural entity
when the maximum is many.
crow's foot notation
a graphical technique used in ERDs to visualize cardinality
chen notation
visualizes ERD structure. includes include rectangles for entities, diamonds for relationships, and ovals for attribute.
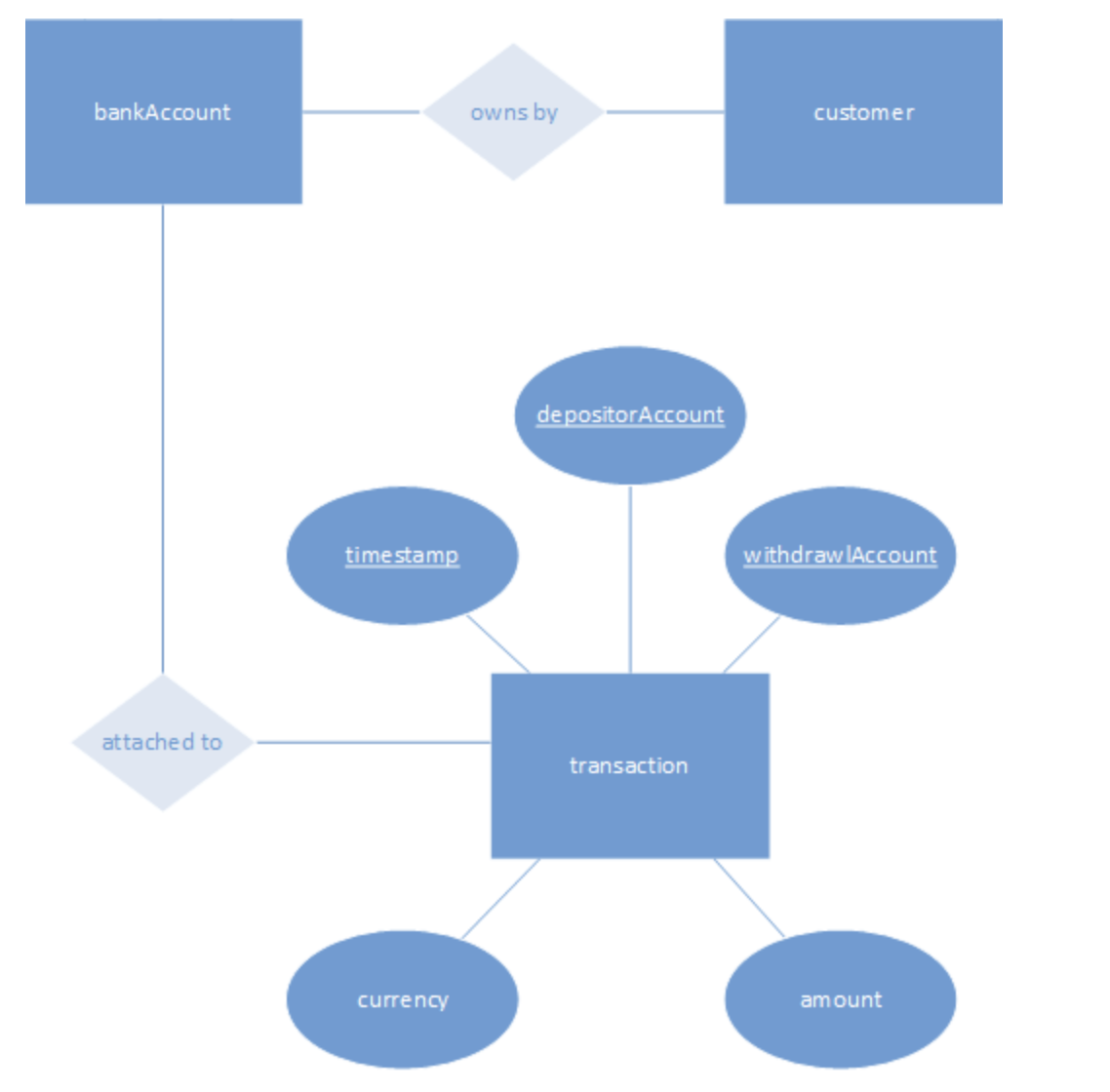
unique attribute
an attribute in which it’s value is distinct for every entity instance.
strong entity
has one or more identifying attributes. each strong entity = one table. one of the identifying attributes may become the primary key. independent.
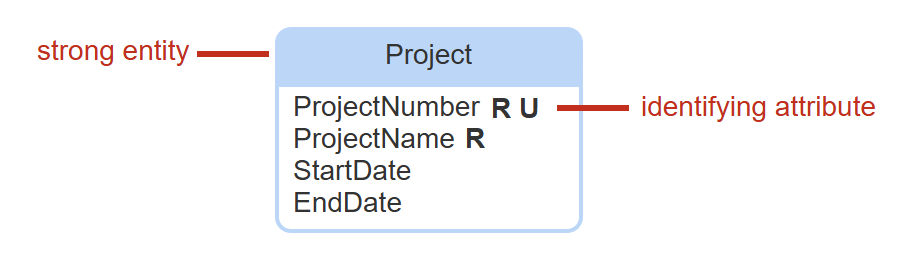
identifying attribute
unique, singular, and required. identifying attribute values correspond one-to-one to, or identify, entity instances.
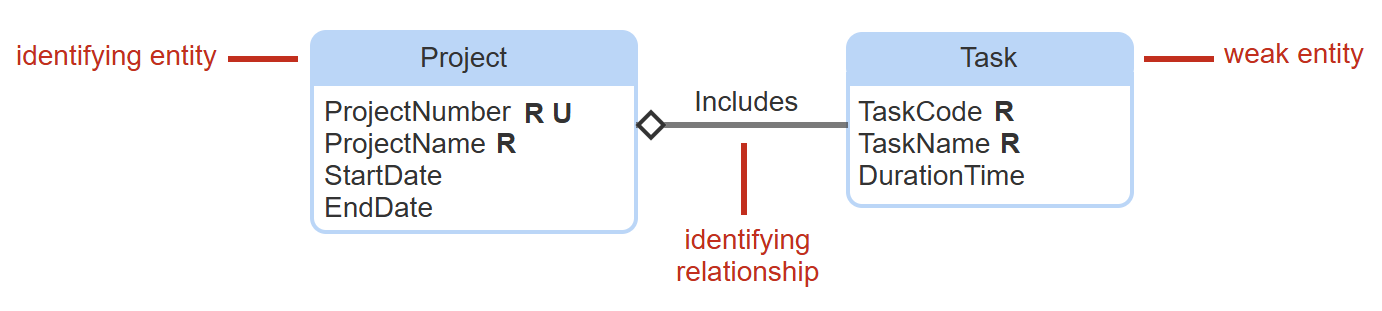
weak entity
an identifying attribute. usually has a relationship, called an identifying relationship, to another identifying entity. dependent. weak entities become weak tables.
identifying entity
must be singular and required in an identifying relationship.
identifying relationship
relationship with identifying entity. ERD has a diamond next to the identifying entity.
subtype entity
a subset of another entity type, called the supertype entity. ex. Manager is a subtype entity of the Employee supertype entity.
supertype entity
has several subtypes. attributes of the supertype apply to all subtypes. attributes of a subtype do not apply to other subtypes or the supertype.
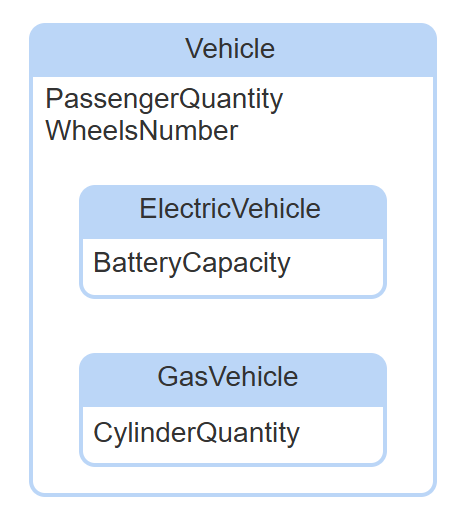
partition
a group of mutually exclusive subtype entities in a supertype entity.
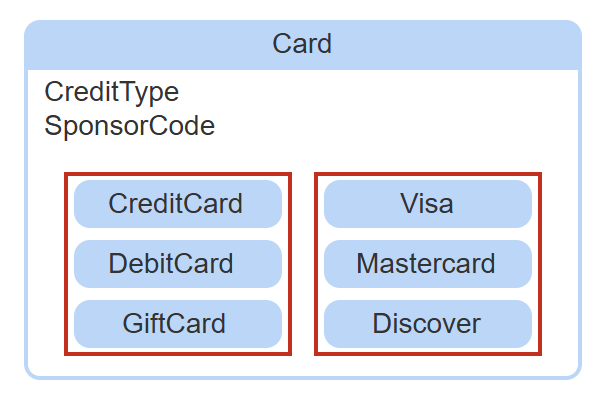
partition attribute
optional, corresponds to a partition of the supertype entity. indicates which subtype entity is associated with each supertype instance.
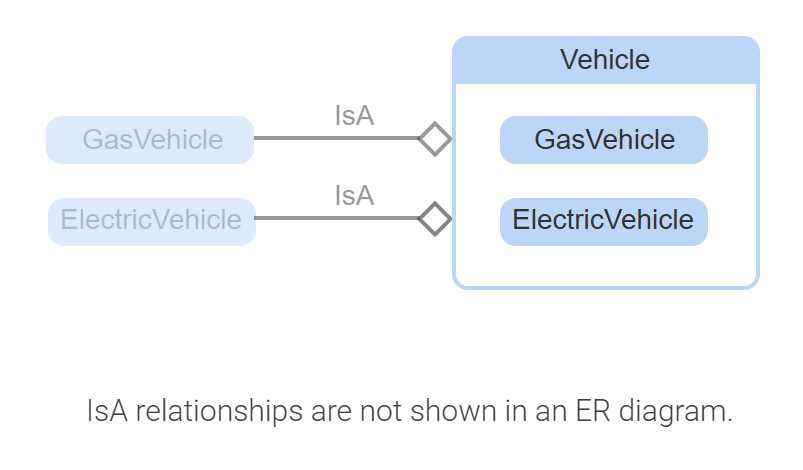
IsA relationship
identifying relationship of supertype entity that identify its subtype entities.
primary keys
must be unique and required (not NULL). also should be stable, simple, meaningless.
artificial key
a simple primary key created by the database designer. usually artificial keys are integers, generated automatically by the database as new rows are inserted to the table.
1-1
one-one relationship becomes a foreign key. the foreign key can go in the table on either side of the relationship. aka 1:1
foreign key
unique, refers to the table on the opposite side of the relationship. name is the name of the referenced primary key, with an optional prefix.
many-many
becomes a new weak table, contains two foreign keys, referring to the primary keys of the related tables. primary key of the new table is the composite of two fks. aka M:N
required attribute
an attribute or relationship that is mandatory, with no null values allowed
NOT NULL
specified for required columns after data type (ex. Name VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL)
UNIQUE
specified for unique columns after data type (ex. Number INT UNIQUE)
PRIMARY KEY
specified for primary key columns after data type (ex. Passenger INT PRIMARY KEY)
functional dependence
dependence of one column on another. 'A depends on B' is denoted B → A.
redundancy
the repetition of related values in a table, ex. “222, Elvira Yin” not just “222”
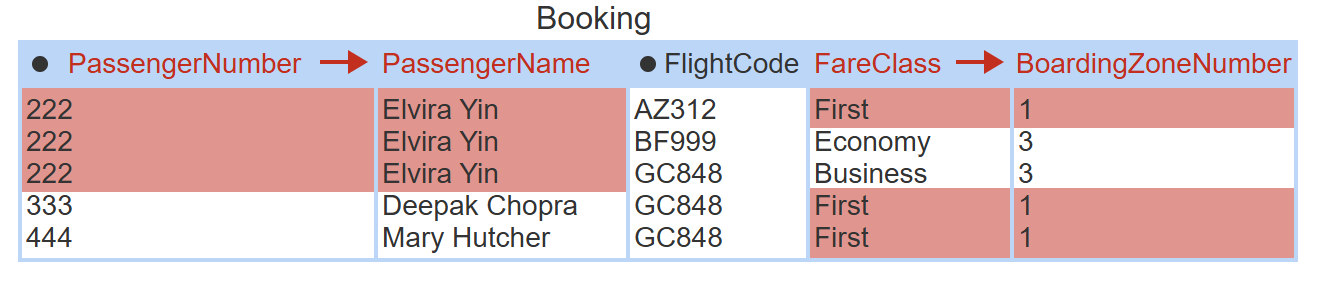
normal forms
rules for designing tables with less redundancy.
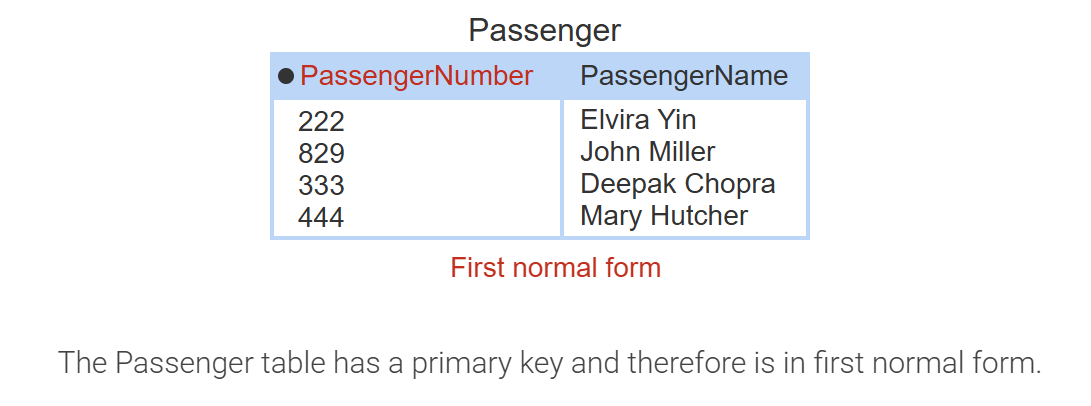
first normal form
each column must contain atomic, single-valued data, and each row must be unique. fix: separate repeating attributes into a new table
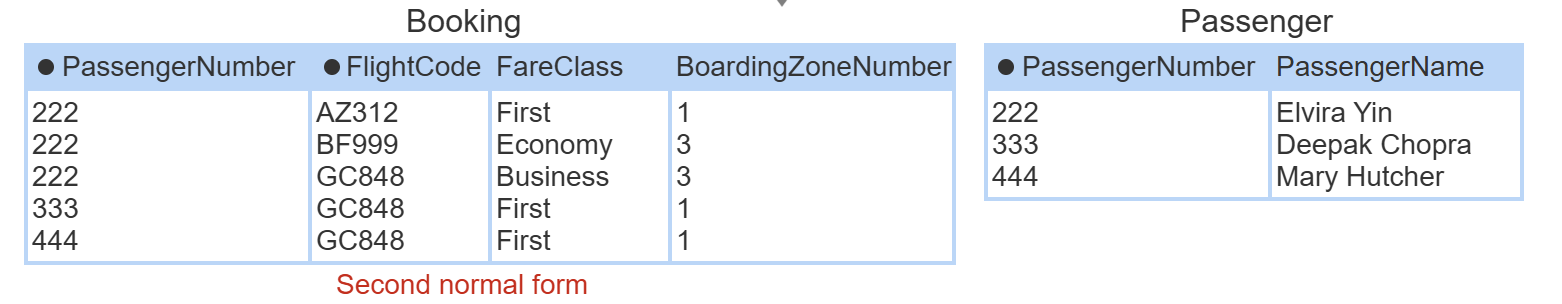
second normal form
in 1NF, and no partial dependency on part of a composite key. fix: move attributes that depend only on part of the key to another table
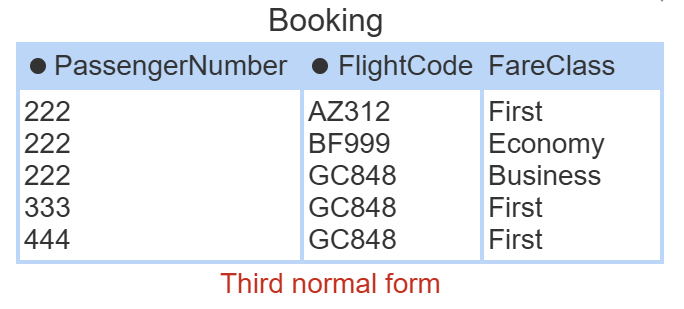
third normal form
further extends 2NF by eliminating transitive dependencies, meaning no non-key attribute should be dependent on another non-key attribute. fix: remove attributes that depend on non-key attributes.
boyce codd
each attribute must represent a fact about the key, the whole key, and nothing but the key. stricter 3NF.
types of attributes
simple: cannot be divided (first name)
composite: can be divide (full name)
multivalued: multiple values (phone numbers)
derived: caluclate (age from birthdate)
optional: may be null (middle name)
tuple
order of elements in a tuple matters, and once a tuple is created, it cannot be changed.
1-many
many side get’s the foreign key, foreign key refers to the primary key of the one side. aka 1:
insertion anomaly
normalization anomaly that occurs when you cannot add a new piece of data to a table without also adding unnecessary or unrelated data.
update anomaly
normalization anomaly where redundant data requires multiple updates for a single change, risking inconsistency if not all instances are updated correctly.
deletion anomaly
normalization anomaly for the unintended loss of data when a record is deleted.
normalization steps
1. No normal form
2. First normal form
3. Second normal form
4. Third normal form
5. Boyce-Codd normal form
6. fourth normal form
7. fifth normal form