Lecture 5 - Heart
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Label the heart (Anterior view).


Label the heart (Posterior view).


What anatomical region houses the heart?
Mediastinum
Describe the orientation of the heart within the thorax using the terms 'base' and 'apex.'
Heart sits obliquely in the thorax, with its:
Base – located on the superior and posterior surfaces
Apex – situated at the 5th intercostal space

The heart functions as 2 pumps arranged in series. Describe the function of the high-pressure pump.
High-pressure pump = Systemic circulation
→ Delivers blood through the body and back to the right side of the heart
The heart functions as 2 pumps arranged in series. Describe the function of the low-pressure pump.
Low-pressure pump = pulmonary circulation
→ Delivers blood from the R ventricle, to and through the lungs, and back to the left side of the heart
Regarding arteries and veins, does their definition depend on the state of oxygenation of the blood within them?
No, the definition has nothing to do with the state of oxygenation of the blood.
Which primary chamber forms the anterior (sternocostal) surface of the heart?
Right ventricle
Which chamber primarily forms the base of the heart (posterior view)?
Left atrium with a small part of the right atrium
Identify the 2 major Outflow Tracts (Great Vessels) exiting the heart.
Pulmonary trunk
Aorta
Identify the 3 major Inflow Tracts (Great Vessels) that return blood to the heart.
Superior Vena Cava (SVC)
Inferior Vena Cava (IVC)
Pulmonary veins
List the arteries that branch off the Aortic Arch.
Brachiocephalic Trunk (includes R Subclavian Artery & R Common Carotid Artery)
there’s no L or R brachiocephalic trunk
L Common Carotid Artery
L Subclavian Artery

What is the path of de-O2 blood after exiting the right ventricle via the pulmonary trunk?
Pulmonary trunk divides → left and right pulmonary arteries → these take de-O2 blood to their respective lungs
How does O2 blood enter the heart after being oxygenated at the capillaries?
Enter L atrium via paired left and right pulmonary veins
What structure exists in fetal circulation to shunt oxygenated blood from the pulmonary trunk to the aorta? What does this structure become after birth?
Ductus Arteriosus
After birth, it constricts to form the ligamentum arteriosum (due to ↑ blood flow to lungs and ↓ blood flow to DA)

What forms the Superior Vena Cava (SVC) and where does it drain?
→ Formed by the union of the R and L brachiocephalic veins, posterior to the costal cartilage of the first rib
superiorly drains into the right atrium

What forms the Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) and where does it drain?
→ Formed by the union of the 2 common iliac veins
Inferiorly drains into the right atrium
What separates the 2 atria?
Interatrial septum
List the structural characteristics of the right atrium.
Smooth & rough walled internal portions
Pectinate muscles comprise rough wall
has a right auricle (muscular appendage)
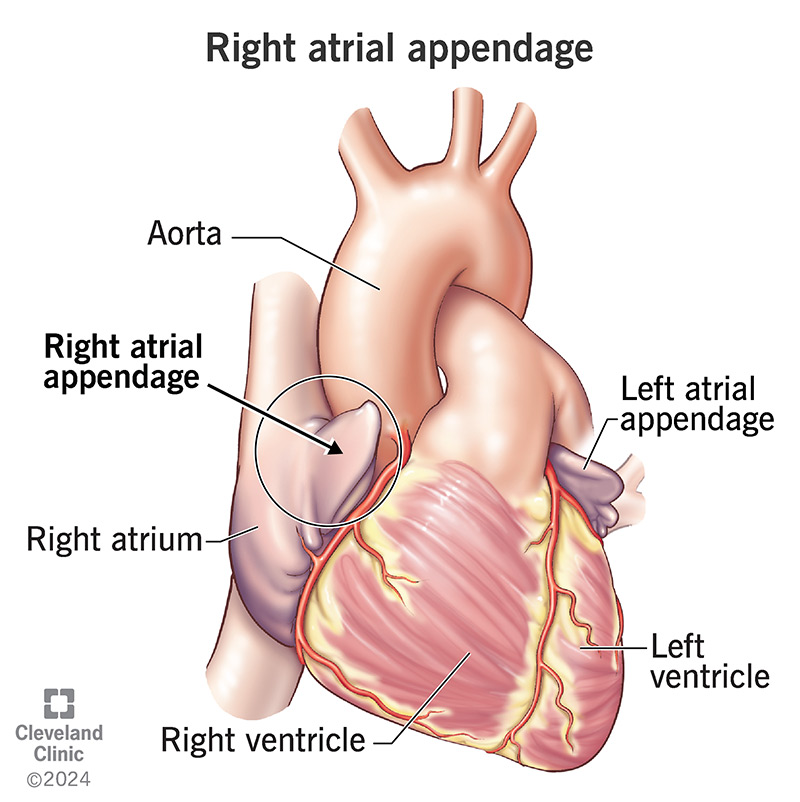
What are the 3 inflow sources right atrium receives de-O2 blood from?
SVC - Head & neck, upper limbs & thoracic wall
IVC - Abdomen, pelvis, lower limbs
Coronary Sinus - Heart (heart needs it’s own O2-blood supply b/c it works hard to pump blood)
What valve does blood pass through to move from the Right Atrium to the Right Ventricle? How many cusps and papillary muscles does this valve possess?
Right AV valve (Tricuspid valve)
3 cusps (anterior, posterior & septal)
3 papillary muscles
What is the structure that appears as a depression on the right side of the interatrial septum wall in the Right Atrium?
Fossa ovalis → remnant of the embryonic foramen ovale

List the structural characteristics of the left atrium.
Smooth & rough walled internal portions
Pectinate muscles comprise rough wall
Left auricle — muscular appendage
How does O2 blood return to the Left Atrium, and what valve does it pass through next?
O2-blood returns to the left atrium via the Pulmonary veins and passes through the Left AV valve (Bicuspid or Mitral)
What separates the 2 ventricles?
Interventricular septum
The LV wall is ___x thicker than the RV.
3x
What is the function of the Left Ventricle?
pumps O2 blood through the aortic valve and aorta to the rest of the body (systemic circulation)
What prevents the prolapse of the AV valve cusps during ventricular systole?
Papillary muscles attached to the valve cusps via chorda tendineae (tendinous cords)
Note: They don’t pull the AV valves open

How do tendinous cords arise?

→ Arise from the apices of papillary muscles papillary muscles - conical muscular projections with bases attached to the ventricular wall
What are the rough, meshwork muscle fibers that comprise the internal walls of the ventricles?
Trabeculae carneae

What is the name and function of the specialized muscular band in the Right Ventricle that conveys a part of the electrical conduction system?
Moderator band (septomarginal trabecula) → muscle band that carries part of the heart’s electrical signal from the interventricular septum to the anterior papillary muscle → prevents electric conduction from being lost

When semilunar valves close, how does the backsurge of blood ensure a tight seal?
Backsurge of blood opens the valve leaflets (like filling an umbrella), pushing them tightly together
The Left AV (Mitral/biscuspid) valve has how many cusps and how many papillary muscles?
2 Cusps (posterior and anterior)
2 Papillary (posterior and anterior) muscles
What blood flow does the pulmonary valve (pulmonic semi-lunar valve) allow for?
Blood flow from the right ventricle → pulmonary trunk → lungs
What blood flow does the aortic valve (aortic semi-lunar valve) allow for?
Blood flow from the left ventricle → aorta → systemic circulation
What is the structure of the cardiac skeleton?
made of a fibrous ring that surrounds the valves
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/cardiac-skeleton/aHEowK2f6aFY57L8mYgDA_Valvular_plane_of_the_heart_-_Diastole.png)
Identify 2 major mechanical roles of the cardiac skeleton.
Anchors muscle fibers and valves
Separates the atria from the ventricles
What is the critical electrical function of the cardiac skeleton, and why is this function necessary?
It acts to insulate electrical impulses
crucial b/c this non-conducting tissue ensures that the atria and ventricles don’t contract at the same time
Trace the complete path of blood flow through the heart, starting when de-O2 blood enters the Right Atrium.
Right atrium (via SVC/IVC)
Through the Right AV (tricuspid) valve into the Right ventricle
Through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary trunk and arteries
Lung
Returns via the pulmonary vein into the Left atrium
Through the Left AV (mitral) valve into the Left ventricle
Through the aortic valve into the Aorta
Rest of the body
Which branch of the Right Coronary Artery (RCA) supplies the posterior walls of both ventricles and the posterior 1/3 of the Interventricular (IV) septum?
Posterior Interventricular artery
Which branch of the Left Coronary Artery (LCA), also known as LAD, supplies the anterior walls of both ventricles and the anterior 2/3 of the IV septum (including the AV bundle)?
Anterior interventricular artery (LAD)
What do the SA nodal artery supply?
R atrium
SA node
What do the AV nodal artery supply?
AV node
What does the Right marginal artery supply?
Apex
R ventricle
What does the Circumflex artery supply?
L atrium
L ventricle
Label the arterial supply to the heart.


Label the coronary arteries.


What is the primary route for venous drainage of the heart?
Coronary sinus → this drains into the right atrium

Which specific set of cardiac veins drains directly into the right atrium, bypassing the coronary sinus?
Anterior cardiac veins
Make a table showing the parallel travelling coronary arteries and cardiac veins.

List the path of the electrical impulse through the conduction system, starting at the pacemaker.
SA node → AV node → AV Bundle (Bundle of His) → Right bundle branch → Left bundle branch → Purkinje fibers
What initiates ventricular contraction after the signal passes through the electrical insulator (cardiac skeleton)?
AV node
followed by propagation through the Purkinje fibers from the left and right bundle branch
How is the rate of the SA node regulated?
SA node has BOTH SNS & PNS inputs → ↑/↓HR