BI108 test 1
0.0(0)Studied by 1 person
Card Sorting
1/141
Earn XP
Last updated 10:20 AM on 2/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
1
New cards
comparative experiments
look for differences between samples that may differ in multiple unknown ways. compares manipulated data from different groups
2
New cards
controlled experiments
manipulate one or more factors being tested. control group and experimental group are the same besides one variable of interest
3
New cards
What does an experiment consist of?
1. **O**bservation
2. **Q**uestion
3. **H**ypothesis
4. **P**rediction
5. **D**esign
4
New cards
The P value must be less than what number to safely reject the null hypothesis?
.05
5
New cards
Levels of biological organization (descending order)
1. Biosphere
2. Ecosystem
3. Community
4. Population
5. Organism
6. Organ Systems
7. Tissue
8. Cell
9. Organelle
10. Molecule
6
New cards
what is within the nucleus : what surrounds the nucleus
protons and neutrons : electrons
7
New cards
what is a chemical reaction
change in the distributions of electrons between atoms
8
New cards
how do van der waal interactions work?
temporary dipoles are formed as electrons move around the nucleus. Temporary partial positive and negative charges can cause a temporary interaction.
9
New cards
how is internal temp maintained
because of the large amounts of water in living tissues. it takes a large amount of energy to change the form of water.
10
New cards
what do acids do in water
release hydrogen ions H+ → resulting molecule is negatively charged
11
New cards
What do bases do in water
release hydroxide ions OH-, can accept H+ → resulting molecule is positively charged
12
New cards
what do functional groups do
influence the properties and behavior of macromolecules
13
New cards
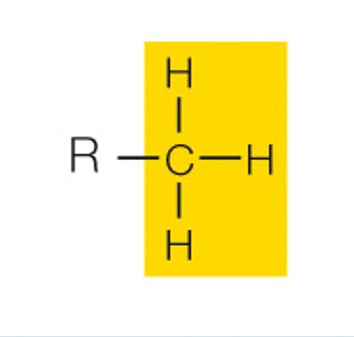
state the name and polarity of this functional group
methyl: nonpolar
14
New cards
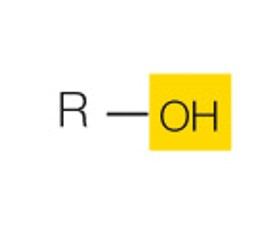
state the name and polarity of this functional group
hydroxyl: polar
15
New cards
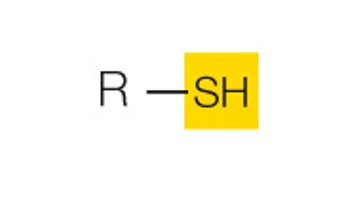
state the name and polarity of this functional group
sulfhydryl: polar
16
New cards
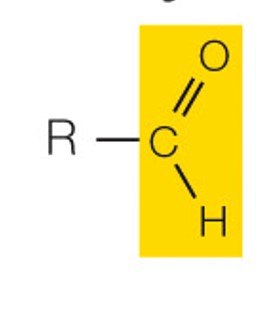
state the name and polarity of this functional group
aldehyde: polar
17
New cards
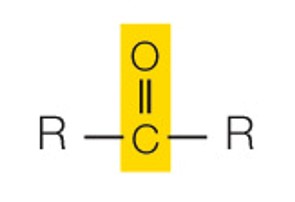
state the name and polarity of this functional group
keto: polar
18
New cards
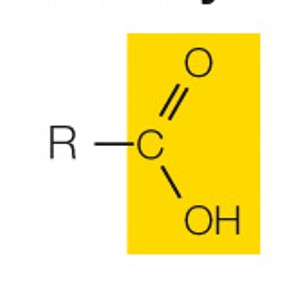
state the name and polarity of this functional group
carboxyl: charged acidic
19
New cards
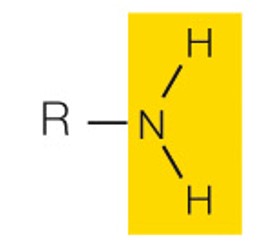
state the name and polarity of this functional group
amino: charged basic
20
New cards
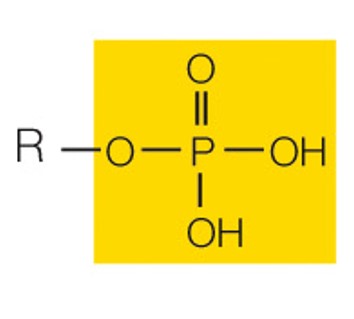
state the name and polarity of this functional group
phosphate: charged acidic
21
New cards
why aren’t lipids a “true” polymer?
because their individual monomers are not covalently bonded to eachother
22
New cards
describe the structure of a triglyceride
three fatty acid chains + glycerol backbone. connected through ester bonds formed by condensation reactions
23
New cards
describe the structure of a phospholipid
two fatty acid chains + glycerol backbone + a phosphate group. hydrophilic head with the charged phosphate group and hydrophobic tails made of the hydrocarbon fatty acids
24
New cards
amphipathic
a molecule with opposing chemical properties
25
New cards
where does a phospholipid bilayer form
in aqueous solutions
26
New cards
how are phospholipid molecules joined together in the bilayer
through non covalent forces
27
New cards
what are the uses of carbohydrates
1. a form of energy storage (within chemical bonds)
2. Used to transport stored energy
3. carbon skeletons for the production of other molecules
4. Extracellular structures
28
New cards
Monosaccharides
simple sugars. can have 5 carbons (pentose) or 6 carbons (hexose) within.
29
New cards
describe the structure of hexoses
six carbon sugars can exist in a ring form or straight chain form. ring forms are favored in aqueous solutions
30
New cards
What differentiates alpha and beta glucose
In Alpha, the hydroxyl group is out of plane. In Beta, the hydroxyl group is in plane
31
New cards
Dissacharides
2 monosaccharides joined together through glycosidic linkages
32
New cards
alpha glycosidic linkages
found in starch and glycogen molecules. bent branched easy to break.
33
New cards
beta glycosidic linkages
found in cellulose which humans can’t digest. linear bonds hard to break.
34
New cards
Oliigosaccharides
3-20 monosaccharides joined by glycosidic linkages. often see additional functional groups attached
35
New cards
where are oligosaccharides commonly found
bonded to proteins and lipids on cell surfaces acting as recognition signals
36
New cards
Polysaccharides
giant polymers of monosaccharides
37
New cards
examples of polysaccharides
1. starch (glucose storage in plants)
2. glycogen (glucose storage in animals)
3. cellulose (strong. found in plants)
38
New cards
integral proteins (location)
hydrophobic portion embedded within the lipid bilayer (amphipathic
39
New cards
anchored proteins (location)
covalently attached to lipids which insert into the lipid bilayer
40
New cards
peripheral proteins (location)
not embedded within the lipid bilayer, but may interact with integral proteins or phospholipid heads (likely polar/charged)
41
New cards
Selective permeability
some substances can pass through while others cannot
42
New cards
diffusion
the net process of random movement toward equilibrium. net movement remains directional until equilibrium is reached
43
New cards
Osmosis
the diffusion of water across membranes from a region of lower solute concentration to higher solute concentration
44
New cards
aquaporins
category of pores that increase the permeability of water
45
New cards
relative concentration of solutes
* Hypertonic: higher solute concentration outside of the cell
* Isotonic: equal solute concentrations
* Hypotonic: lower solute concentration outside of the cell
* Isotonic: equal solute concentrations
* Hypotonic: lower solute concentration outside of the cell
46
New cards
two categories which describe the movement of solutes across a membrane
passive transport + active transport
47
New cards
simple diffusion (passive)
many small, nonpolar, uncharged, or hydrophobic molecules can simply pass through the membrane. (remember there are no covalent bonds in the bilayer. They’re just hanging out close together)
48
New cards
mechanisms of facilitated diffusion (passive)
1. carrier proteins: Integral transmembrane proteins that **temporarily bind** to substances and move them through the bilayer
2. channel proteins: Integral transmembrane proteins that form a channel without binding
49
New cards
ion channel (channel protein)
Integral transmembrane protein - spans the entire length of the bilayer. most are gated: either by a ligand or chemical signal.
50
New cards
what is a ligand
any molecule/ion that binds to a protein by noncovalent bonds
51
New cards
active transport
moves substances against a concentration/electrical gradient and requires an input of energy (often ATP)
52
New cards
sodium potassium pump (primary active transport)
found in all animal cells. cells break a bond in ATP to release enough free energy to move ions against the concentration gradient. (1ATP = 3 Na out 2 K in)
53
New cards
exocytosis
material in vesicles is **expelled** from a cell
54
New cards
endocytosis
material is **brought into** a cell
55
New cards
components of a prokaryotic cell (bacteria and archaea):
* Most have a plasma membrane and cell wall
* no membrane bound nucleus or other compartments
* no membrane bound nucleus or other compartments
56
New cards
components of a eukaryotic cell (plants, animals, protists, fungi)
* nucleus and other organelles are membrane-bound
* some have cell walls (not animals)
* some have cell walls (not animals)
57
New cards
what are the internal and external structures of the cell?
1. extracellular support
2. the cytoskeleton
3. organelle structure
58
New cards
Where is the cell wall (extracellular support) found?
Plants, archaea, bacteria, fungi, and some protists have cell walls exterior to the cell membrane
59
New cards
What is the purpose of the cell wall
provides support. It can provide protection and structural integrity
60
New cards
What do animals have rather than a cell wall?
An extracellular matrix (complicated structure outside of the cell membrane)
61
New cards
what is the extracellular matrix made up of?
large assemblages of proteins and proteoglycan (protein and sugar molecules covalently bonded to proteins)
62
New cards
what are the functions of the extracellular matrix?
1. holds cells in tissues
2. orients cell movement
3. can have filtering properties
4. can have recognition properties
5. contributes to physical properties of cartilage, skin, etc.
63
New cards
what is the cytoskeleton?
a network of protein filaments and tubules in the cytoplasm, giving cells shape and coherence
64
New cards
nucleoid
region that contains the bacterial chromosome
65
New cards
nucleus
largest organelle, surrounded by nuclear envelope
66
New cards
cytoplasm
liquid component of a cell and all the material within it (besides the nucleus)
67
New cards
Prokaryotes relation to membrane
prokaryotes do not have membrane-bound organelles
68
New cards
the three components within eukaryotic cells:
Microfilaments, microtubules, intermediate filaments
69
New cards
functions of the cytoskeleton
1. Supports and maintains cell shape
2. Holds organelles in position
3. Moves organelles
1. Interacts with extracellular structures to hold the cell in place
70
New cards
Nucleus in eukaryotic cells
usually the largest organelle, membrane-bound, site of DNA replication and expression
71
New cards
what is the name of the membrane surrounding the nucleus
the nuclear envelope
72
New cards
Function of nuclear envelope
controls movement of molecules into or out of the nucleus (ex: RNA molecules are transported out of the nucleus as genes are expresssed)
73
New cards
Eukaryotic cells membrane system
Endomembrane system (within the membrane).
network of interconnected membranes in the cytoplasm
Movement through vesicles
network of interconnected membranes in the cytoplasm
Movement through vesicles
74
New cards
what is within the Eukaryotic cells’ membrane system
1. Nuclear envelope
2. Endoplasmic reticulum
1. Smooth and rough
2. Golgi apparatus
75
New cards
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
rough due to ribosomes attached
newly made proteins enter the RER where they are modified, folded, and transported to other regions
newly made proteins enter the RER where they are modified, folded, and transported to other regions
76
New cards
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
More tubular than RER, no ribosomes
chemically modifies small molecules
modifies proteins
chemically modifies small molecules
modifies proteins
77
New cards
Golgi Apparatus
made of flattened sacs and small membrane-enclosed vesicles
receives protein from the RER and can further modify them
concentrates, packages, and sorts proteins
receives protein from the RER and can further modify them
concentrates, packages, and sorts proteins
78
New cards
Ribosomes
site of protein synthesis
not membrane-bound. similar structure in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
not membrane-bound. similar structure in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
79
New cards
ribosomes in eukaryotic cells
in eukaryotic cells, there are free ribosomes as well as ribosomes bound to the RER
80
New cards
Mitochondria
the powerhouse of the cell.
energy in fuel molecules is transformed into the bonds of energy-rich atp
cells that require lots of energy can have many mitochindria
energy in fuel molecules is transformed into the bonds of energy-rich atp
cells that require lots of energy can have many mitochindria
81
New cards
molecules with a double membrane system
mitochondria, chloroplast
82
New cards
chloroplast
unique to plant cells, site of photosynthesis (light energy is converted to the energy of chemical bonds)
83
New cards
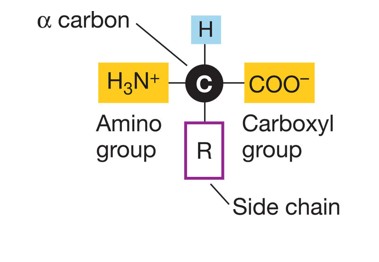
what is this
the base structure of an amino acid
84
New cards
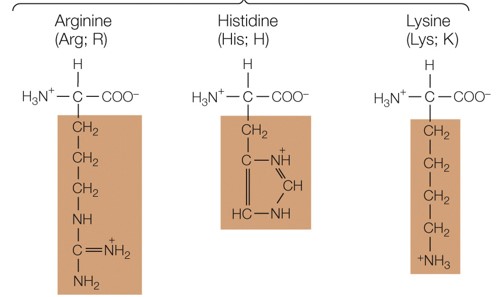
Which amino acid group are these a part of
positively charged polar amino acids
85
New cards
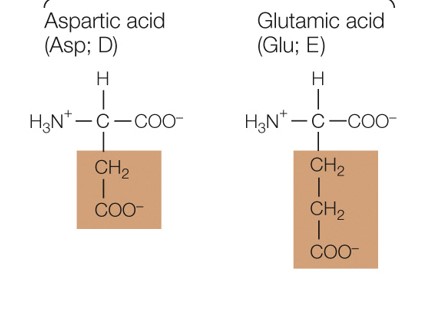
Which amino acid group are these a part of
negatively charged polar amino acids
86
New cards
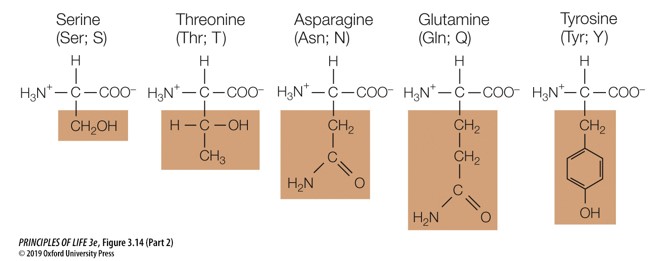
Which amino acid group are these a part of
uncharged polar amino acids
87
New cards
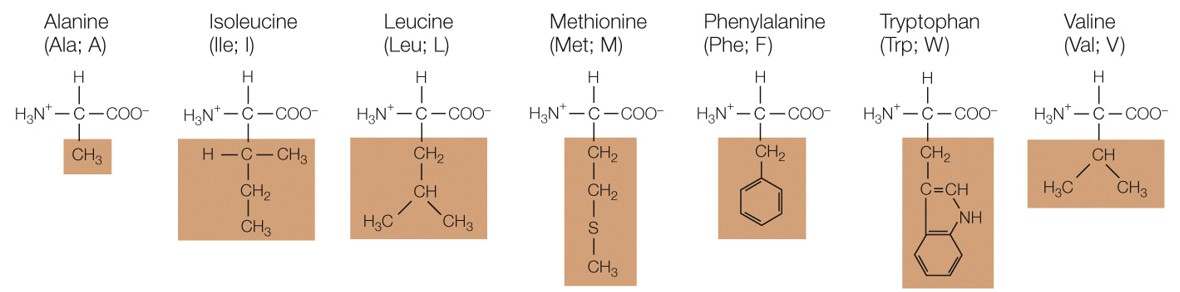
Which amino acid group are these a part of
nonpolar amino acids
88
New cards
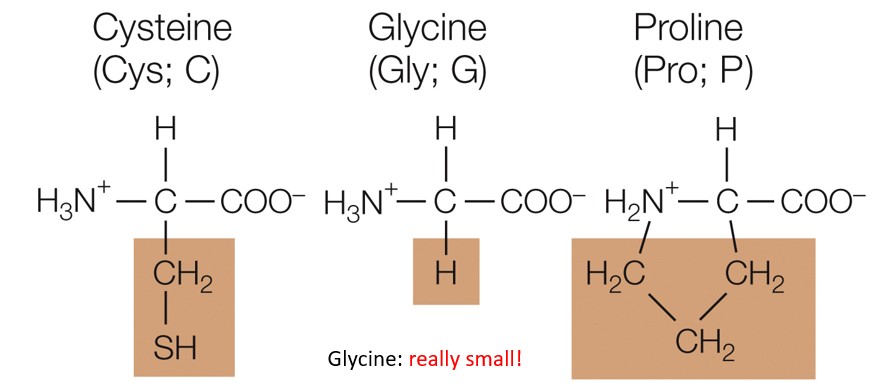
special cases
Which amino acid group are these a part of
89
New cards
cysteine
Terminal sulfhydryl group which can form disulfide bridges
90
New cards
glycine
Can greatly impact the 3 dimensional structure of a larger protein because its tiny
91
New cards
Proline
Really bulky which prohibits bending
92
New cards
how are amino acids bonded together
with covalent peptide bonds in condensation reactions
93
New cards
where is the bond in a protein
peptide bond between the amino group and the carboxyl group
94
New cards
Primary structure of a protein
basic sequence of amino acids
solely maintained by covalent bonds between amino acids
\
solely maintained by covalent bonds between amino acids
\
95
New cards
how many different amino acids exists
20
96
New cards
secondary structure of a protein
introduces fold and bends into the shape
alpha helices and beta pleated sheets
alpha helices and beta pleated sheets
97
New cards
how are alpha helices and beta pleated sheets maintained
hydrogen bonds between the chains
98
New cards
Tertiary structure of a protein
larger bent 3-dimensional structure
dictated by interactions between the side chains
dictated by interactions between the side chains
99
New cards
how are tertiary structures formed
any category of interaction between amino acids (mostly noncovalent with some covalent bonds - disulfide bridges)
100
New cards
Tertiary structure is determined by interactions between…
R groups (side chains attached to the alpha carbon of an amino acid)
* Hydrogen bonds
* Disulfide bridges
* Van der Waals interactions
* Ionic interactions
* Hydrogen bonds
* Disulfide bridges
* Van der Waals interactions
* Ionic interactions
Explore top notes
Personality 210 Psychology Notes (Part 3) Continuing Traits and Trait Traditions
Updated 1344d ago0.0(0)
Personality 210 Psychology Notes (Part 3) Continuing Traits and Trait Traditions
Updated 1344d ago0.0(0)