Chemistry - 6 Electrolysis
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Electrolysis
the decomposition of a substance by an electric current
Cathode
negative electrode
Anode
positive electrode
Electrolyte
an ionic compound whose aqueous solution/molten form conducts an electric current
Anion
negative ion
Cation
positive ion
Why can't solid ionic compounds conduct electricity?
ions are held in place by strong electrostatic forces of attraction
Which electrode has electrons?
cathode
Substances are ... at the cathode
reduced
Substances are ... at the anode
oxidised
... become ... at each electrode
ions, atoms
Water molecule ionising
H₂O ⇌ H⁺ + OH⁻
Which product of ionised water goes to the cathode?
H⁺
Which product of ionised water goes to the anode?
OH⁻
Hydrogen is produced at the cathode if...
the metal is more reactive than hydrogen
Electrodes should be made from ... materials
inert (unreactive)
In the electrolysis of aqueous solutions, ... is usually produced at the anode (positive electrode)
oxygen, O₂
Half equation: anode: aqueous solutions
4OH⁻ → O₂ + 2H₂O + 4e⁻
Half equation: cathode: (some) aqueous solutions
2H⁺ + 2e⁻ → H₂
Order of discharge at anode
halide ion > hydroxide > all other negatively charged ions
Oxygen is released at the anode unless...
the solution contains a halide ion
Uses of aluminium (and its alloys) [7]:
- pans
- overhead power cables
- aeroplanes
- cooking foil
- drink cans
- window and patio door frames
- bicycle frames and car bodies
What compound is electrolysed to procure aluminium?
aluminium oxide, Al₂O₃
Where is aluminium oxide found?
bauxite ore
Aluminium oxide melting point
2050°C
How do we reduce the melting point of aluminium oxide?
mix it with cryolite
Cryolite-aluminium oxide mixture melting point
850°C
Aluminium oxide electrolysis reaction
2Al₂O₃ → 4Al + 3O₂
Aluminium forms at the ... electrode
negative
Oxygen is produced at the ... electrode
positive
Aluminium electrolysis cell [4]
- lined with carbon negative electrode
- molten aluminium is tapped or siphoned off
- carbon dioxide and oxygen gas emitted from anodes
- steel case
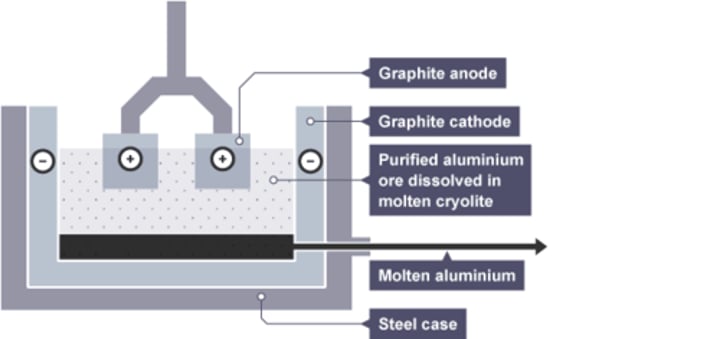
At the cathode (aluminium extraction):
Al³⁺ + 3e⁻ → Al
At the anode (aluminium extraction):
2O²⁻ → O₂ + 4e⁻
Reaction of oxygen with hot carbon anodes:
C + O₂ → CO₂
... have to be replaced regularly
Carbon anodes
Brine
water saturated with salt (sodium chloride)
Products of electrolysis of brine [3]
- chlorine gas
- hydrogen
- sodium hydroxide
At the anode (brine electrolysis):
2Cl⁻ → Cl₂ + 2e⁻
At the cathode (brine electrolysis):
2H⁺ + 2e⁻ → H₂
What is left after brine electrolysis?
sodium hydroxide, NaOH