Component 2 | Section A: Key Theories
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Stuart Hall | Representation Theory
Media representations are constructed through media language and shape audience’s perceptions. Stereotypes are often used to reinforce dominant ideologies.
(Consider how the extract represents social groups | e.g. gender, race, class | through mise - en - scene, dialogue and framing.)
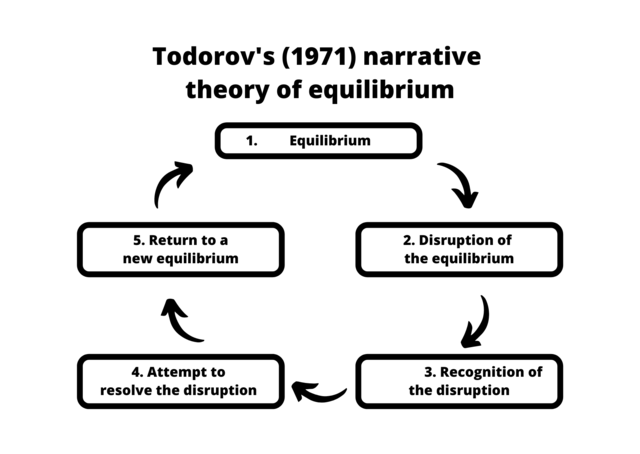
Todorov | Narrative Theory
A theory that outlines a typical narrative structure, consisting of five stages: equilibrium, disruption, recognition, attempt to repair, and new equilibrium.
Ronald Barthes | Semantic Codes Theory
Media texts use signs (visual codes, audio codes) to create meaning. Audiences interpret these based on cultural knowledge.
(Examine symbolic elements | e.g. colors, objects, gestures | that convey deeper meanings in narratives.)
Bell Hooks | Intersectionality & Feminism Theory
Representation is influenced by race, class and gender. Some groups are marginalised more than other in media.
(Analyse how race, gender and class intersect in the extract through costume, setting and character roles.)
Van Zoonen | Gender Theory
Media constructs gender based on cultural expectations. Women are often objectified or represented in traditional roles.
(Look at costume, body language, camera framing and interactions between male and female characters.)
Levi Strauss | Binary Opposites Theory
Meaning is created through contrast (e.g. good vs. evil, light vs. dark). This theory suggests that narratives are structured around opposing pairs to convey deeper meanings and cultural values.
(Identify opposing representations in mise-en-scène, camera work or character interactions.)
Steve Neale | Repetition & Differences Theory
Films are balanced between repetition and differences. Repetition defines the genre, while differences keep it interesting. Too much repetition makes films predictable and dull, whereas too much difference can lead to confusion and a lack of coherence in storytelling.
Steve Neale | Genre Theory
Genre is a categorisation system that helps to sort different films based on common characteristics. The categorisation is based on film content, setting, character types and production values. Recognising genre helps the audience predict the nature of the film and sets out certain expectations.