Molecular Nutrition Final Exam
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
metabolic syndrome
combination of disorders that increase risk for heart disease, diabetes and stroke
3 out of 5 of the following must be present for diagnosis:
high blood glucose, low HDL, high blood triglycerides, large waist circumference, or high blood pressure
obesity
abnormal or excessive fat accumulation impairing health
BMI
body mass index→greater than 25 is overweight and greater than 30 is obese
calculated by taking weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared
what is the proper nomenclature regarding obesity
NOT obese patients; people living with obesity
what are problems with BMI and better ways to overcome this
BMI does not account for body composition therefore people with a lot of muscle but a low body fat such as athletes may have an overweight BMI without the higher fat percentage normally associated with it
in to overcome is by measuring waist circumference which is associated with visceral fat accumulation or a DEXA scan which measures body composition
how does obesity impact health
immediate effects=excessive extra weight placing more stress on joints, impaired sleep quality, effects on thermogenesis
long term=increased risk for diabetes, heart and liver disease, PCOS
2 types of excessive fat
visceral=surrounding the organs
hepatic=in the liver
Irish obesity rates and policies to overcome this
60% of adults are overweight or obese with the rates doubling in the last 20 years
childhood obesity decreased from 25 to 15 percent
2018 irish sugar sweetened beverage tax may have helped decrease obesity in children
what groups have the highest prevalence of metabolic syndrome in the USA
non-hispanic white men and mexican american women
first law of thermodynamic related to obesity
energy cannot be created or destroyed
its a myth that some people have slow metabolism→when caloric intake doesn’t match expenditure changes in body composition will occur
although food intake is an environmental factor it is genetically encoded->mutations in genes encoding brown adipose tissue metabolism and lipid handling
gene associated with obesity
FTO gene increases risk of obesity due to the impairing ability to control how much food is eaten due it interfering with impulse control
gene associated with poor lipid handling
PCSK9→familial hypercholesterolemia; genetics disorder impacting bodies ability to clear LDL cholesterol from blood so LDL increases
PCSK9 inhibitors versus statins
PCSK9 inhibitors=inject PCSK9 protein which binds to LDL receptors on liver degrading them→LDL remains in blood since liver cannot process it→inhibiton leads to an increase in LDL uptake and synthesis by the liver therefore taking it our of blood; helpful for people with statin intolerance
STATINS: impacts cholesterol production in liver by blocking HMG CoA reductase which is used to create cholesterol
leptin and ghrelin
leptin is produced by the fat cells fullness
ghrelin is produced by gastric emptying hunger
mechanism is leptin and implications in mutation
leptin stimulates the leptin-receptor in the hypothalimus producing POMC which stimulates MC4R on vagus nerve controlling satiety and it also blocks neuropeptide-Y which signals to inhibit hunger
leptin deficiency in children leads to unregaulted appetite→recombinant leptin can be used to restablize weight
GLP-1
glucagon like peptdide-1→triggers satiety=orexigenic; produced by L-cells of intestine and some central nervous system neurones
GLP-1 agonsits
Ozempic and semaglutide; intially prescribed for type 2 diabetes
stimulates glucose clearance so it reduced adiposity and stabilizes weight
how to improve obesity and why is it a problem now
exercise; expending more calories
we are more sedentary and dramatic increase in sugar intake; processing of food leads to pre chewed and lower satiety which stimulates reward center along with novel chemicals impacting celluar functions
diabetes mellitus
condition causing high blood sugar greater than 7 mmol/L
diabetes=pass through(urine) mellitus=maltose sugar
English doctors used to taste the pee for sweetness in order to diagnose while Chinese doctors would put pee on an ant hill to detect sugar
why is fructose more dangerous than glucose
10x more glycation than glucose
markers of diabetes
HBA1C=glycated hemoglobin on RBC; more than 6.5 % means you have diabetes→good indicator because it illustrates last 3 months of blood sugar(red blood cells replaced every three months)
experiments relating to diabetes
1889 Minkowski removed pancreas from dog triggering hyperglycemia
1920 Best injected chilled dog pancreas extract in sick pancreatectomized dog, which led to a decline in blood sugar, illustrating insulin function
Dorothy Hodgkin 1969→ described 3D structure of insulin using x-ray crystallography
islets of the pancreas
composed of beta and alpha cells
alpha=glucagon
beta=insulin
fasted state versus fed state
fasted=glucagon→increased glycogenolysis, gluconeogensis, ketogensis; trying to increase blood sugar to normal level of 5mM/L
fed=insulin→inhbits actions of glucagon and promotes glycogen syntehsis and glucose oxidation to lower blood glucose
what type of transporter allows cell to take up glucose
GLUT transporter→GLUT 2 in the liver and pancrease
GLUT 4=insulin dependent in the skeletal muscle
what organ does not require GLUT transporters
the brain
what does insulin do regarding glycogen synthase
blocks glycogen synthase inhibitor→GSK3 which allows the storage of glucose as glycogen
what happens in the adipose tissue when insulin is high
insulin signaling triggers gene transcription for lipid synthesis
when no insulin is present to get glucose inside the cell
stress hormones increase and the liver triggers other subtrate breakdown to increase glucose levels in the blood which only makes the problem worse; leads to lipid breakdwown and ketosis and the breakdown of the TCA cycle therefore increase in lactic acid production and acidosis
is type 1 or type 2 diabetes an auto immune disease
type 1→T-cells attack the beta cells of the pancreas
Alpha cells survive due to expressing more of the ANTiapoptic gene BCL2L1
what causes insulin resistance
nutrient overload
treatments for diabetes
type 1=insulin
type 2= metformin=acts on liver by activating AMP kinase leading to a starvation type response where gluconeogenesis is inhibited along with promoting catabolic pathways to decrease fat synthesis
excercise→skeletal muscle during excerzie can uptake glucose wtihout the need for insulin
weightloss→less fat means less neeed for insulin
sulfonylureas→when metformin does not work; bumps insulin release in the beta cells when exhausted blood suagr drops however increases fat because insulin increases
how are adipose tissue expansion and insulin resistance linked
through inflammation→immune cells infliltrate adipose tissue leads to accumulation of DAMPS causing systematic ctyokine inflammation
type 2 diabetes
adult onset→insulin signaling loses functions in periphery limiting glucose clearance in the blood due to defective GLUT 4 membrane expression causing insulin resistance
oversimulation of insulin signalling leading to phosphyrlation and degradation of insulin receptor subatres adpaator proteins and inhibiits PI3 kinase activity
The phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) signalling cascade, which is activated by insulin, regulates cellular metabolism and cell fate decisions, including cell survival and proliferation.
High insulin levels can promote and sustain tumour growth.
high GI versus low GI foods
glycemic index in foods how much blood sugar is spiked after eating
PI3 kinase
The phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) signalling cascade, which is activated by insulin, regulates cellular metabolism and cell fate decisions, including cell survival and proliferation.
High insulin levels can promote and sustain tumour growth.
gestational diabetes
placental hormones causing mother to have a degree of insulin desensitization leading to an increase in blood sugar and baby then also being exposed
what causes type 1 diabetes
beta cell destruction→T-cell attacking beta cells of pancreas with 80-90 percent beta cell destruction before symptoms arise
which diabetes is associated with kidney and retina probelms
type 2 because it generally manifests as high blood sugar for long amounts of time causing glycation of proteins
whereas type 1 is diagnosed and controlled in childhood
microvascular function destruction and immunity decrease
what is AGE in diabetes
advanced glycosylated end products leading to micro and macro vascular structure destruction and immunity decrease
describe DKA
diabetic ketoacidosis→lipolysis breaks down fat and the liver forms ketone bodies which causes a drop in pH; more likely in type 1
changes in the anion gap: normally at 12 mEq/L but in acidosis, hydrogen ions are released and bicarbonate binds to them leading to its reduction. Therefore the gap increases to 16 mEq/L
HHS
hyperosmol hyperglycemia syndorme(HHS) type 2 diabetics don’t create ketones rather it is due to the liver over breaking down proteins→no ketones little insulin puts little sugar into the cell→slower onset
why is insulin given in subcutaneous shots and not ingested
it would break down in the digestive system
how do sulfonylureas work
they trigger insulin release in pancreatic beta cells by triggering intracellular flux of Ca2+ promoting insulin release
whos most at risk for lactic acidosis with metformin
kidney failure patients since the kidney plays a role to clears lactic acid
level of blood sugar wanted to be maintained by body
5 mM/L
what happens when blood sugar is low
lipolysis breaks down triglycerides into glycerol and fatty acids
glycerol goes into the Krebs cycle and the fatty acids turn into acetyl CoA, which binds together to form ketones and go to the brain, whereas oxaloacetate is not limited
definition of lipid
macromolecules soluble in nonpolar solvents
are fats or carbs more reduced
fats→9 kcal verus 4 in carbs
nonpolar so fats dont bind to water therefore giving 6x more energy than carbs
describe the process of fat digestion(lipolysis)
small amounts of lipid digestion occur in the stomach due to gastric lipase; fats form fat globules
majority of digestion occurs in the small intestine since bile is produced in the liver via cholesterol and then is stored in the gall bladder, which gets released into the small intestine
this breaks down the large fat globules to allow pancreatic lipase and colipases to break down triglycerides into monoglycerides→micelles=broken down parts of fat surrounded by bile salts
microvilli allow the micelles to diffuse into mucosal cells while the bile salts get left behind, where they reassemble into triglycerides and cholesterol and become chylomicrons with the addition of the ApoB48
through exocytosis chylomicron goes into the lymph because its too big to go into the blood stream which allows it to go to the organs of the body
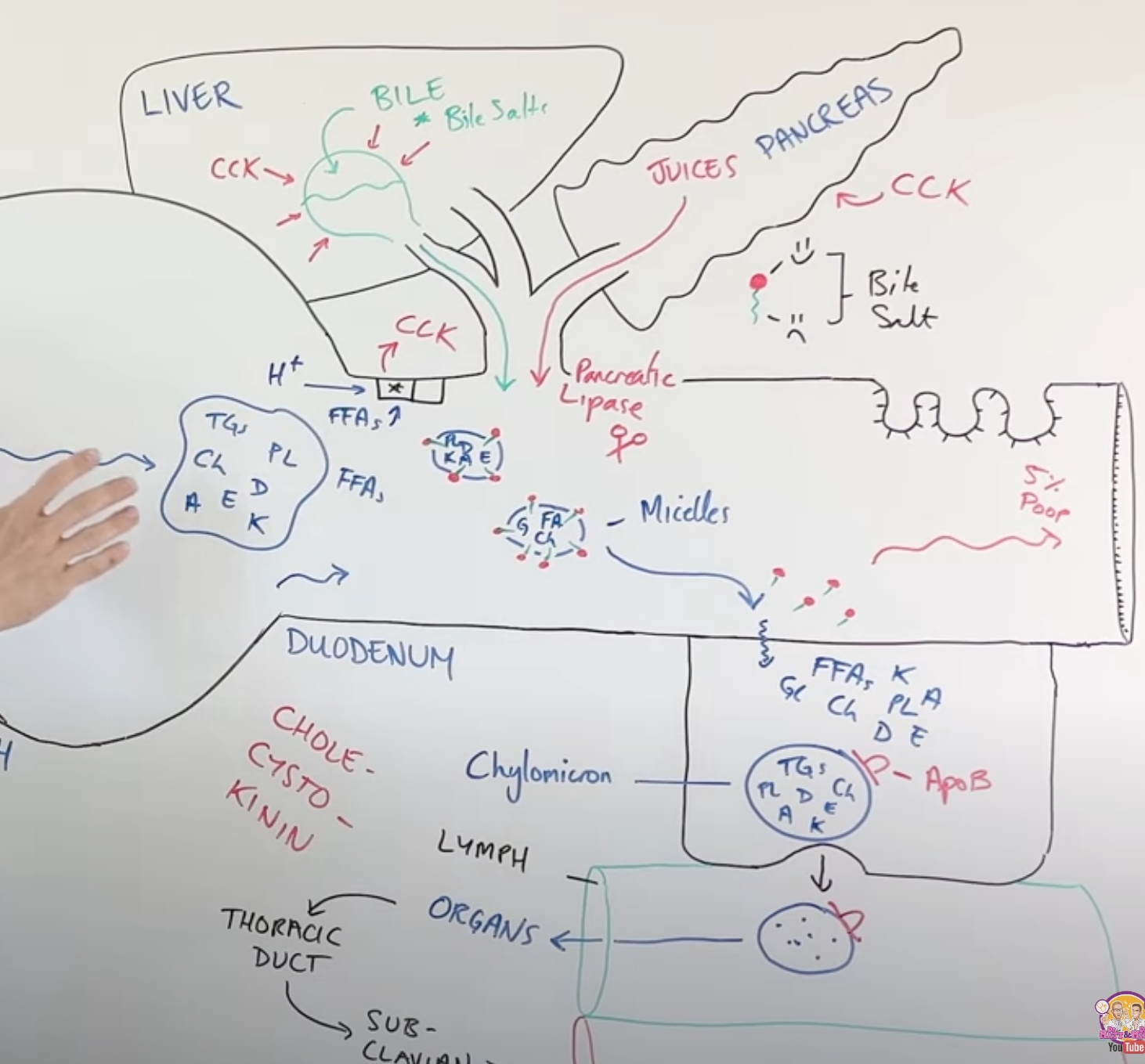
what are all of the lipids we consume
fat-soluble vitamins ADEK
cholesterol
triglycerides
small amounts of phospholipids
describe micelles
lipase and colipases breaking down fat globules with the help of bile salts which surround the broken-down triglycerides and cholesterol facilitating the movement into mucosal cells where the bile salts get left behind
what is cholesterol used for
creating cell membranes, sterol hormones, and bile salts
purpose of insulin beta cell in adipocytes
drives fatty acid and glucose uptake while driving triglyceride synthesis and inhibiting hormone-sensitive lipase which detects glucagon and breaks down fat
what food is high in cholesterol
eggs→70% RDA with 211 mg
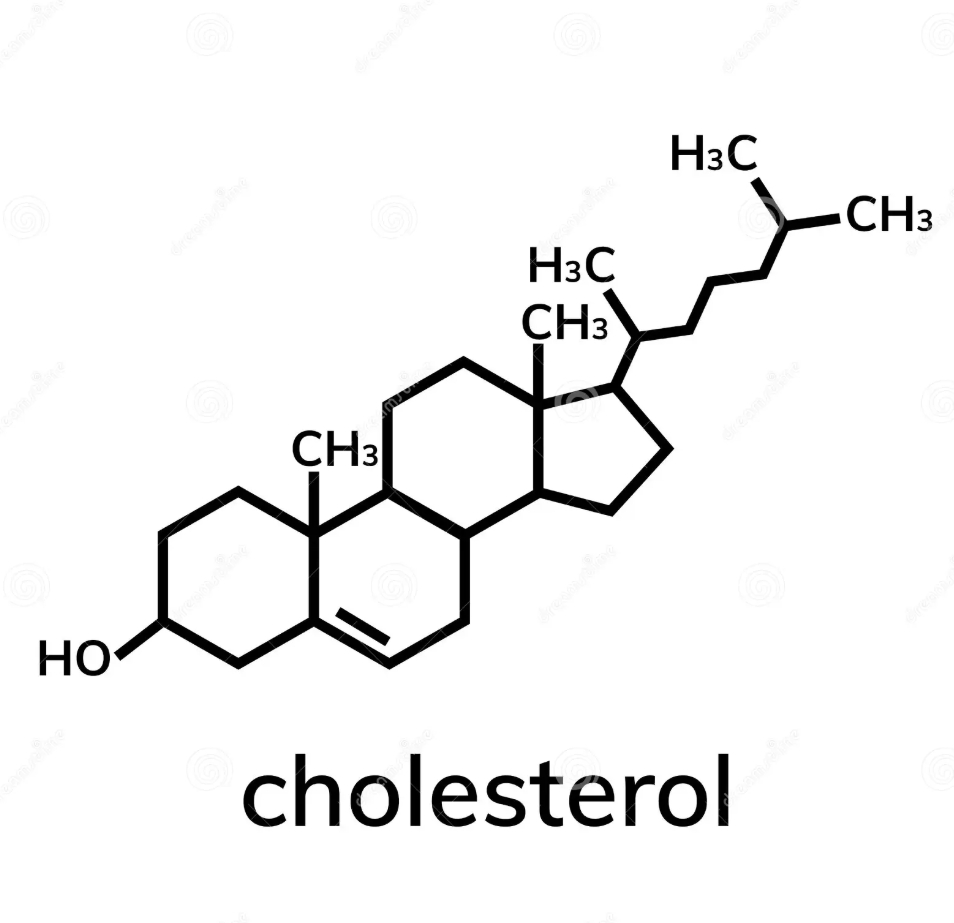
structure of cholesterol and formula
4 linked hydrocarbon rings; biological steroid; polar end has hydroxyl group that is oriented in membranes with hydroxyl group interacting with phospholipid polar head
C27H46O
is cholesterol required in diet
no in a fasted state, humans will synthesize cholesterol from polymerized isoprene units at about 800 mg per day
what levels of cholesterol and triglycerides are ideal in the blood

describe the steps in cholesterol synthesis
step 1: occurs in the cytosol; acetyl CoA to HMG-CoA via HMG CoA synthase and is regulated by feedback inhibition by cholesterol and its derivates
step 2: occurs in the ER; HMG CoA to mevalonate via HMG CoA reductase RATE LIMITING STEP
step 3: mevalonate to isoprene units
step 4: isoprene units to squalene; condensing 6 isoprene units to form 30-carbon sequence squalene
step 5: squalene to cholesterol; first it cyclized to lanosterol then rearranged into cholesterol
AH HM MI IS SC
A Happy Ham Misses My Ingredients So She Laugh Cries
what’s a focus for statins
HMG CoA reductase→they competitively inhibit
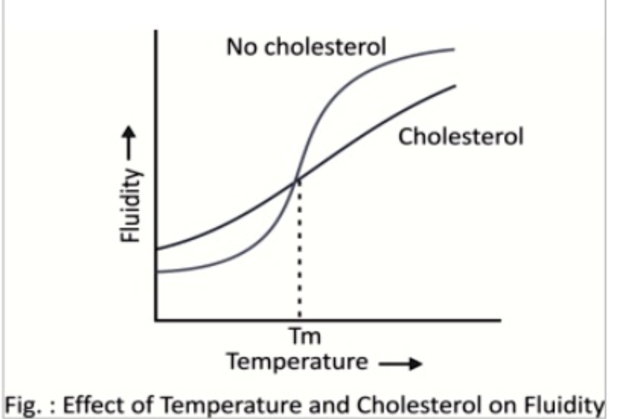
effect of cholesterol on membrane fluidity
sterol hormones built by cholesterol
progesterone-=prepares the uterine lining for pregnancy and maintains pregnancy
androgens including testosterone which is responsible for male secondary characteristics such as deeper voice and body hair and estrogen which is the ovarian cycle
cortisol=promotes gluconeogenesis and is a stress response released by the adrenals
how does cholesterol build vitamin D
takes 7-dehydrocholesterol in the epidermis and combines with UVB light to create pre vitamin D3
heat is required to convert pre-vitamin D3 to cholecalciferol which gets activated by the liver to vitamin D
BOTH DONT REQUIRE ENZYMES
discuss bile
made by liver held in the gallbladder→primary bile acids are cholic and chenodeoxycholic, which become secondary bile salts by losing OH at C7 and becoming deoxycholic and lithocholic
bile salts coming from cholesterol or glycocholate and taurocholate which are highly polar and are effective detergents due to having both polar and non polar elements
name the lipoproteins and their functions
chylomicrons: intestinal transport dietary TAGS and cholesterol APOproteinB48
very low density lipoproteins(VLDL): liver transport endogenous synthesized TAGS
Low density lipoproteins(LDLS): deliver cholesterol to peripheral tissues(arteries): B100 proteins
High Density Lipoprotein(HDL): liver;; removes used cholesterol from tissues to liver
purpose of LPL
lipoprotein lipase removes fatty acids of chylomicrons
ATP binding cassette transporters
ABCA1 and ABCG1: in cell plasma membrane and regulate the removal of cholesterol from cells to HDLs
how does LDL get into cells to deposit cholesterol
through receptor-mediated endocytosis with its APO B-100 protein
process of HDL lowering cholesterol
the free cholesterol is converted by LCAT to cholesterol esters and placed inside HDL along with TAGS and then CEPT facilitates
the transfer of CE to VLDL and the VLDLs TAGS to HDL where the VLDL then brings the cholesterol to the liver to create bile
why do people with anorexia have high cholesterol
they have lower T3 levels due to downregulation of the thyroid and T3 is a regulator of CETP so it becomes dysregulated and thus an increase in cholesterol is seen
alchhol formula
CH3CH2OH
elimination rate of alchol
about 150 mg per hour with the liver doing about 9” percent of this while the remained gets excreted in urine, breath, sweat and tear
what amount of alchohol is metabolically produced
.39mg/liter
alchohol content of beer
.5L of beer with 4 % alc content contains 16g of ethanol
digestion of alchohol not inculuding enzymes
rapidly uptaken from digestive system through diffusion and the max blood alchol level reached at about one hour after consumption and it gets rapidly distributed throughout all tissues with most uptaken by muscle and the brain
what is the lethal amount
.3-.4 percent alchol in the blood
how is alchohol metabolized in the liver
alcohol dehydrogenase oxidizes ethanol into acetaldehyde
aldehyde dehydrogenase oxidizes to acetate
acetate gets converted to acetyl CoA by acetate CoA ligase in ATP dependent reaction
another ADH substrate is methanol which a lot of people have recently died from in Asia due to drinks being homemade or having methanol added because it is cheaper and this breaks down to deadly formaldehyde
Asian flush
50% of asian have inactive ALDH which causes flushing elevated heart rate and nausea and vomiting→disulfram inhibits ALDH so it is used to help alcholhic
describe the mortality of alchohol in a graph
its a U shaped curve with 1-2 drinks per day decreasing risk of death and and more than that increasing
how does moderate alchol consumption influence HDL and what a compound in red wine that is healthy
increases by about 12 percent and resveratrol prevents platelet stickiness
why does alchohol cause liver damage
increases NADH and acetyl CoA which inhibits krebs cycle activity and encourages synthesis of fats and cholesterol therefore increasing fatty acid storage in liver
cirrhosis=chronic alchohoism and it kills liver cells and some liver functino tests are albumin and bilirubin
why is alchol bad for the brain
free radical build up alters cerebellum which leads to impaired thinking and slowed speech
what causes nausea with alchohol in the brain
5-HT3
alchhol effects on the brain and dependece
GABA=increased=inhibitory neutrotransmitter stops neurons from firiing
glutamate=excitaitry neurotransmitter
alchohol is a depressant because it increases GABA and inhibits glutamte
for a neuron to fire Ca2+ needs to jump into the neuron and this flow is decreased with alchohol
in response the brain decreased GABA receptors and increases GLUTamate recpetors thus causing anxiety and seizures in withdrawl due to overacitivity and increased Ca2+ flow
patients are given benzos which enhance GABA at the recpetor to increase relaxation
2 types of alcohol subtypes
type 1=mileiu limited→late onset high reward and harm avoidant
treatment=interaction skills
type 2=male limited→early onset, genentic, novelty seeking
treatment=coping skills
whats used to diagnose alchoholism
AUDIT→alchohol use disorder identificiation test
blood alchohl levels to drive and die
driving is .08 and death is .3
describe the reward pathway
VTA releases dopamine and the nuclease accumbens is sensitive to dopamine and the prefrontal cortex processes what is making the organism feel rewarded
example of experiment with the reward pathway
animals will bar press repeatedly for intracranial injections of alchohol into the VTA