Lecture 2: Adult Neuromuscular Examination/Evaluation
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
what is select?
Select patient/client history components based on patient/client needs
what is identify ?
Identify the components of a systems review based on patient/client
needs and complexity
what is Select?
Select individual tests and measures designated in the Guide to
Physical Therapist Practice
what is integrate?
Integrate data from the examination in order to formulate a clinical
judgment that leads to a diagnosis, prognosis, and plan of care
what is establish?
Establish functional outcomes that specify expected time duration
Multidimensional process
• Process of gathering information
• Reach decisions
• Determine actions
• Basis of patient/client management
• Clinician and patient
Hypothesis: testable explanation
Clinical Reasoning
• Results from the clinical reasoning process
• Evidence
Clinical reasoning: is why you choose something
Clinical decision making is what you chose
Clinical Decision Making
what are 5 Elements of Patient/Client Management
examination
evaluation
diagnosis
prognosis and plan of care
intervention
what is under examination?
history
systems review
tests and measures
• Gathering of data to determine why the patient needs therapy
• Chart Review
• Interview
• Other sources
• Doctors’ Orders
Diagnosis
Precautions
Medications
• Doctors’ Notes
Admission reports
Progress notes
Diagnostic Tests
Surgical Summaries
• Nurses’ notes
Progress notes
• Other (PT, OT, Speech, Social work, etc.)
history
professionalism
undivided attention
addressing the patient
privacy
sit ~ 3 feet away
open ended questions
control the conversation
respect cultural differences
history interview
living environment
stairs
floor plan
where is bedroom located
where is bathroom located
kitchen accessibility
laundry location
hallways
number of people in the household
history environment
what is under living environment ?
• House vs apartment
• How many levels in home
what is under stairs?
• Number of steps into house
• Any railings and can both be reached at the same time
• Stairs to multiple floors
what is under floor plan?
• Layout of living area; What is and is not accessible
• Where is most time spent; Favorite place to sit
• Type of flooring
where is bedroom located ?
• Type of bed (regular vs hospital)
• Bedrails
where is bathroom located?
• Layout of bathroom
• Toilet seat height
• Grab bars
• Tub/shower
what is under hallways?
• Width and type of flooring
• Accessible with assistive device
number of people in the household
• Who does household chores
• Pets in the home
Adaptive Equipment
• Assistive devices
• Wheelchair
• Raised toilet seat
• Grab bars
• Hospital bed
• Braces, orthotics
• Adaptive feeding, dressing, bathing equipment
History: Adaptive Equipment
• Problems an individual may experience in involvement in life situations
• PIP: Patient identified problems
• NPIP: Non-patient-identified problems
• Inability to return to work
• not being able to participate in recreational activities like sports or dancing
• difficulty with self-care tasks like bathing or dressing (IADL’s)
• limited ability to engage in social events
• challenges with household chores like cooking or cleaning
Participation Restrictions
what is PIP
Patient identified problems
what is NPIP
Non-patient-identified problems
what are activity limitations?
• difficulty walking
• climbing stairs
• reaching overhead
• bending down to pick something up
• standing for long periods
• lifting objects
what is Systems Review: Precautions
• DNR
• Cardiac
• Sternal
• Seizures
• ROM limitations
• Weight bearing status
• Orthostatic hypotension
what is Systems Review: Cognition
• Consciousness
• Orientation
• Memory
• Safety awareness
• Ability to make needs known
• Expected emotional/behavioral responses
• Learning preferences (educational needs, learning barriers)
• A x O × 3 (person, place and time)
• Level of Consciousness
Alert: Normal
Lethargy: Drowsy
Obtunded: Difficult to arouse
Stupor: Responsive only to pain/touch
Coma: Arousal impossible
what is Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores?
24-30: normal
21-23: mild impairment
16-20: moderate impairment
15 or less: severe impairment
what is Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MOCA) scores?
26 or higher: Normal cognitive health
18–25: Mild cognitive impairment (MCI)
10–17: Moderate cognitive impairment
Less than 10: Severe cognitive impairment
what is Glasgow Coma Scale?
Level of consciousness in acute brain injury
Examines eye opening, motor response & verbal response
Score ranges from 3-15
Below 8 = severe injury
9-12 = moderate injury
13-15 = mild injury
what is Rancho Los Amigos Level Of Cognitive Functioning (RLA LOCF)?
Descriptive scale to examine cognitive and behavioral recovery in TBI
• Immediate – recall 3 items presented after 3-5 minutes
• Short term – “what did you have for breakfast”
• Long term – “ past events – “where were you born”
• Vision
• Hearing
• Speech
Memory
Heart Rate: 60 – 100 BPM
Blood pressure: 120/80
Oxygen Saturation: 96-100%
Respiratory Rate: 12 to 20 breaths per minute
Systems Review: Cardiovascular and Pulmonary
• Assessment of skin color
• Temperature
• Integrity
• pliability (texture)
• presence of scar formation
Systems Review: Integumentary System
Assessment (through interview or observation) of joint pain
swelling or stiffness,
weakness;
screening tests and measures of gross range of motion (ROM)
gross strength
posture and symmetry
joint temperature and alignment
Five Times Sit to Stand Test.
Systems Review: Musculoskeletal System
• Assessment (through interview or observation) of fatigue
• recent weight loss or gain
• usual level of blood sugar when checked (diabetes);
• screening tests and measures of the Functional
Assessment of Chronic Illness
• Therapy-Fatigue scale,
• 2- or 6MWT
Systems Review: Endocrine System
why systems review?
• confirm the need for further or more detailed examination
• rule out or differentiate specific system involvement
• determine if referral to another health-care professional is warranted
• focus the search of the origin of symptoms to a specific location or body part.
From the History and Systems Review a hypothesis is generated about the patient’s condition
Tests and Measures are then used to further investigate the condition
The Tests and Measures are used to establish a diagnosis, prognosis, plan of care and to select appropriate interventions
Tests and Measures
What test are used to examine sensation?
superficial
deep
combined
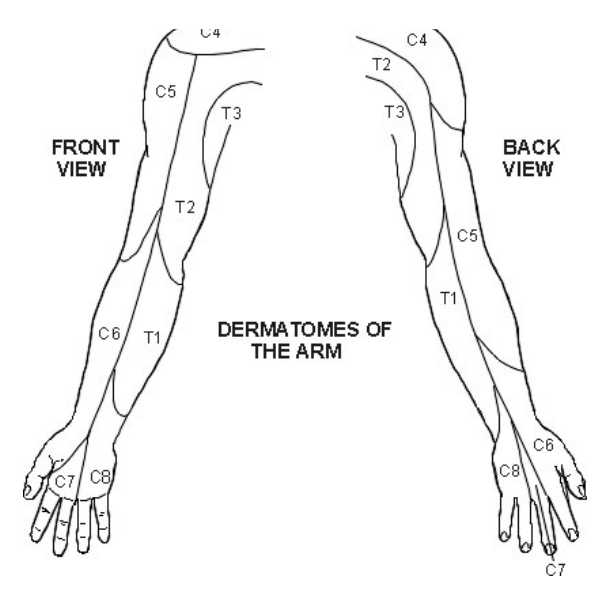
• Complete sensation examination on partner.
• Test for light touch and sharp/dull
• Dermatomes C5-T2
Tests and Measures: Sensation
Temperature Awareness
Cold: 41 – 50 f
Hot: 104 – 113 f
Pressure perception
The therapist's fingertip or a double-tipped cotton swab applies firm pressure on the skin surface
Sensory testing
Kinesthesia
proprioception
Sensory Testing -Deep Sensations
what is kinesthesia?
• awareness of movement
• extremity or joint(s) is moved passively through a relatively small range of motion (ROM)
• describe verbally the direction (up, down, in, out, etc.)
• respond by simultaneously duplicating the movement with the contralateral extremity
what is proprioception?
• joint position sense and the awareness of joints at rest
• extremity or joint(s) is moved through a ROM and held in a static position
• initial, mid-, or terminal range
• Vibration Perception
• tuning fork
what is Combined Cortical Sensations
stereognosis
tactile
two point discrimination
graphesthesia (traced figure identification)
barognosis (recognition of weight)
what is stereognosis
Ability to recognize the form of objects by touch (stereognosis)
what is tactile?
ability to localize touch sensation on the skin (topognosis)
What tests are used to examine coordination
Grading
5. Normal performance
4. Minimal impairment: able to accomplish activity but with less than normal speed and skill
5. Moderate impairment: able to accomplish activity; movements are slow, awkward and unsteady
6. Severe impairment: able only to initiate activity
without completion
1. Activity impossible
What tests are used to examine muscle tone?
Initial observation of resting posture
Passive motion testing
• Quick stretch
• Clasp-knife reflex
• Cogwheel rigidity
• Lead pipe rigidity
• ClonusActive motion testing
Grade 0: No increase in muscle tone
Grade 1: Slight increase in muscle tone, manifested by a catch and release or by minimal resistance at the end of ROM
Grade 1+: Slight increase in muscle tone, manifested by a catch, followed by minimal resistance throughout the remainder (less than half) of the ROM
Grade 2: More marked increase in muscle tone through most of the ROM, but the affected part is easily moved.
Grade 3: Considerable increase in muscle tone, passive movement is difficult.
Grade 4: Affected part is rigid
Tests and measures: modified ashworth scale
PROM and AROM
upper and lower extremities
manual muscle testing
note any contractures, limitations or abnormal synergy patterns
Tests and Measures: ROM and Strength
Lesions of corticospinal tract (i.e. CVA) can produce abnormal obligatory synergies
Voluntary movements that are limited in the ability to adapt to demands placed upon them
Selective movement control is severely disordered.
As CNS recovery progresses, synergies become more variable
Tests and Measures: Abnormal Synergy Patterns
UE flexion testing
scapular retraction & elevation; shoulder abduction & ER, elbow flexion, forearm supination, wrist and finger flexion
UE extension testing
scapular protraction, shoulder adduction & IR, elbow extension, forearm pronation, wrist and finger flexion
LE flexion testing
hip flexion, abduction & ER, knee flexion, ankle dorisflexion & inversion, toe flexion)
LE extension testing
hip extension, adduction & IR, knee extension, ankle plantarflexion & inversion, toe extension
What scale is used to examine DTR’s?
• 0 – no response
• 1+ - present but depressed, low normal
• 2+ - average normal
• 3+ - increased, quicker than average, not necessarily abnormal
• 4+ - very brisk, hyperactive, with clonus
• Biceps, Brachioradialis, Patella, Achilles
• Test biceps DTR on partner
athetosis
choreiform movements
resting tremors
intention tremors
fasciculations
Tests and Measures: Involuntary Movements
Sitting and Standing posture
• Head
• Shoulders
• Scapula
• Upper extremities
• Ribs
• Trunk
• Pelvis
• Lower extremities
Tests and Measures: Posture
Describe assistance needed, verbal cues
• Bed mobility
• Transfers
• Wheelchair mobility
• Gait
• Stairs and elevations
Tests and Measures: Functional Mobility

Levels of Assistance
A standardized assessment instrument of functional status that is part of the
Uniform Data Set for Medical Rehabilitation; it tests 23 items in seven areas
of function and uses a seven-point scale for each item
7: Complete Independence
6: Modified Independence
5: Supervision or Setup
4: Minimal Assistance (75% or more)
3: Moderate Assistance (50-75%)
2: Maximal Assistance (25-50%)
1: Total Assistance (less than 25%
Functional Independence Measure (FIM)
Static vs dynamic balance
Grading Balance Scale
Poor, Fair, Good, Normal
Tolerance to perturbations
Examining Sitting and Standing Balance
• Postural Assessment for Stroke Patient
• Activity-specific Balance Confidence Scale
• Falls Efficacy Scale
• CTSIB
• Tinetti POMA
• Berg Balance Scale
• Functional Reach Test
• Timed Up and Go (TUG)
• One legged stance
• Romberg stance
• Tandem stance
• Stops Walking When Talking
Balance