Protein purification Qs - Ebiolabs
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
At pH 5, what is the charge on a column packed with DEAE-cellulose?
Positive
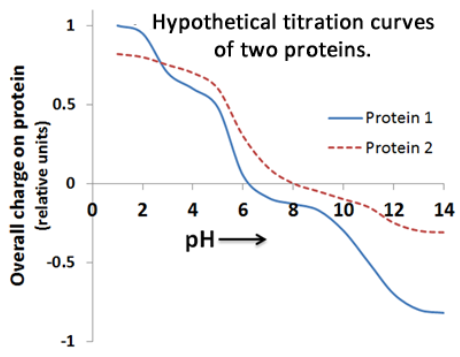
The titration curves of two hypothetical proteins are shown below.
Assume you are using a column packed with DEAE-cellulose.
At pH 7, will Protein 1 bind to the column?
Will protein 2 bind to the column?
At pH 9, will protein 1 bind to the column?
Will protein 2 bind to the column?
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
If a protein is in a buffer at a pH greater than its pI, the overall charge on the protein is:
If a protein is in a buffer at a pH less than its pI, the overall charge on the protein is:
Negative
Positive
Proteins are likely to be more positively charged at pH 5 or 9?
Proteins are likely to be more negative charged at pH 5 or 9?
Positive: 5
Negative: 9
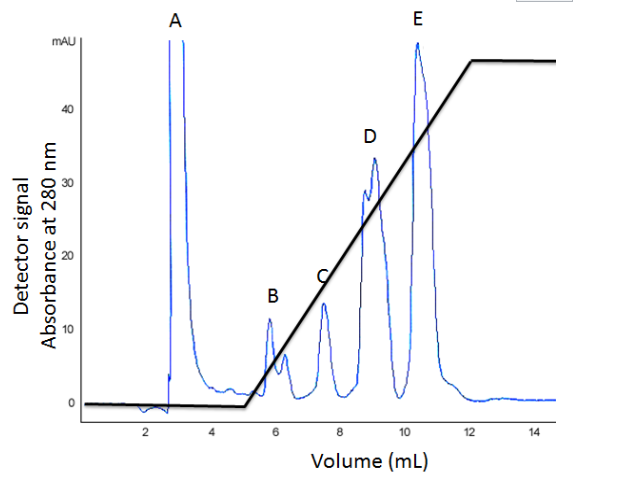
A mixture of proteins was loaded onto a DEAE column at pH 8 and, after
washing, a steadily-increasing NaCl gradient was applied. The
absorbance of the eluate was monitored at 280 nm as shown in the
chromatogram below, the back line indicates the NaCl concentration.
Which fraction contains proteins with a pI greater than 8?
Which fraction contains proteins with the greatest overall negative charge at pH 8?
Which fraction contains proteins that are the most weakly bound?
A
E
B
The Bradford assay measures the concentration of — ———— within a sample. The assay runs in a — — Cuvette for —— —— mins at room temp.
A positive result will cause a colour change from ——- to ——.
The specrophotometer must be set to —- nm to measure the product.
The Bradford assay measures the concentration of all proteins within a sample. The assay runs in a 1ml Cuvette for about 5 mins at room temp.
A positive result will cause a colour change from Brown to Blue.
The specrophotometer must be set to 595 nm to measure the product.
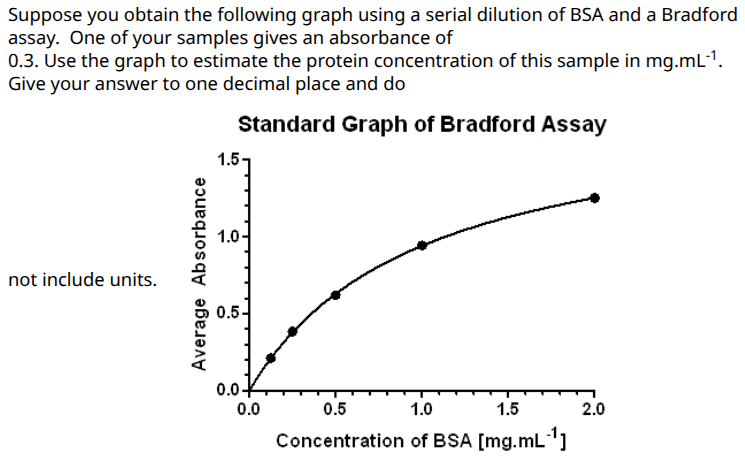
0.2
Amy has purified some ß-galactosidase. One of her fractions has a volume of 1.5 mL and an activity of 2.27 µmol·min-1·mL-1.
Calculate the total activity in this fraction in µmol·min-1.
3.4
Rory has purified some ß-galactosidase. One of his fractions has an activity of 1.3 µmol·min-1·mL-1 and a protein concentration of 0.9 mg·mL-1. Calculate the specific activity of this fraction in µmol·min-1·mg-1.
1.4
Amy has purified some ß-galactosidase. One of her fractions has a volume of 2.8 mL and an activity of 3.55 µmol·min-1·mL-1.
Calculate the total activity in this fraction in µmol·min-1.
Give your answer to one decimal place and do not include units in your answer.
9.9
James has purified some ß-galactosidase. He calculated that the total activity of the crude sample was 7.8 µmol·min-1 and the activity of the purest fraction was 4.5 µmol·min-1. What was the percentage recovery?
58
Lily has purified some ß-galactosidase. She calculated a specific activity of 1.05 µmol·min-1·mg-1in her crude sample and 3.24 µmol·min-1·mg-1 in her purest
fraction. What is her purification factor?
3.1
James has purified some ß-galactosidase. He calculated that the total activity of the crude sample was 3.3 µmol·min-1 and the activity of the purest fraction was 1.2 µmol·min-1. What was the percentage recovery?
37
Lily has purified some ß-galactosidase. She calculated a specific activity of 0.68 µmol·min-1·mg-1in her crude sample and 2.54 µmol·min-1·mg-1 in her purest
fraction. What is her purification factor?
3.7

100 units/mg

800 units/mg

0.8 units

500 units