Fixation Disparity
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
under binocular conditions
allows analysis of groups of data
easy to determine tentative prism rx
easy to use
what are some advantages for fixation disparity?
no direct info about accommodative or oculomotor problems
analysis can be clinically bulky
what are some disadvantages of fixation disparity?
fixation disparity
measure of changes in ocular alignment in response to binocular vergence stimulation &/or accommodative stress
small misalignment of the eyes under binocular conditions
no
does diplopia occur if the pt has fixation disparity?
min of arc
how is fixation disparity measured?
eyestrain/discomfort
fixation disparity can result in what clinical sx?
no
can fixation disparity testing be used in strabismic pt?
higher
the higher the pt’s dissociated phoria, the _____ the demand is on fusional vergence
more
the higher the demand on fusional vergence, the _______ likely there is error making in the vergence system
more
pt w/ high dissociated phorias are ______ likely to have fixation disparity
same
fixation disparity & dissociated phoria are typically in the _______ direction
exo
under convergence results in a _______ FD
eso
over convergence results in a _________ FD
prism adaptation (vergence adaptation, fusional after-effects)
shift to tonic vergence after the use of fusional vergence
clinically shown as a change in dissociated phoria before & after extended prism viewing
forced vergence fixation disparity curve
test to measure the robustness of the binocular vision system
determined by measuring FD when a pt looks through varying amounts of prism
divergence, NFV, eso
when BI prism is introduced, the pt induces _______, must use __________, and results in ________ FD
convergence, PFV, exo
when BO prism is introduced, the pt induces _______, must use __________, and results in ________ FD
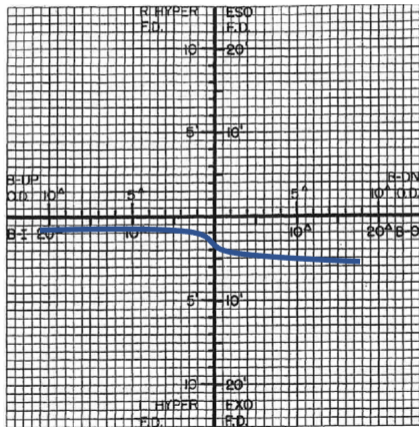
type 1
FVFDC type
equal adaptation to BI & BO
typically asymptomatic
55% of the pop
“normal”
type 2
FVFDC type
more adaptation to BO
most commonly eso pt
30% of the pop
type 3
FVFDC type
more adaptation to BI
most commonly exo pt
10% of the pop
type 4
FVFDC type
unstable binocularity
abnormal sensory or motor fusion (strabismus)
5% of the pop
eso
up on FVFDC is ____
exo
down on the FVFDC is ____
BO
right on the FVFDC is ____
BI
left on the FVFDC is ____
y intercept
the start of the FD test on the curve, when there is no prism in the system, what the pt sees just walking around in everyday life
x intercept (associated phoria)
amount of prism it takes to bring the pt’s FD to 0
same
associated phoria is typically in the ______ direction as the pt’s dissociated phoria
(FD at 3BO - FD at 3BI) / 6^
slope of an FVFDC =
shallow, better
a ______ slope means the pt is less symptomatic, _____ tonic vergence adaptation
steep
a ________ slope means the pt is more symptomatic
center of symmetry
area where the greatest vergence adaptation to changes in fusional vergence occur
flattest central region of the FD curve
useful for prescribing prism
Sheedy’s criterion
substituted for center of symmetry
easier to determine
useful for prescribing prism
identify the flattest segment of the curve
choose the point closest to the y axis (lowest amount of prism)
how do you find Sheedy’s criterion?
down & left
plus lenses shift the FD curve ______
esos
lenses are more beneficial for ______ (exos/esos)
flattens the curve (useful for steep slopes)
what are the effects of VT?
VT
what is the only way to change the slope of the FVFDC?
type of curve
y intercept
x intercept
slope
center of symmetry
Sheedy’s criterion
what are the 6 key FVFDC parameters?
type 1
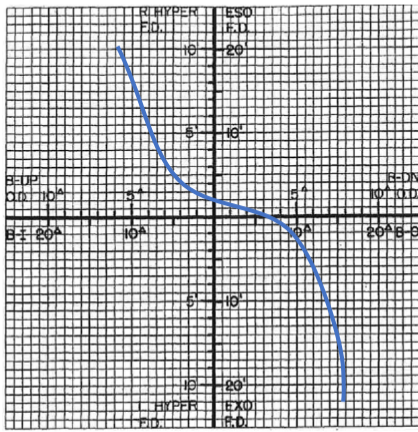
type 2
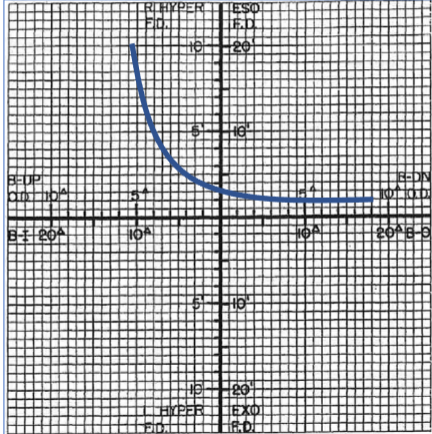
type 3
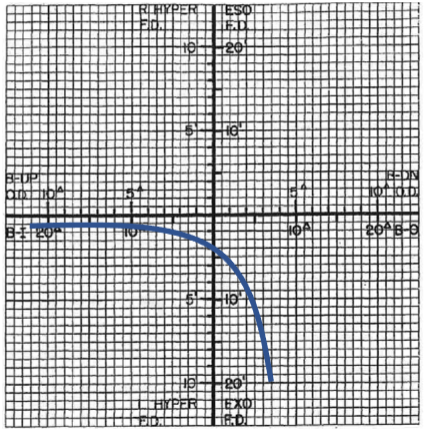
type 4