CB7a
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
The supervenience relation
Background assumptions:
The supervenience relation: consciousness supervenes on brain activity
It is a philosophical background assumption, it seems to be tacitly taken for granted by neuroscientists when studying consciousness
The neural correlates of consciousness = NCC
The principle of Covariance
For each and every conscious event, there is a corresponding brain event (not vice versa)
The principle of ontological dependence
The conscious events somehow owe their existence to the brain activity
denial of cartesian substance dualism
The neural correlates of consciousness
NCC
Standard Definition (Koch 2004): NCC is the minimally sufficient neural system or activity that invariably cooccurs together with a conscious experience of a specific kind
Design of NCC experiments
What are the neural correlates of the subjective experience ”X”? CONTROL CONDITION: experience X is absent (does not occur in the subjet’s mind)
EXPERIMENTAL CONDITION: experience X is present (does occur in the subject’s mind)
everything else is equal or kept constant
what is the difference in brain activity between these two conditions? = NCC-X
Brain electrical activity:
Microelectrodes (animal studies)
EEG
MEG
Brain metabolism and blood flow:
fMRI
PET
Brain stimulation:
direct cortical stimulation
transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)
transcranial electrical stimulation (tDCs, tACs)
Structural Brain Imaging
CT, CAT
MRI
Functional Brain Imaging
PET
fMRI
Electromagnetic Brain Sensing
EEG
MEG
Electromagnetic Brain Stimulation
TMS, tACs, tDCs
direct
EEG and the conscious state
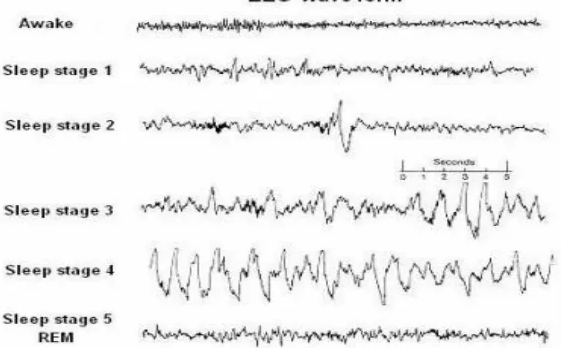
Slow wave EEG
Less complex, les differentiated thalamocortical activity
Consciousness requires complex high frequency activities between thalamus and cortex
Epileptic EEG activity
Sudden abnormal bursts of electrical activity in the brain > epileptic seizures
Coma
State of unarousable unresponsiveness
Typically transient (1-2 weeks)
Vegetative state
Cyclical patter of arousal: wake (eyes open) - sleep (eyes closed)
Unresponsiveness, no behavioural evidence of awareness of self or environment
Permanent if lasts over 1 year
Minimally conscious state
Reliable but inconsistent awareness of self or environment, no reliable communication
How do anesthetics suppress consciousness?
They represent a wide variety of different molecules that have a wide variety of different effects on different parts, mechanisms, and receptors in the brain.
Thalamus is a common target of anesthetics , but there is also a theory that there isnt a single consciousness switch and it probably has something to do with changes in functional connectivity.
How to measure consciousness (when in global disorders)
Degree of baseline brain activity (metabolic activity, blood flow)
Responsiveness of neural networks
Functional connectivity of large scale neuronal networks
Arise from unconscious states
Thalamocortical connectivity
The cortex is completely quiet during the arise of consciousness and it seems like thalamus has a some input but other cortical mechanisms
Anesthesia awareness
Consciously perceiving some sensory perceptual stimuli from the environment
Anesthesia dreaming undergoing internally generated conscious experiences
Measure brain activity
Perturbational complexity index (PCI)
TMS + EEG
> 0,44 - conscious
< 0-31 unconscious