Isomerism
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Constitutional Isomers
Compounds which have the same molecular formula but different in there structures are called?
Structural Isomerism
Constitutional Isomers also called as?
Isomers
Compounds having the same molecular formula and same molecular weight but different structural formula, thus differ in physical and chemical properties.
Chain Isomers
Functional Isomers
Positional Isomers
Metamerism
Tautomerism
Ring-chain
Types of Structural Isomerism
Positional Isomers
These isomers differ in the attachment of the functional group to the chain at different positions.
Metamers
This type of isomerism arises due to the presence of different alkyl chains on each side of the functional group.
It is a rare type of isomerism and is generally
limited to molecules that contain a divalent
atom (such as sulfur or oxygen), surrounded
by alkyl groups.
Tautomers
Isomer of the compound which only differs in the position of protons and electrons.
Stereoisomers
Isomers that have the same composition but that differ in the orientation of those parts in space.
Ring-chain Isomers
One of the isomers has an open-chain structure whereas the other has a ring structure.
Geometrical
Optical
Types of Stereoisomers
Geometrical Isomers (cis-trans isomerism)
These isomers have different spatial arrangements of atoms in three-dimensional space.
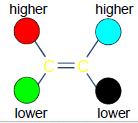
cis-isomers
The one having identical groups on same side of double bond.
trans-isomers
The one having identical groups on opposite side of double bond.
E (Either Side)
A Notational System that has higher ranked substituents on opposite sides.
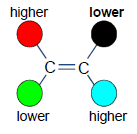
Z (Zame Side)
A Notational System that has higher ranked substituents on same sides.
I > Br > Cl > S > P > F > O > N > C > 2H >H
Rearrange some of the example of Elements from Higher to Lower base on their Atomic number.
( H, I, Br, P, F, Cl, O, S, , 2H, N, C )
Optical Isomers
Compounds having at least one carbon atom joined to four different atoms or groups.
Have identical physical properties except
optical activity.
Dextrorotatory ‘d’ or (+)
Compounds that rotate the plane of plane
polarized light to the right (clockwise) are said
to be?
Levorotatory ‘l’ or ( - )
Compounds that rotate the plane to the left.
Racemic Mixture
A mixture containing equal amounts of d- and l- isomers and is optically inactive denoted by dl or ±.
Chan-ingold-prelog sequence rule
A rule that said higher atomic number outranks lower atomic number.
Diastereomers
A type of Stereoisomers that is non-mirror image or non-identical.
Teratogenic
A drug causing developmental malformation.
Structural Isomers
Stereoisomers
2 types of Isomerism