Organic Chemistry 3.1 Alkanes and Combustion Reactions
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Combustion Reaction
are reactions in which a substance combines with oxygen to produce heat and light, usually resulting in a flame.
Alkanes
Saturated hydrocarbons containing only single bonds between carbon atoms (e.g., methane, ethane, propane).
Complete Combustion
Combustion in which a hydrocarbon burns in the presence of sufficient oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water as products.

Incomplete Combustion
Combustion that occurs with limited oxygen, producing carbon monoxide or soot (carbon) along with water.
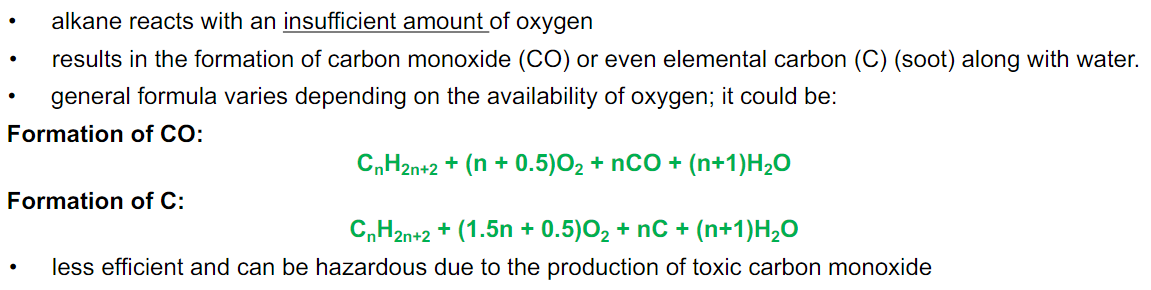
Carbon Dioxide and Climate Change
While this is the “cleaner” byproduct of combustion, it is a greenhouse gas, meaning it traps heat in the Earth's atmosphere. Over time, increasing levels contribute to global warming, which leads to climate change, melting ice caps, rising sea levels, and extreme weather patterns.
Carbon Monoxide and Health Risks
A colorless and odorless gas that is toxic to humans and animals. When inhaled, carbon monoxide prevents oxygen from binding with hemoglobin in the blood, which can lead to severe health issues or even death at high exposure levels.
Particulate Matter and Air Quality
This particulate matter contributes to smog and poor air quality, especially in densely populated and industrial areas. Soot Particles can penetrate the lungs and bloodstream, causing respiratory diseases, cardiovascular issues, and other health problems. They also contribute to reduced visibility and damage to natural and man-made structures.
Acid Rain Formation
Combustion of hydrocarbons often releases sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, which react with water vapor in the atmosphere to form acids. These acids precipitate as acid rain, which can damage forests, harm aquatic ecosystems, and erode buildings and monuments.