chemistry of beta blockers
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
: What are β-blockers, and what do they do?
β-blockers are β-adrenergic blocking agents
Block the effects of the hormone epinephrine (adrenaline)
They lower heart rate, reduce force of contraction, and lower blood pressure,
they also widen veins and arteries to improve blood flow.
How do β-blockers work at the molecular level?
Competitive inhibition of β-receptors
Counters the effects of catecholamines (e.g., epinephrine)
What are the two types of nervous systems in the peripheral nervous system?
Cholinergic system (using acetylcholine)
Adrenergic system (using adrenaline and noradrenaline)
How do the cholinergic and adrenergic systems work together in the peripheral nervous system?
The balance between these two systems allows for fine control of various bodily functions
Cholinergic (acetylcholine) and adrenergic (adrenaline/noradrenaline) systems have opposing actions at various tissues
What is the difference between adrenaline, noradrenaline, and acetylcholine?
Adrenaline is a hormone
Noradrenaline and acetylcholine are neurotransmitters
Their actions at tissues are opposite
What is the function of the α-1 receptor?
Smooth muscle contraction
Mydriasis (pupil dilation)
What is the function of the α-2 receptor?
Mixed smooth muscle effects (depends on tissue type)
What is the function of the β-1 receptor?
Increased cardiac chronotropic (heart rate) and inotropic (contractility) effects
What is the function of the β-2 receptor?
Bronchodilation (relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle)
What is the function of the β-3 receptor?
Increased lipolysis (fat breakdown)
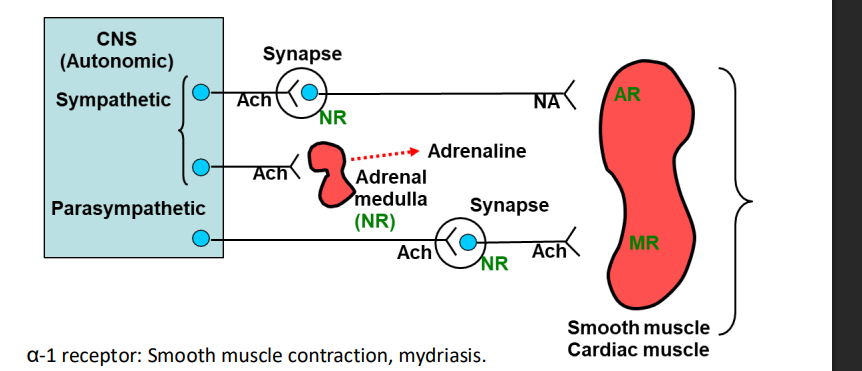
How does the sympathetic nervous system help maintain the body’s environment in response to stress?
Sympathetic nerve stimulation releases noradrenaline
Noradrenaline stimulates the adrenal gland, increasing the release of adrenaline
This response is part of the body’s stress adaptation, preparing the body for a “fight or flight” response
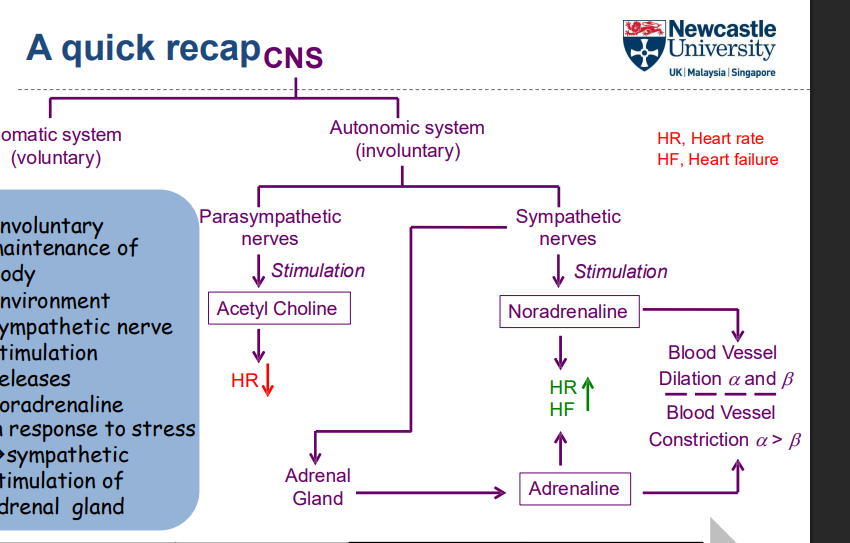
what are the 2 types of adrenoceptors?
alpha: a1+a2
beta: b1,b2,b3
both are g protein coupled receptors
What happens when Phospholipase C is activated?
Phospholipase C activation leads to the formation of:
Ip3
(DAG)
These molecules cause an increase in intracellular calcium levels
How does adenylate cyclase affect cAMP levels?
Adenylate cyclase activation leads to an increase in cAMP levels
Adenylate cyclase inactivation leads to a decrease in cAMP levels
Adrenaline and noradrenaline switch on adenylate cyclase
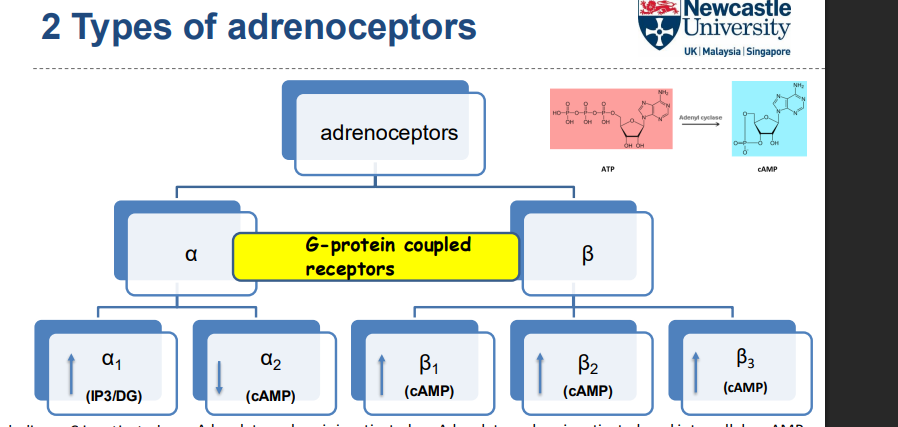
What are G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs)?
Cell surface receptors that are embedded in the plasma membrane
Also called membrane or transmembrane receptors
Bind to extracellular molecules (e.g., hormones, neurotransmitters)
Activate intracellular signaling pathways via G-proteins
Where are β1 and β2 receptors typically found, and what is their function?
β1 receptors are mainly found in the heart (cardiac muscle)
β2 receptors are mainly found in bronchial smooth muscle and blood vessels.
Both α, β, and α/β receptors can contribute to vasodilation depending on receptor type and potency
How does the β1 receptor work at the molecular level?
7-transmembrane receptor (7-TM receptor)
G-protein linked to adenylate cyclase
ATP is converted to cAMP
cAMP activates PKA (Protein Kinase A)
PKA phosphorylates proteins, driving the cellular response
What are the endogenous agonists for adrenergic receptors, and what is the catechol ring structure?
Endogenous agonists: Adrenaline (epinephrine), Noradrenaline (norepinephrine)
Catechol ring structure:
Both adrenaline and noradrenaline have a catechol ring structure
Catechol ring consists of a benzene ring with two hydroxyl groups (-OH) at positions 3 and 4
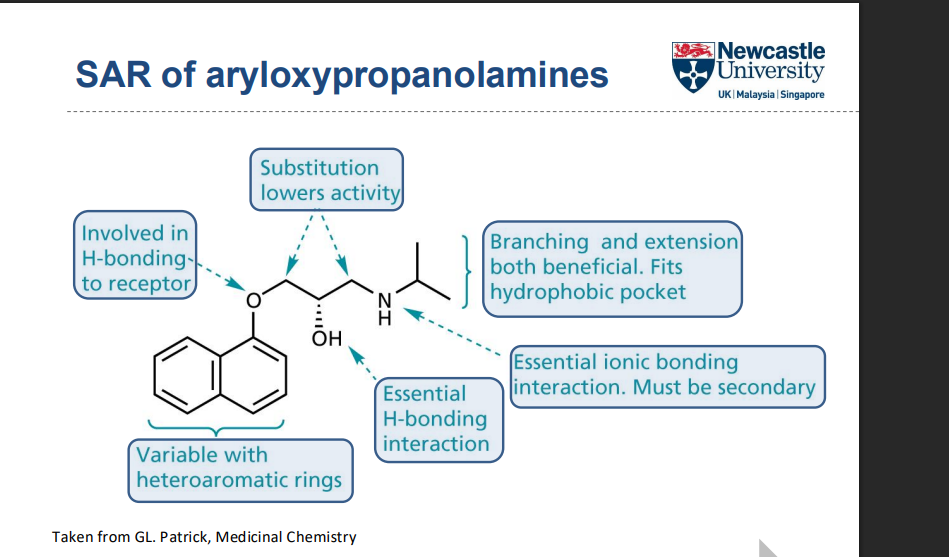
What structural features are important for target binding in this SAR?
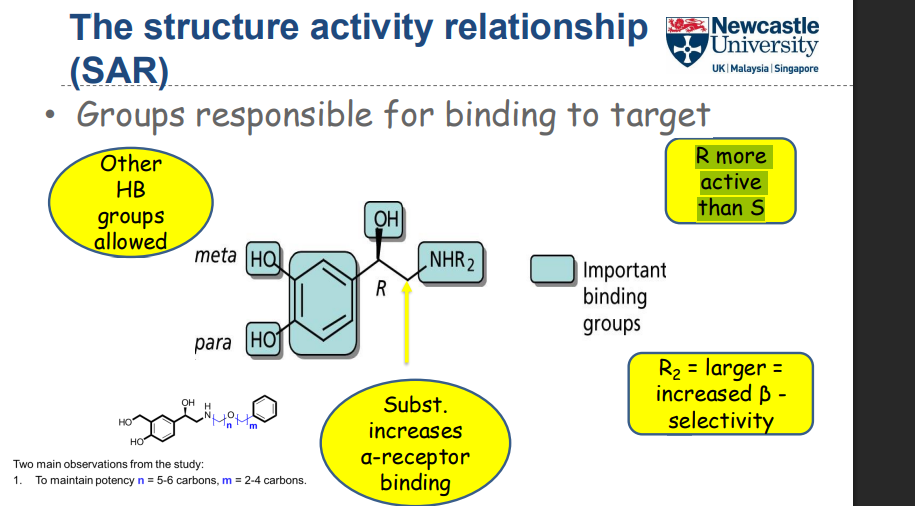
How do stereochemistry and substituents affect receptor selectivity and activity?
R-enantiomer is more active than S
Substitution at R increases α-receptor binding
Larger R₂ substituents increase β-selectivity
Which molecules do not bind effectively to the receptor, and why?
Tyramine ❌
Lacks key hydroxyl (OH) groups needed for hydrogen bonding
Weaker receptor interactions
Amphetamine ❌
Missing aromatic ring OH groups
Reduced ability to bind to the receptor binding site
What was Dichloroisoprenaline (DCI) and why was it important?
Prepared by Eli Lilly (1958)
Catechol modified (3,4-dichloro) → agonist → antagonist
Became the first β-blocker
Acted as a partial agonist
No clinical use, but an important lead compound
How did DCI lead to clinically useful β-blockers?
Sir James Black used sympathetic nerve stimulation assays
Replaced dichloro groups with a carbon bridge
Formed a naphthylethanolamine derivative
Led to pronethalol (1962)
Pronethalol: β-blocker, only weak partial agonist
What was pronethalol used for clinically?
First clinically available β-blocker
Used to treat:
Hypertension
Angina
Certain cardiac arrhythmias
Only marketed for life-threatening conditions
Explain why pronethalol was eventually withdrawn from the market, and what impact did this withdrawal have on beta-blocker development?
Pronethalol was withdrawn due to toxicology concerns, specifically the observation of thymic tumors in rats.
This spurred further research into the structural features of beta-blockers to find safer alternatives.
How did the chemists at ICI initially stumble upon the increased potency of propranolol during their research of pronethalol?
While originally aiming to create a compound better than pronethalol, the chemists used an α-naphthol rather than the intended β-naphthol during the synthesis process, unexpectedly leading to the creation of a compound 20x more potent.
What are epoxides and why are they reactive?
3-membered ring containing an oxygen atom
Highly strained structure
Carbon atoms are electrophilic
React readily with nucleophiles
Why does ring opening of epoxides occur easily?
Ring strain (internal angle ≈ 60°)
Ring opening relieves strain
Provides strong thermodynamic driving force
Reaction may be acid-catalysed
How do reaction conditions affect epoxide ring opening?
Basic conditions / strong nucleophile → attack at less substituted carbon
Acid-catalysed conditions → attack at more substituted carbon
Regioselectivity depends on reaction conditions
What side effects were associated with 1st-generation β-blockers?
Crossed the BBB → dizziness, sedation
Caused bronchoconstriction (problematic in asthmatics)
Lowered cardiac output
Resulted in poor tolerability
Why and how was propranolol modified in later β-blocker development?
Use of “back-up” compounds to improve safety
Issue with propranolol: high lipophilicity (logP = 3.66)
Leads to BBB penetration → CNS side effects
Strategy to reduce logP:
Remove one aromatic ring
Add logP-lowering groups (e.g. acetamide, sulphonamide)
What were the advantages of practolol compared with propranolol?
Contains an amide group → potential H-bonding
More polar (logP ≈ 0.79)
Reduced BBB penetration
Fewer CNS side effects
β₁-selective over β₂ (cardioselective)
Less potent than propranolol but more selective
What were the clinical uses and limitations of practolol?
Launched in 1970
Used for:
Angina
Hypertension
Immediate post-myocardial infarction
Withdrawn due to adverse effects:
Skin rashes
Eye problems
Peritonitis(swelling of the belly)
What are the key structural and pharmacological features of 2nd-generation β-blockers?
Contain an extended para substituent
Capable of hydrogen bonding
β₁-selective (cardioselective)
Fewer side effects than 1st-generation agents
Reduced CNS effects due to increased polarity
What are the clinical considerations for 2nd-generation β-blockers?
Some activity on smooth muscle (β₂)
Use with caution in asthmatics
Acebutolol is a partial agonist
Partial agonism →
Less bradycardia
Reduced cold extremities
How do 1st-generation β-blockers contrast with later generations in terms of safety?
Cause bronchoconstriction → dangerous in asthmatics
Reduced cardiac output → fatigue, limb tiredness
CNS effects due to BBB penetration:
Dizziness
Nightmares
Sedation
Cold extremities (poor peripheral circulation)
Can precipitate heart failure
Excessive reduction in resting heart rate → risk in patients near myocardial infarction
How were short-acting β-blockers developed?
Introduction of labile ester functionality
Aim: rapid hydrolysis → short duration of action
Aryl esters hydrolysed too slowly
Aromatic ring acts as steric shield
Led to identification of esmolol
How do esmolol and landiolol compare?
Landiolol has ~7-fold higher β₁-selectivity than esmolol
8–12× more potent than esmolol
Greater cardioselectivity
Improved control and safety in acute settings
What characterises 3rd-generation β-blockers?
Example: carvedilol
Used in congestive heart failure
Contain an extended amine substituent
Interact with additional regions of the β₁-receptor
Improved selectivity
logP carefully balanced to reduce side effects
What is the significance of LogP in drug design, and how was it utilized to modify propranolol to reduce side effects?
LogP is the logarithm of a compound's partition coefficient and indicates its lipophilicity.
By reducing the LogP value through structural modifications like the addition of polar acetamide and sulfonamide groups, researchers could improve the drug's selectivity and reduce CNS-related side effects.
What is the key difference in the structural design of the 2nd and 3rd generation beta blockers, and how do these changes affect selectivity and potency?
2nd generation beta-blockers contain an extended para-substituent capable of H-bonding, enhancing β1 selectivity
while the 3rd generation beta blockers incorporate an extended amine substituent designed to interact with another part of the β1 receptor and further improving selectivity.use extension strategy to gain extra H-bonding with β1