pathology OSPE (not slides) NMU
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
ساعات بكتب كذا سؤال في كارت واحد وكدا كدا مش هيجي غير سؤال واحد غير ال identify
وهو لو هيطلب enumerate مش هيعوز غير 2 ولا حاجه انا حاطط كله
ياريت ياريت ياريت ياريت لو حد كاتب اي اسئله يبعتهالي ضوري جدااا
بالتوفيق انا قعدت هنا مش اقل من 8ساعات عشان اطلعه بالجوده دي
مش طالب غير دعوه حلوه بس
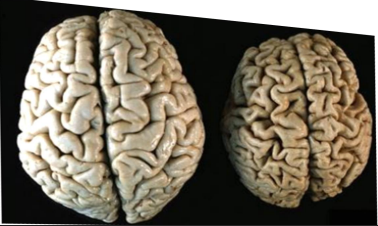
what happened ?
other forms of adaptation ?
brain atrophy
hyperplasia,metaplasia,hypertrophy
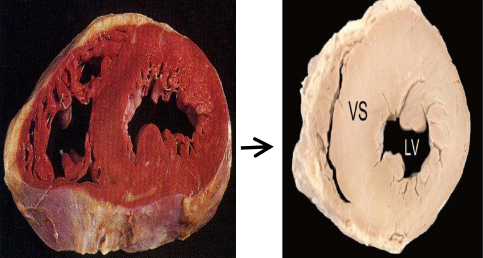
?
reversible or irreversible ?
left ventricular hypertrophy
all adaptation are reversible
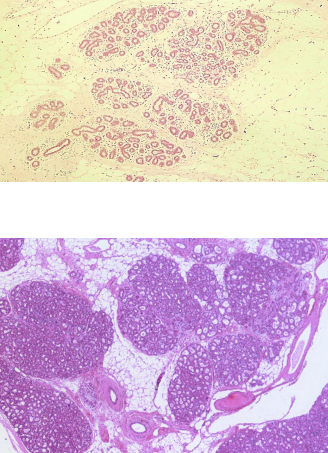
what is this ?
when does it happen ?
breast hyperplasia
• Physiological:
- Hyperplasia of female breast
in puberty, pregnancy and lactation.
• Pathological:
- Prostate and endometrium ( hormones)
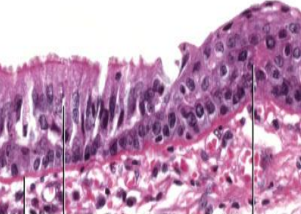
what happened ?
most common complication is ?
squamous cell metaplasia of respiratory epithelium in smokers
most common complication is cancer (squamous cell carcinoma)
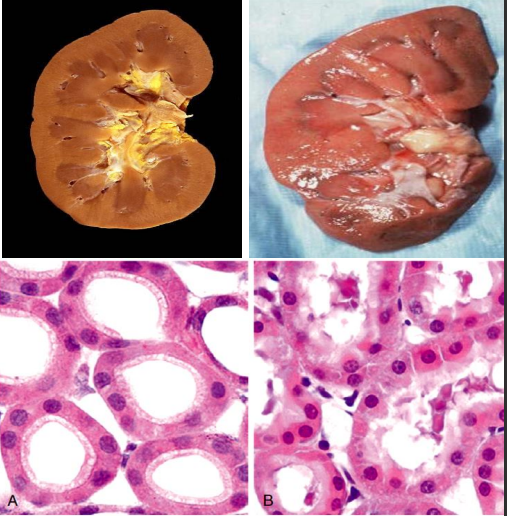
what is this ?
other types of reversible injury ?
reversible injury
cloudy swelling of kidney
other types : hydropic degeneration, fatty change
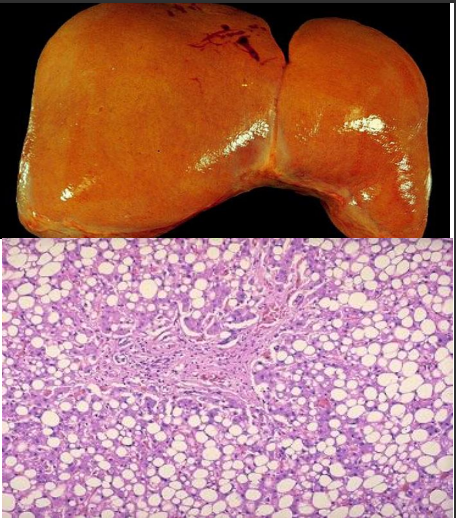
what is this ?
what substance will precipitate here
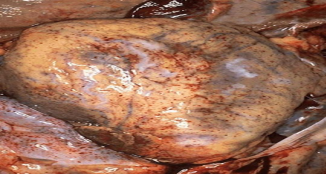
fatty change of liver
neutral fat (triglycerides)
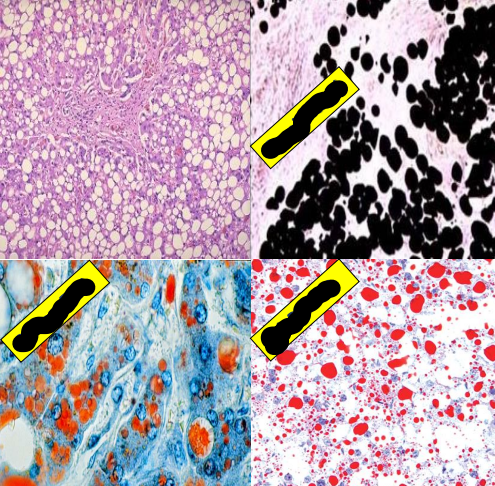
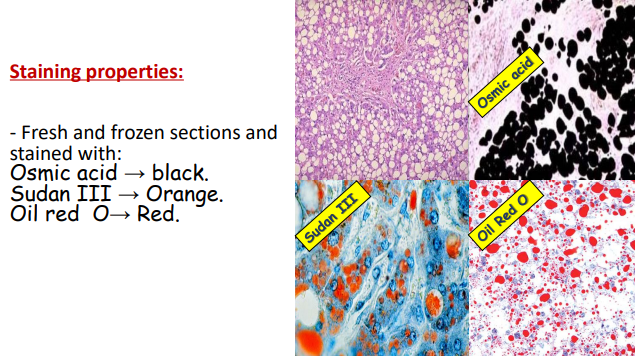
name those stains
used in ?
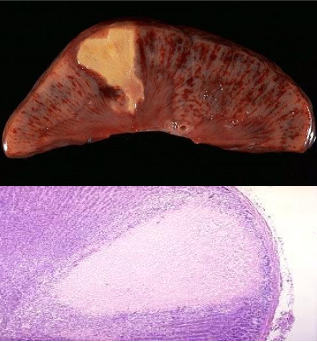
what is this ?
ex ? 3
coagulative necrosis of the kidney
acute ischemia of heart,kidney,spleen.
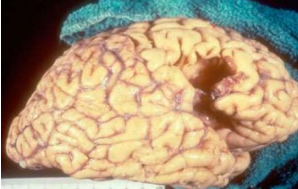
identify ? other examples ?
liquefactive necrosis of the brain
pyogenic abscess
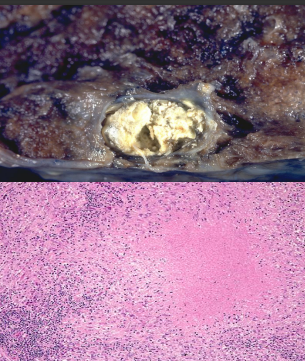
identify ?
examples ?
other types of necrosis ?
caseation necrosis
examples are (TB,Syphilis or fungal infection (any organ))
coagulative necrosis , liquefactive , fibrinoid etc.
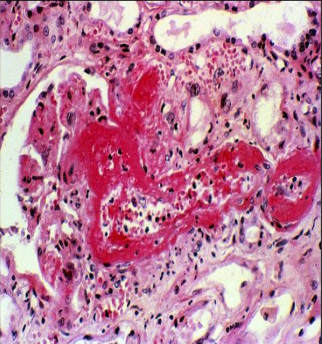
identify ?
occurs when ?
fibrinoid necrosis
in cases of vasculitis and hypertension
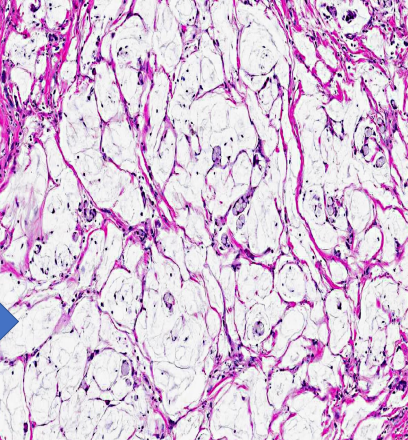
identify ?
other types of carbohydrate deposits ?
other types of tissue accumulation ?
mucoid carcinoma
.
glycogen storage diseases
.
other types of tissue accummulation
hyalinosis
amyloidosis
patho calcification
patho pigmentation
gout
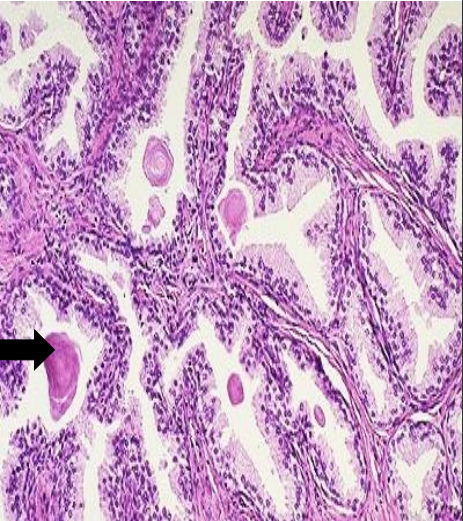
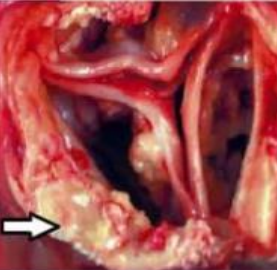
identify ? + arrow ?
other example ?
hyaline deposition line is on corpora amylacia (occurs in senile prostatic hyperplasia)
other example is russell’s body
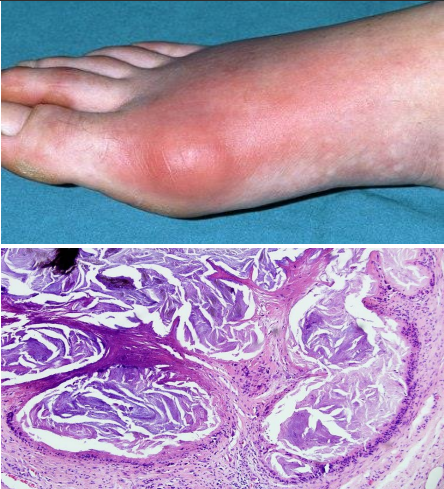
identify ?
site of deposition ?
urate deposition
Na urates deposited in: Skin, Kidney and Joints affecting metatarsophalyngeal joint of big toe .
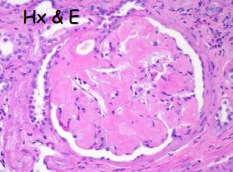
identify ?
how to diagnose ?
amyloidosis of the kidney
.
tissue biopsy —> stain
Hx&E pink
congo red orange
polarized light apple green
identify ?
other examples ?
dystrophic calcification (normal calcium levels in the blood)
.
other examples of dystrophic calcification
1- fat necrosis
2- following hyaline changes
3- wall of chronic abscess
4- old scar
5- dead bilharzial ova
6- fibrosed valve
7- atheroma of large vessels
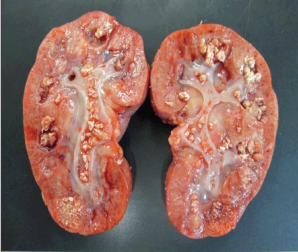
identify ?
other sites ?
metastatic calcification of kidney
.
1-arteries
2-mucosa of the stomach
3-lung alveoli
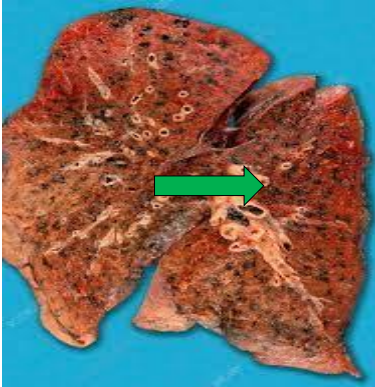
identify ? other types ?
anthracosis
other examples of exo pigments are inoculation (tattoing) ingestion in lead poisoning (plumbism)
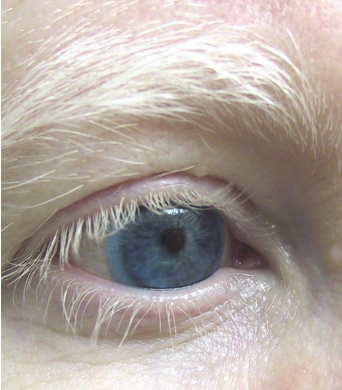
identify ?
other type is ?
albinism
.
vetiligo
identify ?
pigment name ?
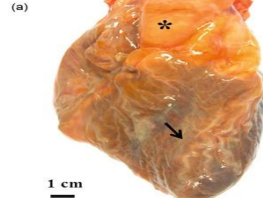
brown atrophy of the heart
lipofuscin pigment
identify ?
characters of inf ?
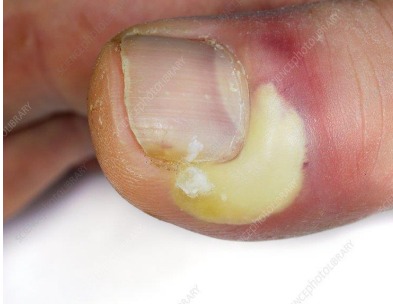
abscess
.
redness hotness swelling pain loss of function
identify ? other cause ?
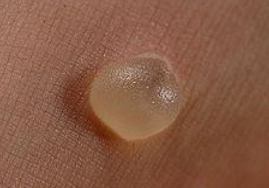
serous inflammation due to burn
other type is due to viral infection (herpes simplex)
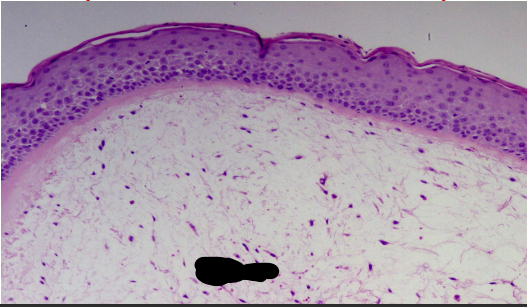
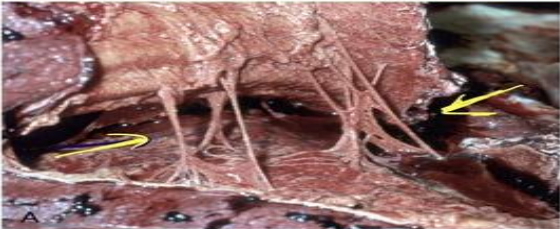
identify ?
serous inflammation (excess fluid exudate)
identify ?
fate ?
occurs where else ?
fibrinous inflammation
organization
peritonium , pericardium
identify ?
type of bacteria ?
complication ?
what is this membrane formed of ?
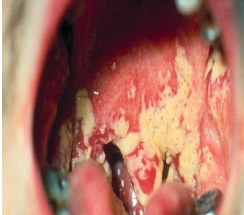
pseudomembranous inflammation
diphtheria
toxemia is the most common complication
(necrotic mucosa + fibrin + inflammatory exudate)
identify ?
type of bacteria ?
complication ?
what is this membrane formed of ?
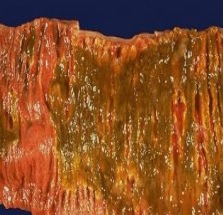
pseudomembranous inflammation
shigella
toxemia is the most common complication
(necrotic mucosa + fibrin + inflammatory exudate)
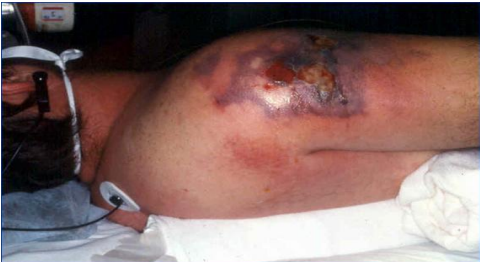
identify ?
complications ?
necrotizing inflammation
gangrene is a complication
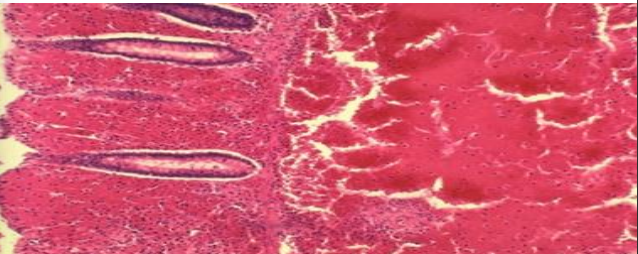
لو حد فاهم السلايد كويس يبعتلي شرحه
identify ?
causes ?
necrotizing inflammation
anthrax and plague
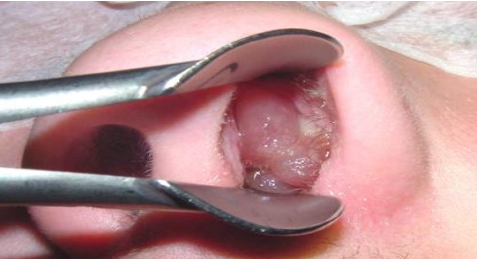
identify ?
composed of ?
causes ? (occurs when?)
allergic inflammation
excess fluid exudate and eosinophils
It occurs in case of hypersensitivity eg urticaria, bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, contact dermatitis
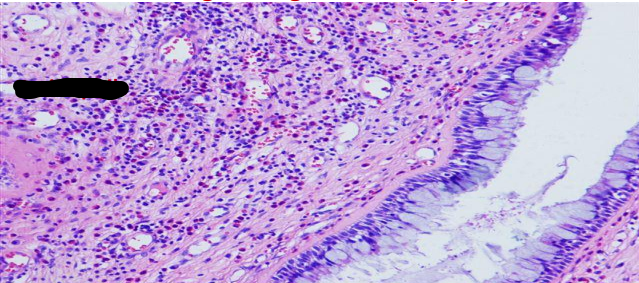
identify ?
composed of ?
causes ?
allergic inflammation
excess fluid exudate and eosinophils
It occurs in case of hypersensitivity eg urticaria, bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, contact dermatitis
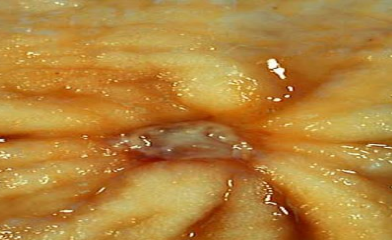
identify ?
ulcerative inflammation
(mixed acute and chronic inflammation coexyst)
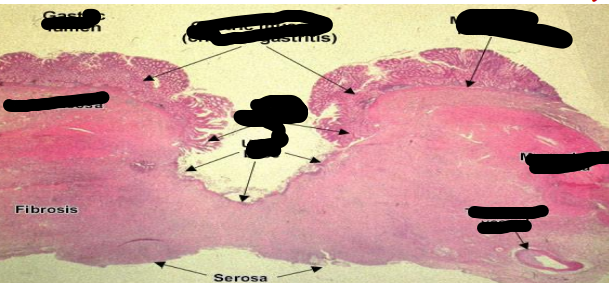
identify ?
ulcerative inflammation
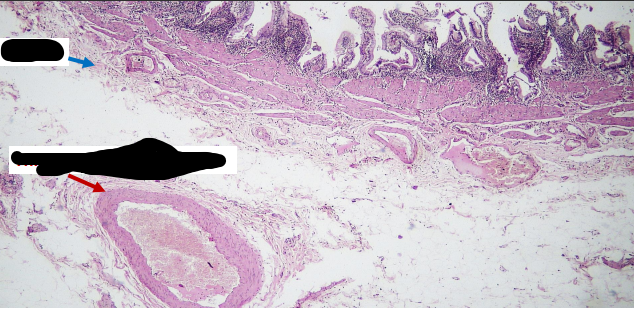
identify ?
chronic cholecystitis
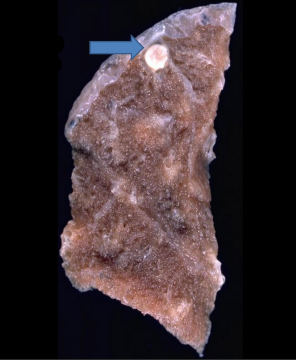
identify ?
the primary complex is formed of ?
primary pulmonary tuberculosis
.
Primary complex:
1- parenchymatous lesion (Ghon focus)
2- Tuberculous lymphadenitis
3- Tuberculous lymphangitis
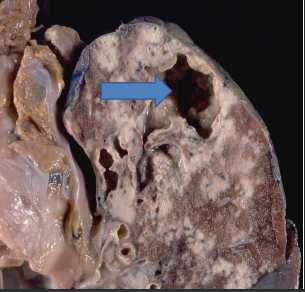
identify ?
lesion name ? (arrow)
fate ?
secondary pulmonary tuberculosis
apical lesion (assmann focus)
in most cases destruction of the lung leads to cavitation
identify ?
where does it occur ?
tuberculoma
it can occur in any organ بس مكتوب اسامي معينه هقولها بردو
lung,kidney,brain,spinal لو سـأل نكتب من دول
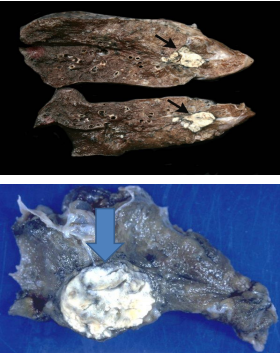
identify ?
when does it occur ?
miliary tb of the spleen
occurs for patiens with very weak immunity
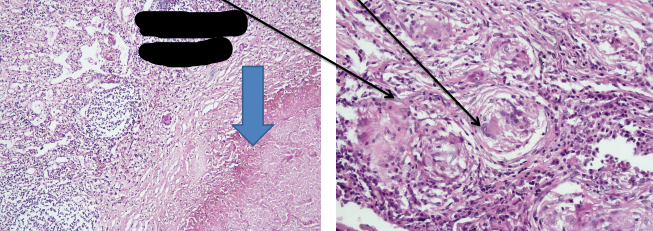
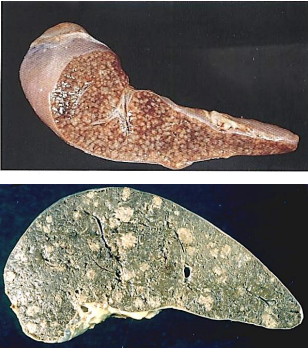
identify ?
composed of ? اكبر من انه يجي فكك
giant cells here are named ?
tuberculosis granuloma (tubercle)
Composed of: Central caseating material (structureless eosinophilic material), epithelioid cells, macrophages, Langhan’s giant cells, lymphocytes and peripheral fibroblastic reaction
langhans giant cells
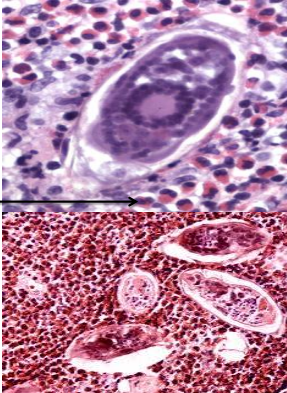
identify ?
most important cells ?
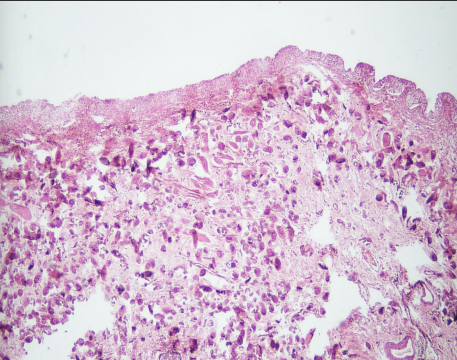
bilharzial granulomatous reaction
most important cells are eosinophils as its an allergic reaction
identify ?
the pathological changes caused by this ?
bilharziasis of the urinary bladder
.
sandy patches
polyps
ulcers
epithelial changes
lesions caused by fibrosis
increases risk of malignancy
identify ?
caused by ?
complications ?
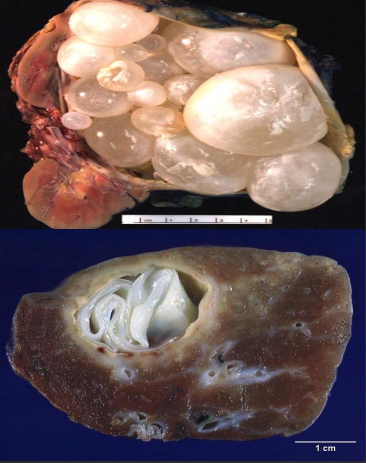
hydatid cyst
caused by ingestion of the eggs of ecchinococcus granulosus
.
1- Allergic manifestations with anaphylactic shock.
2- Abscess formation owing to secondary bacterial infection of the cyst.
3- Pressure atrophy on the surrounding tissue
identify ?
fate ?
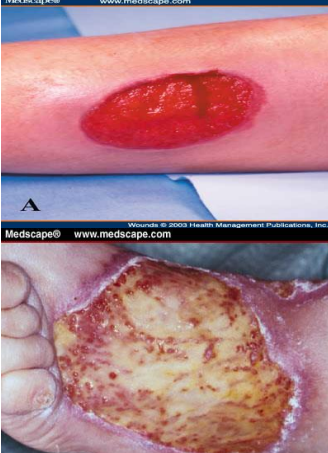
granulation tissue
fibrosis and formation of scar tissue
identify ?
fate ?
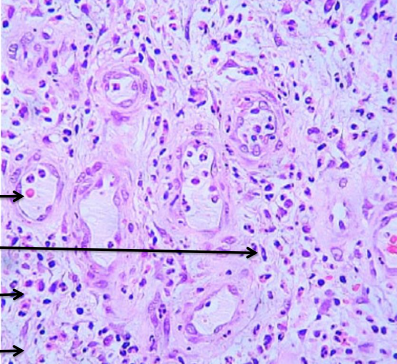
granulation tissue
fibrosis and formation of scar tissue
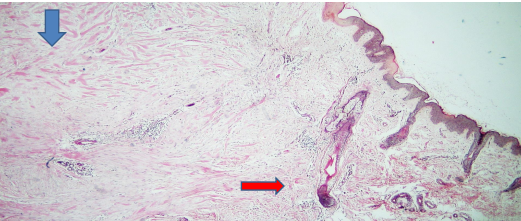
identify ?
blue arrow is on ?
skin scar with adjacent normal skin
collagen bundles
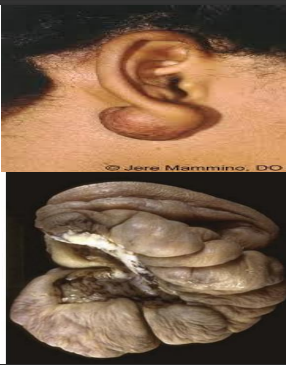
identify ?
caused by ?
complication ?
keloid
caused by lack of proper collagenases to degrade type III collagen (this is thought to have genetic basis)
high rate of recurrence after surgical removal
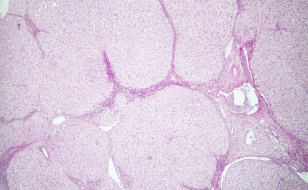
identify ?
when does it occur ?
formed of ?
liver cirrhosis
when liver stroma is damaged
formed of : regenerative nodules surrounded by fibrous tissue septa
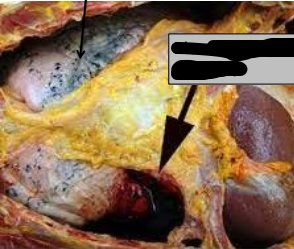
identify ?
mention other types ?
hemothorax
hemoperitonium , haemopericardium , hemoarthrosis
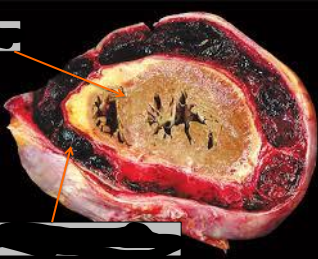
identify ?
other types ?
hemopericardium
hemothorax , hemoperitonium
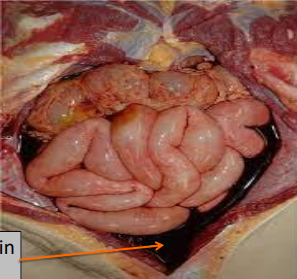
identify ?
نفس الاتنين اللي فاتو بقا
hemoperitonium
identify ?
other types ?
petechial hemorrhage (caused by bleeding of small capillaries but ofc not trauma)
purpura , ecchymoses , hematoma
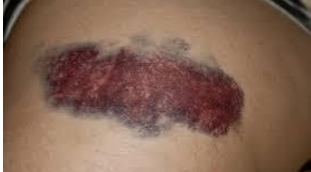
identify ?
causes ?
other types قولناه فوق نفس الاجابه بس بدل
ecchymosis
.
1.Laceration of normal vessel: ex: trauma, tumor
2.Laceration of diseased vessel: ex: hypertension, aneurysm, atherosclerosis
3.Systemic disease: ex: leukaemia 4.Bacterial infection: ex: septicaemia
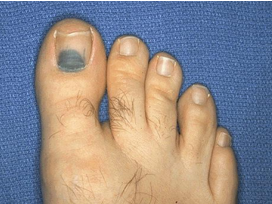
identify ?
causes ?
hematoma
.
1.Laceration of normal vessel: ex: trauma, tumor
2.Laceration of diseased vessel: ex: hypertension, aneurysm, atherosclerosis
3.Systemic disease: ex: leukaemia 4.Bacterial infection: ex: septicaemia
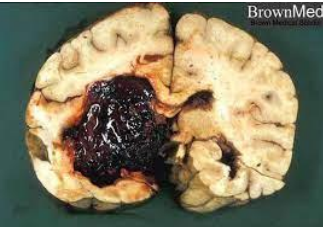
identify ?
causes ?
massive interstitial cerebral hemorrhage
caused by hypertension (extreme) 200/110
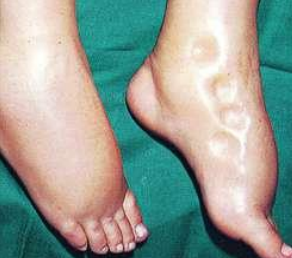
identify ?
caused by ?
type of fluid ?
Pitting edema Caused by:
1- renal edema
2- cardiac edema
3- nutritional edema.
4- Allergic condition.
,
transudate
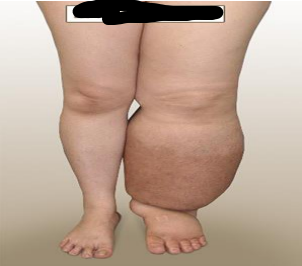
identify ?
caused by ?
type of fluid ?
Non-Pitting edema Caused by:
1- inflammatory edema 2- lymphedema.
exudate or lymph
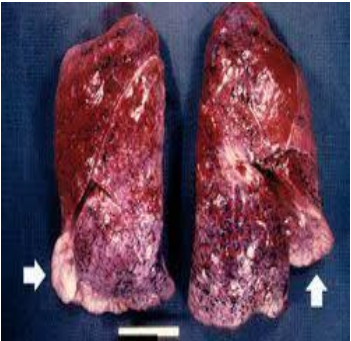
identify ?
cause of this type of consistancy ?
Chronic venous congestion of the lung
.
induration = firm in consistncy
due to fibrosis
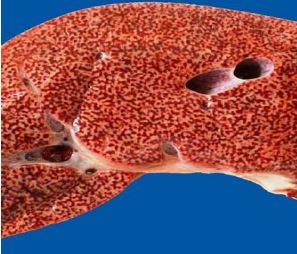
identify ?
caused by ?
chronic venous congestion of the liver
caused by right sided heart failure
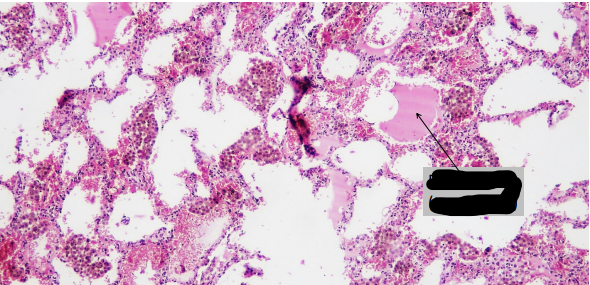
identify ?
arrow on ?
caused by ?
chronic pulmonary venous congestion
edema fluid
caused by left sided heart failure
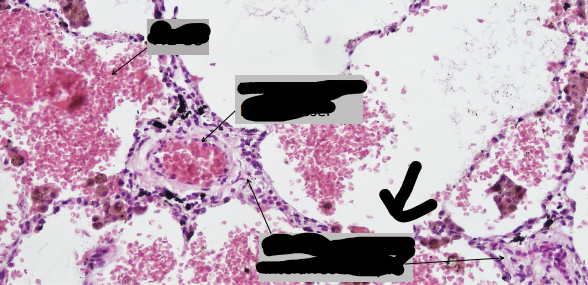
identify ?
arrow on ?
caused by ?
chronic pulmonary venous congestion
fibrosis with thick vessels
caused by left sided heart failure
identify ?
arrow on ?
caused by ?
chronic pulmonary venous congestion
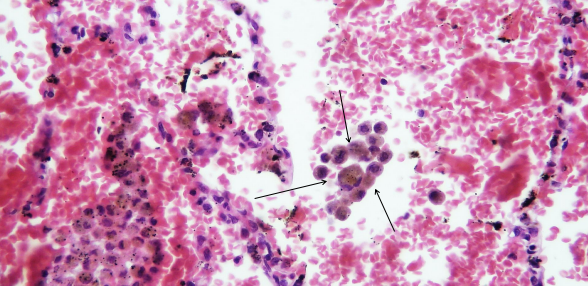
heart failure cells
caused by left sided heart failure
identify ?
composition of it is ?
thrombi in wall of cardiac chamber (mural thrombi)
platelets and fibrin
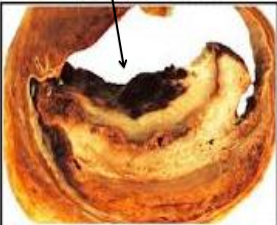
identify ?
composition of it is ?
Valvular thrombi ( vegetation)
platelets and fibrin
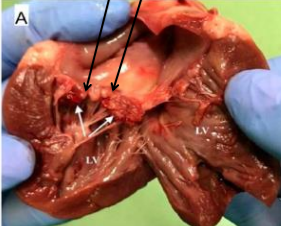
identify ?
composition of arrows ?
microscopic picture of thrombus
RBCs, platelets & fibrin
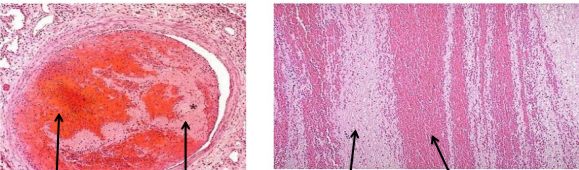
identify ?
occurs when ?
red infarction of lung
.
occurs in soft & vascular organs , tissues with dual circulation (lung & intestine)
when blood is restored to an area of infarcation
identify ?
causes
arrows ?
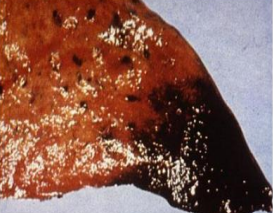
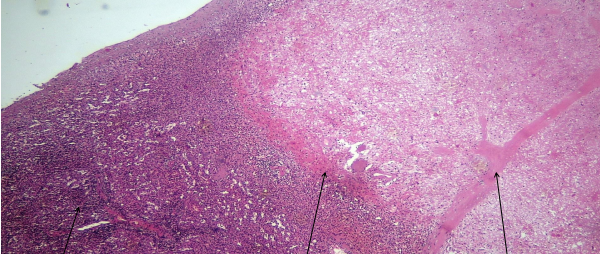
splenic infarction
ischemia
identify ?
occurs where ?
cause ?
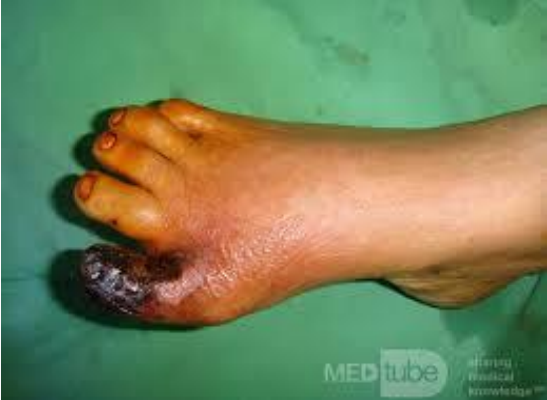
dry gangrene
in extremities
gradual occlusion of arteries
identify ?
occurs due to ?
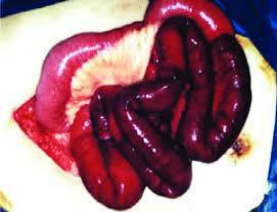
wet gangrene of intestine
occurs due to sudden occlusion of both the artery and the vein
identify ?
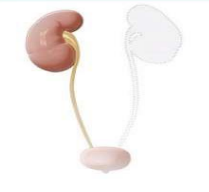
other types of developmental disordered growth
agenesis
aplasia, hypoplasia, atresia, heterotropia, hamartoma
identify ?
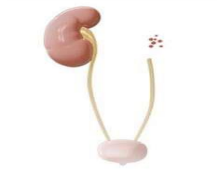
other types of developmental disordered growth
aplasia
agenesis, hypoplasia, atresia, heterotropia, hamartoma
identify ?
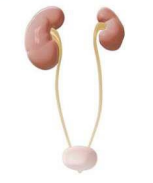
other types of developmental disordered growth
hypoplasia
agenesis, aplasia, atresia, heterotropia, hamartoma
identify ?
other types of developmental disordered growth
atrasia
hypoplasia ,agenesis, aplasia, heterotropia, hamartoma
identify ?
other types of developmental disordered growth
define
heterotropia
hypoplasia ,agenesis, aplasia, atrasia, hamartoma
normal tissue in abnormal location
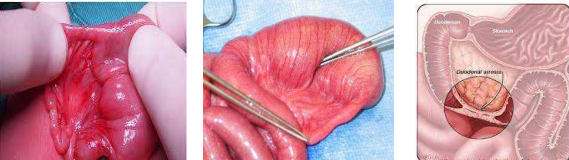
identify ?
other types of developmental disordered growth
thyroid heterotropia in the base of tongue
hypoplasia ,agenesis, aplasia, atrasia, hamartoma
identify ?
define ?
lung hamartoma
normal tissue in normal location but there is a disturbance in the quantity or arrangement of the tissue
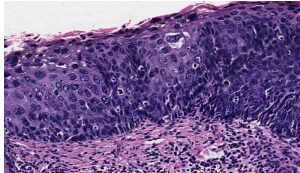
identify ?
other types of Acquired Disordered Growth
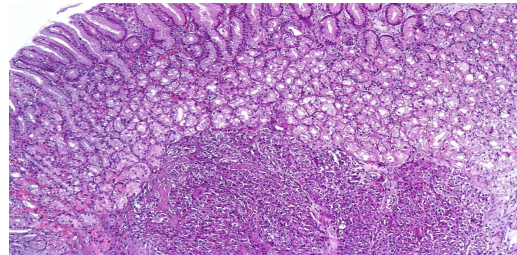
dysplasia of squamous epithelium
adaptation and neoplasia
في الكام سؤال اللي جايين دول انا مش عارف تاني سؤال هيبقي اي فا لو حد عنده فكره ياارريييت يبعتلي
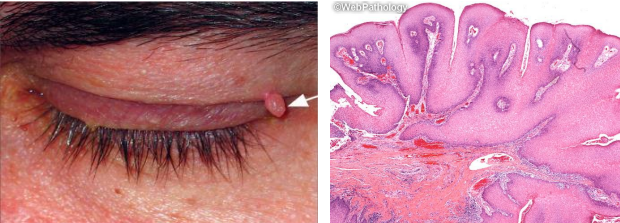
identify
Squamous cell papilloma
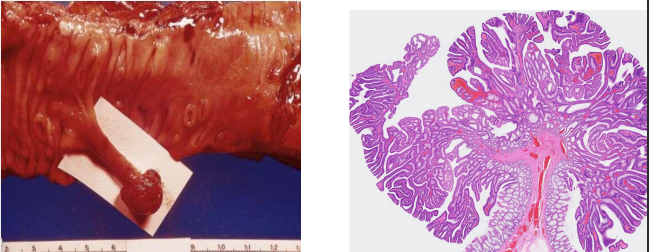
identify ?
colon adenoma (polyp)
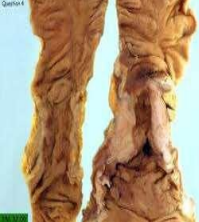
identify ?
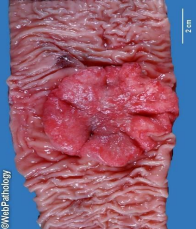
colonic adenocarcinoma infeltrating mass
identify ?
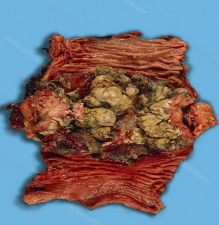
colonic adenocarcinoma fungating mass
identify ?
colonic adenocarcinoma ulcerating mass
identify ?
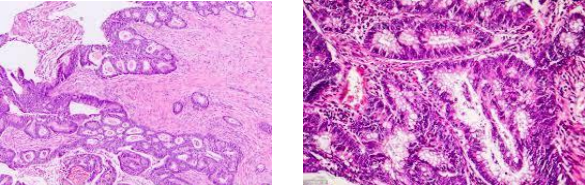
colonic adenocarcinoma
identify ?
squamous cell carcinoma
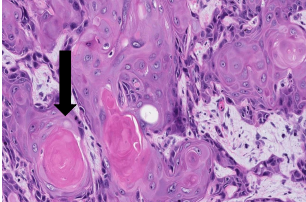
idenitfy ?
arrow ?
squamous cell carcinoma
central keratin pearls (cell nests)
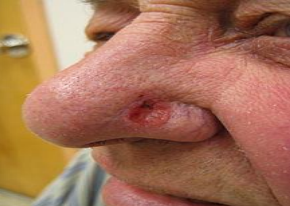
identify ?
other locations ? (اللي يعرف الاحابه ياريت يبعلتي)
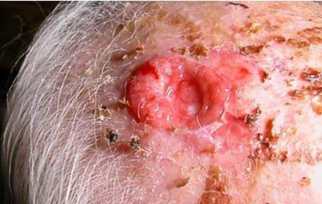
basal cell carcinoma (locally malignant tumor)
ear, nose, scalp, forehead.
( any area above angle between mandible and cheek)
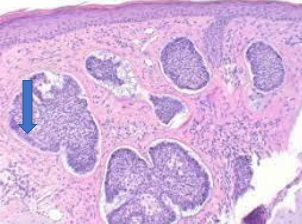
identify ?
cells are ?
basal cell carcinoma
atypical basaloid cells
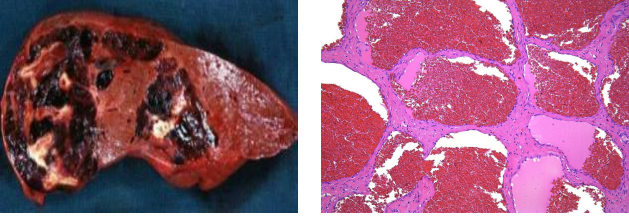
identify ?
most common organ ?
shape under microscope ?
cavernous hemangioma
liver بس مش متأكد الصراحه ياريت حد يبعلتي الاجابه الاكيده …..
Large spaces filled with blood and separated by fibrous tissue septae
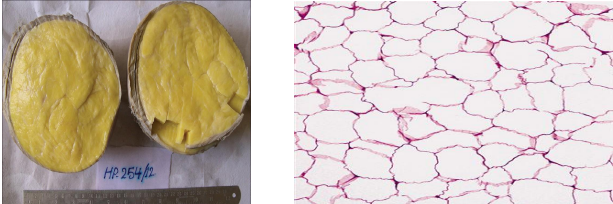
identify ?
describe shape under microscope ?
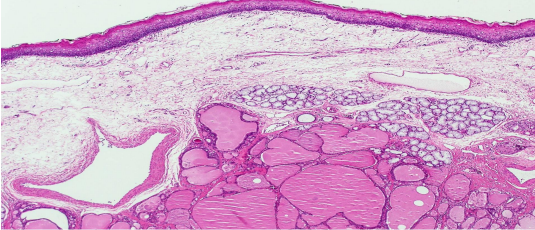
lipoma
Lobules of mature fat cell separated by scanty fibrous tissue stroma
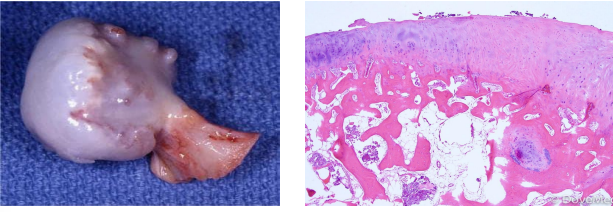
identify ?
describe shape ?
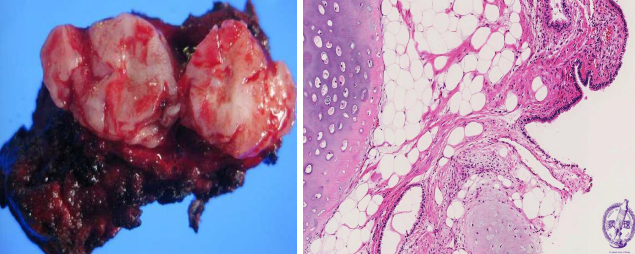
osteochondroma
large bony mass covered by cap of cartilage