KBKF15 - WEEK 5 - KREB CYCLE & ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Very pretty picture of glycolysis / glycogeneous from the lecture that i don’t really understand?
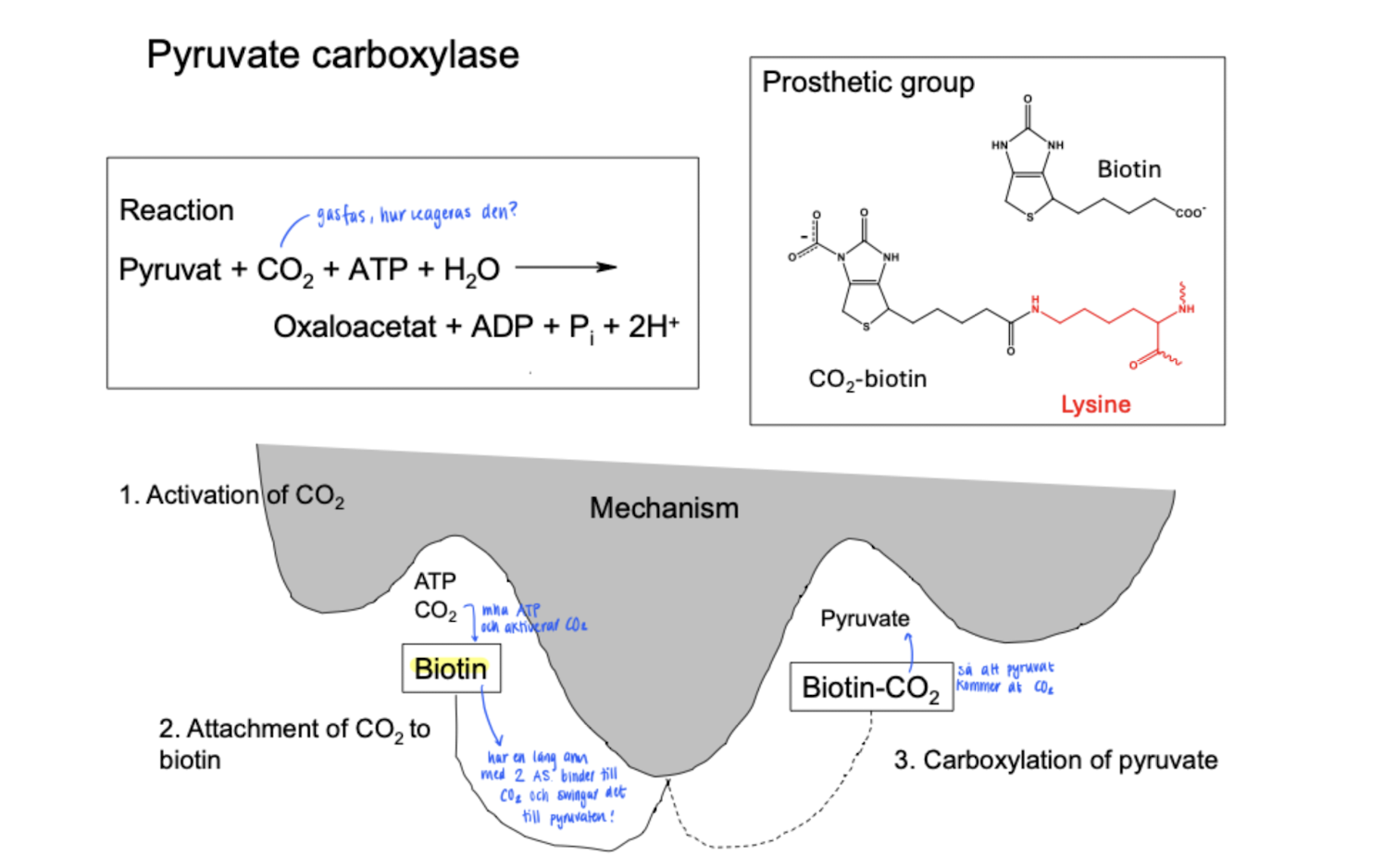
Pyruvate carboxylase - ( pyruvate → oxaloacetate) in gluconeogenesis
The process requires CO2, which is a gas molecule.
uses Biotin to hook the CO2 (g) to the pyruvate by a swinging motion. This requires ATP and activation of CO2.
Activation of CO2, using ATP and HCO3-.
attachment of CO2 to biotin.
Carboxylation of pyruvate to oxalacetate.
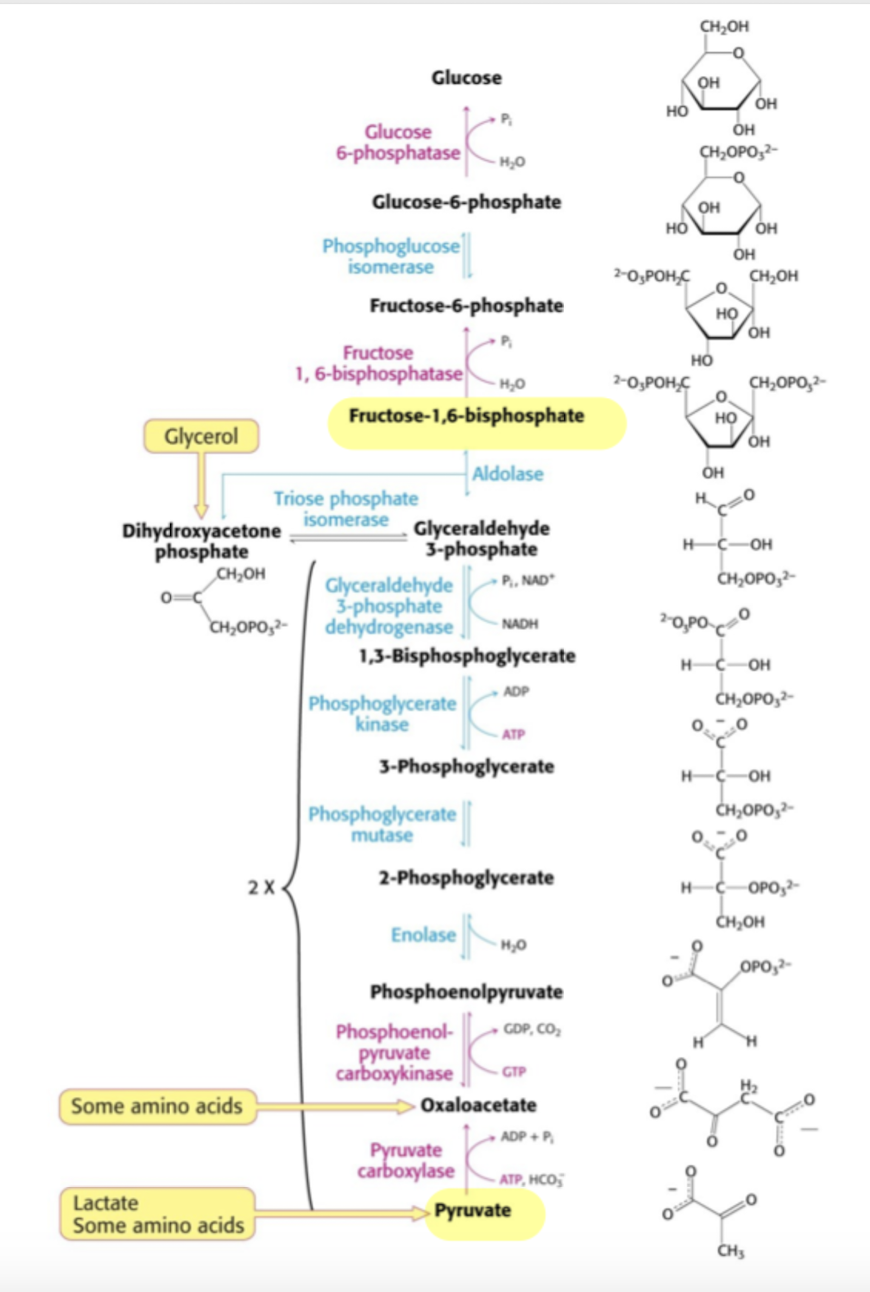
Hur många ATP krävs för att göra en F(1,6)BP (krävs inget därifrån till glucose)
Det krävs 2 pyruvat för 1 glucose. Och det krävs
4ATP + 2GTP för syntes av 1 glucose
Control of gluconeogenesis / glycolysis
Proteinet är bi-funktionellt, och endast en del av proteinet är igång
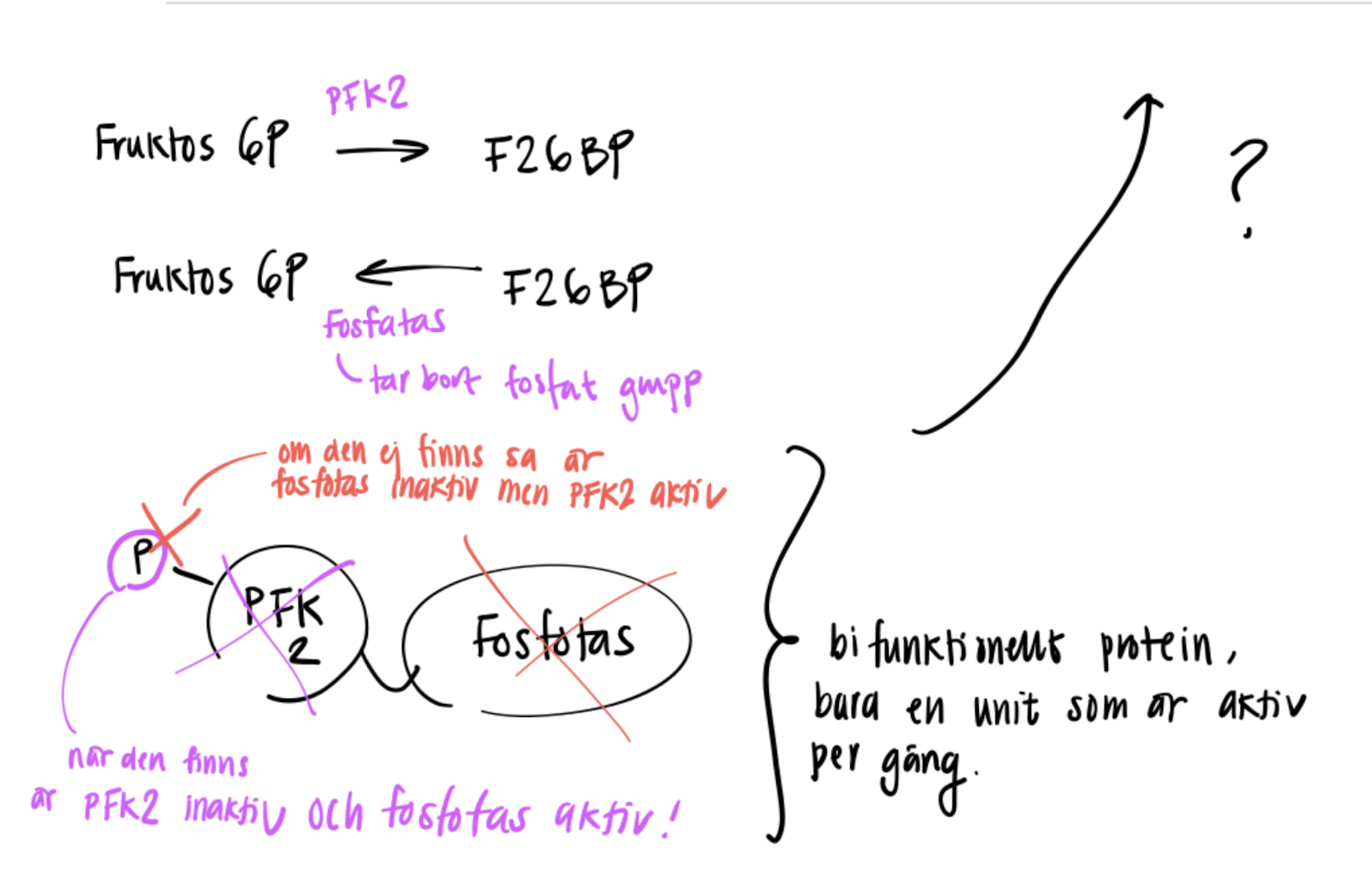
Intereactions between different cell metabolism (olika vävnader)
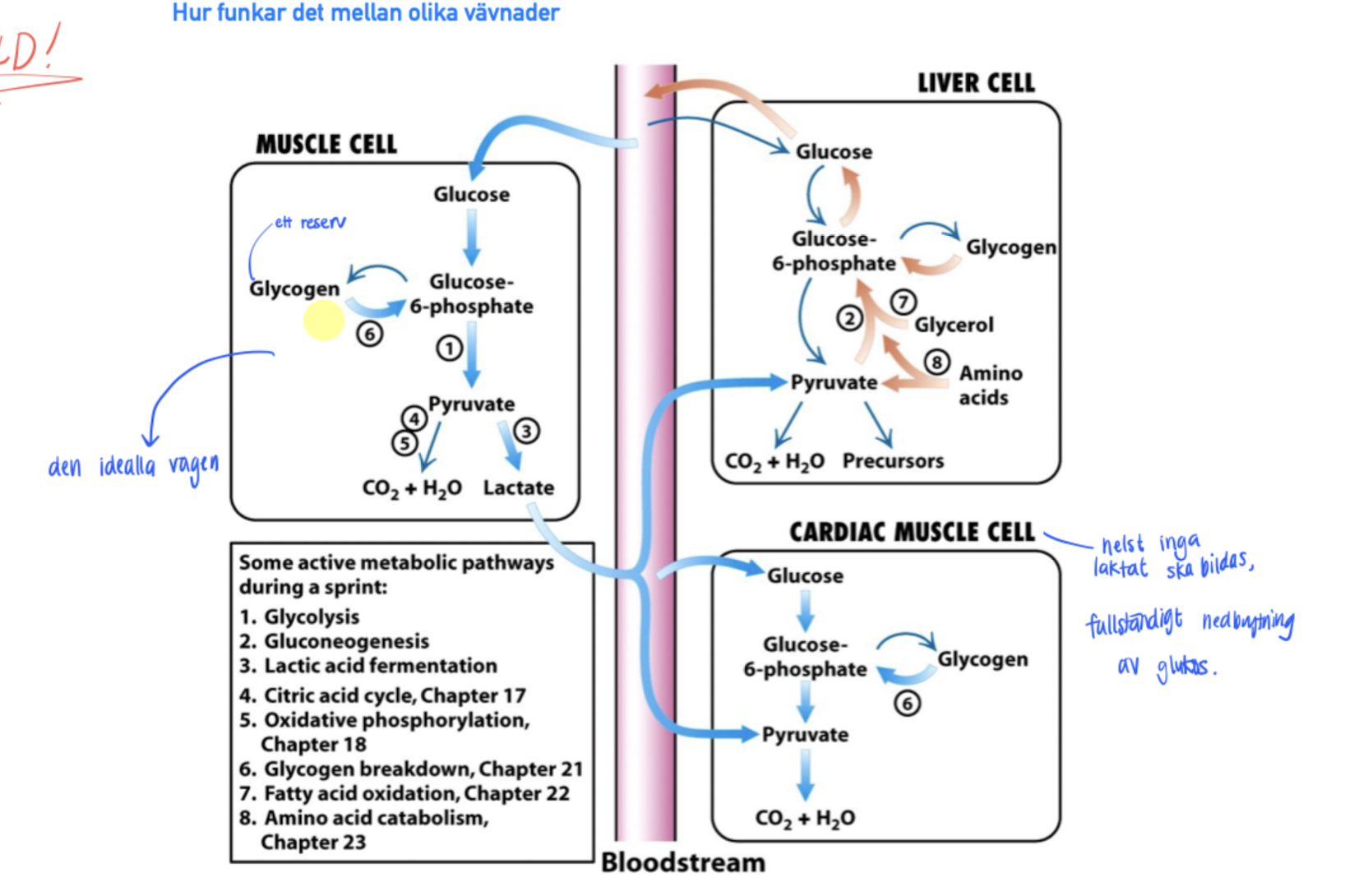
Where does the KREB cycle and electron transport chain take place
KREB cycle
Happens in the matrix of mitochondria.
Electron transport chain
On the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA, hoe does the enzymes look like? PDH
Multi-enzyme complexes - Several enzymes are non-covalently (or covalently) linked together to form a functional unit.
The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is formed by 3 enzymes (E1, E2, E3) through non-covalent interactions.
Converts Pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA with NAD+ → CO2 + NADH + H+.
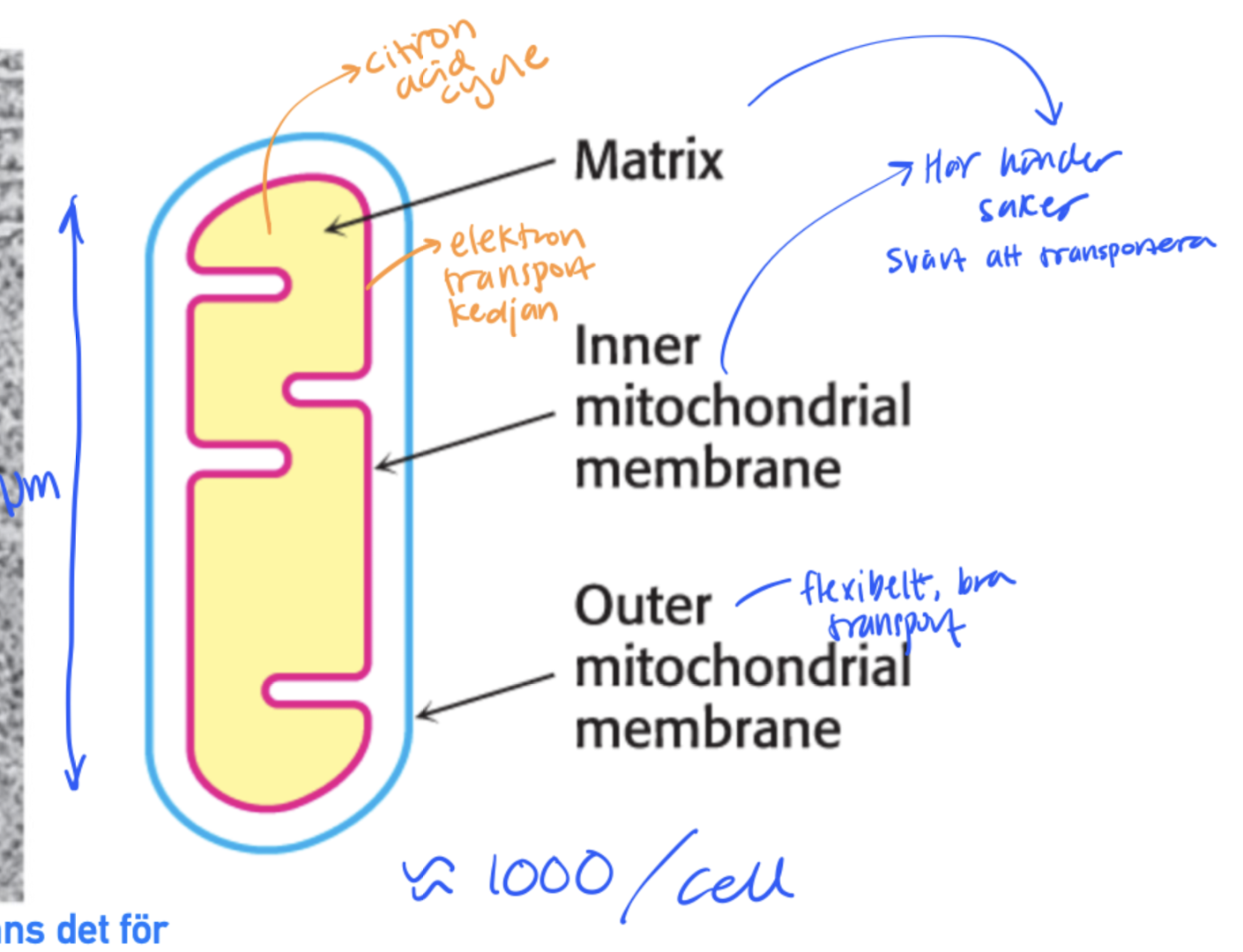
KREB cycle - How much energy do we get out?
From Pyruvate, Lactate and PEP?
1 Pyruvate
Missed the whole glycolysis and is already in the mitochondria
Pyruvate → Acetyl-CoA (PDH) = 1 NADH = 2,5 ATP
3 x NADH (2e-) 2,5 ATP
1 x FADH2 (2e-) 1,5 ATP
GTP → (2e-) 1 ATP
Totalt = 12.5 ATP / pyruvate.
1 Lactate
The NADH formed from lactate (lactate → pyruvate + NADH) in cytoplasm needs to be transported into mitochondria, it needs to converted into FADH2 to enter mitochondria. So basically we will get 1 extra FADH2.
Pyruvate → Acetyl-CoA (PDH) = 1 NADH = 2,5 ATP
3 x NADH (2e-) 2,5 ATP
1 x FADH2 (2e-) 1,5 ATP + 1 x FADH2 (2e-) 1,5 ATP (from lactate)
GTP → (2e-) 1 ATP
Totalt = 14 ATP / Lactate.
1 PEP
PEP → Pyruvate + 1 ATP (no cost for transporting ATP into mito)
Pyruvate → Acetyl-CoA (PDH) = 1 NADH = 2,5 ATP
3 x NADH (2e-) 2,5 ATP
1 x FADH2 (2e-) 1,5 ATP
GTP → (2e-) 1 ATP
Totalt = 14 ATP / PEP.
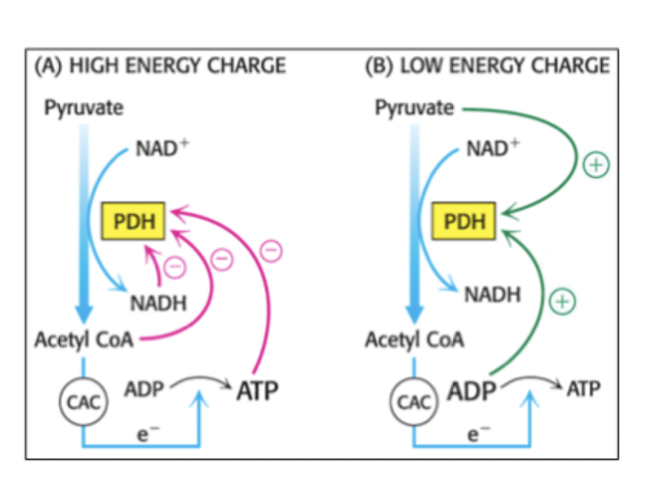
Regulation of KREB cycle - Main focus on PDH
The activity is decreased when a lot of energy is present (ATP, NADH, Acetyl-CoA), these molecules will inhibit the PDH molecule. When ADP is present, the activity is increased.
Other processes are also inhibited by ATP and NADH, and activated by ADP (not as important)
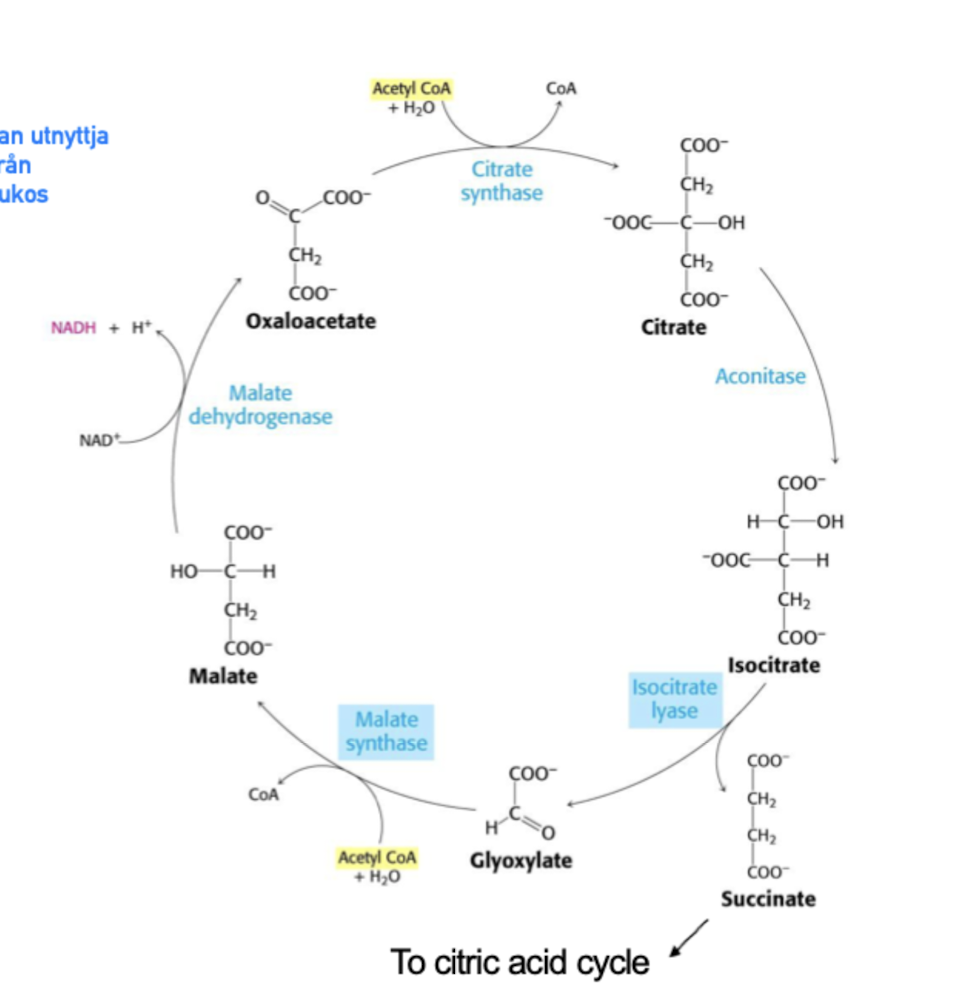
Glyoxylate cycle (osäker om man ska kunan detta)
Främst i växter och sprutar ej ut CO2,
Live on 2C compounds, variant of KREB, 2 decarboxylation steps are skipped.
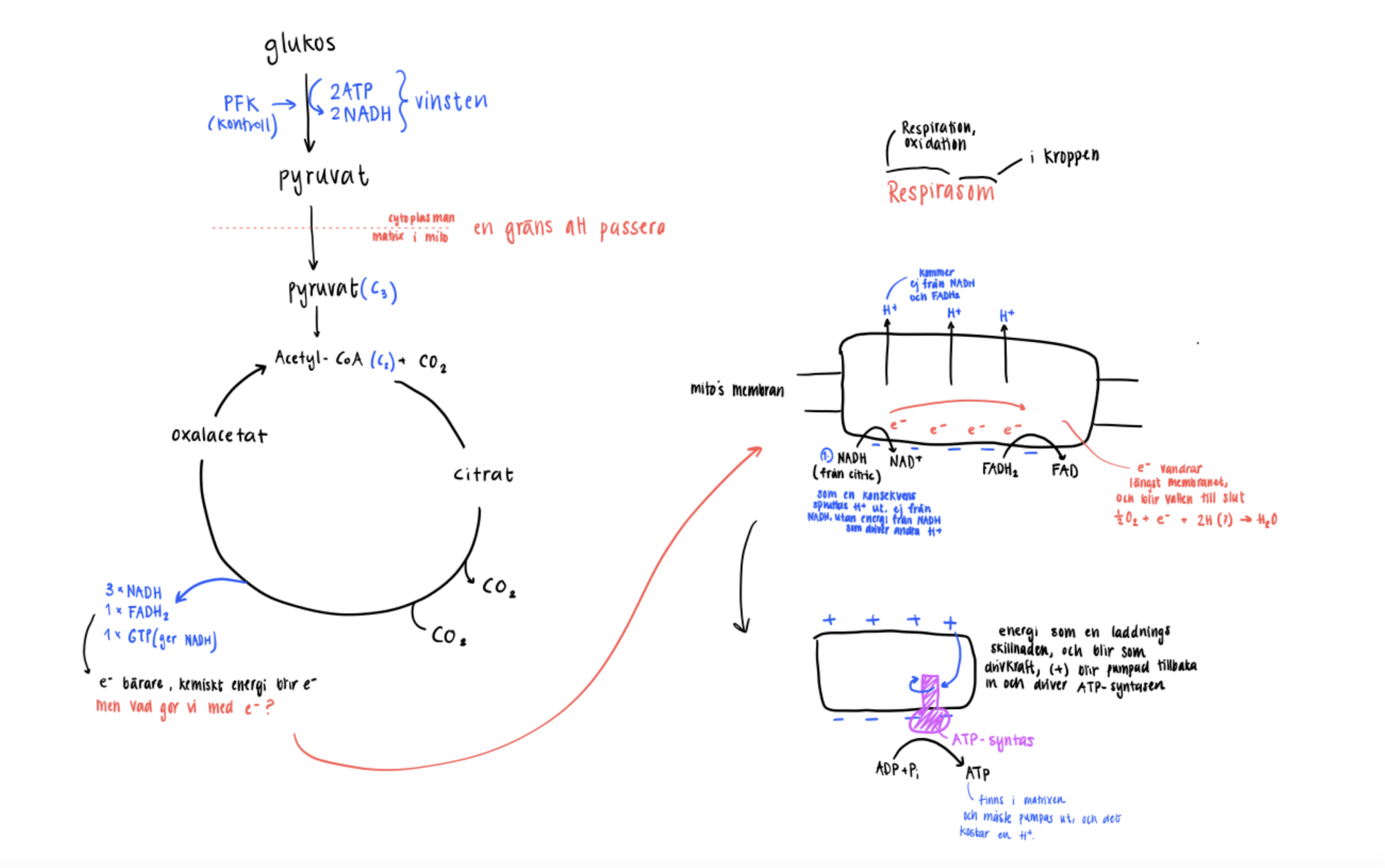
Very general (BUT CUTE) picture of glycolysis + KREB + e- transport chain
change to better picture when drawing done.
oxidative phosphorylation : different parts
Electron transport from reduced electrons carriers (from KRBE?) to oxygen.
Creation of membrane potential and porton gradient to provide driving force for ATP synthesis.
ATP synthesis
The reactions through the inner mitochondrial membrane.
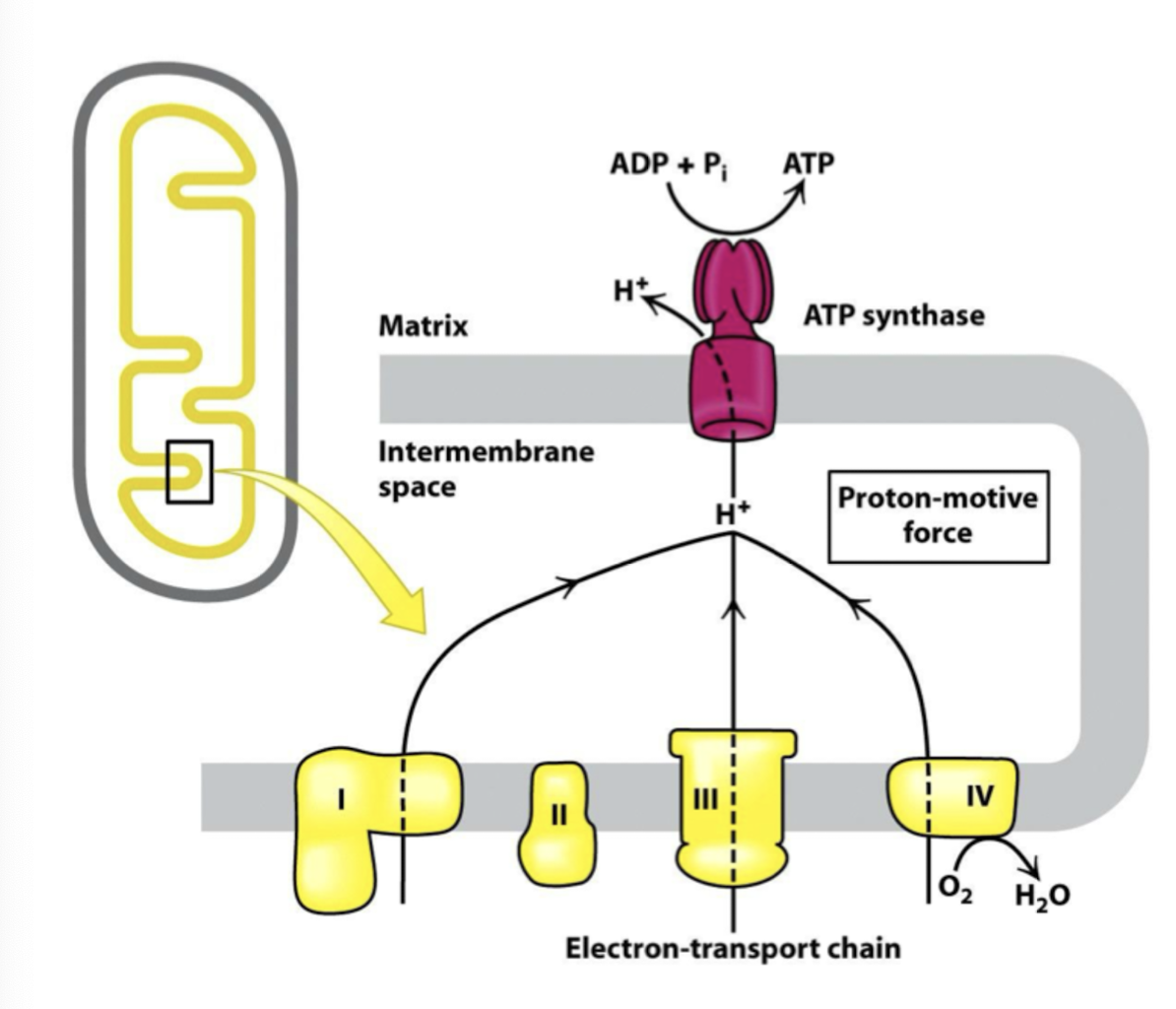
A general picture of the e- transport chain
Consists of 4 protein complexes, Q-complex, Cytosome C and ATP syntase :3
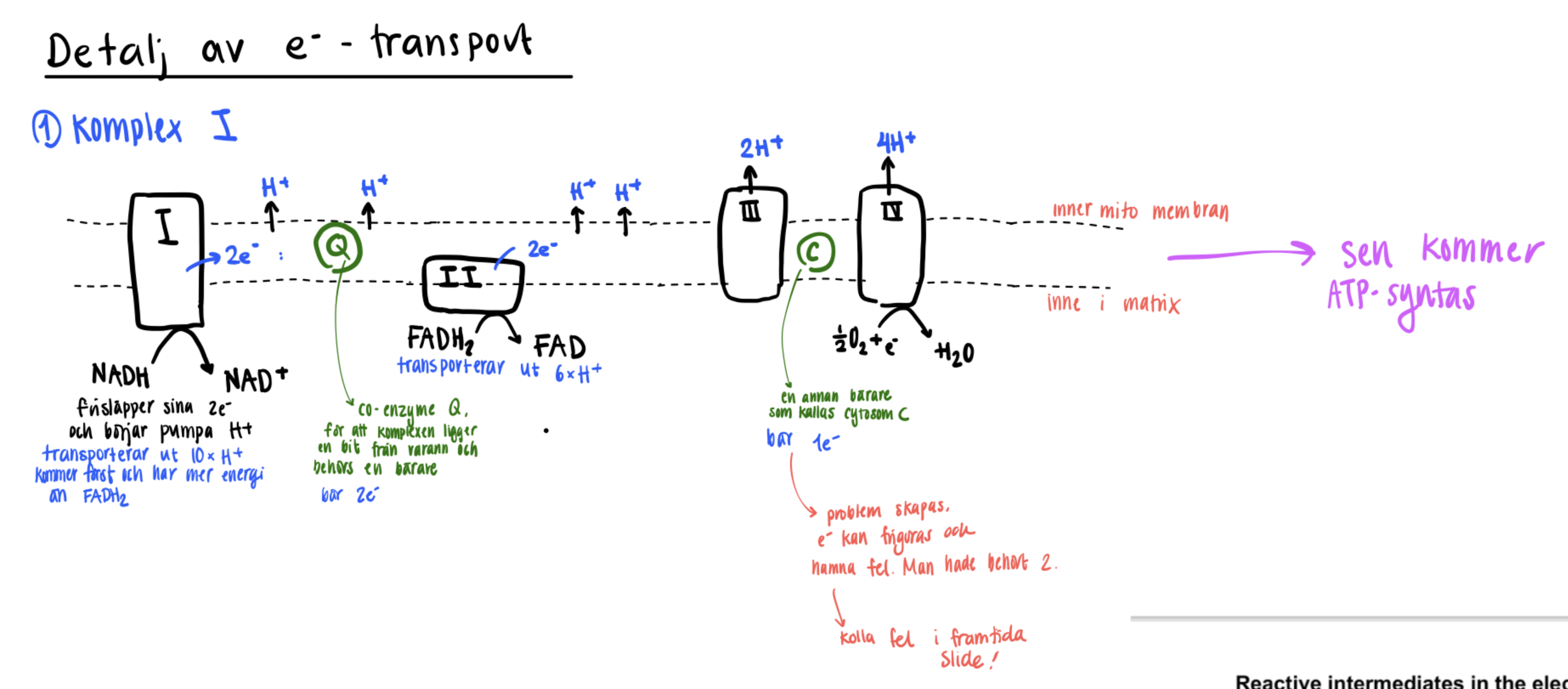
Electron transport chain - more detailed pathway for each e- carrier
The e- are constantly trasnported, and provides energy at all times.
NADH
Complex 1 (integral membrane protein → pumps H+ , each NADH = 2e-)
CoQ (transports e- from complex 1 to 3)
Complex 3 (integral membrane protein —> pumps H+)
Cytochrome C (Transports e- between complex 3 and 4)
Complex 4 (integral membrane protein, pumps H+ and transfers e- to O2 turning it to water.
Each NADH can pump 10 H+.
FADH2
Delivered to CoQ via complex 2, which then follows the same pathway as NADH (?).
Each FADH2 can pump 6 H+.
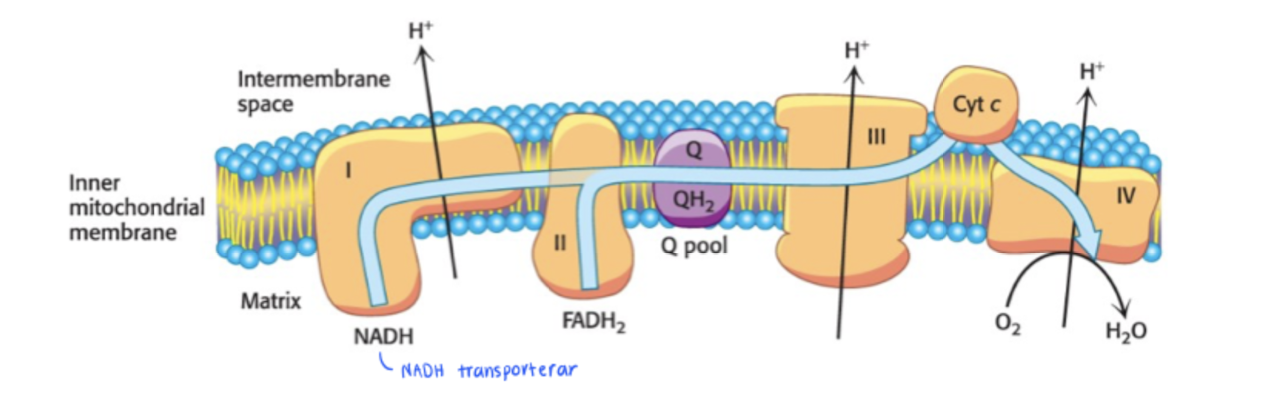
Q-cycle tror ej han skulle ställa någon frågor om detta tbh
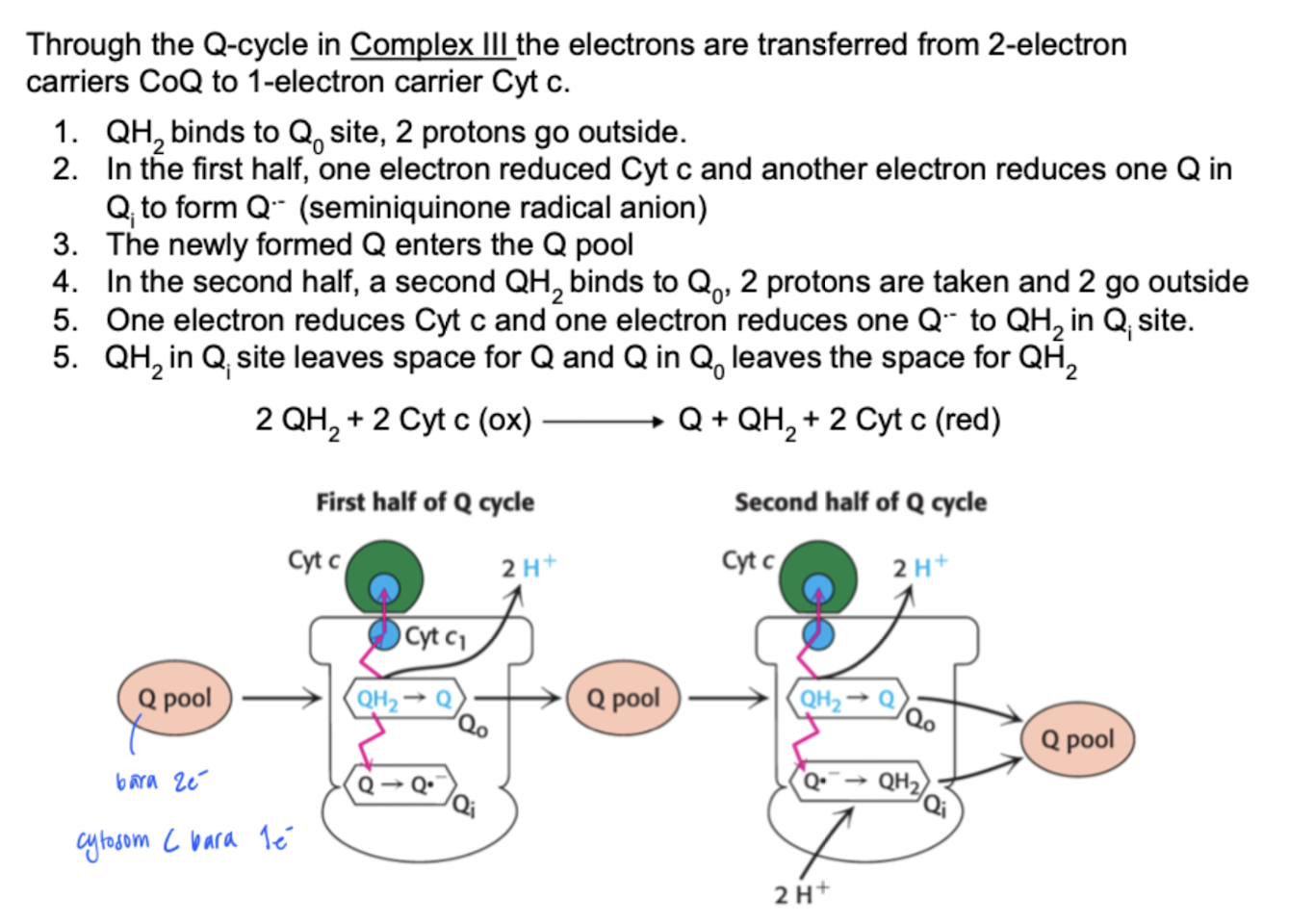
Reactive intermediates in the electron transport chain
If the e- from cytochrome C gets to the wrong places → reactive radicals. These includes ROS e.g O2-, O*H-, H2O2.
We have protective systems that combats these.
Superoxide dismutase: 2O2-* + 2 H+ → ← O2 + H2O2. By working out, we produces more NADH+ and NAD+ which increases the chans of producing radiclals, thus increased amount of the dismutase in our systeme.
Catalase: H2O2 → ← O2 + H2O. The amount decreases with age. Therefore, it is important to consume antooxidants.
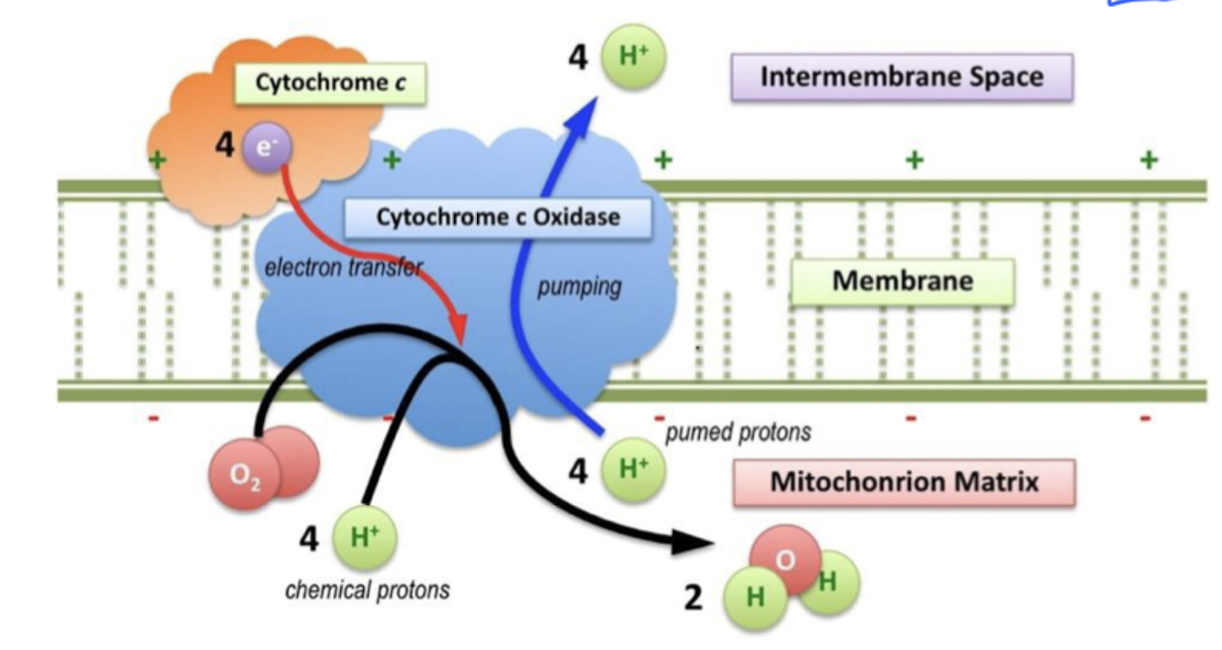
What is Chemiosmotic hypothesis?
potential / pH difference created through pumping out H+ from the mitochondria matrix to the intermembrane space when e- is moved through the respiratory chain.
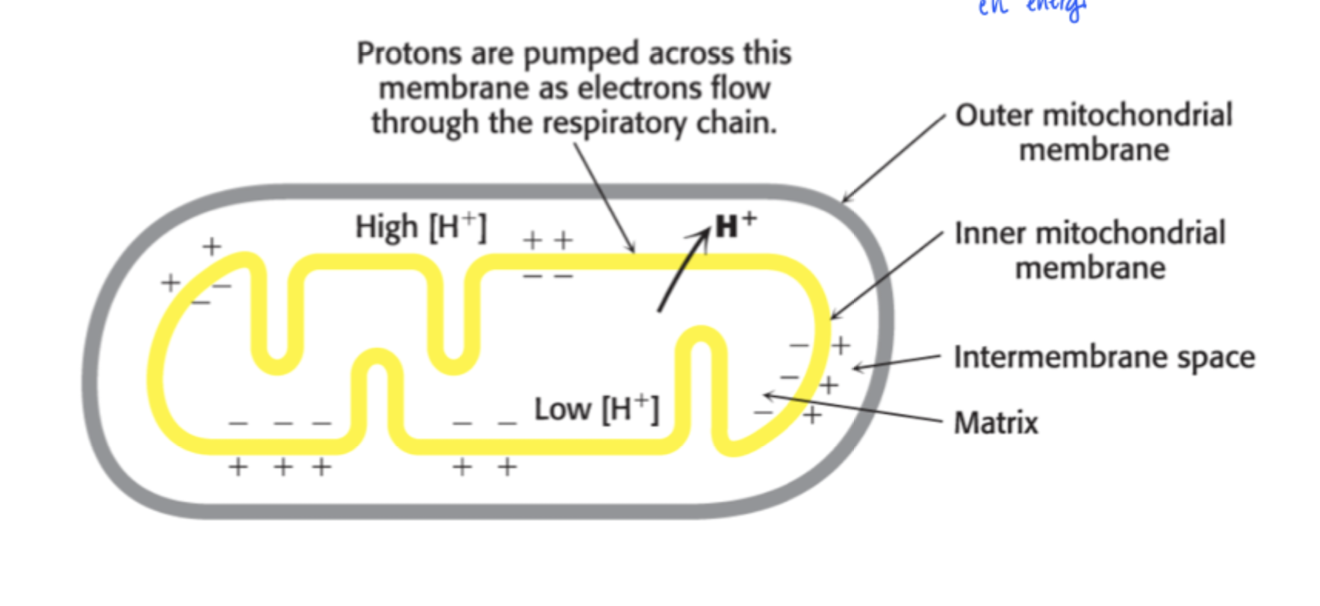
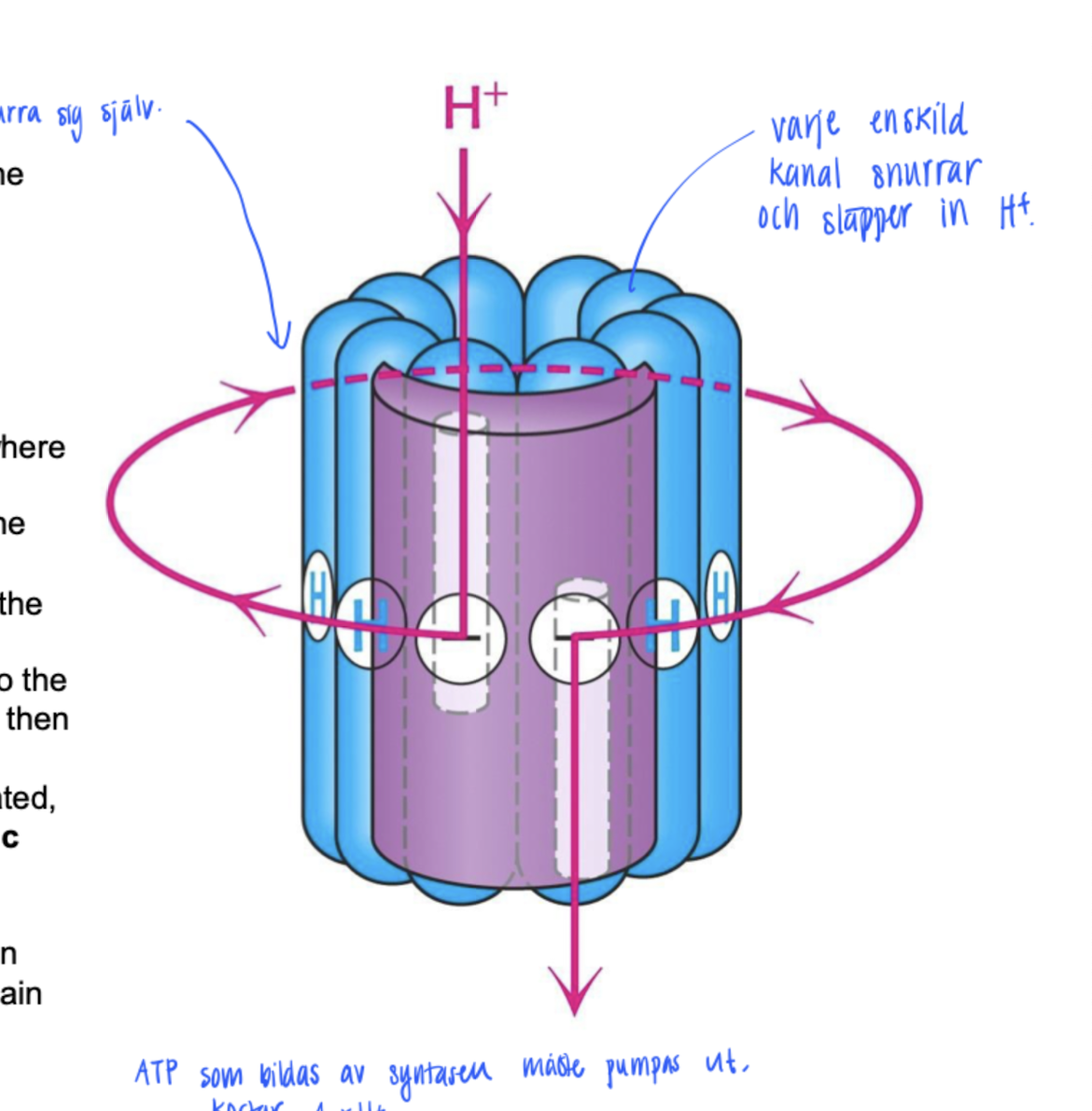
ATP-synthase
formed by different subunits.
β-subunits goes through configuration change LTO
L : loose, binds to ADP and Pi
T : Tight, forms ATP
O : Open : release ATPThe mechanism is carried out through rotation that carries H+ through the ATP synthase. The H+ gets pumped out into the intermembrane space.
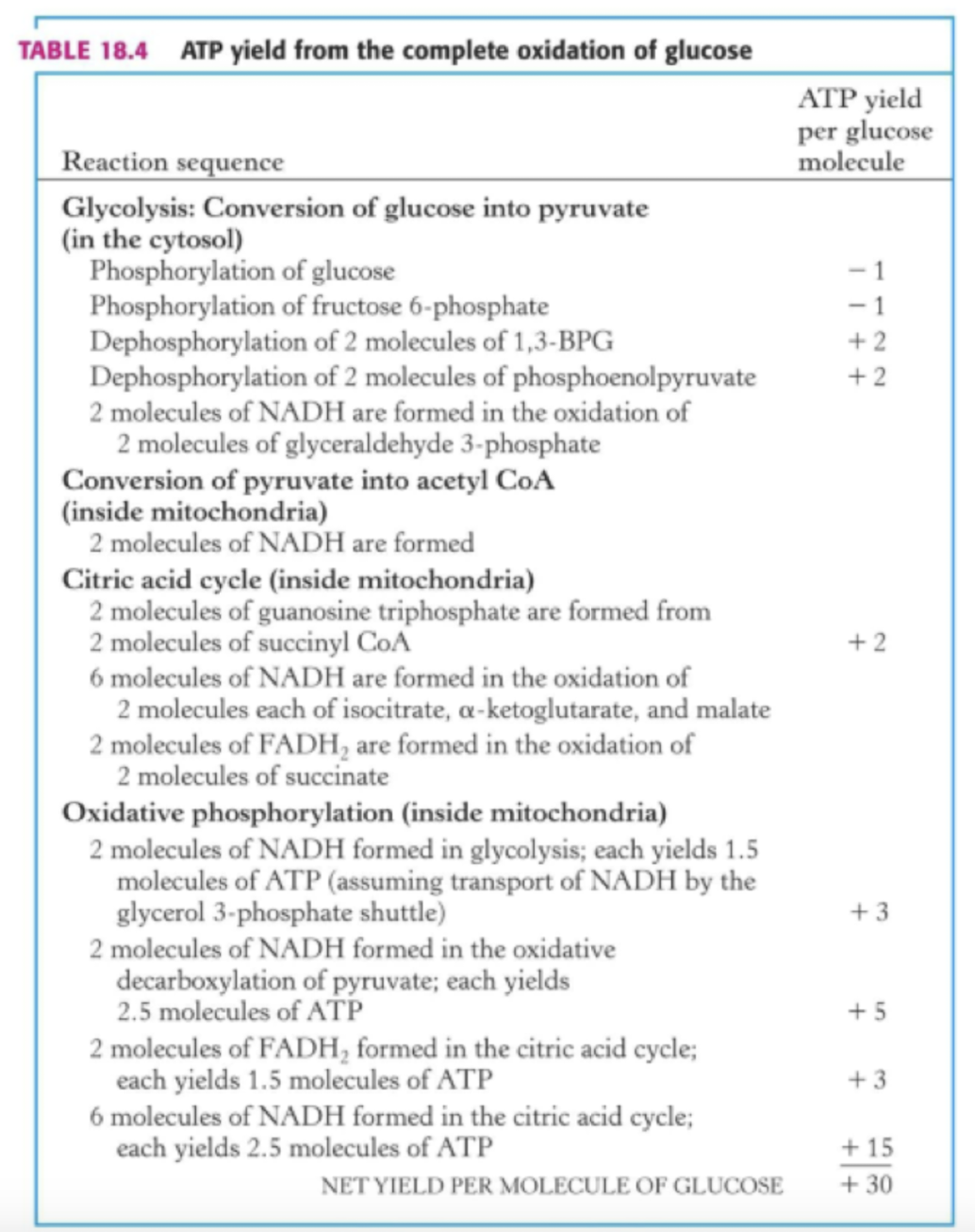
How many ATP is created from 1 glucose
Through the whole process, ATP is formed and utilized. So the net amount is 30 ATP.
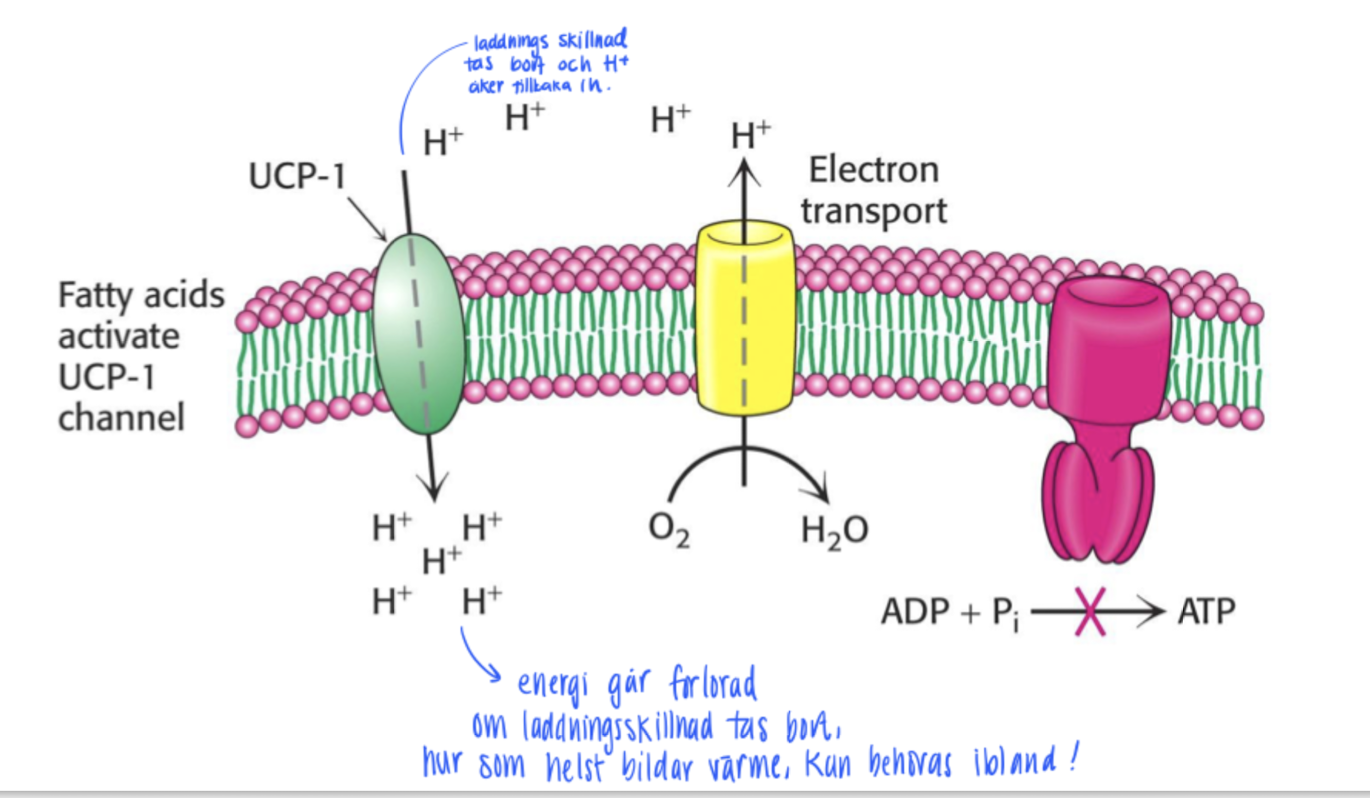
Uncoupler proteins - between electron trasnport, proton displacement and phosphorylation of ADP
Usually, these proteins are coupled, but thanks to uncouplers, e- transport and proton displacement can be decoupled from ATP synthesis.
The H+ gradient is degenerated through H+ getting back in the matrix
Instead of ATP heat is produced instead.
Pentosfosfatvägen (kolhydrat med 5C) Stor fokus i tentan
Processen har 2 syften
Bilda ribose-5-phosphate
Bilda NADPH e.g FA for biosynthesis.
Delas upp i 2 delar
Oxidativa delen (med Co-enzymes involved)
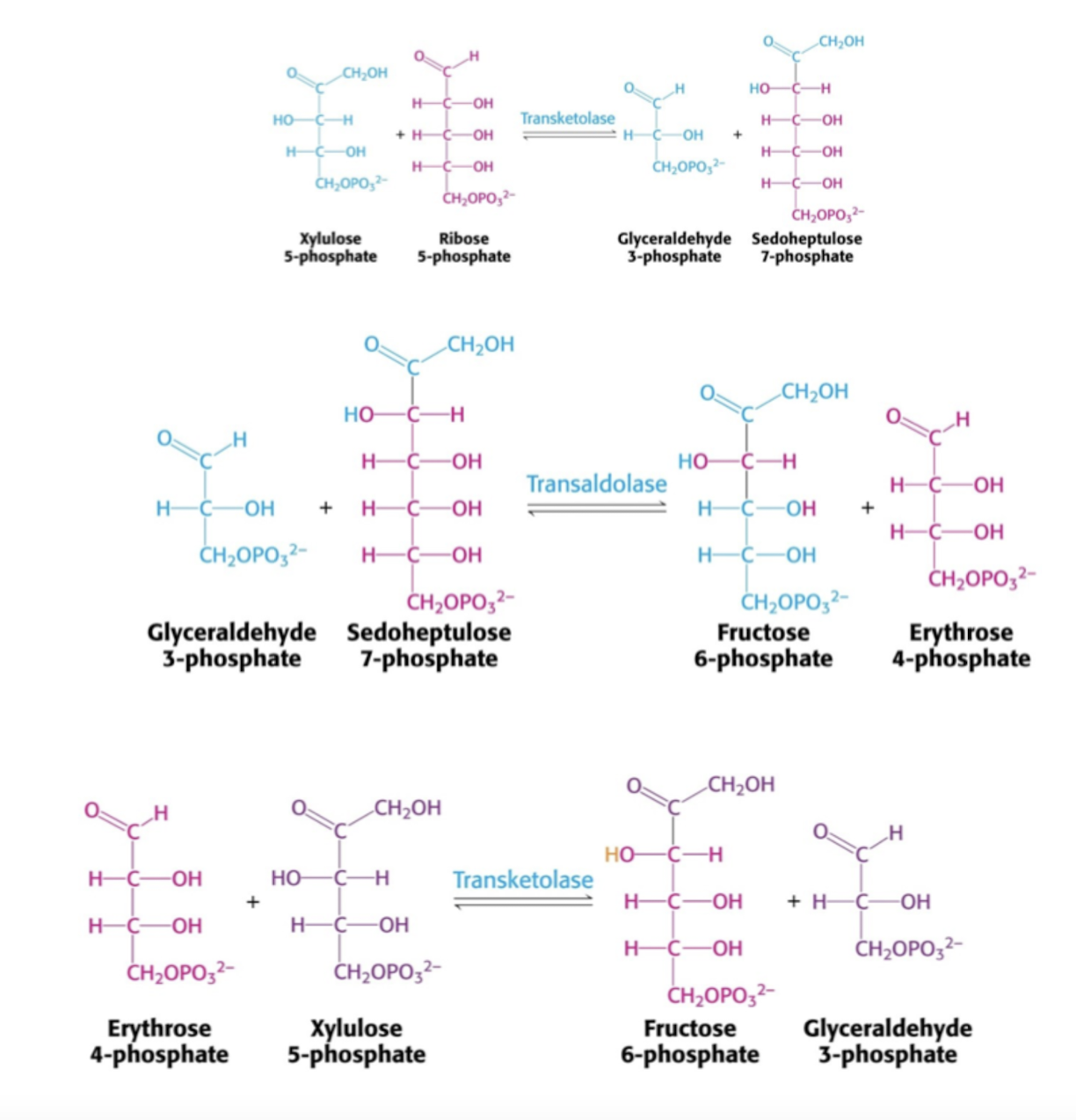
[ Glucose-6-phosphate + 2 NADP+ → Robulose-5-Phosphate + CO2 + 2 NADPH + Pi ].Icke-Oxidativa delen (omvandla antalket kolatomer i kolhydrarerna)
Transaldolas (TA) : Flyttar 3C fragment 1. (C7 + C3 → C4 + C6)
Transketolas (TK) : Flyttar 2C fragment 2. (C5 + C5 → C3 + C7) 3. (C4 + C5 → C6 + C3)
Gör man en blandning av reaktion 1,2,3 får man 3C5 (ribos-5-fosfat) → ← 2 C6 (fruktos-6-fosfat) + C3 (glyceraldehyd-3-fosfat)
![<p>Processen har 2 syften</p><ol><li><p>Bilda ribose-5-phosphate</p></li><li><p>Bilda NADPH e.g FA for biosynthesis.</p></li></ol><p></p><p>Delas upp i <u>2 delar</u></p><ol><li><p><span style="color: blue"><strong>Oxidativa delen</strong></span> (med Co-enzymes involved)<br>[ <strong>Glucose-6-phosphate + 2 NADP+ → Robulose-5-Phosphate + CO<sub>2</sub> + 2 NADPH + P<sub>i </sub></strong>]. <br></p></li><li><p><span style="color: blue"><strong>Icke-Oxidativa delen</strong></span> (omvandla antalket kolatomer i kolhydrarerna) <br><span style="color: blue"><strong>Transaldolas</strong></span> (TA) : Flyttar 3C fragment 1. (C7 + C3 → C4 + C6) <br><span style="color: blue"><strong>Transketolas</strong></span> (TK) : Flyttar 2C fragment 2. (C5 + C5 → C3 + C7) 3. (C4 + C5 → C6 + C3) <br><br>Gör man en blandning av reaktion 1,2,3 får man 3C5 (ribos-5-fosfat) → ← 2 C6 (fruktos-6-fosfat) + C3 (glyceraldehyd-3-fosfat)<br></p></li></ol><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e45c0dc6-8306-49b8-9642-34c5df4fa148.png)
Pentosfosfatvägen - The oxidative pathway
Denna delen består av 3 reaktioner
Glucose 6-phodphate dehydrogense kommer att omvandla G6P till en Lakton (cyckliskt carboxyl ester) och NADPH + H+.
Laktanas hydrolyserar laktonen till en syra (glukonat).
6-fosfoglukonatdehydrogenas dekarboxylerar glukonaten till NADPH och Ribulose-5-phosphate.
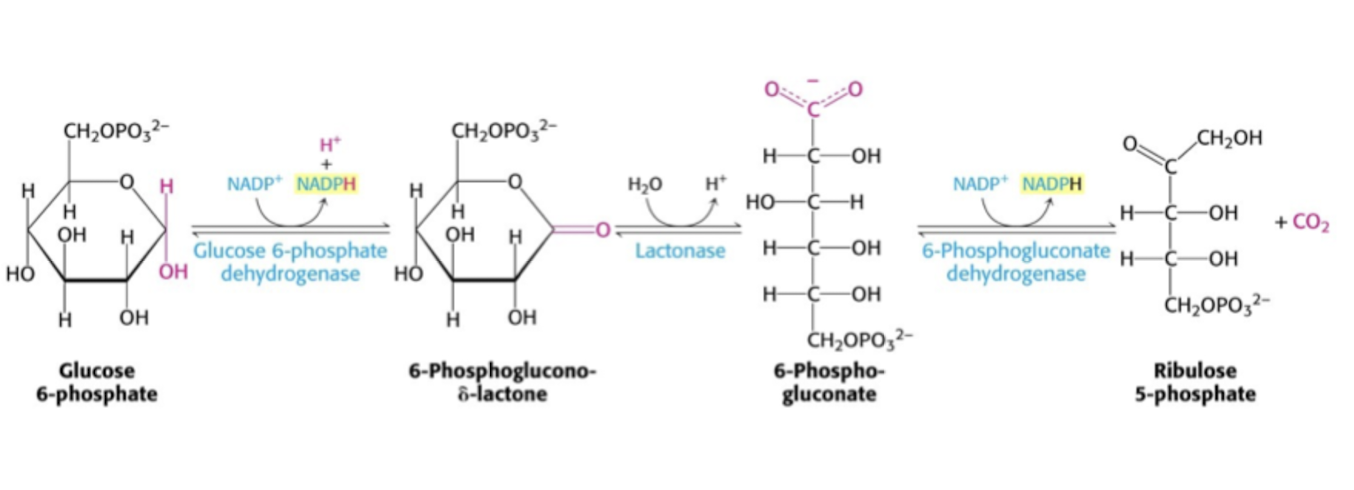
Vad händer med ribulose-5-phosphate?
Ribulose-5-phosphate is a ketos. The molecule can then turn into 2 different molecules.
ribose-5-phosphate (aldos) that is a isomer. → Used in nucleotides
xylulose-5-phosphate through epimerisation. → Used in the non-oxidative part of the pentosphosphate pathway.
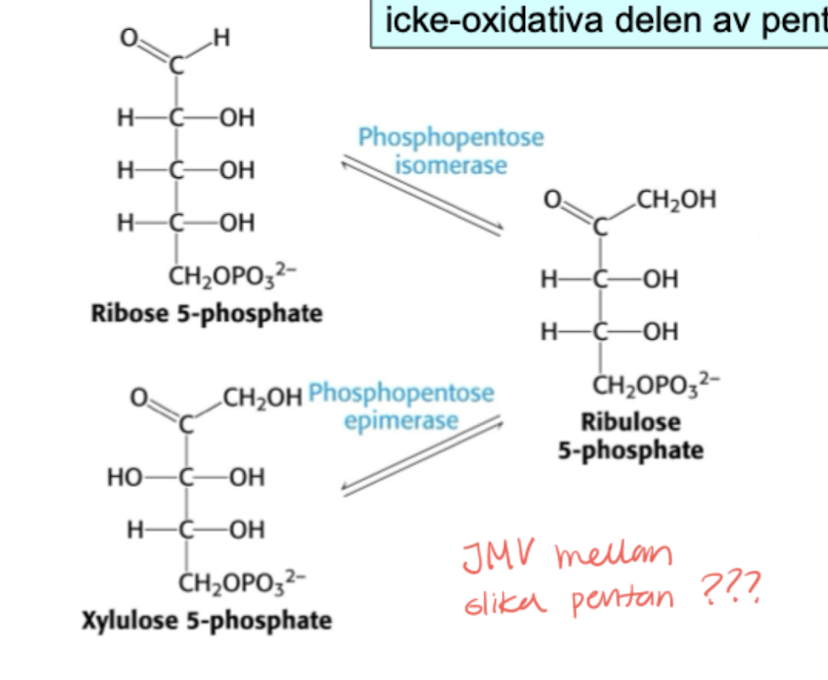
Pentosephosphatepathway - Non oxidative part
a lot can happen here hehe
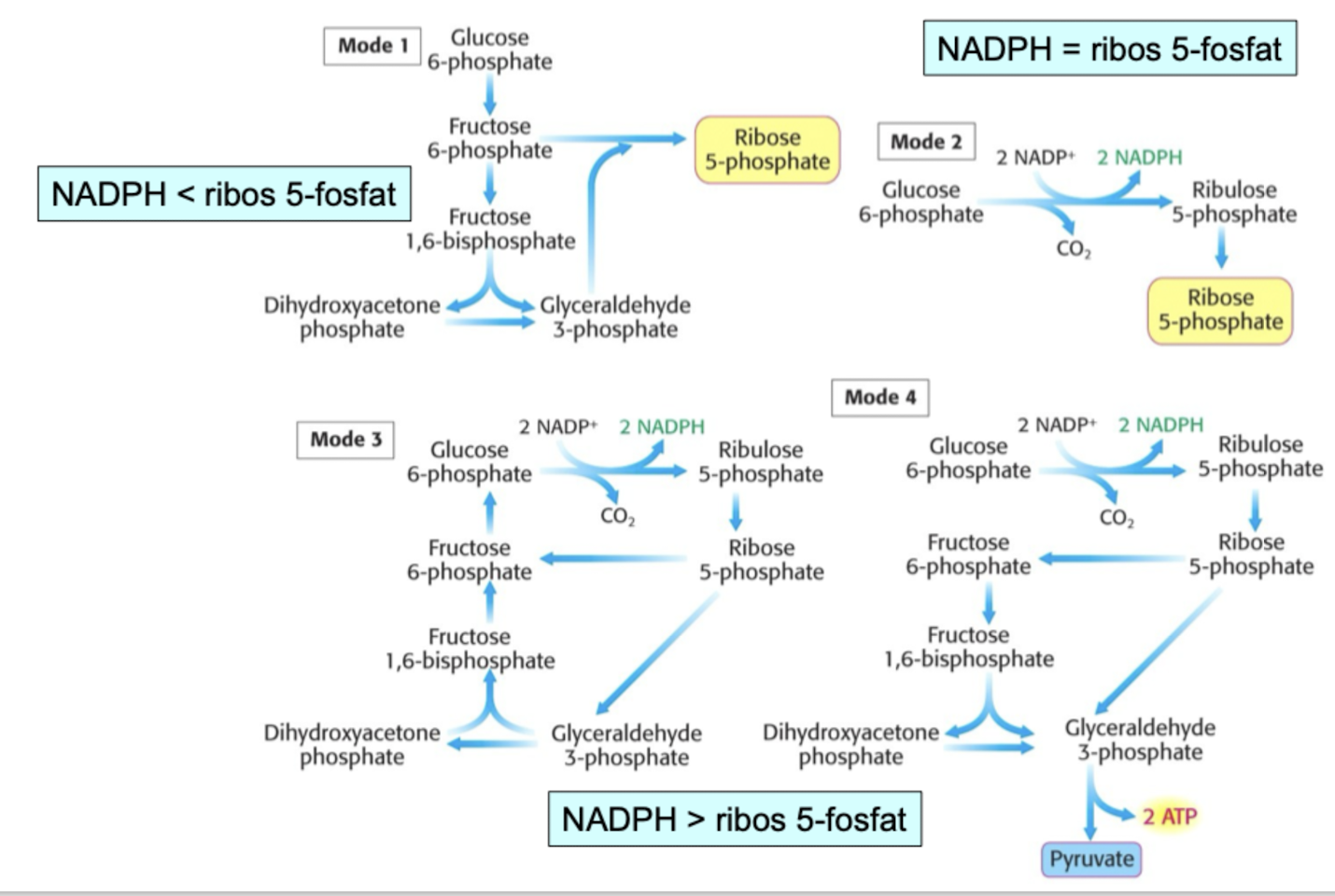
pentosfodfatvägens anpassing till cellens behov
Ribose-5-phosphate > NADPH : Ribose-5-phosphate behövs mycket, e.g när celler delar sig mycket, då är det den icke.oxidativa delen som är mest aktiv (?)
Ribose-5-phosphate = NADPH :Behovet av ribose-5-phosphate = behov av NADPH , då utnyttkas den oxidativa delen.
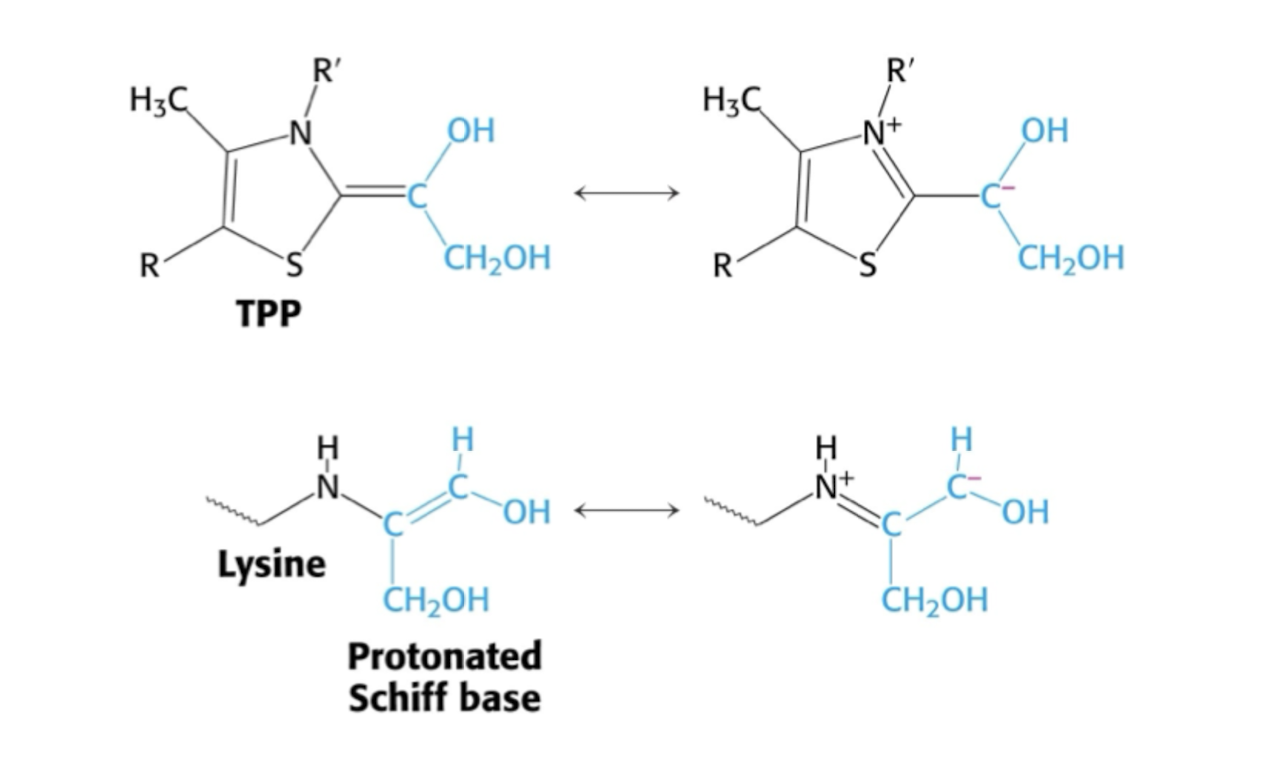
- TA ich TK har liknande aktiva säten → positiv laddning i aktiva sätet. lysin eller TPP.Ribose-5-phosphate < NADPH : 3 och 4 är jag osäker på vad det är som sker. Men det är iaf när behovet av NADPH är större
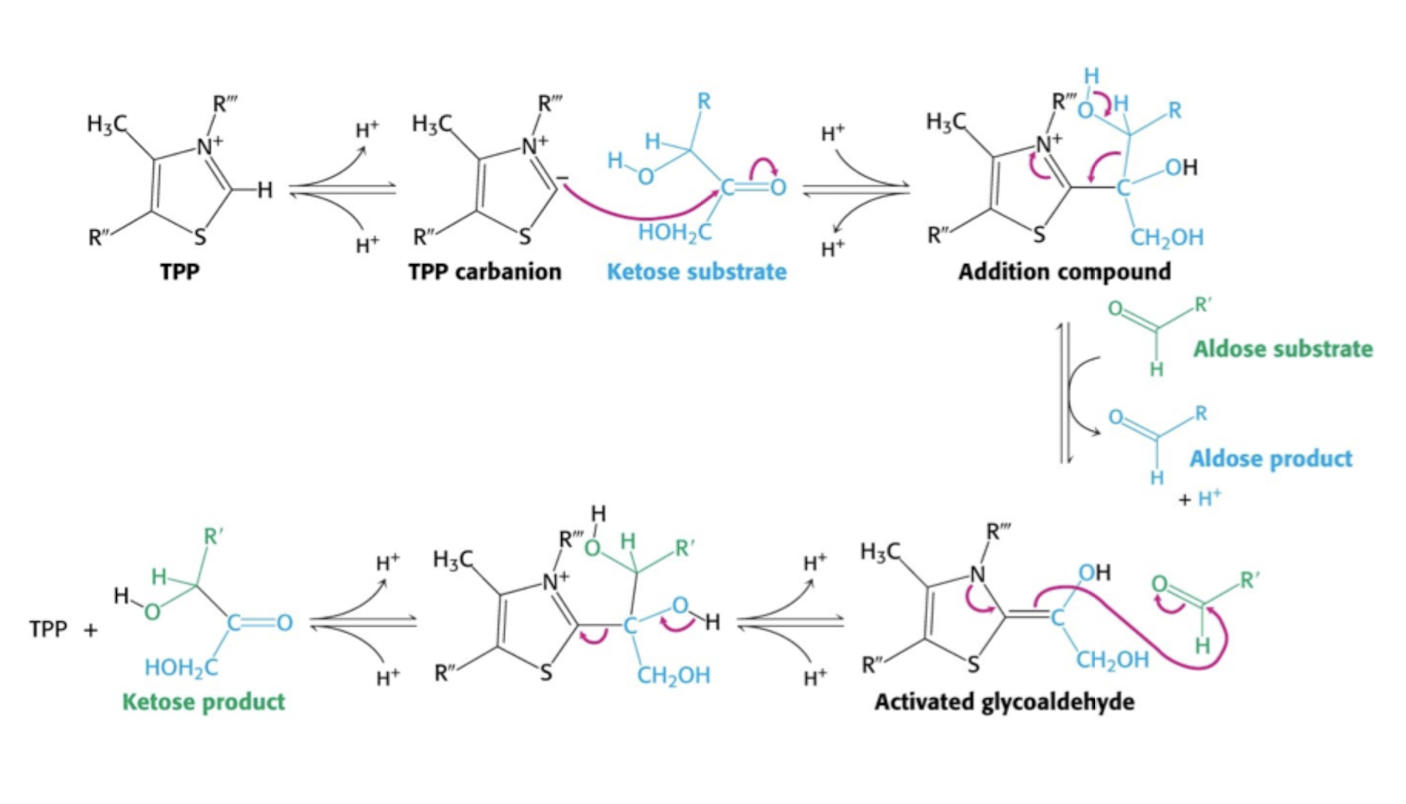
Transketolas (TK) + TPP
Sker på 2 olika sätt (?)
TPP genererar anjon som attackerar ketogruppen i substratet.
Aldosprodukt lämanr och aldossubstrat binder in och reaktionen reverseras.
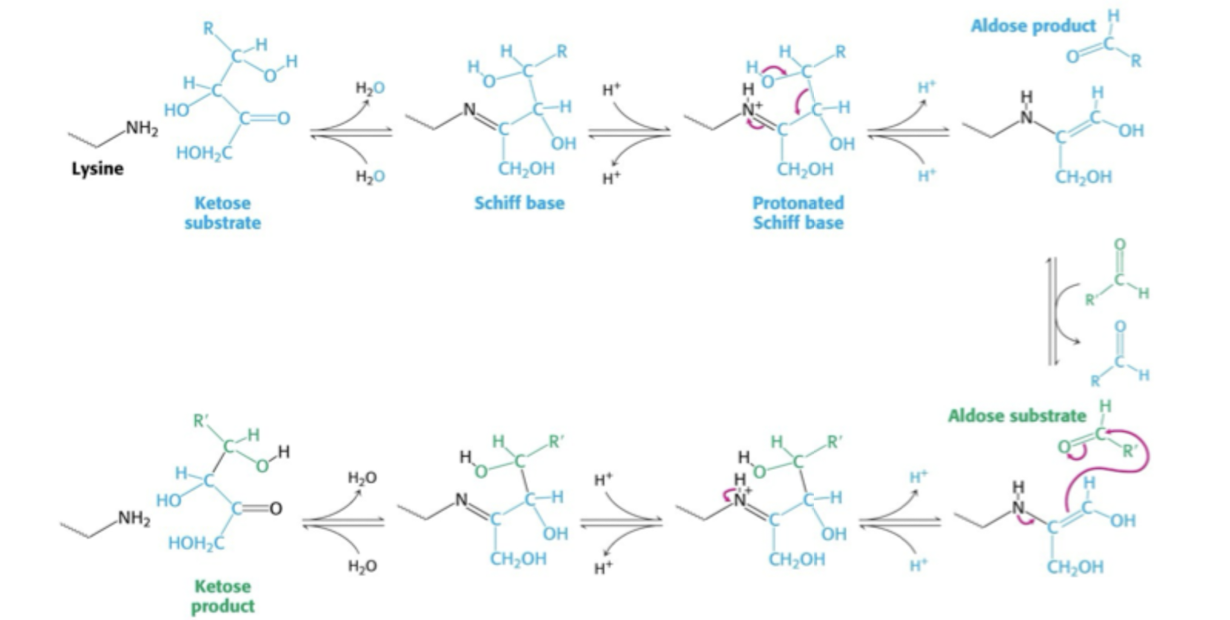
Transaldolas (TA) + Lysin
Lysin bilder schiffsk bas med ketogrupp. isubstratet. Protinerad schiffsk bas stabiliserar den negatova laddningen.
Aldosprodukt lämnar och aldossubstrat binder in och reaktionen reverseras.
TPP vs Lysin