Buoyancy
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What was the Archimedes Principle?
Buoyancy
Buoyancy
Force exerted by a liquid, gas or other fluid, that opposes an objects weight
Were placoderms negatively or positively buoyant?
Negatively buoyant
-Bottom dwellers
-Contained heavy armour
What does a reduction in submerged weight allowed fish to?
-Exploit the midwater region
-Reduce the cost of transport
How was the reductions in submerged fish achieved?
-Reduction of heavy, dense body parts
-Buoyancy aids
What are the 2 ways to counteract lift?
-Dynamic lift (Active)
-Static lift (Buoyancy/Passive)
Is dynamic lift positive or negative in sharks?
Negative
Equation for dynamic lift in sharks?
W=B+C
W→ Submerged weight of fish
B→ Hydrodynamic lift from pectoral fins
C→ Lift from caudal fin
What happens if W=B+C and if W>B+C?
W=B+C
-Neutral buoyancy
W>B+C
-Negative buoyancy (Sink)
What does the paper “Volumetric imaging of shark tail hydrodynamics reveals a three-dimensional dual-ring vortex wake structure“ show?
Volumetric imaging to analyse shark tail hydrodynamics, revealing a three-dimensional dual-ring vortex wake structure that enhances propulsion efficiency
Key points of “Volumetric imaging of shark tail hydrodynamics reveals a three-dimensional dual-ring vortex wake structure“
Objective:
-Investigate the hydrodynamics of shark tail movement using volumetric imaging techniques.
Methodology:
-Used three-dimensional imaging to analyze water flow patterns generated by shark tails.
Findings:
-Identified a dual-ring vortex wake structure, different from traditional single-ring vortex wakes seen in other aquatic animals.
Significance:
-Suggests that sharks use a unique propulsion mechanism, enhancing efficiency and manoeuvrability.
Implications:
-Provides insights into shark locomotion and informs biomimetic designs for underwater robotics.
Citate “Volumetric imaging of shark tail hydrodynamics reveals a three-dimensional dual-ring vortex wake structure“
Flammang et al., 2011
What are the advantages of static lift from lipids?
Lipids are incompressible
-Buoyancy not affected by depth
What are the disadvantages of static lift involving lipids?
Lipids only slightly less dense than water
-So need large amount of lipids
Quantity of lipid cannot be adjusted quickly
-No ability to compensate for short term changes
Where do elasmobranchs store lipids?
Liver
-Liver can exceed 20% of body weight
How much does teleost liver make up their bodyweight?
1-2%
What lift is more economical at high speed and actively seeking prey?
Dynamic lift
What lift is more economical at low speed and opportunistic prey ecounters?
Static lift
Which 2 bladders can be used for gas buoyancy (Static lift)?
Swim or Gas bladder
Advantages of using gas as buoyancy aid?
-Gas is less dense than lipid
-Quantity of gas can be adjusted quickly to compensate for short term changes
Disadvantages of using gas as a buoyancy aid?
Boyles Law
Boyles Law
At a constant temp the volume of a gas varies inversely with pressure
What happens if the fish swim descents and ascents?
Descent
-Swim bladder compresses (Negatively buoyant)
-To maintain neutral buoyancy more gas into the gas bladder
Ascent
-Swim bladder will expand (Positively buoyant)
-To maintain neutral buoyancy more gas needs to be expelled from gas bladder
2 type of gasbladders
Physostomatous and Physoclistous
Physostomatous
Pneumatic duct between swim bladder and gut open throughout life
-Lower teleosts (Clupeids, Anguilla)
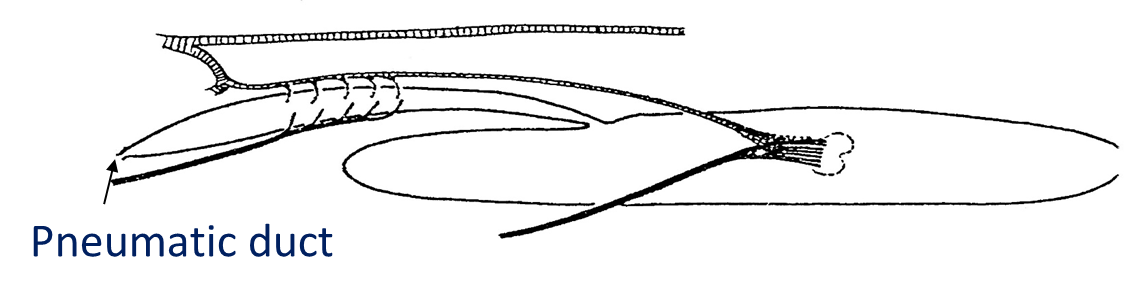
Physoclistous
Pneumatic duct closes early in development
-Advanced teleosts
How to physostome get gas into the bladder?
-Simply shallow gas at the surface
-Some species have a special organ to inflate bladder (Gas Gland)
→Anguillids
How to physostome release gas to prevent descent with massive positive buoyancy?
Burp it out
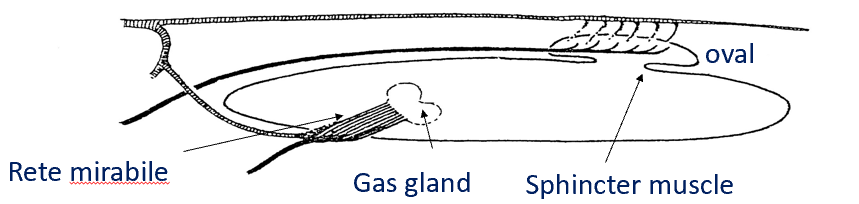
How to physoclist get gas into their bladders?
Gas gland that inflate the bladder
-Uses passive diffusion to get oxygen into gas bladder lumen
-Relies on differential partial pressure
How does gas gland maintain diffusion rate?
Rete mirabile
Rete mirabile
Counter current exchange system with large numbers of arterial and venous capillaries running counter to and in very close proximity to one another
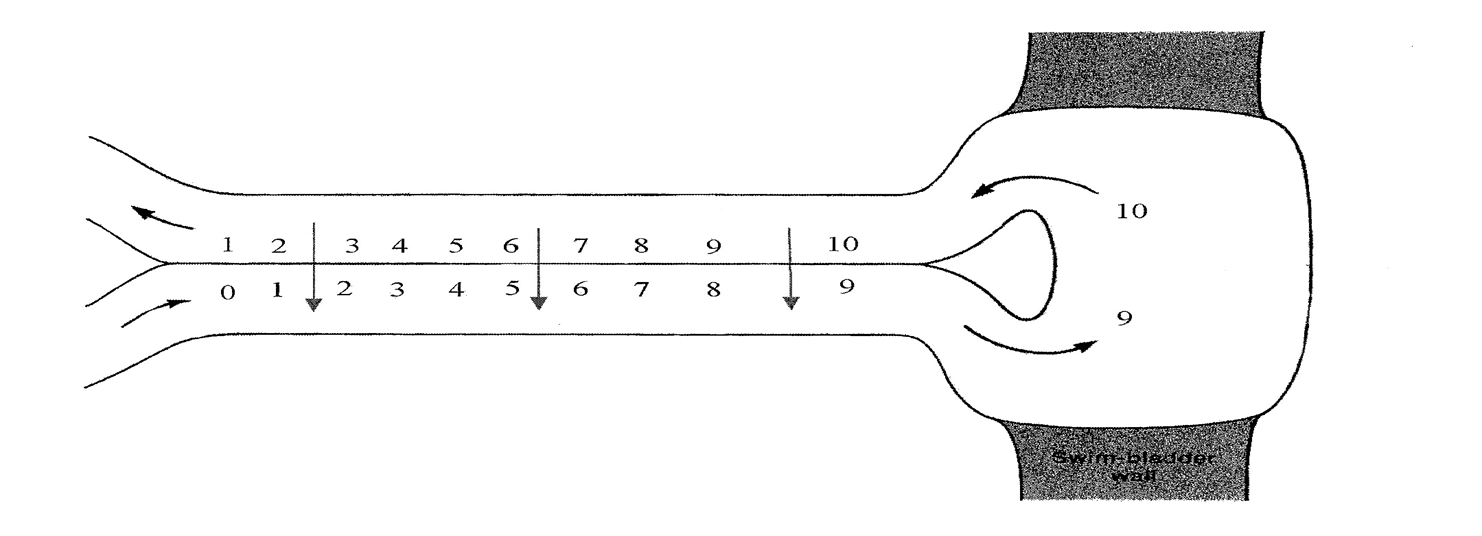
How does rete mirabile work?
-Blood enters gas gland
with oxygen primarily bound to haemoglobin (hb)
-O2 needs to disassociate from hb and go into solution
-Increase in pp leads to passive diffusion
What is the mechanism of rete mirabile?
Cells surrounding the gas gland are rich in glycogen, secreting lactic acid (anaerobic metabolism)
What are the implications of increased acidity in the gas gland?
Bohr effect
-A reduction of O2-Hb affinity
Root effect
-A reduction in the O2 carrying capacity of Hb
Salting out effect
-Increase in ionic content of blood reduces carrying capacity of all gases
Dissociation of carbon dioxide from bicarbonates
-CO2 reacts with Hb and plasma proteins to produce Carbamino compounds, further reduce O2-Hb affinity
How does a fish increase the O2 multiplication at depth?
Having a longer rete mirabile
-Bassozetus taenia has a rete mirabile of 25 mm and lives at a depth of 5000m
How do physoclistous retain gas in the bladder?
-Wall of SB had cells containing sheets of guanine crystals reducing permeability 1000-fold
-Restrict access of O2 in swim bladder to blood supply
Adaptations of physoclistous for vertical movement?
-Large oval for size of swim bladder
-Large blood vessels supplying oval
-Diffusion distance between swim bladder and capillaries <1μm
-Lose swim bladder altogether
Examples of fish with no swimbladder?
Scombrids
-Allow rapid vertical movement o evade predators and capture prey
-Avoid detection by toothed whales
What are the adaptations for buoyancy in deep-sea fish?
-Larger oval per volume of swim bladder
-Lightly ossified skeleton
-Few, if any scales
-Reduced musculature (important if weak bones)