safety precautions in healthcare facilities
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Medical malpractice
the breach of the duty of care by a medical provider or medical facility. The duty of care is based on what another professional in the same position and with the same knowledge would have done in that situation.
Liability
refers to being legally responsible for causing harm.
Personal liability
refers to healthcare workers being responsible for causing harm
Supervisory liability
refers to supervisors of healthcare workers being responsible for workers causing harm.
Employer liability
refers to employers of healthcare workers being responsible for workers causing harm.
R - Rescue:
Anyone who is not involved in extinguishing the fire must leave the scene.
A - Alarm:
Pull the alarm or assign someone to pull the alarm.
C - Contain:
If possible, keep the fire in an enclosed area by closing windows and doors.
E - Extinguish or Evacuate:
the fire is small and in a confined area, extinguish the fire with a fire extinguisher. If the fire is large, move everyone, including yourself, out of danger.
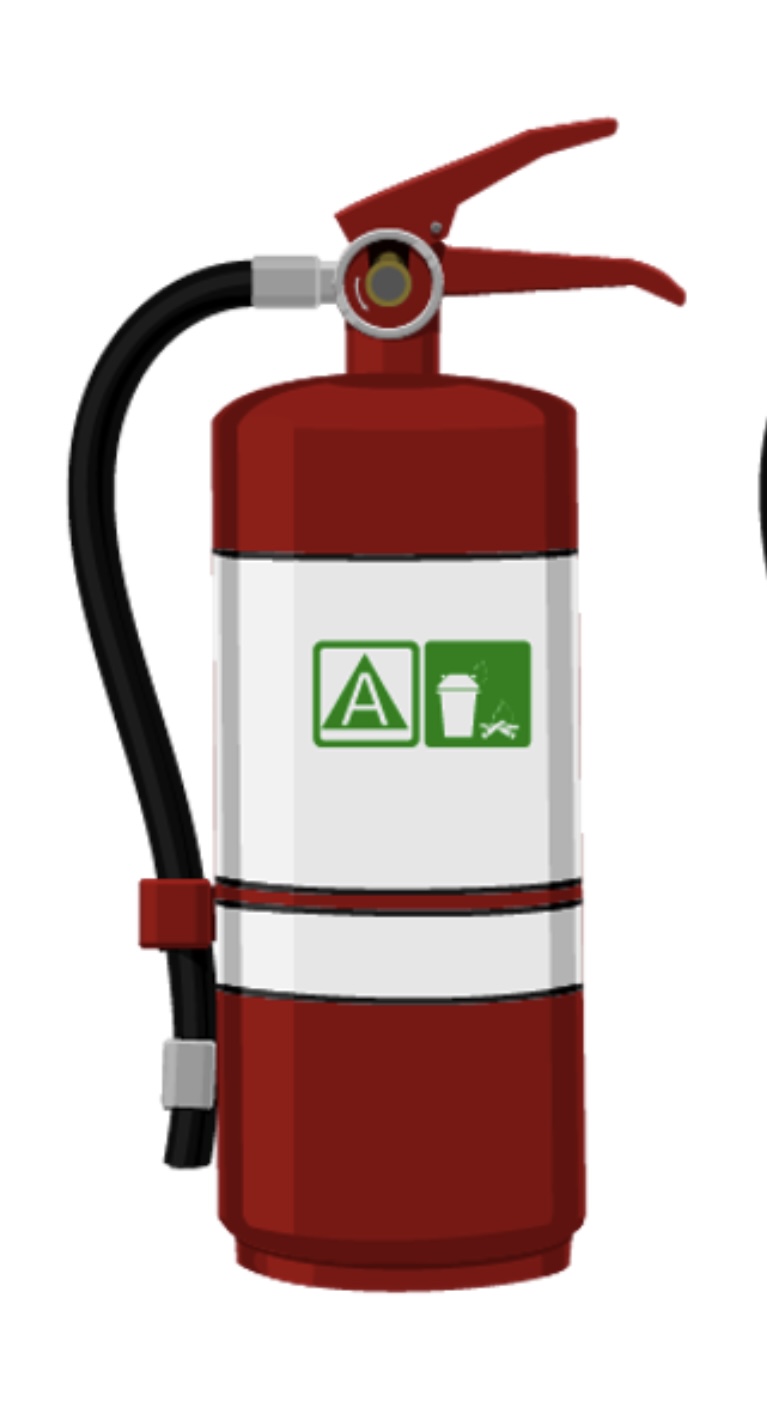
Type A
is made of pressurized water and should be used on common combustibles, such as wood.
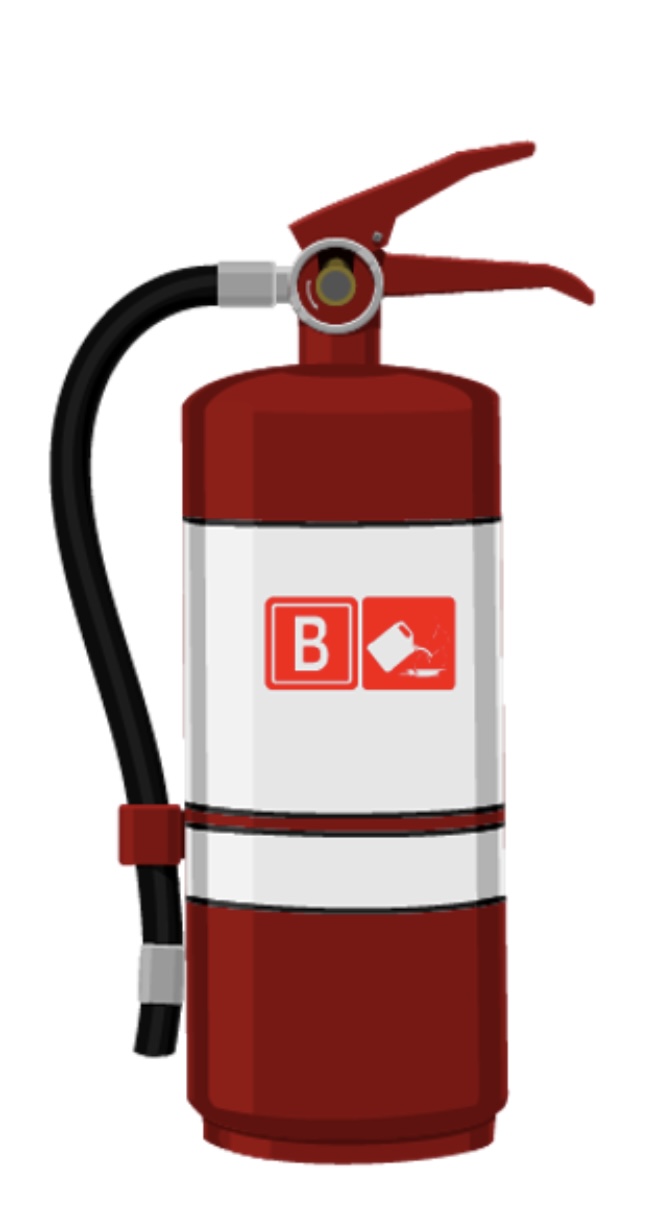

Type B
is made from carbon dioxide and is useful for flammable liquid fires, including grease, gasoline, and oil.
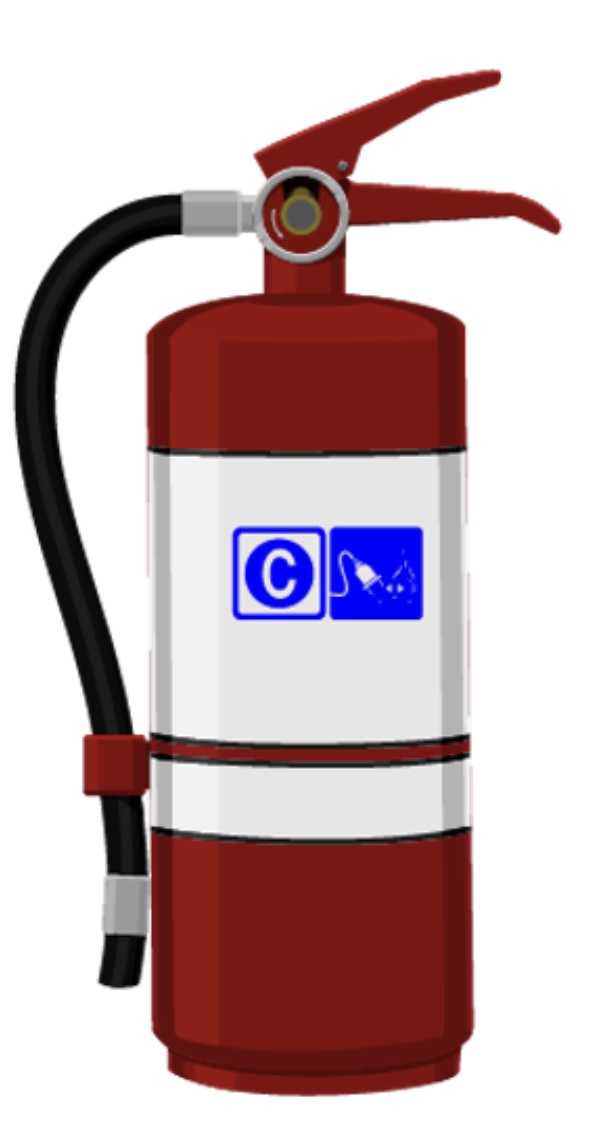

Type C
is composed of potassium bicarbonate and is used to put out fires that are electrically energized.
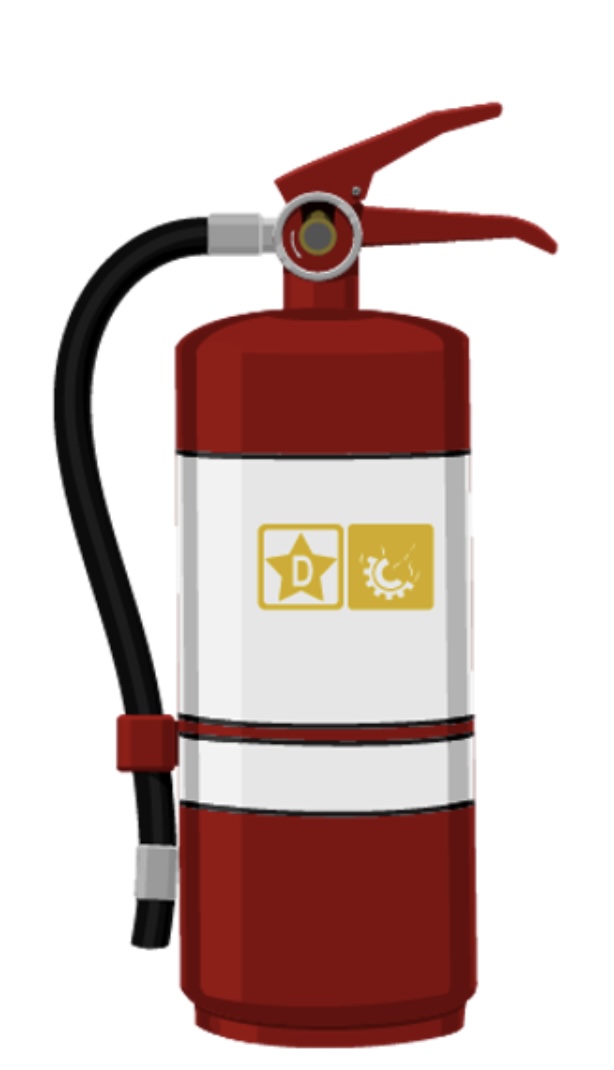

Type D
is used on flammable metals. Its makeup depends on the type of flammable metal it was intended for.
Because each Type D extinguisher is highly specific, employees should read the label and become familiar with the uses of this extinguisher before a fire ever occurs.
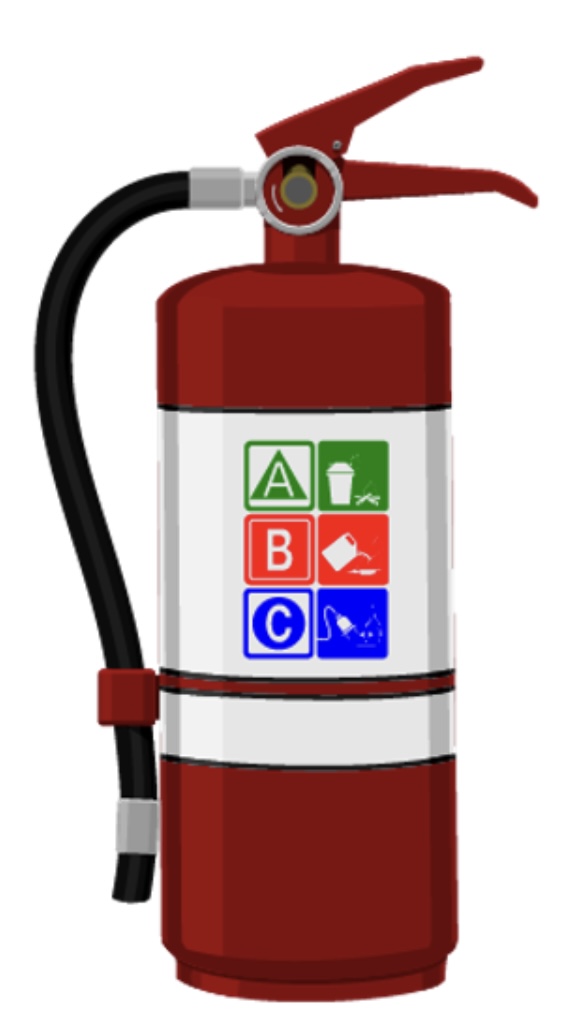

Type ABC
is made of a chemical compound and can be used on any A, B, or C fire. is the most common type of fire extinguisher.
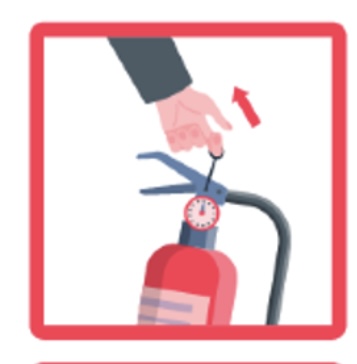
P-
Pull the pin

A-
Aim at the base of the fire

S-
Squeeze the handle

S- 2
Sweep the nozzle from side to side
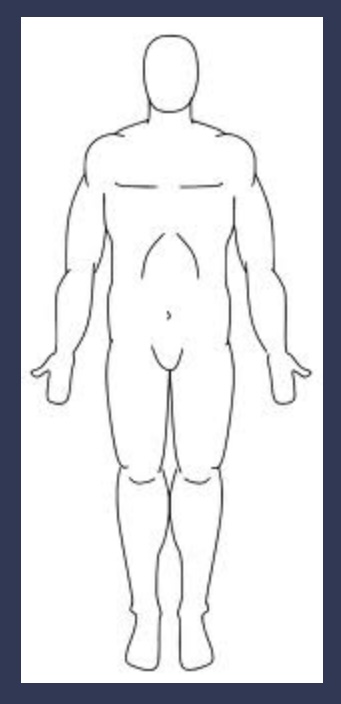
Erect Standing (anatomic)
Patient stands upright with arms at sides and palms facing forward
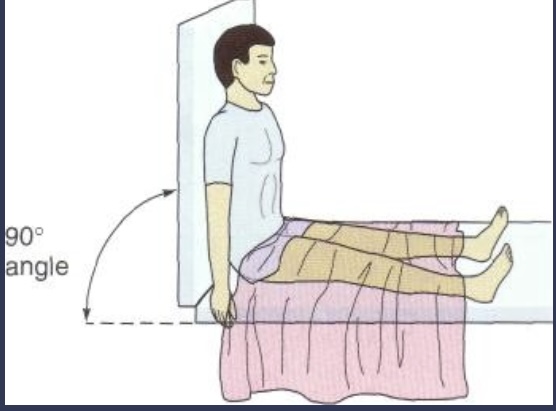
High Fowlers position
Same as fowlers except at 90 degrees. Basically the same as fowlers
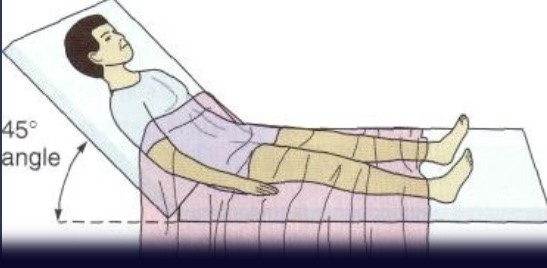
Semi Fowlers
Same as fowlers except at 45 degrees
Fowlers position
Fowler's positions are tilted back. In medicine, Fowler's position is a standard patient position. It is an intervention used to promote oxygenation via maximum chest expansion and is implemented during events of respiratory distress.
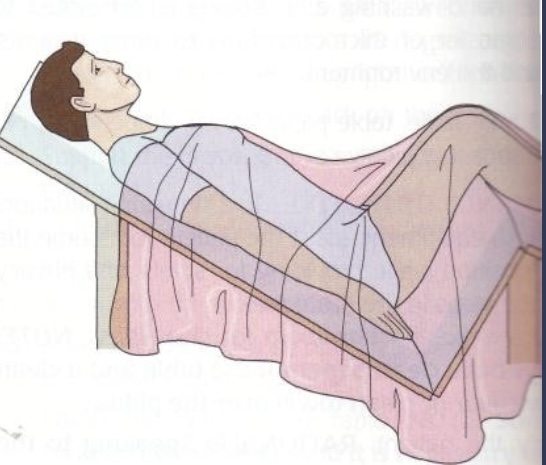
Jackknife ( reclining)
Patient lies on the back with shoulders elevated, knees flexed, thighs flexed at right angles to the trunk. Used for when passing a urethral sound
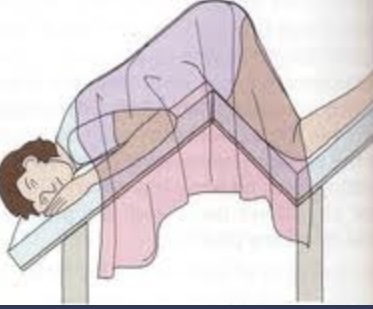
Proctologic
Have your patient put their butt in the air but put the exam table in a more sharp position like they are being alien probe.
Used for proctologic exams (Colorectal surgery is a field in medicine, dealing with disorders of the rectum, anus, and colon.)
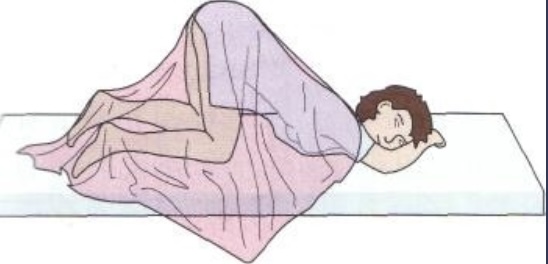
Knee-chest (genupectoral)
Have the patient put their butt in the air like a five year old. Used for proctologic
exams
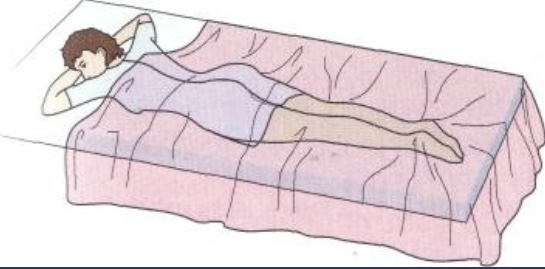
Prone
Patient lies flat on their stomach with the head turned slightly to the side. Arms can be positioned above the head and extended or alongside the body.
Used for Back or neck procedures (cervical to sacral), Procedures of the occipital or postero-lateral cranium
Sacral, perianal & perineal procedures
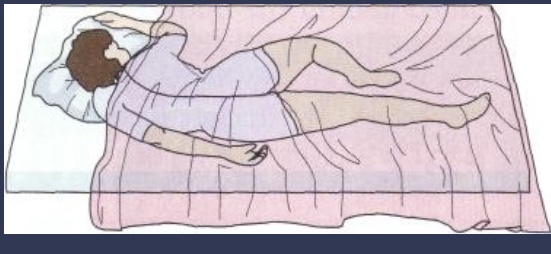
Sims Lateral
Patients lies on the their left side with the left arm behind the body and right arm forward, flexed at the elbow. Both legs flexed at knee and the right leg is sharply flexed and positioned next to the left leg, which is slightly flexed.
Used to rectal examination, treatments and enemas
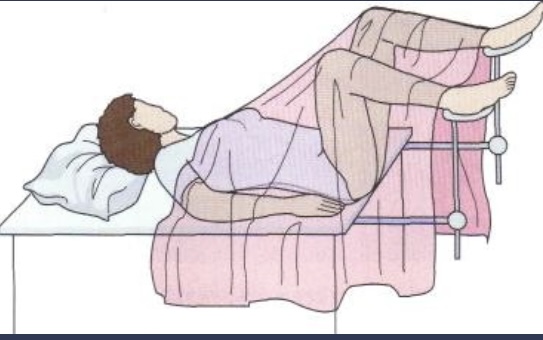
Lithonomy
Female patients assume the dorsal recumbent position with feet in the stirrups.
Knees are bent and butt moved to the edge of the exam table. Used for pap smear and pelvic exams
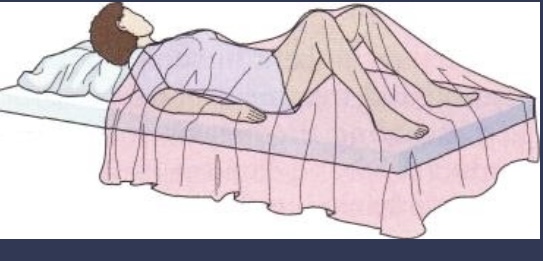
Dorsal Recumbent
Patient is in supine position with legs flexed at the knees and feet flat on table.
Used for genital and rectum exam
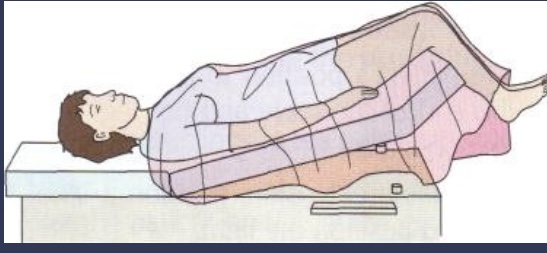
Trendelenberg
Patients lies supine position with foot of the table elevated. Treatment for shock or 4) & abdominal surgery