[BIO 120.11] Module 4 Part 1
1/155
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
156 Terms
TRUE
T/F: Biofilms are an attached polysaccharide matrix containing embedded bacterial cells
FALSE
T/F: Biofilms are an attached lipid matrix containing embedded bacterial cells
Water or moist soil
For biofilms to form, the surface must be immersed where?
FALSE
T/F: Biofilms can either functional or dead microbial communities
TRUE
T/F: Biofilms are composed of functional and growing microbial communities
FALSE
T/F: Biofilms are made of only one species of bacteria to prevent competition from happening
TRUE
T/F: Biofilms may contain one or multiple species of bacteria
700
How many phylotypes of bacteria are found in human mouth biofilm?
Bacteria, Archaea, Yeasts
Biofilm formation can occur with what organisms
Attachment, Colonization, Development, Active Dispersal
What are the 4 stages of biofilm formation?
Attachment
Stage of Biofilm Formation: Adhesion of a few motile cells to a suitable solid surface
Pili, Fimbriae, Capsule, Flagella
What parts of a bacteria can be used for attachment?
Colonization
Stage of biofilm formation wherein EPS is produced
Colonization
Stage of Biofilm Formation: Characterized by intercellular communication, growth, and polysaccharide formation
Intercellular communication, growth, polysaccharide formation
What are 3 things we can observe in the colonization stage of biofilm formation?
Extracellular Polymeric Substances
Substances needed for biofilm formation and explains the calcified nature of biofilmsD
Development
Stage of Biofilm Formation: Characterized by more growth and polysaccharideA
Active Dispersal
Stage of Biofilm Formation wherein cells migrate outside of the biofilm to transfer biofilms or live a planktonic lifestyle
Active Dispersal
Stage of Biofilm Formation triggered by environmental factors such as nutrient availbaility
Water channels
Source of moisture in biofilms
Development
Stage of biofilm formation wherein we can observe water channels
Nutrient Availability
What is an example of an environmental factor that can trigger active dispersal in biofilm formation stage?
Protection, Trap nutrients, Allow complex microbial interactions
3 Advantages of a biofilm lifestyle
Harmful chemicals, phagocytosis, bacterial grazing by protists
Having a biofilm lifestyle can protect against what 3 things?
Implicated in difficult-to-treat infections, Dental cavities and gum disease, Fouling, plugging, and corrosion in tubes and pipes, Contamination of fuel (storage tanks)
What are 4 consequences of biofilm formation for humans?
Waste treatment (longer viability), Bioremediation
What are 2 positive benefits of biofilm formation for humans?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Vibrio cholerae
What are 2 model bacteria for biofilm studies?
Cystic Fibrosis
What disease is caused by P. aeruginosa?
AHL
In P. aeruginosa, what triggers the expression of the subset of biofilm-related genes?
Explosive Death
What triggers P. aeruginosa biofilm formation?
Positive regulation
What kind of QS is needed for P. aeruginosa biofilm formation
Expression of lysis protein by an inactive prophage in P. aeruginosa geneome
What causes explosive death in P. aeruginosa?
Stressful conditions, can occur occasionally as random event under normal conditions
What triggers explosive death in terms of environmental conditions?
DNA release
In P. aeruginosa, this event is critical to EPS formation
Low Cell Density
When is V. cholerae biofilm formation promoted?
VpsR, VpsT
Transcriptional regulators in V. cholerae that activate expression of matrix protein genes
c-di-GMP
This component must be bound to VpsT before transcription of biofilm genes in V. cholerae can occur
VpsT
In what transcriptional regulator must c-di-GMP be bound to before V. cholerae biofilm translation can occur?
HapR
Protein that represses VpsR and VpsT
High cell density
When is HapR among V. cholerae expressed?
Bacteria
Causal agents of infectious diseases
Disk Diffusion Assay, Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
What are 2 ways to do antimicrobial activity assays?
FALSE
T/F: Disk diffusion assay is quantitative test
TRUE
T/F: Disk diffusion assay is qualitative assay, but can be standardized
Disk Diffusion Assay
Test for antibiotic susceptibility of clinical isolates
Antimicrobial agent, Solubility, Diffusion Coefficient, Overall effectiveness
What are the 4 factors that affect the zone of inhibition?
Zone of inhibition
What is being measured in the disk diffusion assay?
Mueller Hinton Agar
What agar is recommended for Disk Diffusion Assay?
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration Assay
Smallest amount of the agent needed to inhibit the growth of a test organism
TRUE
T/F: The Minimum Inhibitory Concentration refers to the smallest amount of an antibiotic agent to inhibit growth
FALSE
T/F: The Minimum Inhibitory Concentration refers to the concentration of an antibiotic with no cells growing at all
Minimum Bactericidal Concentration
Refers to concentration of antibiotics with no cells growing at all
Microdilution or Microtiter Plate
What is the most common way of doing MIC assays?
Over-prescribing of antibiotics, Patients not finishing their treatment, Over-use of antibiotics in livestock and fish farming, Poor infection control in hospitals and clinics, Lack of hygiene and poor sanitation, Lack of new antibiotics being developed
What are the 6 causes of Antibiotic Resistance Development?

Intrinsic, Adaptive, Acquired
What are 3 types of resistance based on mechanisms?
Intrinsic
Resistance that result from the inherent characteristics of microorganisms
Efflux pumps, Reduced permeability among Gram negatives and capsulated bacteria
What are 2 examples of intrinsic resistance?
Acquired Resistance
Resistance that occurs when there is a change in the genome of a bacterium
Mutations or HGT
What is an example of acquired resistance?
Adaptive Resistance
Resistance that refers to the capacity to become resistant to antibiotics in response to environmental signals
FALSE
T/F: Acquired resistance is temporary
FALSE
T/F: Adaptive resistance is permanent
TRUE
T/F: Adaptive resistance is temporaryA
Adaptive Resistance
What type of resistance is temporary?
Biofilm formation
What is an example of adaptive resistance?
Alteration of target, Antibiotic Degrading Enzymes, Antibiotic Altering Enzymes, Efflux Pumps
What are 4 mechanisms of antibiotic resistance?
Antimicrobial Drug Resistance
The acquired ability of a microorganism to resist the effects of an antimicrobial agent to which it was formerly susceptible
MDR, XDR, PDR
What are 3 types of antimicrobial drug resistance?
Multidrug Resistance (MDR)
ADR: Nonsusceptibility to ≥1 agent in ≥3 antimicrobial categories
Multiantibiotic
Organism that is resistant to 3 drugs, but all belonging from one class
Extensively Drug Resistance (XDR)
ADR: Susceptibility limited to ≤2 categories
Pan Drug Resistance (PDR)
ADR: Nonsusceptibility to all agents in all antimicrobial categories
Molecular processes targeting antibiotics, Cell membrane and cell wall-targeting antibiotics
What are 2 types of antibiotics based on antibiotic targets?
Antibiotics
Antimicrobial agents produced by microorganisms (bacteria and fungi)
Bacteria, Fungi
What organisms produce antibiotics?
Antibiotics
Agents that have the ability to either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria
Antimicrobial Agents
Natural or synthetic chemicals that kill or inhibit the growth of microorganisms
-cidal Agents, -static Agents, -lytic Agents
What are the 3 types of antimicrobial agents>
-cidal Agents
Agents that kill by binding tightly to their cellular targets
TRUE
T/F: In -cidal Agents, dead cells are not lysed
FALSE
T/F: In -cidal Agents, dead cells are also lysed
Formaldehyde
What is an example of a -cidal agent?
Optical Density
What is an example of a bacterial counting technique that measures both dead and living cells
Plate Count
What is an example of a bacterial counting technique that measures only living cells
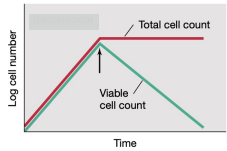
-cidal Agents
What is the antimicrobial agent that will show the data in the graph?
-static Agents
Antimicrobial agents that serve as inhibitors of important biochemical processes
-static Agents
Antimicrobial agent that bind relatively weak
-static Agents
Antimicrobial agent that serve as growth inhibitors (keep a pathogenic bacterium from multiplying until the immune system can rid the body of the pathogen)
Sulfonamides
Example of a -static Agent
-lytic Agents
Antimicrobial agent that kills by cell lysis and release of cytoplasmic contents
Penicillin, Detergents
What are 2 examples of -lytic agents?
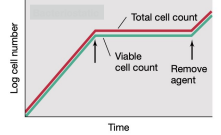
-static Agents
What is the antimicrobial agent that will show the data in the graph?
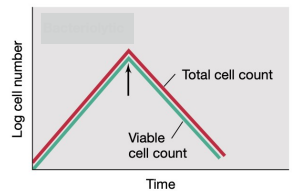
-lytic Agents
What is the antimicrobial agent that will show the data in the graph?
Food infection
FBD: Ingestion of food containing viable pathogens
Food Infection
FBD: Sufficient to cause colonization and growth of the pathogen in the host
Food Infection
FBD: With longer incubation time
Food Poisoning or Intoxication
FBD: Ingestion of foods containing preformed microbial toxins
Food Poisoning or Intoxication
FBD: Bacterial cells do not have to grow and are non-viable
Food Poisoning or Intoxication
FBD: Short incubation time
Toxin activity
What causes the illness in food poisoning or intoxication?