Introduction to Heart Anatomy
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pre-lecture content
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
heart function + location
the pump that drives the movement of blood around the cardiovascular system
located in thoracic cavity, posterior to sternum and on the superior surface of the diaphragm
pointed apex facing down, forward, and to the left
different between right and left side chambers
right side chambers more anterior (right atrium + ventricle)
left side chambers more posterior (left atrium + ventricle)
pericardium
supports + anchors heart in thoracic cavity; fibrous sac
fibrous pericardium (outermost)
serous pericardium
fibrous pericardium
outermost layer of dense CT
attaches to central tendon of diaphragm and sternal ligaments to anchor
serous pericardium
parietal: lines cavity wall
pericardial cavity: space between parietal and visceral pericardium that is filled with serous fluid
visceral: lines the heart
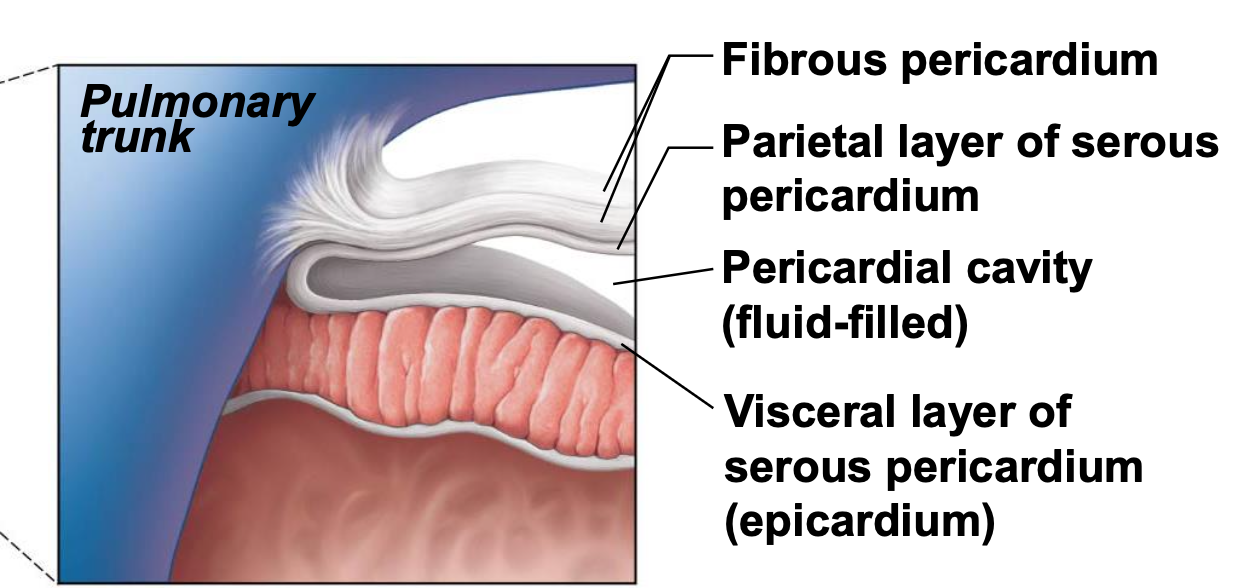
layers of the heart wall deep to pericardium
epicardium
myocardium
endocardium
epicardium
superficial layer made of visceral pericardium; underlying CT layer contains coronary vessels, nerves, and fat
myocardium
middle layer, made of cardiac muscle; important for impulse generation, propagation, and endocrine secretion
endocardium
deep layer, made of single layer squamous cells; subendocardial layer- loose CT with Purkinje fibers for conduction
cardiac muscle
in the myocardium; contraction of heart chambers
structural characteristics:
striated involuntary muscles
uni or bi nucleate cells
branched cells
contain intercalated discs
constant communication between cells by gap junctions
desmosomes hold muscle cells together
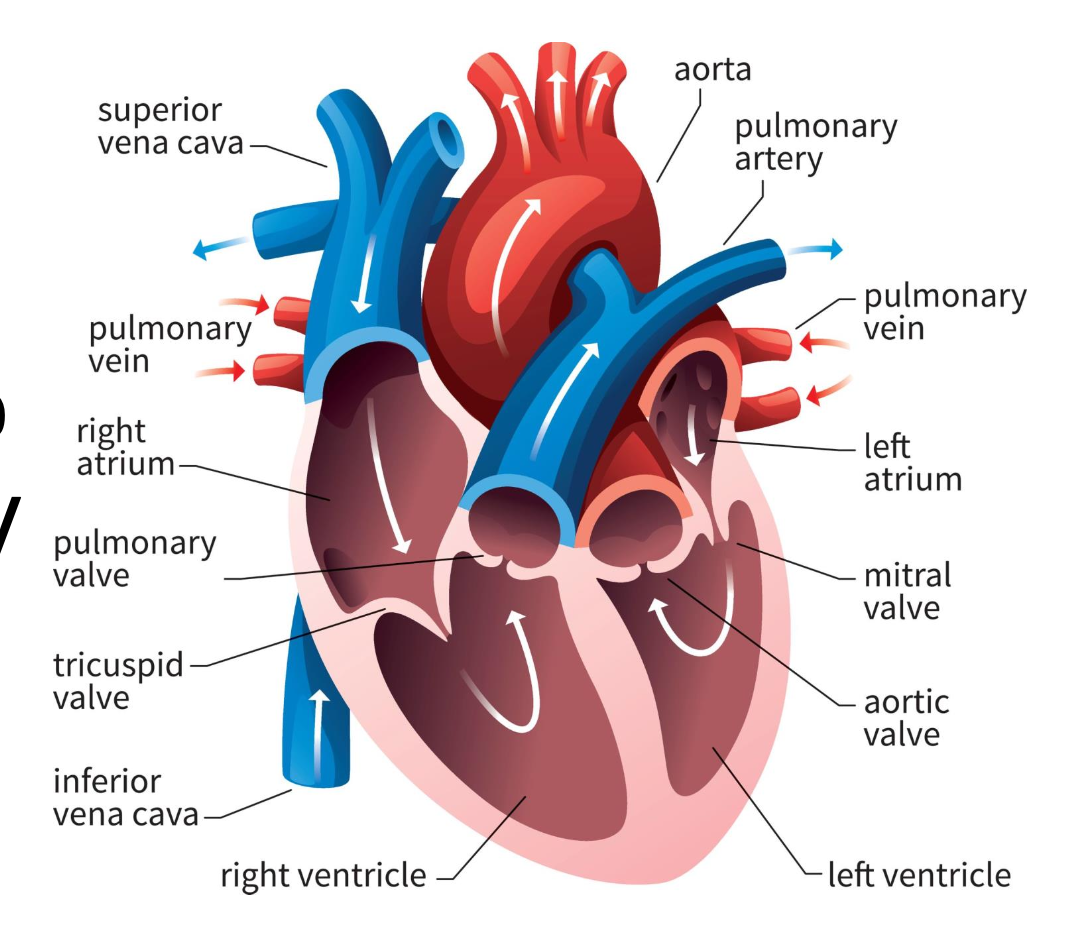
left ventricle
pump for systemic circuit; high pressure to get blood all over the body
right ventricle
pump for pulmonary circuit; doesn’t need as much pressure; does not need to pump as hard as left
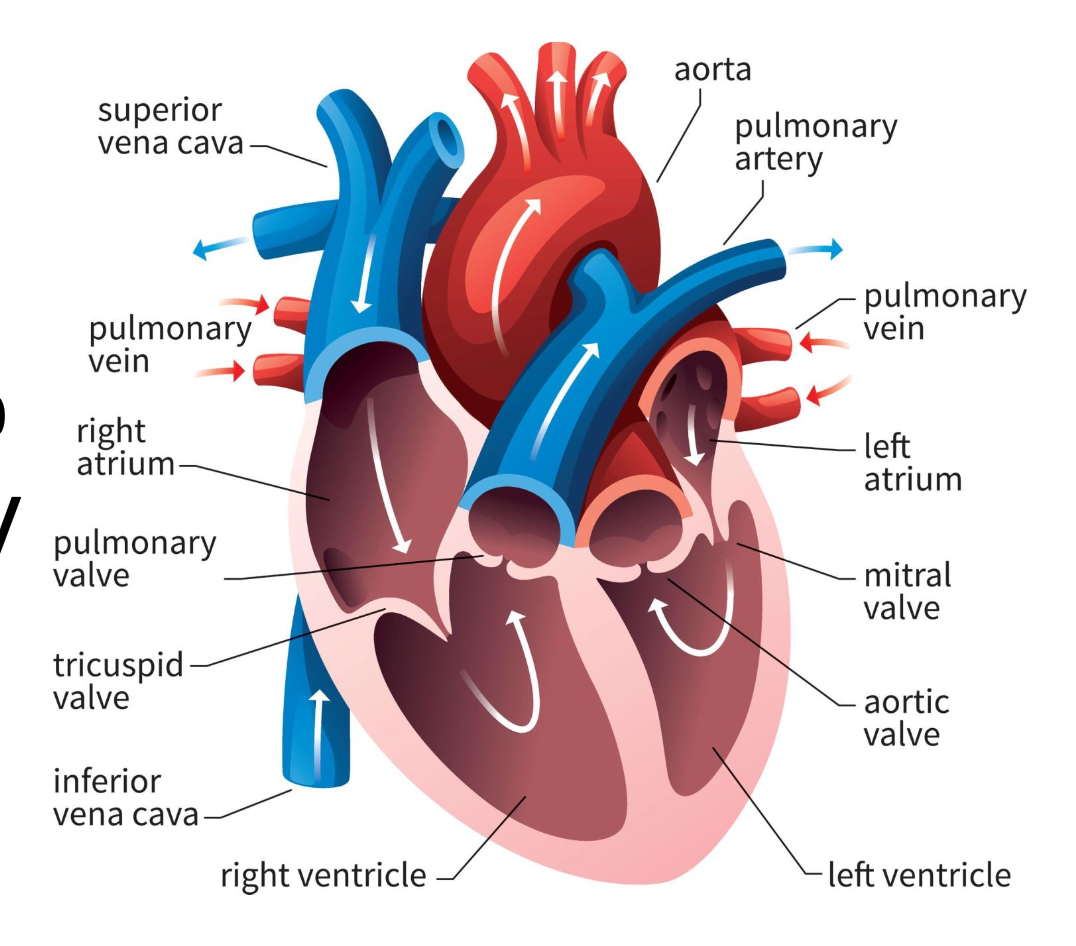
great vessels
bring blood back to the heart or take blood away from the heart
arteries
carry blood away from heart (usually O2 rich)
veins
carry blood back to heart (usually oxygen poor)
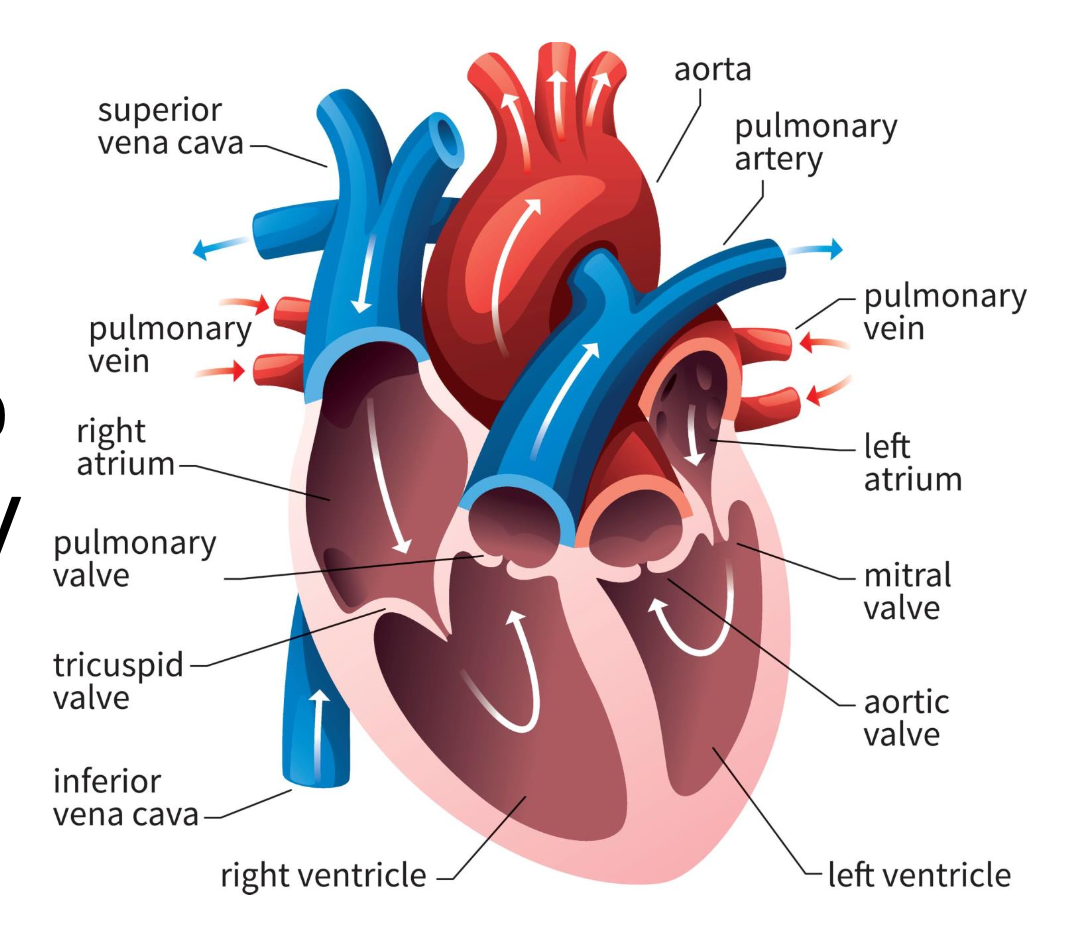
chambers
receive and pump blood (atrium and ventricle)
atrium
receives blood
ventricle
pumps blood out of heart
right atrium
blood from vena cavas and coronary sinus
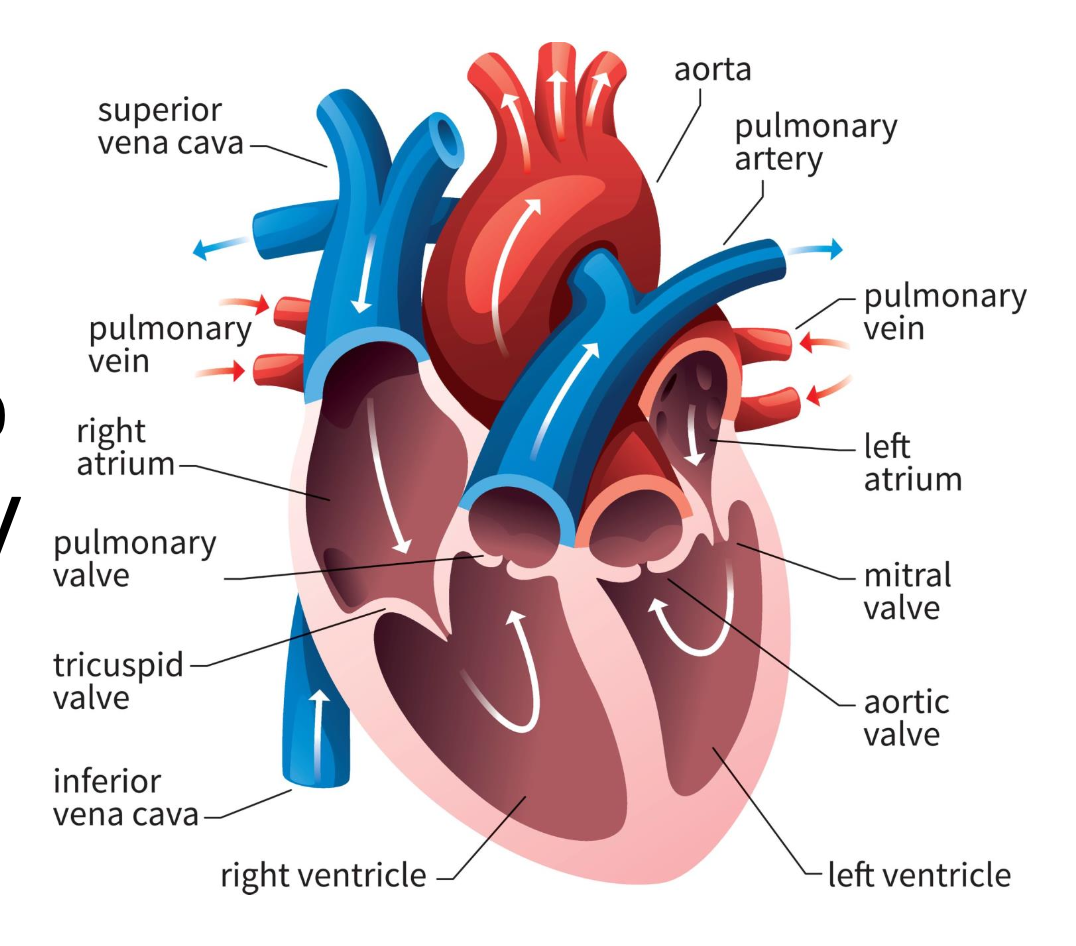
right ventricle
pumps blood toward lungs
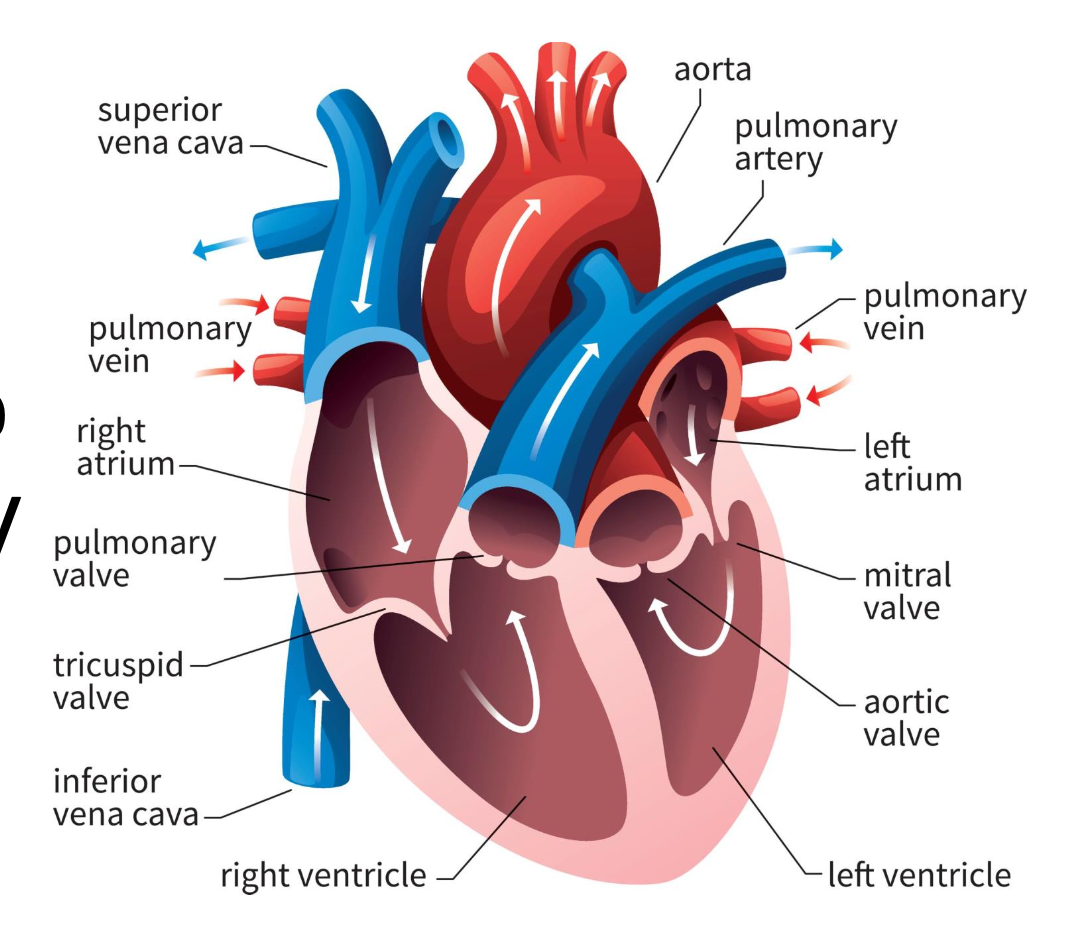
left atrium
blood from the pulmonary veins
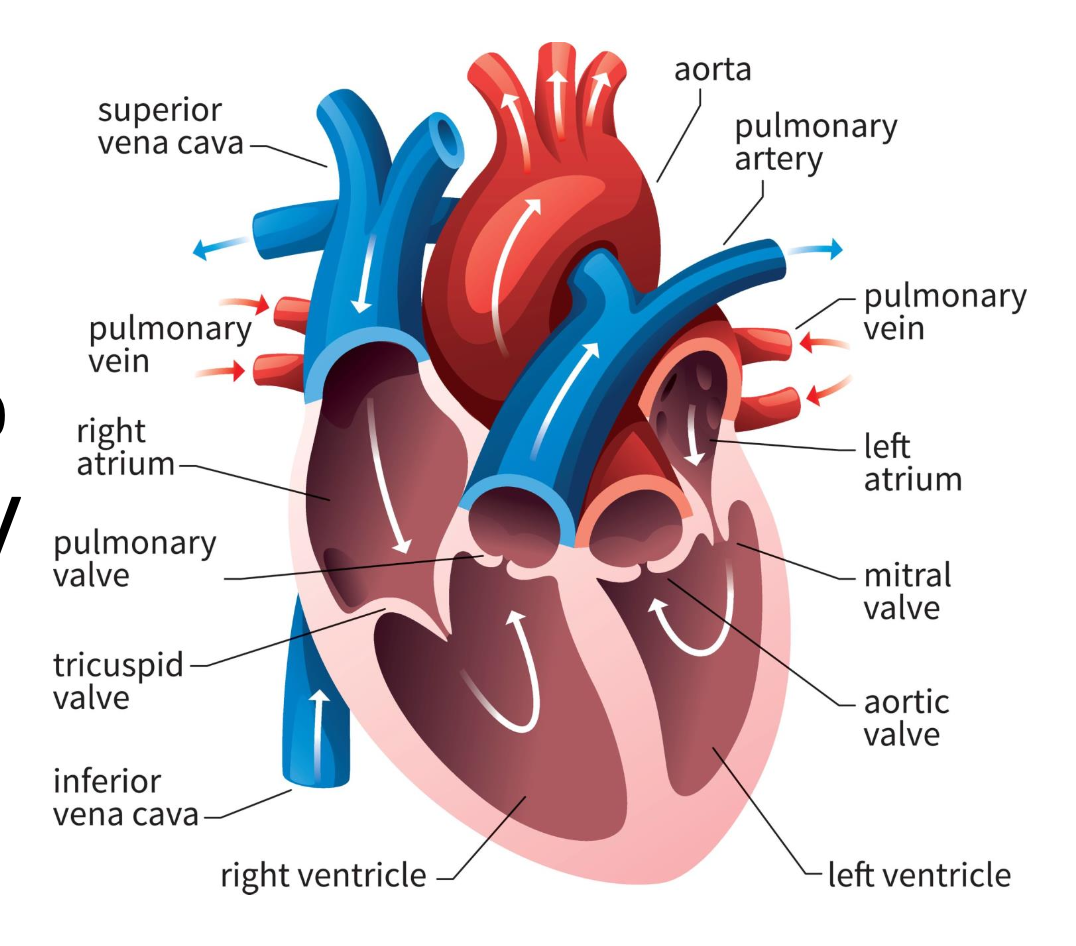
left ventricle
blood toward systemic tissues via the aorta
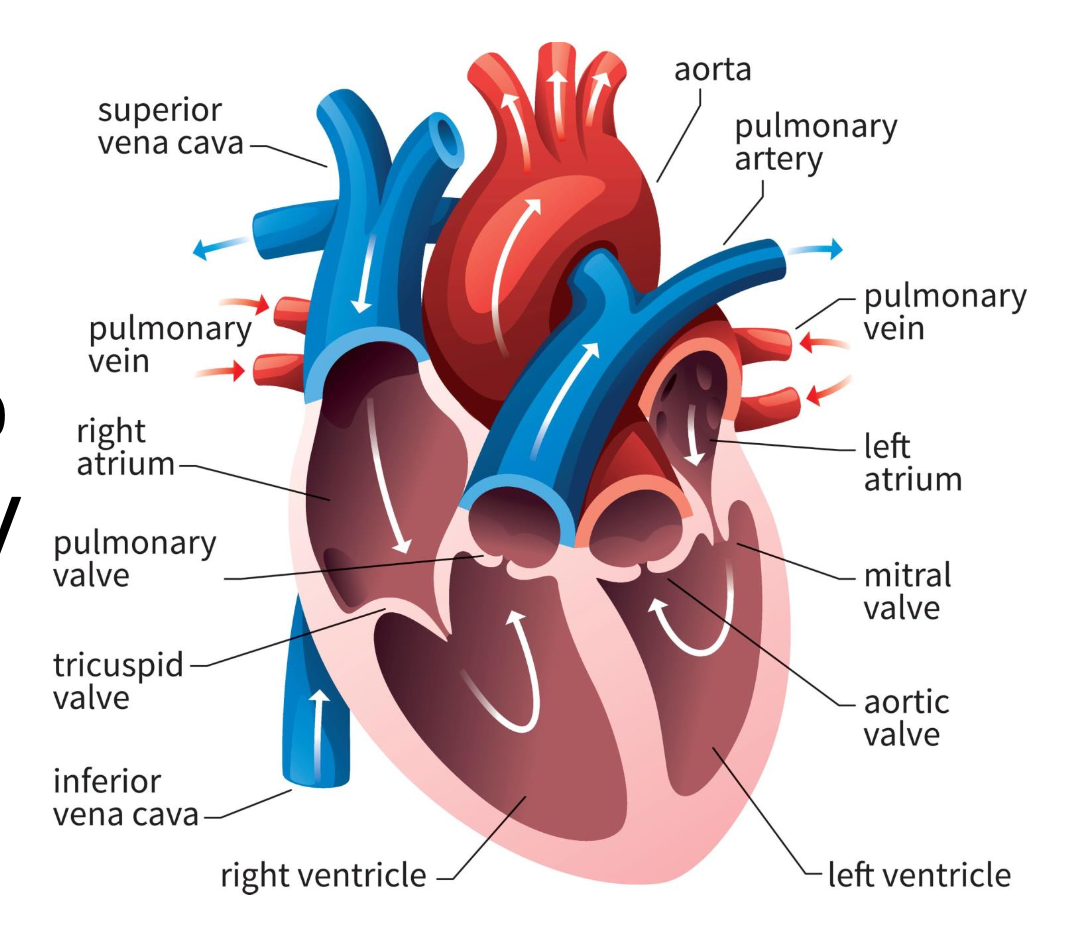
valves
separate ventricles and atria to prevent backflow of blood
right atrioventricular valve (tricuspid)
3 cusps; separate right atrium from ventricle
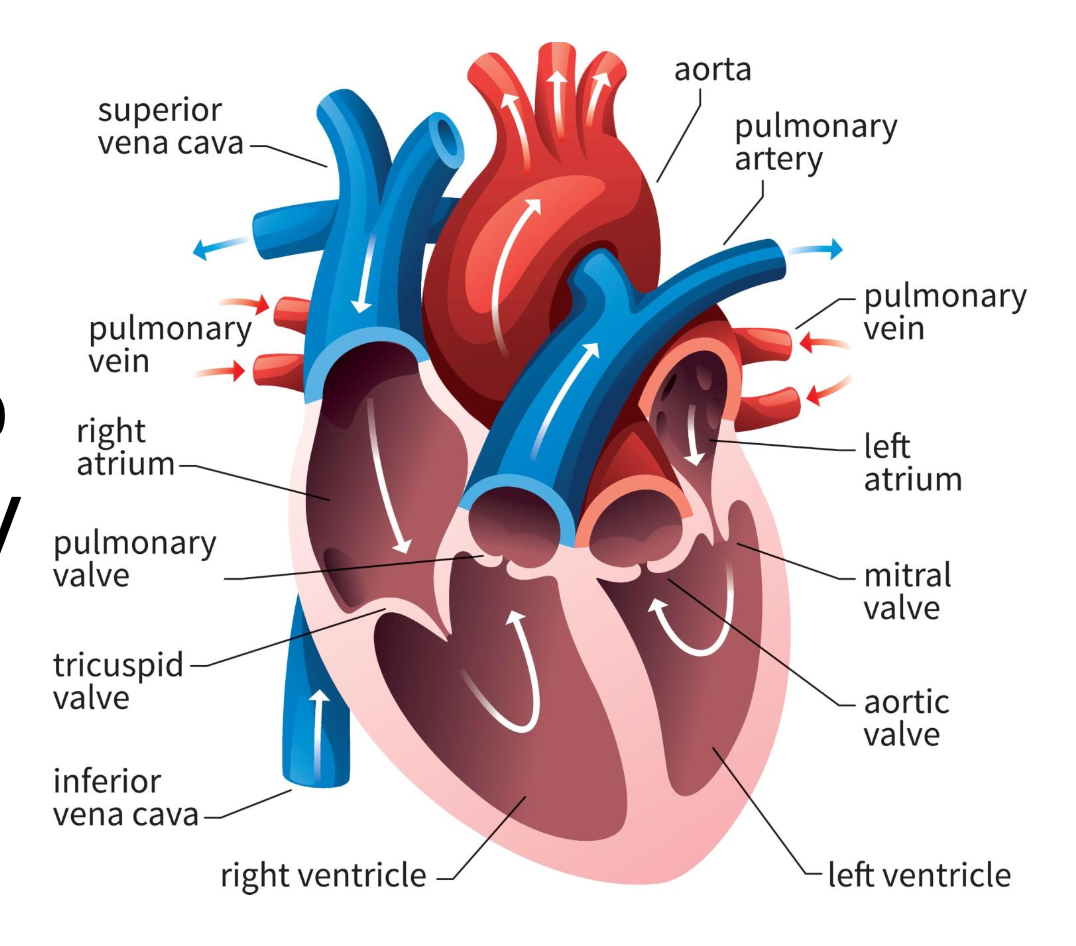
left atrioventricular valve (bicuspid)
2 cusps; separate left atrium from ventricle
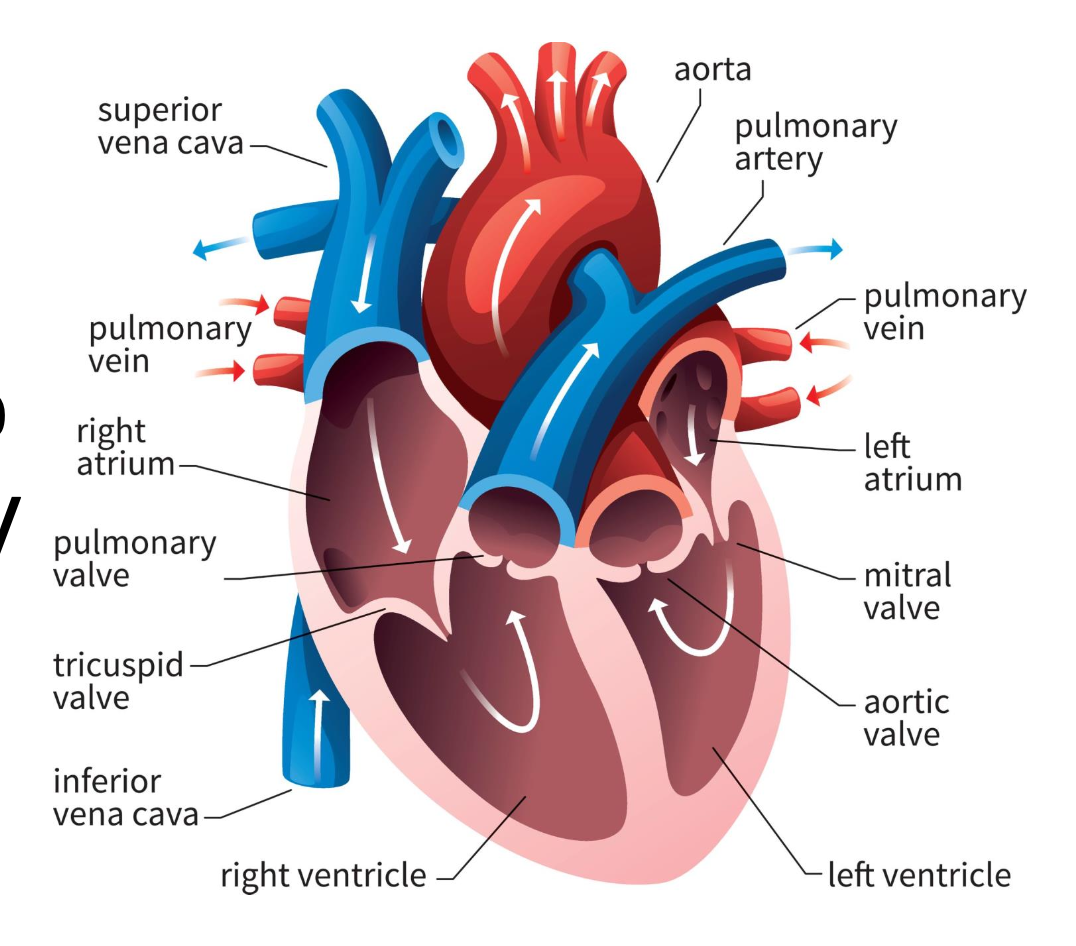
semilunar valves
separate ventricles from circuits
pulmonary semilunar valve
connects right ventricle and pulmonary trunk to pulmonary arteries to lungs
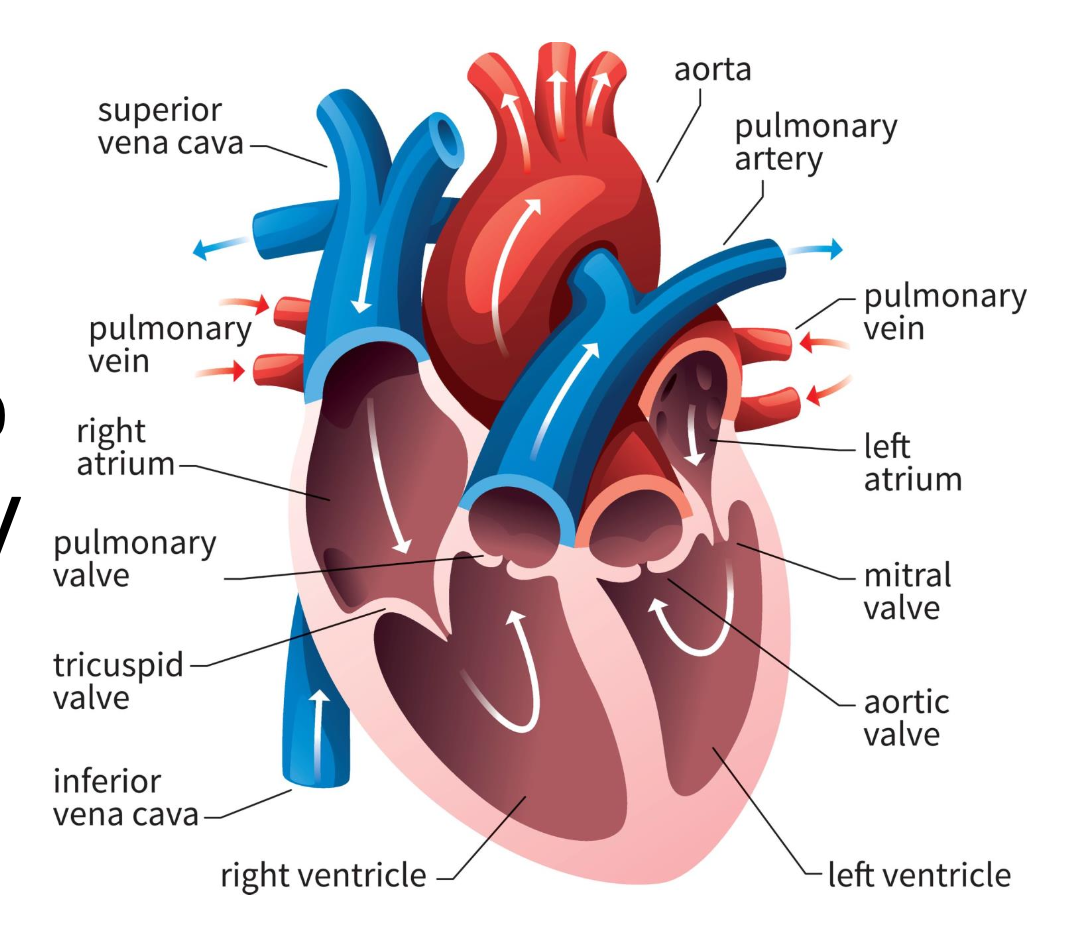
aortic semilunar valve
blood is pumped from left ventricle into systemic circuit via aorta