2BIO Cells
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Cell membrane
Double layer of lipids enclosing the cytoplasm
acts as a protective barrier to transport substances in and out the cell
formula for ANAEROBIC respiration
C6H12O6 -> 2C3H6O3
formula for AEROBIC respiration
C6H12O6+6O2→6CO2+6H2O+ATP
formula for photosynthesis
6CO2+6H2O+Light Energy→C6H12O6+6O2
Cell wall
Cellulose layer that surrounds plant cells
provide structural support, maintain shape
Cells
the basic building blocks of living things
chloroplast
organelle which is the site of photosynthesis
cillia
hair-like projections used by the cell to move
cytoplasm
semi-fluid substance filling the cell interior
a jelly-like fluid that holds organelles in place and provide a place where chemical reaction can happen
cytoskeleton
structure which maintains the shape of the cell
endoplasmic reticulum
system of membranes and connecting tubes
purpose is to synthesize proteins (RER) and steroids (SER) and to transport them
flagellum
A whip-like extension which enables locomotion (movement of organism)
Golgi Body
Flat disc-shaped sacs in the cytoplasm
purpose is to transport, sorting and modification of both protein and lipid
lysosome
sac containing digestive enzymes
breaks down dead or worn out organelles
Mitochondria
organelle where aerobic respiration happens
generates most of the cells energy in form of ATP through cellular respiration
nucleus
structure in cell containing genetic information as DNA in chromosomes
organelles
various structures within the cytoplasm
Ribosomes
site where protein synthesis happens
vacuole
sac containing water or storage products
Active transport
using energy to move molecules against a concentration gradient
concentration gradient
difference in concentration either side of a semi-permeable membrane
diffusion
moving from high to low concentration
endocytosis
taking large molecules into a cell by moving the cell membrane to form vesicles
facilitated diffusion
A passive transport method that uses one type of molecule to move another
flaccid
a cell that has lost its shape due to a loss of turgor pressure
ion pump
a protein channel in the cell membrane that moves ions against the concentration gradient
osmoregulation
the control of osmotic pressure inside cells
Osmosis
the movement of water from an area of high to low water potential
passive transport
any method that moves a substance down a concentration gradient without using energy
phagocytosis
type of active transport that “eats” large particles such as bacteria. located in white blood cells.
pinocytosis
taking water into the cell by cytosis (cell drinking
semi-permeable
A membrane that will let through very small molecules but not larger ones (controls which substances can pass through while others cant)
surface area:volume ratio
a measure of how much surface area there is per unit volume.
If SA and V increase the SA:V ratio decreases
If SA and V decreases the SA:V increases
turgor
osmotic pressure inside a cell that helps it keep its shape
vesicle
used for transporting substances to or from the cell membrane
activation energy
amount of energy needed to start a reaction
active site
part of enzyme which substrate fits into
aerobic respiration
releasing energy from food using oxygen
anaerobic respiration
occurs in the absence of oxygen
ATP
carries small amounts of energy for the cells to use for processes
catalyst
reduces the activation energy for a reaction
cofactor (non protein) AND coenzyme (organic)
a chemical that acts WITH an enzyme; completes the active site
electron transport chain
reactions on cristae of mitochondria; generates most ATP; H2O = waste
enzyme
biological catalyst with an active site specific to the substrate(s)
fermentation
results in alcohol and carbon dioxide gas
glycolysis
splits glucose into two pyruvate molecules
kreb's cycle
series of enzyme catalysed reactions in the mitochondrial matrix CO2 = waste
light dependent phase
uses sunlight to split water into hydrogen and oxygen; also charges up ATP
light-independent phase
fixes carbon as glucose
substrate
chemical that an enzyme acts upon
membrane bound organelles
regular organelles found in the cytoplasm
prokaryotic cells
no membrane bound organelles
eukaryotic cells
have membrane bound organelles
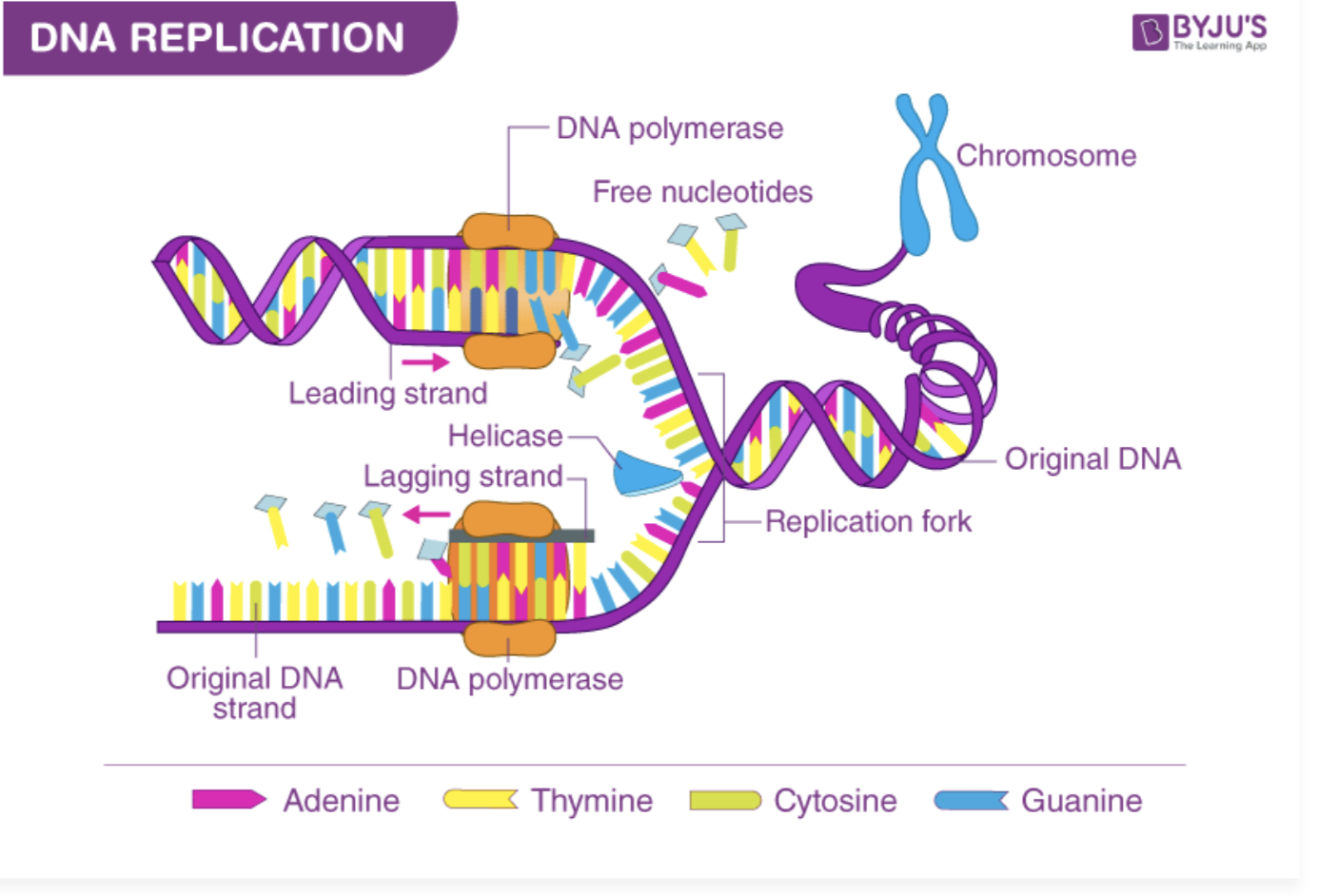
DNA replication
to create two identical copies of the DNA, making sure that during cell division each daughter cell has a set of genetic instruction
Double helix
DNA consists of two long strands which are twisted around each other forming a helix. The strand runs from opposite directions (5' to 3’) and (3’ to 5’)
DNA polymerase
synthesizes new strands by adding nucleotides
Helicase
The enzyme responsible for unwinding the DNA during cell division by breaking hydrogen bonds
Primase
synthesizes a short RNA primer since DNA polymerase needs this primer for DNA synthesis
DNA synthesis
AKA DNA replication where two copies of the DNA are produced
RNA primer
a short segment of RNA nucleotides that acts as a starting point in DNA synthesis
DNA ligase
joins the okazaki fragments which creates a continuous strand
Leading strand
synthesized continuously TOWARDS the replication fork
lagging strand
made up of short fragments (okazaki fragments) AWAY from the replication fork
replication fork
location where ezymes do their jobs like
helicase : unwinding the strands
synthesized
build or made
okazaki fragments
short fragments of DNA synthesized on the lagging strand during DNA replication
synthesized mean by how DNA polymerase copies that specific strand during replication