Behavioral Neuroscience - Exam 2
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
what is a zygote?
A single fertilized cell
What are the three stages of prenatal development?
germinal stage
embryonic period
fetal period
Germinal stage
conception through first two weeks of pregnancy.
embryonic period
2-8 weeks, the fetus begins to mature.
fetal period
8 weeks - birth
the fetus, eventually the baby, continues maturing.
blastocyst
clump of multiplying cells.
trophoblast
considered as the “life support”, consists of the placenta and the umbilical cord.
implantation
the egg goes into the uterus.
endoderm
digestive, respiratory systems
mesoderm
cirulatory, reproductive systems + bones
eetoderm
nervous system + skin
placenta
an organ that develops in the uterus. filters out the bad to protect the fetus
umbilical cord
a temporary organ that attaches the mom and the baby
amnion
the fluid that cushions the baby
when does the neural tube development start?
around the 3rd week of pregnancy
what does the neural tube eventually become?
the brain and the spinal cord
what is organogenesis?
the creation of organs
fetal development
2 months - birth
continued growth of the fetus and organ maturation of the organs that emerged from the previous period
when is a baby viable (able to breathe on its own)?
24 weeks
phases of neurodevelopment
induction of the neuroplate
neuralproliferation - making more neurons
migration and aggregation - making a structure with connections
axon growth and synapse formation
neuron death + synapse arrangement
the neuron plate…
folds and diffuses
ventricular zone
neural stem cells, where neurons are made
totipotent vs. multipotent
totipotent cells can become any cell in an organism
multipotent cells are limited in what type of cell they can become
stem cells
are also in the nervous system
now come from the placenta and the umbilical cord
radial migration
newly formed neurons are perpendicular to the neural ventricular surface.
tangential migration
newly formed neurons are parallel to the pial surface (of the developing brain)
somal translocation
similar to radial migration excluding the grial cells
glia-mediated migration
the neuron gets on an extended glial cell to the ventricular surface
aggregation
becoming a neural structure
growth cone
the tip of the growing axon
chemoaffinity hypothesis
the growth cone will be attached to certain chemicals
guidance molecules…
guide the growth cone to the target
pioneer growth cone
the cone that has found the path first.
synapse formation (synaptogenesis)
the process of forming synapses; it is important for the synapses to make connections for communication
at birth, the brain is about ____ the size of an adult brain
25%
brain weight ______ over the course of the first ____ years of life.
triples
two
when does pruning occur?
it occurs throughout development
why is it important for the prefrontal cortex to develop?
to have a working memory
to plan and carry out sequences of actions
to inhibit responses that are inappropriate in the current context.
deprivation vs. enrichment
depriving resources, experiences, and stimuli can negatively affect brain structure, cognition and behavior.
allowing individuals to do so can assure proper growth of the brain structure, more appropriate behavior, and proper cognition.
competitive nature of the brain
if one part of the brain is not fully developed, another part of the brain takes over (plasticity), meaning that processing is less efficient.
topographic sensory cortex map
a map of the brain that shows the arrangement of sensory receptors preserved in the cortical area.
a representation of sensory information
neuroplasticity in adults
we do not make new neurons, so we have to form synaptic connections
what are the effects experiences have on connections?
experiences make those connections stronger.
your reality is your ___________. (ex. colorblind people, synethisia)
perception
sensation v. perception
input sensory physical stimuli (s)
psychological interpretation (p)
irises
the colored part of your eye that is located behind the cornea.
sensitivity
the ability to detect movement and edges
acuity
color and fine details
lens
the elastic structure located behind the iris by which light is focused on to the retina.
accommodation
the ability to change your focus from farther to nearer objects by changing the lens
binocular disparity
the image being shown will be different in your left eye
left hemisphere - right eye, right hemisphere - left eye
optic chiasm
where all the information gets flipped
what are the receptors for the visual system?
cones and rods
cones
light-sensitive cells located in the retina. hot colors, best in bright light
rods
photoreceptor cells located in the retina. cool colors, best in low light
what is the issue with rods?
the light would have to go through four layers in and back.
what is the difference between photopic and stotopic visions?
photopic focuses on visual while stotopic focuses on movement
spectral sensitivity core
how biological and/or digital sensors respond to different wavelengths of light.
phototopic spectral sensitivity core
the (human) eye’s responses to bright light
stotopic spectral sensitivity core
peak sensitivity of the rods in the eye, which is 507mn blue-green
purkinje effect
the movement from rods to cones, and how that leads to us being sensitive to some colors.
saccades
changes from fixation to fixation, frequent action leads to change blindness
fixation
the ability to focus your eye on a specific subject
change blindnesss
when you cannot notice the difference in your visual environment
inattentional blindness
you don’t perceive (or pay attention) to what was infront of you.
sensory cortex
a region of the brain that processes sensory information (touch, pain, temperature, pressure)
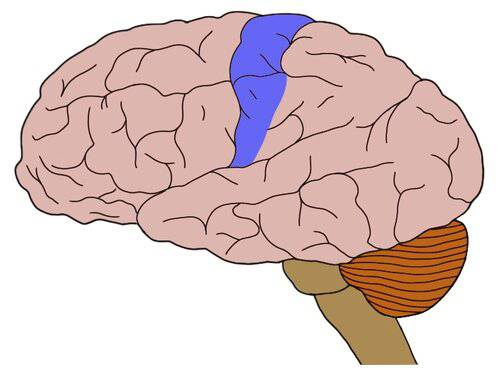
primary sensory cortex
first level of processing sensory information for vision, hearing, touch
secondary sensory cortex
second level of processing sensory information, integrates sensory information
association cortex
brain regions that integrate sensory information, plan motor actions, and supports complex cognitive functions