Pulmonary Exam 1: Histology - Respiratory System (Dr. Sun)
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
what are the 3 types of epithelium encountered in the respiratory system?
- Olfactory epithelium
- Conducting/respiratory epithelium
- Gas exchange epithelium
What is the type of epithelium for isolated locations of olfactory epitehlium pathway?
SSNKE
What cells are found in gas exchange epithelium?
types I, II alveolar cells (pneumocytes)
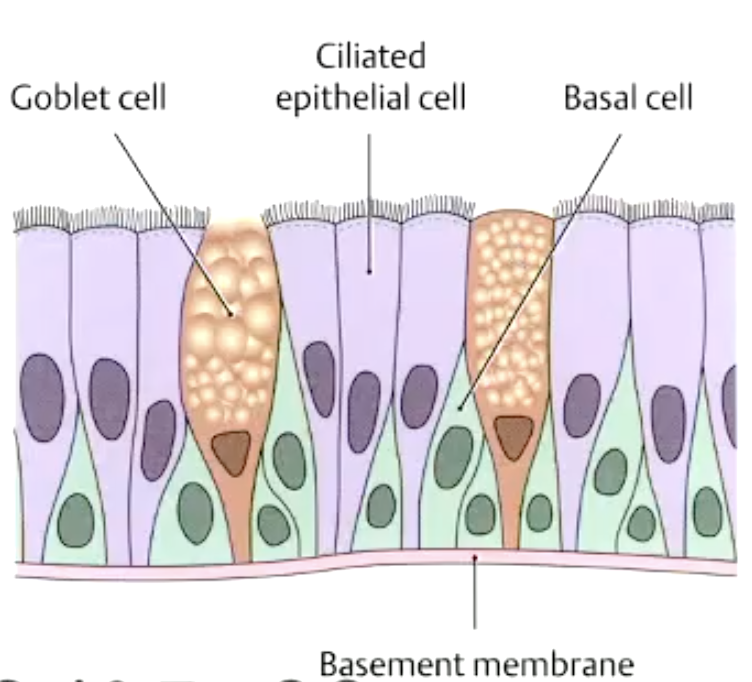
Name this epithelium
pseudostratified, ciliated, columnar epithelium with goblet cells
conducting/respiratory epithelium
where in the respiratory tract can conducting epithelium be found? (5)
- nasal cavity
- larynx, trachea
- bronchi
- intrapulmonary bronchi
as you move distally down the trachea in deeper passageways, the epithelium goes from pseudostratified, ciliated, columnar epithelium to ________
non-ciliated cuboidal epithelium
what are the 3 cells found in olfactory epithelium?
- Supporting cells (sustentacular cell)
- Olfactory cells (bipolar neuron)
- Basal cells
this part of the olfactory epithelium can be regenerated, but regeneration ability is reduced in patients with Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases
Bipolar neuron (olfactory cells)
Bipolar neurons in olfactory cells have a regenerative capability, but this can be reduced in Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases, consequently reducing...
Odor discrimination
what type of glands can be found in olfactory epithelium?
olfactory (Bowman) gland
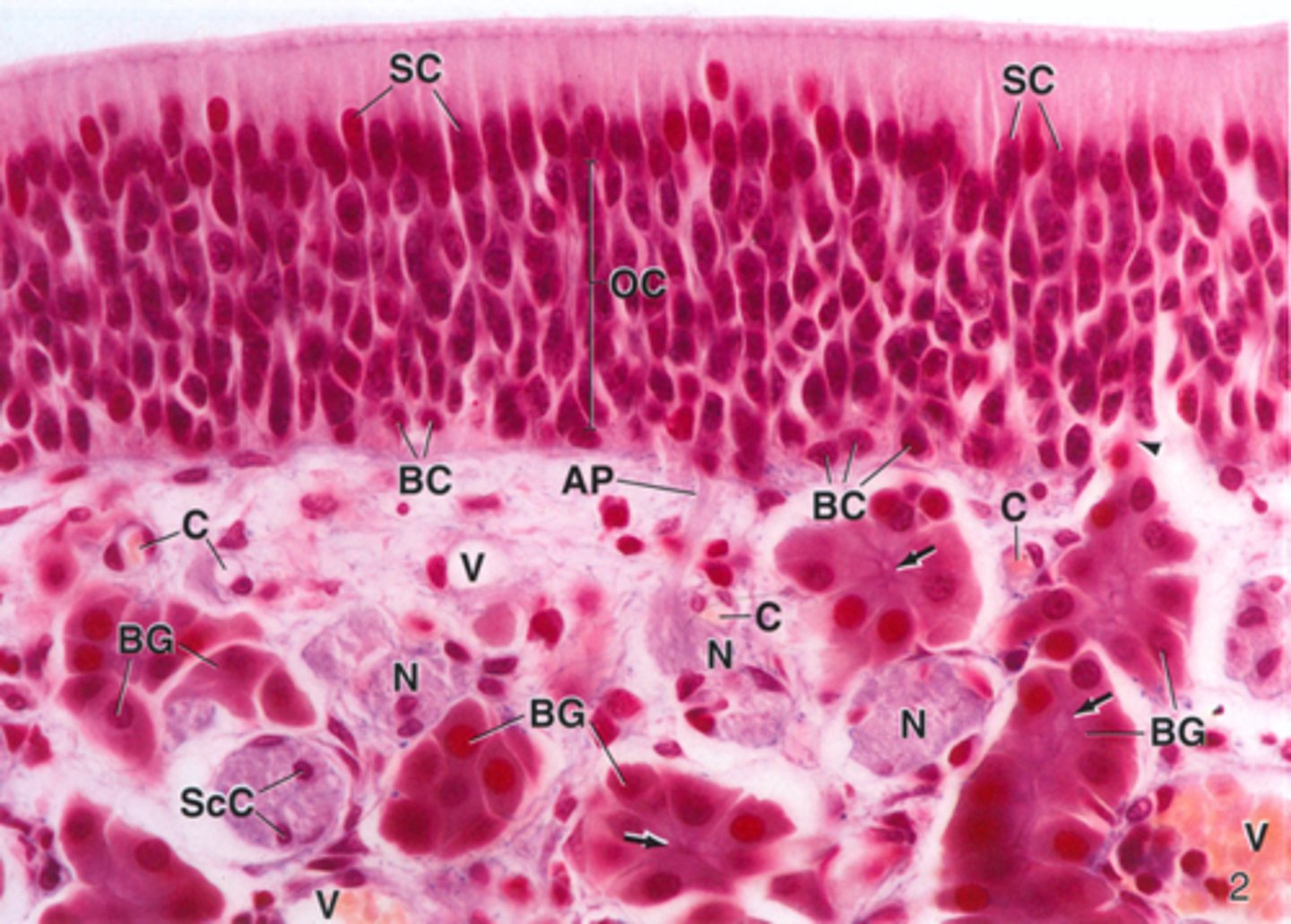
ID the type of epithelium:
olfactory epithelium
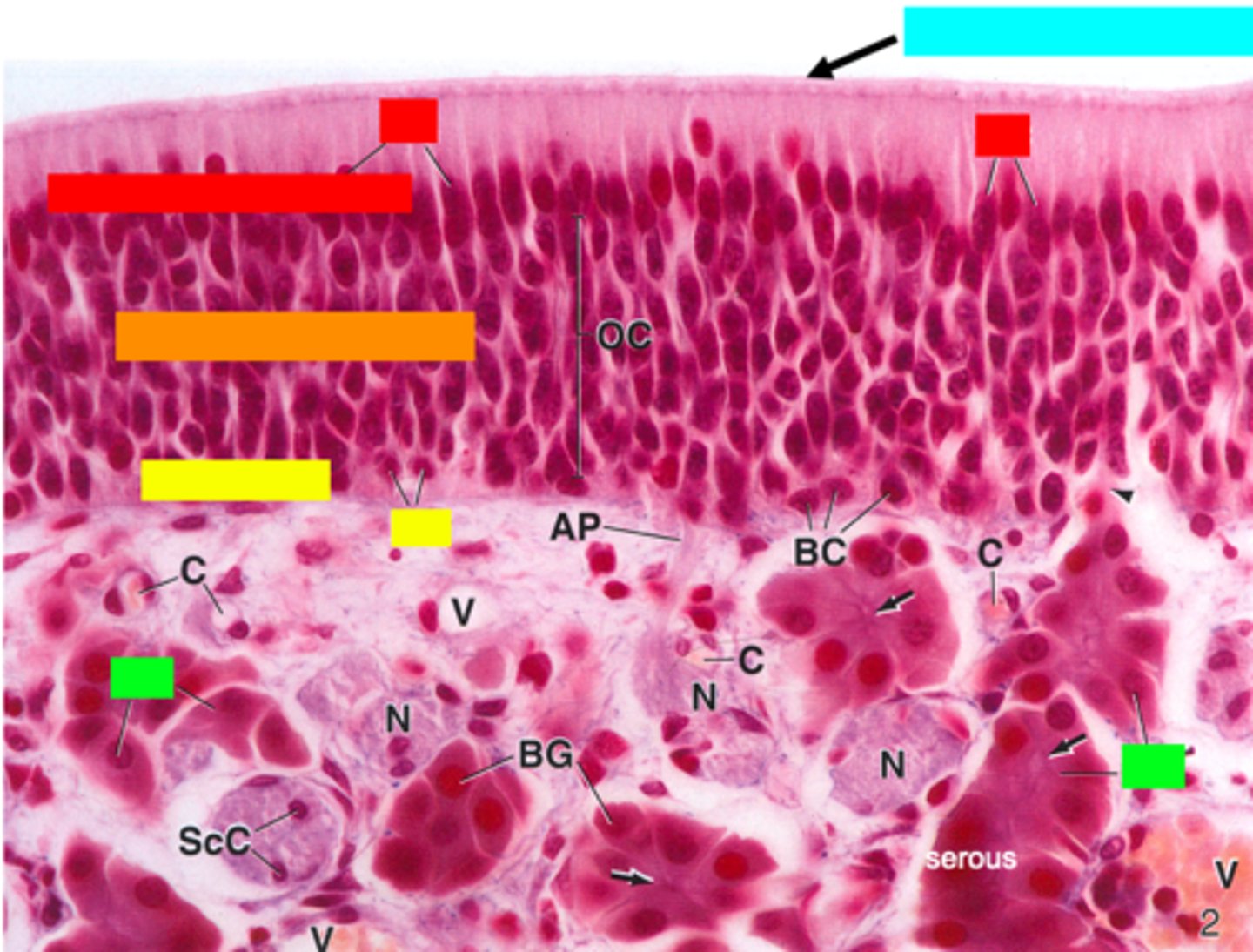
ID the red box:
supporting cells
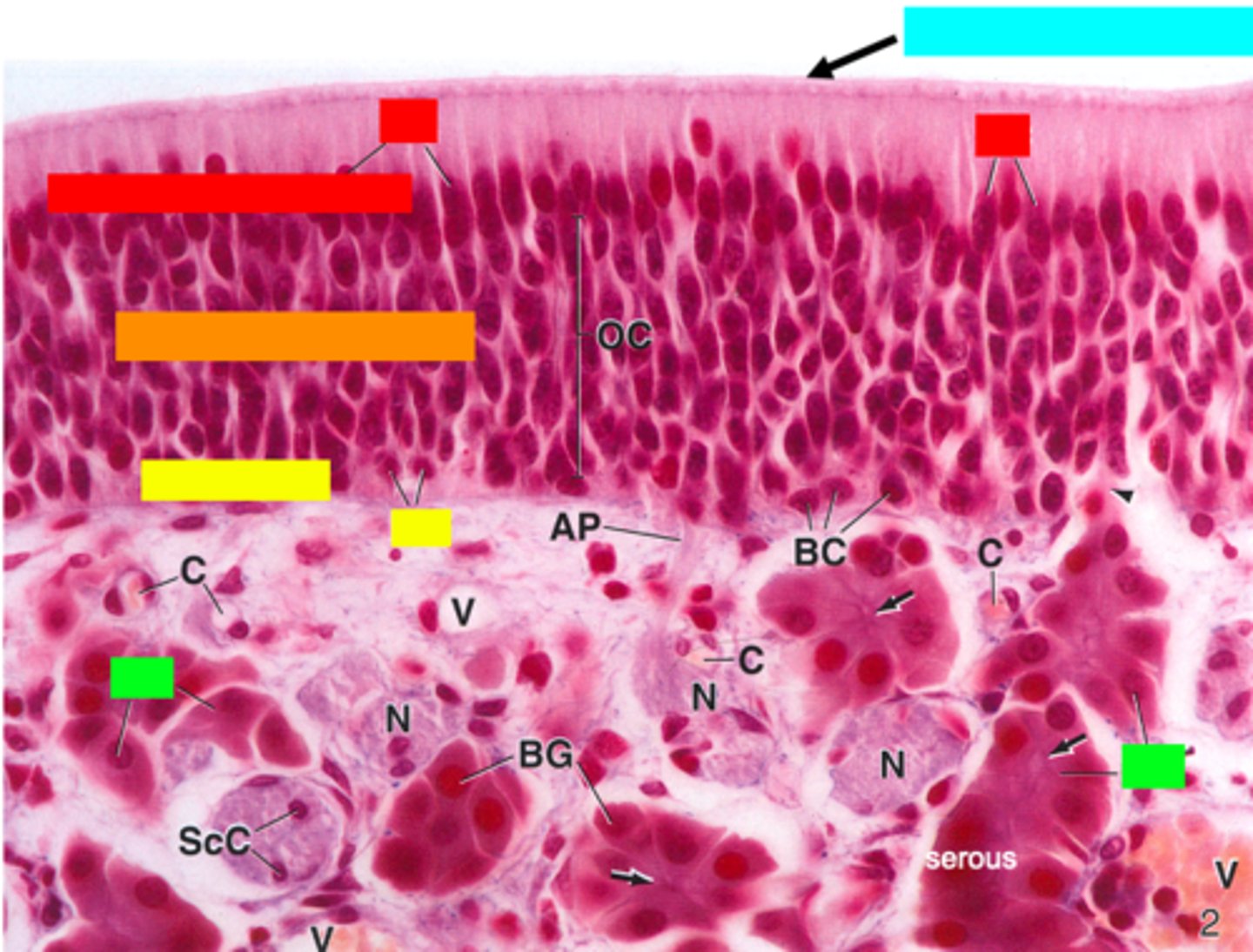
ID the orange box:
olfactory cells/bipolar neurons
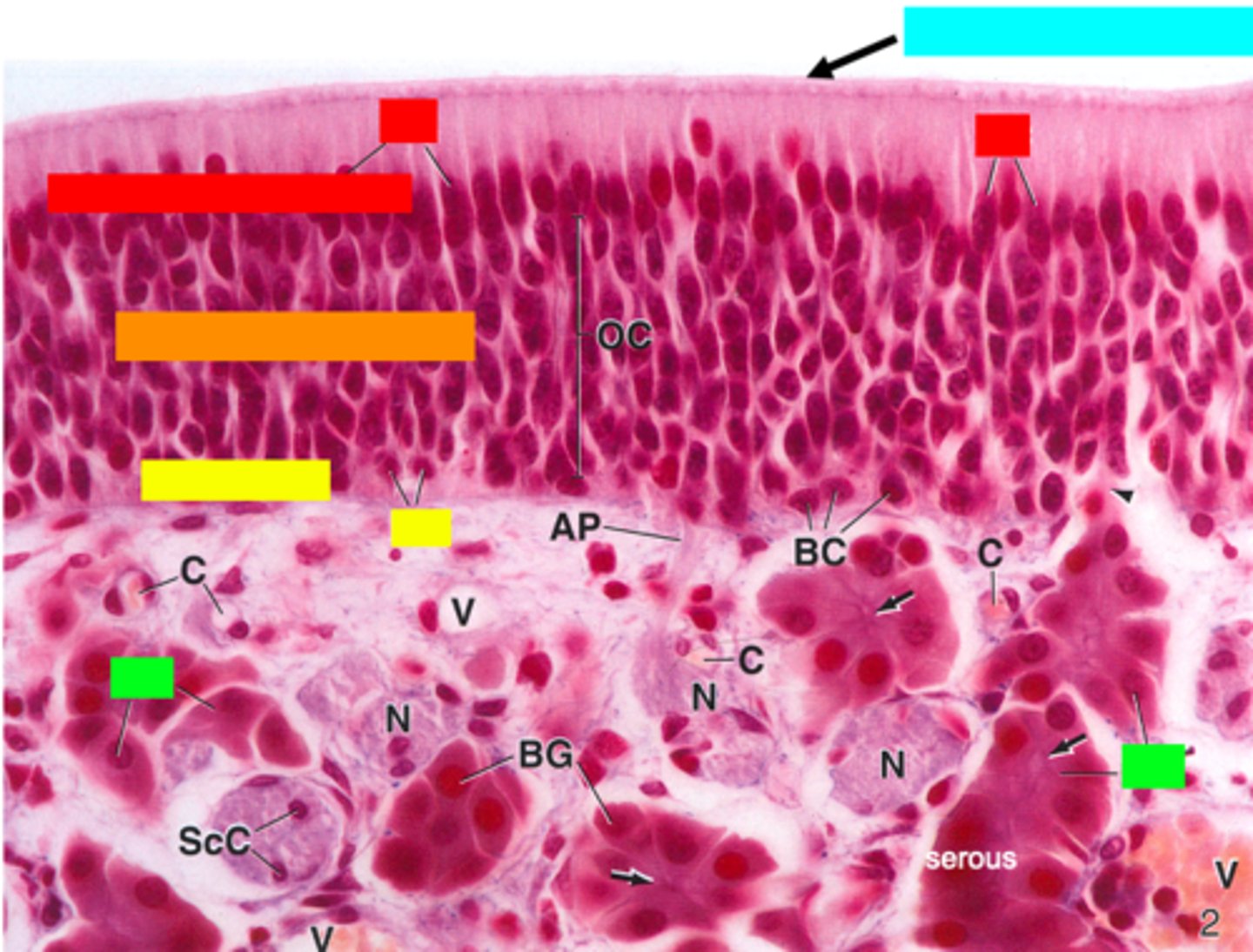
ID the yellow box:
basal cells
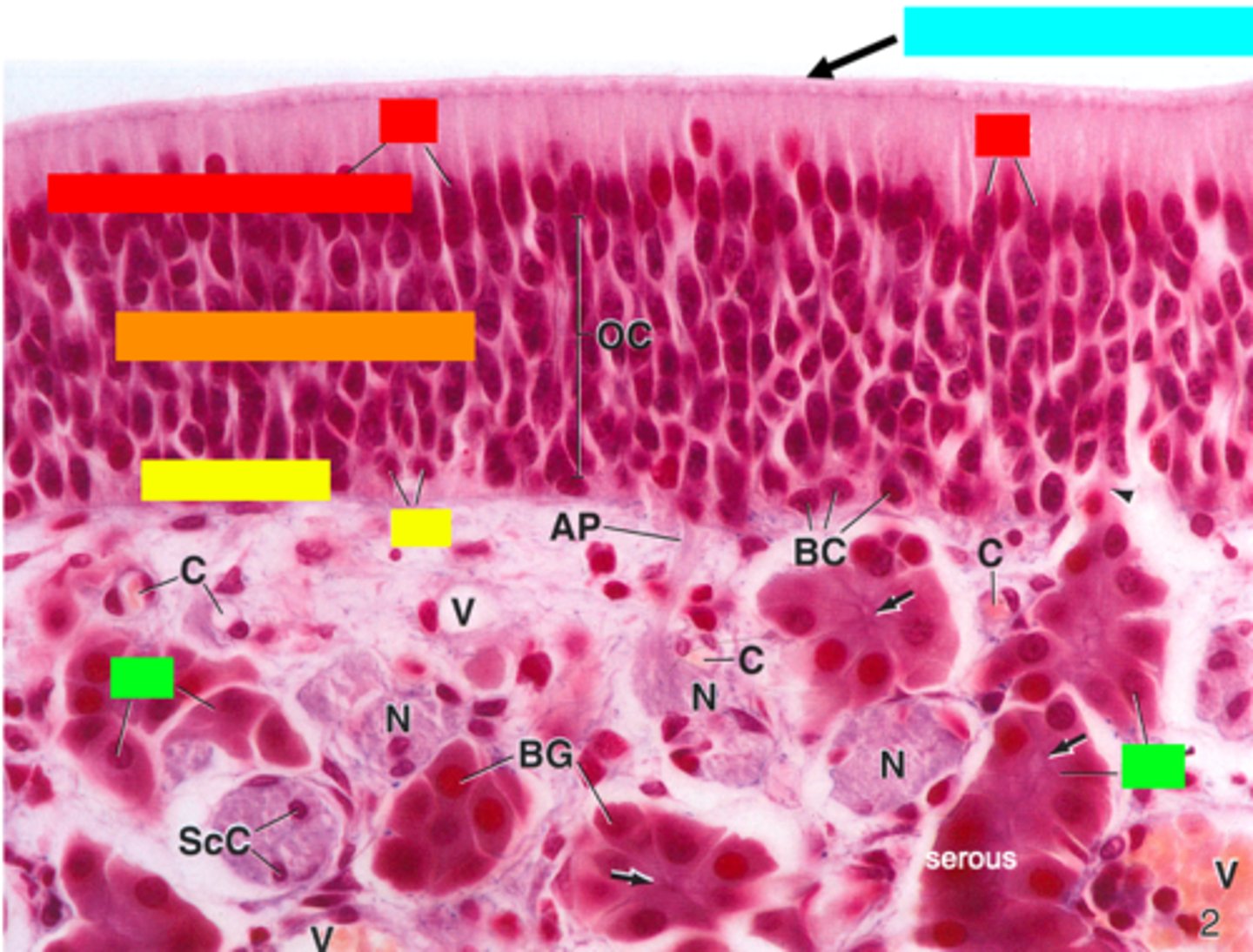
ID the green box:
olfactory (Bowman) gland
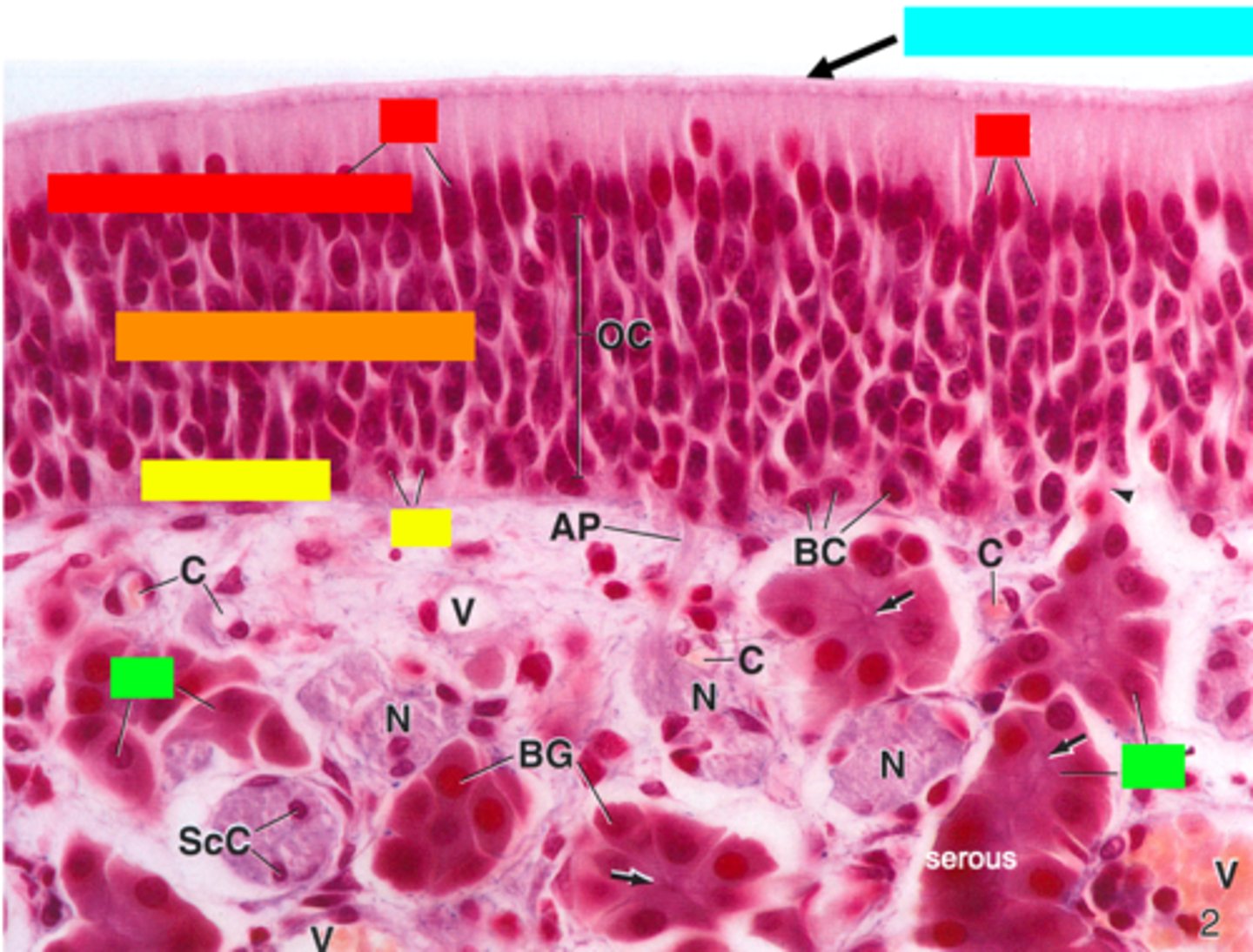
ID the blue box:
non-motile cilia
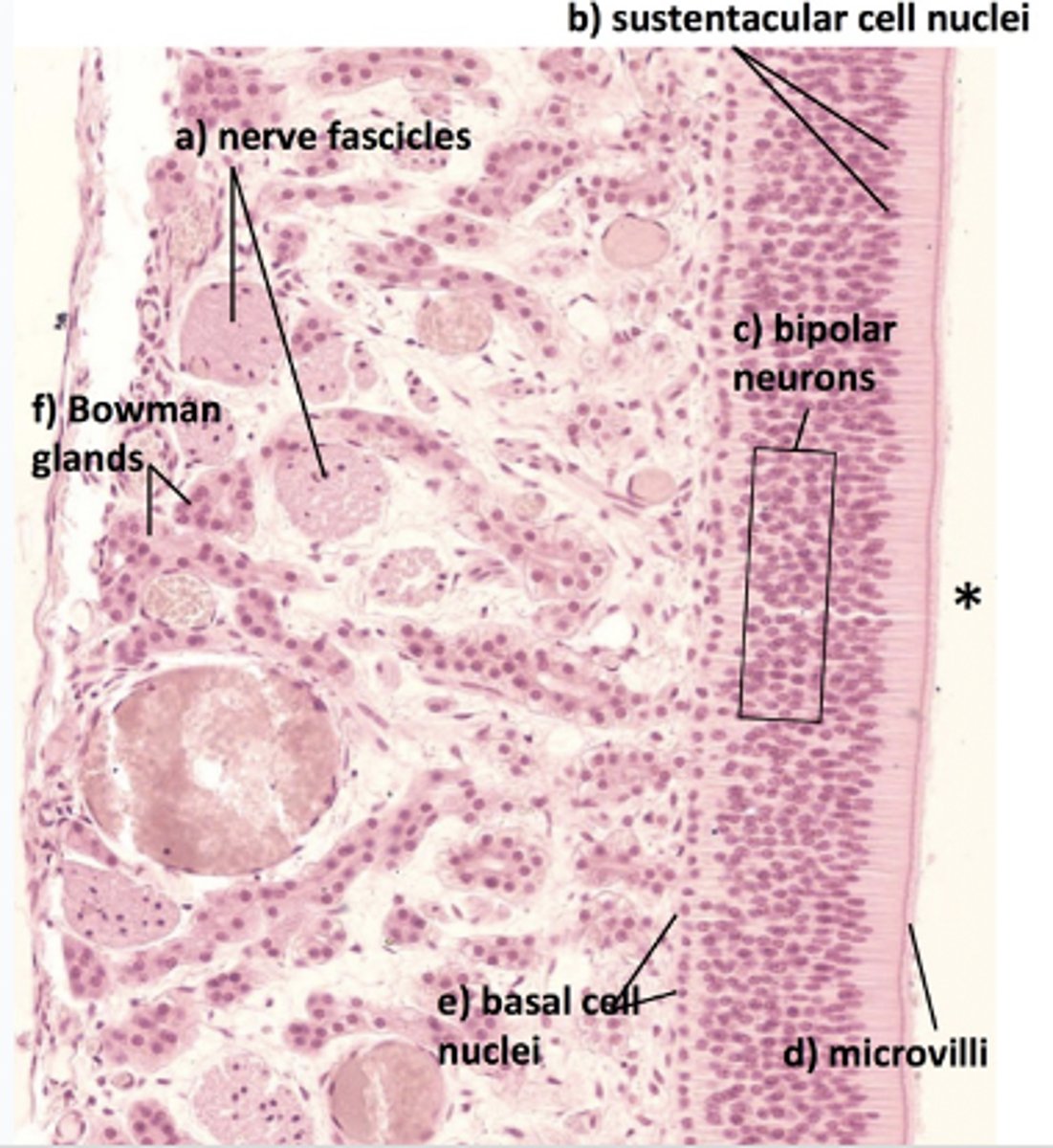
What is mislabeled?
D (non-motile cilia)
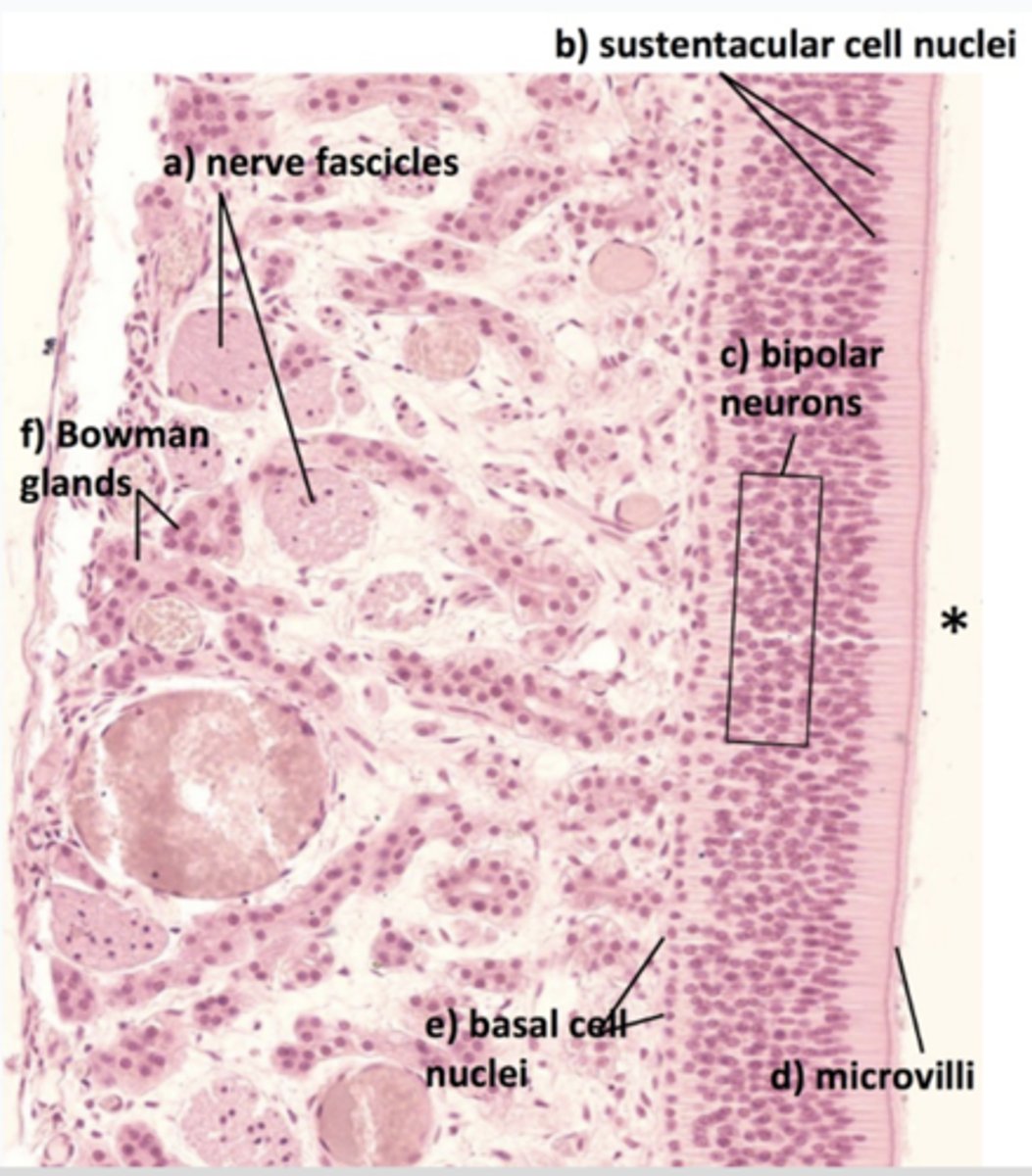
In what region is the asterisk located?
Olfactory epithelium (top 1/3 of nasal cavity)
what type of glands are Bowman's glands?
serous
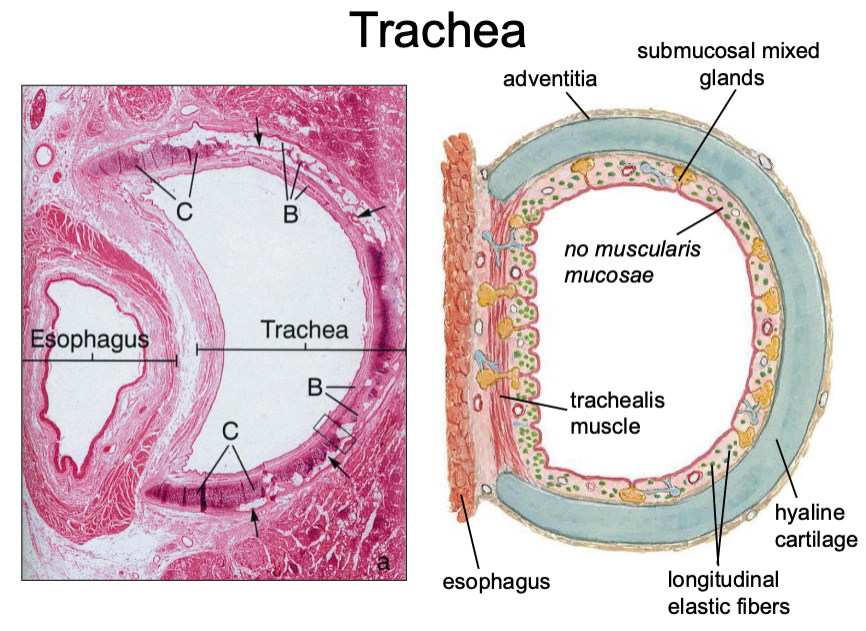
what muscle sits between the esophagus and the trachea?
trachialis muscle
What space is known as inside the lung?
Intrapulmonary
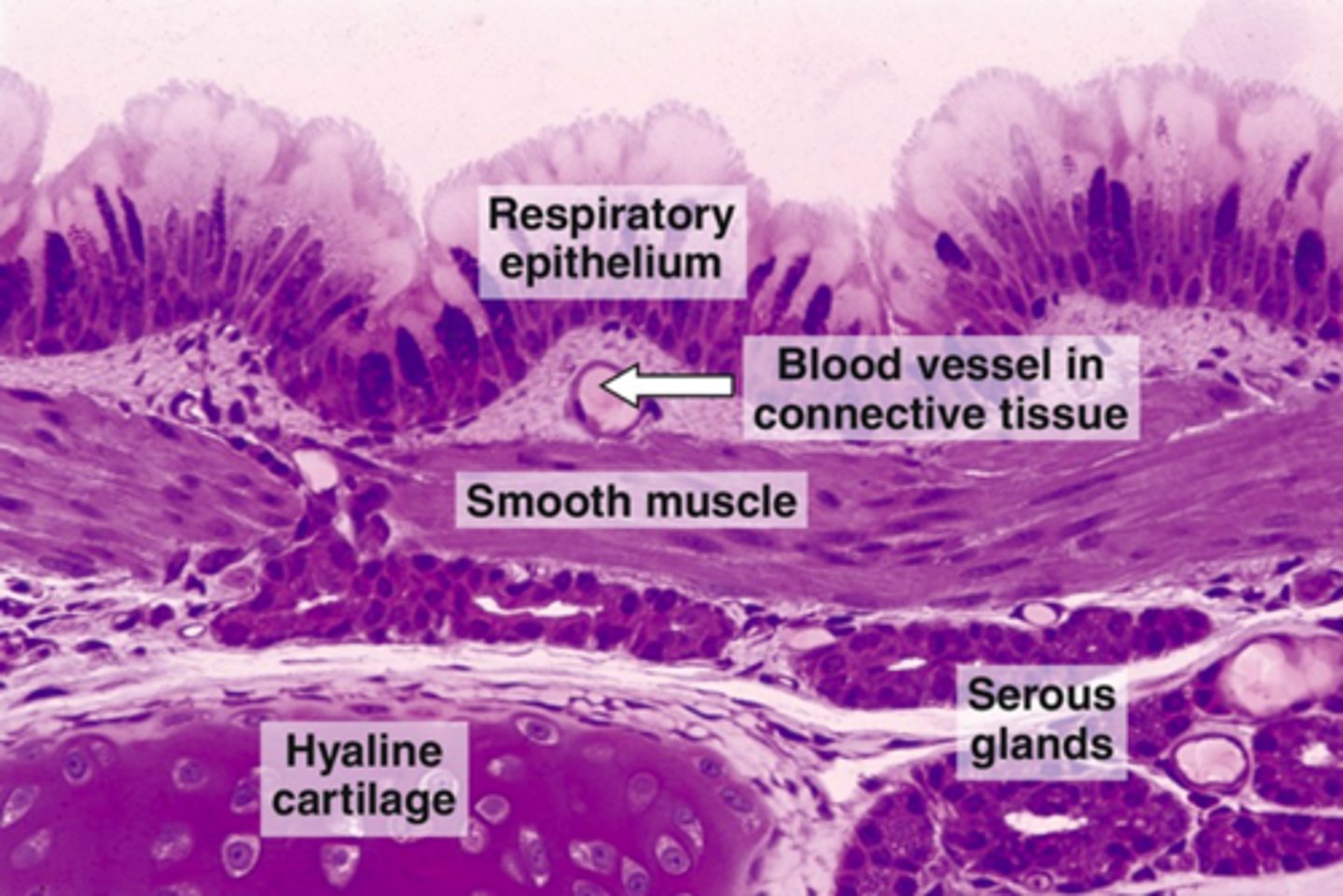
t/f: the glands found in the trachea are mixed
true
t/f: the inner trachea contains a muscularis mucosae and a hyaline cartilage
false, no muscularis mucosae
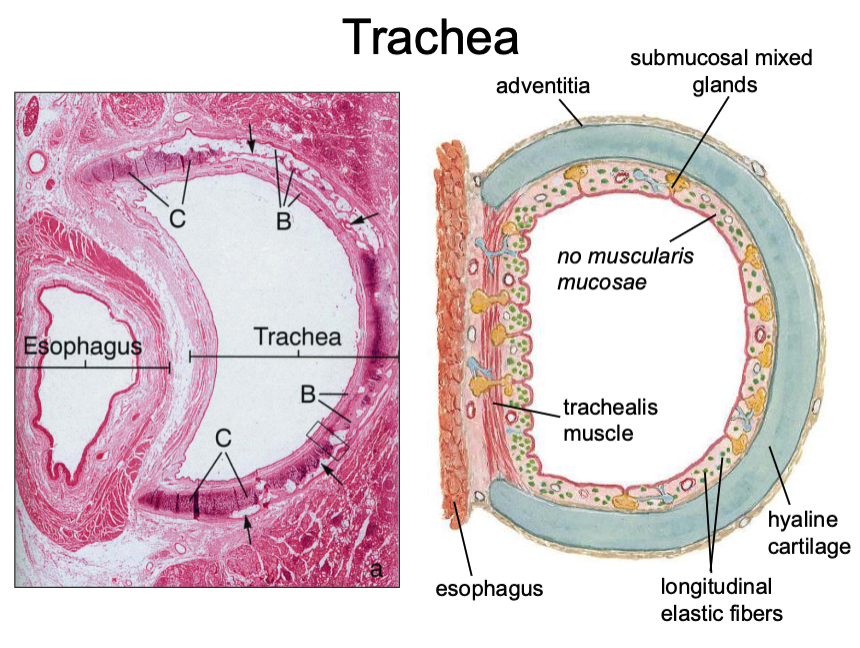
what type of cartilage is found in the adventitia of the trachea?
hyaline cartilage
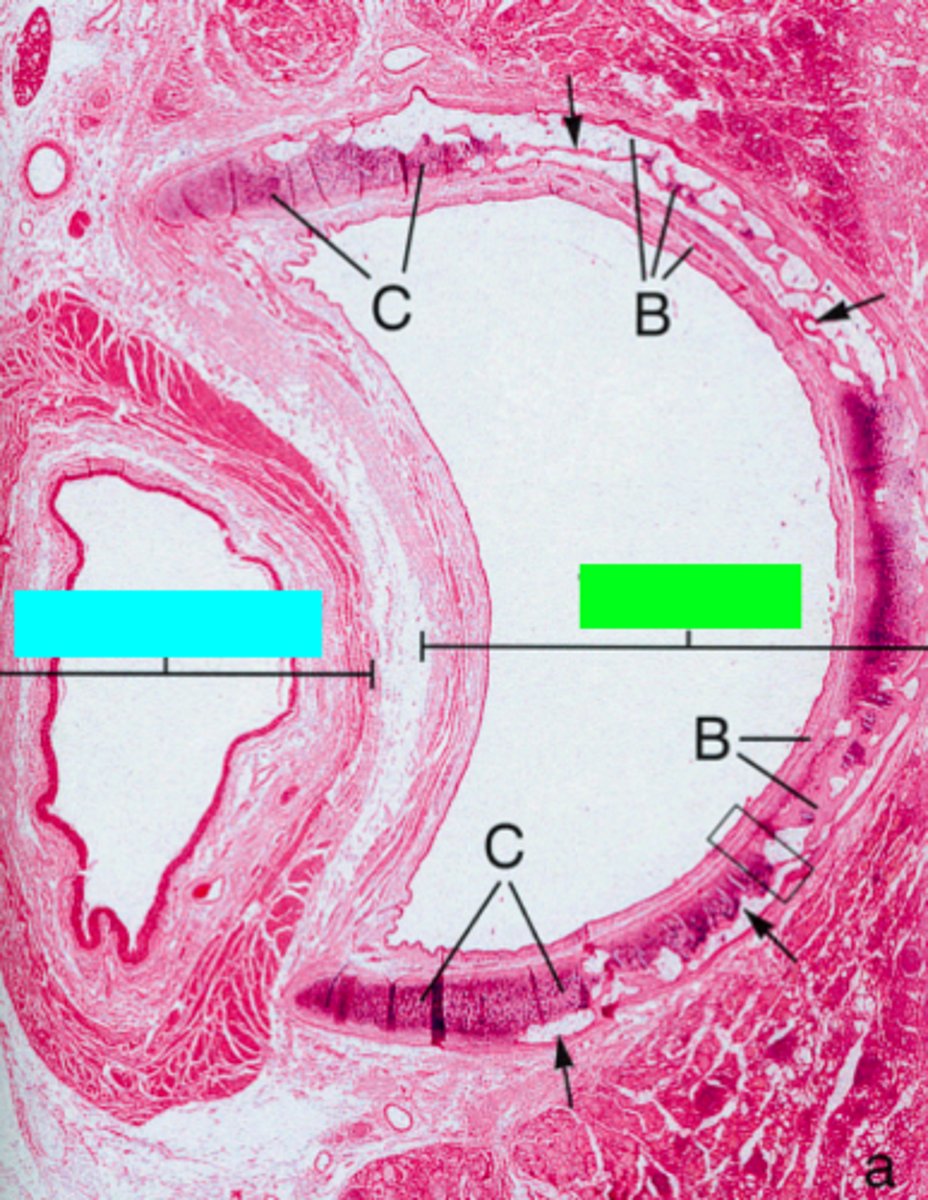
ID the green box:
trachea
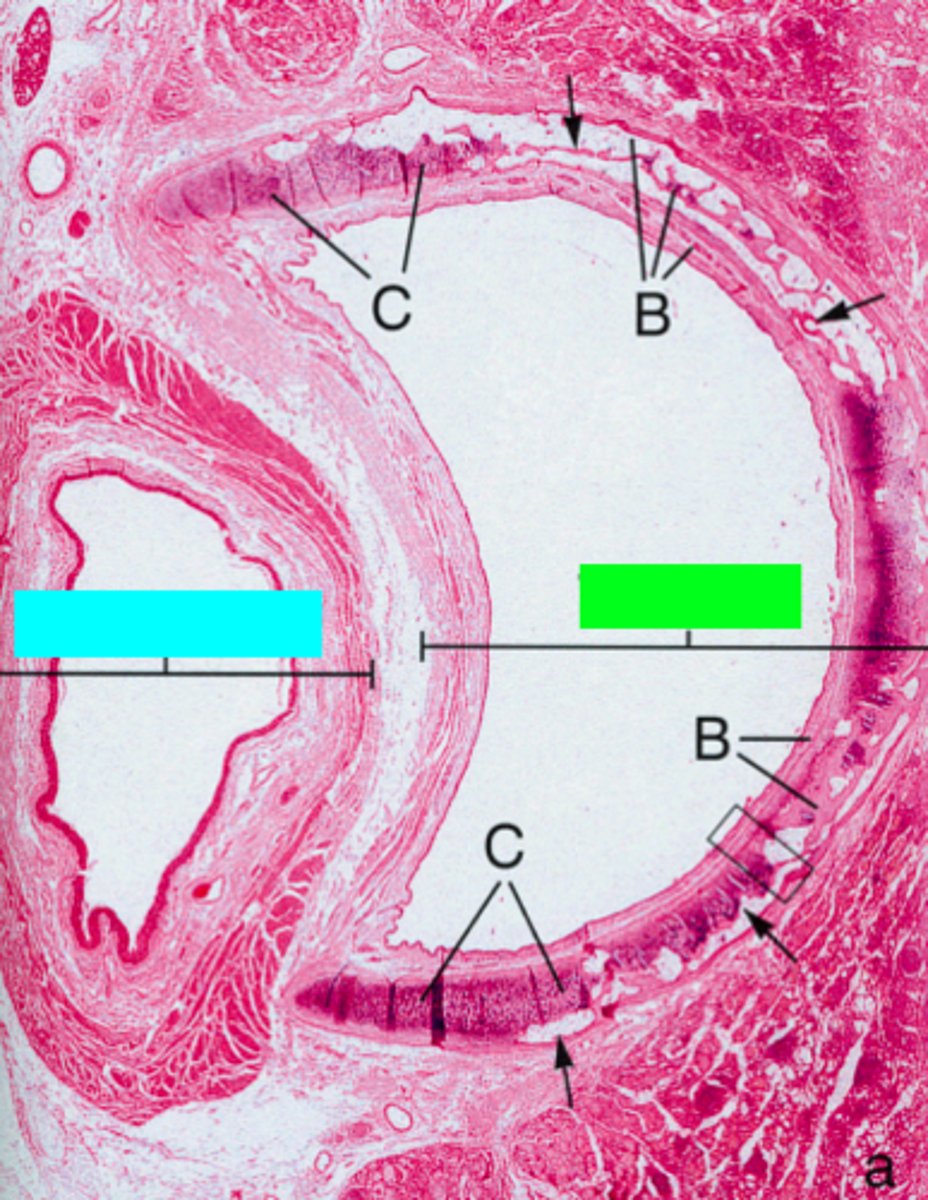
ID the blue box:
esophagus
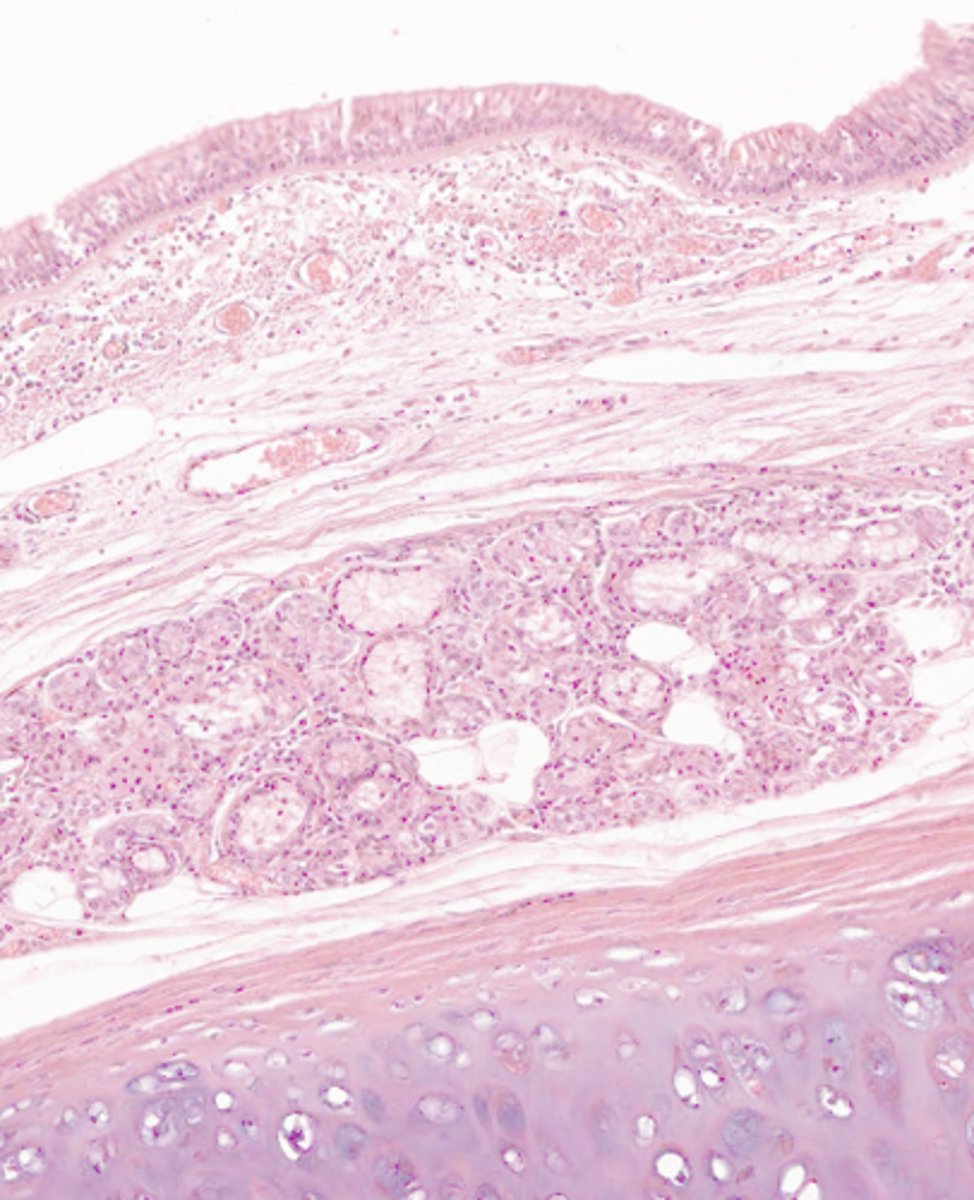
where would the following histo slide be taken from?
trachea and primary bronchi
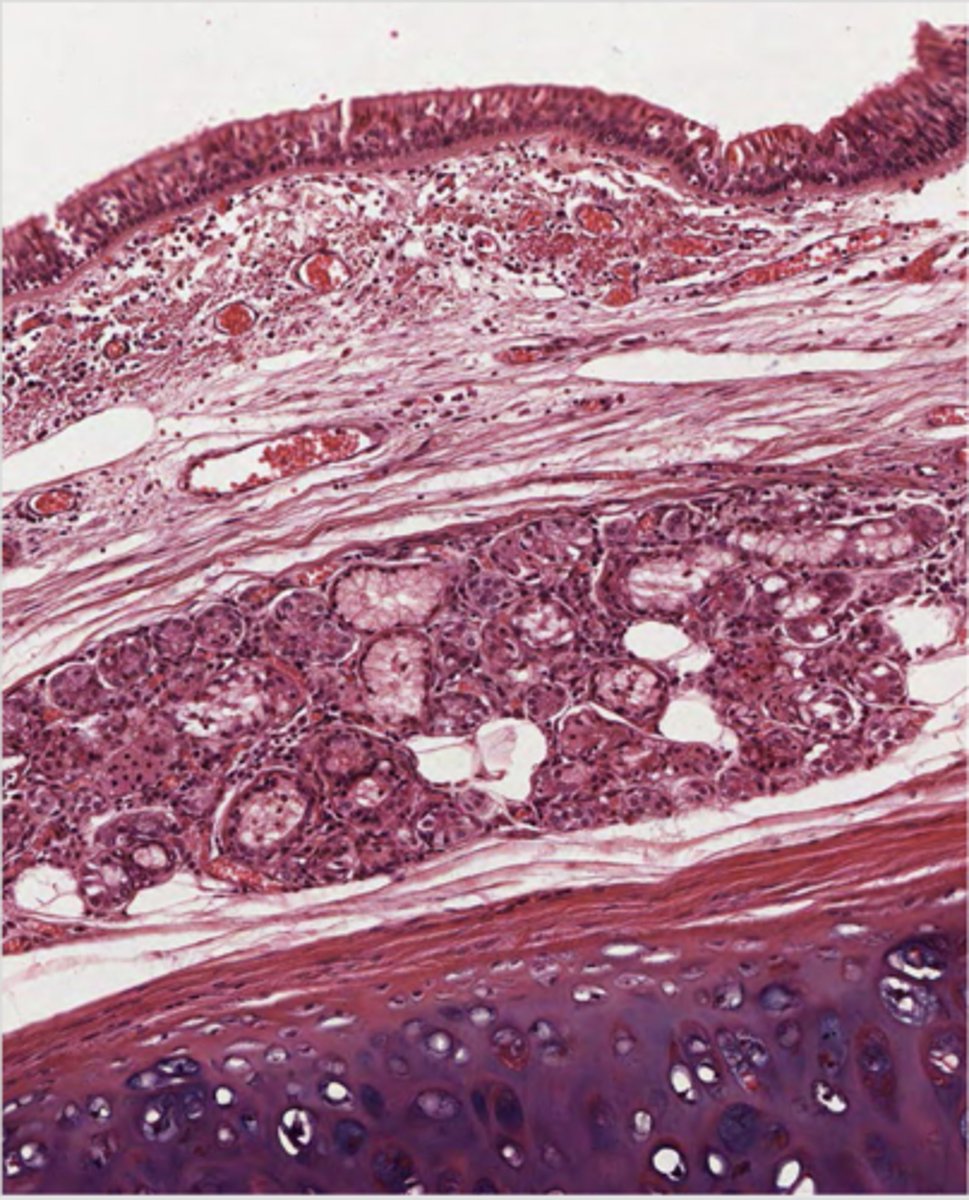
ID the region of this epithelium?
Trachea and primary bronchi
in the trachea, the mixed glands are found in what layer?
submucosa
What has the following characteristics:
- Thickened basement membrane
- Lack of a muscularis mucosae
- Seromucous glands in the submucosa
- Hyaline cartilage in the adventitia
Trachea
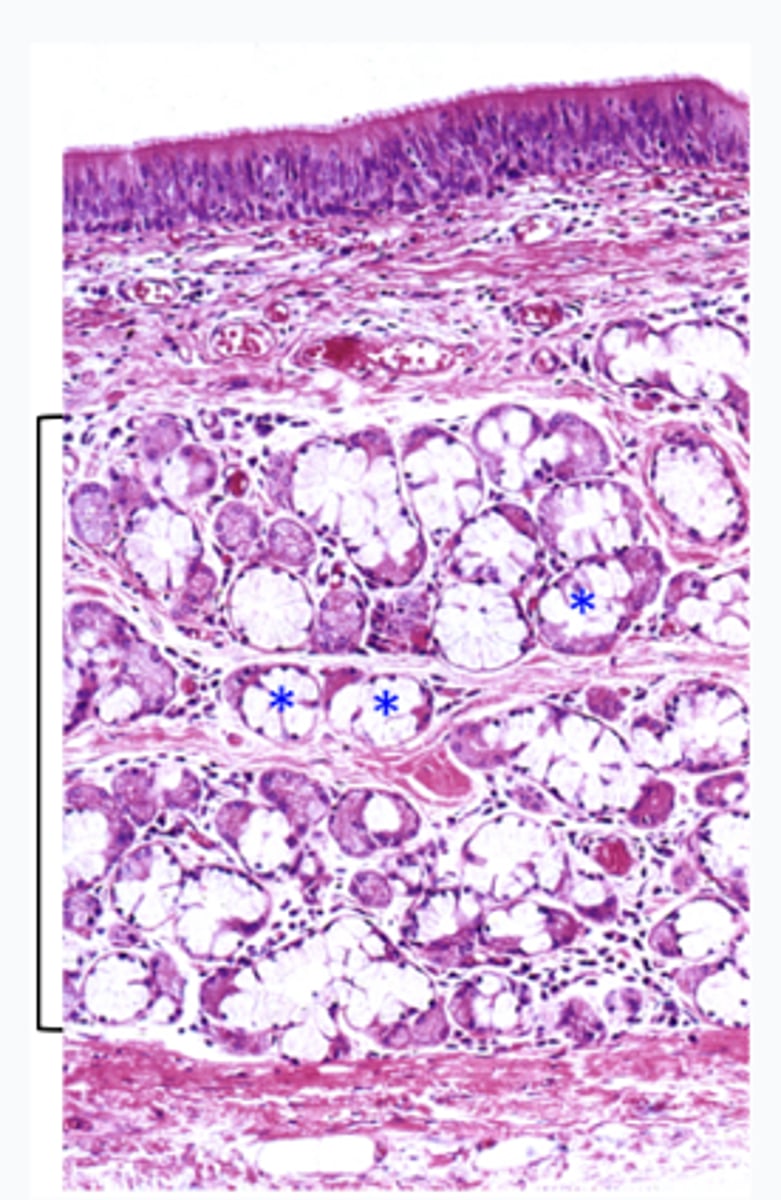
This micrograph is representative of what structure?
trachea
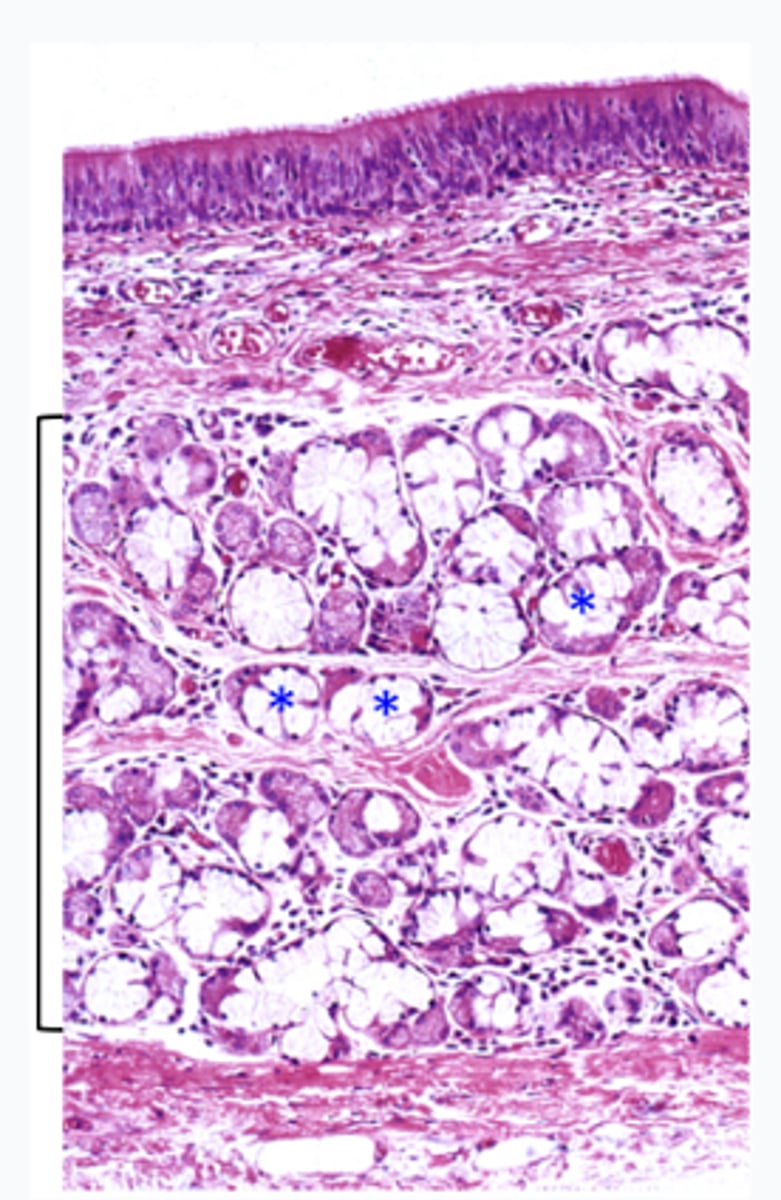
What are the asterisks and where are they located (name of bracketed region)?
serous gland in the submucosa (of trachea)
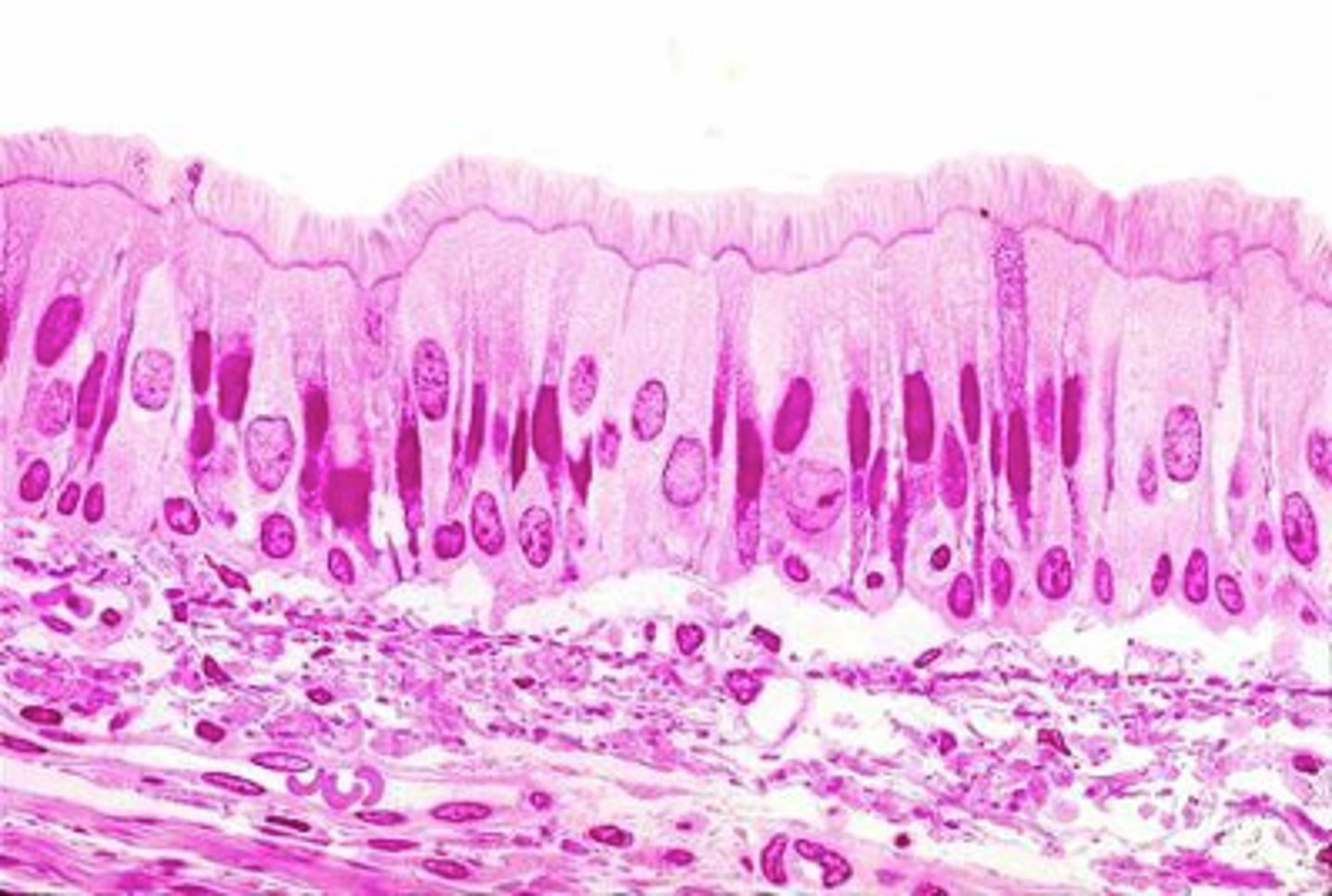
ID the epithelium:
conducting/respiratory epithelium
ID the epithelium:
conducting/respiratory epithelium
t/f: gas exchange occurs at the level of respiratory epithelium
false, no gas exchange occurs here
t/f: goblet cells are ciliated
false
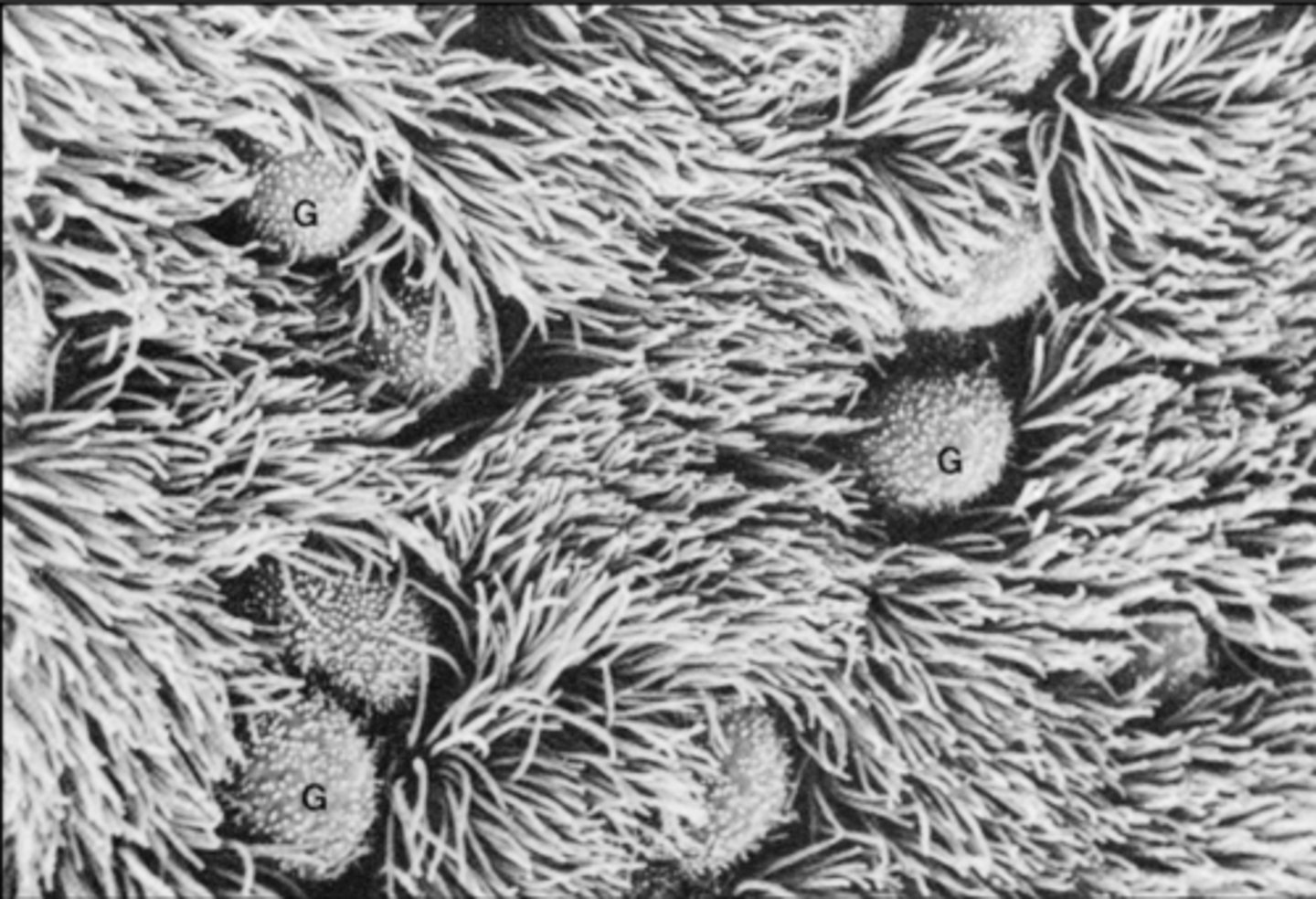
What is it called when pathogens are swept towards the oral cavity?
mucociliary clearance
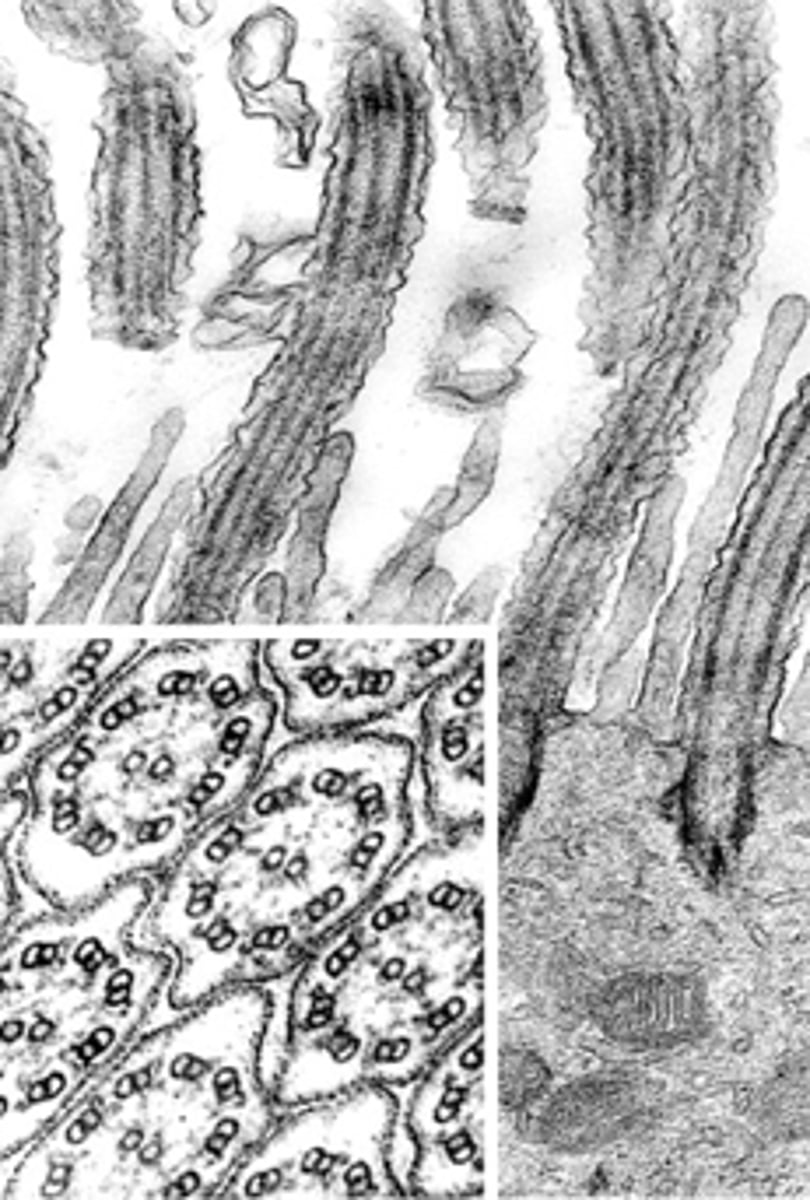
ID the structure:
cilia
what is the molecular motor of cilia?
dynein
what is the microtubule subunits for cilia?
tubulin dimers
what are the 3 cells of the respiratory epithelium?
goblet cells
ciliated cells
basal cells
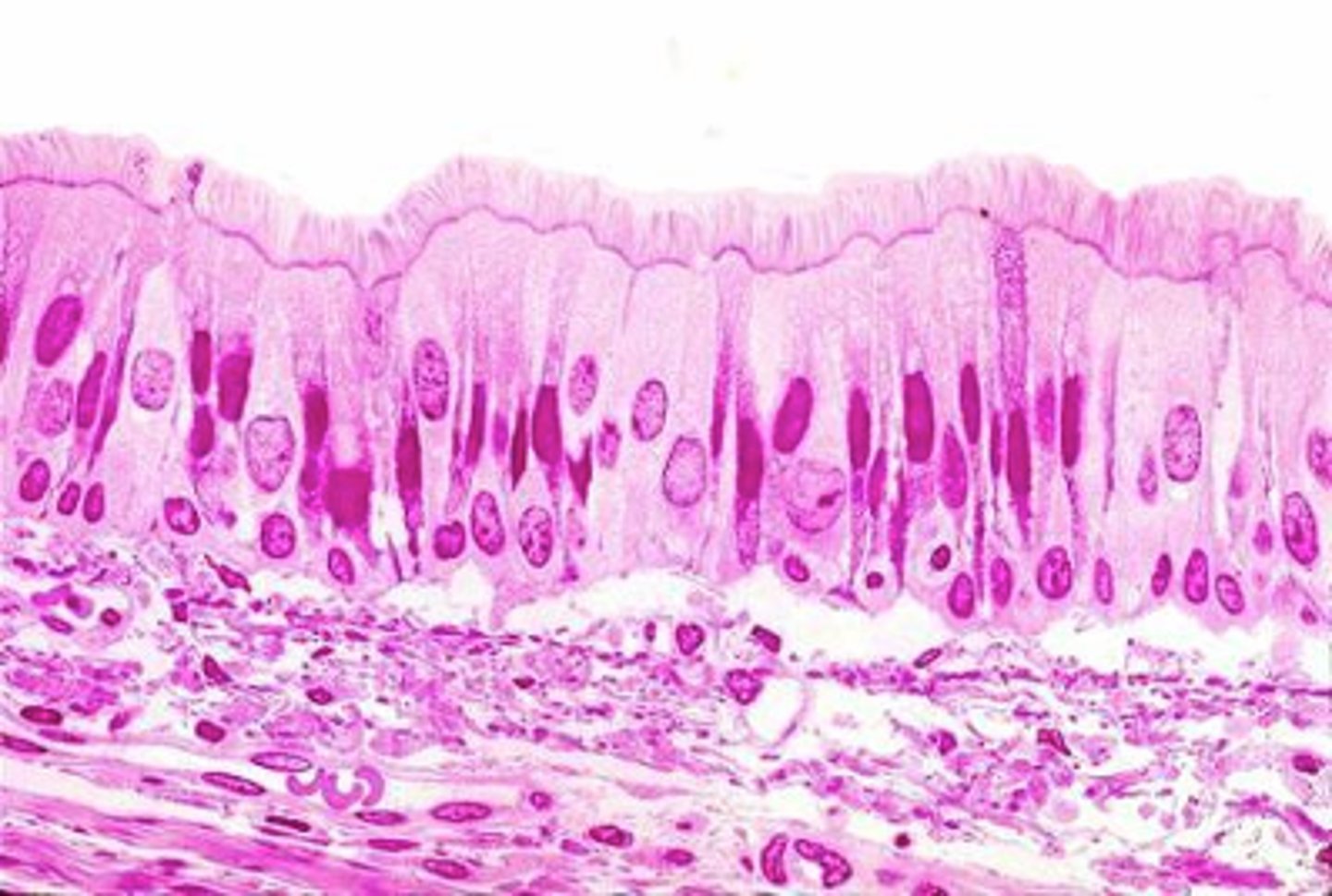
what makes the pink line under the cilia?
basal bodies
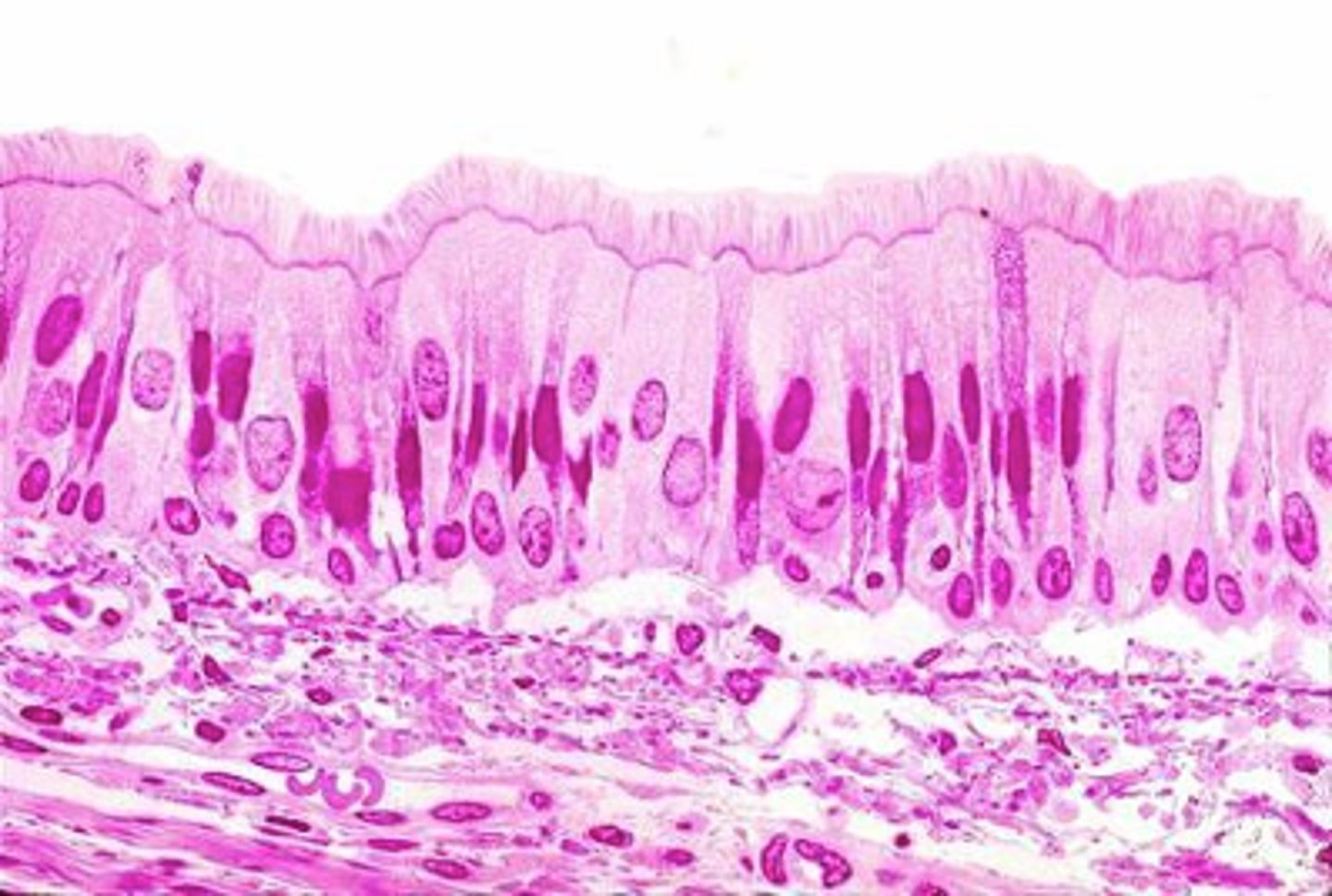
which cells reach the surface, but do not have cilia apically?
goblet cells
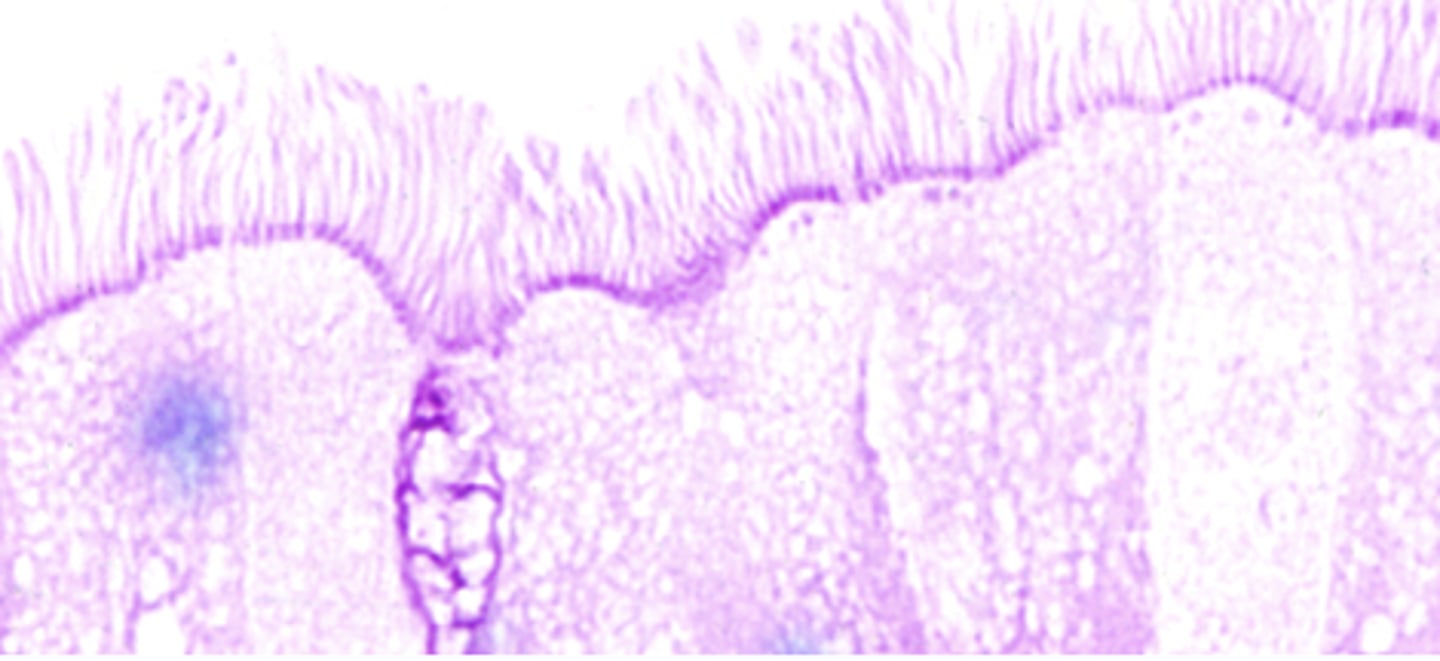
What is this stained for? (darker purple underneath cilia)
basal bodies
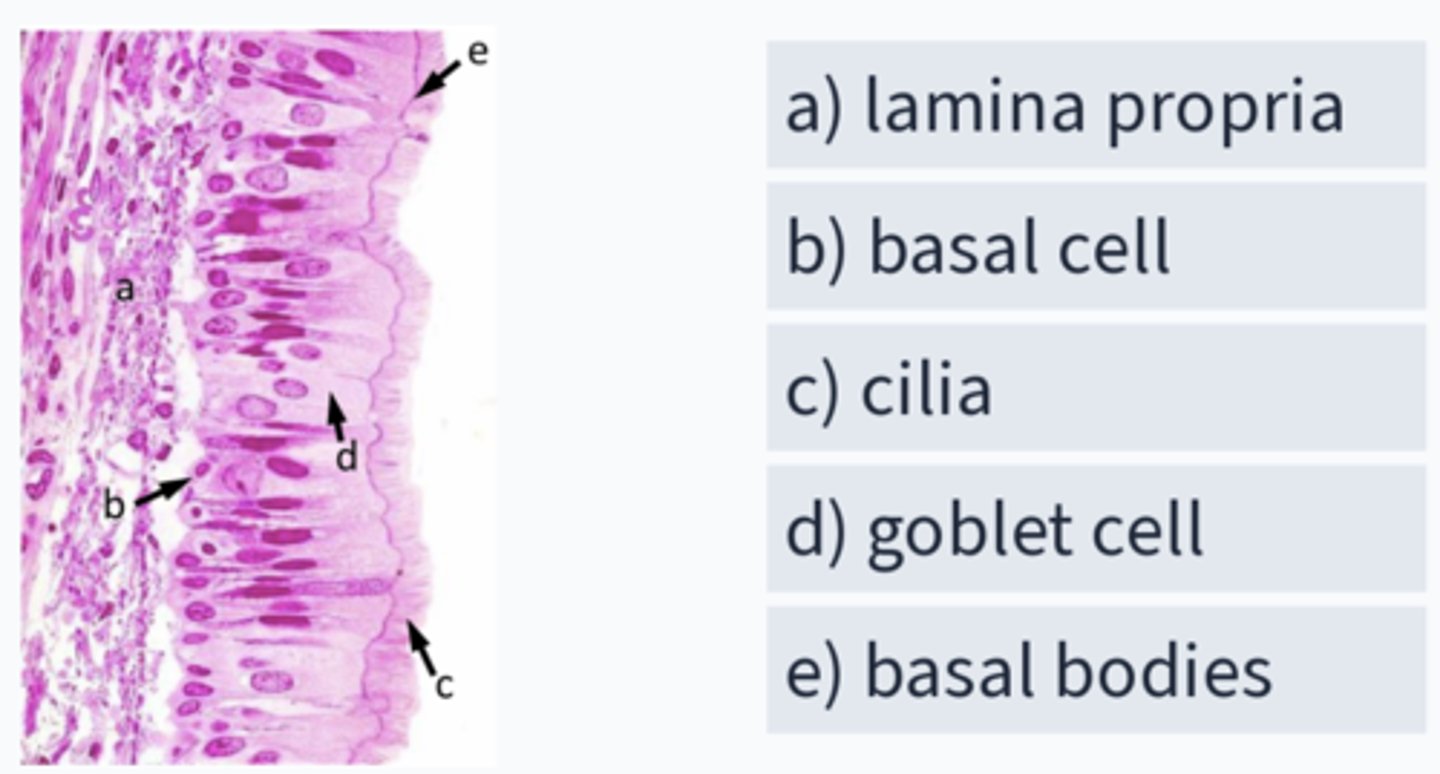
Which is mislabeled?
D- goblet cell (ciliated cell, not goblet)
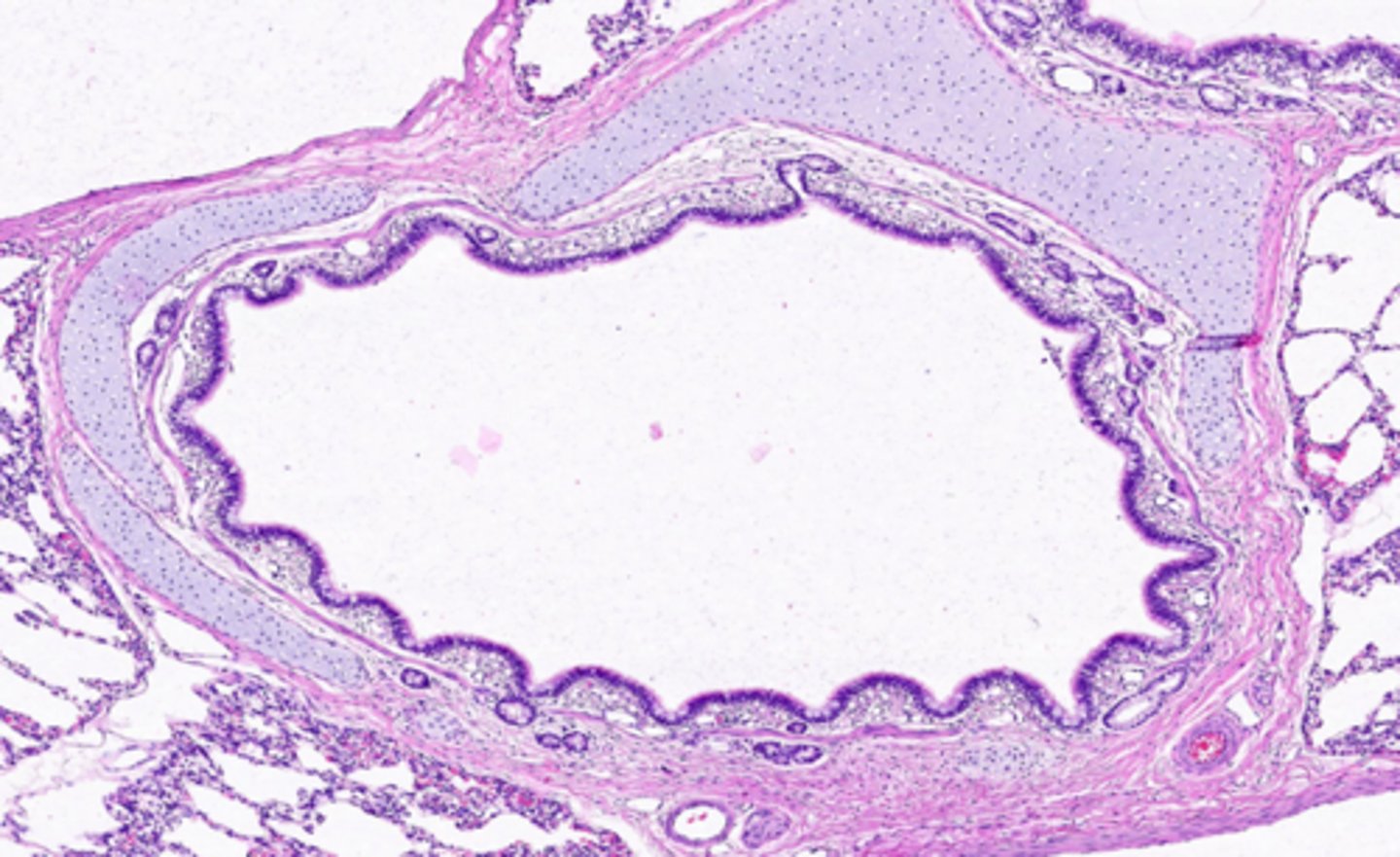
ID the location of this slide:
intrapulmonary bronchus
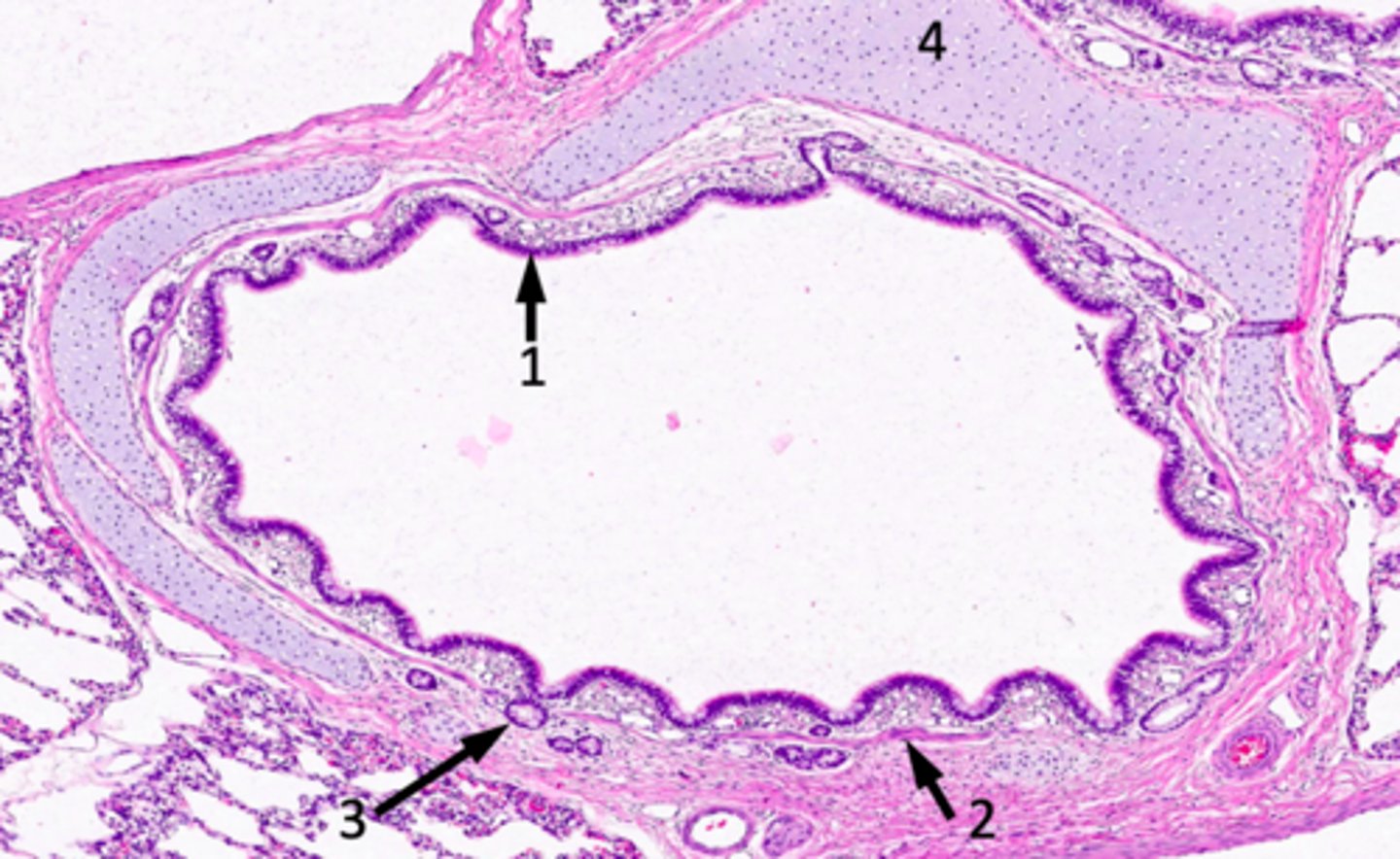
ID #1:
conducting/respiratory epithelium (lamina propria with blood vessels and connective tissue)
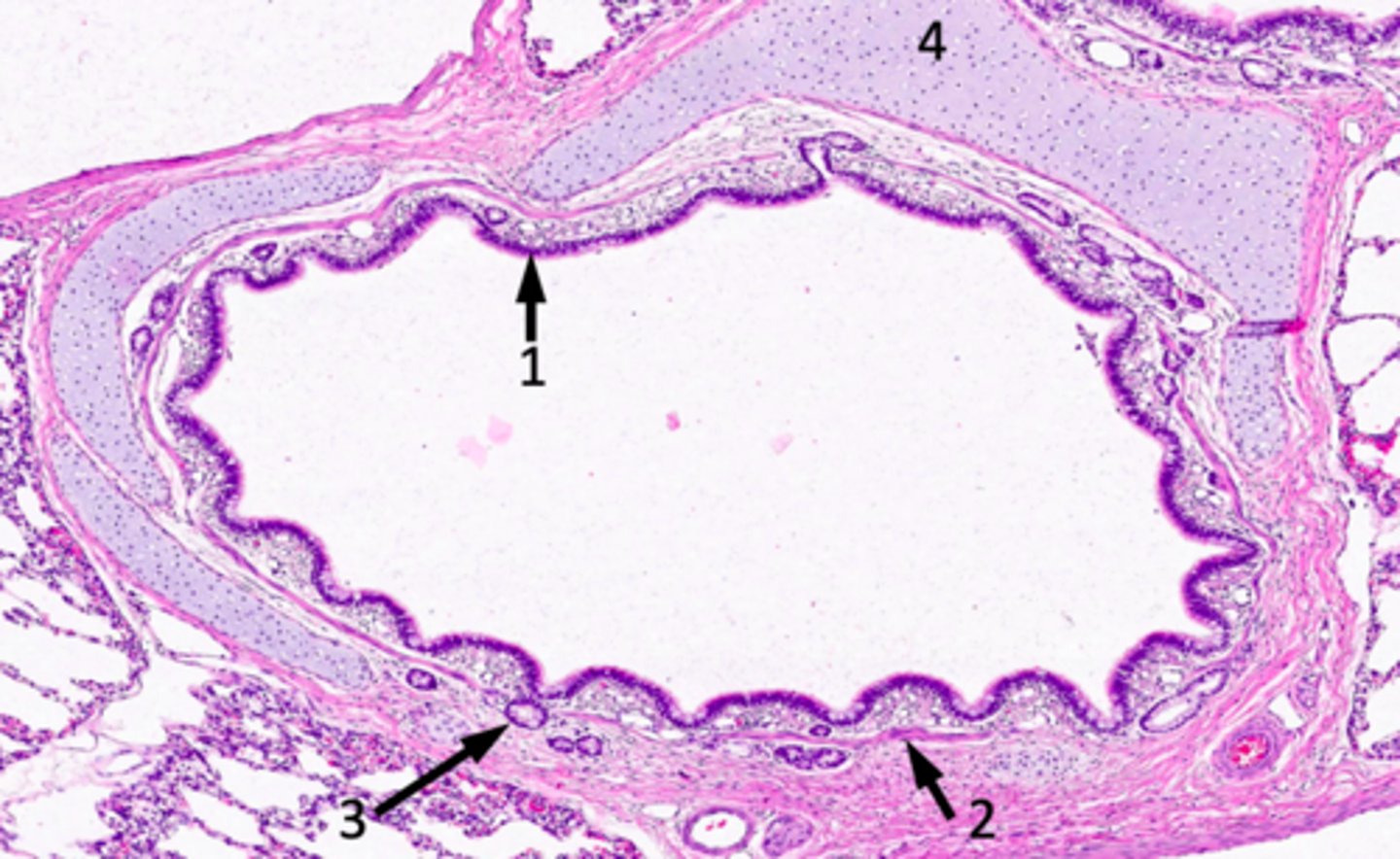
ID #2:
muscularis mucosae (smooth)
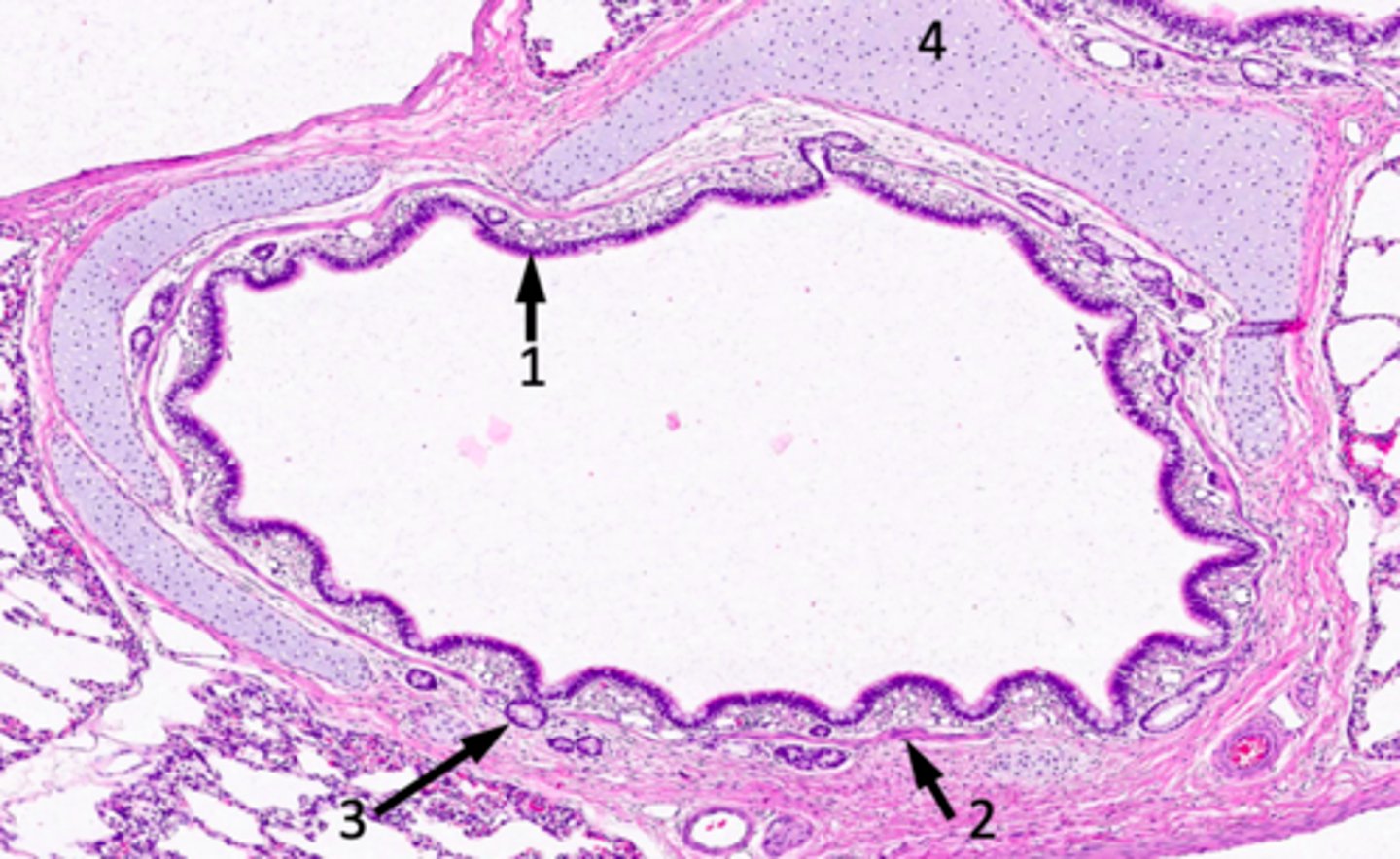
ID #3:
seromucous glands
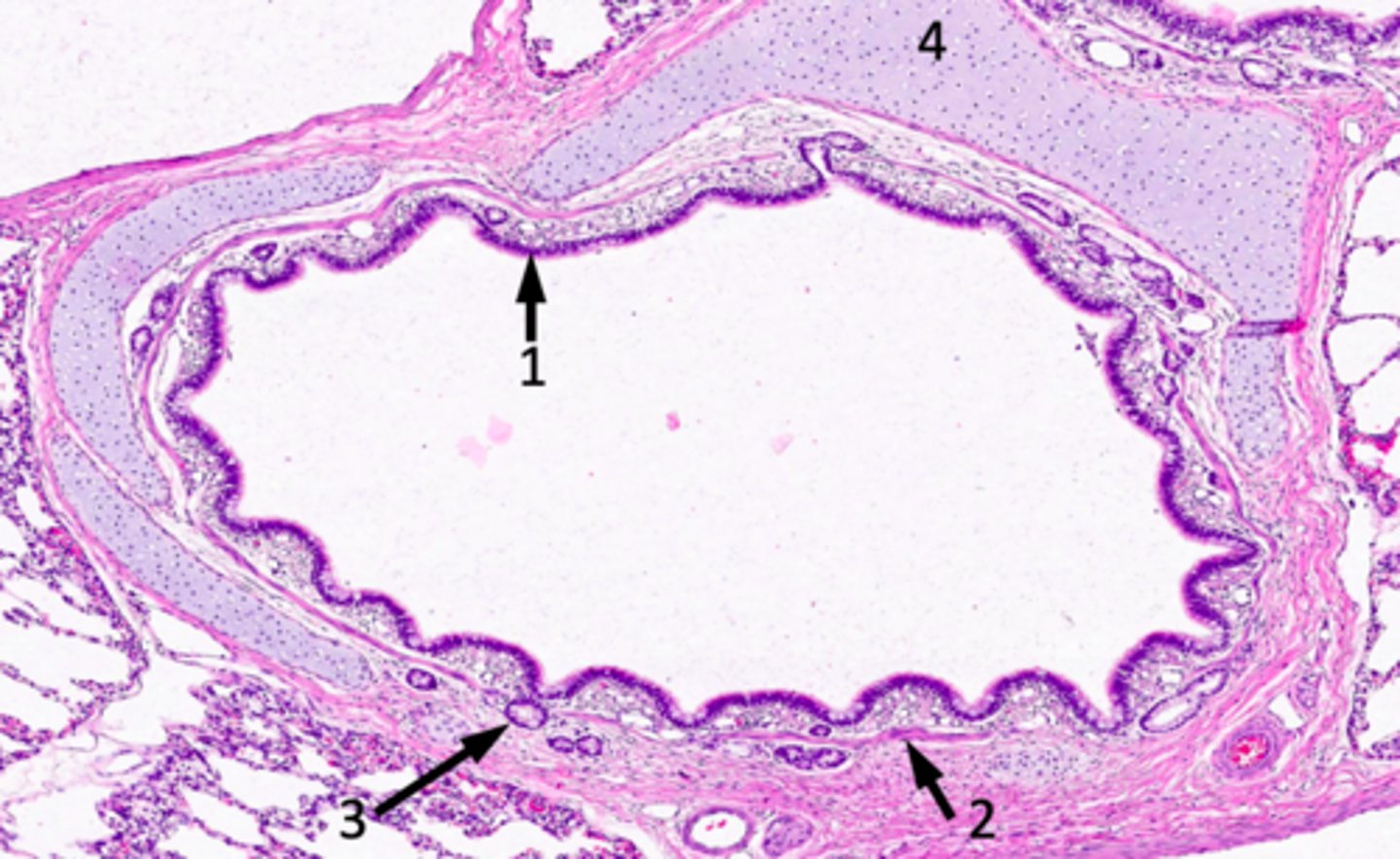
ID #4:
hyaline cartilage
ID the location of the slide:
intrapulmonary bronchus
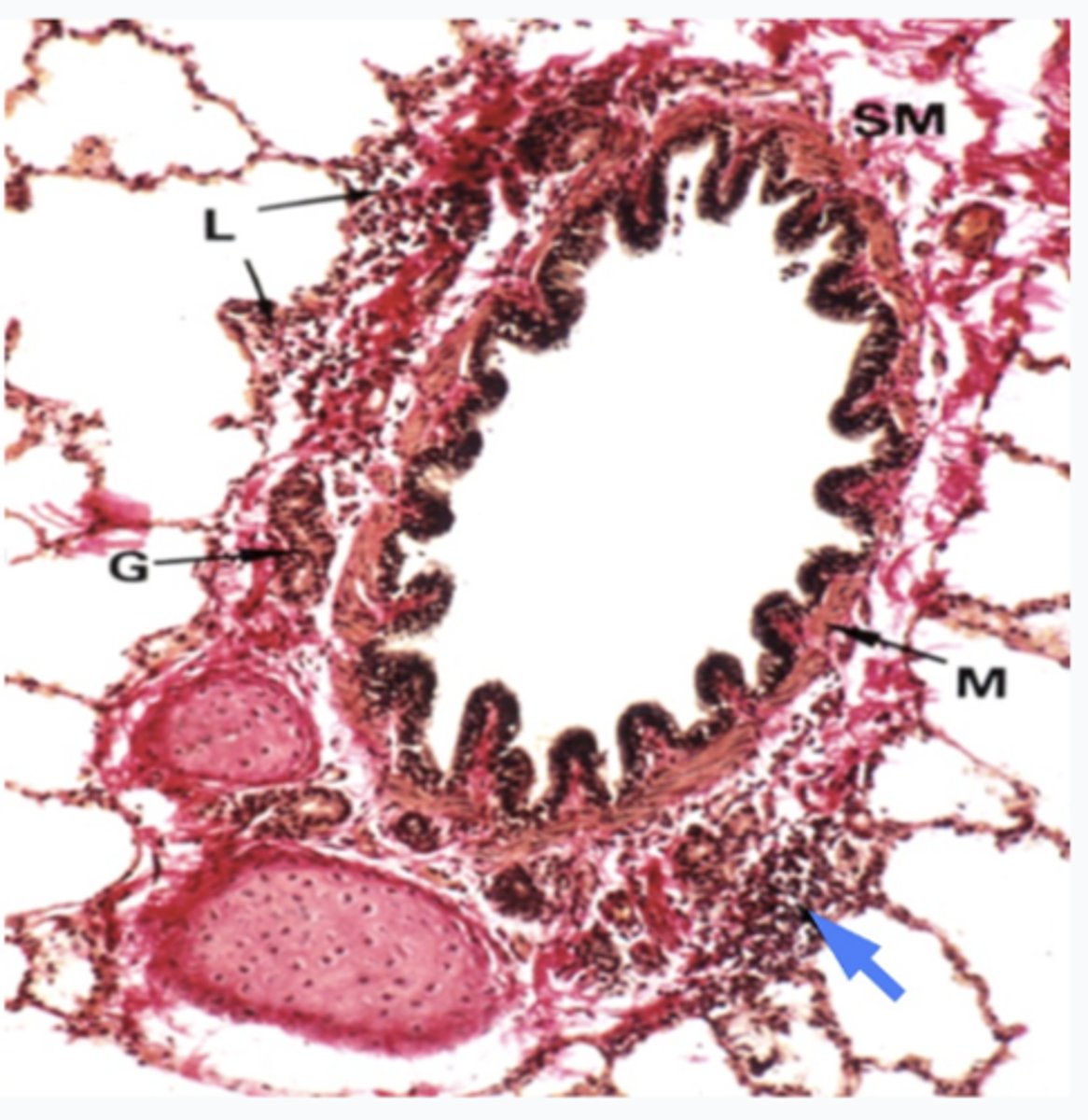
What does the image show?
intrapulmonary bronchus
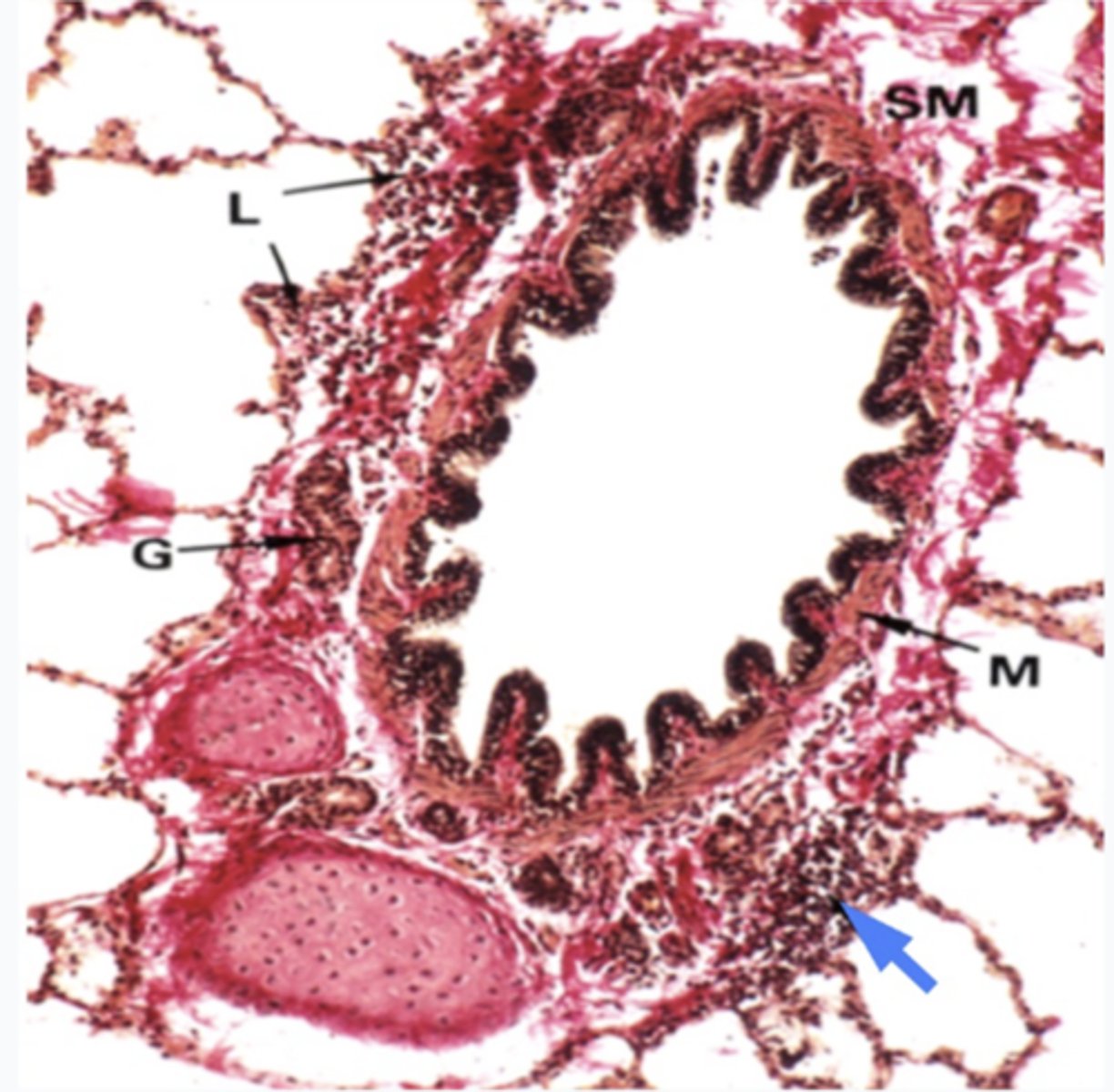
What is the region at the blue arrrow?
Lymphoid tissues
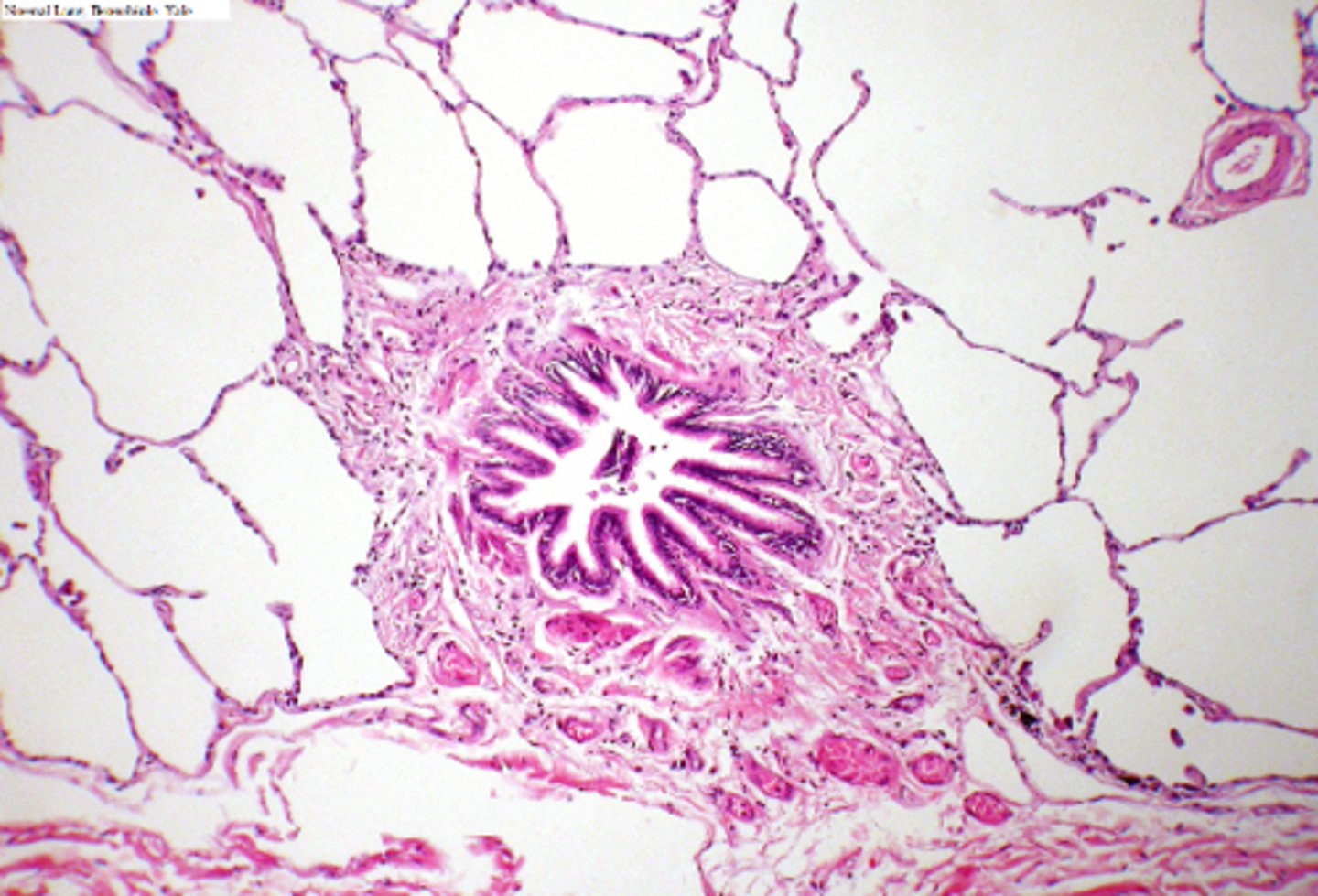
ID the location of the slide:
bronchioles
What has the following characteristics?
- No mucosal glands
- Club cells, increasing distally
- No cartilage
- Goblet cells decreasing distally
bronchiole
patients with what condition have bronchioles that become inflamed, narrow and swell, and produce extra mucus, which makes it difficult to breathe.
asthma
____________ is a condition in which a person's airways become inflamed, narrow and swell, and produce extra mucus, which makes it difficult to breathe. The tightening of s.m. contributes to the narrowing of the airways. Bronchiolar epithelium contains an increased number of goblet cells (thus produces more mucus).
Asthma
In asthma, bronchiolar epithelium contains an ______ number of goblet cells, thus produces more mucus
increased
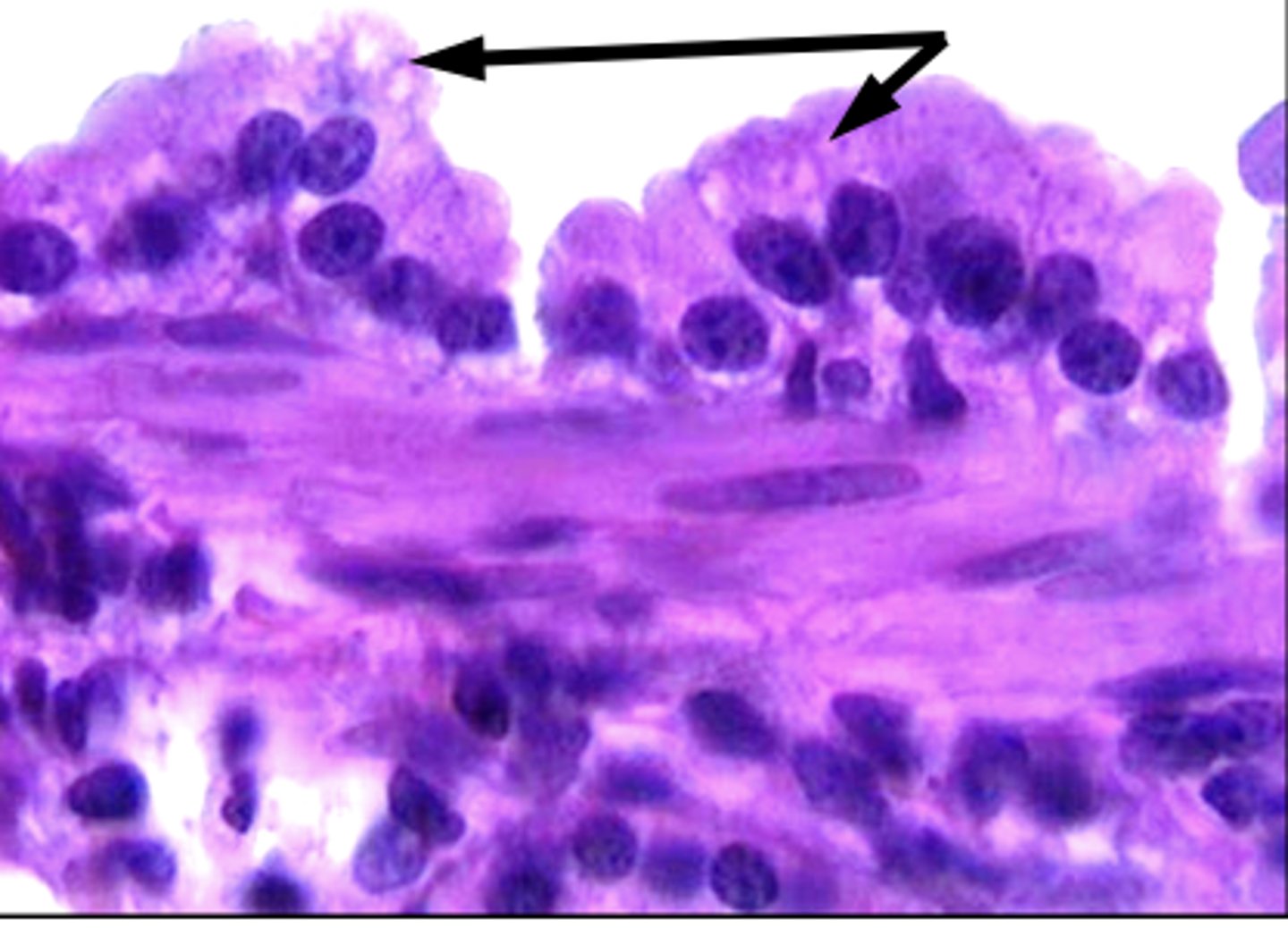
these cells are found in the bronchioles and mostly like the epithelium
Secretory granules in club cells
What has the following characteristics?
- Their secretions coat the surface of the bronchioles which is sometimes called ‘bronchiolar surfactant’.
- They play important roles in regeneration and repair
club cells
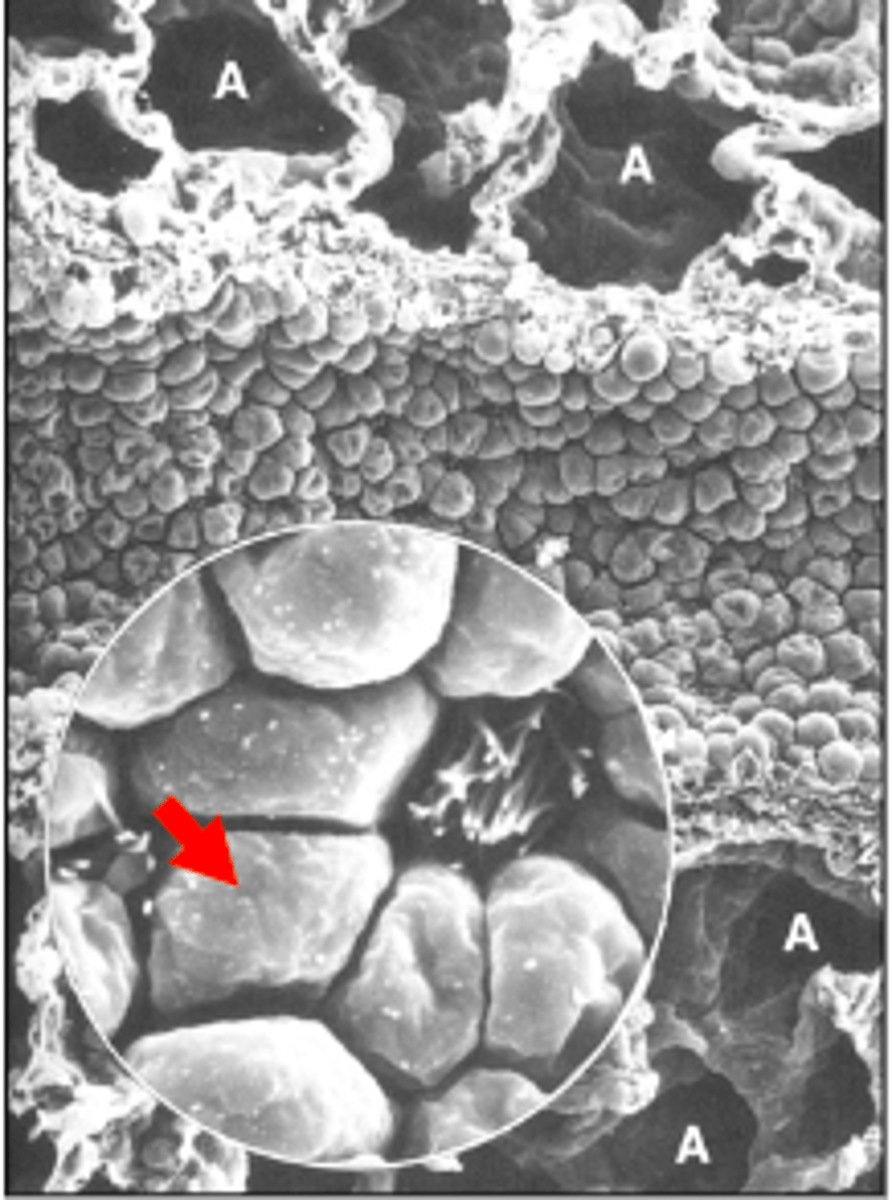
ID the cell:
-non-ciliated
-involved in repair processes (stem cells)
-inhibit inflammation/fibrosis
-secretory product elevation in plasma may
be indicative of epithelial injury
club cells
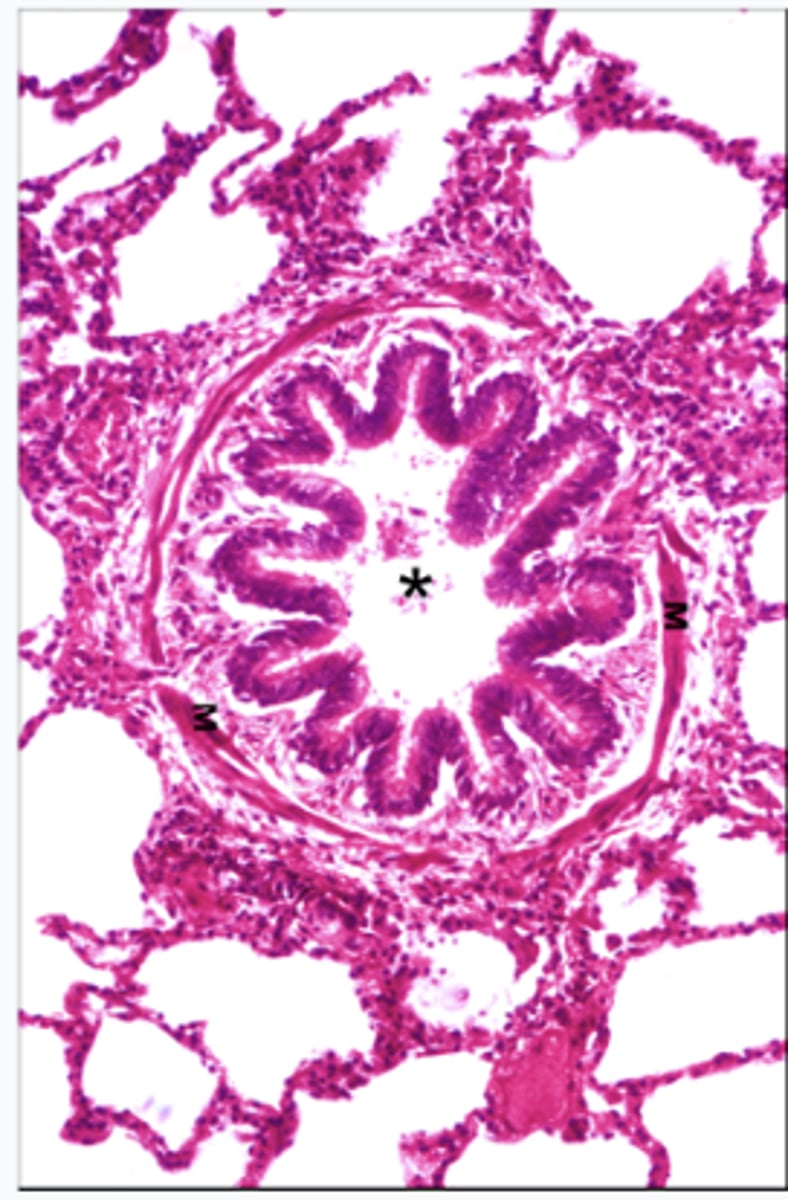
This is a micrograph of which structure?
bronchiole (asterisk are club cells lining interior)
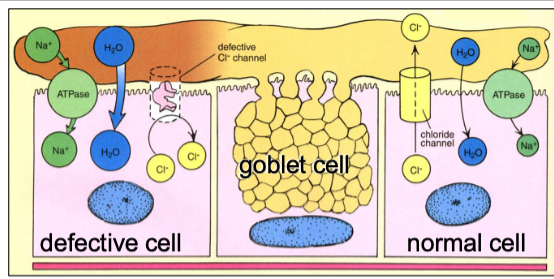
Cystic fibrosis is caused by a mutation in the chloride channel protein, CFTR. This primarily affects the function of which cell?
ciliated cells
Cystic fibrosis is caused by a mutation in the chloride channel protein, CFTR. This primarily affects the function of which one of the following cells?
A. Club cells
B. Type I pneumocytes
C. Basal cells
D. Ciliated cells
E. Type Il pneumocytes
D. Ciliated cells
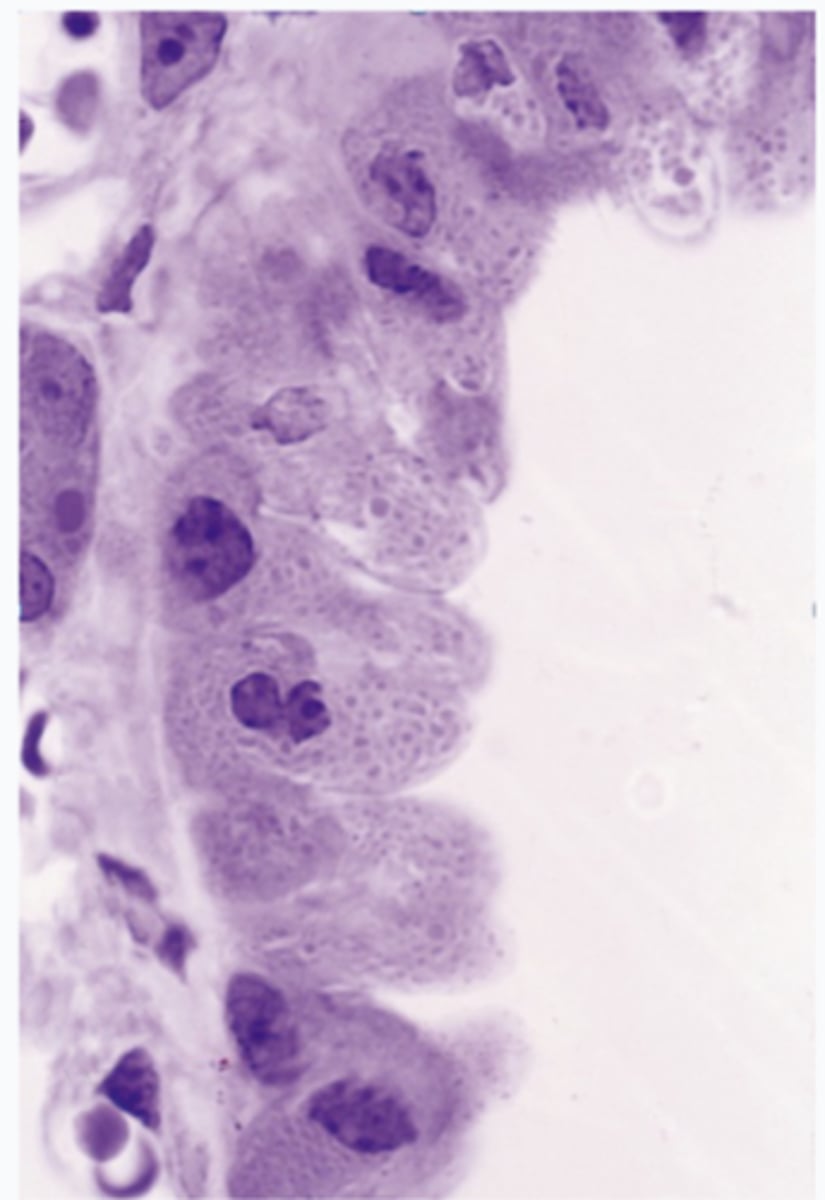
What type of cells are these?
club cells
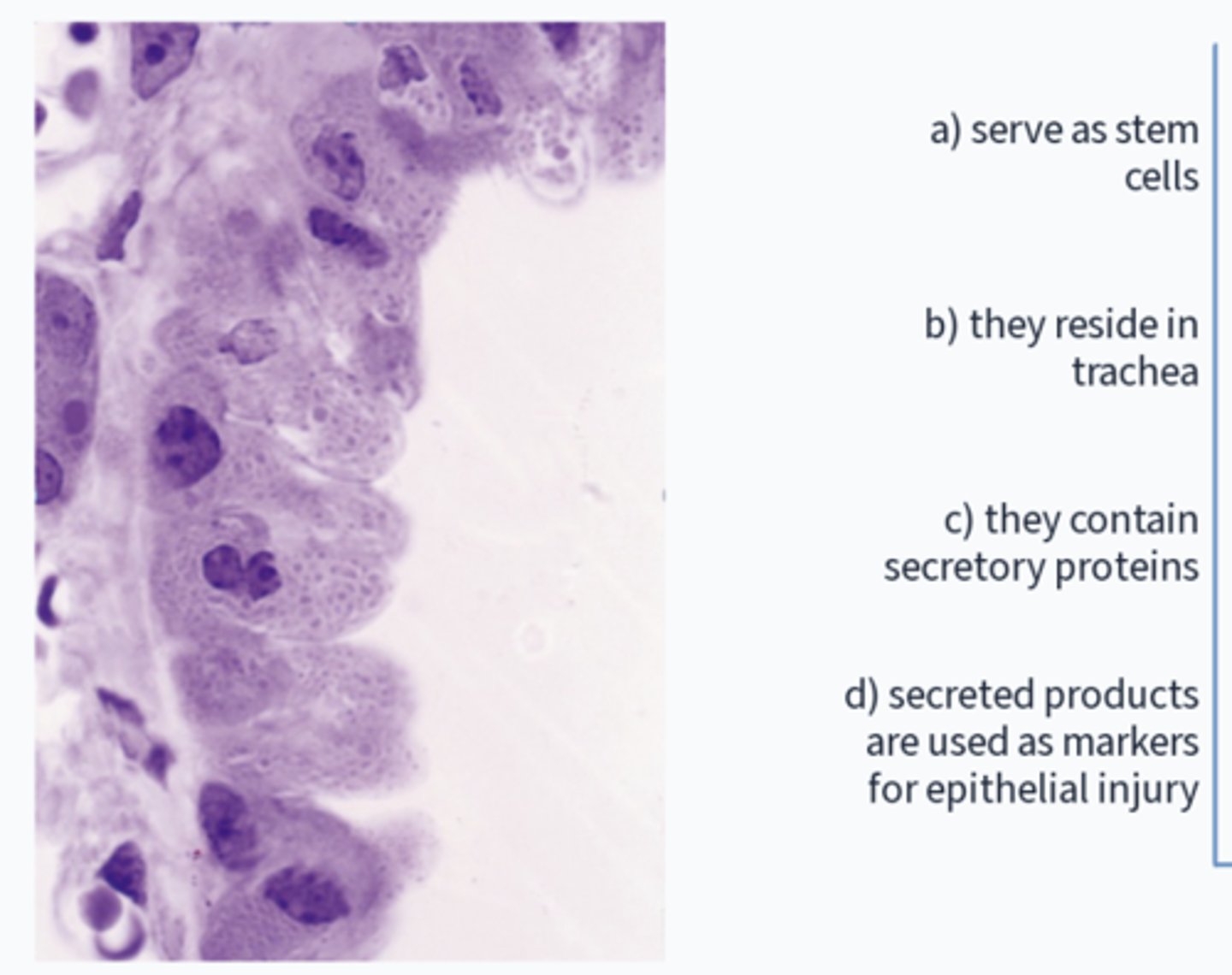
What is incorrect?
b) they are in the trachea (in bronchioles)
Pulmonary arteries, carrying ______________ blood, parallel the conducting airway; pulmonary veins, travel alone in a 'sea of alveoli'
Deoxygenated
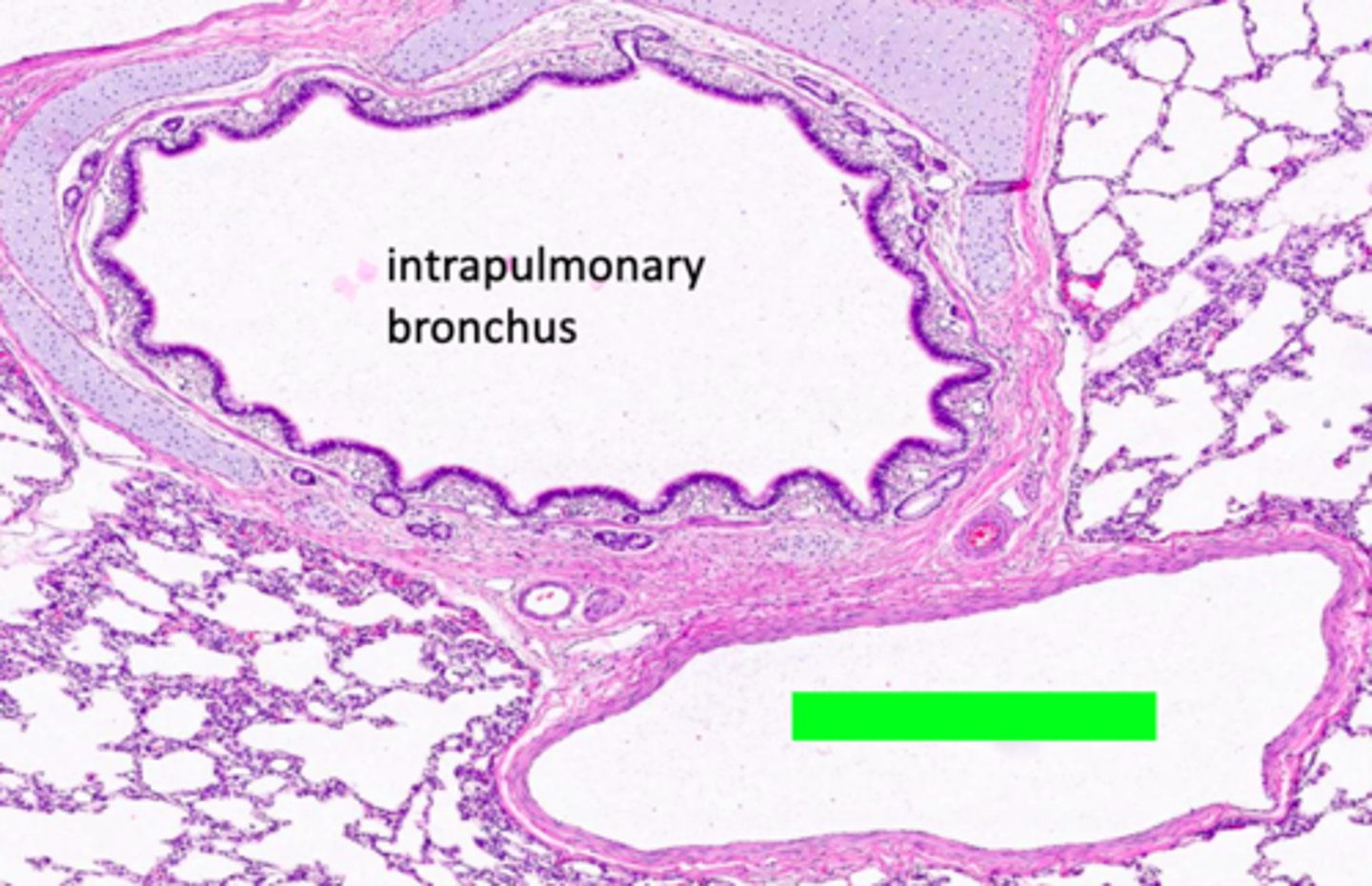
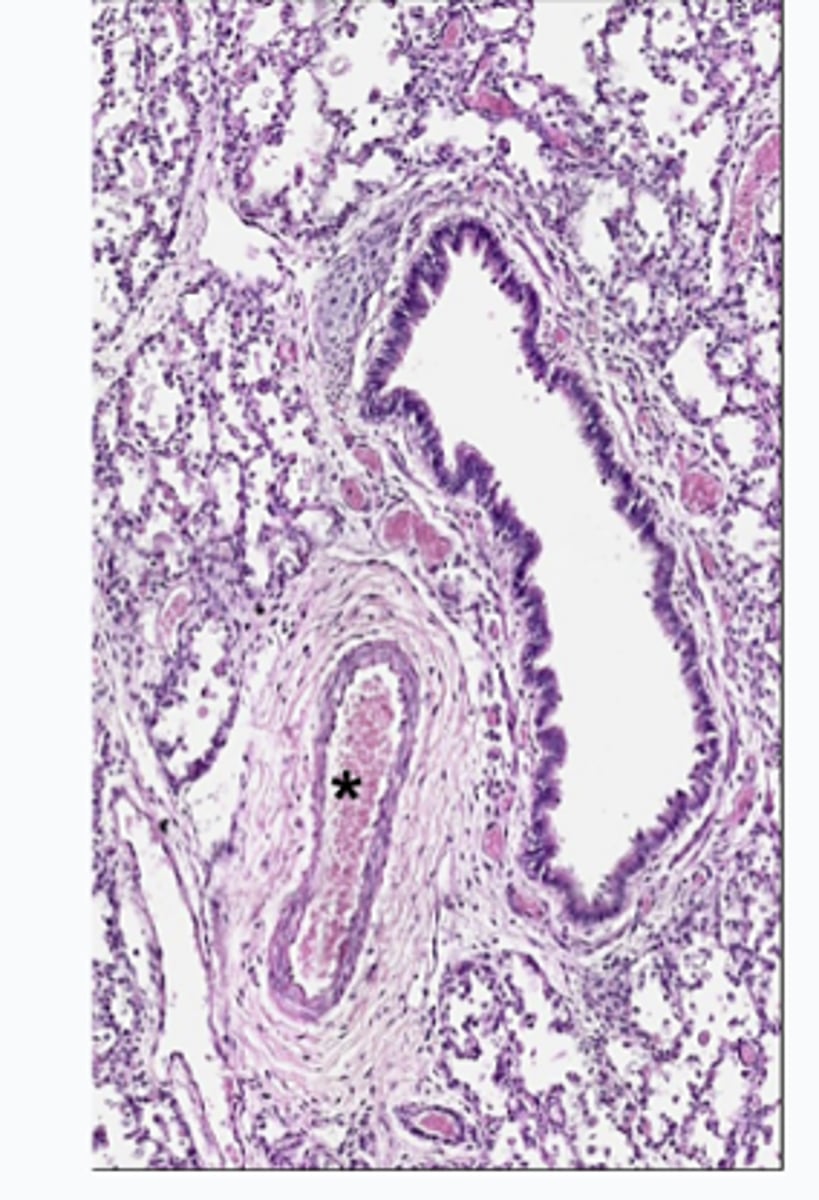
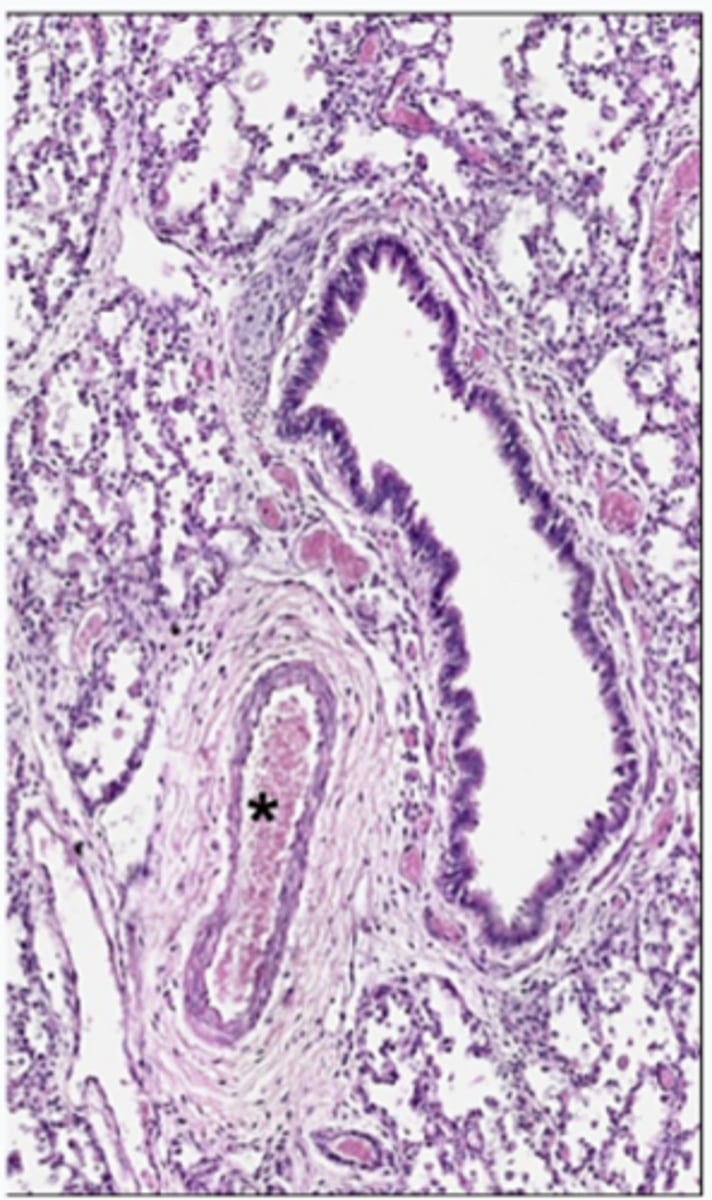
ID the structure:
pulmonary artery
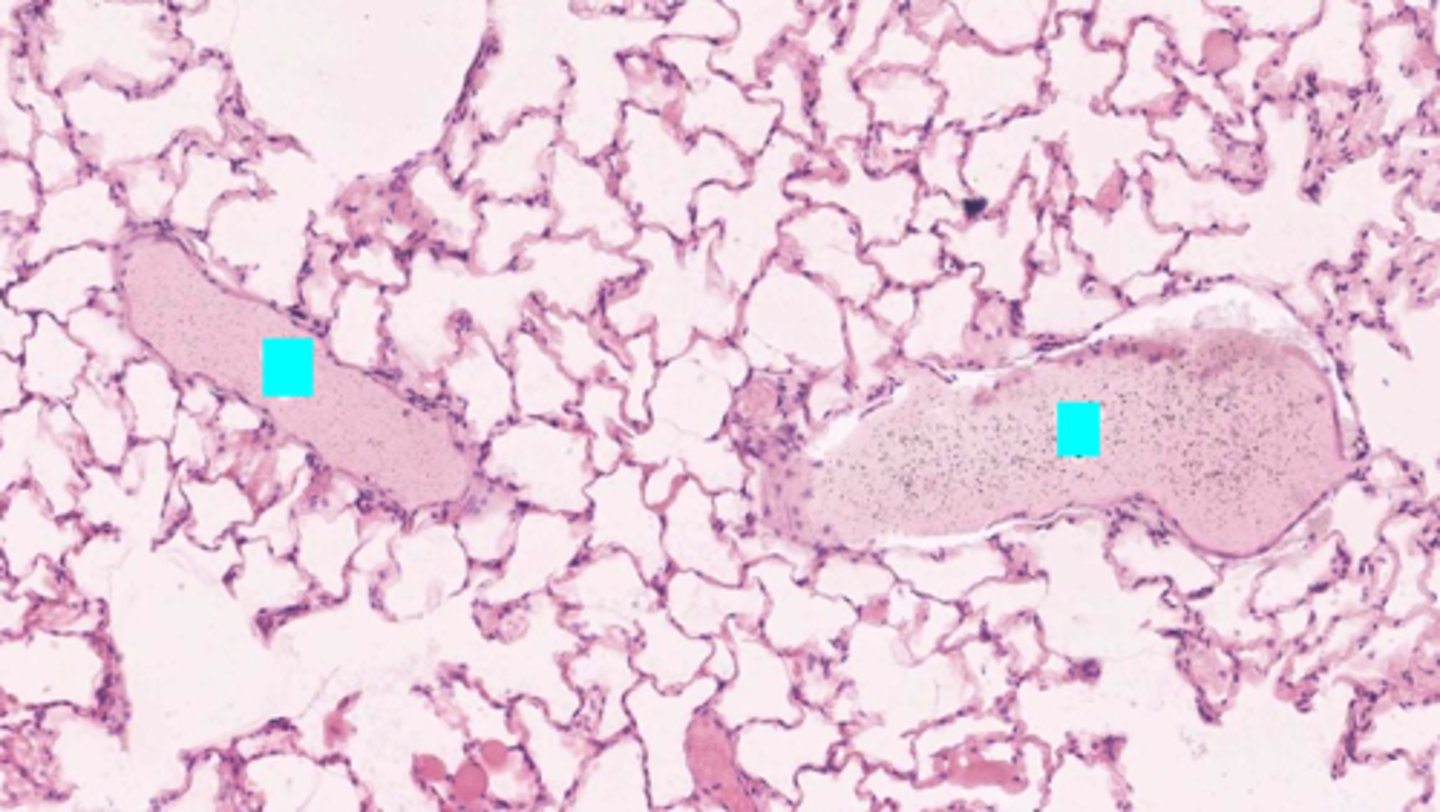
ID the structure:
pulmonary vein
What is the structure with an asterisk?
pulmonary artery
Is the asterisked vessel conveying blood toward or away from the heart?
Away from the heart
Up to this point, the walls of the conducting airways are too thick for gas exchange:
terminal bronchioles
First appearance of alveoli where the walls are thin enough for gas exchange:
respiratory bronchioles
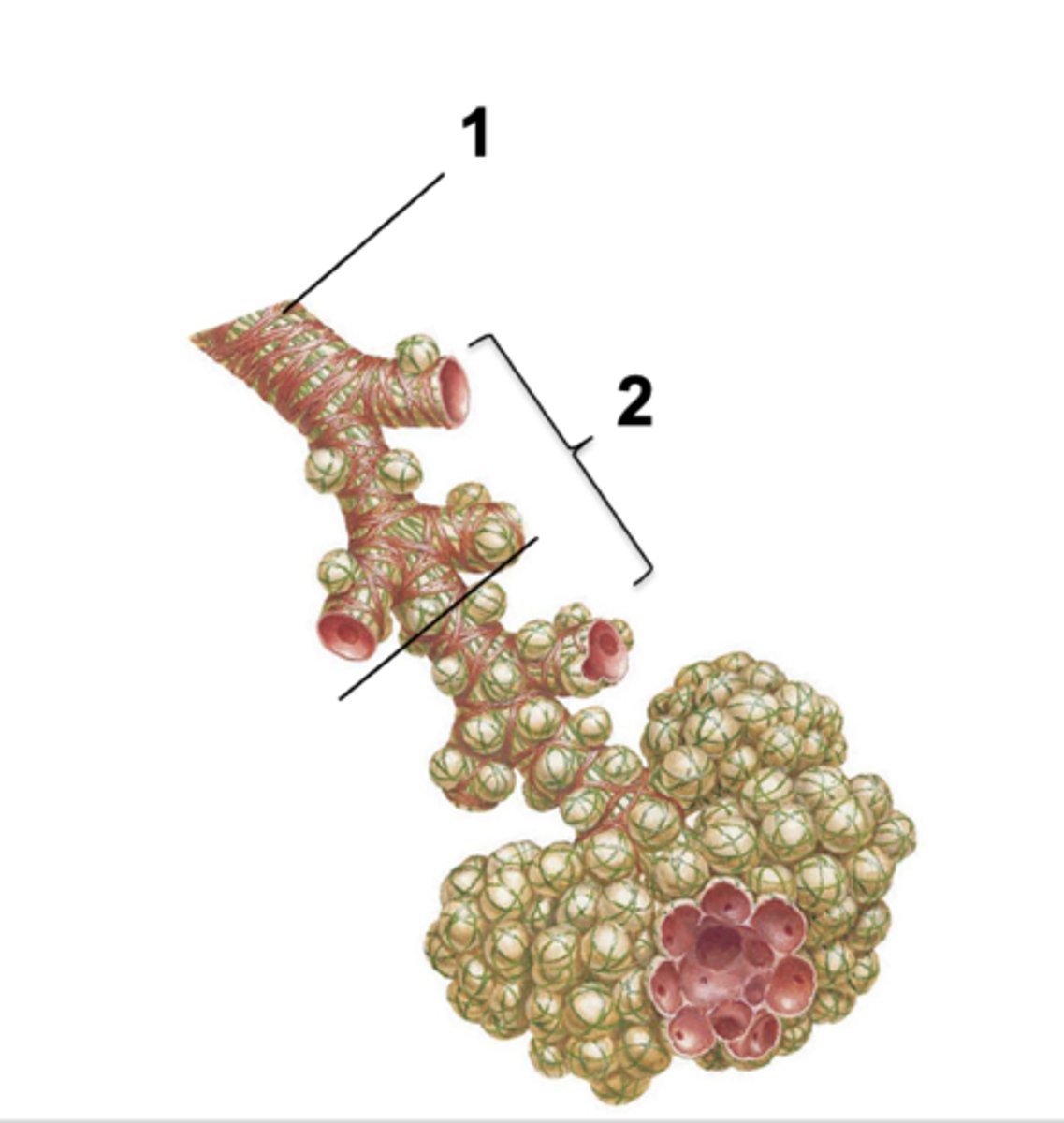
ID the structure at #1:
Terminal bronchiole
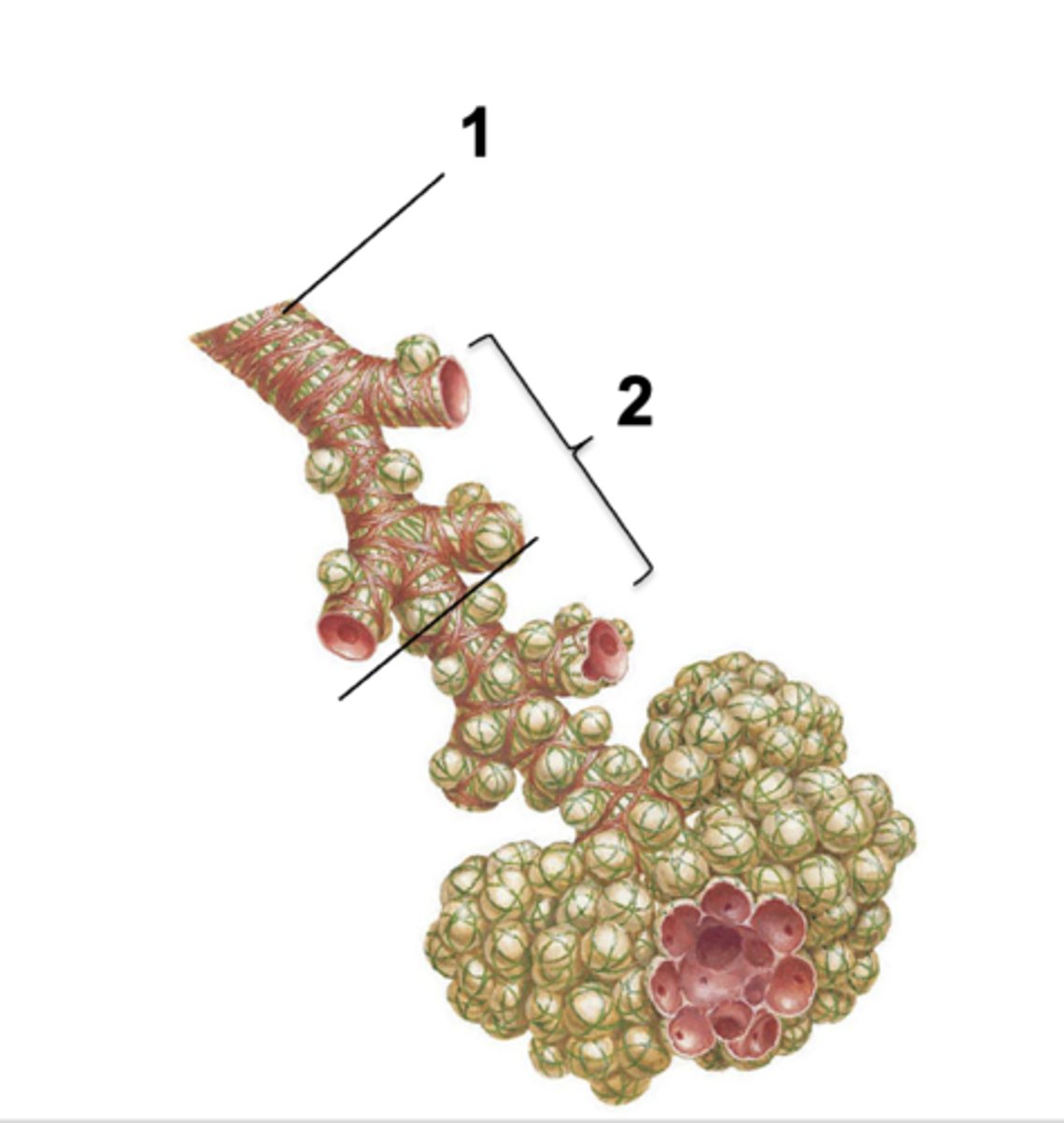
ID the structure at #2:
Respiratory bronchiole
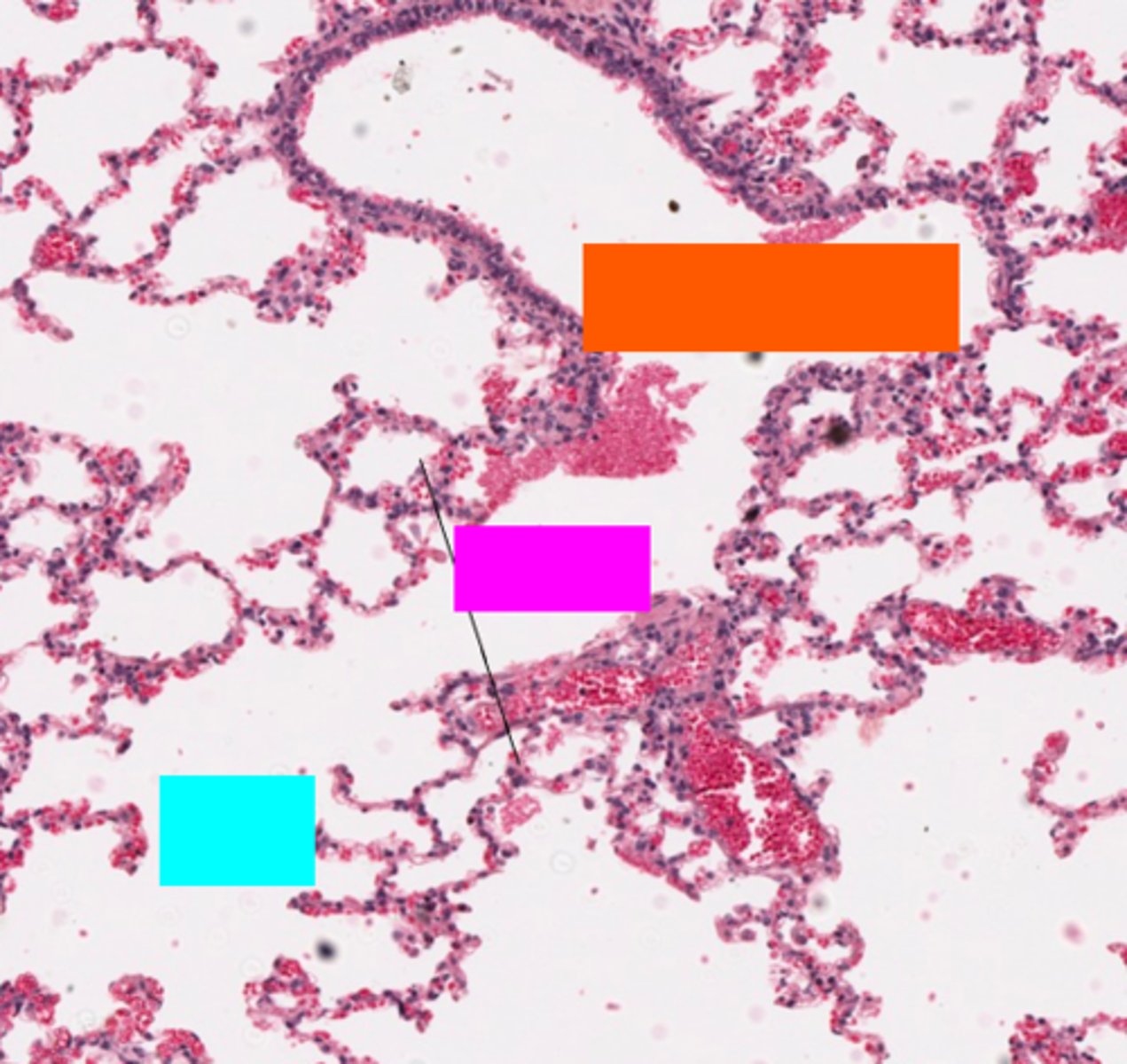
ID the orange box:
branching terminal bronchioles
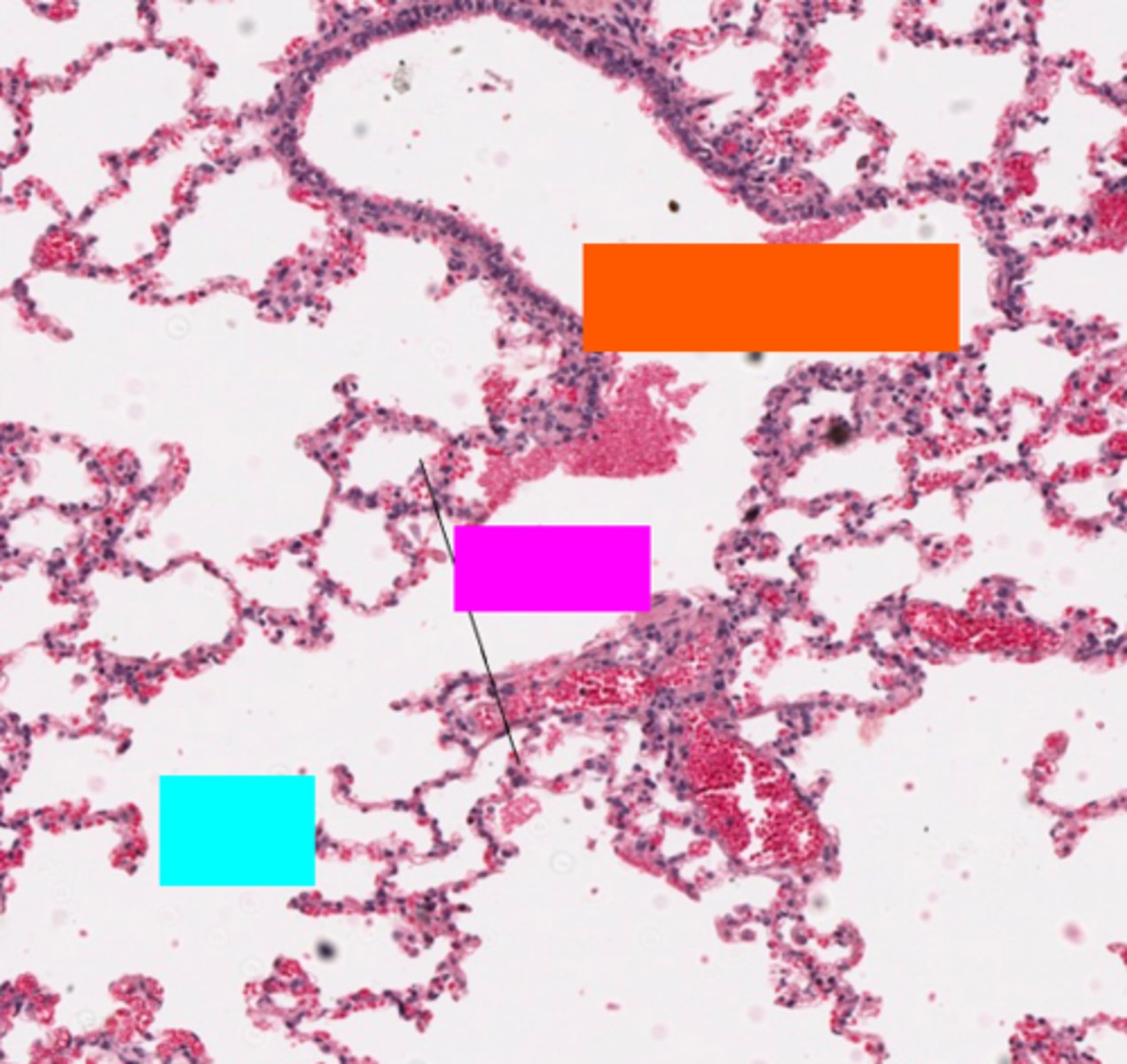
ID the purple box:
respiratory bronchioles
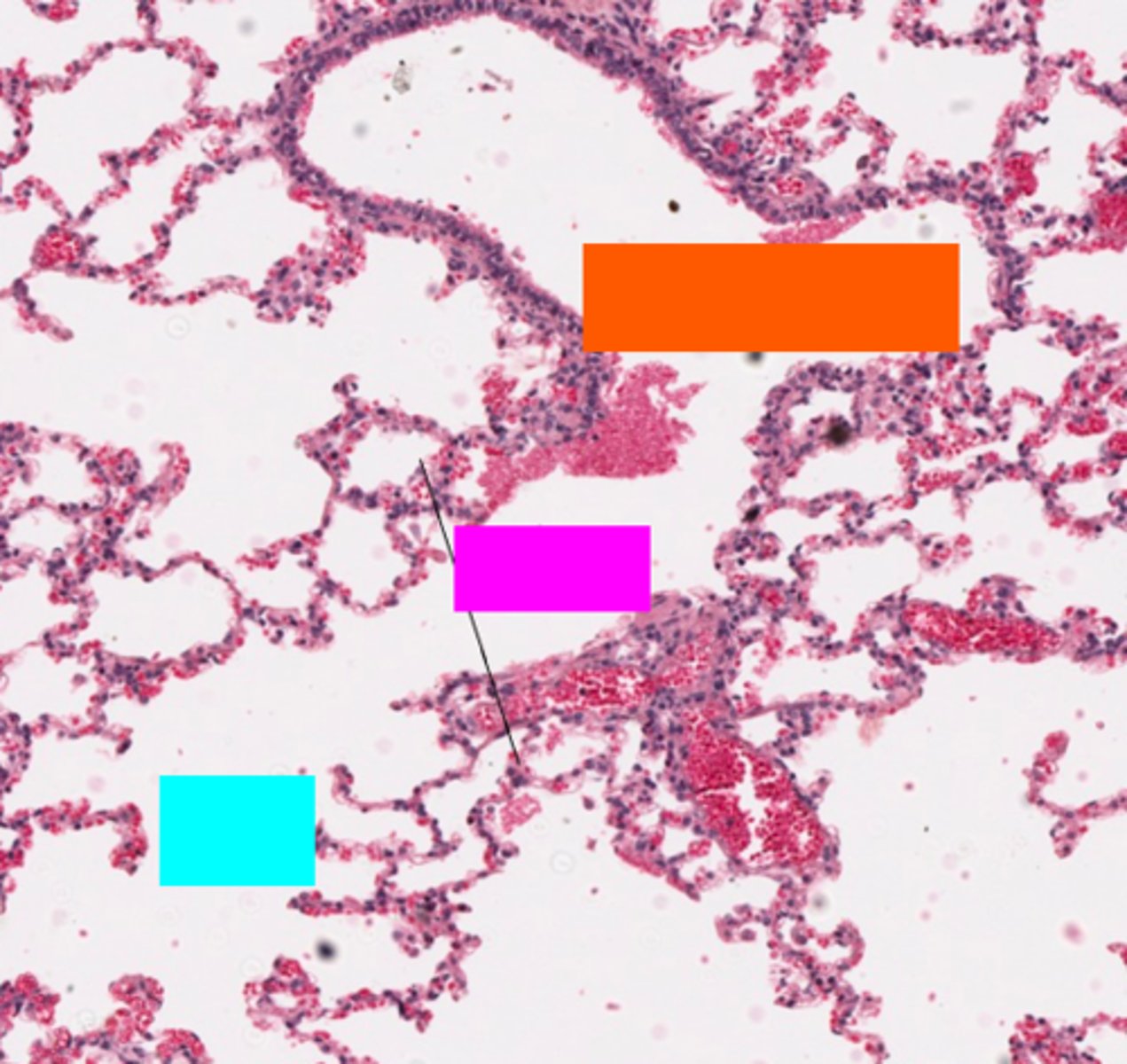
ID the blue box:
alveolar ducts
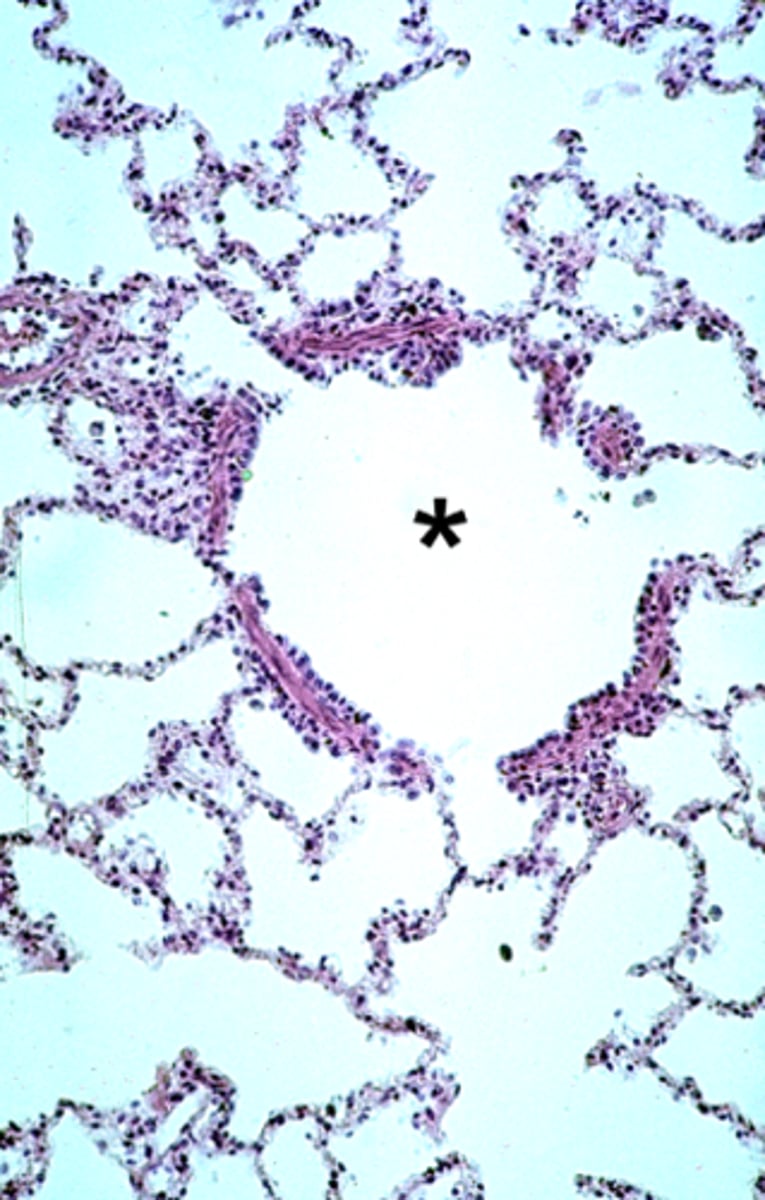
ID the structure at the asterisk:
respiratory bronchioles
What has the following characteristics?
- 40% of cells
95% of surface area
type I cells
What has the following characteristics?
- 60% of cells
- 5% of surface area
type II cells
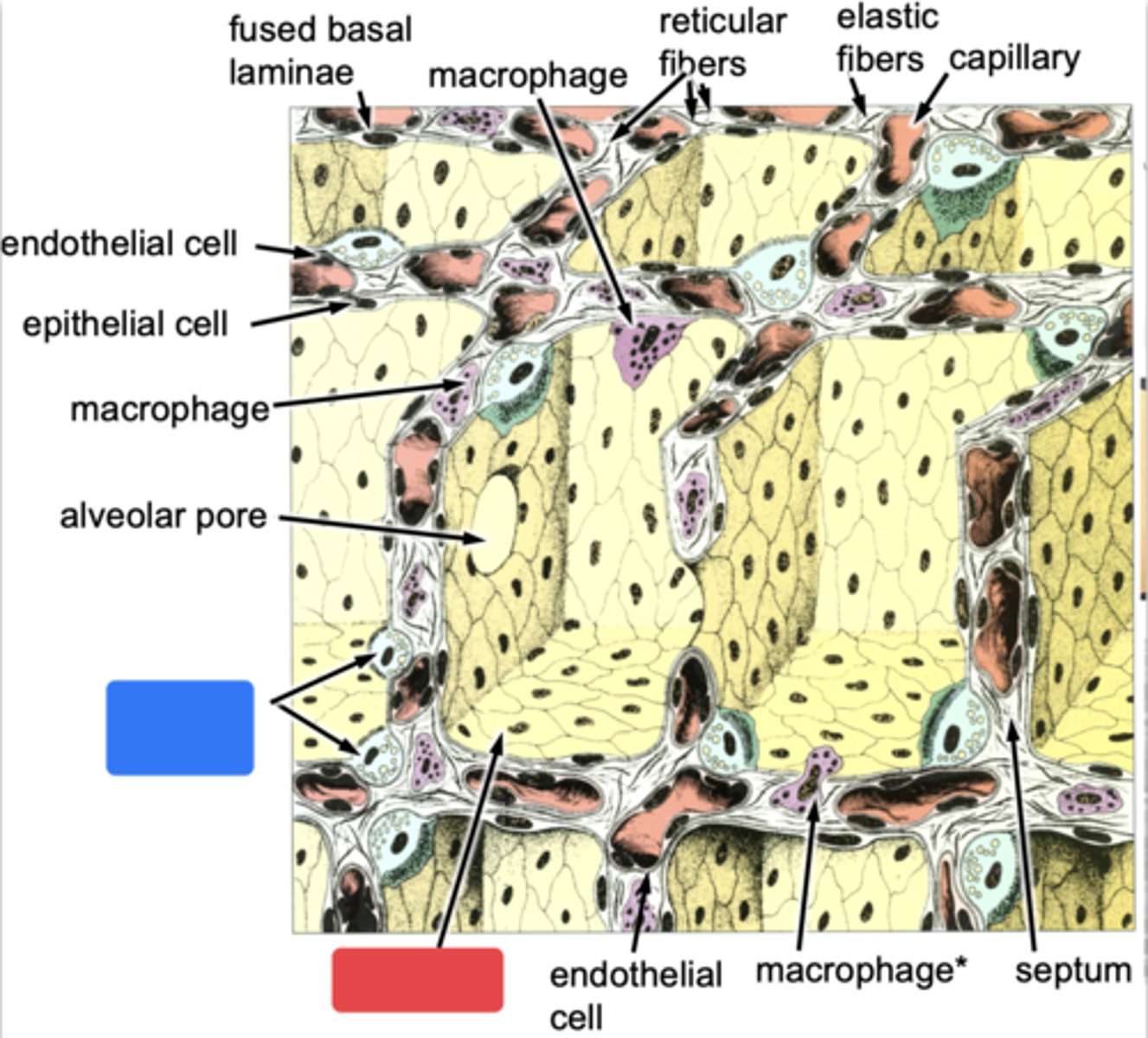
ID the cells at the blue box
type II cells
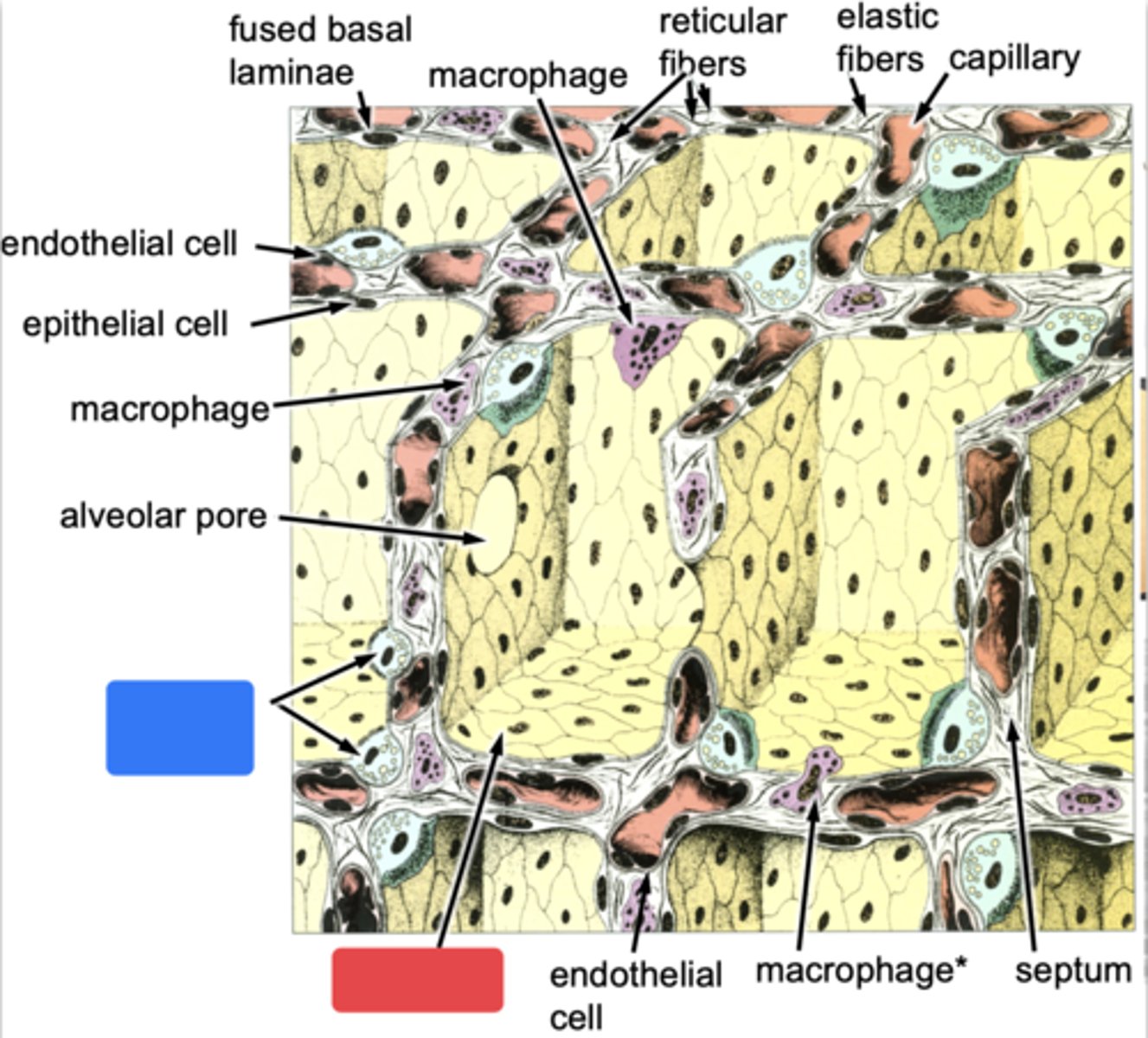
ID the cells at the red box
type I cells
____________ may occur with premature babies that have insufficient surfactant; administration of corticosteroids will increase the surfactant levels
respiratory distress syndrome
What has the following characteristics?
- Produced by type II pneumocytes
- Mixture of lipids and proteins
- Reduces surface tension at the air-blood surface
- Helps maintain shape and alveoli and prevent collapse during expiration
surfactant
surfactant within alveoli does what?
- Reduces surface tension by making lungs more compliant
- Prevents atelectasis (collapse)
Production of surfactant in fetus occurs during _____ month
6th
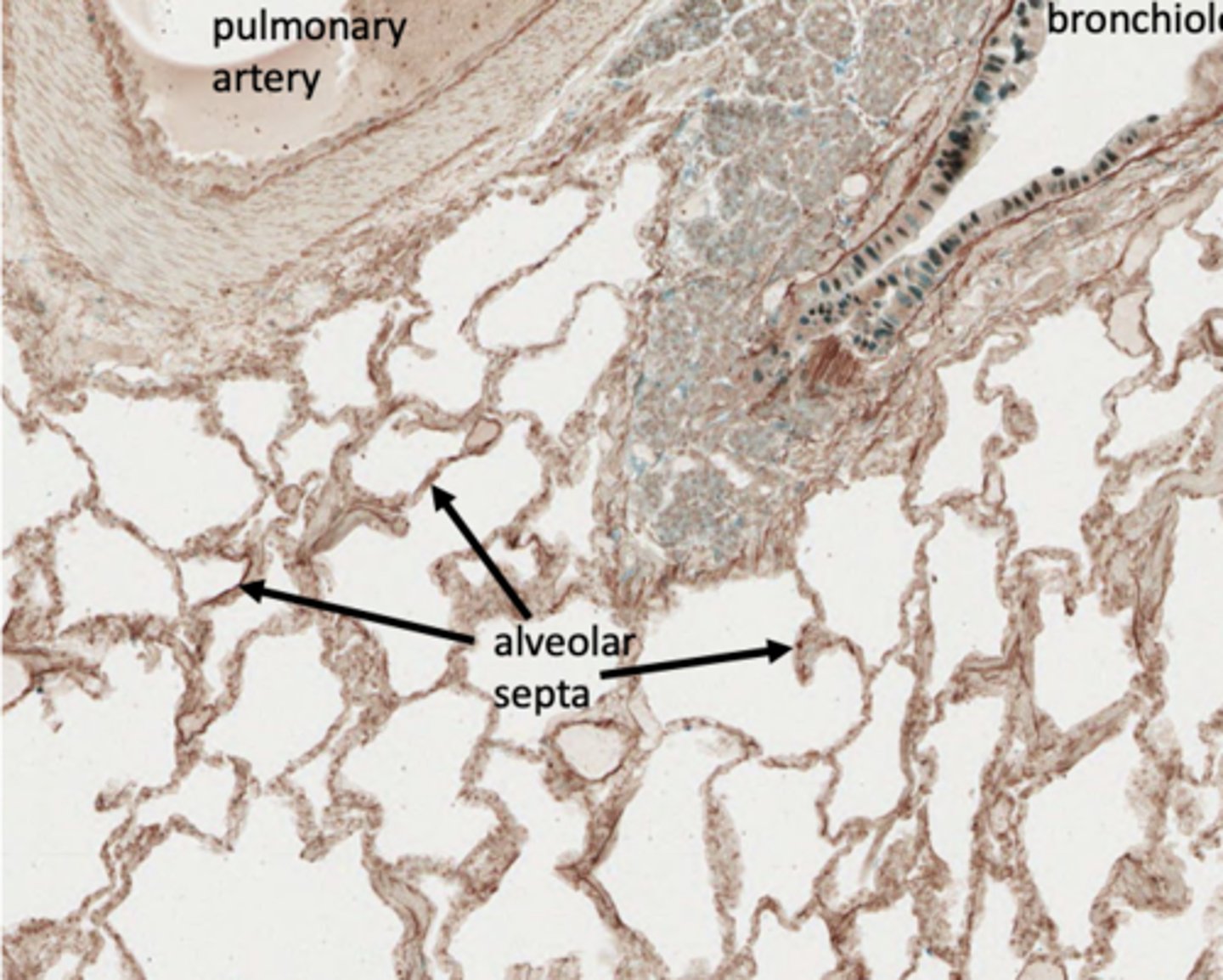
This is stained with what to show a key feature of alveoli?
elastin
____________ are extremely thin squamous cells that line 95% of the alveolar surface and form the barrier between the air space and the septal wall
Type I pneumocytes
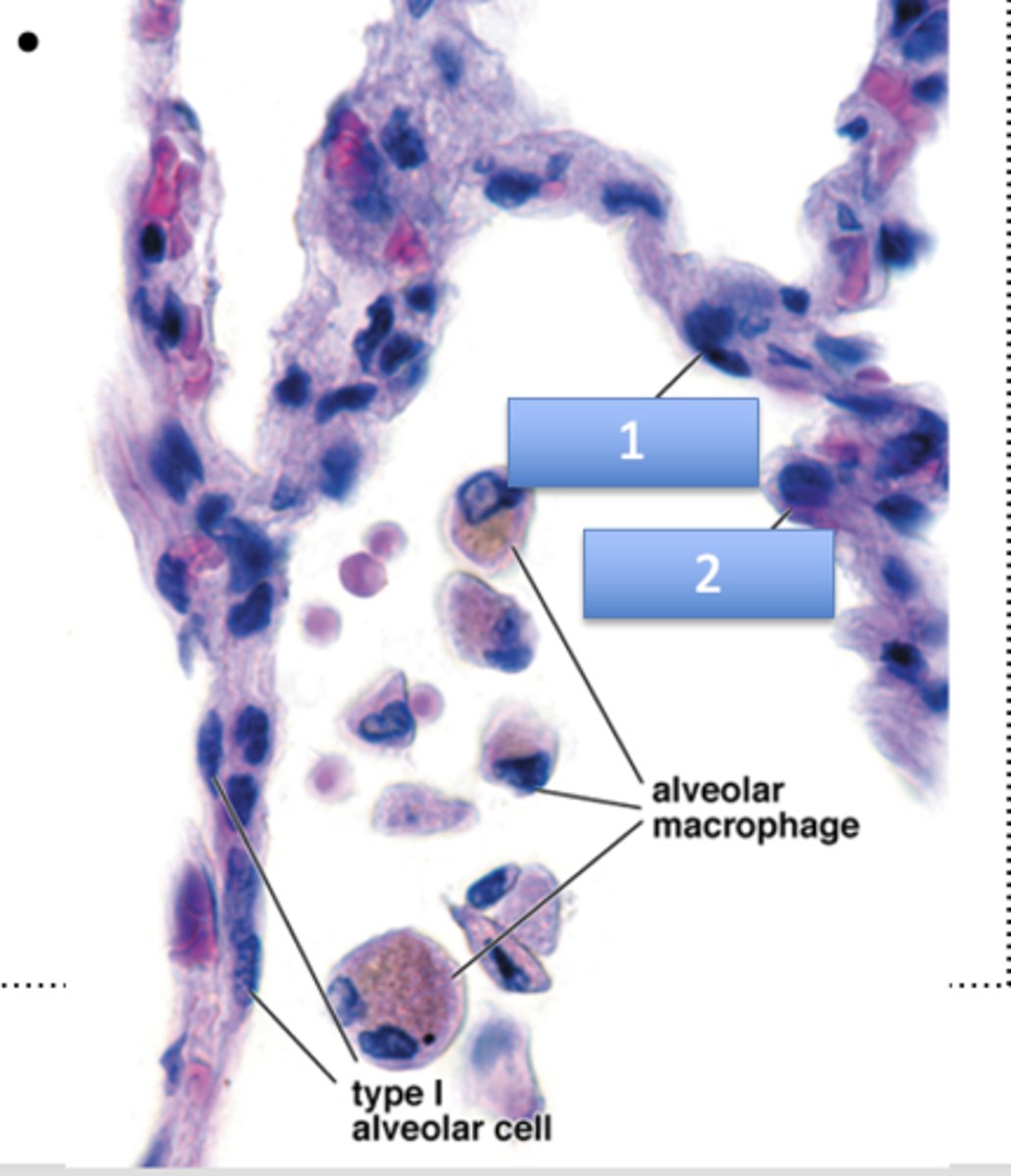
What is 1?
type I alveolar cell (flattened nuclei)
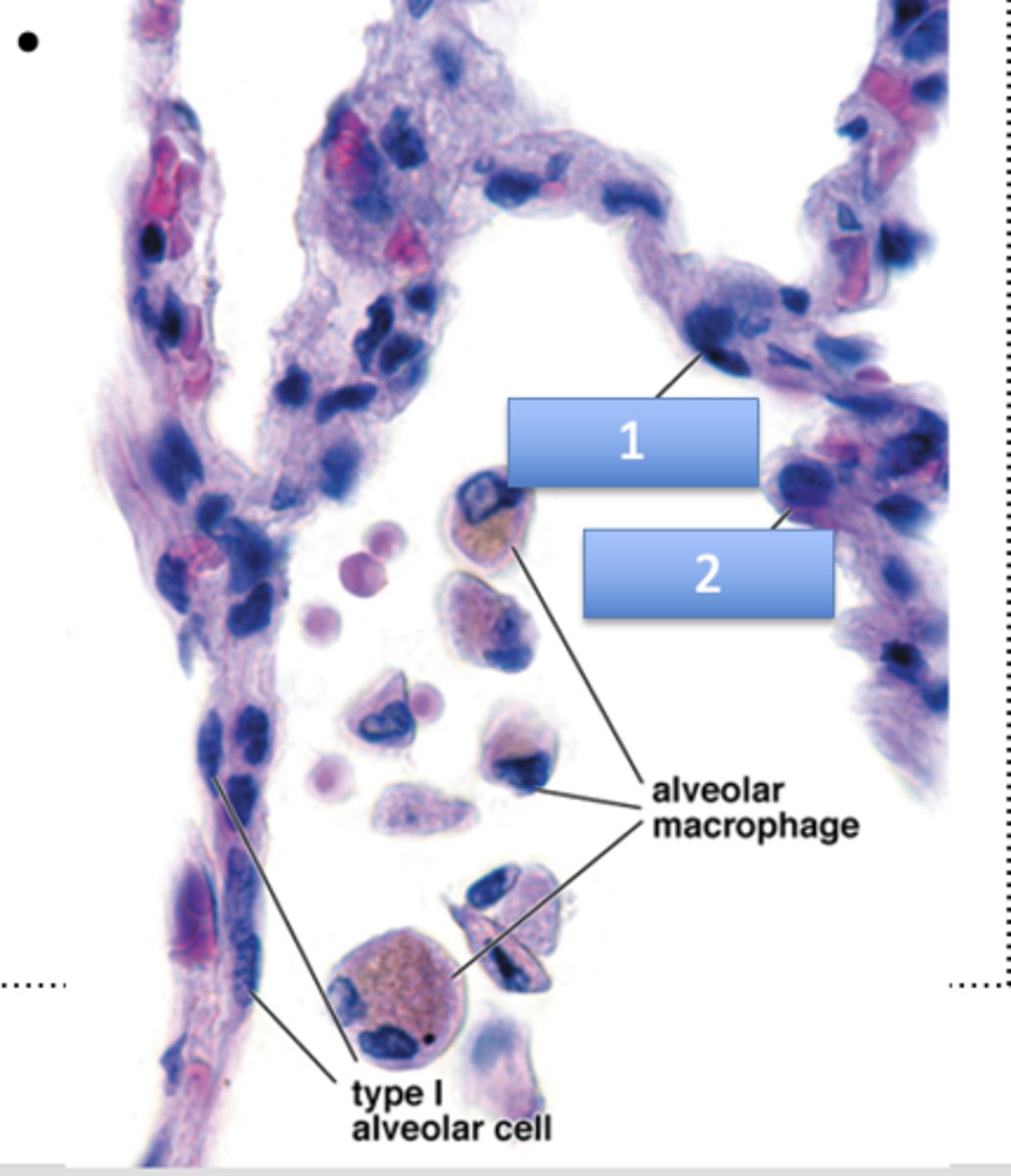
What is 2?
type II alveolar cell (rounded nuclei)
what are the components of the Blood-air barrier? (3)
- Type 1 Pheumocytes
- Basement membrane
- Endothelium
t/f: type I pneumocytes are post-mitotic cells; they are replaced following injury by progeny of the type II pneumocytes
true
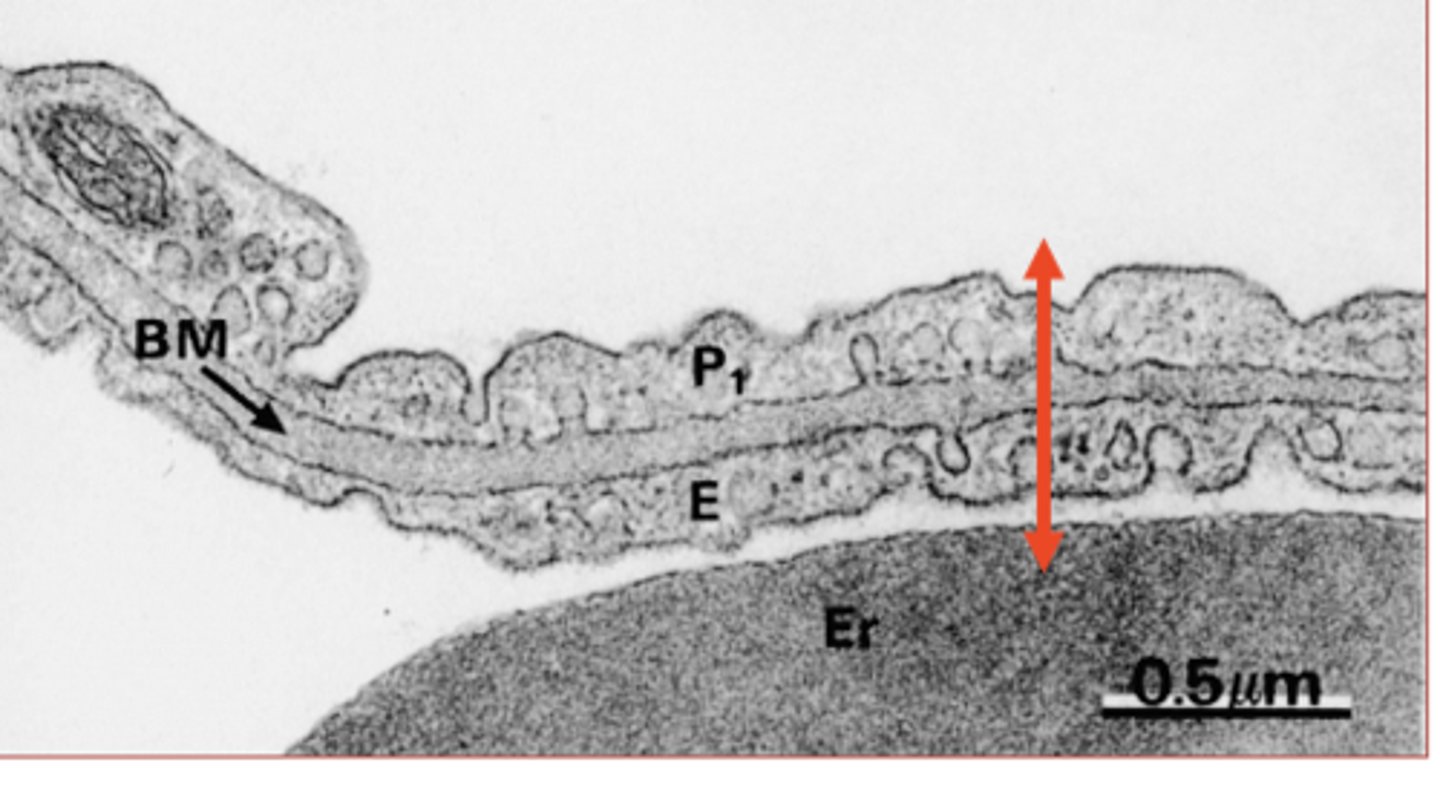
What is the red arrow showing?
gas exchange barrier
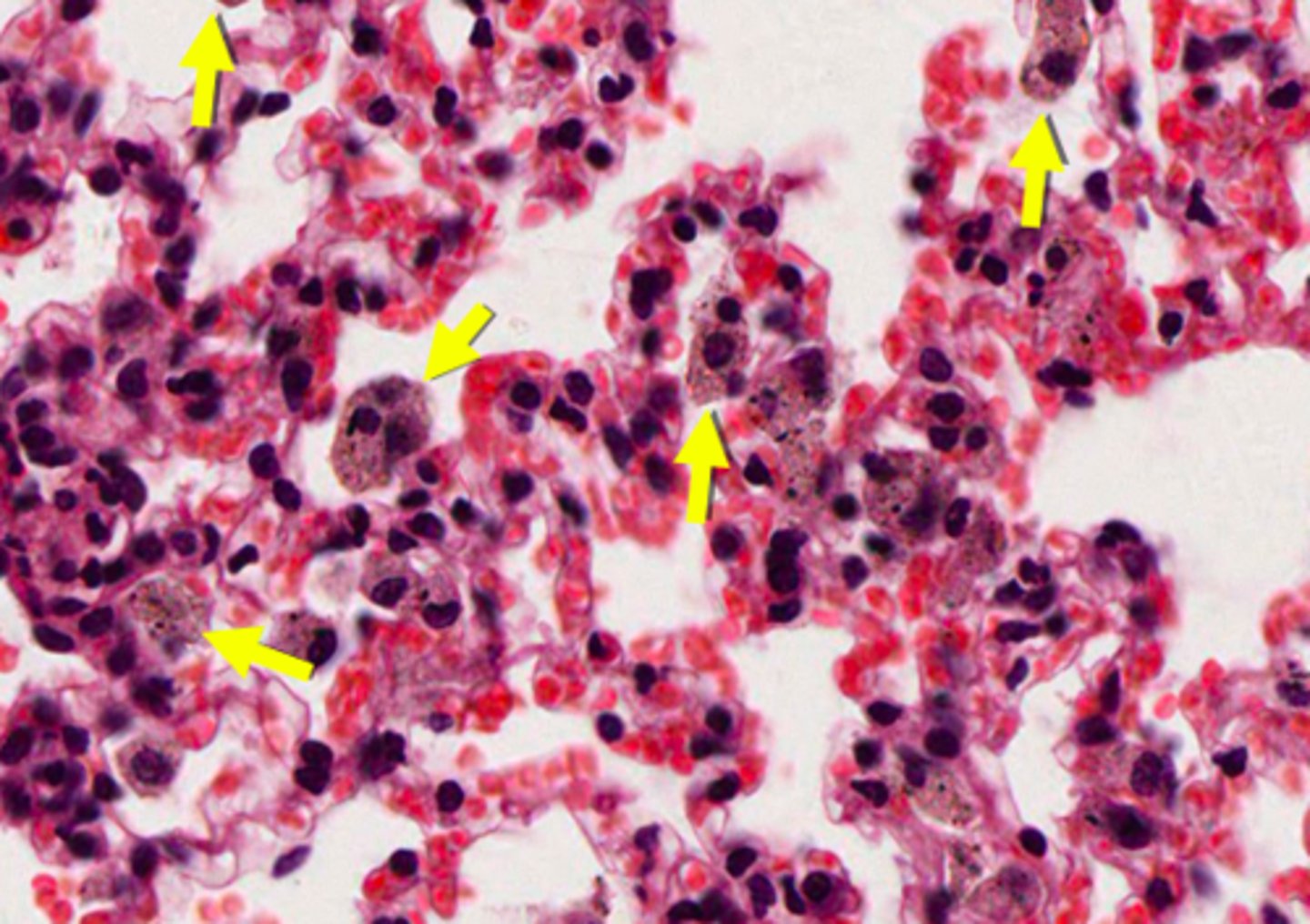
ID the cells:
dust cells (alveolar macrophages)
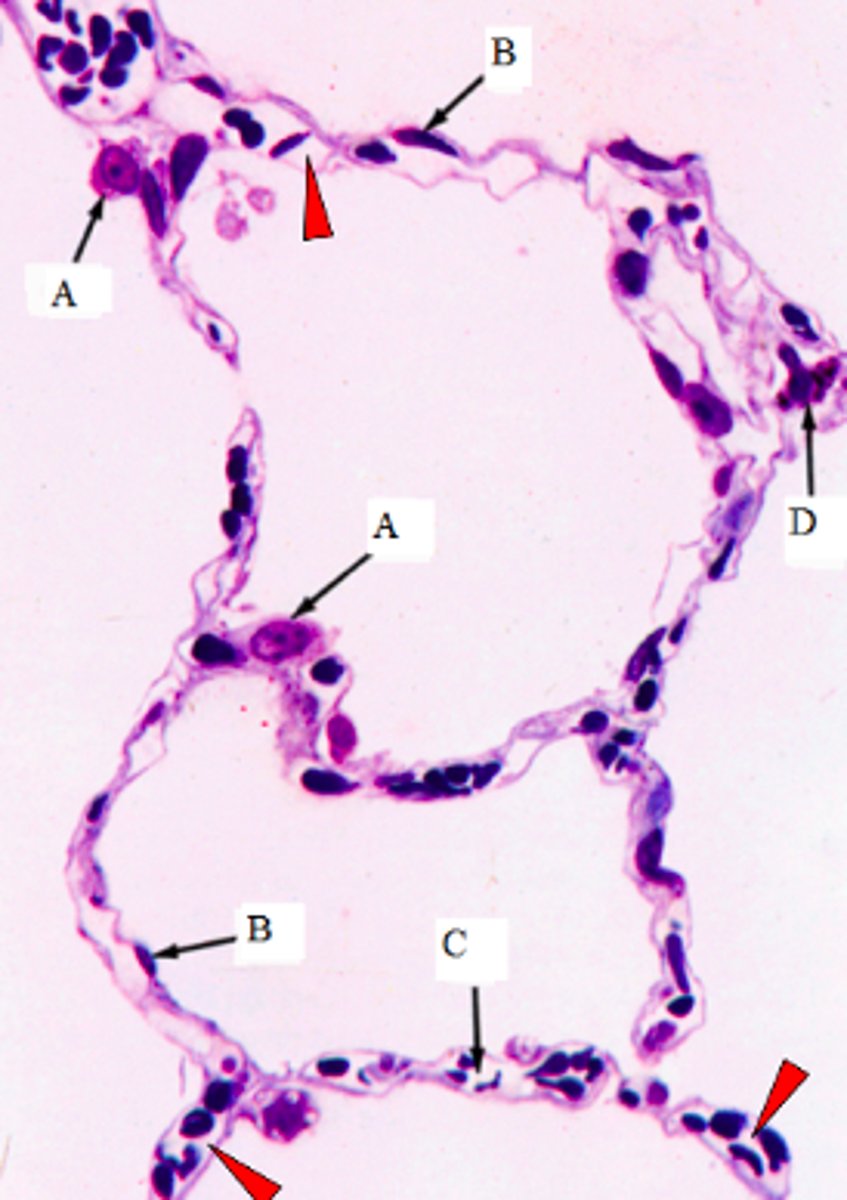
ID the cells marked w/ the letter A:
Type II pneumocytes
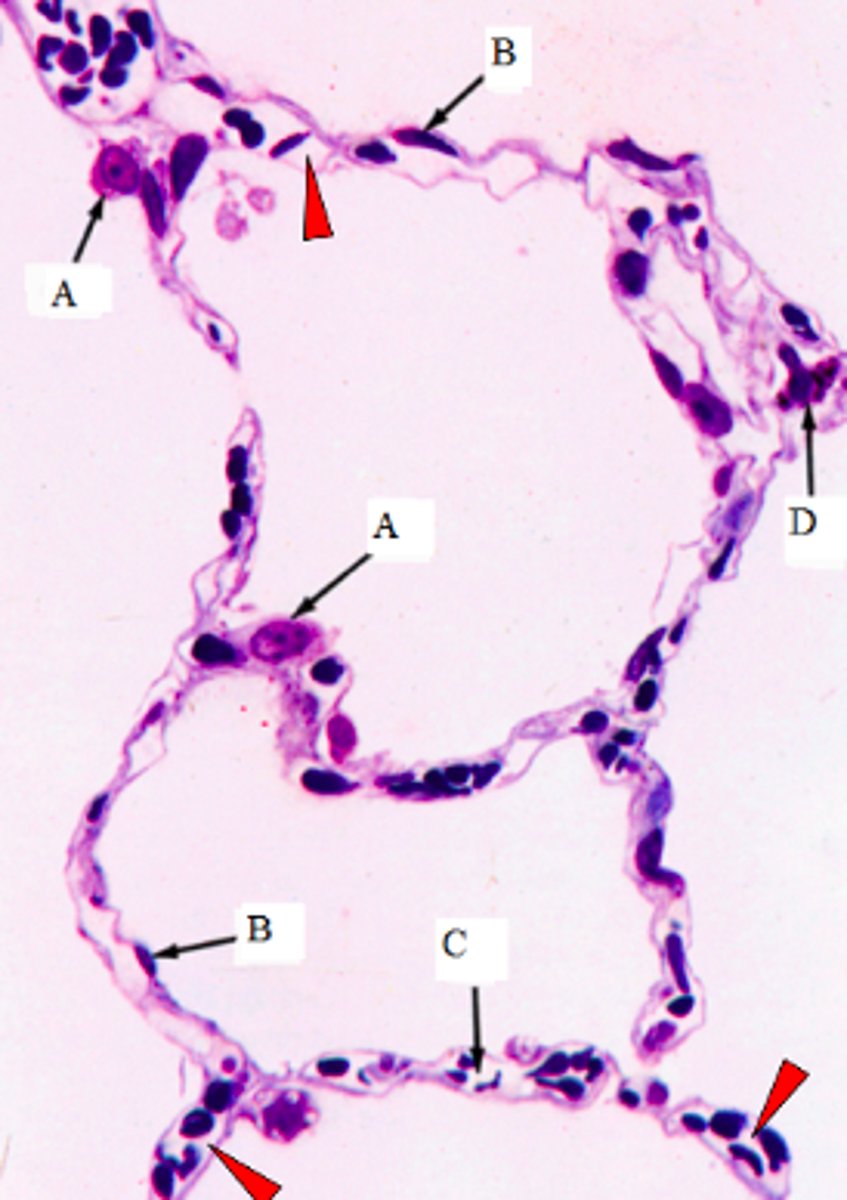
ID the cells marked w/ the letter B:
Type I pneumocytes
ID the cells marked w/ the letter C:
Capillaires
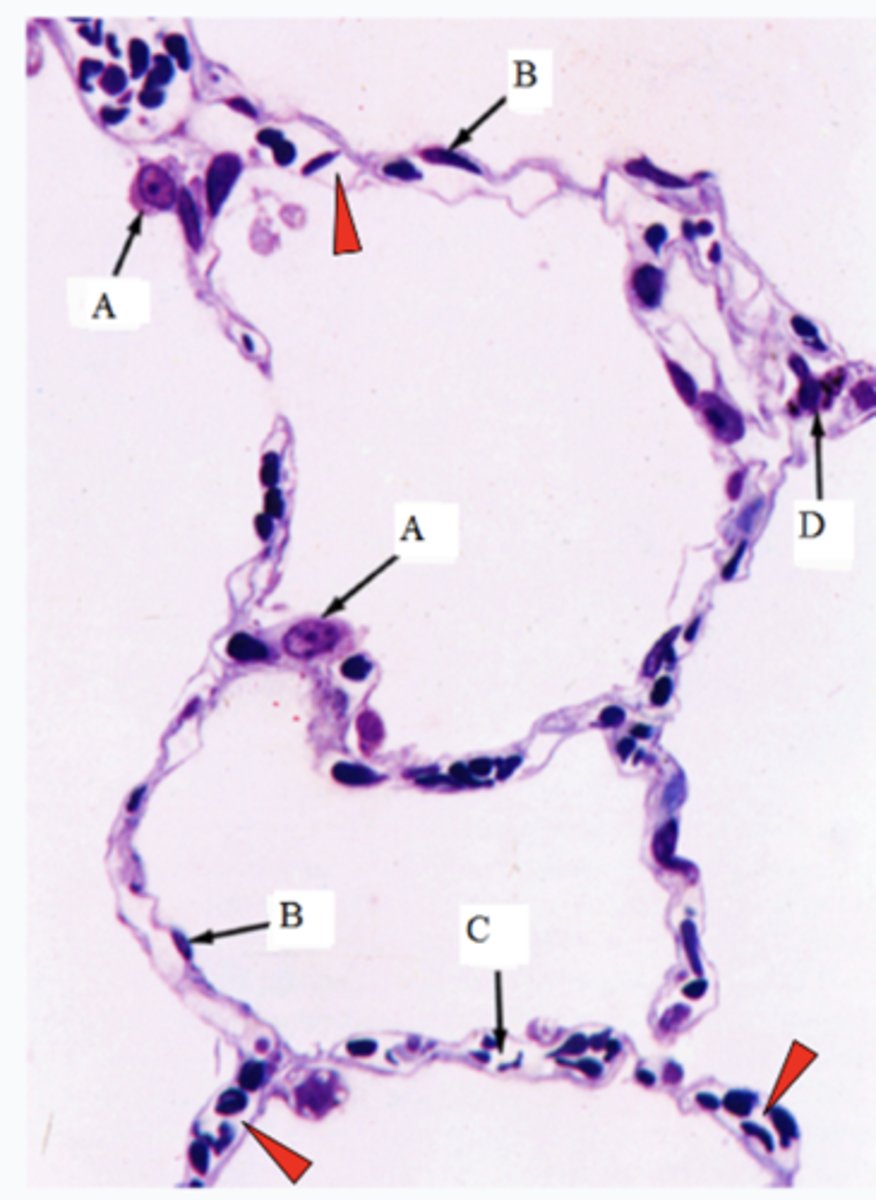
ID the cells marked w/ the letter D:
Macrophages
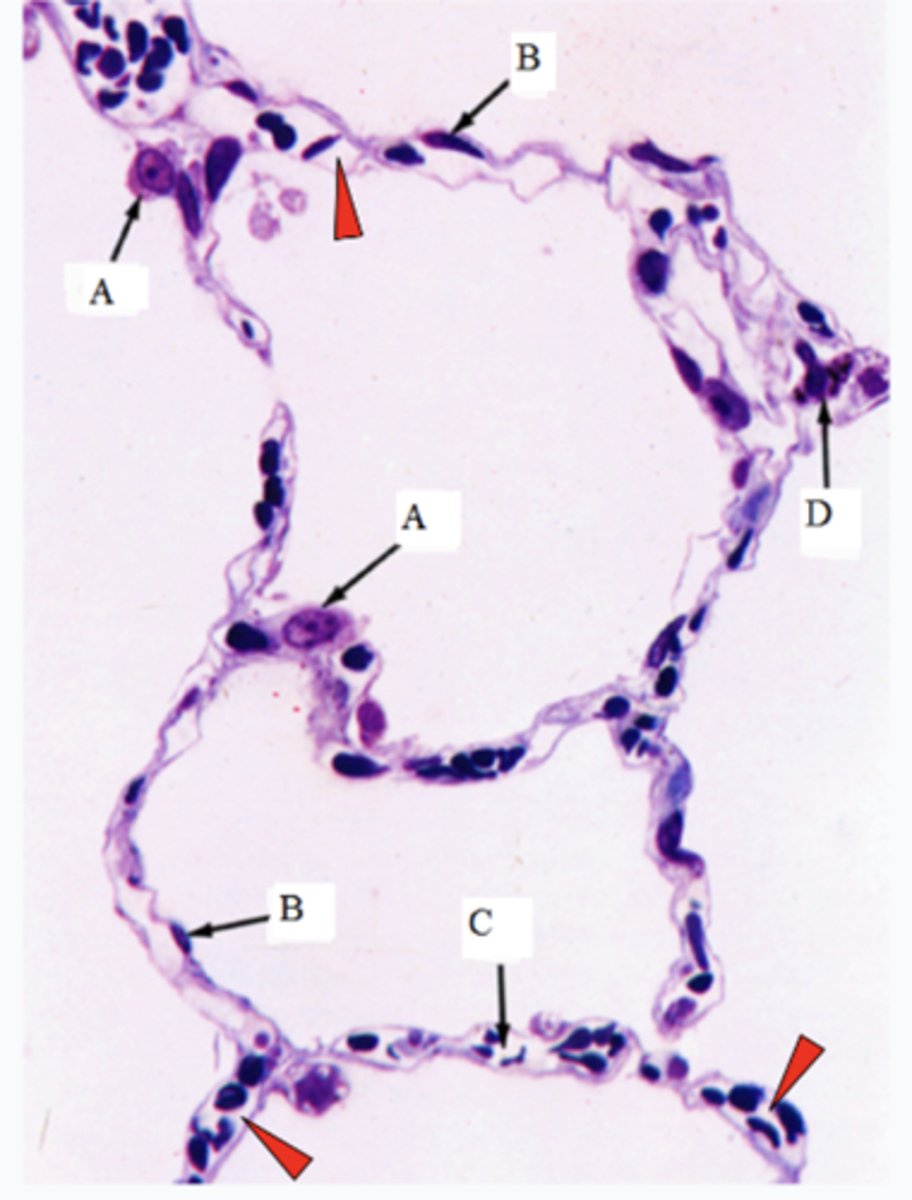
The arrowheads point to the lumen of what structures?
Lumen of capillaires