4.1-4.3
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Prejudice
an unjustified judgment, opinion, or attitude directed toward certain people based on their membership in a particular group
Discrimination
unjustifiable negative behavior toward a group and its members

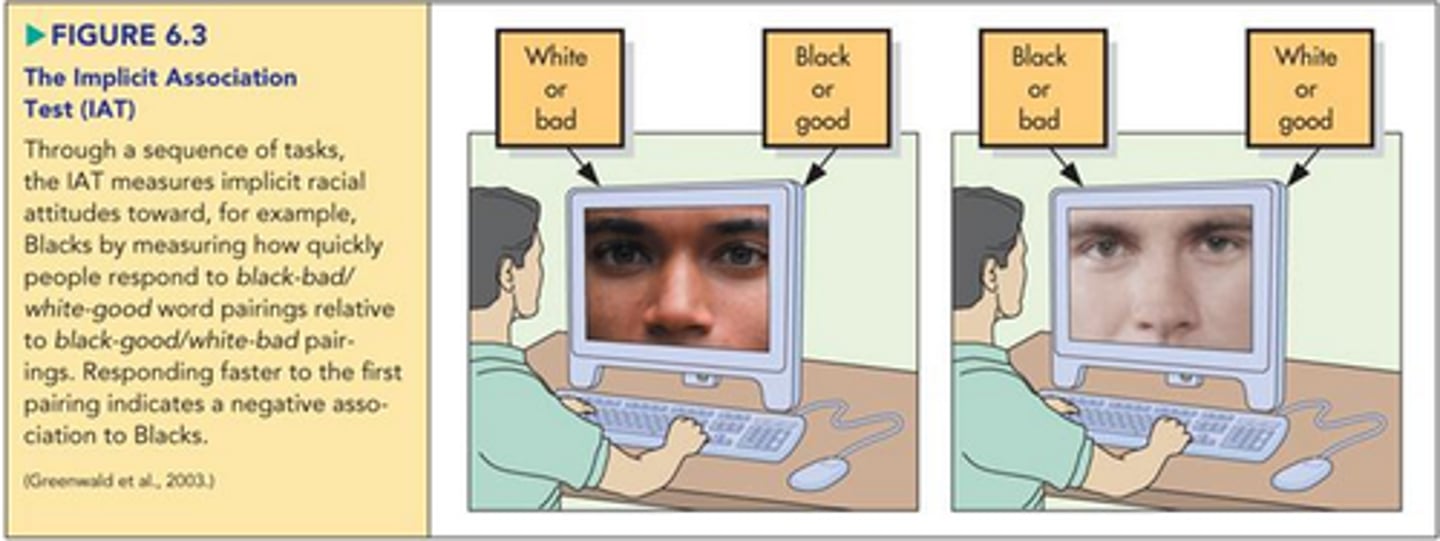
Implicit attitudes
attitudes that influence a person's feelings and behavior at an unconscious level
Ethnocentrism
the tendency to look at the world primarily from the perspective of one's own culture

Out-group homogeneity bias
the perception that individuals in an out-group are more similar (homogeneous) than they really are, as compared to members of one's in-group
In-group bias
the tendency to favor one's own group over other groups

Belief perseverance
the tendency to continue believing something even after the evidence supporting it has been contradicted
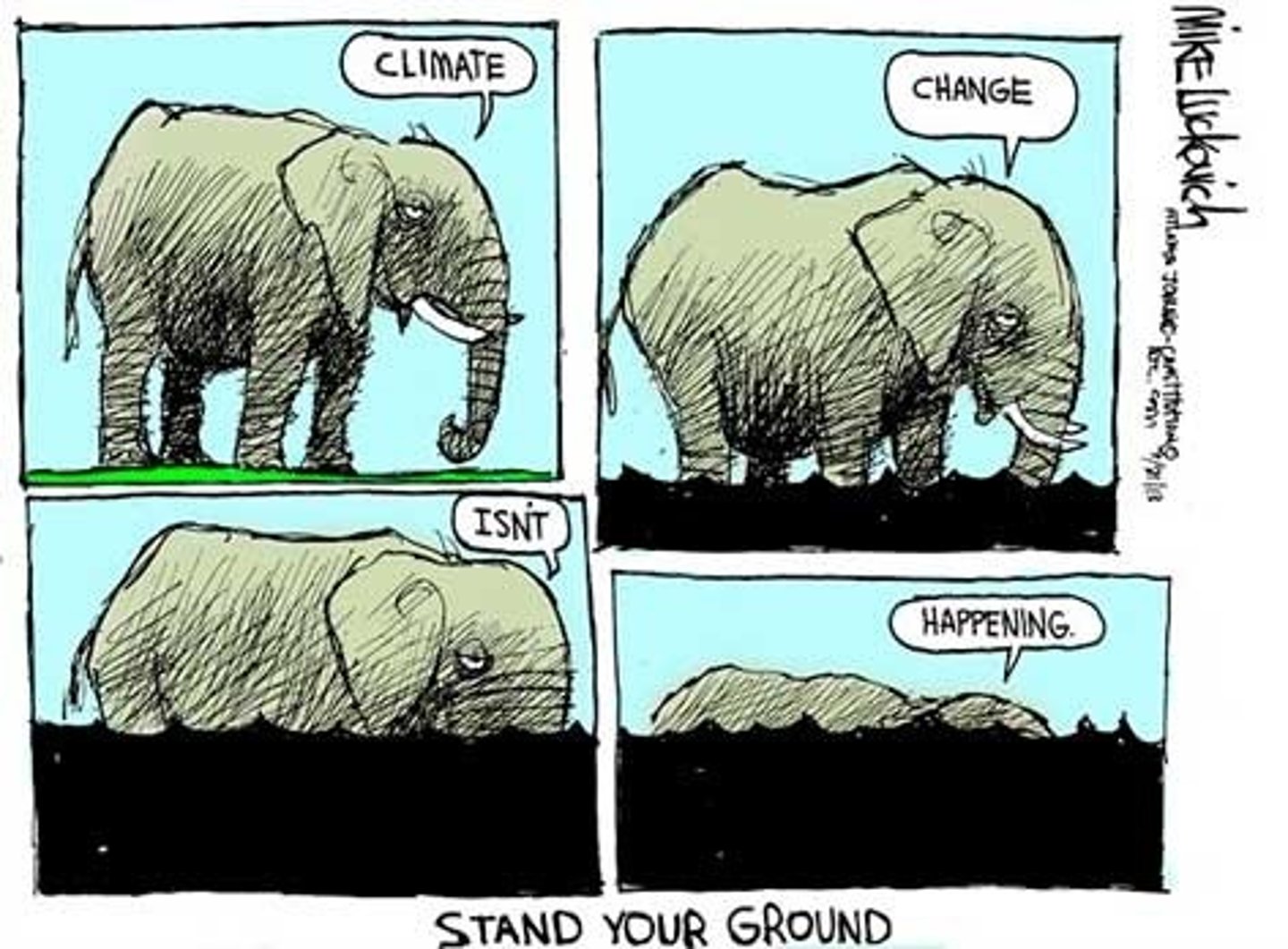

Confirmation bias
a tendency to search for information that supports one's preconceptions and to ignore or distort contradictory evidence

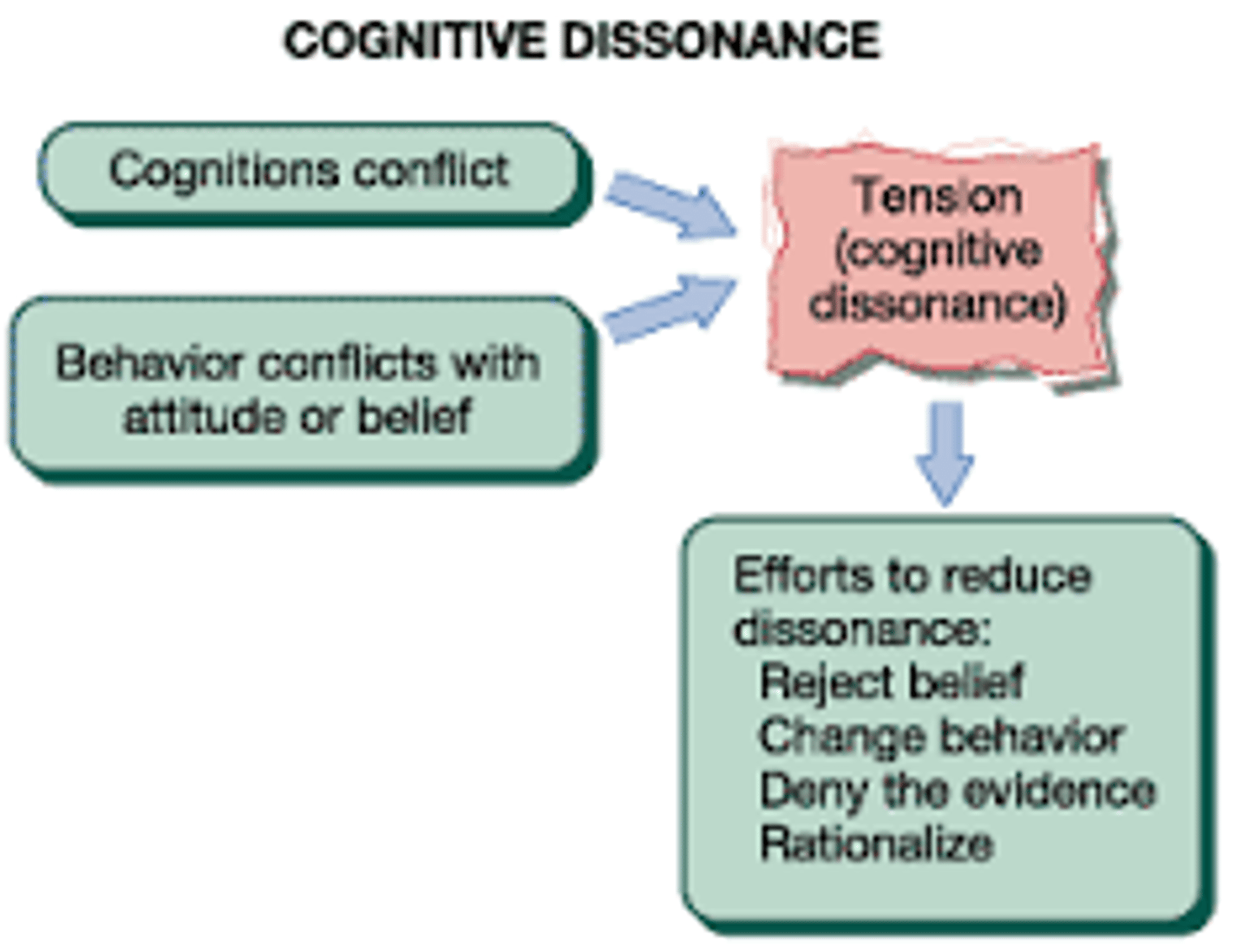
Cognitive dissonance
the discomfort a person feels when their beliefs are inconsistent with their actions
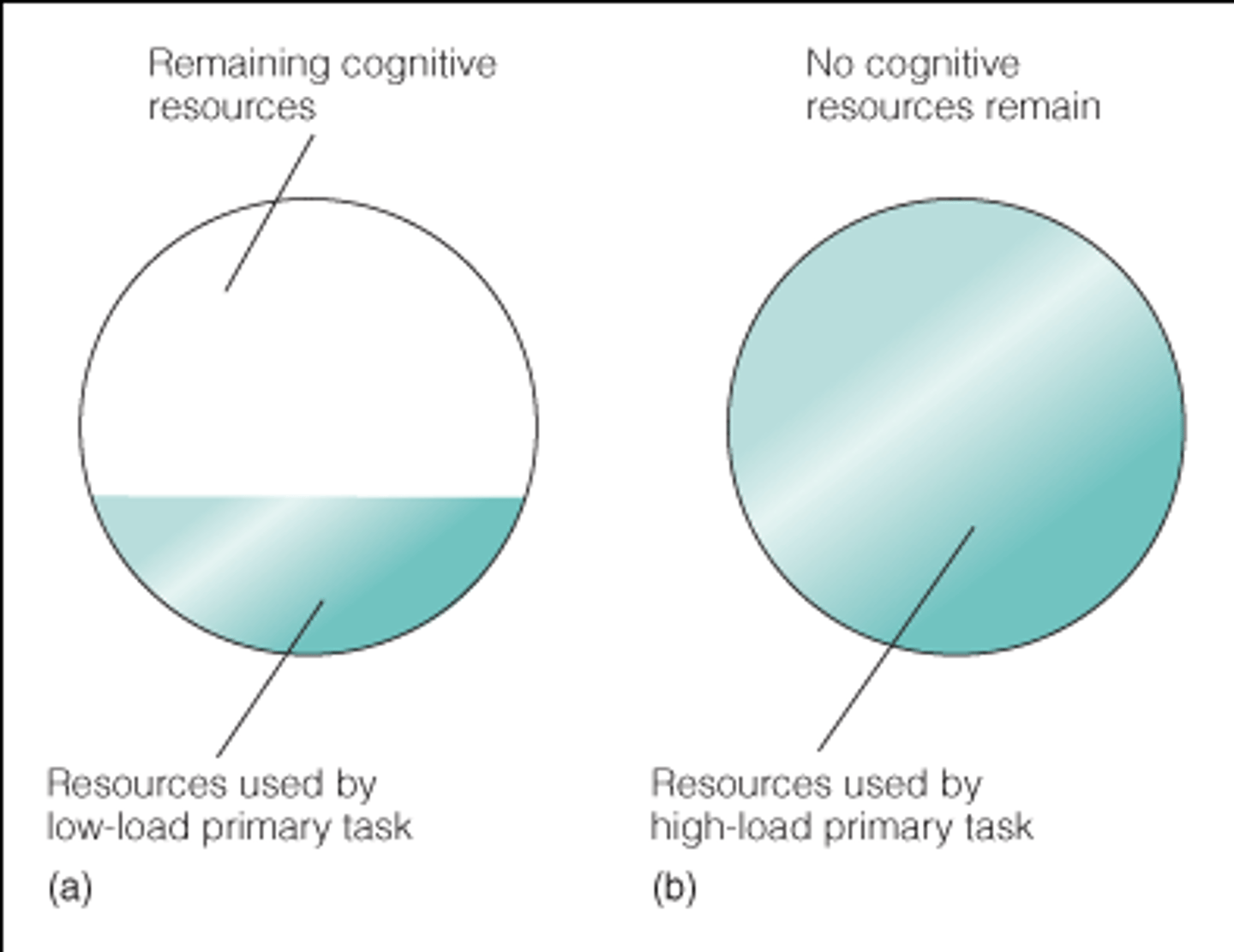
Cognitive load
the amount of information the working memory can process at any given time
Attribution
the process of explaining one's own behavior and the behavior of others
situational attribution
attribution to factors external to an actor, such as the task, other people, or luck
explanatory style
A person's characteristic way of explaining his experiences. Consistently attributing bad experiences to internal, global, and stable causes may increase vulnerability to depression.
actor-observer bias
the tendency to blame our actions on the situation and blame the actions of others on their personalities
fundamental attribution error
refers to an individuals tendency to attribute another's actions to their character or personality, while attributing their behavior to external situation factors outside their control
self-serving bias
the tendency for people to take personal credit for success but blame failure on external factors
internal locus of control
the perception that we control our own fate
external locus of control
the perception that chance or outside forces beyond your personal control determine your fate.
Mere Exposure Effect
the tendency for liking to increase with the frequency of exposure
self-fulfilling prophecies
Process the witch and originally false expectation leads to its own confirmation
Social Comparison
the comparison of oneself to others in ways that raise one's self-esteem
Stereotype
a generalized (sometimes accurate but often overgeneralized) belief about a group of people
just-world phenomenon
the tendency for people to believe the world is just and that people therefore get what they deserve and deserve what they get
out-group homogeneity bias
our tendency to see out-group members as being pretty much all alike
In-group bias
tendency to favor individuals within our group over those from outside our group
Ethnocentrism
Belief in the superiority of one's nation or ethnic group.
cognitive dissonance
an unpleasant state that arises when a person recognizes the inconsistency of his or her actions, attitudes, or beliefs
Social Norms
A group's expectations regarding what is appropriate and acceptable for its members' attitudes and behaviors.
Social Influence Theory
People are more likely to do whatever they see as being the norm. It states that people have a tendency to change their behavior according to those around them, and those nearby have stronger effects than those further away.
Central route persuasion
A method of convincing others to take an action or make a decision based on facts and evidence of the merits of the outcome
peripheral route persuasion
Uses positive association with cues such as beauty, fame, and positive emotions
foot-in-the-door
the tendency for people who have first agreed to a small request to comply later with a larger request
door-in-the-face
people are more likely to agree to a small request after they have refused a large request
Conformity
Adjusting one's behavior or thinking to coincide with a group standard.
Obedience
A form of compliance that occurs when people follow direct commands, usually from someone in a position of authority
Individualism
giving priority to one's own goals over group goals and defining one's identity in terms of personal attributes rather than group identifications
Collectivism
giving priority to the goals of one's group (often one's extended family or work group) and defining one's identity accordingly
Multiculturalism
A perspective recognizing the cultural diversity of the United States and promoting equal standing for all cultural traditions
group polarization
the enhancement of a group's prevailing inclinations through discussion within the group
Groupthink
the mode of thinking that occurs when the desire for harmony in a decision-making group overrides a realistic appraisal of alternatives
diffusion of responsibility
the tendency for individuals to feel diminished responsibility for their actions when they are surrounded by others who are acting the same way
Social Loafing
the tendency for people in a group to exert less effort when pooling their efforts toward attaining a common goal than when individually accountable
Deindividuation
the loss of self-awareness and self-restraint occurring in group situations that foster arousal and anonymity
social facilitation
improved performance on simple or well-learned tasks in the presence of others
false consensus effect
the tendency to overestimate the extent to which others share our beliefs and behaviors
Social Trap
a situation in which the conflicting parties, by each rationally pursuing their self-interest, become caught in mutually destructive behavior
Superordinate goals
shared goals that override differences among people and require their cooperation
Altruism
Unselfish regard for or devotion to the welfare of others
Social Reciprocity Norm
The belief that if someone does something for you then you should do something for them
Bystander Effect
the tendency for any given bystander to be less likely to give aid if other bystanders are present
Dispositional Attribution
assuming that another's behavior is due to personality factors, not situational ones (internal)
Situation Attribution
the assumption that another person is doing something because of factors in the environment or the situation they are in (external)
ex- lost job, disabled veteran
Fundamental Attribution Error
the tendency, when analyzing others' behavior, to overestimate the influence of personal traits and underestimate the effects of the situation (only focused on behavior of others)
Saliency Bias
situations are less salient (noticeable) than internal traits
Self serving bias
-a readiness to perceive oneself favorably
-take credit for success but blame failure on external factor
ex- good vs. bad SAT scores
Actor-observer Bias
a tendency to blame personal shortcomings on external factors and the shortcomings of others on internal qualities
ex- tripping on the sidewalk, good or bad score on tests
Cultural Bias (individualistic)
emphasize independence and personal responsibility
-places like US, Canada
-more likely to commit FAE and self serving bias
Cultural Bias (collectivist)
emphasize independence and collective responsibility
-places like Japan, China
-more likely to be aware of how situational factors influence behavior
Hindsight Bias
the tendency for people to perceive events as having been more predictable than they actually were
-"I knew it all along"
ex- Battle of Gettysburg
False Consensus Effect
a tendency to see our own attitudes and behaviors as being typical
-a desire to view ones own thoughts as appropriate, normal and correct
ex- environmental issues, terrible movie
Confirmation bias
favors information that confirms you existing belief
ex-choosing college, poltical views
Halo Effect
a type of bias where the overall impression of a person influences the way we feel about their character, also called "physical attractiveness stereotype"
ex- jury convictions, educators