Ap Human Geo - unit 5 test
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
As a result of the Columbian exchange, which crop was transferred from the Americas to Europe, and later, spread through the world?
Maize (corn)
An agricultural hearth is a location where
Plants and animals were first domesticated
In which state or province is the long lot land, division most common
Quebec
Mediterranean agricultural products are most commonly grown in
Southern Spain and California
A meal that includes olives, pita bread, cheese, figs, lamb, and wine is most associated with which of the following?
Greece
Using the image above, which of the following is the most important identifier of the public land survey system
Square and rectangular fields
Rice and beans are very common ingredients used in Latin American food today. Which of the following scenarios best explains this?
Rice diffused from Europe and was added to meals using beans
Which of the following is not considered to be a negative consequence of the green revolution?
Family Farms disappeared, because they cannot compete with the corporate farms in the increased cost of farming
Which statement best explains a result of crop rotation?
Maintains soil fertility by restoring nutrients
The research and scientific discovery that fueled the green revolution occurred, mostly in the United States, which of the following regions, benefited the most from the green revolution?
South Asia
The greatest impact of the second agricultural revolution was
An increase in available food supplies
Which statement about 1961 to 2011 is best supported by the graph
Green Revolution techniques worked better in Asia than in Africa.
Which is a characteristic of the second agricultural revolution?
increased mechanization of farming
Which of the following is most accurate about agriculture today?
Productivity of land is increased as her concerns about sustainability.
According to Carl Sauer, which of the following is true about plant domestication?
It first occurred in diversified habitats with a variety of species.
A food assemblage that includes olives, pita bread, cheese, figs, lamb, and wine is most associated with which of the following?
Greece.
Which of the following best explains the potential impact of rising global temperatures on agricultural regions?
The wheat belt will shift northward.
Which of the following best explains the importance of climate to agricultural practices?
Midlatitude climates tend to support similar agricultural crops and practices, such as wheat farming in the United States and China.
Which of the following pairs of agricultural types occupies the largest percentage of the world's total land area?
Shifting cultivation and nomadic herding.
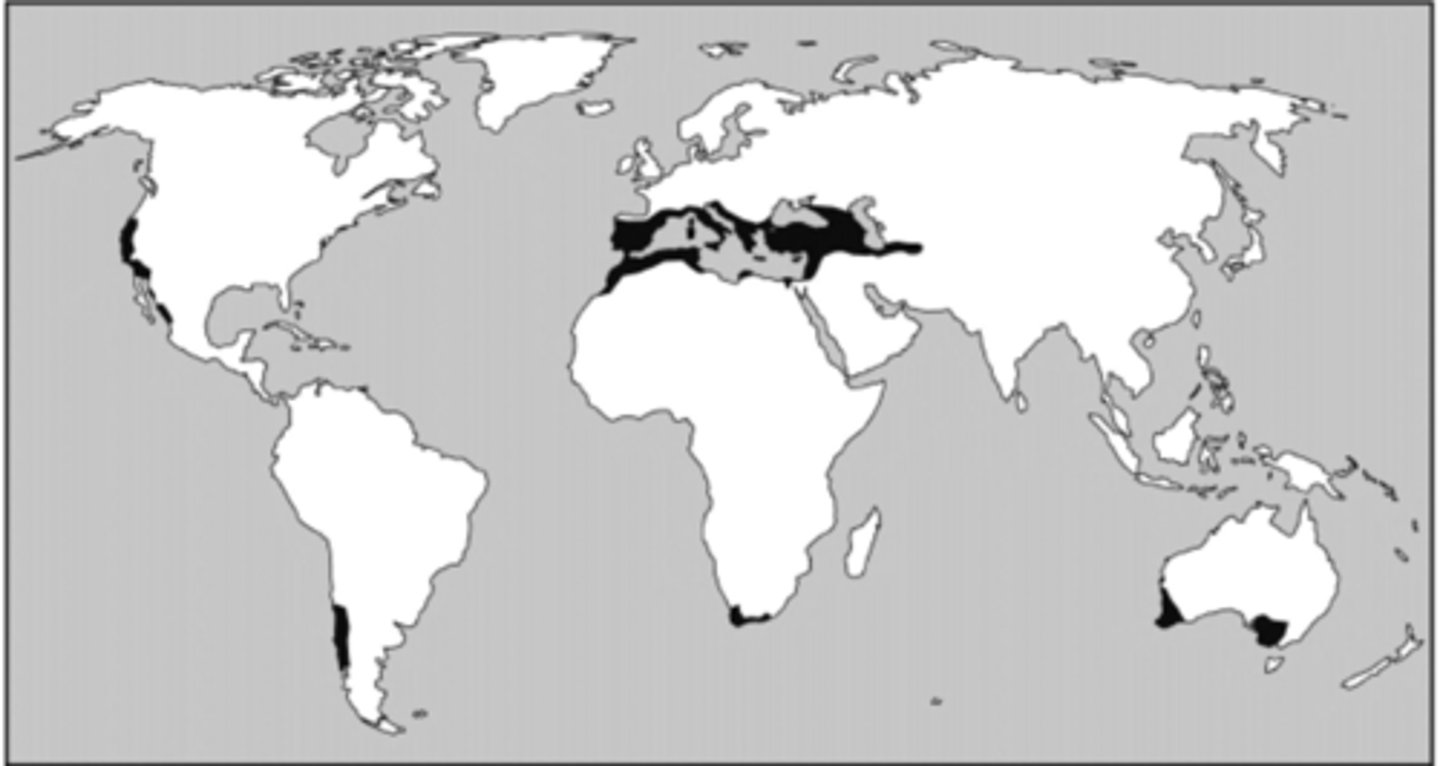
What kind of agriculture is primarily practiced in the dark-shaded areas on the map above?
Mediterranean.
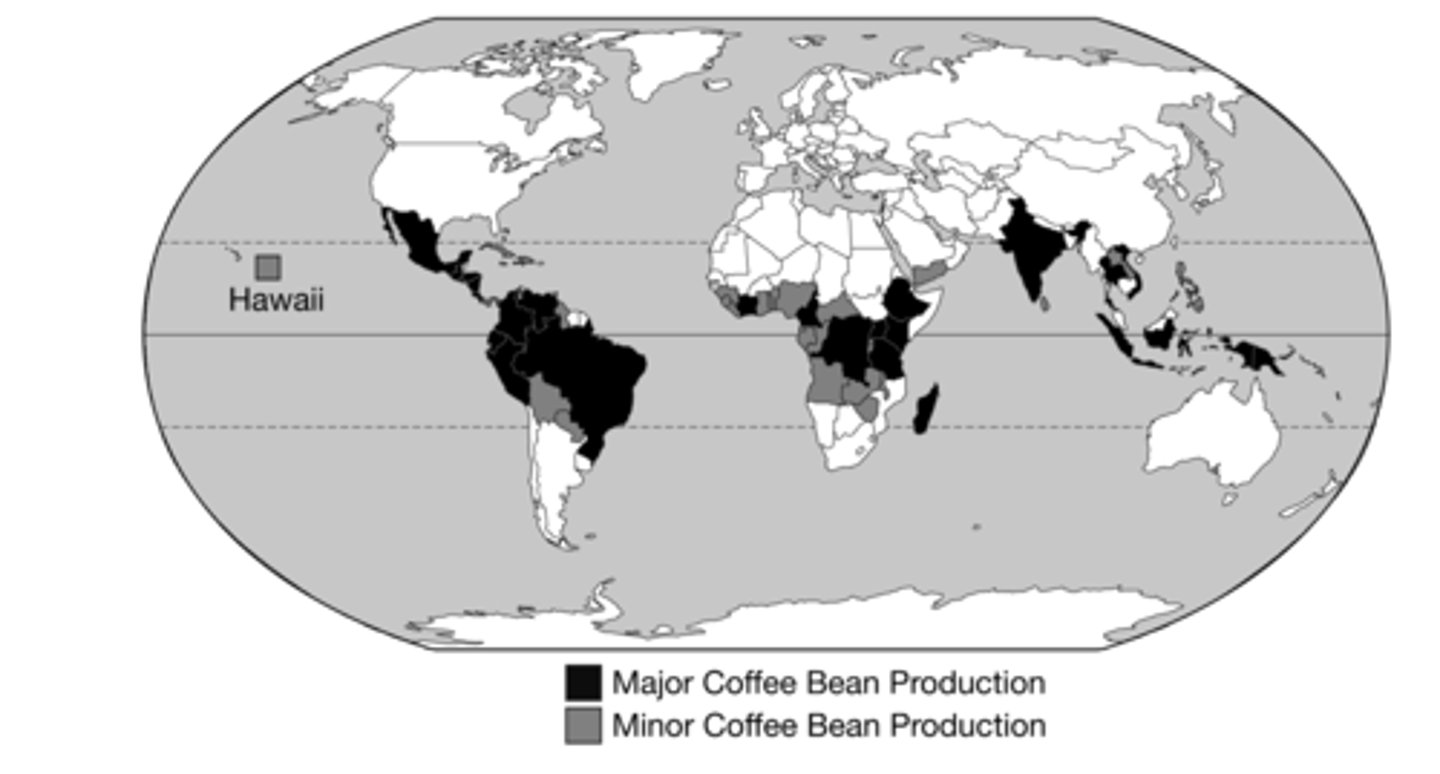
With the exception of Hawaii, the map shows the pattern of production for coffee beans by country.
If the map was reproduced at the subnational state or provincial scale, as Hawaii is on the map, what changes in pattern would be expected in other parts of the world?
The states in northern Mexico and northern India would not show any production.
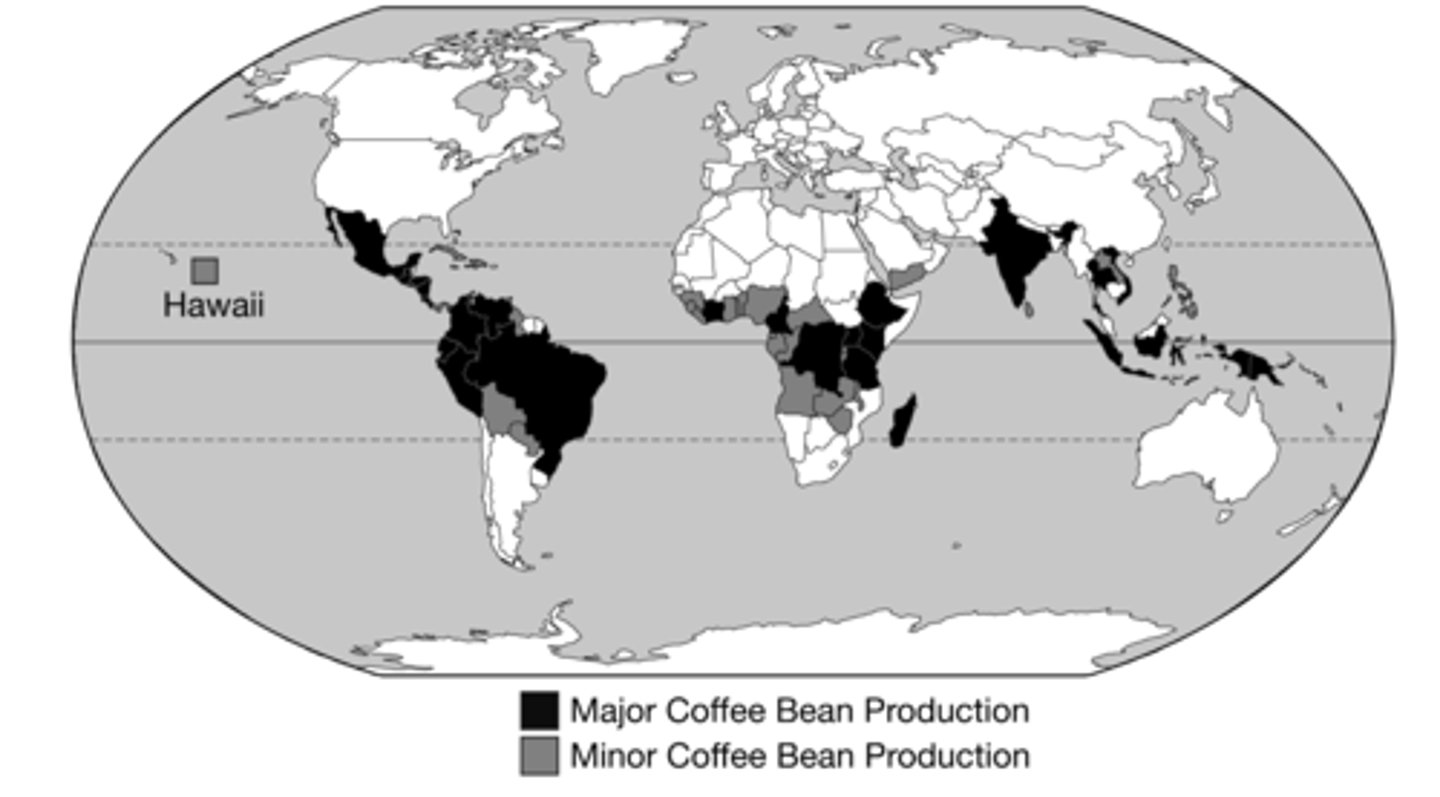
With the exception of Hawaii, the map shows the pattern of production for coffee beans by country.
Which of the following best describes the pattern of coffee bean production at the global scale?
Within tropical latitudes.
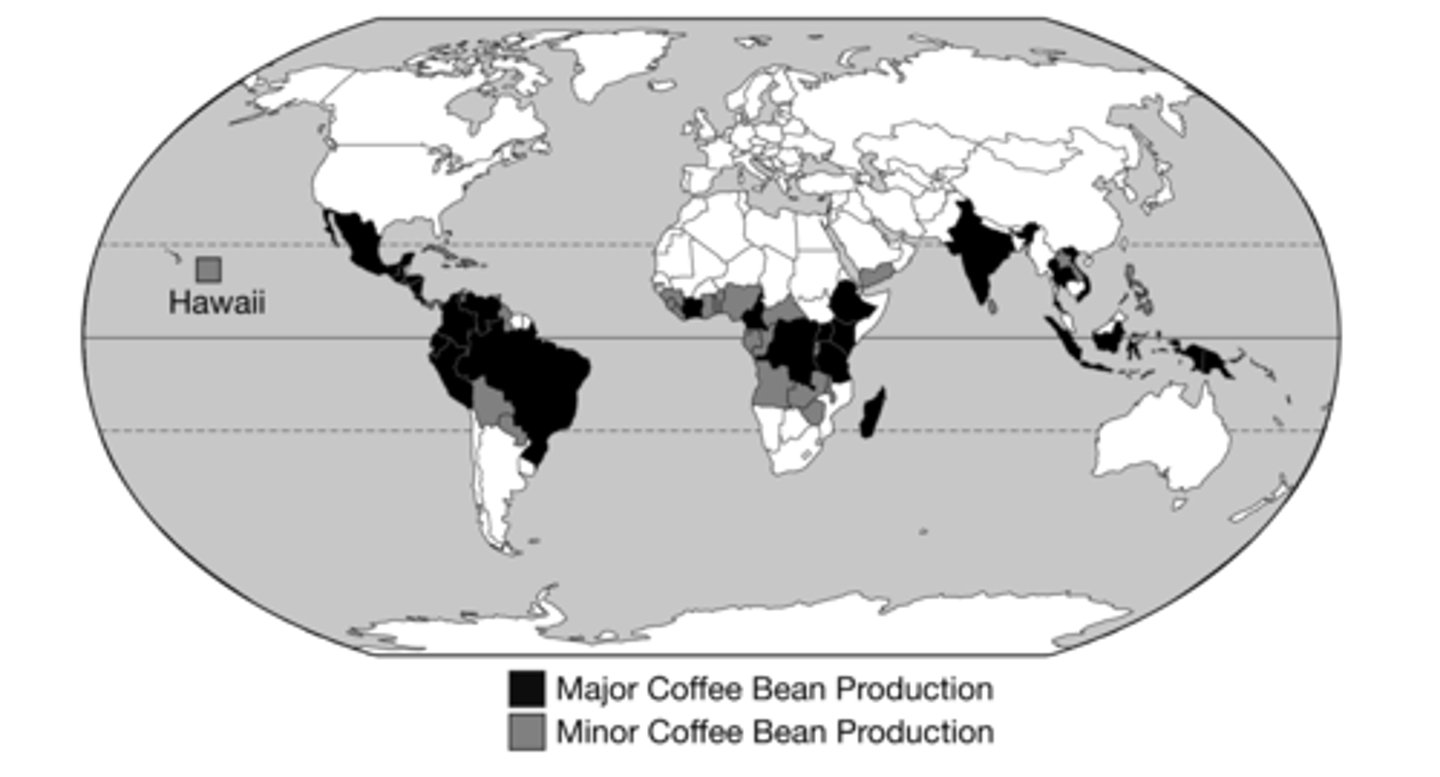
With the exception of Hawaii, the map shows the pattern of production for coffee beans by country.
Which of the following explains the limitations of the map shown for identifying the agricultural production regions of coffee beans?
The map mainly identifies all land within a country, as opposed to the foothills and upland areas where coffee beans are grown.
Which of the following explains why multiple early hearths of domestication and diffusion of plants and animals arose across the world in Central America, the Fertile Crescent, the Indus River valley, and Southeast Asia?
Responses
Domestication of plants and animals evolved in each hearth independently of one another as societies in each area learned and applied the process to local plants and animals.
Which of the following is the essential requirement of lowland rice production?
abundant water.
Which of the following forms of agriculture would best be described as extensive farming?
cattle ranching and wheat farming.
Which of the following is the best example of extensive land use in agriculture?
a sheep ranch.
Sheep production in New Zealand and poultry production in Arkansas produce food animals for human consumption. Which of the following best describes the differences in the agricultural practices and land use for these products?
Sheep production is an example of extensive agriculture requiring large pastures, whereas poultry production is an example of intensive agriculture often practiced indoors.
Labor-intensive intertillage is often practiced in
southeast Asia.
On the map above, the shaded area is most associated with which of the following types of agriculture?
rice cultivation.
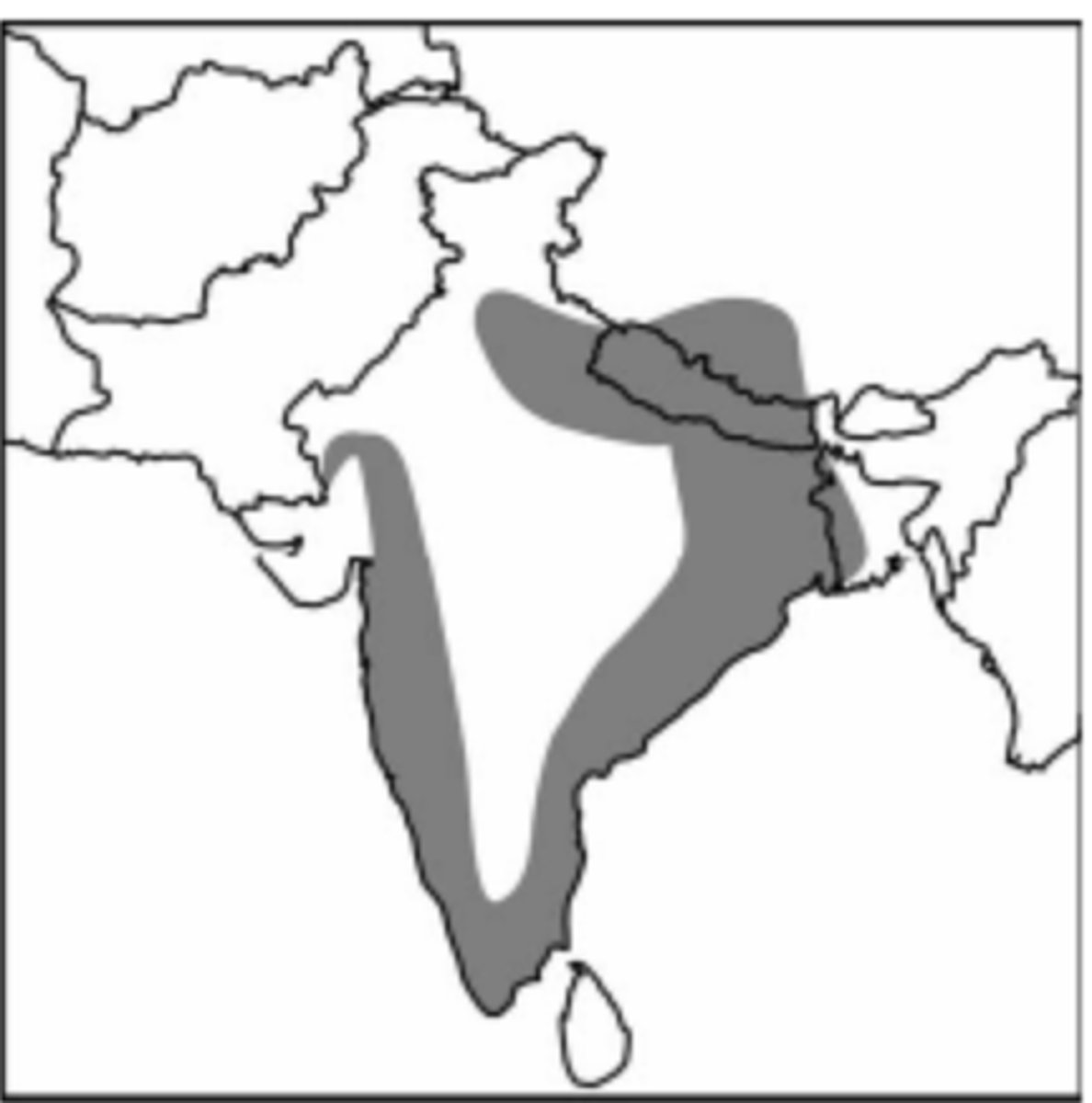
Which of the following best explains the diffusion of plants and animals from their hearths of domestication?
Both domesticated plants and animals spread across the globe through contagious diffusion in early years by farmers and traders, and later by relocation diffusion through European exploration and colonialism.
Which of the following explains the diffusion and successful cultivation of many plants and animals in new regions of the world through the Columbian Exchange?
The plants and animals diffused to a region with climate and geography similar to that of their point of domestication.
Which of the following best explains the differences between the patterns of land use in the township-and-range system and the long-lot system, as shown in the images?
The township-and-range survey system was based on a geometric grid pattern, while the long-lot system was a rectilinear pattern based upon waterways or roads.
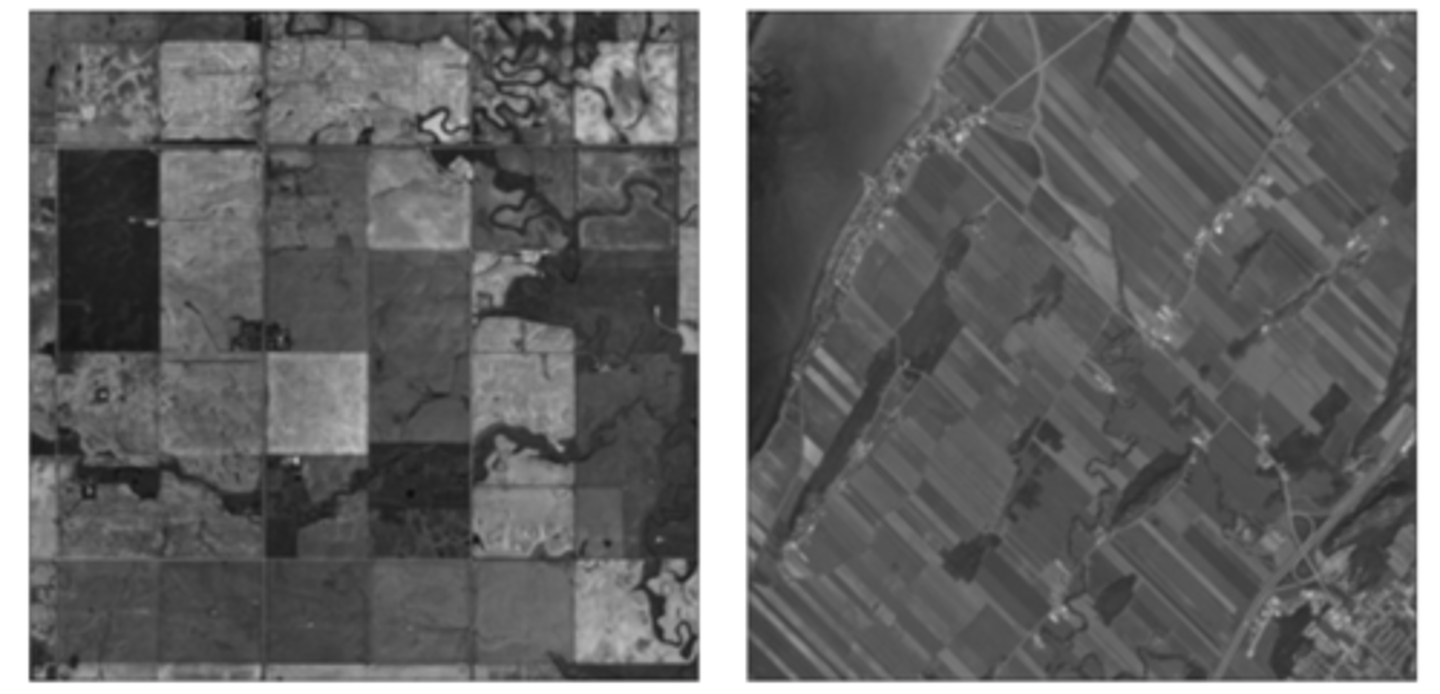
Which of the following best explains the reasons for the similarities and differences between the two land survey systems shown?
Both systems require geometric calculations to survey property lines. However, the township-and-range system uses simplified calculation to create a more ordered landscape.
The two images represent different agricultural land survey patterns.
Comparing the two images, which survey system was more efficient in terms of trade?
The river in the long lot survey system provided better access to waterways to transport goods to market.

The township and range land survey system in the United States contributed to which of the following?
A dispersed rural settlement pattern.
In less developed countries, pesticides are typically applied by hand, whereas pesticides are typically applied by tractors or aircraft in more developed countries.
Which of the following best explains the risks associated with pesticide applications
Farmers' health is at risk in less developed countries, whereas environmental pollution is a risk in more developed countries.
Between 1950 and 1990, wheat production in India in average pounds per acre more than tripled, which allowed India to meet its population's need for food.
Which of the following best explains this change?
The use of improved plant hybrids and agricultural chemicals.
During the Green Revolution, agricultural practices from more developed countries diffused to less developed countries in Asia and Africa.
Which of the following best explains the Green Revolution's highly variable level of success in increasing agricultural yields?
Small-scale farmers in Asia often lacked the resources necessary to acquire the hybrid seeds and the chemical inputs to grow them, leaving large gaps in the success of the Green Revolution outside of urban cores.
Which of the following agricultural inputs were the most recent technological innovations employed in less developed countries during the Green Revolution?
Chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
In which of the following world regions has the Green Revolution had the least impact on agriculture?
Sub-Saharan Africa.
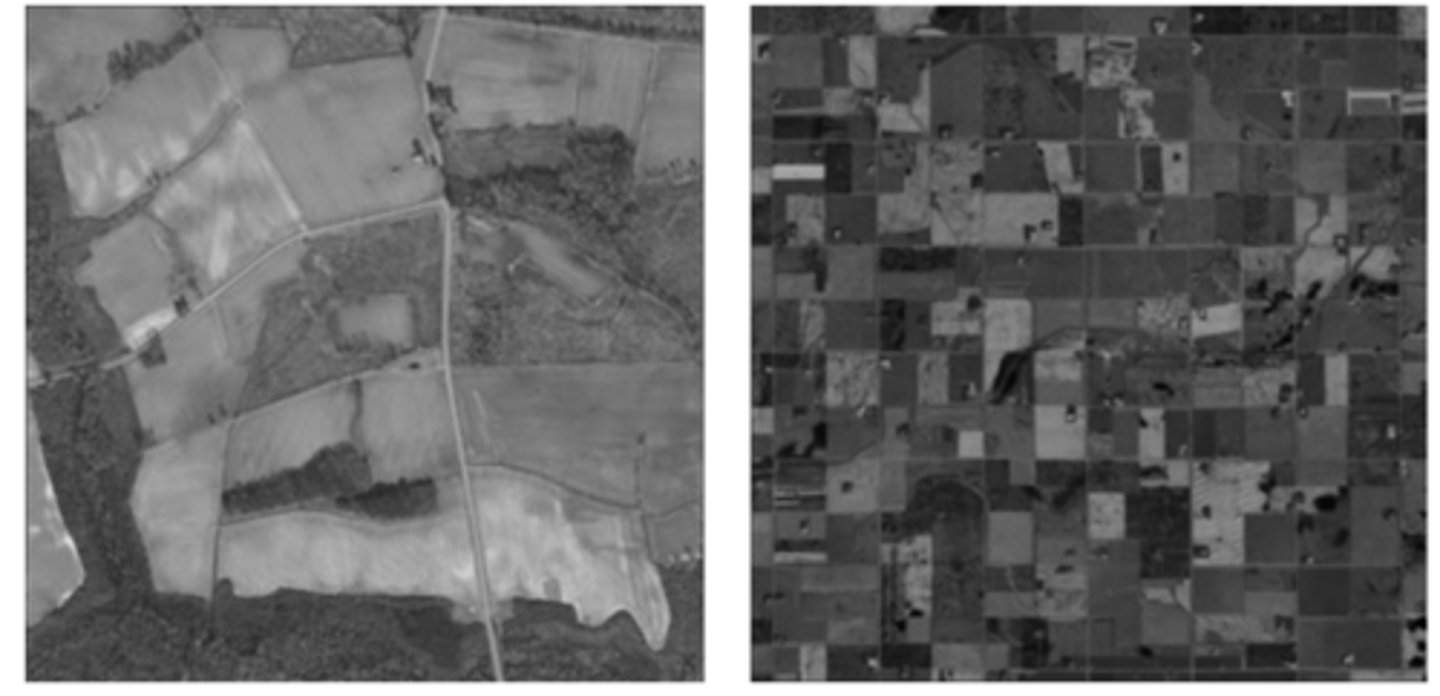
The two images show different agricultural methods. In the context of the Second Agricultural Revolution, which of the following trends is represented in these images?
The mechanization of farming in the Second Agricultural Revolution resulted in more reliable crop harvests and healthier populations in areas where the mechanization was adopted.
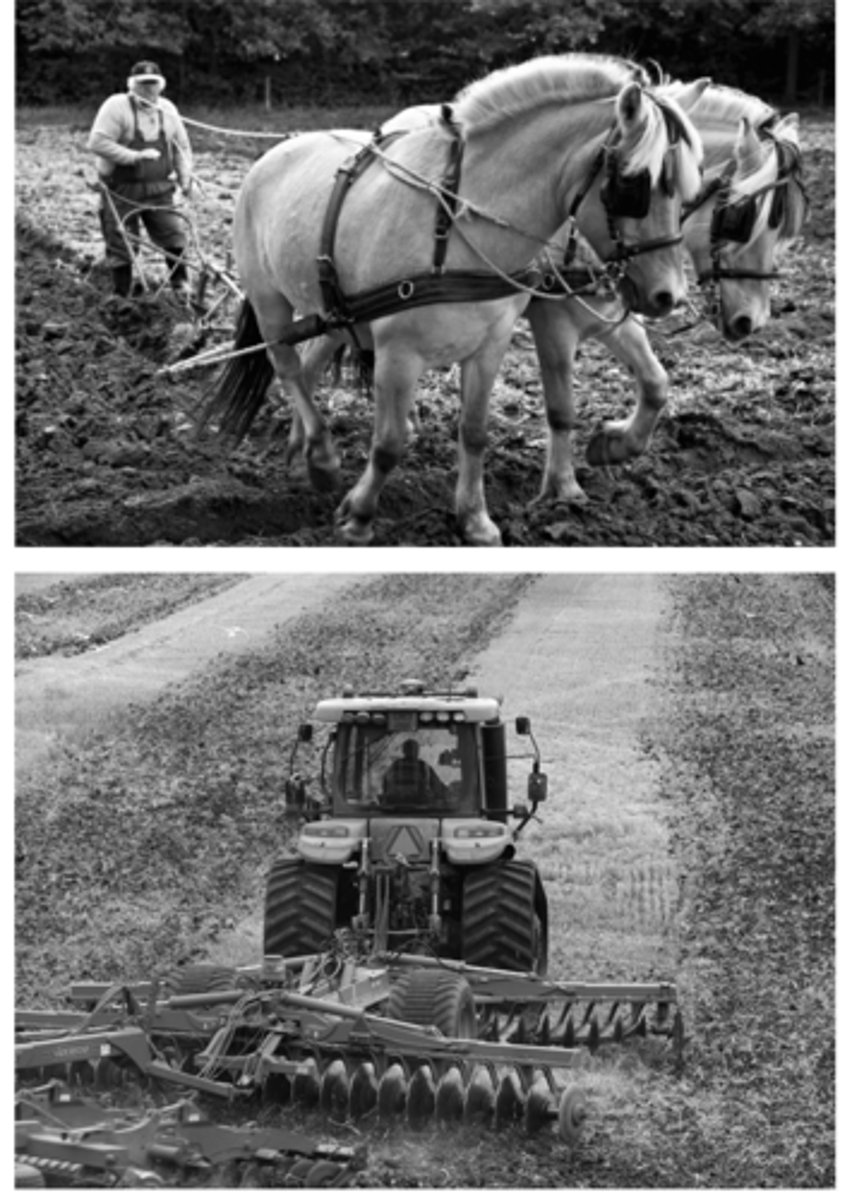

The images show devices developed during the Second Agricultural Revolution.
Which of the following best describes the impacts of the Second Agricultural Revolution?
Technological innovations, such as the devices shown in the images, and increased agricultural productivity led to better diets, longer life expectancies, and more people available for work in factories.

The images shown illustrate a change that took place as the Second Agricultural Revolution coincided with the Industrial Revolution.
Which of the following compares this geographic relationship between these revolutions?
The mechanization of farm work allowed many young people to migrate and join a growing urban industrial workforce.

The von Thüen model has changed because of developments in transportation. The change that is most evident is that the?
width of the rings has increased.
Based upon the bid price curve above, in which zone should corn be grown?
7.6 to 11.0 miles.
One results of the developments of cool chains is that they?
increased the distance that fresh fruits and vegetables could travel.
The two graphs shown above provide support for which of the following statements regarding cocoa production and chocolate consumption?
cocoa production is highest in periphery and semi peripheral countries and chocolate consumption is greatest in core countries.
Which statement best explains why a large number of agricultural products are imported into the United States from Chile?
the growing season in Chile allows U.S. consumers to have fresh fruits and vegetables in the winter.
Which lists products in the order in which they will be produced, starting closest to the market, according to Von Thunen's model?
dairy cattle, forest, grain, beef cattle.
A very large corporate farm in the US is most likely to take advantage of which of the following opportunities?
vertical integration strategy.
Which of the following best explains why farmers would plant both strawberries and watermelons in the same field?
limited farmland encourages intensive farming with intercropping to produce high yields.
Which of the following spatial patterns is best explained by bid-rent theory?
concentric rings of different agricultural activities surrounding a city in the midwestern United States.
A set of economic and political relationships that organizes food production from the development of seed to marketing the products is known as?
agribusiness.
Subsistence agriculture is always characterized by?
production only for family consumption.
Why have many family farms in North America been replaced by agribusiness farms since the 1980s?
agribusiness farms have the resources to take advantage of economies of scale.
The industrialization and mechanization of agriculture in the United States during the past 70 years have resulted in?
a decrease in the number of farms and an increase in the size of farms.
Traditional labor-intensive agriculture often involves which of the following?
field terracing.
The growth potential of alternative agricultural practices such as the growing of amaranth grain and the raising of deer, elk, emus, and buffalo for meat is limited because?
the growers have not established an integrated commodity chain.
Which of the following explains the role of commodity chains in the average size of farms?
commodity chains have led to changes in the spatial organization of agriculture from dispersed family farms to large corporate farms that produce, process, and distribute the products.
Which of the following is an explanation for the similar impact of large-scale commercial agriculture in developed countries and plantation agriculture in developing countries?
both farming practices involve the consolidation of family farms and displacement of rural communities.
Subsistence agriculture is most common in which of the following regions?
Amazon Basin.
In the South Asian country of Sri Lanka, tea is farmed as a monoculture. Which of the following best explains why tea plantations are common in Sri Lanka and tea exports are important to the country's economy?
tea plantations were established in Sri Lanka by a former European colonial power.
Compared to North American ranchers, commercial ranchers in the Pampas of Argentina, Uruguay, and southern Brazil are more likely to?
raise livestock primarily for export.
Palm oil, an edible vegetable oil used in processing packaged food products, is obtained from the fruit of the oil palm tree, grown only in the tropics. Which of the following explains how global demand for palm oil has proved beneficial and detrimental for countries such as Indonesia and Malaysia?
palm oil exports provided substantial corporate profits, but the growth in the industry resulted in heavy deforestation in both countries.
During the winter months in North America, the primary source of fruits and vegetables found in grocery stores is?
Chille.
Which of the following explains an impact of globalized agricultural commodity chains on consumers as compared to producers?
drought and depletion of groundwater sources in developing countries cause a rise in global grain prices and associated higher costs for food.
In 2017 the Ivory Coast exported $5.6 billion worth of cocoa beans and cocoa-derived products, such as cocoa butter. This represented 55 percent of the country's exports and was worth four times the country's combined gold and oil exports in that year. Which of the following best explains the international trade economy of the Ivory Coast?
high level of dependency on a single agricultural commodity that increases national economic risks during times of global economic crisis.
Which of the following best explains why the New England region, located in the northeastern United States, would specialize in market gardening agriculture rather than other types of agriculture, such as grain farming?
several large cities on the East Coast provide a growing market and shorter distances for transporting market gardening products.
The above map shows von Thünen’s model applied to a map of the contiguous United States. Which of the following realities would NOT be accounted for by the theoretical predictions shown on the map?
Florida's government has a Department of Citrus.
According to the von Thünen model, which of the following economic factors determine the pattern of land use shown on the diagram?
costs of labor, transport, and land rent.
Which of the following developments is predicted by the von Thünen model of land use around cities?
large-scale growing of flowers and vegetables in the Netherlands.
Based on von Thünen's model of rural land use in an isolated state, which statement explains the most suitable place for a farmer to purchase a large parcel of land necessary for raising livestock?
the ring farthest from the market, because the land is less expensive and outweighs transportation costs to get the livestock to market.
Based on the diagram of von Thünen's model of agricultural land use, which statement best explains the connection between land value and agricultural production regions?
grain crops require extensive acreage and are grown on land that is less costly and farther away from the market than other agricultural land uses.
Which of the following correctly explains the placement of an agricultural product within von Thünen's agricultural land-use model?
tomatoes are grown closest to the market because they spoil quicker than beef or grain.
Which concept is demonstrated in the picture above?
the use of terrace farming.
Which is a major concern related to the practice shown in the image?
maintenance of the field is difficult.
Deforestation has resulted in?
more farmland in some places but more desertification in others.
In which group of countries are GMOs used most widely?
United States, Brazil, and Argentina.
Slash-and-burn agriculture is often used in areas that have?
soil that lacks sufficient nitrogen to grow food crops quickly.
What is the main reason that female farmers in periphery countries are not as productive as male farmers?
gender inequalities prevent female farmers from access to the same resource as male farmers.
What does the graph indicate about the effects of farming with genetically modified crops?
yields increase and farm profits increase even more.
Which of the following agricultural practices has the most significant long-term environmental impact in tropical regions?
burning extensive areas of forested land to create pasture, which decreases biodiversity.
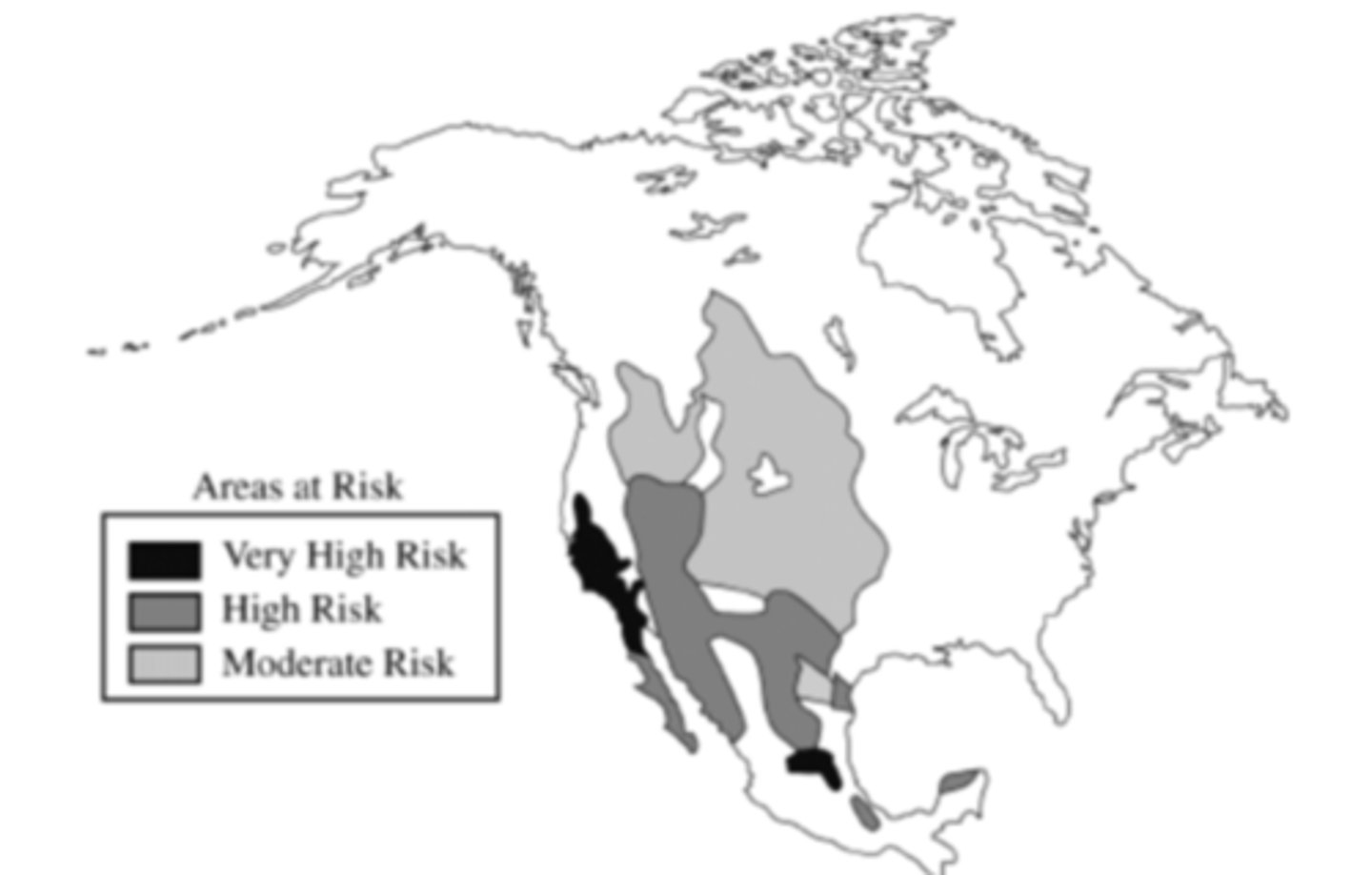
The shaded areas on the map above most likely indicate regions that are affected or threatened by which of the following?
desertification.
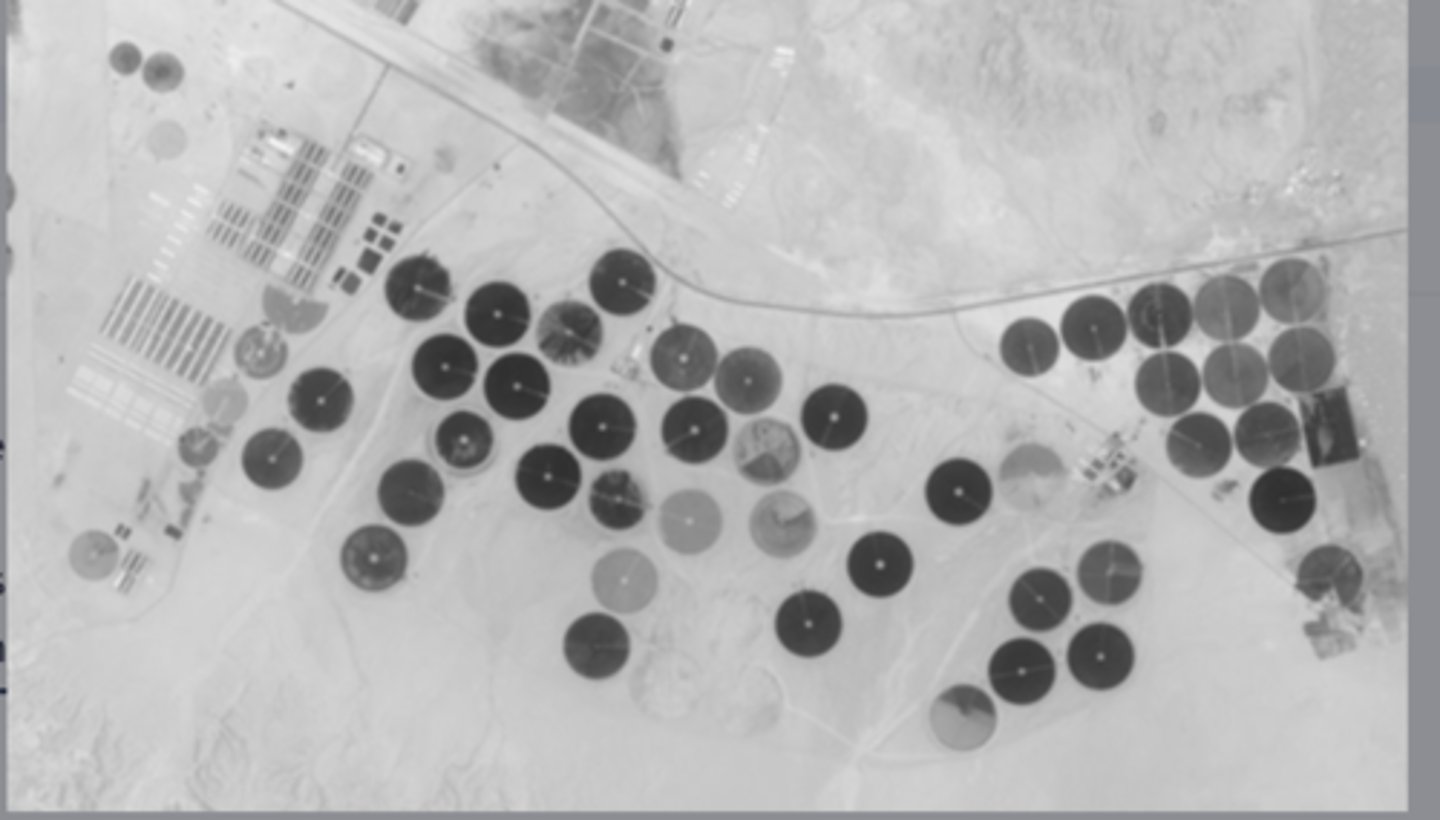
Based on the different types of land use shown in the image, which of the following best explains why soil salinization is a concern in the arid landscape shown?
irrigation increases the salt content of the soil, which disrupts the growth of crops and degrades soil fertility.

Which of the following best explains the economic advantage of the type of farm-produced goods shown in the images?
compared to plain milk or fresh fruit, these value-added agricultural goods significantly increase the price of the farm products sold and increase earnings for farmers.

Which of the following is the most often cited environmental benefit of the eat-local movement?
less fossil fuel is used in transporting food to market.
The two images represent two different methods of raising livestock in the United States. Which of the following statements most accurately compares these two agricultural practices?
feedlots can minimize costs associated with livestock production because feedlots do not use as much space as cattle ranching.
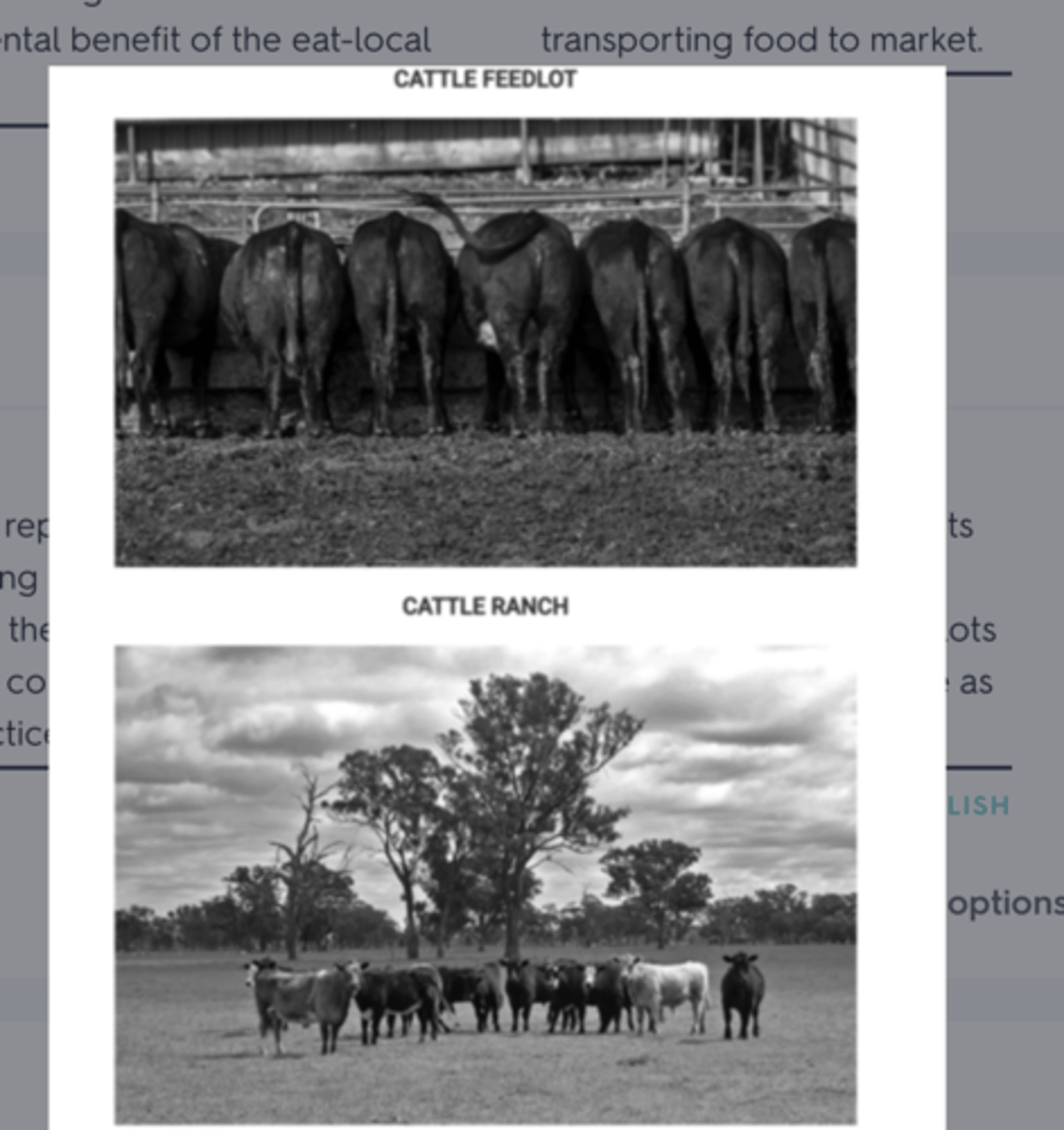
Which of the following best explains how the expansion of feedlots for raising cattle has affected environmental sustainability in rural areas?
runoff from animal waste has increased the pollution in local water supplies.
Which of the following is indicated on the graph above?
worldwide fertilizer use is increasing but faster in peripheral developing countries.
The chickens shown in the image are an example of value-added agriculture used by small family-run farms to compete with large agribusiness poultry and egg farms. Which of the following types of value-added products best describes the kind of agriculture shown in the image?
free-range.

Genetic engineering of agricultural crops has primarily increased the productivity of modern farming by?
increasing plants' drought resistance and resistance to pests.
Which of the following social or environmental impacts is most directly related to the use of chemicals in agriculture?
an increase in land and water pollution from agricultural runoff.
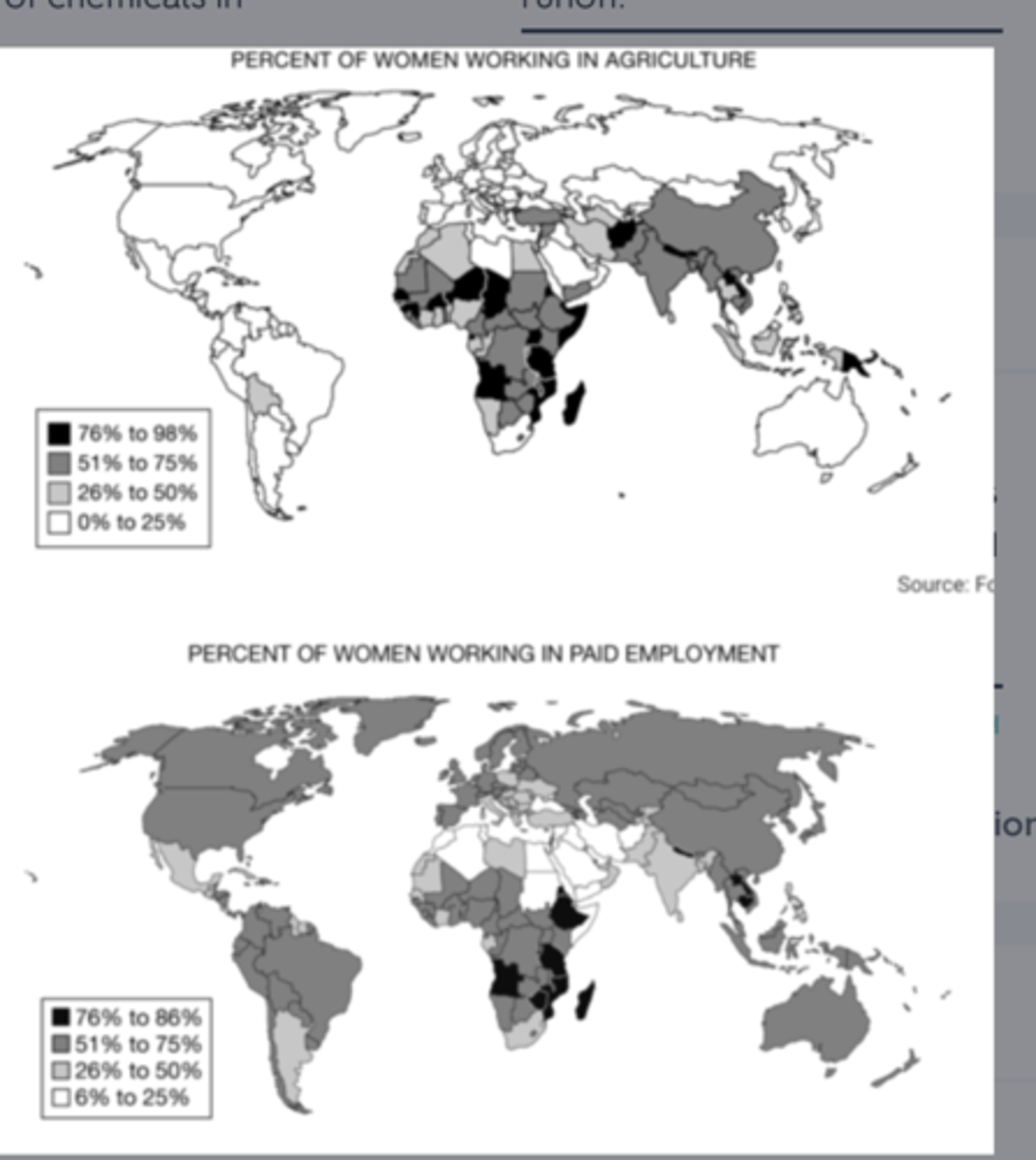
Compare the two maps and examine the data for Africa, the Middle East, and South Asia. Which of the following statements is supported by the comparison of the two maps?
many women in these regions work on farms and grow food for their families, but not all are paid to do this work.
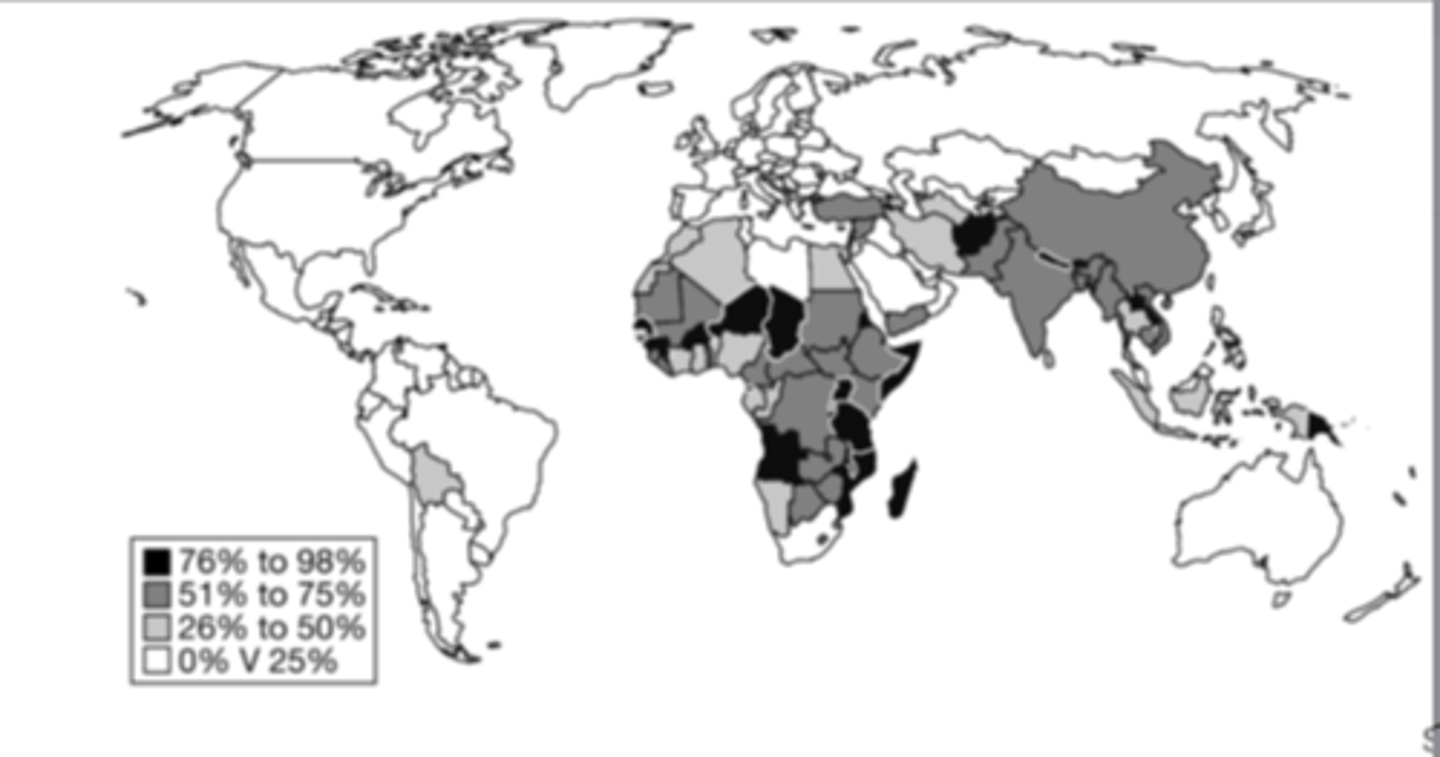
Based on the map, which of the following explains the similarities of the world regions where at least 51 percent of women work in agriculture?
these regions are composed of less-developed countries with large rural populations.
Which of the following explains the significance of the similarities between Asia and sub-Saharan Africa in terms of the percent of women working agriculture?
in the subsistence-based rural economies in these regions, female farmers produce much of the food that their families need for survival.
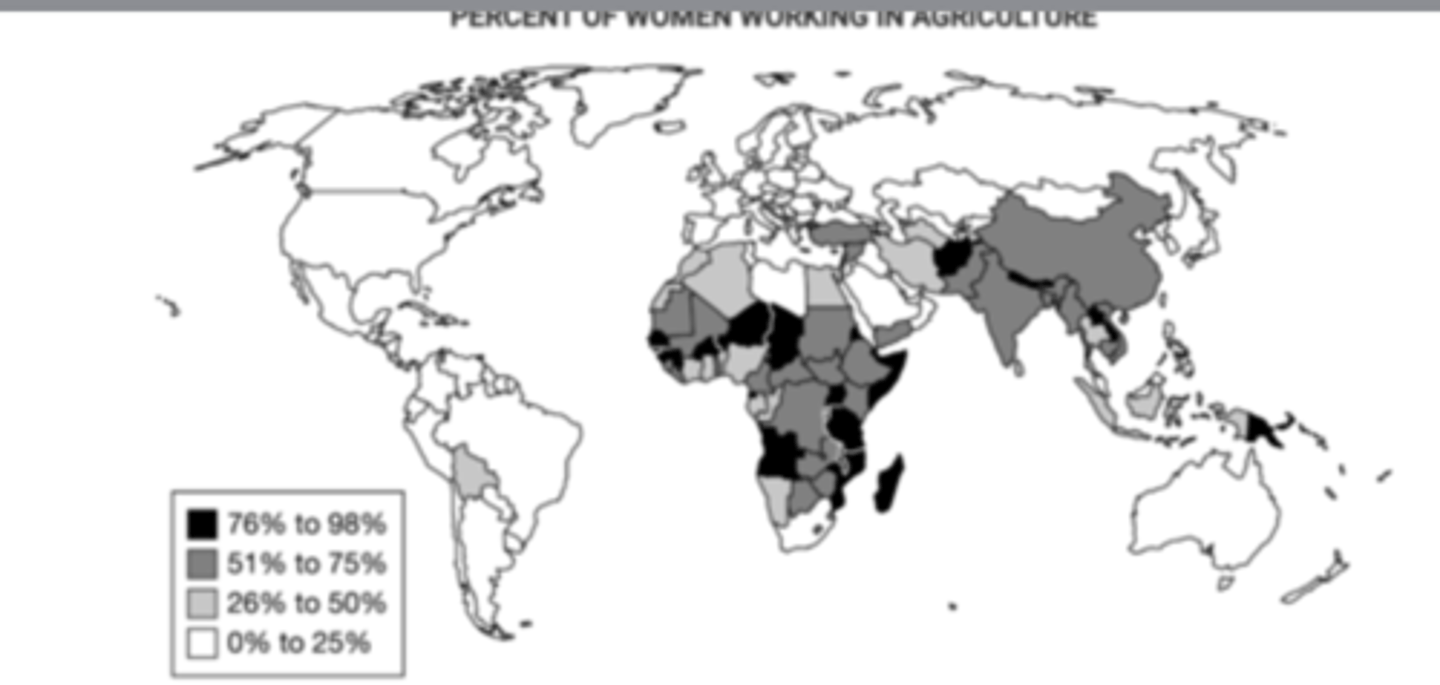
Which of the following best describes the roles of women in the rural, agricultural economies of sub-Saharan Africa?
non wage workers on small, family-run farms.