photosynthesis & cellular respiration
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Autotroph
-organisms that make their own food (plants, algae, bacteria)
-photoautotrophs: use sunlight to make their own food (chemical energy)
-chemoautotrophs: use chemicals to make their own food
heterotroph
-organisms that must eat their own food
eat autotrophs or other heterotrophs
photosynthesis
-most important process for making chemical energy
-process of plants with chlorophyll using sunlight energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen
chloroplast
-the organelle were all of the reactions of photosynthesis occur
-contains thylakoids
chlorophyll
-major green pigment in plants which uses the energy of the sun to break the hydrogen atoms off water
-form photosystems (part that collects energy from the sun)
pigment
-substances that absorb visible light and help harness the energy of the light
thylakoid
-sacks with chlorophyll, where the light dependent reaction of photosynthesis happens, arranged in sacs known as grana
stroma
The place outside of the thylakoid where the Calvin cycle occurs
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
-used by all cells to provide the free usable energy they need
-a chemical compound that stores in release for cells
NADPH
-energy holder/electron carrier
Light-dependent reaction
-uses suns energy, and happens in the thylakoid membrane
-light energy breaks bonds in water
-comes out: ATP & NADPH (provide energy for 2nd reaction) h+, O2 gas (waste)
-goes in: light energy & water
light independent reaction (Calvin cycle)
-doesn’t use suns energy, happens in stroma
-2nd reaction in photosynthesis
-converts CO2 to glucose using (atp & nadph)
goes in: NADPH & ATP, CO2
comes out: glucose ADP+P, NADP+
stomata
-tiny openings in under sides of leaves that can open and close under different conditions to allow CO2 into the cell and prevent water loss through transpiration
-surrounded by guard cells that swell and open the stomata when there’s plenty of water
-shrink and close the stomata when water is lacking
describe how the structure of ATP leads to the function of ATP
-energy from ATP comes from breaking bonds between phosphate groups
chemical equation for photosynthesis
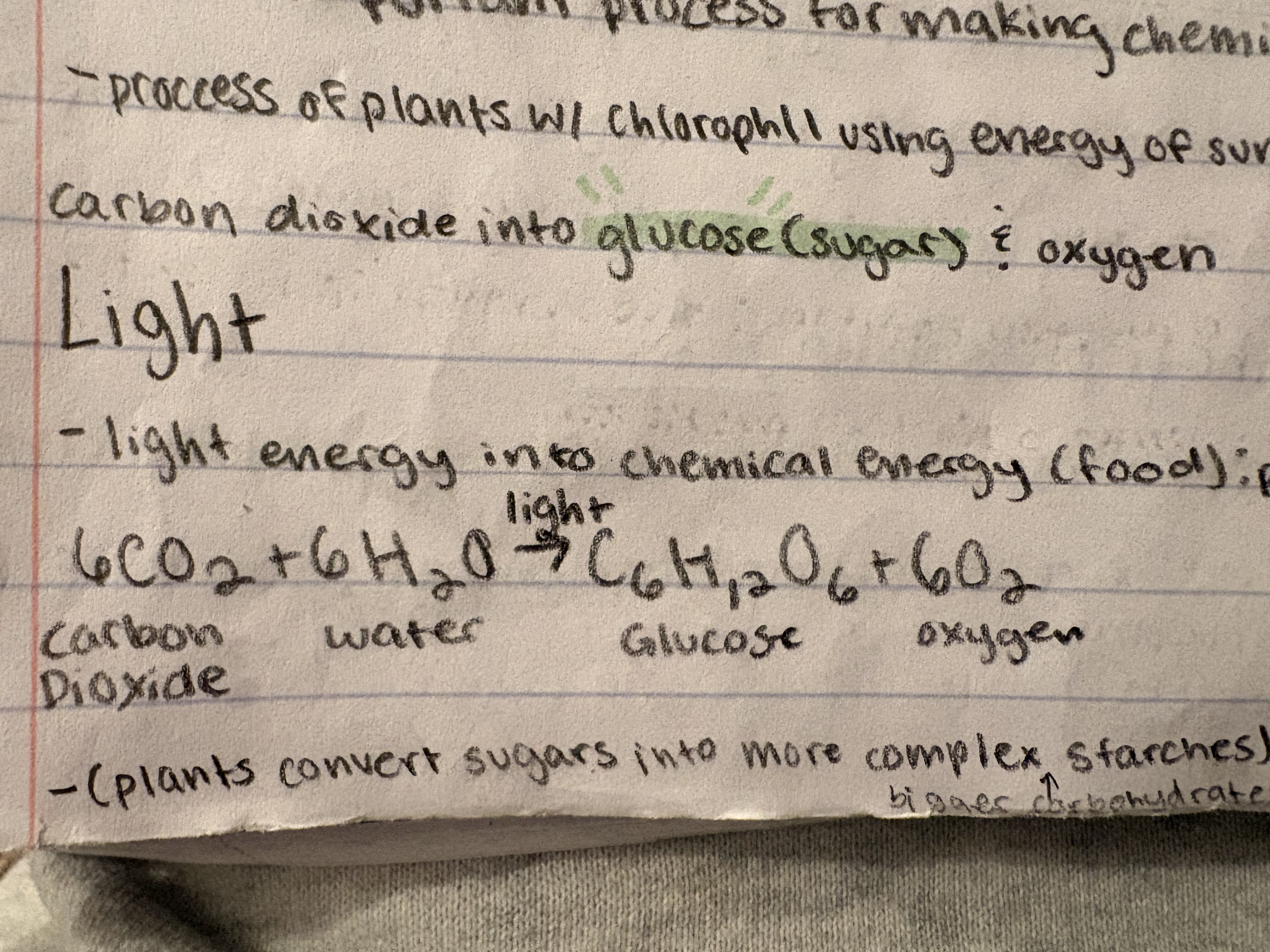
describe how pigments function in photosynthesis
-pigments help harnessed the energy of the light
-absorbed specific light wavelengths and reflects green light
describe the structure of a chloroplast and related to its function
- contain thylakoids (where are the light dependent reaction happens)
-contains stroma (where the Calvin cycle happens)
compare and contrast light-dependent reactions and light-independent reactions
-light-dependent reaction uses suns energy, independent does not
-work together
-light dependent reactions convert sunlight into ATP & NADPH
-light independent reactions use that ATP and NADPH to produce stable, high energy sugars from carbon dioxide and water
how does temperature affect the rate of photosynthesis?
as temp increases, the rate of photosynthesis increases until 25C where the rate levels off as the temperature continues to rise
how does light intensity affect the rate of photosynthesis?
As light increases, photosynthesis increases until the light reaction is saturated with light (until all chlorophyll is being used)
how does CO2 and O2 concentrations affect the rate of photosynthesis?
-as the concentration of CO2 increases photosynthesis increases to a point, then it has no effect
-as the concentration of O2 increases photosynthesis decreases
Cellular respiration
The energy in glucose is converted to ATP in the presence of oxygen
Glycolysis
-happens in cytoplasm
-breaks glucose in half to make 2 molecules of pyruvic acid and a little bit of ATP&NADH (to fuel other reactions)
-both aerobic and anaerobic respiration start with it
Krebs cycle
-pyruvic acid molecules enter the matrix of the mitochondria and go into the Krebs cycled.
-what goes in: 2 pyruvic acid (glycolysis)
-comes out: CO2 (waste), high energy, electron carriers (NADH & FADH2), 2 ATP
electron transport chain
-where high energy electrons get passed down to
-goes in: NADH & FADH2 (krebs), O2
-come out: H2O, 36 ATP, NAD+&FAD+
NADH/NAD+
-crucial electron carriers acting as a rechargeable battery
FADH2/FAD+
High energy, electron carries
relate the structure of mitochondria to its function
matrix: where Kreb cycle occurs
inner membrane: where the electron transport chain is
Chemical equation for cellular respiration

compare and contrast, alcoholic, fermentation, and lactic acid fermentation
alcohol: carried out by yeast, forms, alcohol, and carbon dioxide as wastes
lactic acid: is carried out when muscles run low on oxygen after heavy exercise, makes little ATP, used to make dairy products
-both occur when oxygen isn’t present
comparing contrast in aerobic and aerobic respiration
-aerobic: occurs with oxygen, releases, lots of energy (36 ATP)
-anaerobic: occurs without oxygen, releases a little bit of energy (2 ATP)
compare and contrast, photosynthesis and cellular respiration
-opposites in reaction: the reactants of one reaction are the products of another
-opposites in energy flow: photosynthesis stores, energy in glucose and cellular respiration releases the energy from glucose
The significance of electron carriers
they are able to carry electrons to the electron transport chain, enabling the massive production of ATP (used throughout the cell)