the nervous system
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
the nervous system is divided into 2 parts
central nervous system (CNS)
brain
spine
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
somatic nervous system
autonomic nervous system
somatic nervous system
which carries messages between the muscles and sense organs to and from the CNS allowing us to sense and interact with our environment
autonomic nervous system
which regulates the body’s vital functions automatically and involuntarily. Controls heartbeat, digestion, breathing, and circulation
sympathetic vs. parasympathetic nervous system
Sympathetic system get activated in response to the environment; prepares for optimal responses to stimuli.
Parasympathetic system “rests and digests” and returns the body to it’s non-arousal state deactivating the sympathetic response. Both systems work involuntarily
what is the parasympathetic system responsible for?
Responsible for emotions – emotions occurring at incorrect moments are often a source of psychological disorders. E.g. Anxiety, Panic, Depression, Mania.
Any disorder based on disconnection between bodily or emotional state and the environment
neuron definition
nerve cells that run through the body and communicate with each other
basic neuron types
bipolar (interneuron)
unipolar (sensory neuron)
multipolar (motoneuron)
pyrimidal cell
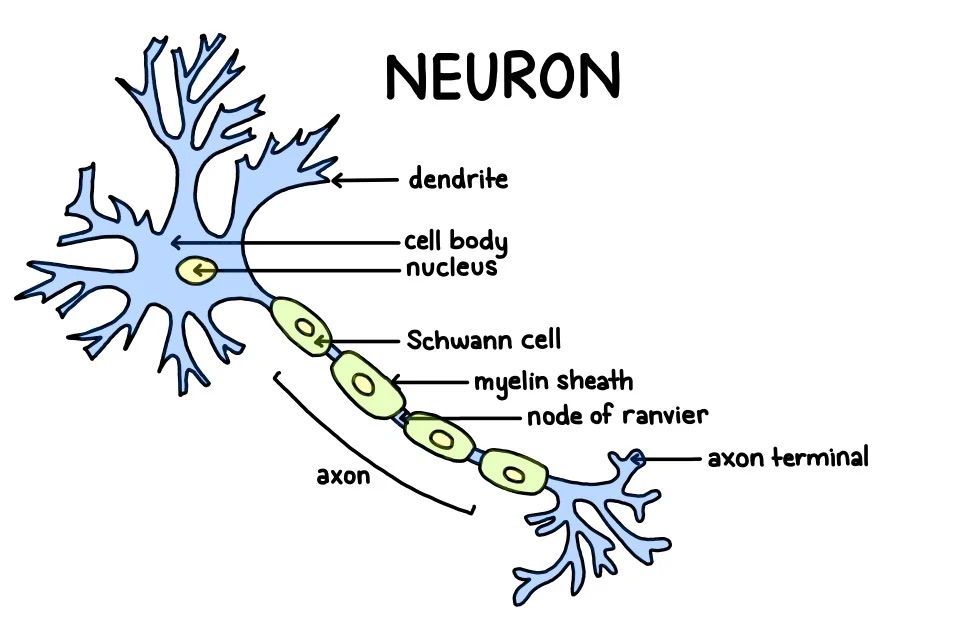
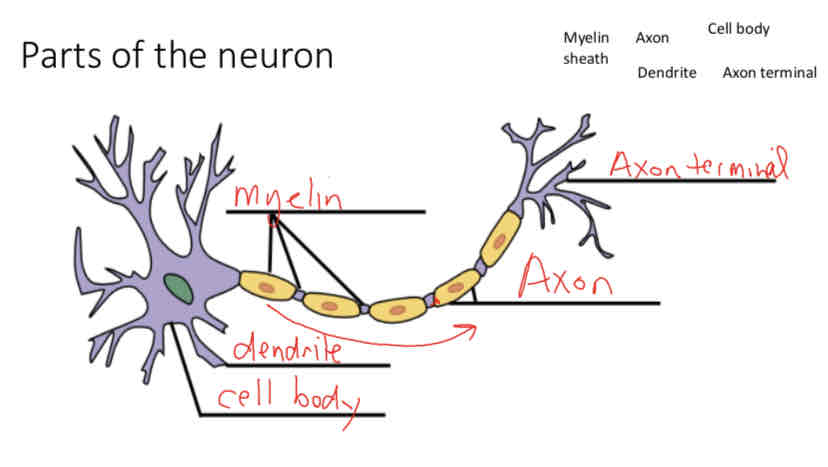
parts of the neuron
neuroplasticity definition
the brain has the ability to reorganize itself by altering connections between neurons to adjust to changes in the environment, injury or disease
synapse definition
the junction between the axon terminals of one neuron and the dendrites of another
sensory neuron definition
carries information received by the senses to the CNS
motor neuron definition
carry messages from the CNS to the muscles and glands and influence their functioning
spinal reflex definition
a body’s automatic response to a trigger without the involvement of the cortex
the neural impulse
Neurons fire when triggered by:
The presence of a critical amount of key chemicals emitted by neighbouring neurons
The stimulation of an attached specialized structure by input from the environment.
Firing consists of a directional impulse – action potential
Moves at 200mph
the electrochemical signal
The signal that travels the length of the neuron is actually a change in the polarity of the outside of the axon.
The resting charge on the cell is -70 millivolts.
This charge is created by a membrane around the cell that keeps positively charged sodium ions (Na+) on the outside of the cell and positively charged potassium ions (K+) in the inside – selectively permeable
impulse
Once the threshold is achieved in the cell body, the protein “gates” of the axon open and Na+ ions rush in.
For 1 millisecond, the outside of the axon body becomes – and the interior becomes +
all or none response
Once the impulse is triggered, the intensity of the signal is constant
All or None Law–the stimulus does not provide the energy of the nervous impulse. A neuron’s reaction is either firing or not firing
This means that a stronger sensation is caused by a greater number of neurons being stimulated, not a stronger impulse
synaptic transmission
Scientists had always believed that there was some mechanism connecting two neurons together.
This was finally proven in 1920 by Otto Loewi
Lowei’s experiment proved that the transmission from one neuron to the next involved a chemical substance
synaptic transmission (2)
As the impulse reaches the axon terminals, tiny sacs of specialized proteins called synaptic vesicles rupture at the surface of the terminal
These vesicles pop and release a chemical into the synapse called a neurotransmitter
neurotransmitters definition
chemical messengers that travel across the synaptic gap and have an excitory or inhibitory effect on the adjacent neuron
receptors
CNS (brain, spine) and PNS (somatic, autonomic).
neurotransmitters
There are over 100 different identified
2 types – must be in balance for optimal functioning
Excitatory – facilitate impulse crossing the synapse
Inhibitory – stop the impulse from crossing the synapse
agonists & antagonists
Agonists – chemicals that enhance the action of a neurotransmitter eg SSRIs
Antagonists – chemicals that counteract a neurotransmitter eg GABA
The interaction of all these classes of neurotransmitter make simple cause and effect links between a chemical and a behaviour difficult
lock & key model
Each neurotransmitter is paired with the special receptor at the end of the post-synaptic neuron.
Each receptor can only be activated by it’s paired neurotransmitter
reuptake, oxidation, & drift
Excess neurotransmitter in the synapse is removed to lower neurotransmitter levels to a sub-critical level to prevent prolonged stimulus or interference in several ways:
The axon terminal will reabsorb excess back into the neuron cell.
Enzymes break down excess neurotransmitter rendering them unable to bond with receptors and affect receiving neurons