BIO 216L (7-11)
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
Which tool will you use to inoculate the semi-solid medium when conducting the motility test?
Toothpick
Inoculating loops
Inoculating needle
Pipette tip
Inoculating needle
2. Which of the following describes a characteristic of motile bacteria in the motility test?
Solution:
They form a compact growth pattern around the stab line.
They disperse from the inoculation line, producing a diffuse growth pattern.
They exhibit no growth in the semi-solid media.
They produce a distinct color change in the medium.
They disperse from the inoculation line, producing a diffuse growth pattern.
What is the role of cytochrome c oxidase in aerobic respiration in bacteria?
It synthesizes ATP
It transfers electrons from the Electron Transport Chain to oxygen
It accepts electrons from water
It synthesizes hydrogen peroxide
It transfers electrons from the Electron Transport Chain to oxygen

4. In the image below, which of the strips indicates a species that is positive for cytochrome c oxidase?
A
B
B
5. What do you add to the oxidase reagent strip before adding a bacterial sample?
Alcohol
Crystal Violet Die
Water
HCl
Water
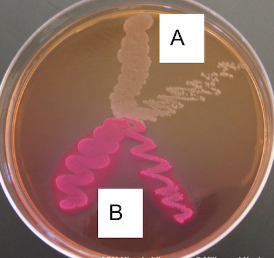
6. In the image below, bacteria are grown on MacConkey Agar. Which species is Gram-negative?
Solution:
A
B
Both
Neither
Both
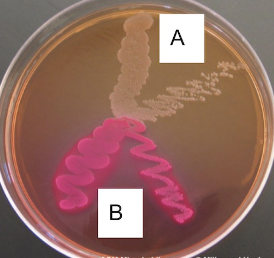
7. In the image above, bacteria are grown on MacConkey Agar. Which species produce an enzyme that ferments lactose?
A
B
Both
Neither
B
MacConkey Agar was used by Alfred MacConkey to test for:
Solution:
Fecal contamination of drinking water
The pH needed to eliminate bacteria growth
The effectiveness of a course of antibiotics
Sulfide, motility and indole production
Fecal contamination of drinking water
How did MacConkey select for the growth of enteric (think gut) bacteria?
He included bile in the agar.
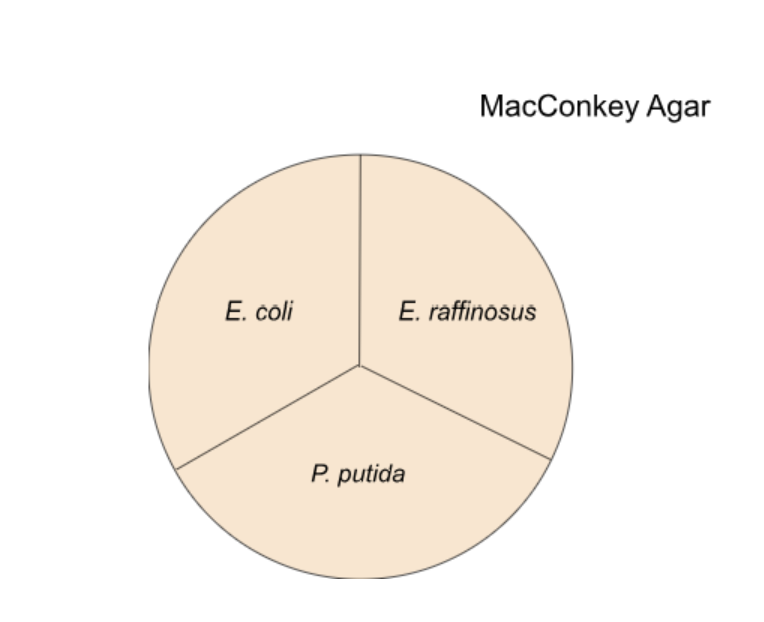
10. Examine the image above, what do you expect to observe where you have streaked E. coli?
Solution:
No bacteria grow
Bacteria grow and pink/red agar
Bacteria grow and agar remains the same color
Bacteria grow and pink/red agar
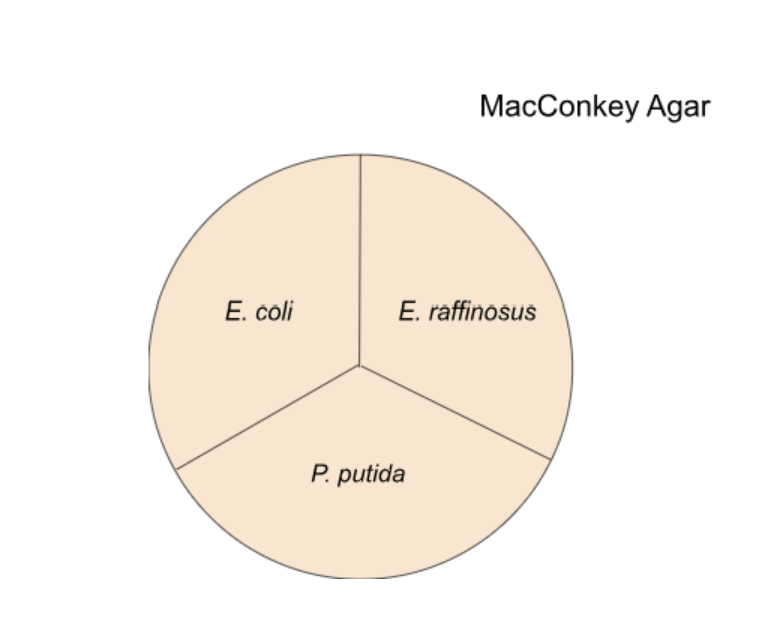
11. Examine the image above, what do you expect to observe where you have streaked E. raffinosus?
No bacteria grow
Bacteria grow and pink/red agar
Bacteria grow and agar remains the same color
No bacteria grow
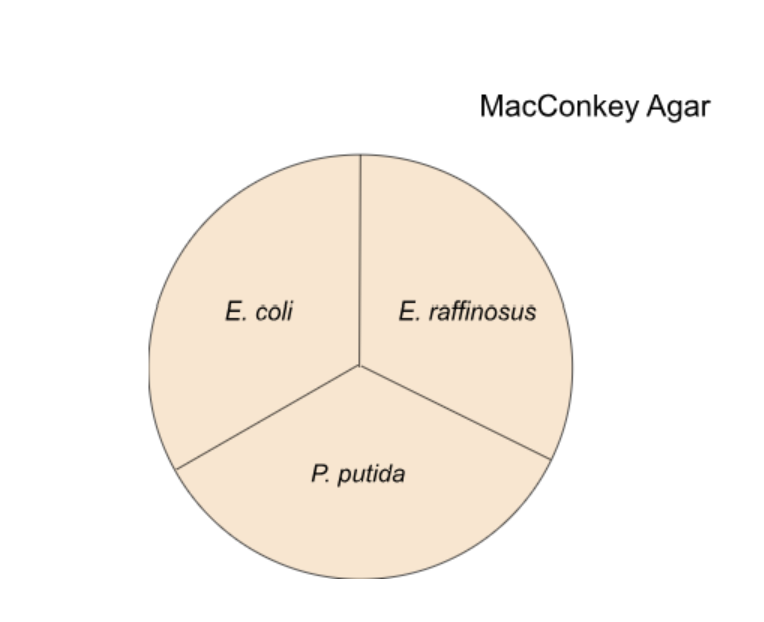
Examine the image above, what do you expect to observe where you have streaked P. putida?
Solution:
No bacteria grow
Bacteria grow and pink/red agar
Bacteria grow and agar remains the same color
Bacteria grow and agar remains the same color
Let's say that you determined through the Gram staining procedure that a soil isolate is Gram-positive. Do you expect to see any bacteria grow when you streak this isolate on MacConkey agar?
Bacteria should not grow
Bacteria should grow
Bacteria should not grow
Why does a clear zone surround beta-hemolytic bacteria?
The zone forms because the bacteria are producing antibiotics.
The zone forms because the bacteria are being killed by an antibiotic.
The zone forms because the bacteria are motile.
The zone forms because the bacteria are breaking down red blood cells.
The zone forms because the bacteria are breaking down red blood cells.
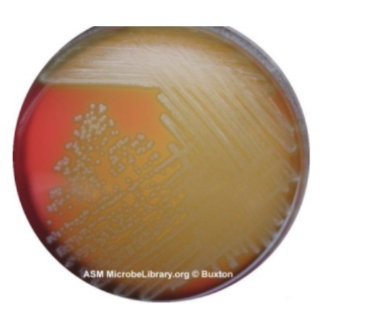
15. What type of hemolysis do you see in FIG. 10 below?
Alpha
Beta
Gamma
Alpha
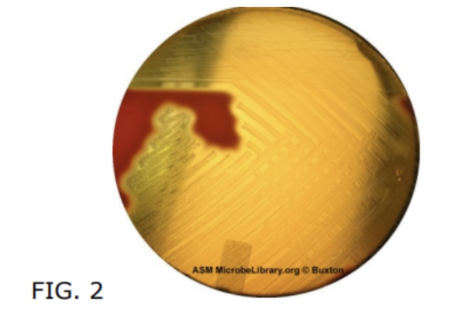
16. What type of hemolysis do you see in FIG. 2 below?
Alpha
Beta
Gamma
Beta
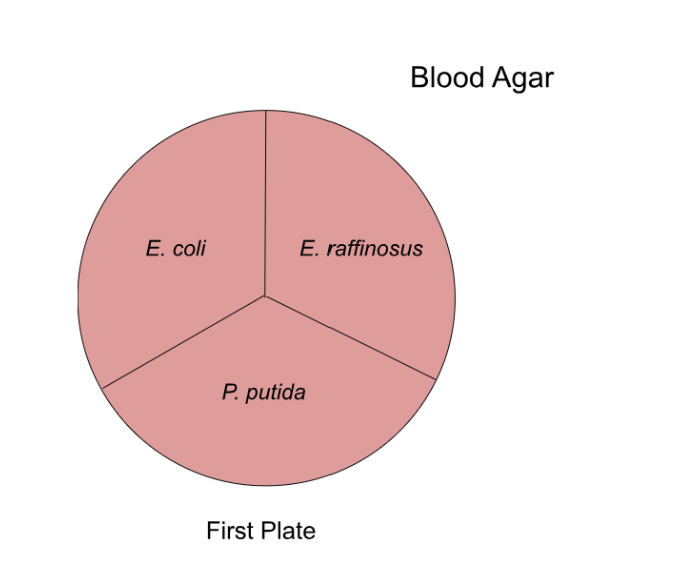
17. Examine the image above, what do you expect to observe where you have streaked E. coli?
Solution:
No bacteria grow
A clear zone
Green coloration
Agar remains the same color
A clear zone
Examine the image above, what do you expect to observe where you have streaked E. raffinosus
Solution:
No bacteria grow
A clear zone
Green coloration
Agar remains the same color
A clear zone
19. Examine the image above, what do you expect to observe where you have streaked P. putida?
Solution:
No bacteria grow
A clear zone
Green coloration
Agar remains the same color
Green coloration
20. How many Blood Agar plates will you use this coming week?
Solution:
One
Two
Three
Fou
Two
22. Where will you conduct your Catalase Test?
At your table
In the fume hood
2 Fume hood
21. What do you find in the bubbles produced by Catalase-positive bacteria?
Water
Carbon dioxide
Oxygen
Hydrogen peroxide
oxygen
23. How many drops of hydrogen peroxide will you add to your sample?
1-2 drops
5 drops
10 drops
20 drops
1-2 drops
24. Why is catalase an important enzyme?
It breaks down antibiotics.
Hydrogen peroxide can damage cell components.
It produces oxygen bacteria need for respiration.
It allows aerobic bacteria to live in anaerobic environments.
Hydrogen peroxide can damage cell components.
. E. raffinosus grown on blood agar would test Catalase-positive, giving a false-positive result. Why?
E. raffinosus produces hydrogen peroxide only when grown on blood agar.
E. raffinosus transcribes the Catalase gene only when grown on blood agar.
Catalase is produced by mammals and found in mammalian blood.
Mammalian blood releases hydrogen peroxide when treated with catalase.
3
26. Match the test to its description:Tests for the presence of aerobic respiration
Oxidase
Tests for the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide
Catalase Test
Tests for the breakdown of lactose
MacConkey Agar
Tests for the presence of flagella
Motility Test
Tests for the breakdown of red blood cells
Hemolysis Test
1. Ribosomes are made of:
Just DNA
DNA and protein
Just RNA
RNA and protein
RNA and protein
Where is the 16S rRNA gene found?
The gene is encoded by bacterial ribosomes
The gene is found encoded in the nucleus of a bacterium
The gene is encoded by a bacterium's circular chromosome
The gene is found encoded in the cytoplasm of a bacterium
The gene is encoded by a bacterium's circular chromosome
The 16S rRNA gene is a sequence of:
Solution:
Nucleotides
Amino acids
Ribosomes
rRNA's
Nucleotides
Which of the following best describes the function of the 16S rRNA gene?
Encoding proteins for ribosome assembly
Serving as a sequence of nucleotides on a bacterium's chromosome
Regulating gene expression within the bacterial chromosome
Provide instructions for synthesizing ribosomal RNA
Provide instructions for synthesizing ribosomal RNA
Which of the following statements about the 16S rRNA gene sequence is correct?
It acts as a blueprint for synthesizing bacterial lipids.
It serves as a marker for identifying the presence of bacteria in a sample.
It codes for enzymes involved in bacterial metabolism.
It regulates the expression of antibiotic resistance genes within bacteria
It serves as a marker for identifying the presence of bacteria in a sample.
True for False. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a process that makes millions of copies of an entire chromosome.True
True/False
False
True or False: PCR is a process that makes millions of copies of a targeted sequence of nucleotides on a chromosome.
True
False
True
8. What targeted sequence will you amplify using PCR?
The entire bacterial chromosome
16S rRNA gene
RNA
The ribosome
16S rRNA gene
What is the name of the custom-made DNA molecules that help us find the beginning and end of the 16S rRNA gene?
DNA polymerase
Nucleotides
Primers
Ribosomes
Primers
Identify the Steps in order
Open up the DNA (Denaturation)
Find the target DNA with Primers (Annealing)
Copy the target DNA by DNA polymerase (Extension)
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Which enzyme in the Master Mix adds nucleotides to the growing complementary strand of DNA?
The 16S rRNA gene
The 27F Primer
The 1492 Primer
Taq polymerase
Taq polymerase
True or False: The 27F and 1492R Primers ONLY blind to the 16S rRNA gene.
True
False
True
. How long (in base pairs) is the region of the 16S rRNA gene that we will amplify with PCR?
16 base pairs
20 base pairs
1,465 base pairs
The entire bacterial chromosome
1,465 base pairs
This week we will provide you with a colony of Escherichia coli bacteria. Next week you will repeat these procedures with your own soil isolates. Why should you see the same region amplified in your colony next week?
Your soil isolate is also E. coli.
All species of bacteria have the 16S rRNA gene.
All living organisms have the 16S rRNA gene
All species of bacteria have the 16S rRNA gene.
Imagine that you add a sample of your skin cells to the PCR tube. Would the 27F and 1492R Primers bind to anything? Explain your answer.
If you add a sample of your skin cells to the PCR tube, the 27F and 1492R primers will not bind to anything. The 16S rRNA gene are found in bacteria and archaea, not human
What will be present in your E. coli Colony PCR tube at the end of the reaction?
Solution:
Millions of copies of the 16S rRNA gene
Millions of copies of the bacterial chromosome
Millions of copies of the ribosomal subunit
Millions of copies of bacteria
Millions of copies of the 16S rRNA gene
17. What is the difference between the E. coli Colony PCR tube and the Negative Control tube?
Only the Colony PCR tube has Master Mix
Only the Colony PCR tube has the Primer Mix
Only the Colony PCR tube has a colony sample
Only the Colony PCR tube is placed in the thermal cycler
Only the Colony PCR tube has a colony sample
What does one band in the gel represent?
One DNA molecule
DNA molecules of different lengths
Millions of DNA molecules of the same size
Millions of DNA molecules of the same size
19. Why is Agarose Gel Electrophoresis a fundamental technique in biology
It allows you to determine whether the DNA has a negative or positive charge
It allows you to determine the size of DNA fragments
It provides you with the DNA sequence
It creates copies of the DNA molecules
It allows you to determine the size of DNA fragments
True or False: Shorter pieces of DNA move more quickly toward the far side of the gel (the side with the positive charge).
True
When you are pouring a gel, what is the purpose of the comb?
It carries the current
It stains the DNA
It creates wells to add a sample
It creates a positive charge to attract DNA
It creates wells to add a sample
23. What is a DNA ladder?
A series of DNA fragments of known lengths
The sugar-phosphate backbone that forms a ladder in DNA
The piece of equipment used to pour the gel
The piece of equipment used to create wells in the gel
A series of DNA fragments of known lengths
When do you add a DNA stain that allows you to visualize the location of the DNA?
When making the gel
When adding the buffer solution
When applying the electrical current
When turning on the blue light
When making the gel
. Let's say that you do see a band in the Negative Control Lane. What has happened?
This scenario shows that contamination or unintended amplification has occurred.
Which of the following describes the band in the Colony PCR lane.
Millions of copies of the 16S rRNA gene
Evidence for the presence of bacteria in the colony sample
Amplicons measuring about 1,500 base pairs in size
Products of PCR
All of the above
All of the above
When using the plunger to pipette your PCR sample into a well, you should only go to the
First stop
Second stop
First stop
When do you release the plunger after pipetting your PCR sample into the well?
Release the plunger slowly after reaching the desired volume.
When placing your gel in the electrophoresis rig, you will place the wells of the gel closest to the black electrode. Your DNA will then migrate toward the red electrode or "run to red." What is the charge of the red electrode?
The red electrode is positive
The red electrode is negative
The red electrode is positive
Which enzyme is essential for PCR amplificaiton?
DNA polymerase
RNA polymerase
Ligase
Helicase
DNA polymerase
4. Which of the following is NOT a step in a typical PCR cycle?
Denaturation
Annealing
Sequencing
Extension
Sequencing
Which temperature is commonly used for the denaturation step in PCR?
37 °C
55 °C
72 °C
95 °C
95C
Which component is typically NOT included in PCR Master Mix?
DNA polymerase
Nucleotides
Primers
Primers
Which of the following terms is analogous to 'amplify'?
Solution:
Copy
Delete
Denature
Sequence
Copy
The 27F and 1492R primers will anneal to _______, providing a starting point for Taq polymerase.
Solution:
bacterial DNA
bacterial RNA
bacterial proteins
bacterial ribosomes
bacterial DNA
9. The DNA sequence amplified when the 27F and 1492R primers are used measures approximately ...
20 base pairs in length.
100 base pairs in length.
1,000 base pairs in length.
1,500 base pairs in length.
1,500 base pairs in length.
10. By using 27F and 1492R primers, we ensure that.
only the 16S rRNA gene found on bacterial chromosomes is copied.
the bacteria are lysed, and the DNA is denatured.
contamination of the Negative Control is minimized.
if any type of DNA is present in the sample (bacterial and eukaryotic), it is detected.
only the 16S rRNA gene found on bacterial chromosomes is copied.
. What happens during the denaturation step of PCR?
Solution:
Bacteria are lysed
Double-stranded DNA separates
Primers anneal to complementary sequences
Taq polymerase synthesizes complementary strands
Double-stranded DNA separates
True or False: Taq polymerase synthesizes primers.
False
True or False: Taq polymerase can only synthesize complementary DNA if it's given a primer.
True
False
True
. What happens during the coolest stage of PCR?
Bacteria are lysed
DNA is denatured
Primers anneal to complementary sequences.
Taq polymerase synthesizes complementary strands of DNA.
Primers anneal to complementary sequences.
At which temperature is Taq polymerase active?
95 °C
72 °C
55 °C
32 °C
72 °C
What is in the PCR tube after the reaction ends IF a bacterial chromosome IS in the tube and the reaction occurred as expected?
Millions of copies of the 16S rRNA gene sequence
Millions of copies of the entrire bacterial chromosome
Millions of copies of the ribosomes
Millions of bacteria
Millions of copies of the 16S rRNA gene sequence
17. What is in the Negative Control PCR tube after the reaction ends if there is NO contamination?
Millions of copies of the 16S rRNA gene sequence.
No copies of the 16S rRNA gene sequence.
No copies of the 16S rRNA gene sequence.
. True or False: The 16S rRNA gene should be amplified in the Positive Control PCR Tube if the reaction occurs as expected.
True
How will you know that the 16S rRNA gene has been successfully amplified when looking at the gel?
You will not see a band in the lane.
You will see two bands in the lane.
You will see a ladder in one lane.
You will see a band with amplicons measuring 1,500 bp in size.
You will see a band with amplicons measuring 1,500 bp in size.
. How will you know that bacteria have not contaminated your reagents when looking at the gel?
You will not see a band in the Negative Control lane.
You will see two bands in the lane.
You will see a ladder in one lane.
You will see a band with amplicons measuring 1,500 bp in size in the Positive Control lane.
You will not see a band in the Negative Control lane.
21. True or False: You should see a band measuring 1,500 bp in size in the Positive Control lane in the gel if the reaction occurred as expected.
True
22. Let's say you were unable to lyse the bacteria, and the PCR reagents could not access the bacterial chromosome. Will amplification occur? Will there be a band in the gel?
Solution:
Yes, Yes
No, No
Yes, No
No, Yes
No, No
24. What is the purpose of the agarose gel used in Agarose Gel Electrophoresis?
It keeps the samples from evaporating.
It separates DNA molecules based on their size.
It produces the current.
It amplifies the DNA
It separates DNA molecules based on their size.
25. Place the following Agarose Gel Electrophoresis procedures in the correct order.:
1. place the gel in the electrophoresis chamber
add running buffer
make a solid agarose gel
measure the presence and size of the DNA molecules using a DNA ladder
load the DNA ladder and PCR tube samples
apply an electrical current
make a solid agarose gel, place the gel in the electrophoresis chamber, add running buffer, load the DNA Ladder and PCR Tube samples, Apply an electrical current, measure the presence and size of the DNA molecules using a dna ladder
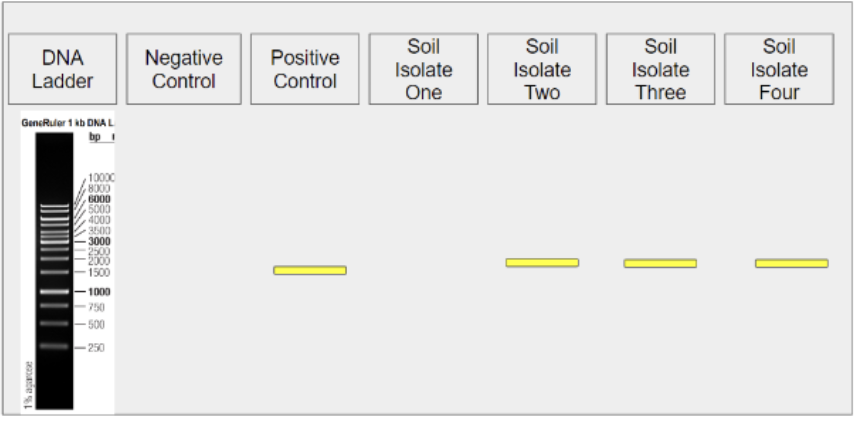
26. What lane do you look at to determine whether the reagents are contaminated?
DNA Ladder lane
Negative Control lane
Positive Control lane
Any soil isolate lane
Negative Control lane
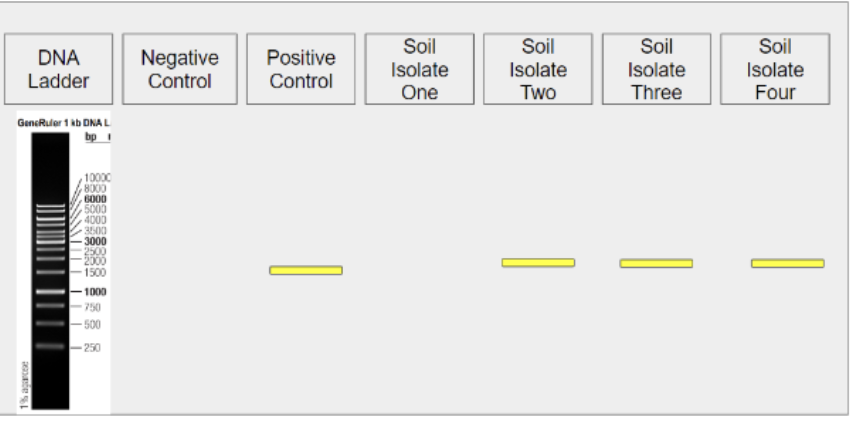
27. Examine the gel image above. Does it appear that the reagents, thermocycler, and overall PCR process functioned as expected?
Yes
No
Yes
What lane do you look at to determine whether the process functioned as expected?
DNA Ladder lane
Negative Control lane
Positive Control lane
Any soil isolate lane
Positive Control lane
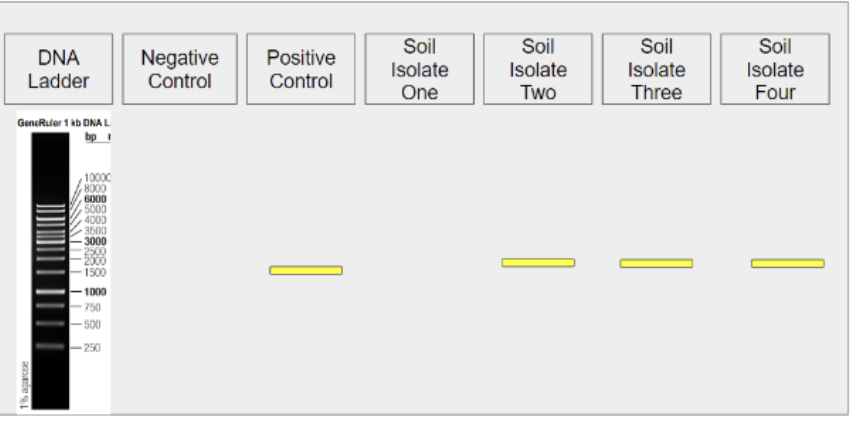
29. Examine the gel image above. Does it appear that Soil Isolate One was a colony of bacteria?
Yes
No
No
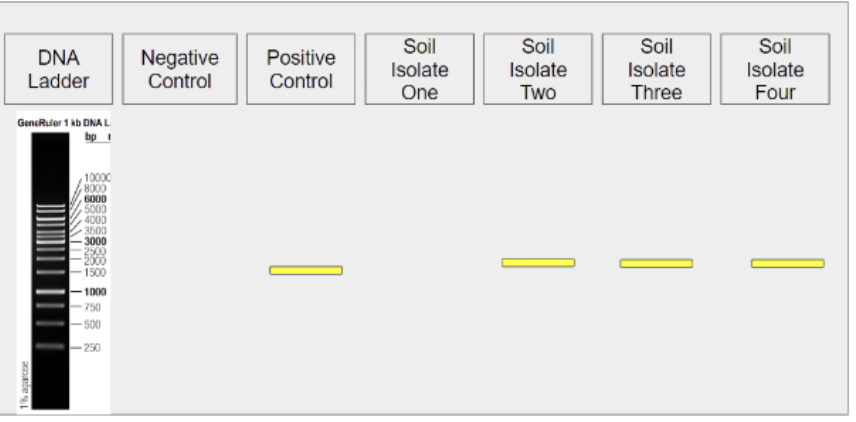
Examine the gel image above. Does it appear that Soil Isolate Two was a colony of bacteria?
Yes
No
Yes

1. Which microscope part should you rotate to align the 10X objective?
Coarse focus knob
Fine focus knob
Nosepiece
Condenser
Nosepiece
What is the total magnification when the 40X objective is in alignment?
4x
40x
160x
400x
400X
Which of the following is an example of higher (or better) resolution?
When (r) = 200 nanometers
When (r) = 1000 nanometers
When (r) = 200 nanometers
What is the resolution (r) of your microscope, when the 40X objective is in alignment? The Numerical Aperture of the 40X objective is equal to 0.65.
Solution:
40 nm
65 nm
385 nm
400 nm
385 nm
What is the relationship between magnification and the number of micrometers per reticle unit?
As magnification increases the number of micrometers per reticle unit increases.
As magnification increases the number of micrometers per reticle unit decreases.
As magnification increases, the number of micrometers per reticle unit decreases. This means that at higher magnifications, each unit on the reticle represents a smaller distance in micrometers.
You measure the width of a Paramecium with the 10X objective in alignment. You determine it measures 5 reticle units. How many micrometers does this equal?
Solution:
5 µm
12.5 µm
50 µm
75 µm
50 µm
With which objective will you have the biggest field of view?
Solution:
4x
10x
40x
100x
4x
With which objective will you have the largest depth of field remain in focus?
4x
10x
40x
100x
4x
You can use the coarse knob to focus on the specimen when which objective is in alignment?
Solution:
4x
10x
40x
100x
4x
You must use immersion oil when which objective is in alignment?
Solution:
4x
10x
40x
100x
100x
Should the 100X objective lens come into direct contact with the immersion oil?
Solution:
Yes
No
Yes
12. What should you use to clean the objective lens and slide after using immersion oil?
Solution:
Ethanol
Paper towels
Water
Lens cleaner and Lens paper
Lens cleaner and Lens paper