3.1.7 Redox
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What does redox mean? (1)
Reactions which involve both reduction and oxidation
What is oxidation? (1)
Process of electron loss
What is reduction? (1)
Process of electron gain
what is oxidation in terms of oxidation states
oxidation number increases
what is reduction in terms of oxidation states
oxidation number decreases
what is a redox reaction in terms of oxidation states
a reaction where the oxidation state of at least one element changes
what is a disproportionation reaction
a reaction in which an element is both oxidised and reduced
What is an oxidising agent? (1)
Electron acceptor
what part is an oxidising agent exactly
the reactant
not the element
What is a reducing agent? (1)
Electron donor
what does an oxidation state (number) tell you
total number of electrons it has donated or accepted.
summary table of the oxidation number rules
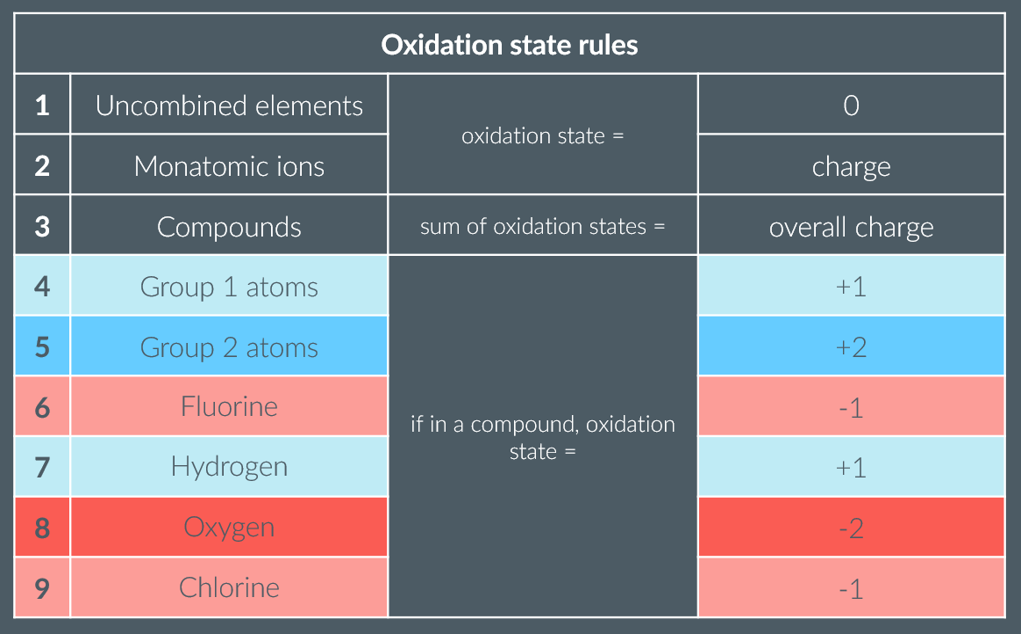
what are the oxidation state rules ranked in order of
priority
mneumonic for remembering the order of priority for the later oxidation states
Fairies
Hate
Orange
Clover
What is the oxidation state of uncombined elements? (1)
0
What is the oxidation state of elements bonded to identical elements? (1)
0
what is the oxidation state of compounds/polyatomic ions?
sum of the oxidation states equals the overall oxidation state
This overall oxidation state is equal to the overall charge on the ion.
What is the oxidation state of oxygen in compounds, except in peroxides? (1)
-2
What is the oxidation state of oxygen in peroxides? (1)
-1
whats the molecular formula of hydrogen peroxide
H2O2
What is the oxidation state of hydrogen in compounds, except in metal hydrides? (1)
+1
What is the oxidation state of hydrogen in metal hydrides (e.g., NaH)? (1)
-1
What is the oxidation state of Group I metals in compounds? (1)
+1
What is the oxidation state of Group II metals in compounds? (1)
+2
What is the usual oxidation state of Group 7 in compounds? (1)
-1
do oxidation states have a +/_ before or after the number
before
how do we assign oxidation states in covalent molecules
assign oxidation states based on charges each element would have if the compound was ionic
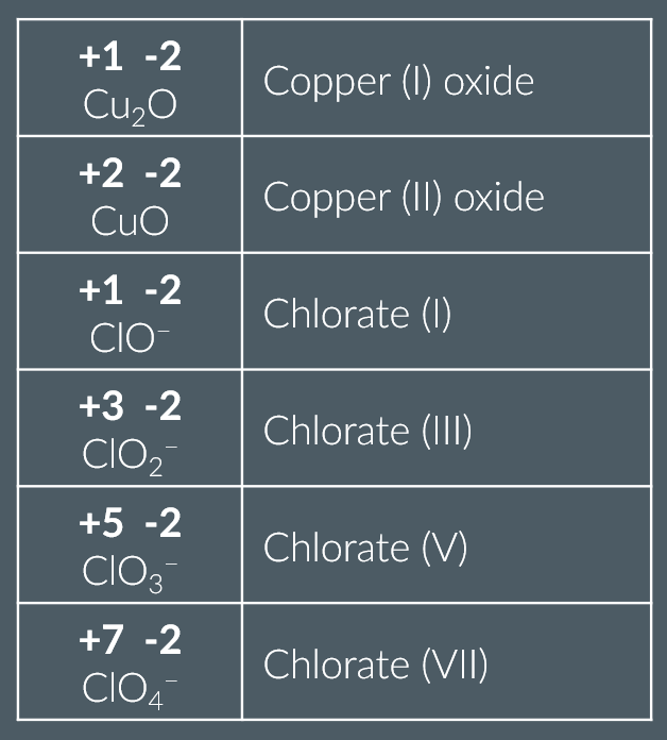
Finding the oxidation states from systematic names
If an element can have multiple oxidation states (or isn’t in its ‘normal’ oxidation state) its oxidation state is sometimes shown using Roman numerals,
e.g. (I) = +1, (II) = +2, (III) = +3 and so on. The Roman numerals are written after the name of the element they correspond to.
what are examples of molecules that have multiple oxidation states
ions that end in -ate
transition metals
examples of naming ions with oxidation states
what are the 2 methods for balancing redox equations
Constructing and combining half equations
Using oxidation states
what does a half equation show
half-equations show oxidation or reduction
The electrons are shown in a half-equation so that the charges balance.
EXAMPLE - give the half equation for the oxidation of iron
Fe → Fe3+ + 3e–
EXAMPLE - give the half equation for the reduction of chlorine
Cl2 + 2e– → 2Cl–
What is the most important thing to remember when combining half equations to form full balanced equations
Just make sure both half-equations have the same number of electrons in
when do we use the half equation balancing method
if we know the products of that redox reaction
what is the method for constructing and combining half equations to find the balanced equation from the half equation
Construct half-equations:
Construct separate equations for oxidation and reduction
2) Balance the atoms ...
.. other than hydrogen and oxygen
oxygen by adding H2O
hydrogen by adding H+
Balance the charges by adding e
To combine half-equations:
Multiply the half-equations so that the electrons cancel (as in the number of electrons in both half equation is the same)
Combine the half-equations
Double check its all balanced
summary/example of finding the balanced equation from half equations

why can we balance an equation using oxidation states
the sum of the oxidation states in the reactants must equal the sum of the oxidation states in the products.
this can be used to work out the stoichiometric coeficients
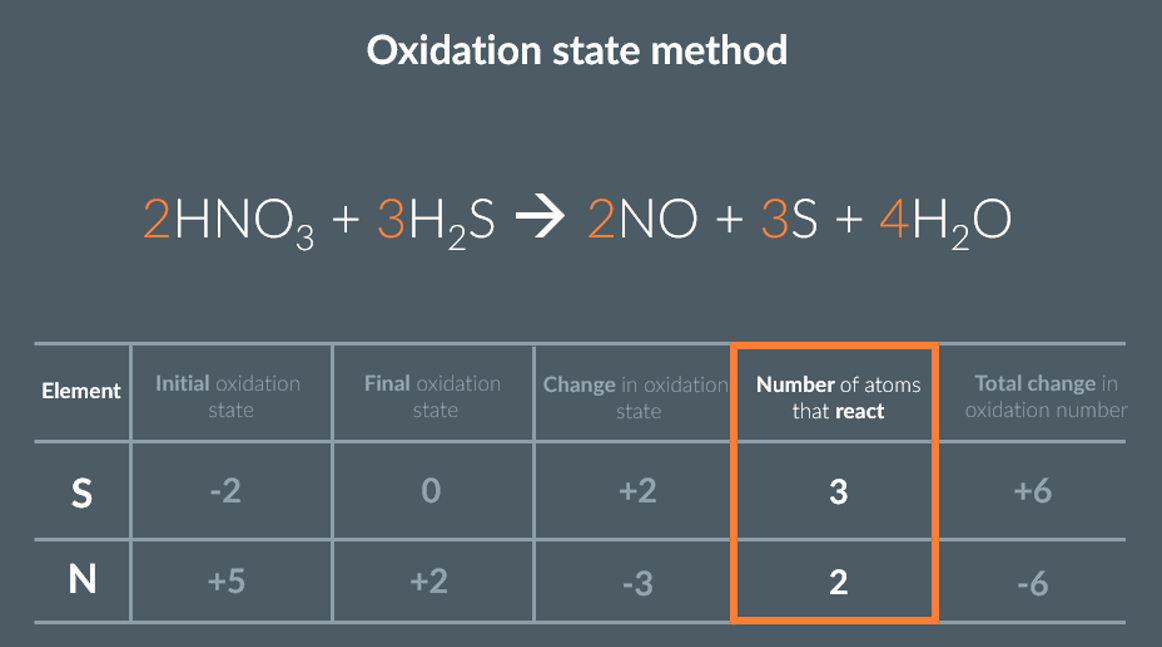
what is the method of balancing equations using oxidation states
by assigning oxidation states figure out which element is oxidised and which element is reduced
write these in a table, noting their initial and final oxidation state and the change in oxidation states
overall changes in oxidation state must add to zero. THEREFORE, multiply so the changes are equal for both elements
this multiplier is the coefficient that goes in front of the elements
deduce the rest of the equation
summary/example of the method of balancing equations using oxidation states
How to test for SO2
dichromate
How to test for H2S
test using lead nitrate