CAM I - MSK Missed Concepts (Not on Upper Cohort Quizlets)
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Nursemaid's elbow (pulled elbow)
Most common in 1-4 yo's, results from sudden "jerk" of the arm - pulling arm motion
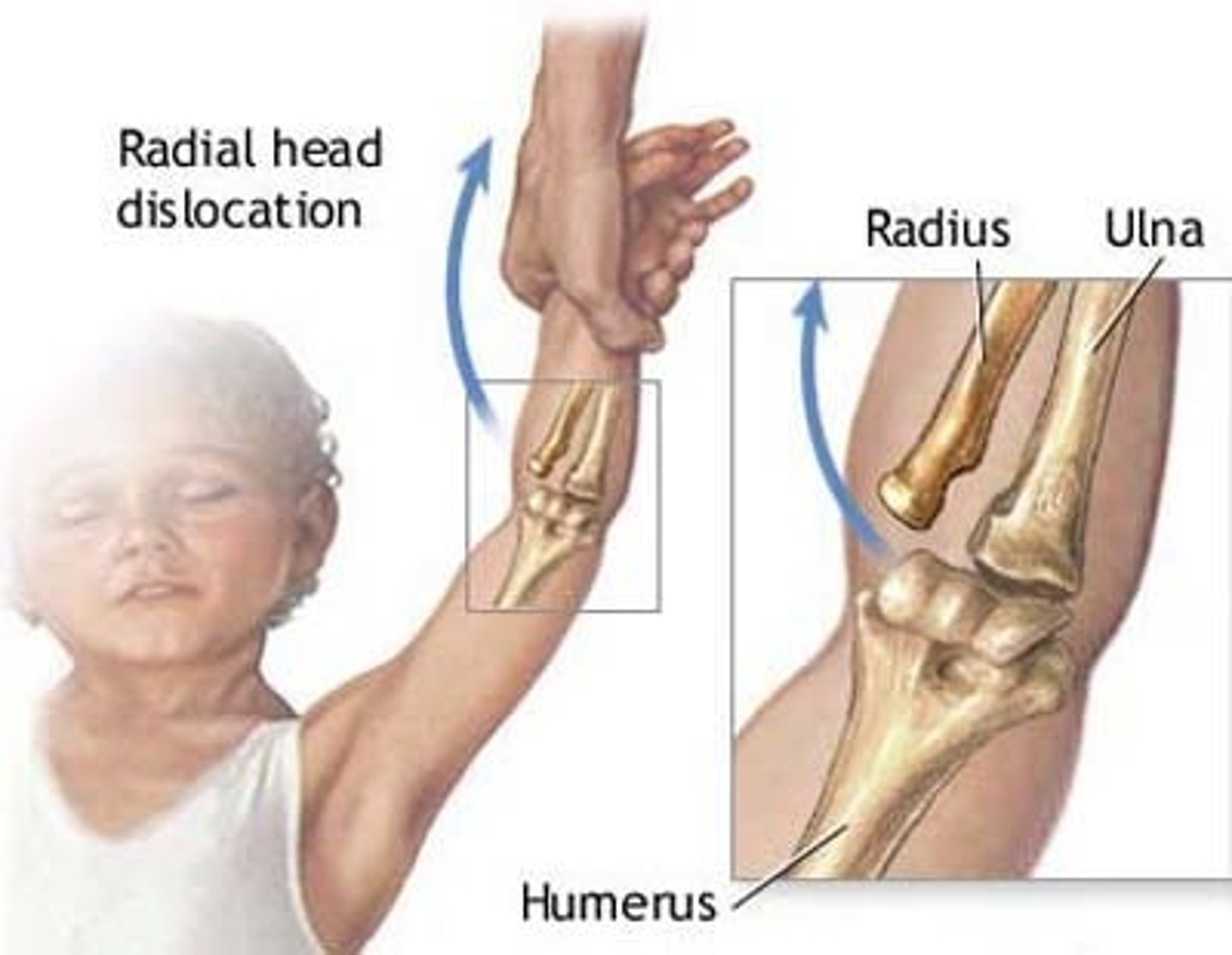
Arm flexed
forearm pronated
no deformity, eccymosis, swelling, or bony tenderness
What are the clinical manifestations of nursemaids elbow?
clinical (can do x-ray- not often needed, obtain if deformity, ecchymosis, swelling, or concerns of fx)
How do you diagnose nursemaids elbow?
bedside reduction (hyperpronation or supination/flexion)
How do you treat nursemaids elbow?
Pediatric elbow
Most common in peds, typically a condylar fracture
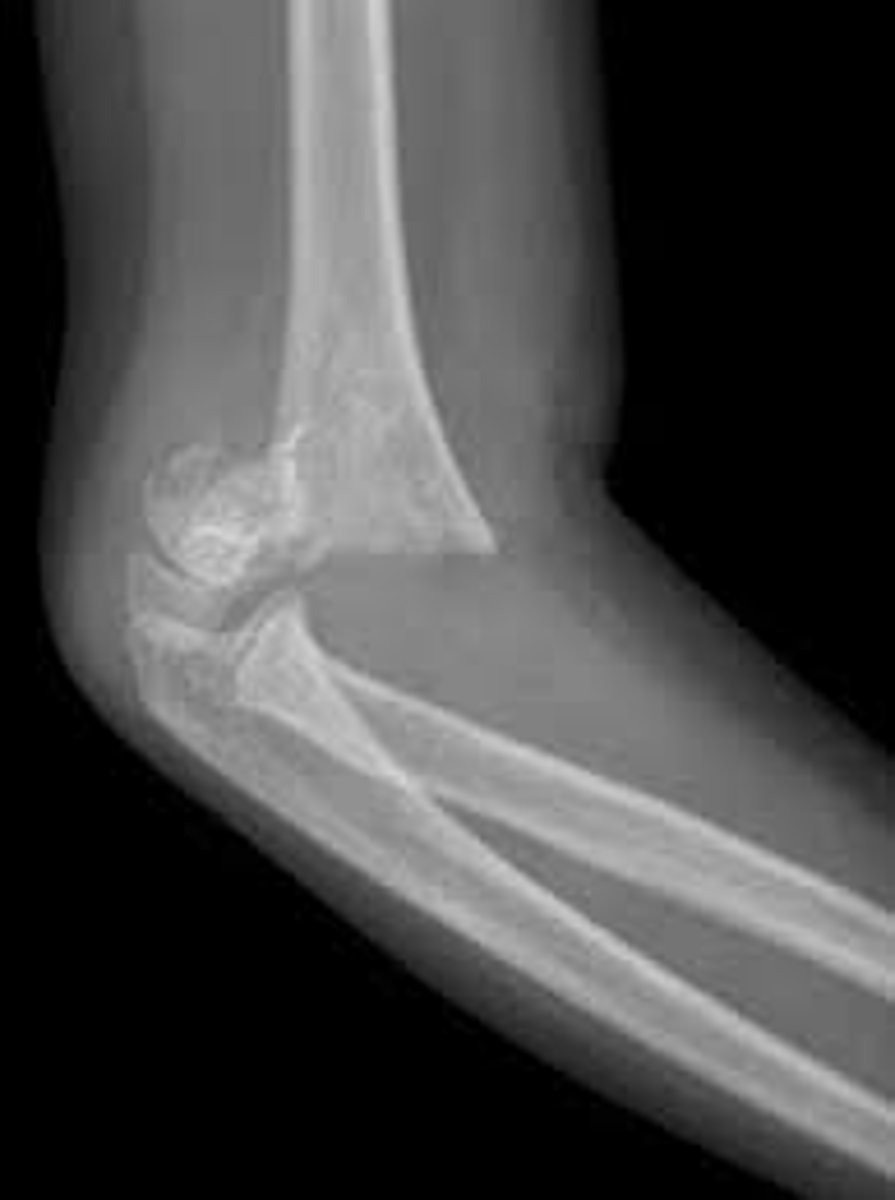
posterior fat pad and/or anterior sail sign
occult fracture - pain, swelling, tenderness over radial head/proximal ulna
What are the clinical manifestations of pediatric elbow?
lateral x-ray (presence of posterior fat pad)
How do you diagnose pediatric elbow?
long arm splint, refer to peds ortho (if available - if not, general ortho)
How do you treat pediatric elbow?
elbow dislocation
Majority of posterior dislocations - FOOSH injury
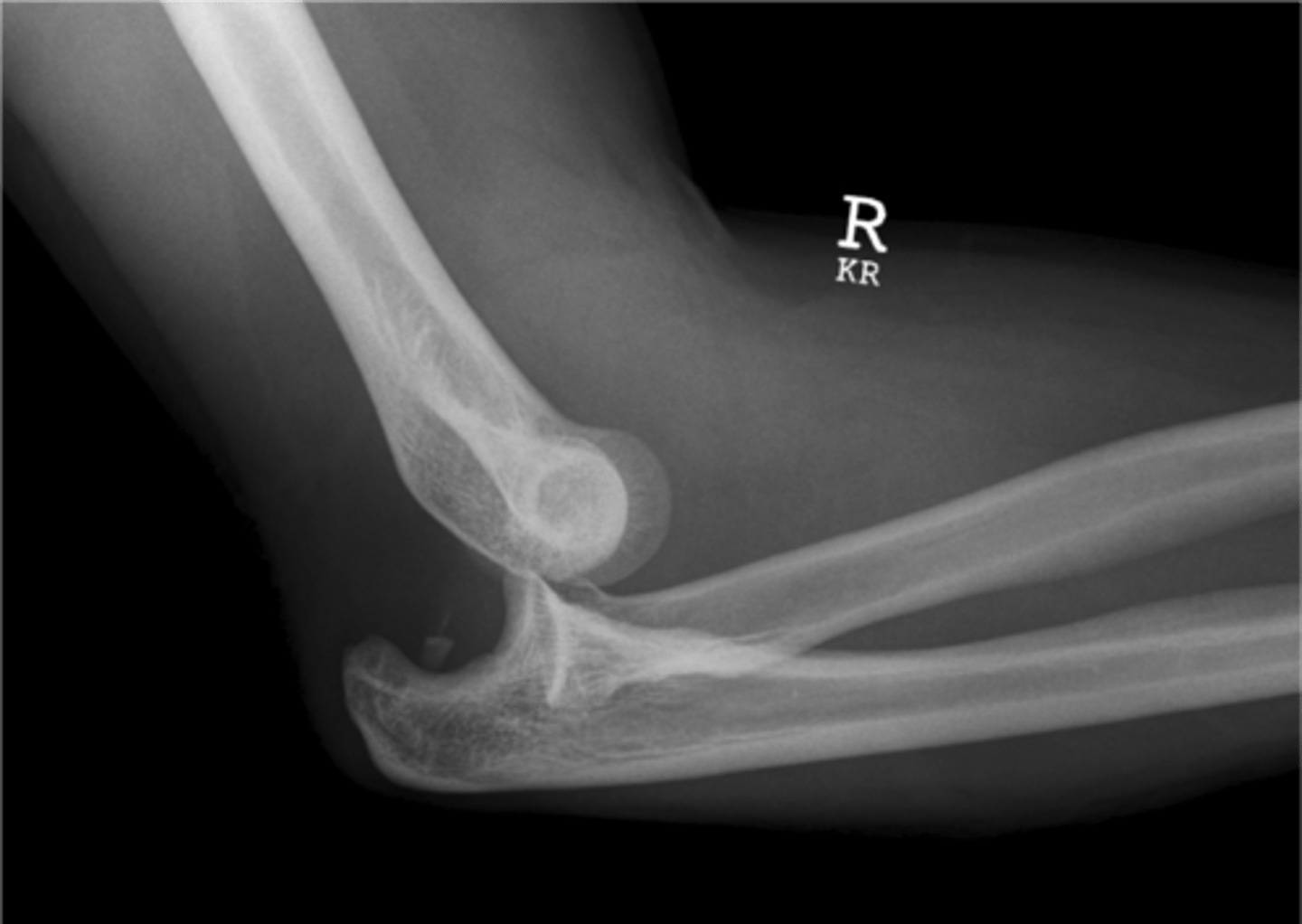
Essential to assess NV status
pain/significant swelling at elbow
elbow at 45 degree flexion, severely restricted ROM
What are the clinical manifestations of elbow dislocation?
AP x-ray (medial and lateral displacement of ulna/radius)
lateral x-ray (both ulna/radius displaced)
How do you diagnose elbow dislocation?
REDUCTION
Assess NV, post reduction x-ray, long arm splint, close ortho follow up
How do you treat elbow dislocation?
Shoulder dislocation
Displacement of the humeral head from the glenoid fossa
ANTERIOR - MOST COMMON (95%) - arm abducted and externally rotated
Posterior - often due to seizures, electrocution, or trauma
inferior - rare
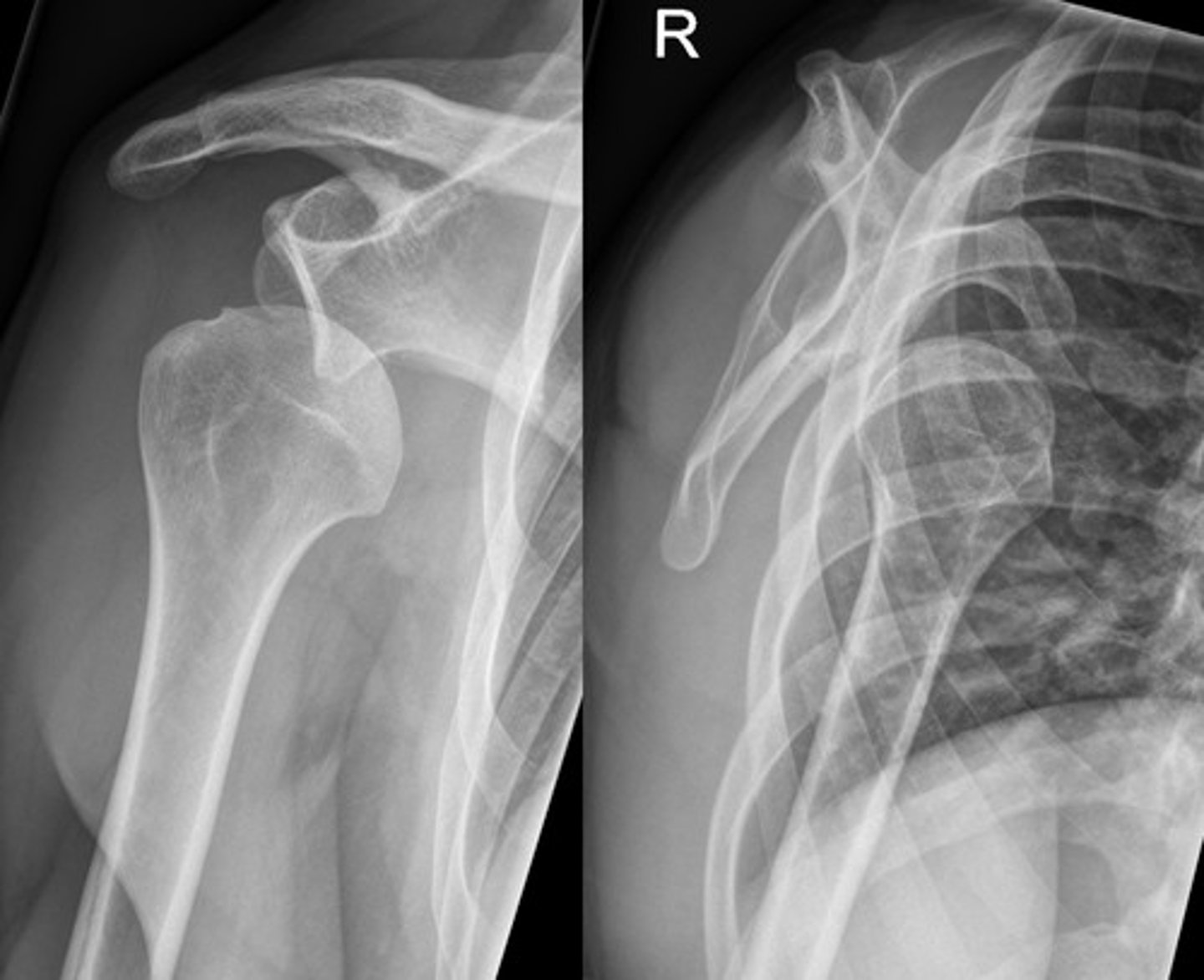
visible deformity
"squared off" shoulder
prominent acromion
arm held in slight abduction and external rotation
numbness/tingling if nerves involved (axillary nerve injury is most common - deltoid numbness, once popped back into place - numbness should go away)
What are the clinical manifestations of shoulder dislocations?
x-ray (AP, axillary, scapular Y views)
before and after reduction
How do you diagnose a shoulder dislocation?
reduction techniques
immobilization in sling
PT for rehab
Surgery (if recurrent or associated injury)
How do you treat a shoulder dislocation?
recurrent dislocations
Bankart (labral injury) and Hill-Sachs lesions (fracture)
RTC tears
Nerve or vascular injury
What are some complications of a shoulder dislocation?
paronychia
Infection of the lateral or proximal nail fold (usually more superficial)
acute or chronic
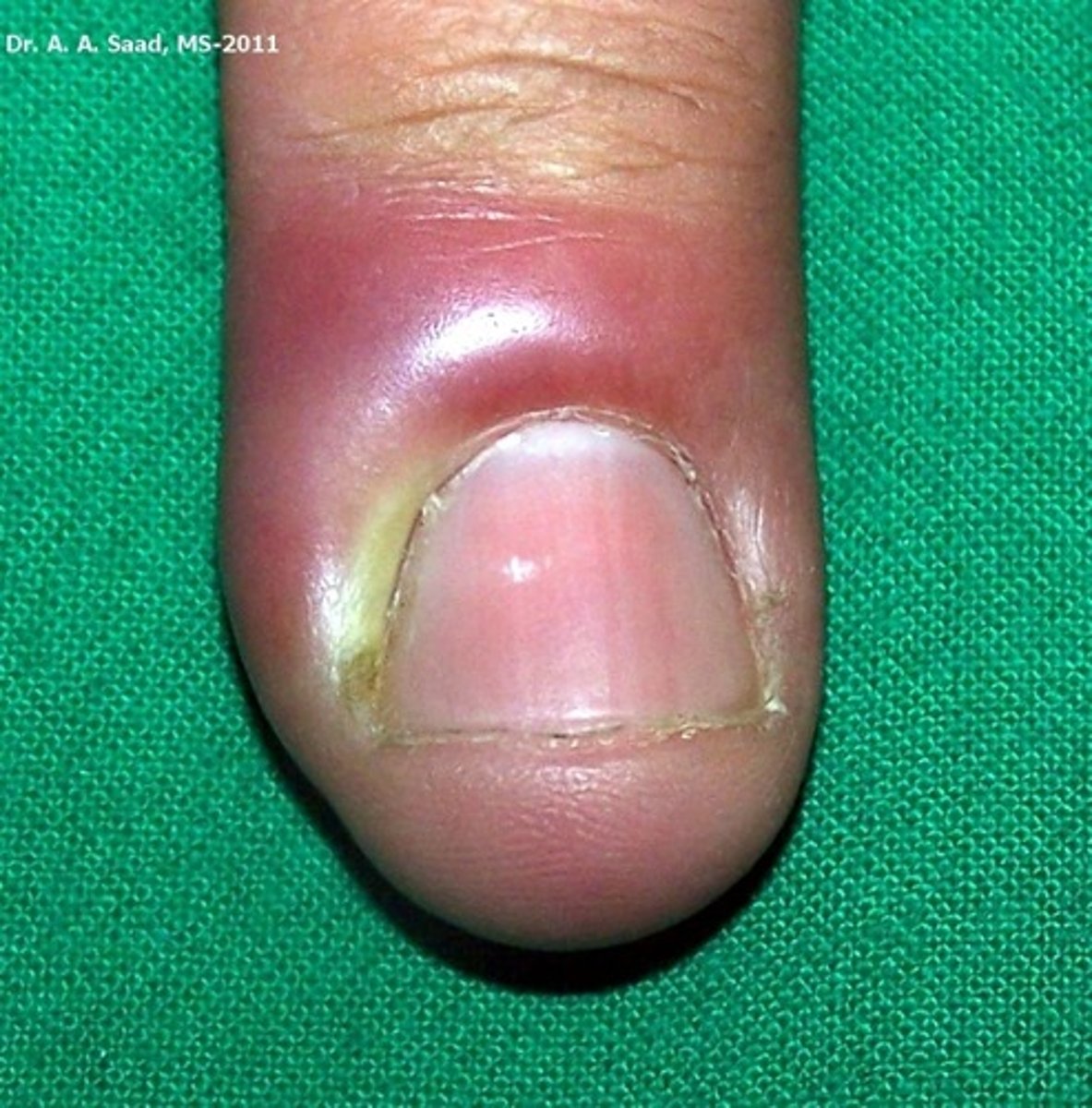
staph aureus (nail biting)
what causes acute paronychia?
often candida or irritant exposure (wet work)
what causes chronic paronychia?
redness
swelling
tenderness around the nail
possible pus collection (fluctuance)
nail changes in chronic cases
What are the clinical manifestations of a paronychia?
clinical diagnosis
How do you diagnose a paronychia?
mild cases:
warm soaks (3-4 times day)
topical antibiotics (ex: mupirocin)
More severe cases:
I&D if abscess present
oral antibiotics if cellulitis (ex: cephalexin)
How do you treat acute paronychia (<6 weeks) mild vs severe?
topical steroids
reduce water exposure
How do you treat chronic paronychia (>6 weeks)?
persistent droop
swan-neck deformity if left untreated
what are some complications of a paronychia?
mallet finger
Injury to the extensor tendon at the distal interphalangeal (DIP) - causing inability to extend finger tip
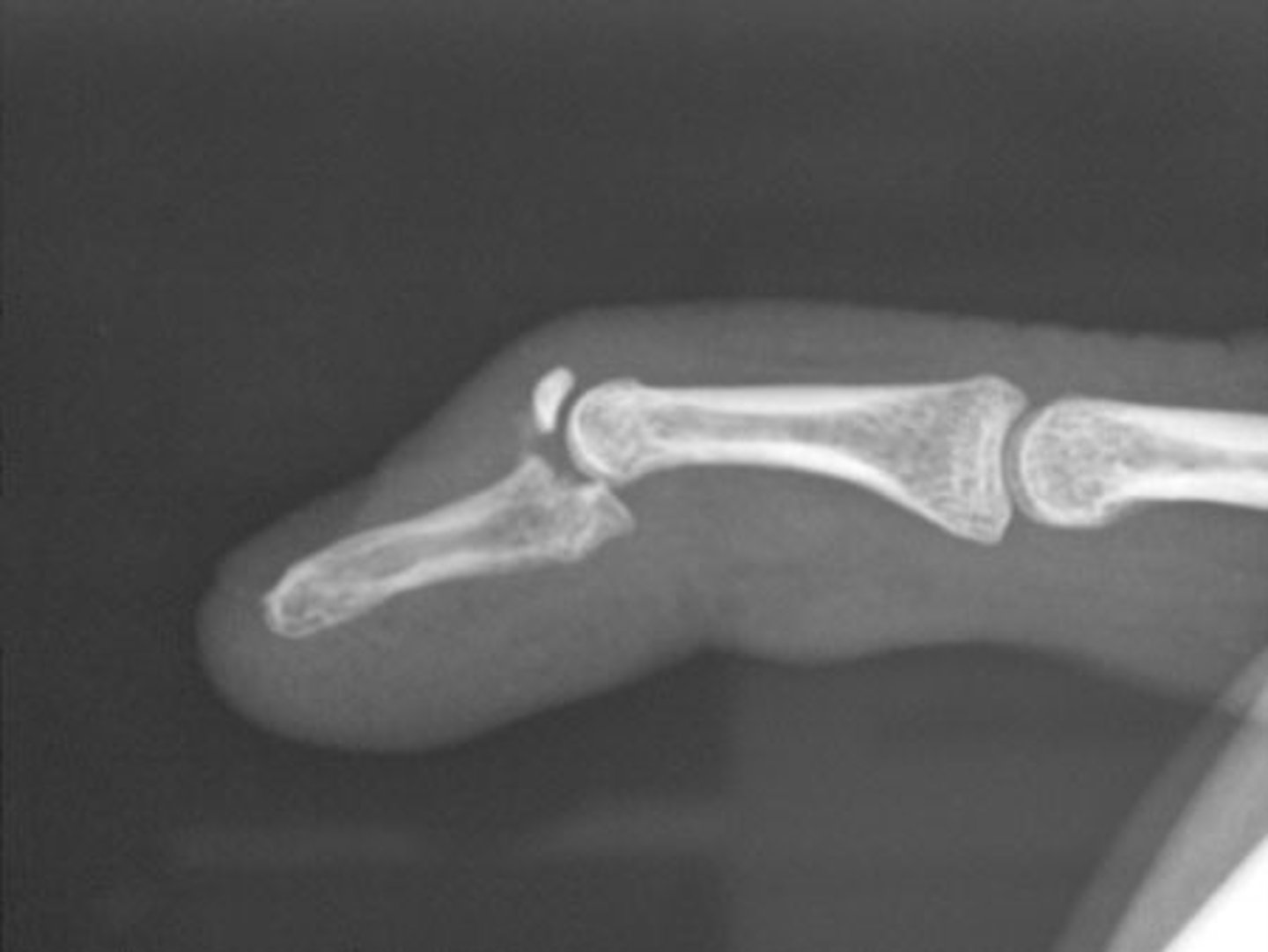
sudden forceful flexion of an extended finger (ex: ball striking the tip - common in sports)
What causes mallet finger?
DIP joint held in flexion
inability to actively extend fingertip
swelling/tenderness at the dorsal DIP joint
What are some clinical manifestations of mallet finger?
x-ray (rule out avulsion fracture or joint subluxation)
How do you diagnose a mallet finger?
splinting DIP in full extension for 6-8 weeks
surgery (only if large fracture fragment or joint subluxation)
How do you treat a mallet finger?
Gamekeeper's Thumb (Skier's Thumb)
Injury to the ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) of the thumb or the thumb metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint
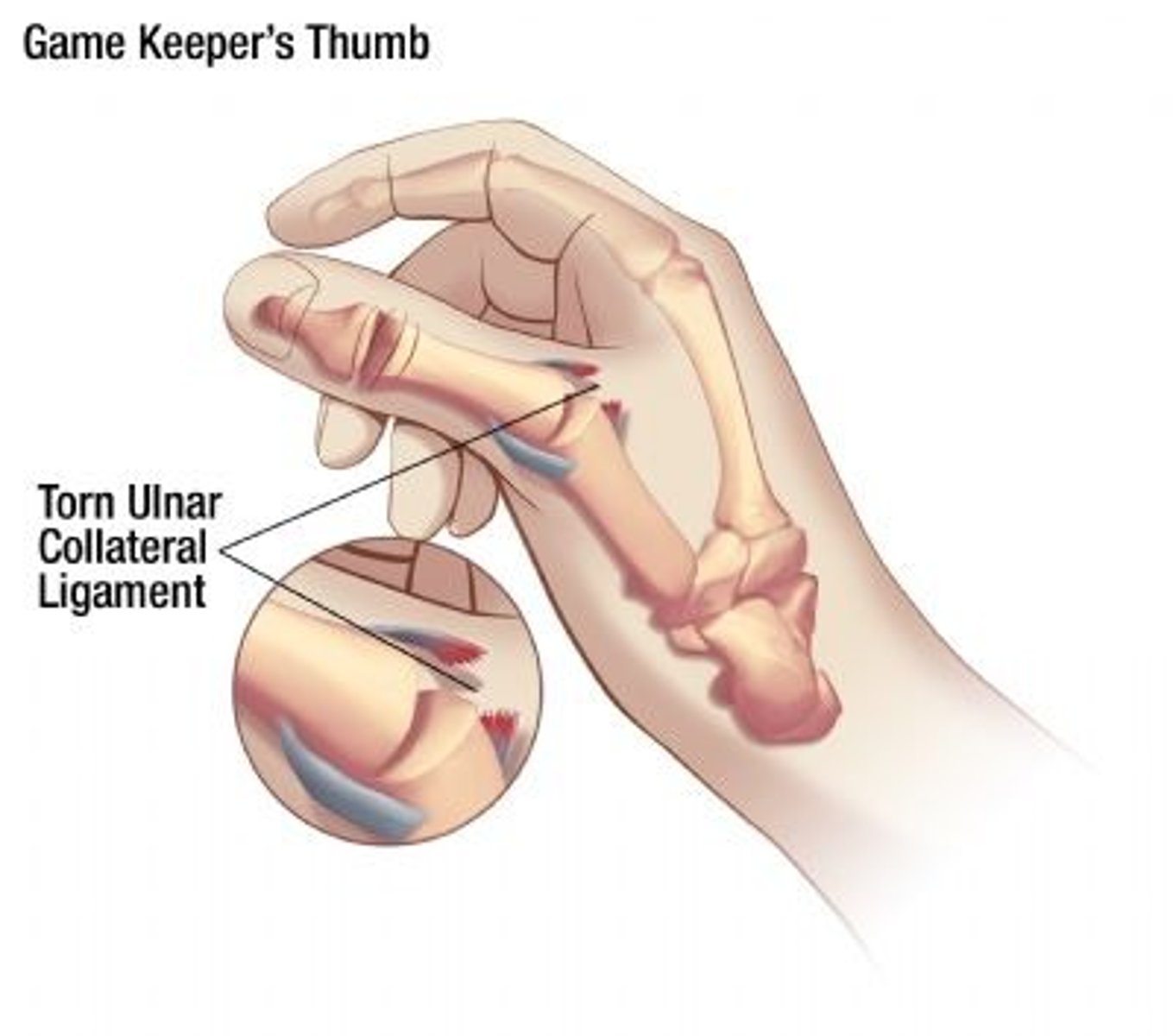
forced abduction or hyperextension of the thumb (common in skiers, falls with thumb caught on object)
What causes gamekeepers thumb?
pain/swelling over ulnar aspect of MCP joint
weak/painful pinch grip
instability with vagal stress
What are some of the clinical manifestations of gamekeepers thumb?
Physical exam - valgus stress testing
x-ray (rule out avulsion fracture or Stener lesion)
MRI (if diagnosis is unclear - or high suspicion)
How do you diagnose game keepers thumb?
partial tear: thumb spica splint/cast vs brace (4-6 weeks)
complete tear or Stener lesion: surgery
How do you treat game keepers thumb?
chronic instability
weak pinch grip
early arthritis if not treated
What are some complications of game keepers thumb?
Cervical Dystonia (Torticollis)
spasmodic torticollis or wryneck - an acquired issue in adults
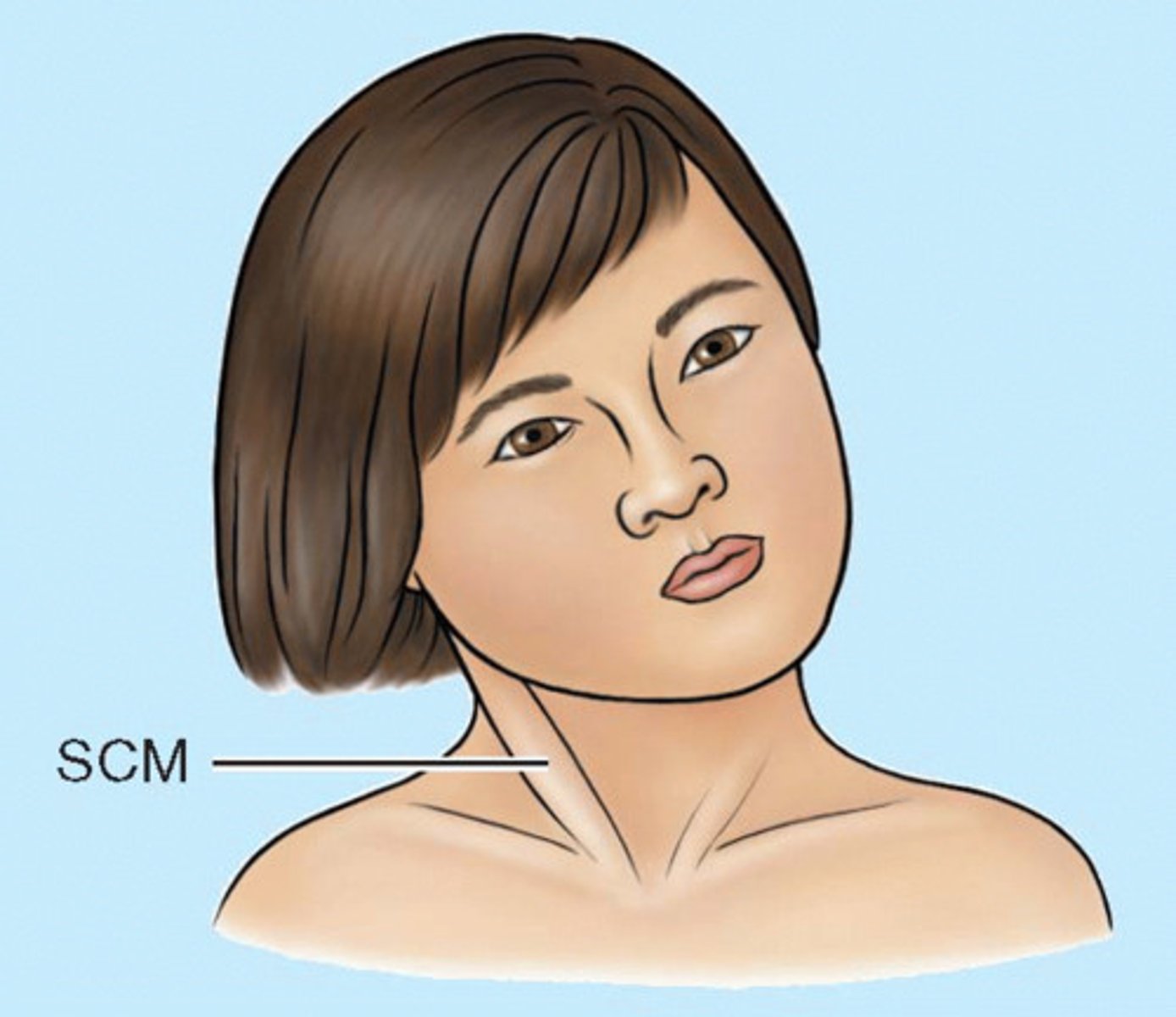
trauma or injury (can be minor/severe)
burn - scaring
can be congenital (children)
How does cervical dystonia occur?
severe/sudden muscle spasm (sternocleidomastoid)
muscle often "locked" in spasm
neck muscle pain
"constant involuntary spasms"
twisting of neck (abnormal position of the chin)
head tilt
What are some clinical manifestations of cervical dystonia?
clinical
if trauma: +/- neurological sx.- MRI may be warranted
How do you diagnose cervical dystonia?
NSAIDs
muscle relaxants
rest
PT - stretching
botox injections (administered directly into muscle)
How do you treat cervical dystonia?
cauda equina
A surgical emergency caused by compression of the cauda equina (nerve roots below conus medullaris)
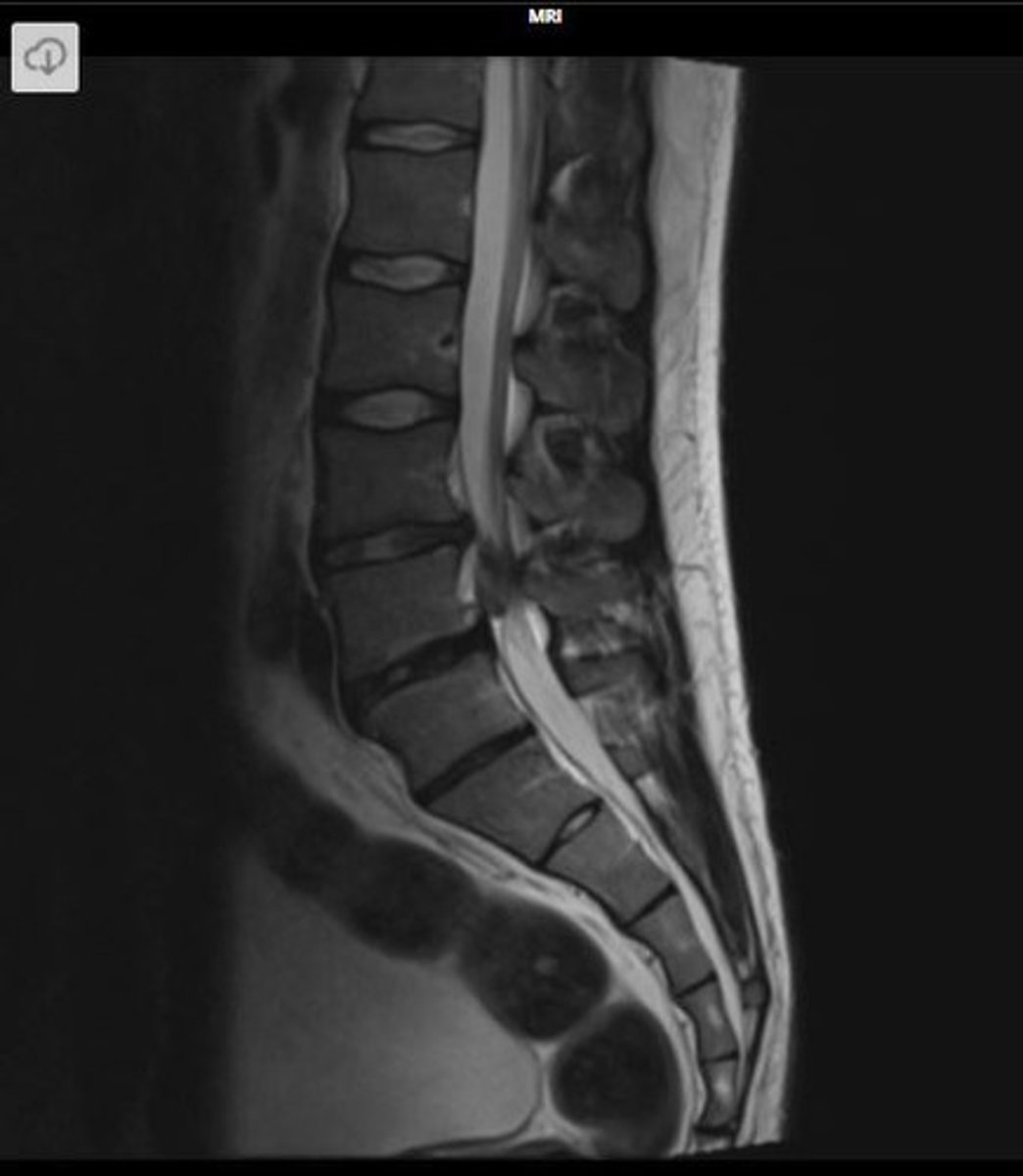
large central disc herniation (most common)
tumor
trauma
abscess
spinal stenosis
hematoma
How does cauda equina occur?
1. saddle paresthesia
2. bladder and bowel dysfunction
3. severe bilateral leg pain
4. decreased lower extremity reflexes (especially achilles reflex)
5. decreased anal sphincter tone DRE
What are some clinical manifestations of cauda equina?
MRI of lumbar spine (TEST OF CHOICE)
hx and physical exam:
neural deficits, urinary retention, and saddle anesthesia
DRE:
decreased anal sphincter tone
URGENT NEUROSURG CONSULT!
What are some clinical manifestations of cauda equina?
EMERGENT SURGICAL DECOMPRESSION!! (best outcome with early intervention)
delay - increases risk of permanent paralysis, incontinence, and sexual dysfunction
How do you treat cauda aquina?
always assess saddle sensation and urinary function in patients with new back pain + neuro symptoms
(cauda equina = back pain + bowel/bladder dysfunction + saddle anesthesia = MRI stat)
What are some clinical pearls for cauda equina?
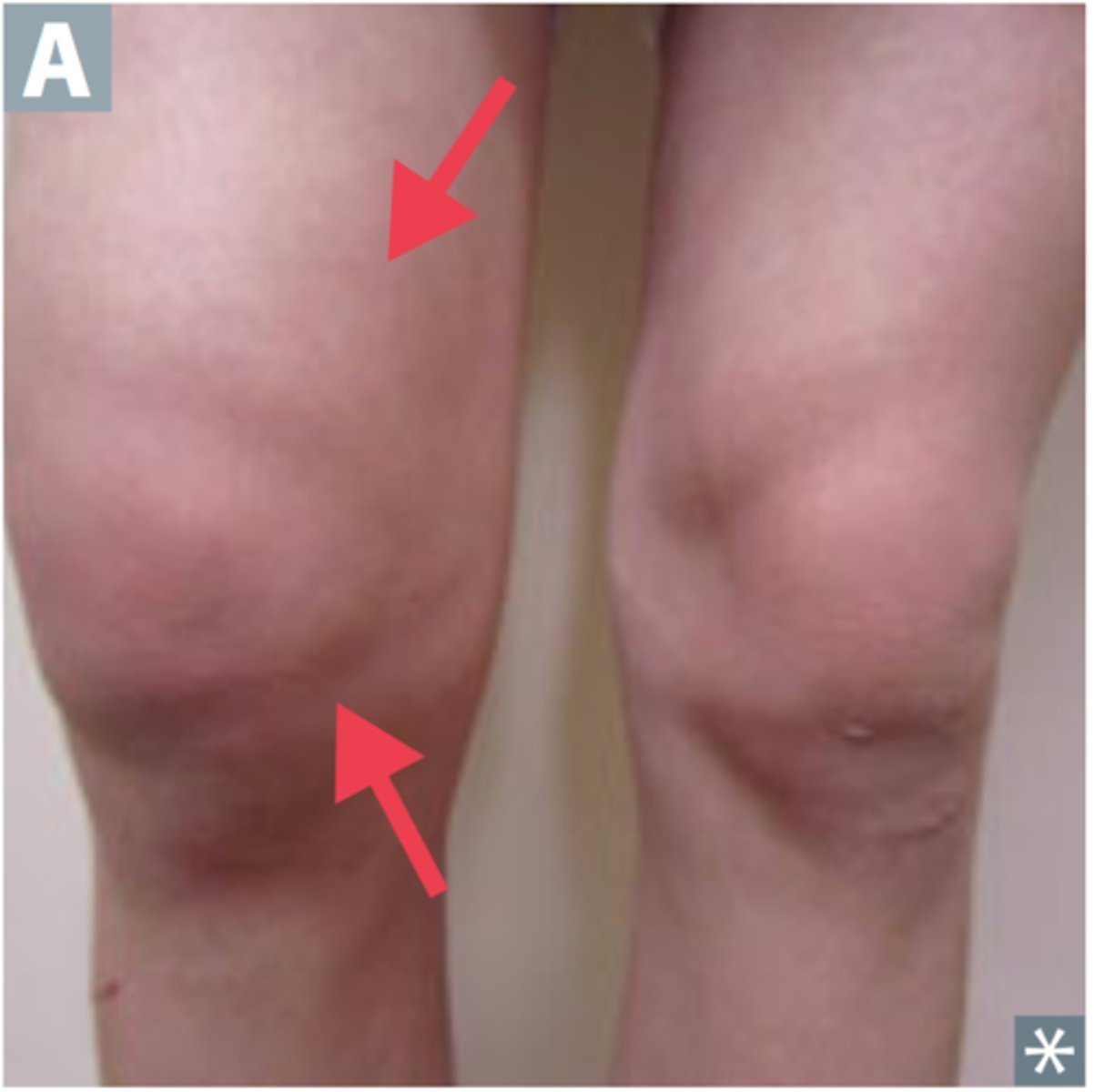
septic arthritis
monoarthritis characterized by intra-articular infection and joint destruction (S. Aureus - including MRSA - most common)
where: native and prosthetic joints (ex: dental work)
how: most cases result from hematogenous seeding
How/where does septic arthritis happen?
hip and KNEE - 80% of cases (large joints > small joints)
What are the clinical manifestions of septic arthritis?
joint aspiration promptly (quickest and most crucial step if infection suspected) - cell count, gram stain, culture, etc.
CBC
ESR
CRP
cultures
how do you diagnose septic arthritis?
irrigation and debridement followed by IV antibiotics
How do you treat septic arthritis?
hip dislocation
Posterior dislocation is the most common (90%)
risk of vascular damage and nerve injury
weak hip flexion, knee extension, ankle dorsiflexion (common perineal nerve)
can lead to avascular necrosis/osteoarthritis
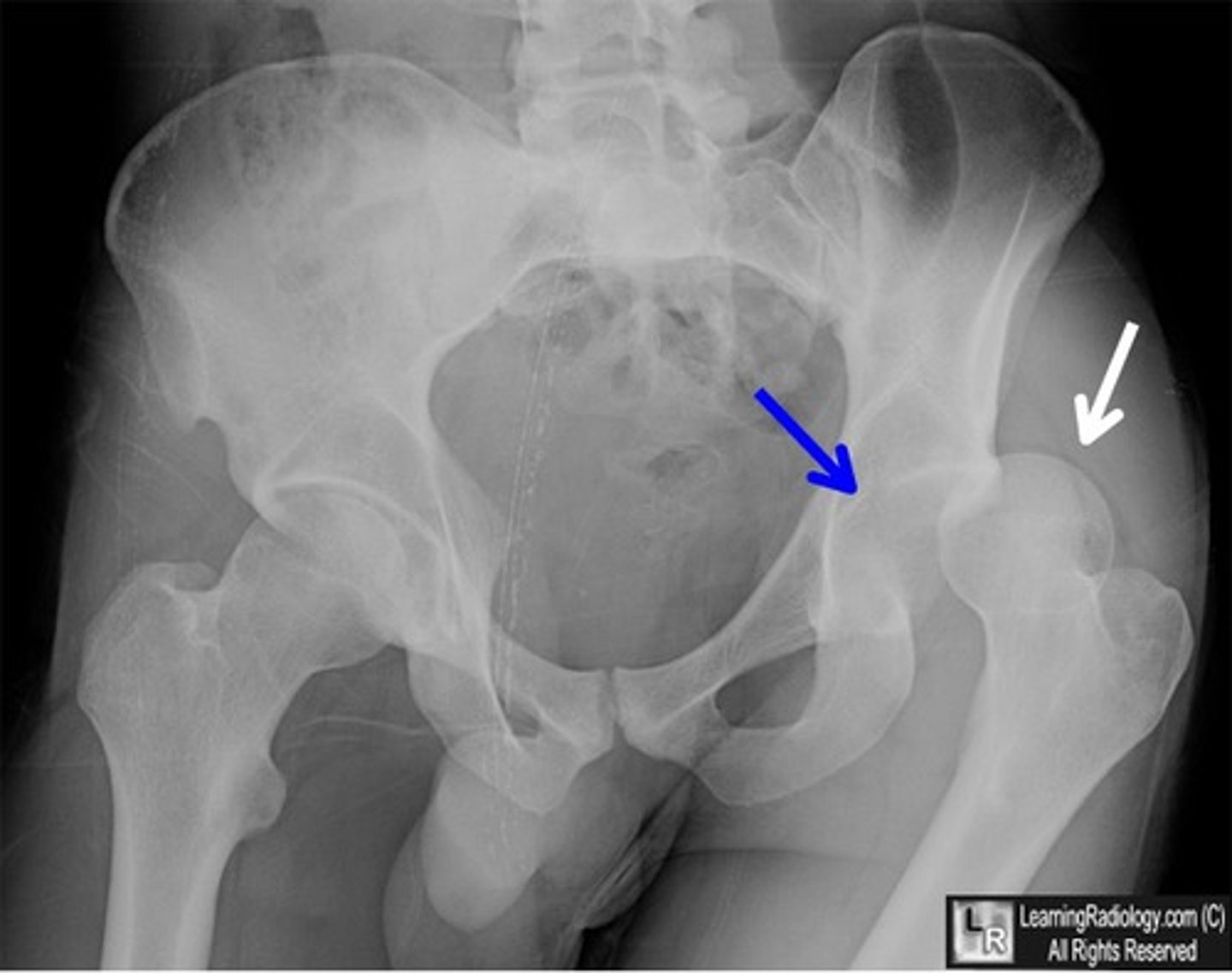
traumatic - high energy, MVC, falls
nontraumatic - can occur after hip replacement
How does a hip dislocation occur?
posterior: leg shortened, internally rotated, ADDucted, hip/knee slightly flexed (likely to cause pelvic fracture)
anterior (much less common): leg shortened, externally rotated, ABDucted
What are the clinical manifestations of a hip dislocation?
x-ray
CT
neurovascular assessment: check sciatic nerve (post) or femoral nerve (ant)
check for motor function, sensation, and pulses
How do you diagnose a hip dislocation?
put the hip back into place
How do you treat a hip dislocation?
developmental dysplasia
"ball and socket" do not form properly, shallow socket - uncovering femoral head and can lead to dislocation
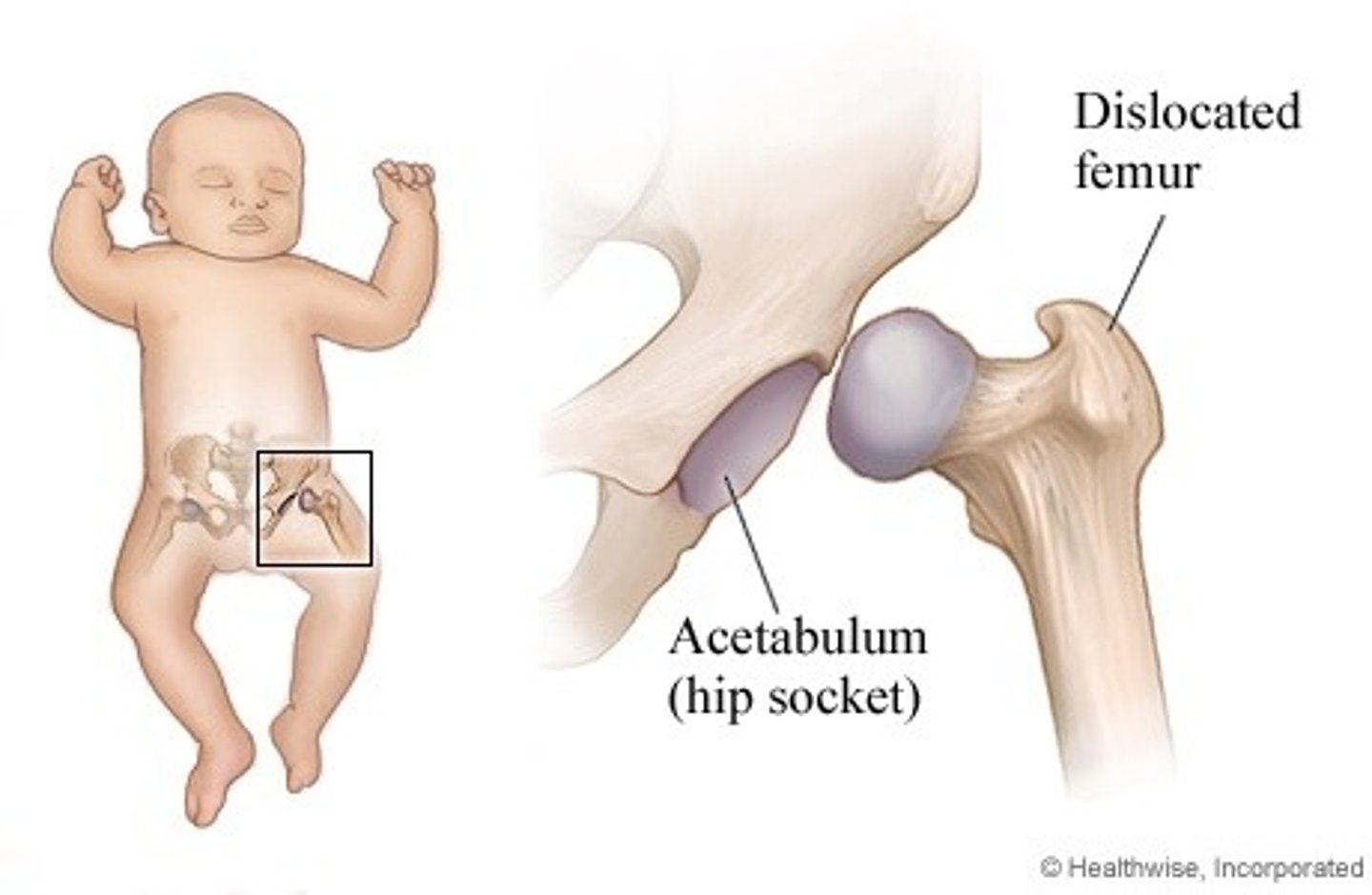
female > males, first born, breech presentation, tight swaddling, and + fam hx
What are the risk factors for developmental displasia?
asymmetry in thigh/gluteal folds
leg length discrepancy
limited hip abduction
What are the clinical manifestations of hip dislocation?
barlow
developmental dysplasia: moves hip posteriorly either subluxation or dislocation
ortolani
developmental dysplasia: moves hip anterior reducing dislocated joint
Galeazzi sign
developmental dysplasia: done in older infants - apparent leg-length discrepancy when hips and knees are flexed
<6 months: ultrasound (femoral head is CARTILAGENOUS until 6-months)
>6 months: x-ray
How do you diagnose developmental dysplasia?
pavlik harness, closed vs open reduction with casting if severe
How do you treat developmental dysplasia?
labral tears
early onset OA
gait abnormalities
need for hip replacement - if severe
what are some complications of developmental dysplasia?
Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE)
OBESE CHILDREN (teens and preteens)
adolescents
F: 10-14 yo
M: 12-16 yo
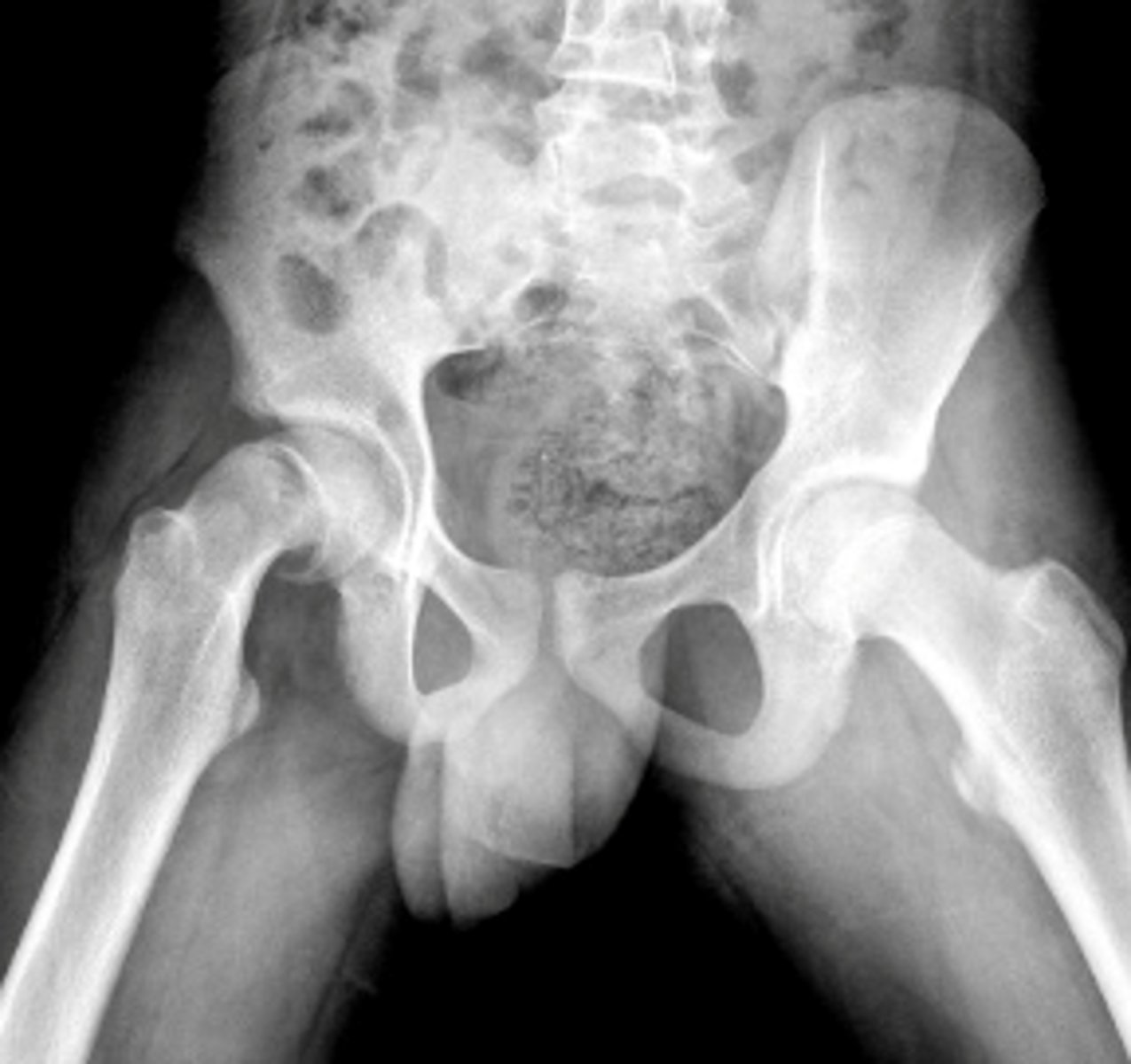
GROWTH SPURTS!
What is Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE) associated with?
EXTERNAL ROTATION OF AFFECTED LEG +/- LEG LENGTH DISCREPANCY
Pain (groin, hip, knee)
altered gait
worse with activity
decrease ROM (abduction and internally rotated)
inability to bear weight
What are the clinical manifestations of Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE)?
x-ray (Klein Line) - ICE CREAM FELL OFF THE CONE
Widened/displaced physis
how do you diagnose Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE)?
surgery - in situ fixation
What is the treatment for Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE)?
Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease
AVN of the hip
Kids: 3-12 yo
Boys > girls x 4
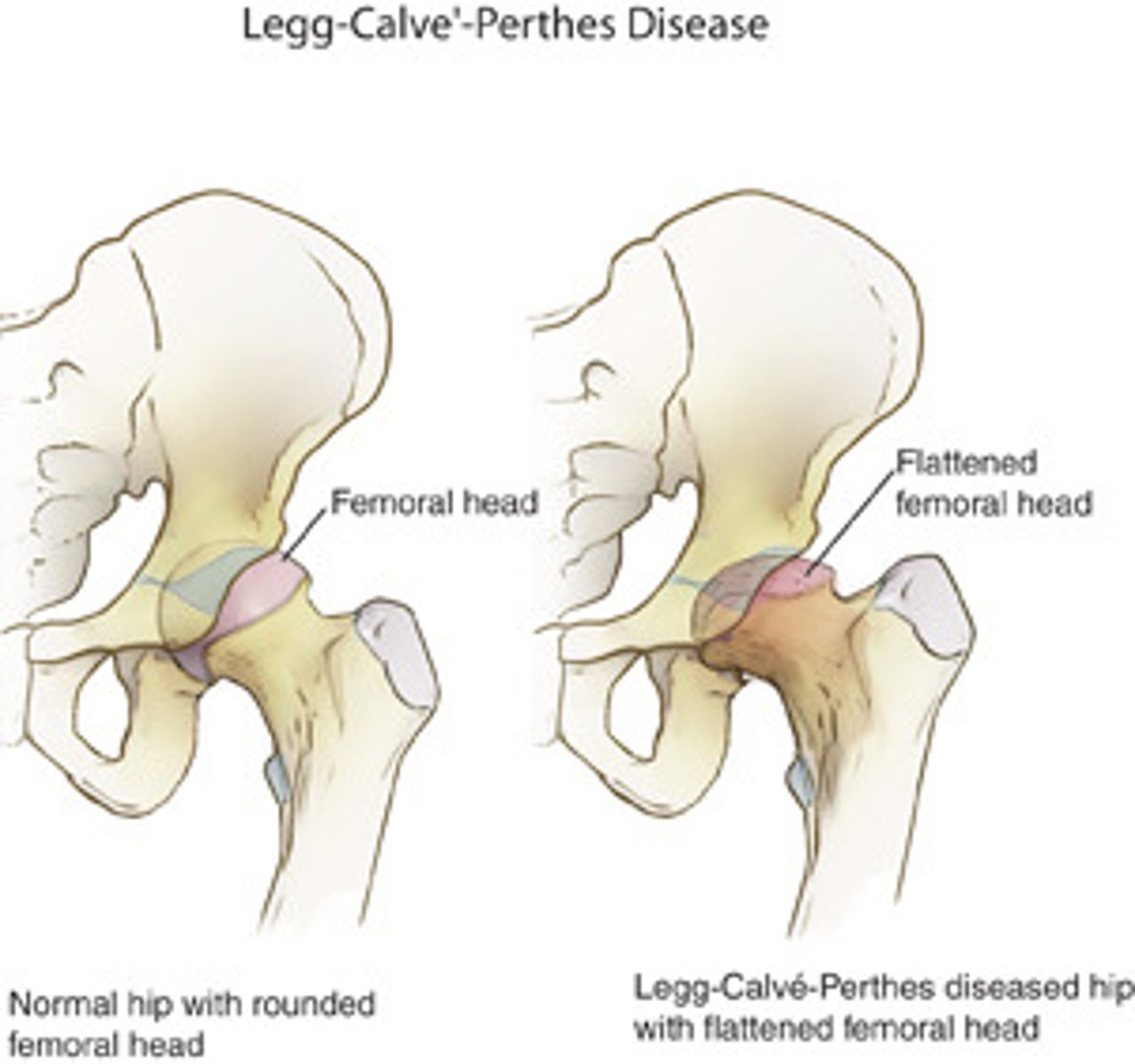
no, idiopathic (unknown cause)
Do we know the cause of Legg-Calve Perthes Disease?
pain groin/hip, worse w/ activity
What are the clinical presentations of Legg-Calve Perthes Disease?
doesnt say? (x-ray since we have an x-ray picture on slides?)
How do you diagnose Legg-Calve Perthes Disease?
conservative tx - casting, bracing, NSAIDs
refer to peds ortho
potential surgical involvement
How do you treat Legg-Calve Perthes Disease?
Salter Harris
Fractures involving the growth plate (epiphyseal plate) in children and adolescents - can affect bone growth and development - leading to potential deformities if untreated
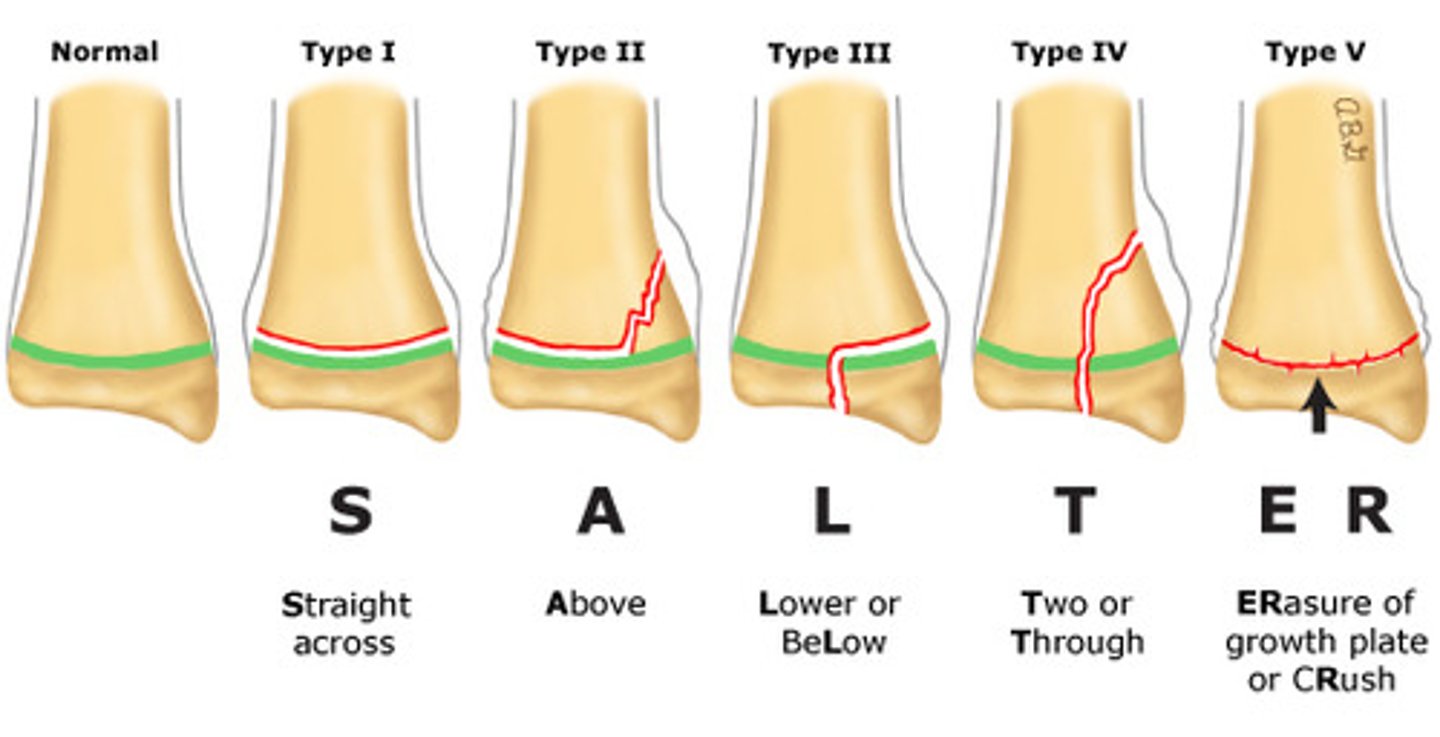
Slipped or straight across (Type I)
Above or away from joint (Type II)
Lower (Type III)
Through or transverse or together (Type IV)
Ruined or rammed (Type V)
How do you classify the types of Salter Harris fractures? (remember SALTR)
pain to palpation at epiphysis/growth plate
What are the clinical manifestations of Salter Harris fracture?
x-ray typically
(type 1 fracture may not show on x-ray, but still treat if pain at epiphysis)
MRI if more detailed evaluation is needed
How do you diagnose Salter Harris fractures?
non-surgical tx w/ cast or splint
What is the treatment for Type 1 and 2 fractures?
May require reduction and immobilization
What is the treatment for Type 3 and 4 fractures?
often requires surgical intervention for realignment
What is the treatment for Type 5 fracture?
Compartment syndrome
MOST COMMON IN ANTERIOR COMPARTMENT OF LEG
Increased pressure within a closed fascial compartment - compromises circulation and tissue perfusion
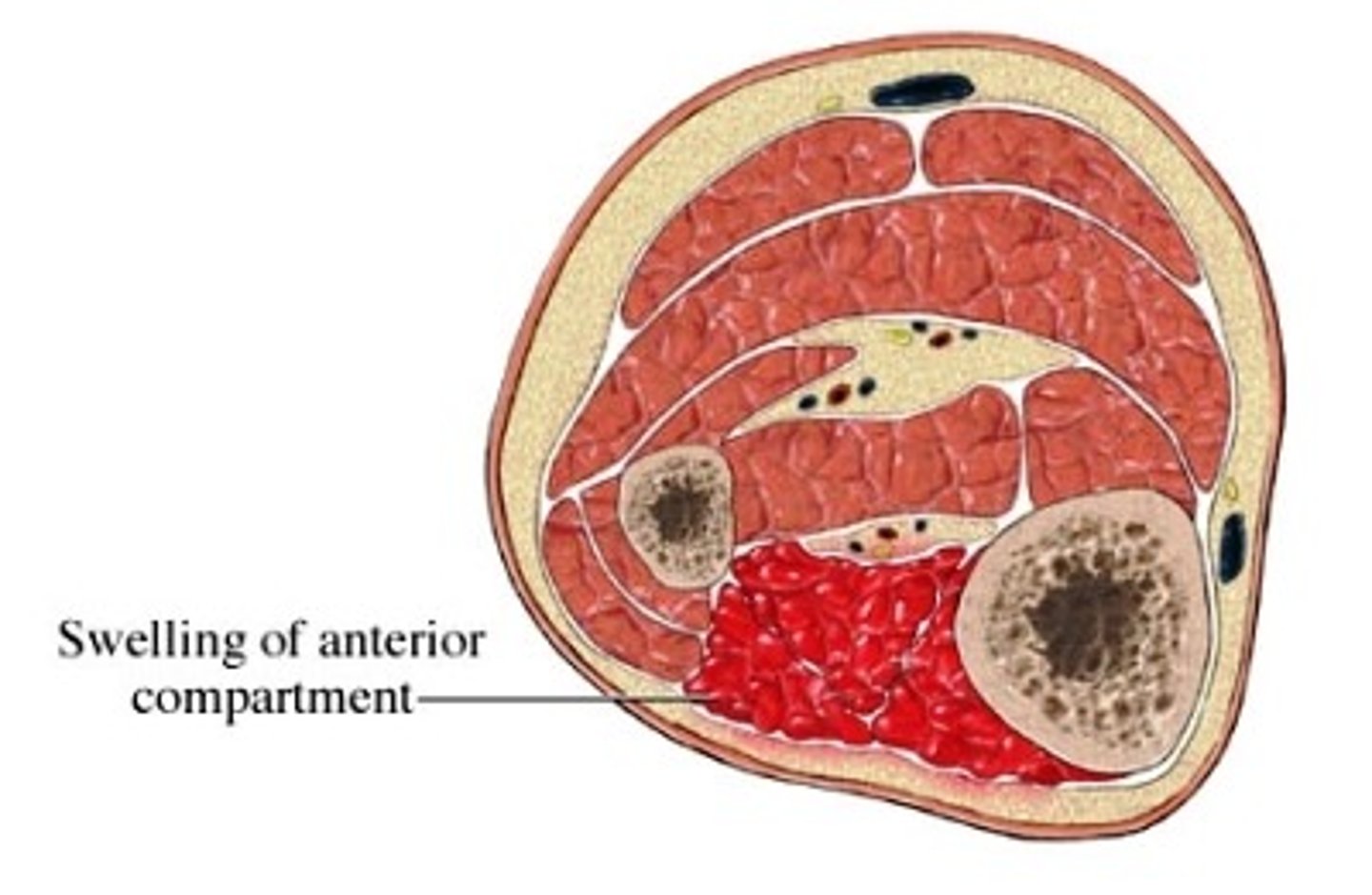
trauma fracture (especially tibial fracture)
crush injury
reperfusion after trauma
What is the mechanism of injury for compartment syndrome?
pain with passive stretch (moderate swelling and tightness of skin)
"wood like" feeling on palpation
P's:
pain out of proportion
parasthesias
pallor
pulselessness (late)
paralysis (late)
What are the clinical manifestations of compartment syndrome?
do not delay for imaging if suspicion is high
LABS MAY SHOW RHABDO (INCREASED CK, MYOGLOBINURIA) IF SEVERE
How do you diagnose compartment syndrome?
EMERGENT FASCIOTOMY OF ALL AFFECTED COMPARTMENTS
(infection risk since leaving wound open but pros > risk)
How do you treat compartment syndrome?
talipes equinovarus (clubfoot)
Congenital foot deformity characterized by:
plantar flexion
inversion
adduction
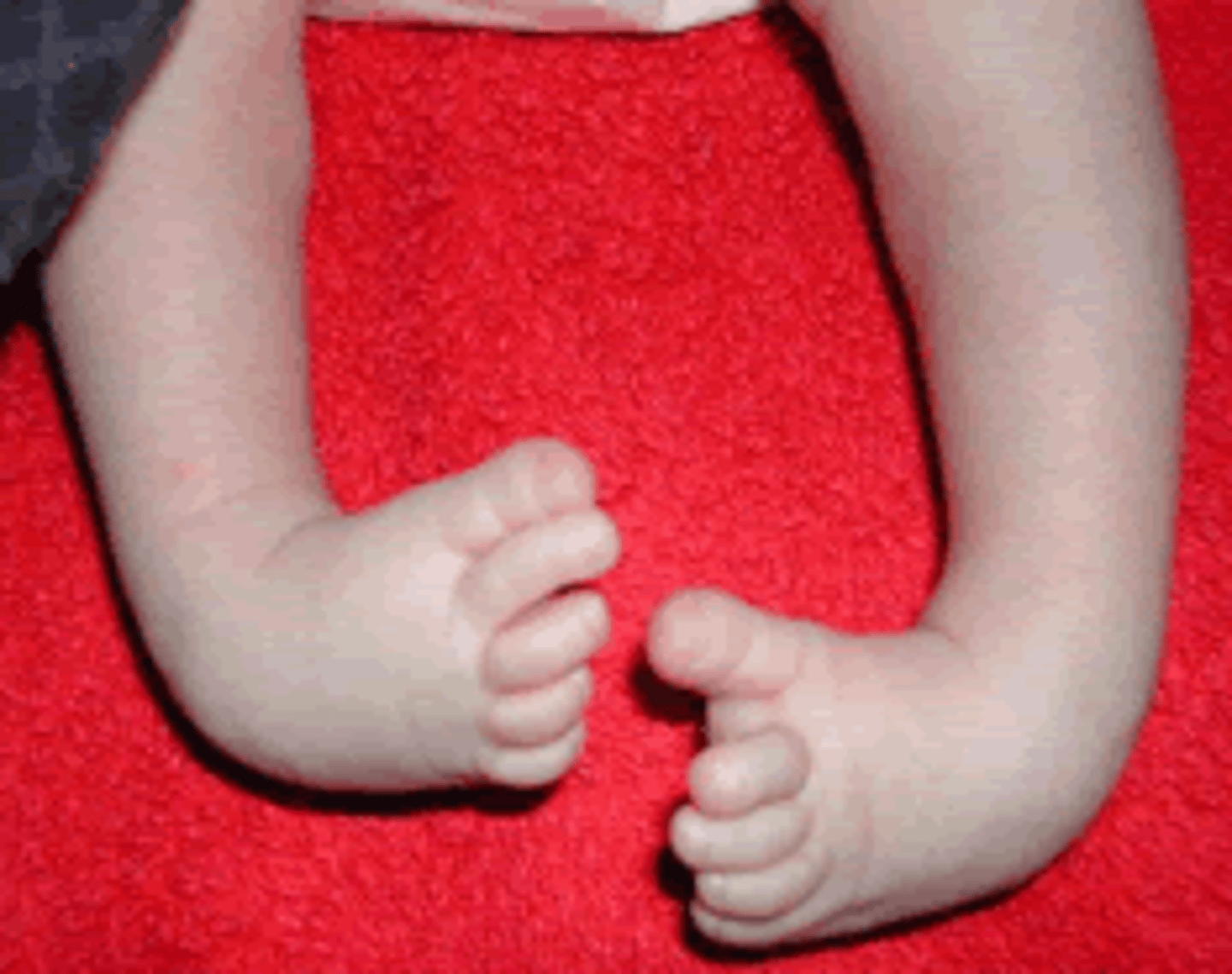
unknown cause - genetic factors may play a role, fam hx increases risk
How does talipes equinovarus occur?
xrays or ultrasound (severe cases - if there is uncertainty about the extent of the deformity)
How do you diagnose talipes equinovarus?
non-surgical (preferred approach):
Serial casting (gradually correct position)
achilles tenotomy
bracing
PT
Surgical:
severe or nonresponsive cases (tendon lengthening, realignment of bones, etc.)
How do you treat talipes equinovarus?
pes cavus
Often associated with neuromuscular conditions (ex: Charcot-Marie-Tooth)
"high arches"
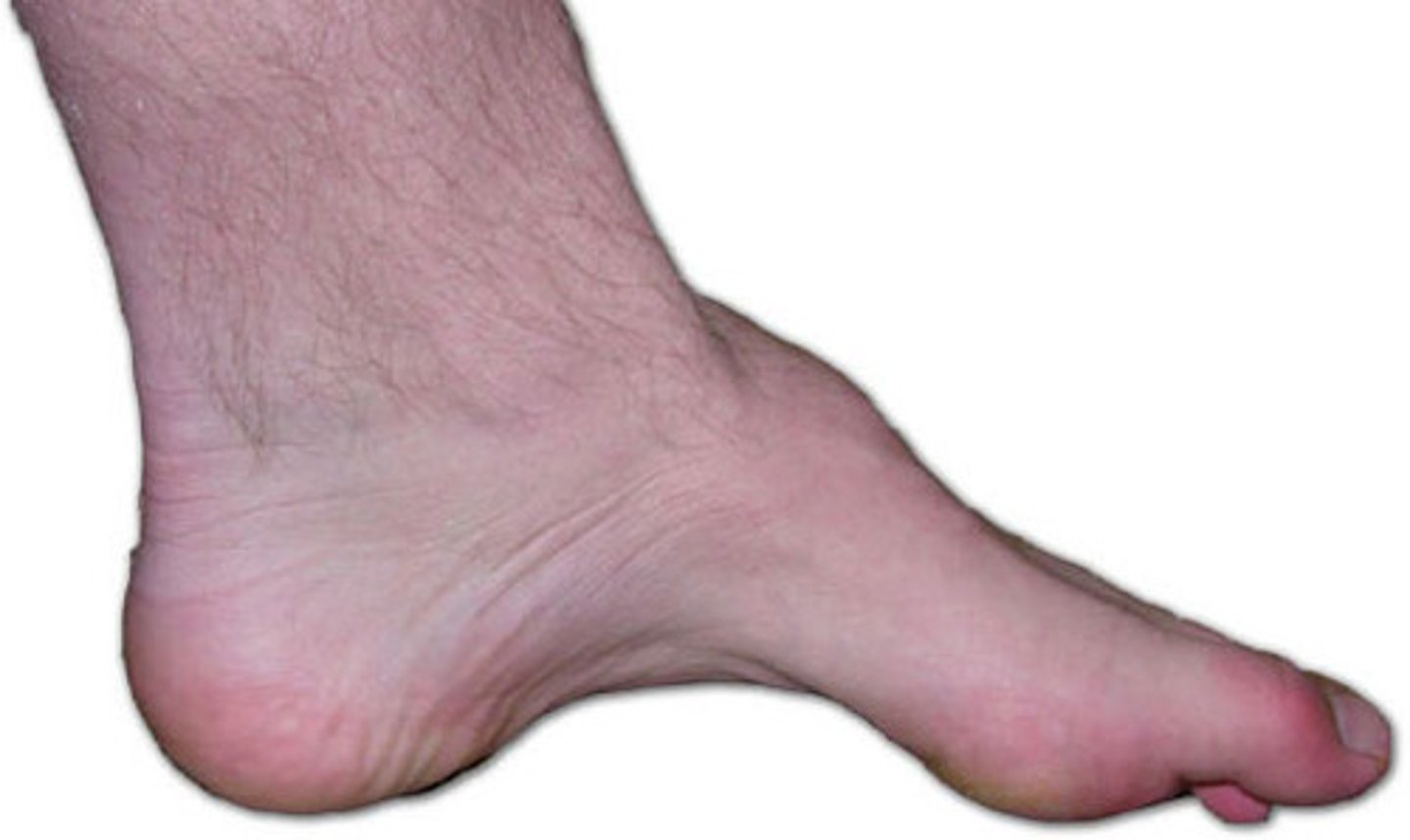
congenital
How does pes cavus occur?
rigid high arch
frequent ankle sprains or lateral foot pain
calluses on heel/ball of foot
may have claw toes
What are the clinical manifestations of pes cavus?
physical exam
x-rays (increased calcaneal pitch)
How do you diagnose pes cavus?
shoe modification (rigid high arch support, wide toe box)
orthotics
PT
surgical correction (severe or progressive)
How do you treat pes cavus?
Pes planus
Can be flexible (common in children) or rigid (pathologic in adults)
"flat foot"
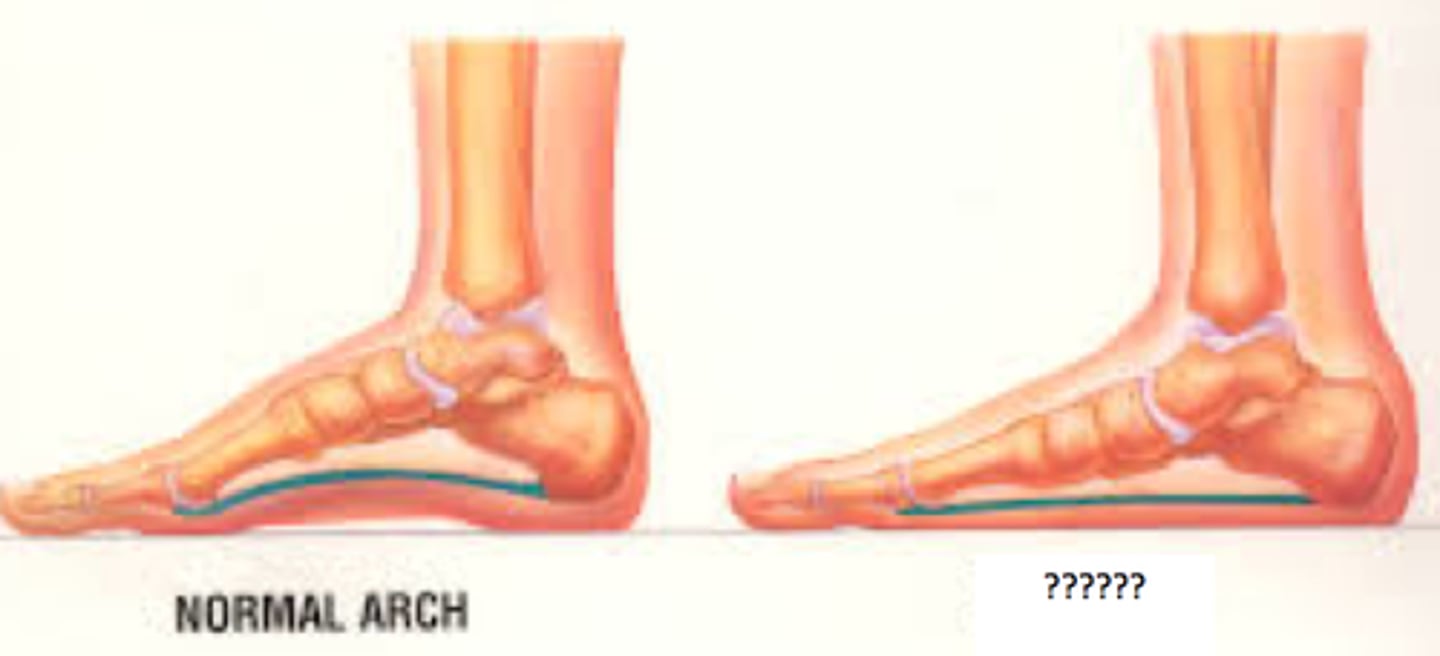
congenital
How does pes planus occur?
foot fatigue
arch/heel pain
medial ankle bulging
overpronation when walking
What are the clinical manifestations of pes planus?