Astronomy - from our Star to Cosmos
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
What is a nebula?
A giant cloud in which stars and planets are forming.
What is a lightyear?
The distance traveled by light in one year.
Why are temperatures warmer in the summer?
More daylight
Sun is higher in the sky which causes the sun’s rays to be more concentrated on the Earth’s surface.
What is the top-like motion of the Earth called?
Precession
How long does it take the Earth to complete one precession?
26,000 years
In approximately 15,000 years what will be Earth’s northstar?
Vega
Due to the expansion of the universe galaxies tend to move ______ from each other.
Away
Why do we not feel the Earths motion?
We can only feels the affects of acceleration.
When does a new moon occur?
When the moon is between the Earth and the Sun.
When does a full moon occur?
When the moon is opposite to the sun.
When does a solar eclipse occur?
When the moon passes in front of the sun while it's orbital plane is aligned with the sun’s.
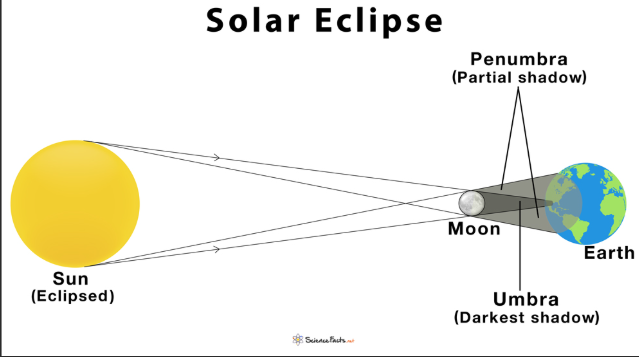
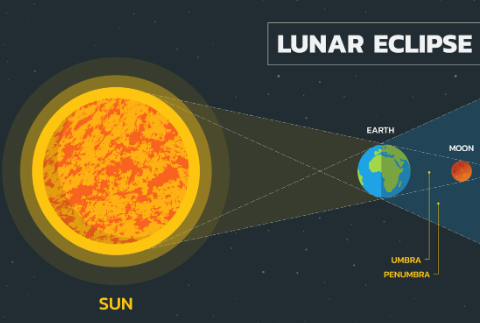
When does a lunar eclipse occur?
When the moon passes though the earth’s shadow.
Why do solar eclipses not happen every month?
Because the moon’s orbital plane is 5.2 degrees off from the ecliptic.
What is the avg earth-moon distance
384, 000 km
Definition of perigee?
Moon’s closet approach to earth.
Definition of Apogee?
Moon’s furthest point from earth.
What coincidence allows total solar eclipses to be seen on earth?
The sun and moon have nearly the same angular diameter as seen from earth.
Supermoon
When a full moon occurs near perigee.
Micro moon
When a full moon occurs near apogee
When will a total solar eclipse occur?
If a solar eclipse occurs when the moon is at perigee.
What are the two parts of the Earth’s shadow?
Umbra - Darkest part where light is completely blocked.
Penumbra - Lighter area where light is only partially blocked.
When does a Partial lunar eclipse occur?
When the moon passes partial through the umbra but is never completely inside of it.
When does a Total lunar eclipse occur?
When the entire moon passes though the umbra.
What are the three types of Lunar eclipses?
Full, Partial, Penumbra
When does a partial solar eclipse occur?
When a solar eclipse occurs when the moon is at apogee.
Parallax
The apparent motion of an object against a distance background from two different viewing points.
What is the affectof a longer baseline when triangulating?
A longer baseline correlates to more accurate measurement.
Parallax is _______ to distance.
Inversely proportional.
(An object that is further away will be less affected by parallax)
Annual Parallax
When an object is beyond our solar system we need a larger baseline so opposite sides of earth’s orbit is used as a baseline.
When is annual parallax used?
To measure the distances of objects beyond our solar system.
When is Diurnal parallax used?
When measuring the distance of objects within our solar system.
What baseline is used for Diurnal parallax?
Earth’s diameter.
Parsec
The distance to an object that gives a parallax of 1-arc-second
What does one par-sec correlate to in light years?
3.26 LY
The more distance an object is the ______ it will appear
dimmer
Hubble’s Law fromula?
v = H_o d
v = H_o d what does each variable correlate to?
v = recession velocity
H_o is Hubble’s constant
d = distance
What principle is Hubblel’s law based upon?
The velocity of a galaxy is directly proportional to it’s distance from us.
Ie) the farther away a galaxy is from us, the faster it is moving away
What are kepler’s three laws of planetary motion?
Planetary orbits around the sun are elliptical.
The planets sweep equal distances over equal periods of time.
The square of a planet’s orbit is equal to the cube of it’s semimajor axis.
Perihelion
Closest approach to sun
Anphelion
Furthest distance from sun
Velocity
speed and direction (a vector)
Acceleration
Change is velocity. (so change in direction of speed)
What did galileo observe about gravity
All objects fall with the same acceleration regardless of their mass.
The equivalence principle?
Light is affect in the same way a mass is by gravity and acceleration.
Specular Reflection
the mirror like reflect of light
Diffuse Reflection
light is scattered
How was the speed of light first discovered?
Through timing the orbit of Juipiter’s moon Io. Ole Rømer studied the timing of Io passing behind Jupiter and discovered that the timing of these eclipses depended on Earth's position in its orbit. When Earth was farther from Jupiter, the eclipses were delayed; when closer, they were early.
What does it mean if a material has a high index of refraction?
Light travels slowly through that material.
Def of raditation
Energy transported through space from one object to another.
Sound waves are ________
compressions of air molecules.
What are lights wave like properties?
Diffraction, interference.
Which type of radiation has a longer wave length UV vs X-rays
UV rays have a longer-wave length/lower frequency than x-rays
List the different types of radiation from largest to smallest wavelength
Radio →micro → infrared →visible → UV → X-rays → Gamma rays
What type of radiation is the Earth’s atmosphere transparent to?
Radio, visible, and a small portion of UV and IR.
As an object gets hotter the thermal radiation it emits gets ______
brighter
The wavelength of thermal radiation depends on ______
Temperature
Significance of absolute 0
All molecules stop moving
What is a blackbody
A theoretical perfect absorber and perfect emitter of electromagnetic radiation.
Two main laws of blackbody radiation?
As an object is heated the radiation it emits peaks at higher and higher frequencies.
Total energy emitted per unit time is proportional to the fourth power of temperature.
What does Wien’s law state?
Peak wavelength is inversely proportional to temperature
What does the Stefan-Boltzmann law state?
Total energy per unit time is proportional to the fourth power of temp in kelvin.
When it redshift observed?
When the light source is moving away from the observer.
When is blueshift observed?
When the light source is moving towards the observer.
When is no red or blueshift observed?
If motion is perp to the lightsource.
What can spectral analysis tell us about a star?
Chemical comp, temp, recession velocity, magnetic field.
How is a absorption spectra produced?
When a cool gas is placed between a continuous spectra light source and the spectrometer.
Kirchhoff’s three laws of Spectroscopy:
A lumis solid liquid or dense gas will produce a continuous spectrum.
A low density hot gas produces an emission spectra.
A continuous spectrum incident on a cool thin gas produces an absorption spectra.
Lyman Series Transition
Transitions from any excited state to the ground state.
Balmer Series Transition:
A transition from any excited state to n=2.
What is the significance of the Balmer series to spectroscopy.
Balmer series transitions produce visible light.
What five types of information can be determined using Spectral line analysis
Chemical composition
Temperature
Recession Velocity.
Rotation velocity.
Magnetic field
How is chemical composition studied using spectral analysis?
From absorption lines
How is recession studied using spectral analysis?
Spectral line broading due to the doppler effect
How are the magnetic fields of starts studied using spectral analysis?
The Zeman effect: the presence of a strong magnetic field causes spectral lines to split into three.
What are the two types of decay after the absorption of a photon causes an electron to jump to the second energy level or higher?
1) Direct decay: Electron jumps back to ground state in one step. (Emits same energy photon is absorbed)
2) Cascade decay: Electron returns to ground state one orbital at a time. (Multiple photons of different energy levels are emitted)
How are absorption lines created?
When atoms in a gas absorb photons.
How are emission lines created?
When excited atoms quickly return to ground state.
How can the temperature of a star be studied using spectral analysis?
The strength of spectral lines tells us the temperature of Stellar Surfaces. A hotter start will have darker absorption lines and brighter emission lines.