Ch4 Genes, DNA, and Chromosomal Abnormalities: Genetic Diseases and Inheritance
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
How many genes do humans have?
Humans have approximately 20,000 to 25,000 genes.
What can a single error in a gene result in?
A single error in a gene may result in a genetic disease.
How many human genetic traits have been identified?
About 23,000 human genetic traits have been identified.
Name some common diseases known to have genetic components.
Hypertension, coronary heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
What influences the cell alongside genetic factors?
Environmental factors influence the cell.
What is contained within the nucleus of a cell?
The genetic code for all living beings.
What are chromosomes composed of?
Chromosomes contain genes, which are the basic unit of inheritance.
What is the structure of DNA?
DNA has a double helix structure.
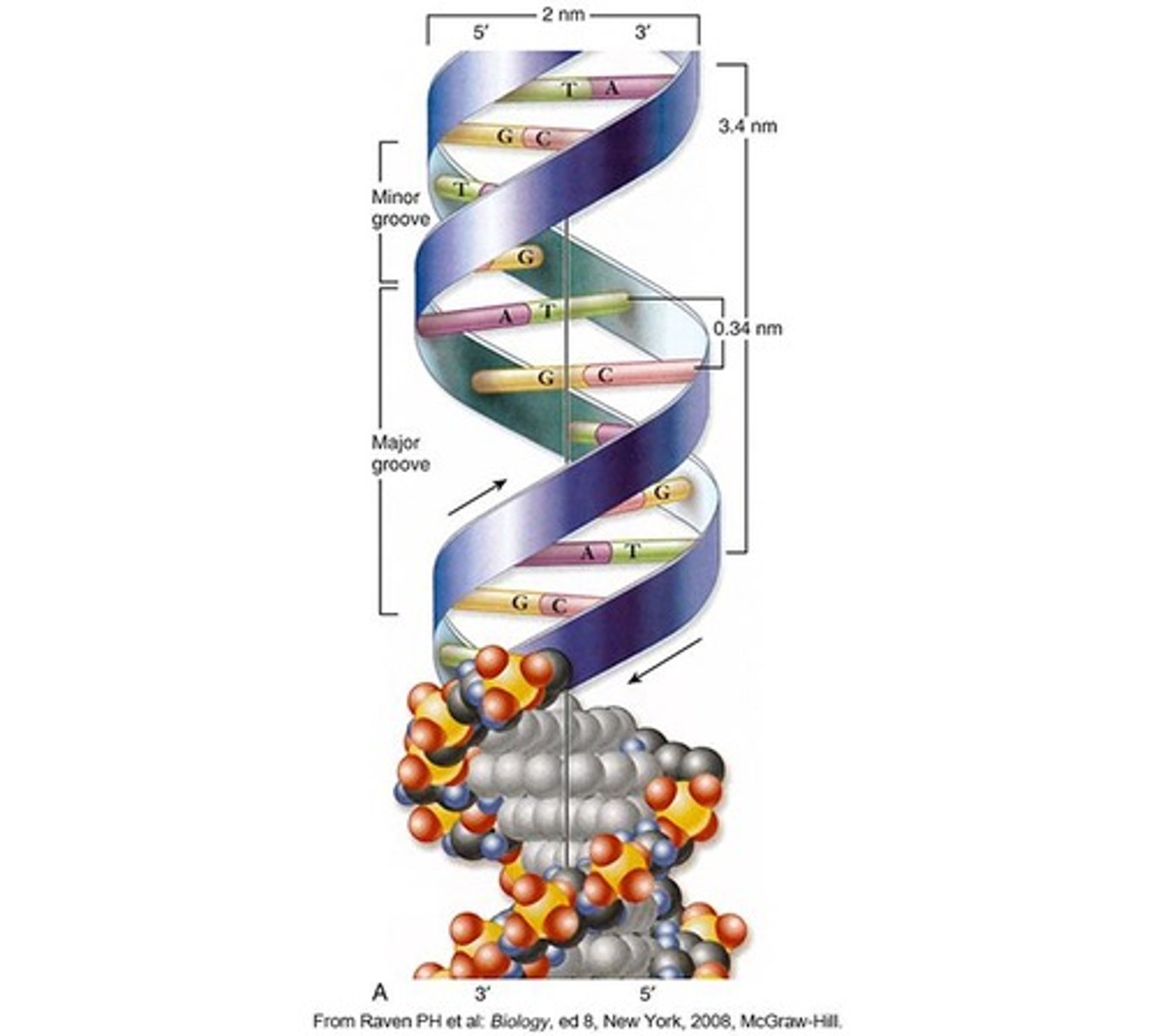
What are the components of a nucleotide in DNA?
A nucleotide contains one pentose sugar (deoxyribose), one phosphate group, and one nitrogenous base (cytosine, thymine, adenine, or guanine).
What is the role of DNA in the body?
DNA provides the code for all body proteins.
What are polypeptides composed of?
Polypeptides are composed of amino acids.
What directs the production of amino acids during protein synthesis?
The sequence of three bases (codons) directs the production of amino acids.
What is the function of DNA polymerase during replication?
DNA polymerase pairs complementary bases and adds new nucleotides, proofreading the new DNA strand.
What is a mutation?
A mutation is any inherited alteration of genetic material.
What is a base pair substitution mutation?
A base pair substitution involves substituting one base pair for another, which may change the amino acid sequence.
What is a frameshift mutation?
A frameshift mutation involves the insertion or deletion of one or more base pairs in the DNA molecule.
What are mutagens?
Mutagens are agents, such as radiation and chemicals, that increase the frequency of mutations.
What is the process of transcription?
Transcription is the synthesis of mRNA from a DNA template via RNA polymerase.
What is the role of ribosomes in translation?
Ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis, helping mRNA and tRNA form polypeptides.
What is the difference between DNA and RNA?
RNA is a single strand and contains uracil instead of thymine, while DNA is double-stranded.
What is the role of tRNA in protein synthesis?
tRNA carries amino acids and has an anticodon that is complementary to the codon on the mRNA strand.
What happens when the ribosome reaches a termination signal during translation?
Translation and polypeptide formation cease.
What are the two types of human cells?
Somatic cells and gametes.
How many chromosomes do somatic cells contain?
46 chromosomes (23 pairs).
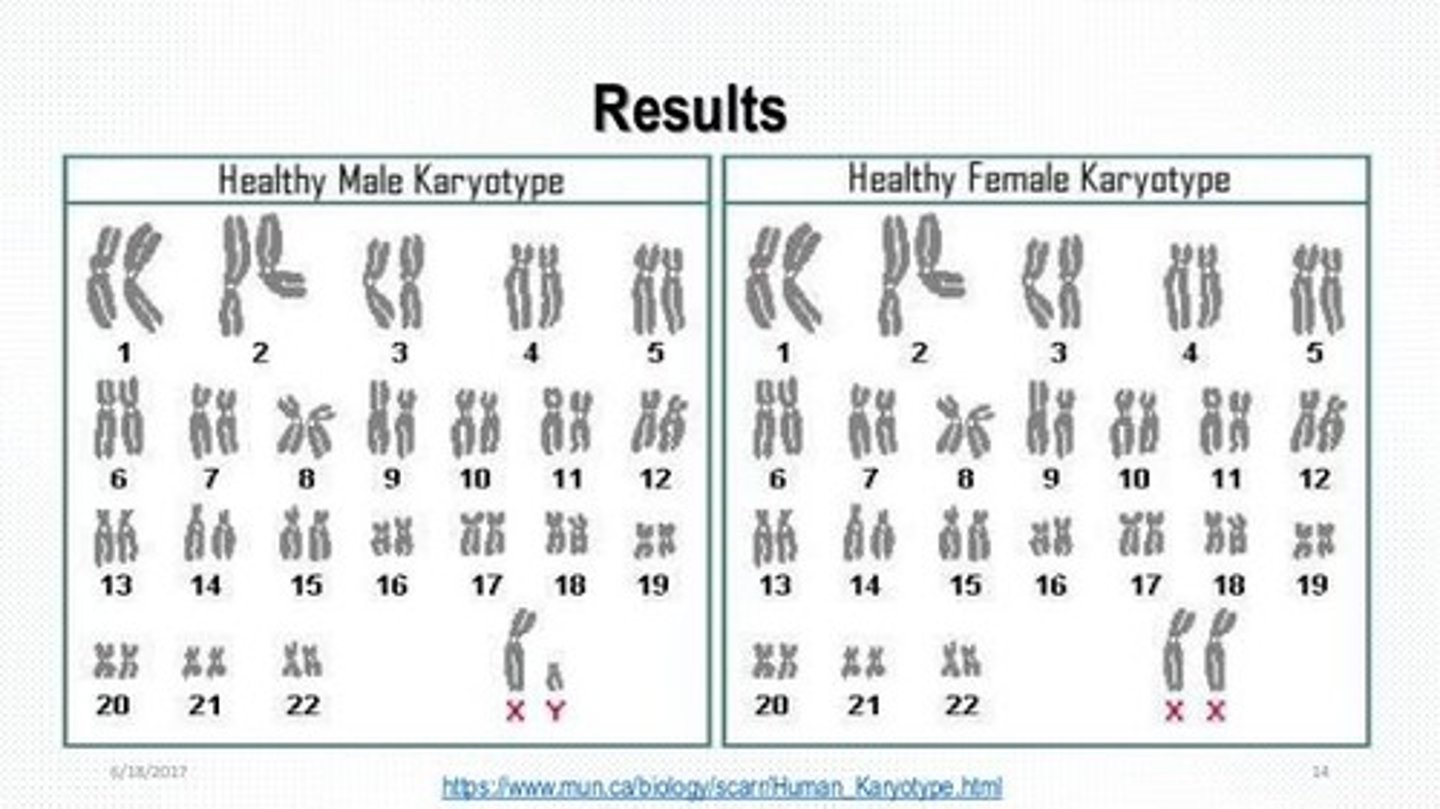
What type of cells are gametes and how many chromosomes do they contain?
Gametes are sperm and egg cells containing 23 chromosomes (haploid).
What is meiosis?
The formation of haploid cells from diploid cells.
What are autosomes?
The first 22 of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in males and females, which are homologous.
What are sex chromosomes and how do they differ in males and females?
The remaining pair of chromosomes; females have a homologous pair (XX) and males have a non-homologous pair (XY).
What is a karyotype?
An ordered display of chromosomes determined by length and centromere location.
What are chromosomal aberrations?
Chromosome abnormalities that can lead to mental retardation and miscarriage.
What are euploid cells?
Cells that have a multiple of the normal number of chromosomes.
What is triploidy?
A zygote that has three copies of each chromosome (69 total).
What is tetraploidy?
A condition where a cell has four copies of each chromosome (92 total).
What is aneuploidy?
A somatic cell that does not contain a multiple of 23 chromosomes.
What is trisomy?
A condition where a cell contains three copies of one chromosome.
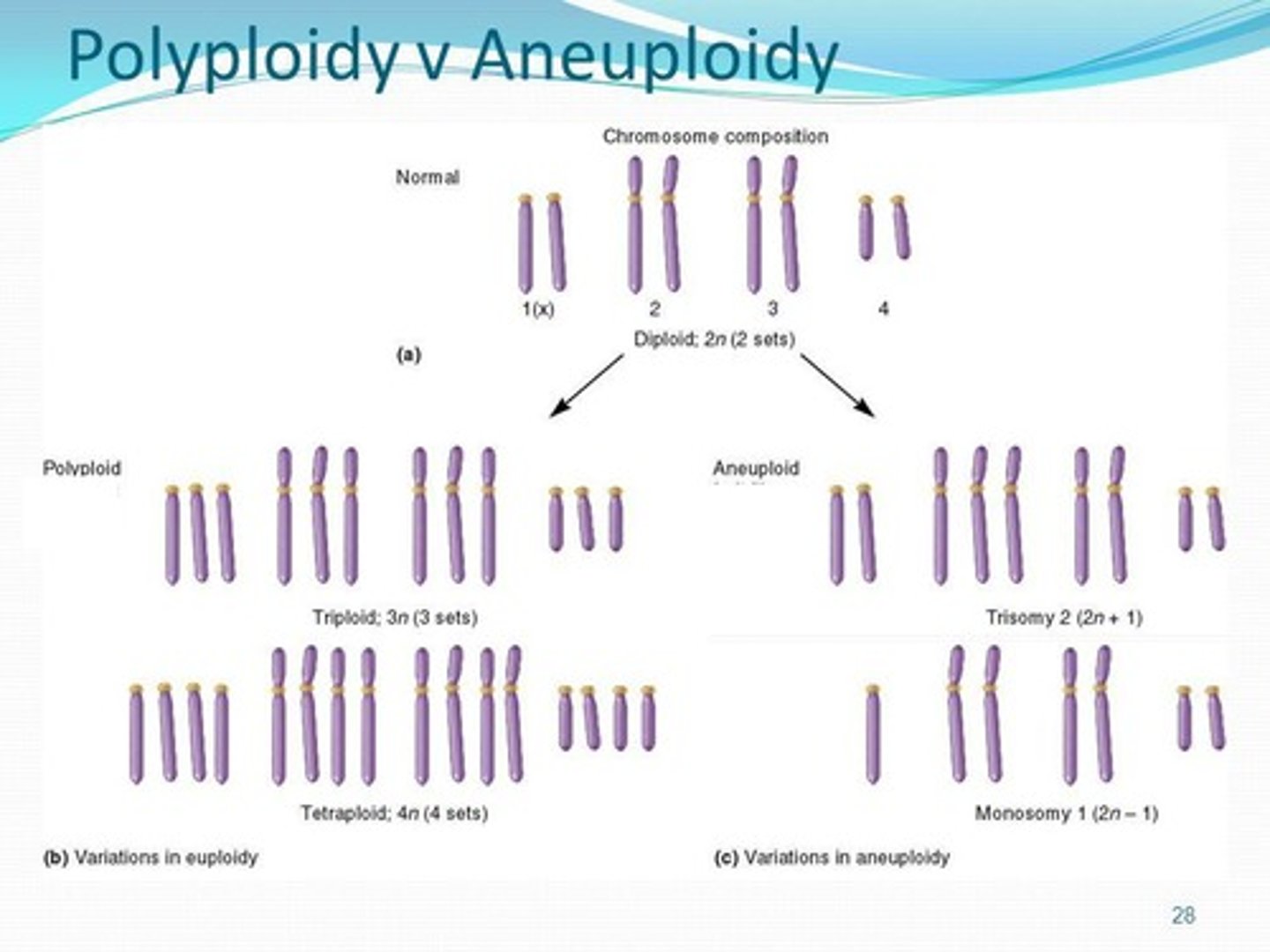
What is monosomy?
The presence of only one copy of any chromosome, often fatal.
How does aneuploidy of sex chromosomes typically compare to autosomal aneuploidy?
Aneuploidy of sex chromosomes usually presents less serious consequences than autosomes.
What is Down syndrome?
A well-known example of aneuploidy, characterized by three copies of chromosome 21 (trisomy 21).
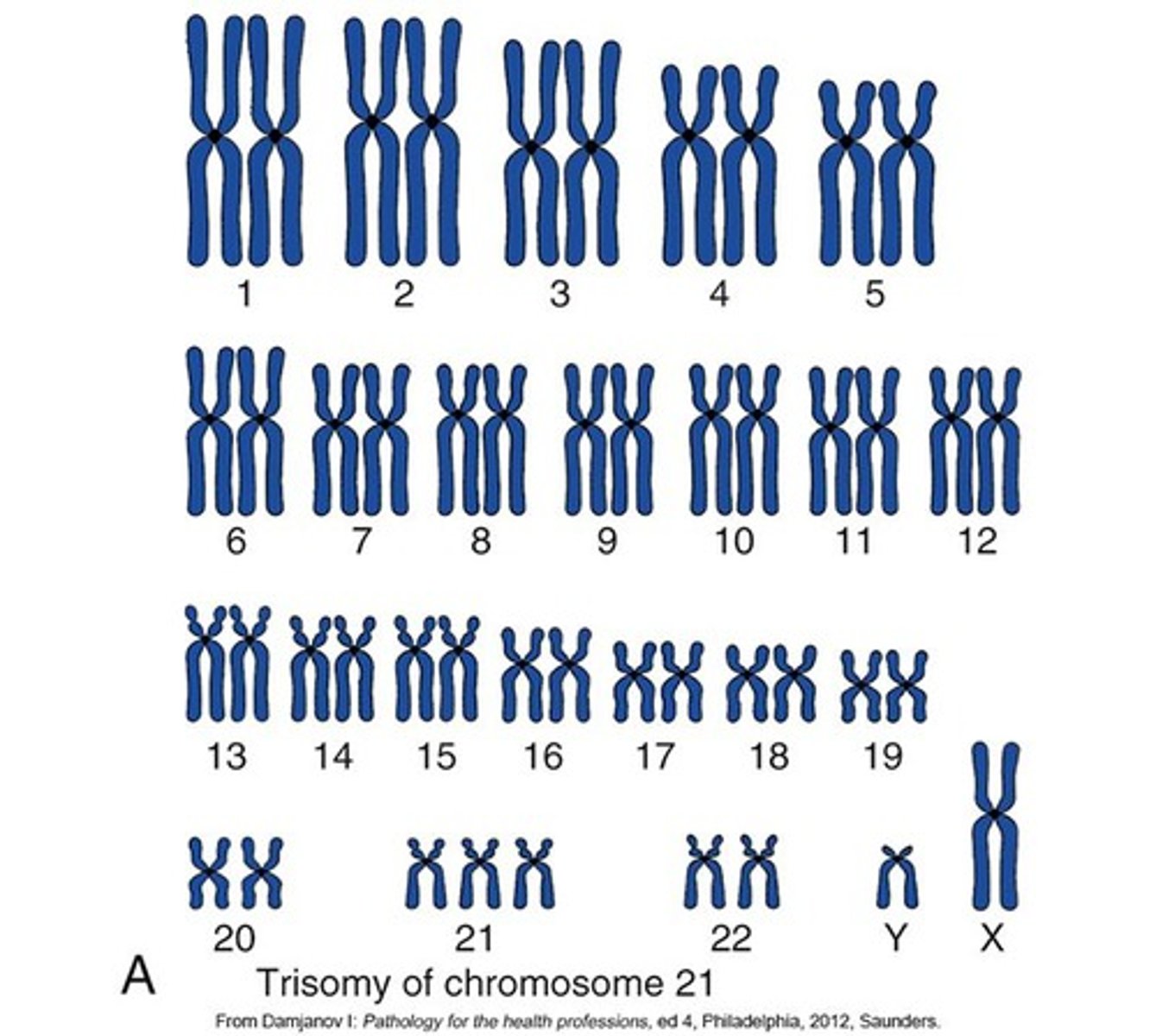
What are some manifestations of Down syndrome?
Mental challenges, low nasal bridge, epicanthal folds, protruding tongue, flat low-set ears, short stature, and poor muscle tone.
What is the incidence rate of Down syndrome?
Occurs in 1 in 800 live births.
What is Turner syndrome?
A condition where females have only one X chromosome (karyotype 45,X), leading to sterility and other physical characteristics.
What are some characteristics of Turner syndrome?
Absence of ovaries, short stature, webbing of the neck, widely spaced nipples, and a high number of aborted fetuses.
What is the incidence rate of Turner syndrome?
Occurs in 1 in 2500 female births.
What is Trisomy X?
A condition where females have three X chromosomes, occurring in 1 in 1000 female births.
What are some symptoms of Trisomy X?
Variable symptoms including sterility, menstrual irregularity, and cognitive deficits.
What is Turner syndrome and its inheritance pattern?
Turner syndrome is a condition caused by the absence of one X chromosome, usually inherited from the mother, occurring in 1 in 2500 female births.
What are the characteristics of Klinefelter syndrome?
Klinefelter syndrome is characterized by male appearance, female-like breasts (gynecomastia), small testes, and sparse body hair, typically occurring in individuals with at least one Y and two X chromosomes.
What is the incidence rate of Klinefelter syndrome?
Klinefelter syndrome occurs in approximately 1 in 1000 male births.
How does the number of X chromosomes affect Klinefelter syndrome?
Individuals can be XXXY or XXXXY, maintaining a male appearance, but abnormalities increase with each additional X chromosome.
What are common agents that cause chromosome breakage?
Common agents include ionizing radiation, chemicals, and viruses.
What is Cri du chat syndrome?
Cri du chat syndrome is caused by a deletion on chromosome 5, leading to low birth weight, mental challenges, and microcephaly.
What are the four major types of genetic diseases?
The four major types are autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, X-linked dominant, and X-linked recessive.
What is the recurrence risk in autosomal dominant inheritance?
The recurrence risk for each child is one half if one parent is affected by an autosomal dominant disease.
What is consanguinity and its effect on genetic diseases?
Consanguinity, or inbreeding, is the mating of related individuals, which dramatically increases the recurrence risk of recessive disorders.
How do X-linked disorders differ between males and females?
Females have two X chromosomes and can be homozygous or heterozygous, while males have one X chromosome and are hemizygous, expressing the disease if they inherit an X recessive gene.
What is a characteristic of X-linked recessive inheritance?
The gene can be transmitted through female carriers, often resulting in a skipped generation.
How is an X-linked recessive gene passed from father to children?
An affected father passes the gene to all his daughters, who become phenotypically normal carriers, transmitting it to approximately half of their sons.
What are the effects of chromosome breakage?
Chromosome breakage may or may not have serious consequences; breaks can heal without damage or alter the chromosome structure.
What is a deletion in the context of chromosomal abnormalities?
A deletion refers to the loss of DNA from a chromosome, which can lead to genetic disorders like Cri du chat syndrome.
What is a duplication in chromosomal abnormalities?
A duplication refers to excess genetic material, usually resulting in less serious consequences compared to deletions.
What is inversion in chromosomal abnormalities?
Inversion is a chromosomal rearrangement where a segment of the chromosome is inverted, e.g., ABCDEFG becomes ABEDCFG.
What is the significance of maternal age in Klinefelter syndrome?
The risk of Klinefelter syndrome increases with the mother's age.
What is the impact of independent events on recurrence risk?
Each birth is considered an independent event in calculating recurrence risk for genetic diseases.
What is the definition of hemizygous?
Hemizygous refers to having only one allele for a gene, as seen in males with their single X chromosome.
What is the typical outcome for offspring of first cousins regarding genetic diseases?
The risk of genetic diseases in offspring of first cousins is approximately double that of the general population.
What is the primary characteristic of X-linked dominant inheritance?
In X-linked dominant inheritance, the gene is expressed in both males and females, but females may exhibit milder symptoms.
What is the role of female carriers in X-linked recessive inheritance?
Female carriers can pass the X-linked recessive gene to their sons, who may then express the disease.