MS Exam 2 study guide
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/140
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
1
New cards
Atmospheric and ocean currents transport heat around the globe by
* Conduction
* Convection
* Radiation
* FedEx and UPS
* Conduction
* Convection
* Radiation
* FedEx and UPS
Convection
2
New cards
Atmospheric convection cells are characterized by
* Warm air rising in one location and cold air sinking in another
* Cold air rising in one location and warm air sinking in another
* Warm air rising and cold air sinking in the same location
* None of the above
* Warm air rising in one location and cold air sinking in another
* Cold air rising in one location and warm air sinking in another
* Warm air rising and cold air sinking in the same location
* None of the above
Warm air rising in one location and cold air sinking in another
3
New cards
Atmospheric convection cells are characterized by
* Elevated precipitation where warm air rises
* Dry conditions where cold air sinks
* Elevated precipitation where cold air sinks
* Dry conditions where warm air rises
* Both A and B
* Both C and D
* Elevated precipitation where warm air rises
* Dry conditions where cold air sinks
* Elevated precipitation where cold air sinks
* Dry conditions where warm air rises
* Both A and B
* Both C and D
Both A and B
4
New cards
The coriolis effect causes moving fluids to
* travel in straight lines
* deflect to right in N hemisphere and left in S hemisphere
* deflect to left in N hemisphere and right in S hemisphere
* None of the above
* travel in straight lines
* deflect to right in N hemisphere and left in S hemisphere
* deflect to left in N hemisphere and right in S hemisphere
* None of the above
* deflect to right in N hemisphere and left in S hemisphere
5
New cards
Where does warm, moist air rise as part of the atmospheric convection cells?
near equator
6
New cards
Where would you find the trade winds
about 30 degrees north and south of the equator
7
New cards
Where would you find the westerlies
from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude
8
New cards
Where would you find the polar easterlies
begins at approximately 60 degrees north and south latitude and reaches to the poles
9
New cards
What direction are winds moving during the rainy monsoon season
* from land to ocean
* from ocean to land
* parallel to coast
* none
* from land to ocean
* from ocean to land
* parallel to coast
* none
from ocean to land
10
New cards
Cool sea breezes at the coast are due to
* Land heating faster than the ocean during the day
* Land cooling faster than the ocean during the night
* The ocean heating faster than the land during the day
* The ocean cooling faster than the land during the night
* Land heating faster than the ocean during the day
* Land cooling faster than the ocean during the night
* The ocean heating faster than the land during the day
* The ocean cooling faster than the land during the night
Land heating faster than the ocean during the day
11
New cards
Which of the following is true about hurricanes
* they form over the warmest, tropical waters
* they are low pressure systems
* they follow major atmospheric wind bands
* they transport large amounts of heat from the tropics towards the poles
* all of the above
* they form over the warmest, tropical waters
* they are low pressure systems
* they follow major atmospheric wind bands
* they transport large amounts of heat from the tropics towards the poles
* all of the above
all of the above
12
New cards
Separation of different layers of water due to density differences is called
* Mixing
* Layering
* Stratification
* Densification
* Mixing
* Layering
* Stratification
* Densification
stratification
13
New cards
What is the top layer of the surface ocean called?
mixed layer
14
New cards
What is the middle layer of the surface ocean called
thermocline
15
New cards
The region of the water column with rapidly changing temperature is called the
* Lysocline
* Thermocline
* Halocline
* Pcynocline
* Lysocline
* Thermocline
* Halocline
* Pcynocline
Thermocline
16
New cards
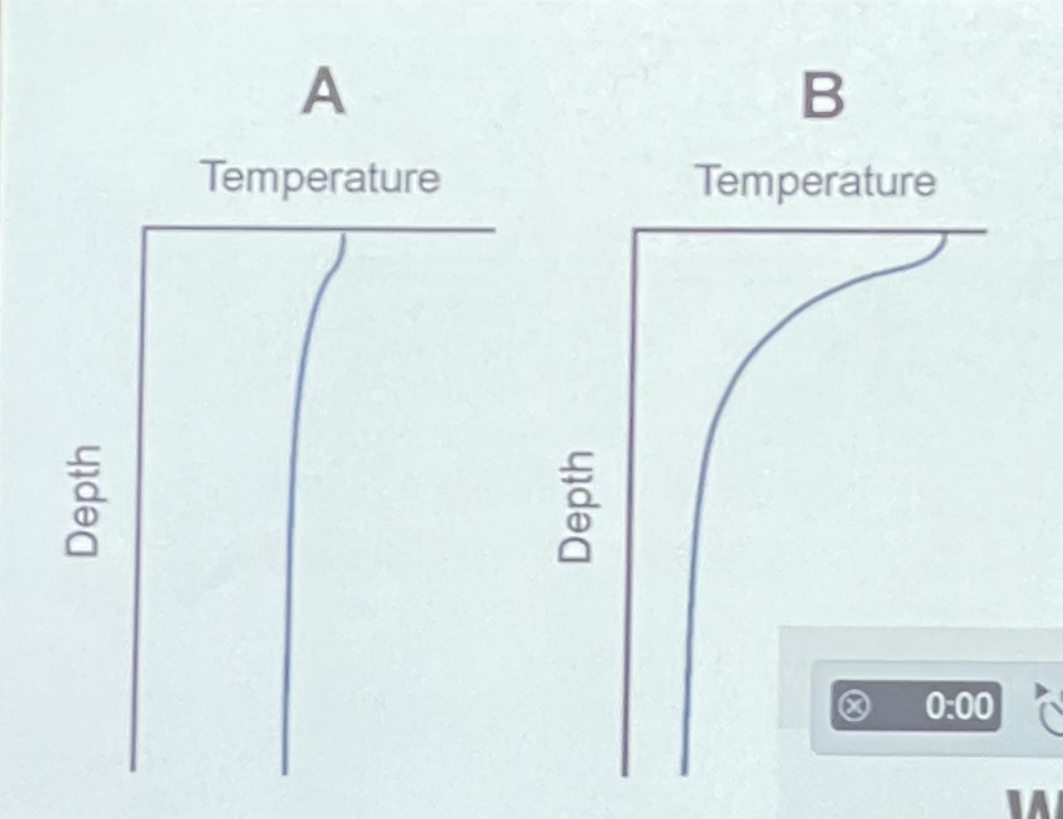
Which statement about these two temperature profiles is true
* A is more strongly stratified and typical of winter
* A is more strongly stratified and typical of summer
* B is more strongly stratified and typical of winter
* B is more strongly stratified and typical of summer
* A is more strongly stratified and typical of winter
* A is more strongly stratified and typical of summer
* B is more strongly stratified and typical of winter
* B is more strongly stratified and typical of summer
B is more strongly stratified and typical of summer
17
New cards
What direction do surface ocean currents travel in the Northern Hemisphere
* In the same direction as the wind
* 45 degrees to the right of the wind
* 90 degrees to the right of the wind
* 45 degrees to the left of the wind
* 90 degrees to the left of the wind
* In the same direction as the wind
* 45 degrees to the right of the wind
* 90 degrees to the right of the wind
* 45 degrees to the left of the wind
* 90 degrees to the left of the wind
45 degrees to the right of the wind
18
New cards
In the Northern Hemisphere, what is the direction of net water transport in an Ekman spiral
* in the same direction as the wind
* 45 degrees to the right of the wind
* 90 degrees to the right of the wind
* 45 degrees to the left of the wind
* 90 degrees to the left of the wind
* in the same direction as the wind
* 45 degrees to the right of the wind
* 90 degrees to the right of the wind
* 45 degrees to the left of the wind
* 90 degrees to the left of the wind
90 degrees to the right of the wind
19
New cards
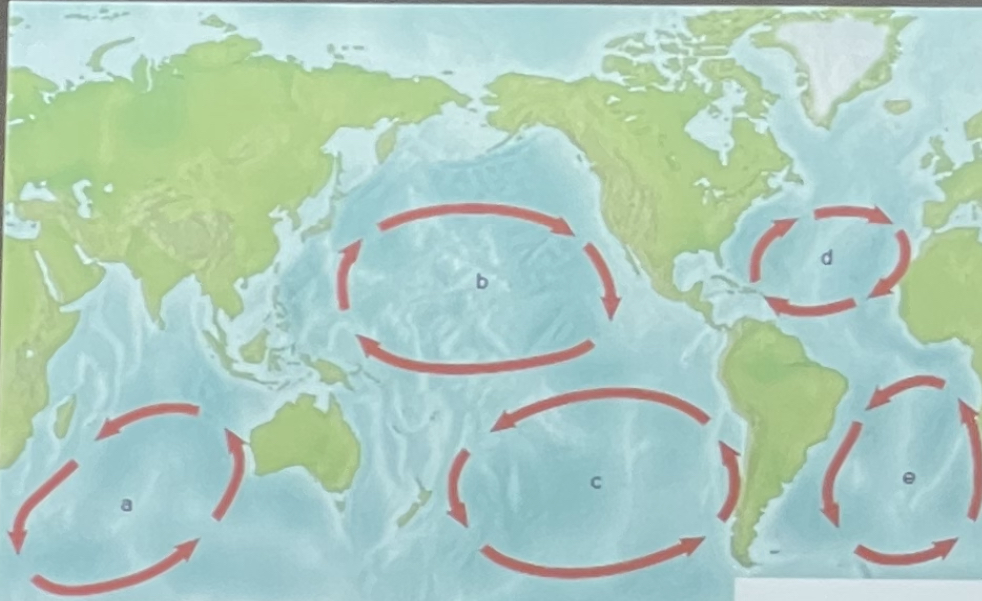
What are these large, circular currents in the major ocean basins called?
Geostrophic gyres
20
New cards
What two forces are balanced in a geotropic gyre
* Coriolis force and winds
* Convection and coriolis force
* Coriolis force and gravity
* Gravity and buoyancy
* Coriolis force and winds
* Convection and coriolis force
* Coriolis force and gravity
* Gravity and buoyancy
Coriolis force and gravity
21
New cards
Which of the following describes an El Nino event?
A. reversal of the Indonesian low and south pacific high
B. reversal of the Indonesian high and south pacific low
C. flow of warm water across the pacific from west to east
D. flow of cold water across the pacific from east to west
E. Both A and C
F. Both B and D
A. reversal of the Indonesian low and south pacific high
B. reversal of the Indonesian high and south pacific low
C. flow of warm water across the pacific from west to east
D. flow of cold water across the pacific from east to west
E. Both A and C
F. Both B and D
Both A and C
22
New cards
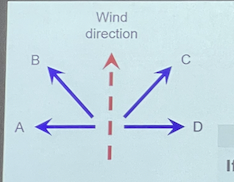
If you are in the Southern Hemisphere and the dashed arrow is the wind direction, which statement is true
* A is the direction of the surface currents, B is the direction of Ekman transport
* B is the direction of the surface currents, A is the direction of Ekman transport
* C is the direction of the surface currents, D is the direction of Ekman transport
* D is the direction of the surface currents, C is the direction of Ekman transport
* A is the direction of the surface currents, B is the direction of Ekman transport
* B is the direction of the surface currents, A is the direction of Ekman transport
* C is the direction of the surface currents, D is the direction of Ekman transport
* D is the direction of the surface currents, C is the direction of Ekman transport
B is the direction of surface currents, A is the direction of Ekman transport
23
New cards
In what direction do the geostrophic gyres rotate
* Clockwise in both hemispheres
* Counterclockwise in both hemispheres
* Clockwise in the N Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the S Hemisphere
* Counterclockwise in the N Hemisphere and clockwise in the S Hemisphere
* Clockwise in both hemispheres
* Counterclockwise in both hemispheres
* Clockwise in the N Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the S Hemisphere
* Counterclockwise in the N Hemisphere and clockwise in the S Hemisphere
Clockwise in the N hemisphere and counterclockwise in the S Hemisphere
24
New cards
The middle of the geostrophic gyres can be described as
* Zones of convergence with a depend thermocline
* Zones of convergence with an elevated thermocline
* Zones of divergence with a depend thermocline
* Zones of divergence with an elevated thermocline
* Zones of convergence with a depend thermocline
* Zones of convergence with an elevated thermocline
* Zones of divergence with a depend thermocline
* Zones of divergence with an elevated thermocline
Zones of convergence with a depend thermocline
25
New cards
The gulf stream is an example of
* Western intensification
* Eastern intensification
* Northern intensification
* Southern intensification
* Western intensification
* Eastern intensification
* Northern intensification
* Southern intensification
western intensification
26
New cards
Which statement is true about western and eastern boundary currents
* WBCs tend to be faster, narrower, and deeper
* EBCs tend to be faster, narrower, and deeper
* They tend to have the same speed, width, and depth
* WBCs tend to be faster, narrower, and deeper
* EBCs tend to be faster, narrower, and deeper
* They tend to have the same speed, width, and depth
WBCs tend to be faster, narrower, and deeper
27
New cards
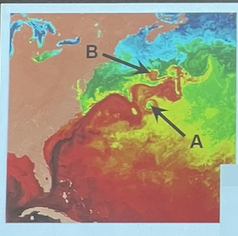
Which statement is true
* A and B are warm core eddies
* A and B are cold core eddies
* A is a warm core eddy and B is a cold core eddy
* A is a cold core eddy and B is a warm core eddy
* A and B are warm core eddies
* A and B are cold core eddies
* A is a warm core eddy and B is a cold core eddy
* A is a cold core eddy and B is a warm core eddy
A is a cold core eddy and B is a warm core eddy
28
New cards
Convergence zones are characterized by
* A deepened thermocline and downwelling
* A deepened thermocline and upwelling
* An elevated thermocline and downwelling
* An elevated thermocline and upwelling
* A deepened thermocline and downwelling
* A deepened thermocline and upwelling
* An elevated thermocline and downwelling
* An elevated thermocline and upwelling
a depend thermocline and downwelling
29
New cards
Divergence zones are characterized by
* a deepend thermocline and downwelling
* a deepened thermocline and upwelling
* An elevated thermocline and downwelling
* An elevated thermocline and upwelling
* a deepend thermocline and downwelling
* a deepened thermocline and upwelling
* An elevated thermocline and downwelling
* An elevated thermocline and upwelling
an elevated thermocline and upwelling
30
New cards
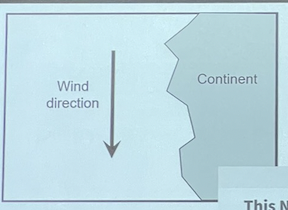
This northern hemisphere location is likely to be characterized by
* downwelling
* upwelling
* neither
* downwelling
* upwelling
* neither
upwelling
31
New cards
Where does costal upwelling usually occur
* Western boundary currents
* Eastern boundary currents
* Northern boundary currents
* Southern boundary currents
* Western boundary currents
* Eastern boundary currents
* Northern boundary currents
* Southern boundary currents
eastern boundary currents
32
New cards
What effect does El Nino have on the Peruvian upwelling zone
* Deepens the thermocline and enhances upwelling
* Shallows the thermocline and enhances upwelling
* Deepens the thermocline and reduces/reverses upwelling
* Shallows the thermocline and reduces/reverses upwelling
\
* Deepens the thermocline and enhances upwelling
* Shallows the thermocline and enhances upwelling
* Deepens the thermocline and reduces/reverses upwelling
* Shallows the thermocline and reduces/reverses upwelling
\
Deepens the thermocline and reduces/reverses upwelling
33
New cards
Which statement about the El Nino - Southern Oscillation is not true
* El Nino is the relatively warm phase; La Nina is the relatively cool phase
* El Nino is the relatively cold phase, La Nina is the relatively warm phase
* El Nino events occur about every 3-7 years
* El Nino events affect climate around the globe
* El Nino is the relatively warm phase; La Nina is the relatively cool phase
* El Nino is the relatively cold phase, La Nina is the relatively warm phase
* El Nino events occur about every 3-7 years
* El Nino events affect climate around the globe
B
34
New cards
A large body of water that has similar values of temperature and salinity throughout is called a
water mass
35
New cards
The boundary between two water masses is called a
front
36
New cards
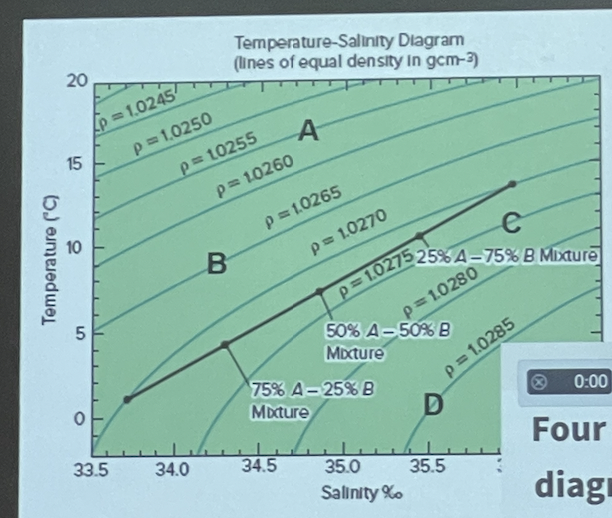
Using the T-S diagram, what is the density of water with T=10 and S=35.1
\
\
1\.0270
37
New cards
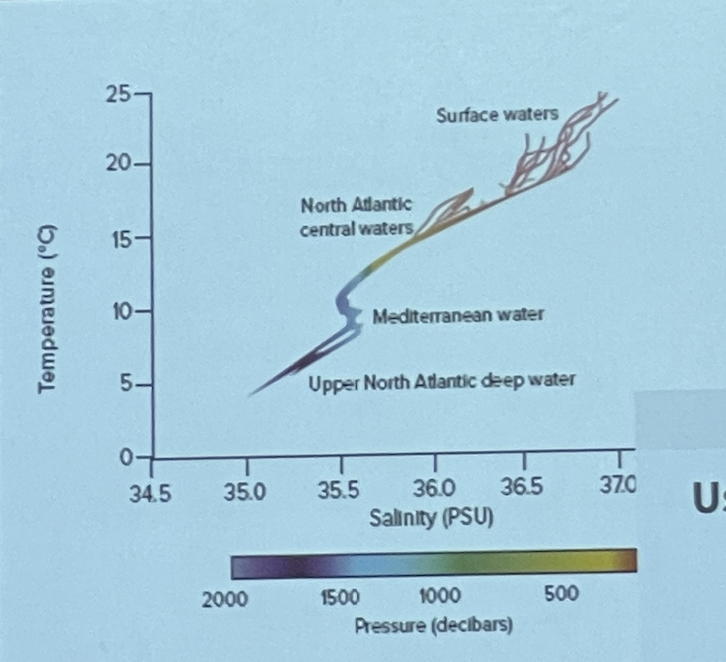
Using the T-S diagram, what values are typical of Mediterranean water
T=10, S=35.6
38
New cards
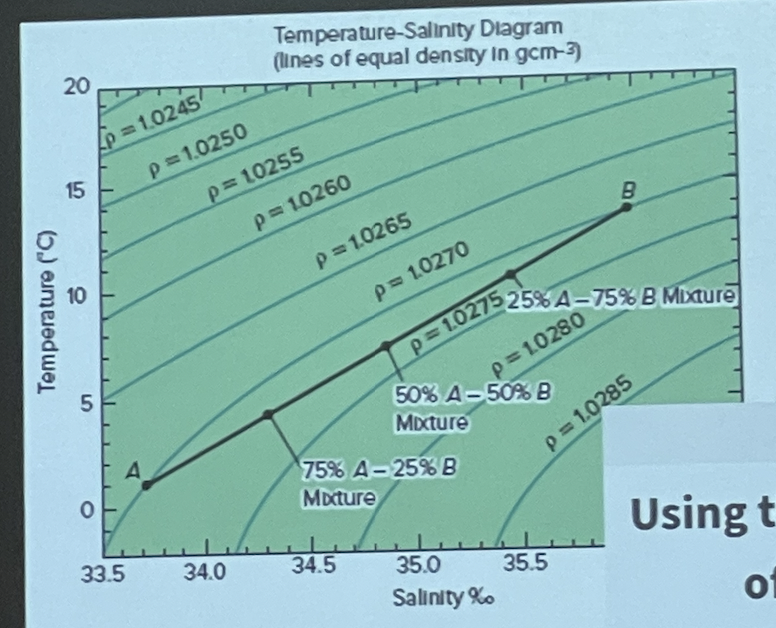
Four water masses are plotted on the T-S diagram. Which one will reside at the bottom of a stable water column
D
39
New cards
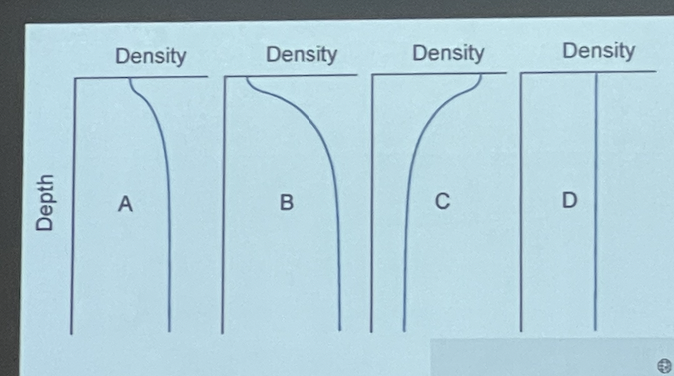
Which profile depicts an unstable water column
C
40
New cards
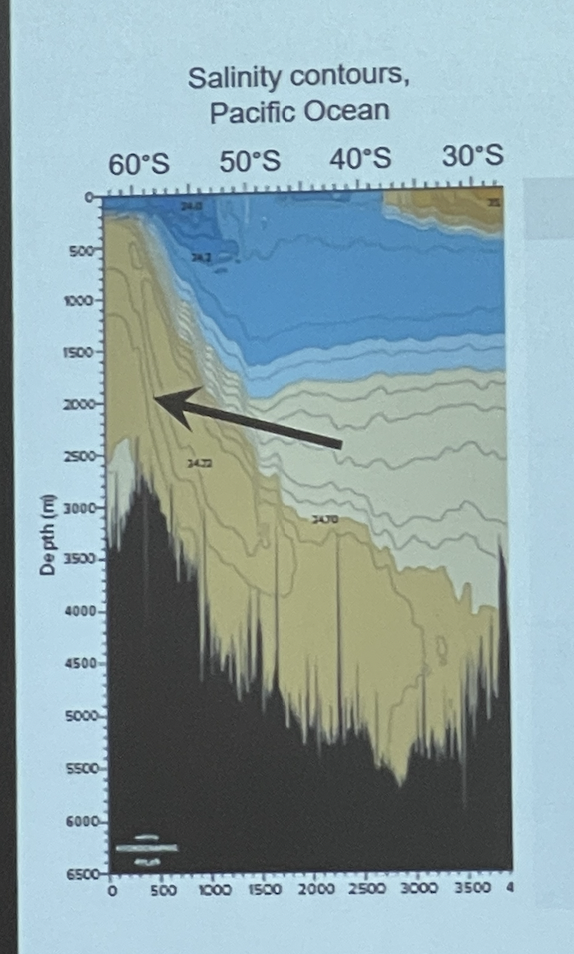
What is happening to ocean water at the location identified by the arrow
formation of deep water
41
New cards
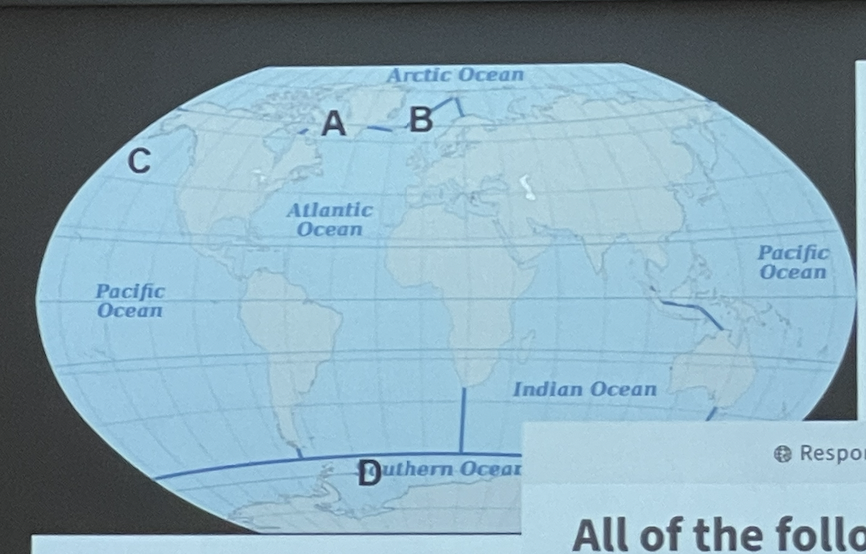
All of the following are locations of deep water formation except
C
42
New cards
What causes the formation and sinking of deep water
* surface water gets cold and fresher as it moves towards the poles
* surface water gets cold and saltier as it moves towards the poles
* surface water gets warm and saltier as it moves towards the poles
* surface water gets warm and saltier as it moves towards the equator
* surface water gets cold and fresher as it moves towards the poles
* surface water gets cold and saltier as it moves towards the poles
* surface water gets warm and saltier as it moves towards the poles
* surface water gets warm and saltier as it moves towards the equator
surface water gets cold and saltier as it moves towards the poles
43
New cards
As deep water forms and sinks near the poles, water must come in from elsewhere to replace it. Where does this new water come from?
equator
44
New cards
Thermohaline circulation moves heat around the planet by
* Conduction
* Radiation
* Convection
* Conduction
* Radiation
* Convection
Convection
45
New cards
Due to climate change, thermohaline circulation in the Atlantic ocean is
* strengthening
* weakening
* staying the same
* strengthening
* weakening
* staying the same
weakening
46
New cards
The region of the water column with enough light for photosynthesis is called the
* illuminated zone
* twilight zone
* photic zone
* aphotic zone
* illuminated zone
* twilight zone
* photic zone
* aphotic zone
photic zone
47
New cards
Benthic refers to which region of the ocean
* pelagic zone
* neurotic zone
* abyssal zone
* the seafloor
* pelagic zone
* neurotic zone
* abyssal zone
* the seafloor
seafloor
48
New cards
As ocean depth increases, light…
* decreases linearly
* decreases exponentially
* stays the same
* increases linearly
* increases exponentially
* decreases linearly
* decreases exponentially
* stays the same
* increases linearly
* increases exponentially
decreases exponentially
49
New cards
Which wavelength of light penetrates deepest in ocean water
* red
* orange
* yellow
* green
* blue
* red
* orange
* yellow
* green
* blue
blue
50
New cards
Which group of marine organisms are unable to move against the currents?
* plankton
* nekton
* benthos
* sea birds
* plankton
* nekton
* benthos
* sea birds
plankton
51
New cards
Which group of plankton conduct photosynthesis
* bacterioplankton
* phytoplankton
* zooplankton
* icthyoplankton
* bacterioplankton
* phytoplankton
* zooplankton
* icthyoplankton
phytoplankton
52
New cards
As size of marine organisms increases, their abundance
* increases
* decreases
* stays the same
* increases
* decreases
* stays the same
decreases
53
New cards
As the size of marine organisms decreases, their surface area to volume ratio
* increases
* decreases
* stays the same
* increases
* decreases
* stays the same
increases
54
New cards
Which group of marine organisms are able to swim against the currents
* plankton
* nekton
* ethos
* bacteria
* plankton
* nekton
* ethos
* bacteria
nekton
55
New cards
Which group of plankton are autographs
* bacterioplankton
* phytoplankton
* zooplankton
* ichthyoplankton
* bacterioplankton
* phytoplankton
* zooplankton
* ichthyoplankton
phytoplankton
56
New cards
Which group(s) of plankton are heterotrophs
* bacterioplankton
* phytoplankton
* zooplankton
* A and C
* bacterioplankton
* phytoplankton
* zooplankton
* A and C
bacterioplankton and zooplankton
57
New cards
Which group of plankton are the primary consumers in the oceanic food chain
* bacterioplankton
* phytoplankton
* zooplankton
* ichthyoplankton
* bacterioplankton
* phytoplankton
* zooplankton
* ichthyoplankton
zooplankton
58
New cards
Which group of plankton are the major decomposers in the ocean
* bacterioplankton
* phytoplankton
* zooplankton
* ichthyoplankton
* bacterioplankton
* phytoplankton
* zooplankton
* ichthyoplankton
59
New cards
Which is new primary production
* Total amount of organic matter produced
* Amount of organic matter produced minus autotrophic respiration
* Amount of organic matter produced minus all respiration
* Total amount of respiration
* Total amount of organic matter produced
* Amount of organic matter produced minus autotrophic respiration
* Amount of organic matter produced minus all respiration
* Total amount of respiration
Amount of organic matter produced minus autotrophic respiration
60
New cards
Mineral elements necessary for growth and maintenance of life are called
nutrients
61
New cards
Which of these is true about respiration
* it releases energy stores in organic matter
* it consumes O2
* It rprocues CO2
* It recycles nutrients
* all of the above
* it releases energy stores in organic matter
* it consumes O2
* It rprocues CO2
* It recycles nutrients
* all of the above
all of the above
62
New cards
A linear representation of feeding relationships is called a
* Food chain
* food web
* Tropic web
* Trophic pyramid
* Food chain
* food web
* Tropic web
* Trophic pyramid
food chain
63
New cards
What is an adaptation plankton have to reduce sinking
flagella, oil deposits, spikes
64
New cards
What is one reason plankton undergo diel vertical migration?
avoid predation or food
65
New cards
Which statement is true as depth increases in the ocean
* Light decreases and nutrient concentrations remain constant
* Light and nutrient concentrations decrease
* Light decreases and nutrient concentrations increase
* Light remains constant and nutrient concentrations increase
* Light decreases and nutrient concentrations remain constant
* Light and nutrient concentrations decrease
* Light decreases and nutrient concentrations increase
* Light remains constant and nutrient concentrations increase
Light decreases and nutrient concentrations increase
66
New cards
Which statement is true as depth increases in the ocean
* Photosynthesis and respiration both decrease
* Photosynthesis decreases and respiration remains constant
* Photosynthesis decreases and respiration increases
* Photosynthesis remains constant and respiration increases
* Photosynthesis and respiration both decrease
* Photosynthesis decreases and respiration remains constant
* Photosynthesis decreases and respiration increases
* Photosynthesis remains constant and respiration increases
Photosynthesis decreases and respiration remains constant
67
New cards
GPP is equal at the
* Mixed layer depth
* Compensation depth
* Euphotic depth
* Critical depth
* Mixed layer depth
* Compensation depth
* Euphotic depth
* Critical depth
compensation depth
68
New cards
What is the correct Redfield Ratio
* 106 N : 16P : 1 Si
* 106 C : 16N : 1Fe
* 106 C : 16 N : 1P
* 106 C : 16 N : 1 Si
* 106 N : 16P : 1 Si
* 106 C : 16N : 1Fe
* 106 C : 16 N : 1P
* 106 C : 16 N : 1 Si
106 C : 16 N : 1P
69
New cards
Outside of the HNLC regions, what is the most limiting nutrient in the ocean?
* C
* N
* P
* Si
* Fe
* C
* N
* P
* Si
* Fe
N
70
New cards
What is the most limiting nutrient in the HNLC regions
* C
* N
* P
* Si
* Fe
* C
* N
* P
* Si
* Fe
Fe
71
New cards
A large accumulation of phytoplankton biomass is called a
bloom
72
New cards
For a bloom to occur, phytoplankton have to remain above the
* Mixed layer depth
* compensation depth
* euphotic depth
* critical depth
* Mixed layer depth
* compensation depth
* euphotic depth
* critical depth
critical depth
73
New cards
What causes the spring phytoplankton bloom?
shallowing mixed layer, high nutrients, increasing light
74
New cards
Why don’t plankton tend to bloom during summer in the temperate ocean?
strong stratification, low nutrients, zooplankton grading
75
New cards
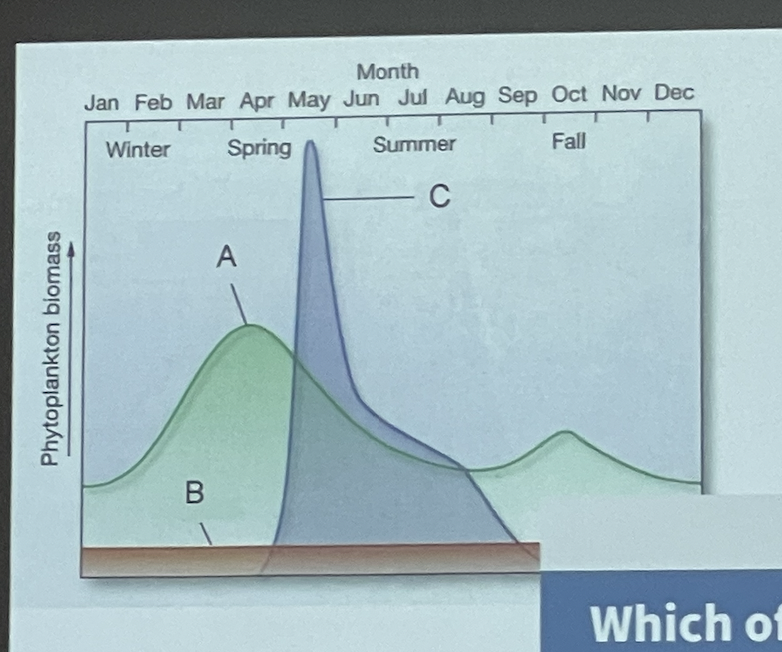
Which of these annual phytoplankton cycles represents the tropical ocean?
B
76
New cards
In temperate regions, which season is characterized by high nutrients, a developing mixed layer, and greatest productivity?
* Winter
* Spring
* Summer
* Fall
* Winter
* Spring
* Summer
* Fall
Spring
77
New cards
Which oceanic region is characterized by a single, large bloom in summer?
* Arctic ocean
* north Altlantic
* Sargasso Sea
* Tropical regions
* Arctic ocean
* north Altlantic
* Sargasso Sea
* Tropical regions
Arctic ocean
78
New cards
The large ocean gyres are oligotrophic due to
* Convergence
* downwelling
* depression of pycnocline
* Low nutrient concentrations
* all of the above
* Convergence
* downwelling
* depression of pycnocline
* Low nutrient concentrations
* all of the above
All of the above
79
New cards
What regions are entropic due to their shallow depths and riverine input of nutrients
* Ocean gyres
* Upwelling zones
* Coastal margins
* temperate and polar oceans
* Ocean gyres
* Upwelling zones
* Coastal margins
* temperate and polar oceans
Coastal margins
80
New cards
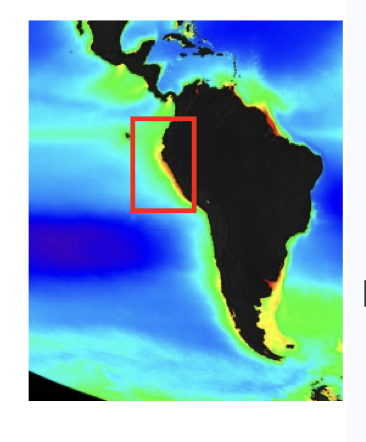
Why is the region in the red box so eutrophic
* Coastal upwelling
* convergence and downwelling
* river input of nutrients
* winter mixing followed by stratification in spring/summer
* none of the above
* Coastal upwelling
* convergence and downwelling
* river input of nutrients
* winter mixing followed by stratification in spring/summer
* none of the above
Coastal upwelling
81
New cards
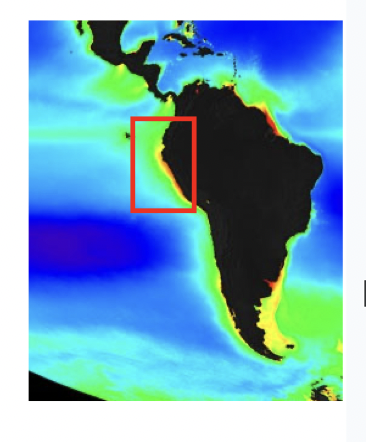
What happens to primary production in this area during El Nino
* increases
* decreases
* remains the same
* increases
* decreases
* remains the same
Decreases
82
New cards
Which oceanic regions tend to have the highest rates of primary production per m2
* Open ocean
* Coastal ocean
* Estuaries
* Upwelling regions
* Open ocean
* Coastal ocean
* Estuaries
* Upwelling regions
Upwelling regions
83
New cards
Which oceanic regions fix the most carbon across the entire planet
* Open ocean
* Coastal ocean
* Estuaries
* Upwelling regions
* Open ocean
* Coastal ocean
* Estuaries
* Upwelling regions
Open ocean
84
New cards
Carbon fixed by phytoplankton GPP can
* support a phytoplankton bloom
* move up the food chain
* Cycle through the microbial loop
* sink to depth
* all of the above
* support a phytoplankton bloom
* move up the food chain
* Cycle through the microbial loop
* sink to depth
* all of the above
All of the above
85
New cards
The microbial loop is the process where
* phytoplankton are consumed by zooplankton which are consumed by fish
* bacteria recycle nutrients through respiration
* leached organic matter is taken up by bacteria which are consumed by small zooplankton
* leached organic matter sinks to depth where it is consumed by bacteria
* phytoplankton are consumed by zooplankton which are consumed by fish
* bacteria recycle nutrients through respiration
* leached organic matter is taken up by bacteria which are consumed by small zooplankton
* leached organic matter sinks to depth where it is consumed by bacteria
Leached organic matter is taken up by bacteria which are consumed by small zooplankton
86
New cards
The biological pump is the process by which
* CO2 is released from the ocean to the atmosphere
* CO2 is sequestered in the deep ocean by sinking organic matter
* Nutrients are sequestered in the deep ocean by sinking organic matter
* Nutrients are recycled in the deep ocean by respiration
* CO2 is released from the ocean to the atmosphere
* CO2 is sequestered in the deep ocean by sinking organic matter
* Nutrients are sequestered in the deep ocean by sinking organic matter
* Nutrients are recycled in the deep ocean by respiration
CO2 is sequestered in the deep ocean by sinking organic matter
87
New cards
The constant rain of organic matter from surface waters to the deep ocean is called
Marine snow
88
New cards
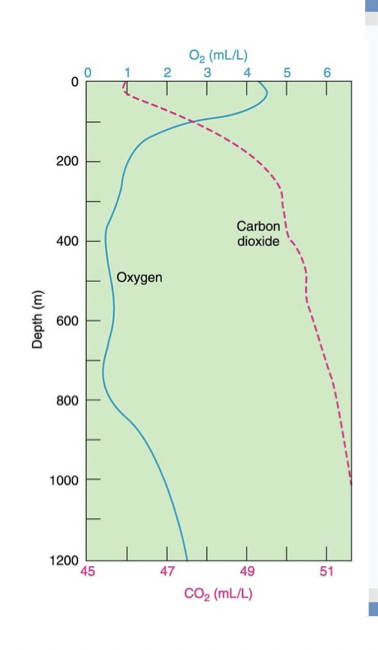
What explains the decreasing O2 and increasing CO2 with depth in the profile
* photosynthesis at depth
* respiration at depth
* balanced photosynthesis and respiration
* upwelling
* none of the above
* photosynthesis at depth
* respiration at depth
* balanced photosynthesis and respiration
* upwelling
* none of the above
Respiration at depth
89
New cards
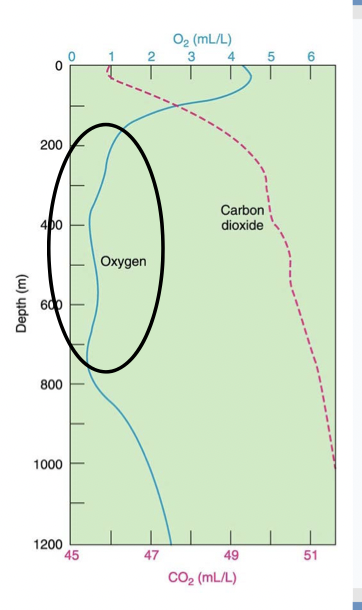
What is the circled region on the O2 profile called
Oxygen minimum zone
90
New cards
What are some adaptations nekton use to swim without sinking
streamlined body shape, fins, and buoyancy control
91
New cards
What are some adaptations nekton use to deal with cold temperatures, salinity, and /or high pressure
countercurrent heat exchange , regulating salt content, fill gas bladders with fat cells
92
New cards
What is an adaptation nekton use to reproduce
93
New cards
What is an adaptation nekton use to avoid predators
migrations, camouflage, bioluminescence
94
New cards
What are some adaptations nekton use to find and capture food
large mouth, hinged jaw, needle-like teeth
95
New cards
What role do nekton play in the ocean food chain
* Secondary, tertiary, and quaternary consumers
* Heterotrophs
* top predators
* all of the above
* Secondary, tertiary, and quaternary consumers
* Heterotrophs
* top predators
* all of the above
All of the above
96
New cards
Regions with greater fish abundance and catches are generally associated with
* Greater GPP
* Lower GPP
* there is no relationship
* Greater GPP
* Lower GPP
* there is no relationship
Greater GPP
97
New cards
El Nino events are associated with
* increased upwelling, GPP< and anchovy catch
* Increased upwelling and GPP< but decreased anchovy catch
* Decreased upwelling and GPP, but increased anchovy catch
* Decreased upwelling, GPP and anchovy catch
* increased upwelling, GPP< and anchovy catch
* Increased upwelling and GPP< but decreased anchovy catch
* Decreased upwelling and GPP, but increased anchovy catch
* Decreased upwelling, GPP and anchovy catch
Decreased upwelling, GPP, and anchovy catch
98
New cards
What part of the earth has the most positive heat balance
* tropics
* mid-latitudes
* polar regions
* heat balance is equal across the planet
* tropics
* mid-latitudes
* polar regions
* heat balance is equal across the planet
tropics
99
New cards
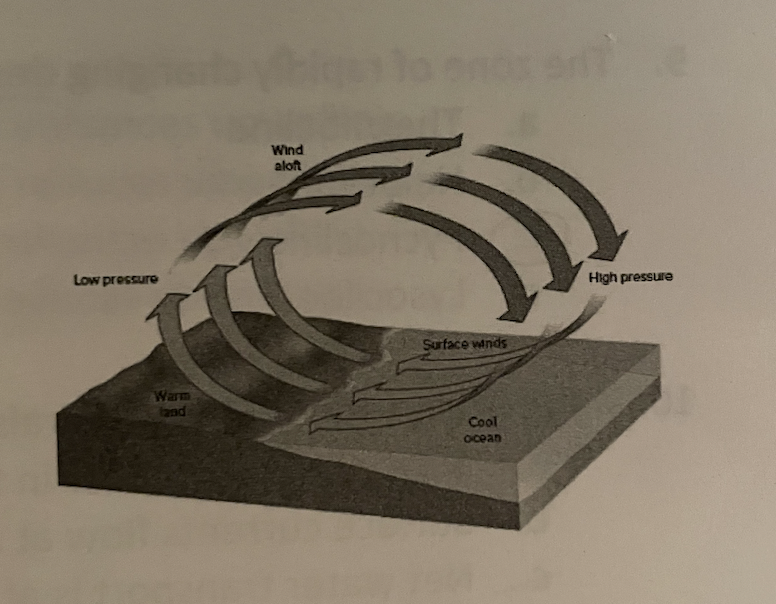
What is shown in the digram to the right
* atmospheric conduction cell
* atmospheric convection cell
* atmospheric radiano cell
* atmospheric thermal cell
* atmospheric conduction cell
* atmospheric convection cell
* atmospheric radiano cell
* atmospheric thermal cell
atmospheric convection cell
100
New cards
Rising war air is usually associated with
* dry, high pressure conditions
* wet, high pressure conditions
* dry, low pressure conditions
* wet, low pressure conditions
* dry, high pressure conditions
* wet, high pressure conditions
* dry, low pressure conditions
* wet, low pressure conditions
wet, low pressure conditions