CLASS 9 TEST (Femur, Hip, and Pelvis)
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
What positioning landmark is the same level as the pubic symphysis?
Greater trochanters
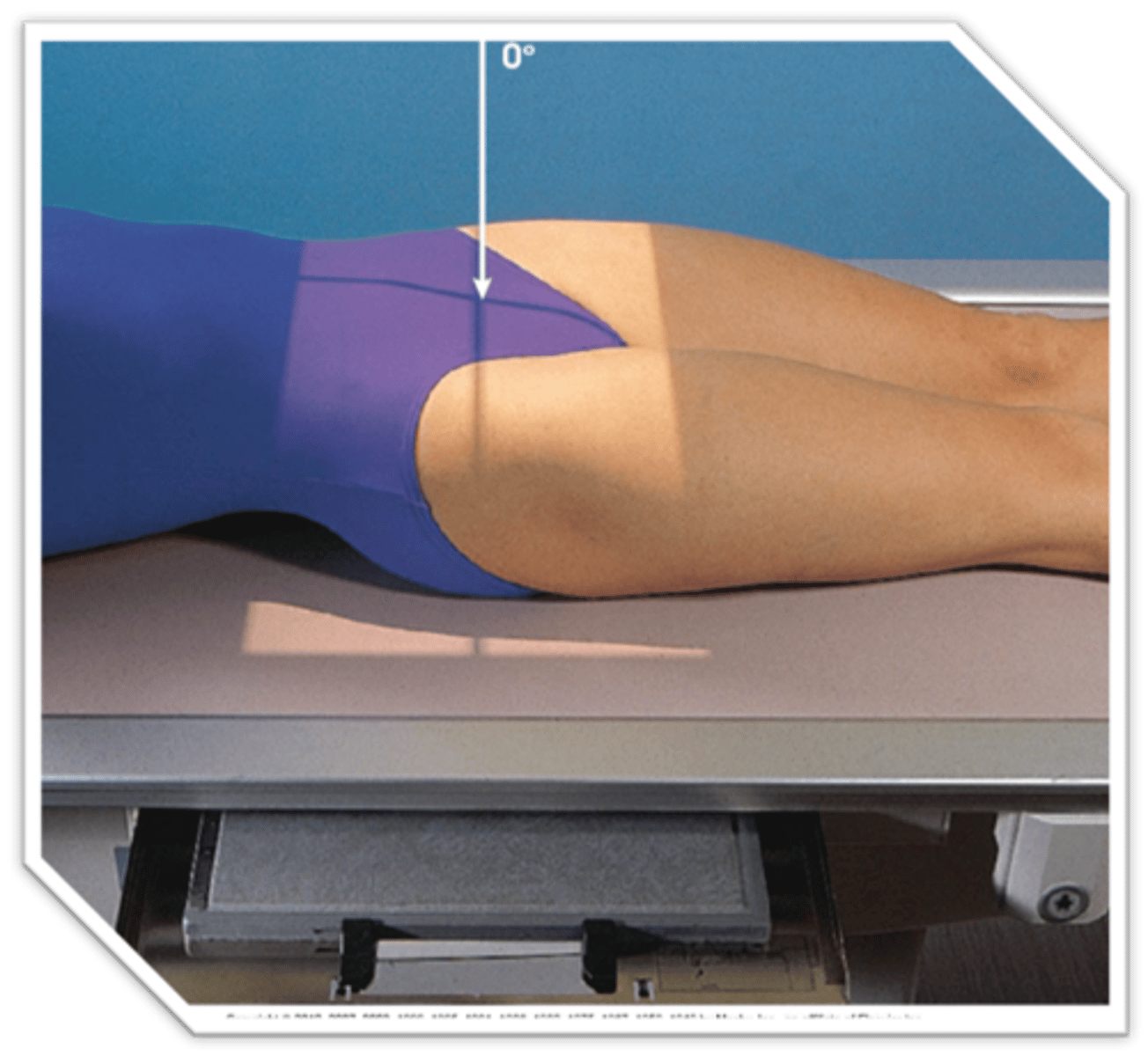
How much should the feet and lower limbs be inverted on an AP pelvis?
15-20 degrees
What is the method name for an AP oblique hip?
Modified Cleaves method
What is the method name for an Axiolateral hip?
Danelius-Miller method
What is the method name for a lateral hip?
Lauenstein method
What is the difference btwn the Lauenstein and Hickey methods?
The Hickey method has a 20-25 degree cephalic angle
CR location for a Lateral femur:
CR perpendicular and 1/3 from the anterior surface of the femur.
CR location for an AP pelvis:
CR perpendicular and 1/2 way btwn the pubic symphysis and the ASIS at the MSP.
CR location for an AP hip:
CR perpendicular to the femoral neck.
CR location for an AP oblique hip:
CR perpendicular to the femoral neck. (1" superior to PS)
CR location for a Lateral hip (Lauenstein):
CR perpendicular to the femoral neck
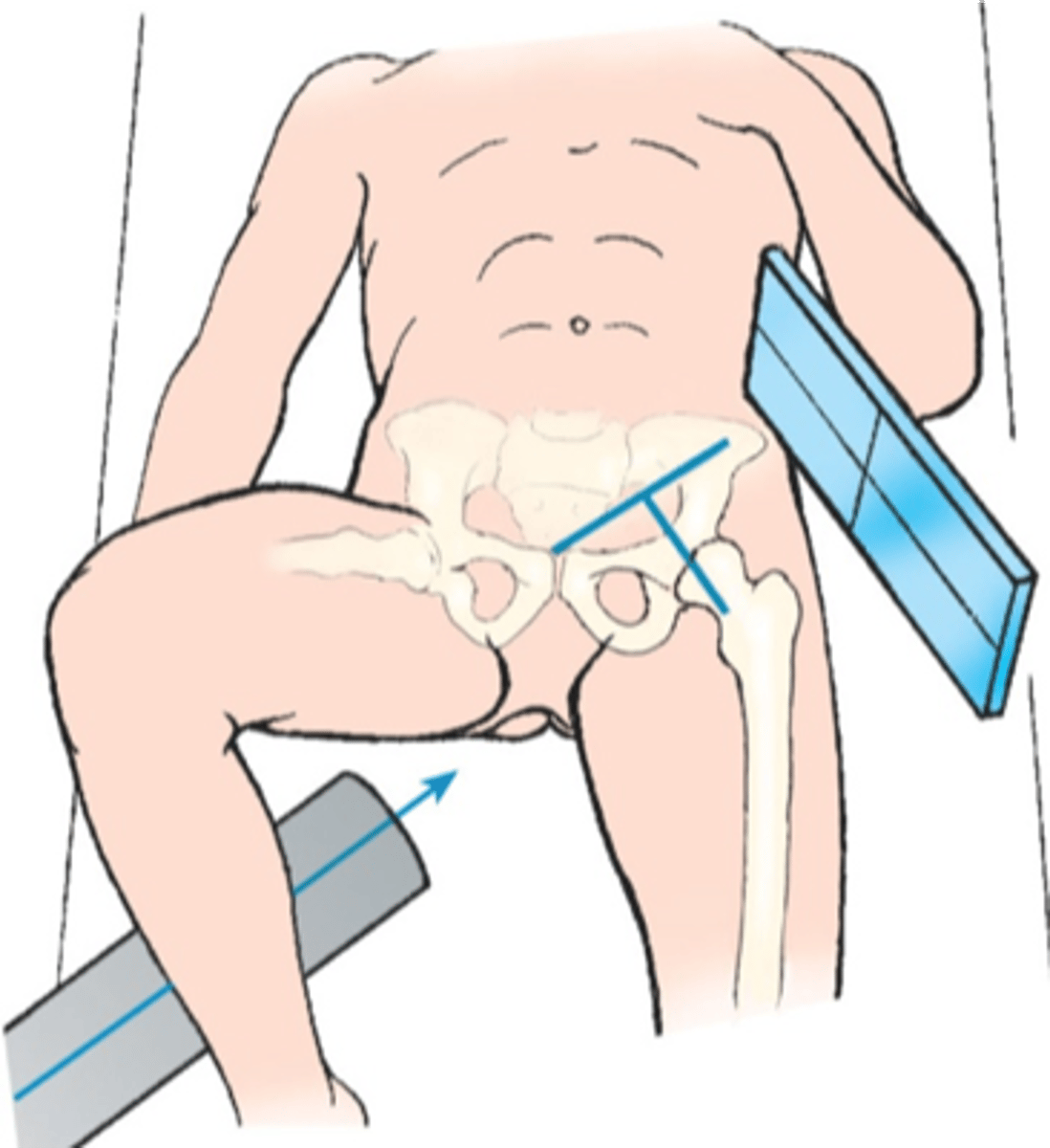
CR location for an Axiolateral hip:
CR is horizontal and perpendicular to the femoral neck.
The central ray for an AP pelvis is directed perpendicular to the center of the IR. The central-ray entrance point will be about _____ inches _____ to the pubic symphysis.
2; superior
How many degrees should the feet and lower limbs be internally rotated for an AP pelvis radiograph?
15 to 20 degrees
The respiration phase for the axiolateral projection of the hip (Danelius-Miller) is:
suspended respiration
Which of the following methods will demonstrate the hip in a lateral projection?
Lauenstein, Hickey
Which of the following methods demonstrate the hip in an axiolateral projection?
Danelius-Miller
The neck of the femur projects anteriorly at an approximate angle of _____ degrees.
15 to 20
Where is the central ray directed for the AP oblique projection (modified Cleaves) of the femoral necks?
1 inch superior to the pubic symphysis
Which of the following describes the direction of the central ray for an axiolateral projection of the hip (Danelius-Miller)? 1. Perpendicular to the IR 2. Perpendicular to the long axis of the femoral neck 3. Perpendicular to the long axis of the femur
1 and 2
Which of the following will be shown "in profile" if the lower limbs are in correct position for an AP pelvis?
Greater trochanters
Which of the following methods will demonstrate the femoral necks in the AP oblique projection?
Modified Cleaves
Which of the following describes the position of the IR for the axiolateral projection of the hip (Danelius-Miller)? 1. Parallel with the long axis of the femoral neck 2. Its upper border in the crease above the iliac crest 3. Perpendicular to the long axis of the femur
1 and 2
Unless contraindicated, the lower limb and leg should be internally rotated for an axiolateral projection of the hip (Danelius-Miller). How many degrees of rotation are required?
15-20
Which of the following is an important and frequently used radiographic positioning reference point?
Anterior superior iliac spine
The hip bone is composed of which of the following? 1. Ilium 2. Pubis 3. Ischium
1, 2, and 3
Where is the IR centered for an AP pelvis?
Midway between the ASIS and the pubic symphysis
The ilia articulates with the sacrum posteriorly at the:
sacroiliac joints
The strongest bone in the body is the:
femur
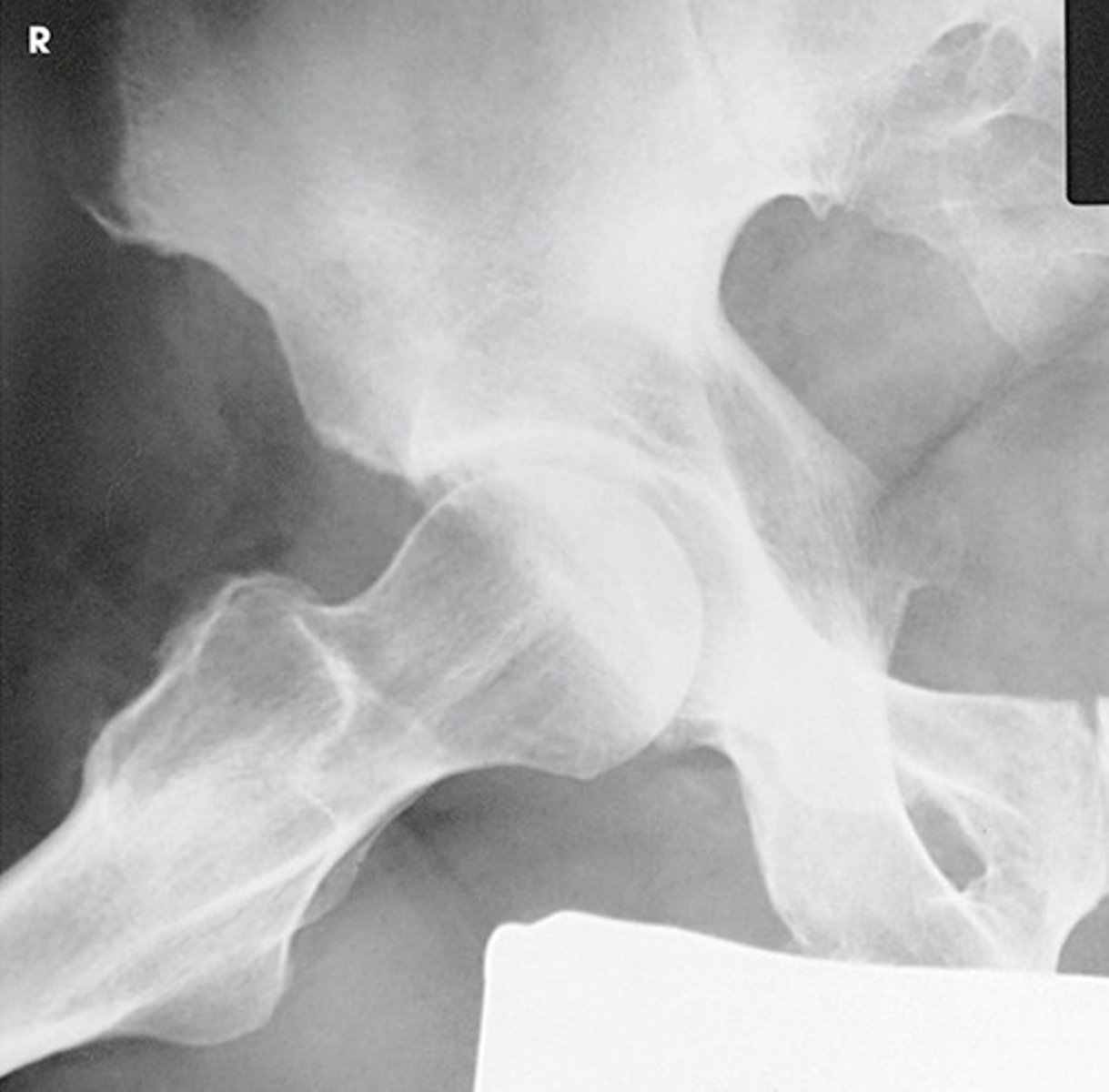
What positioning error is evident in the image below?
The lower limbs were not internally rotated
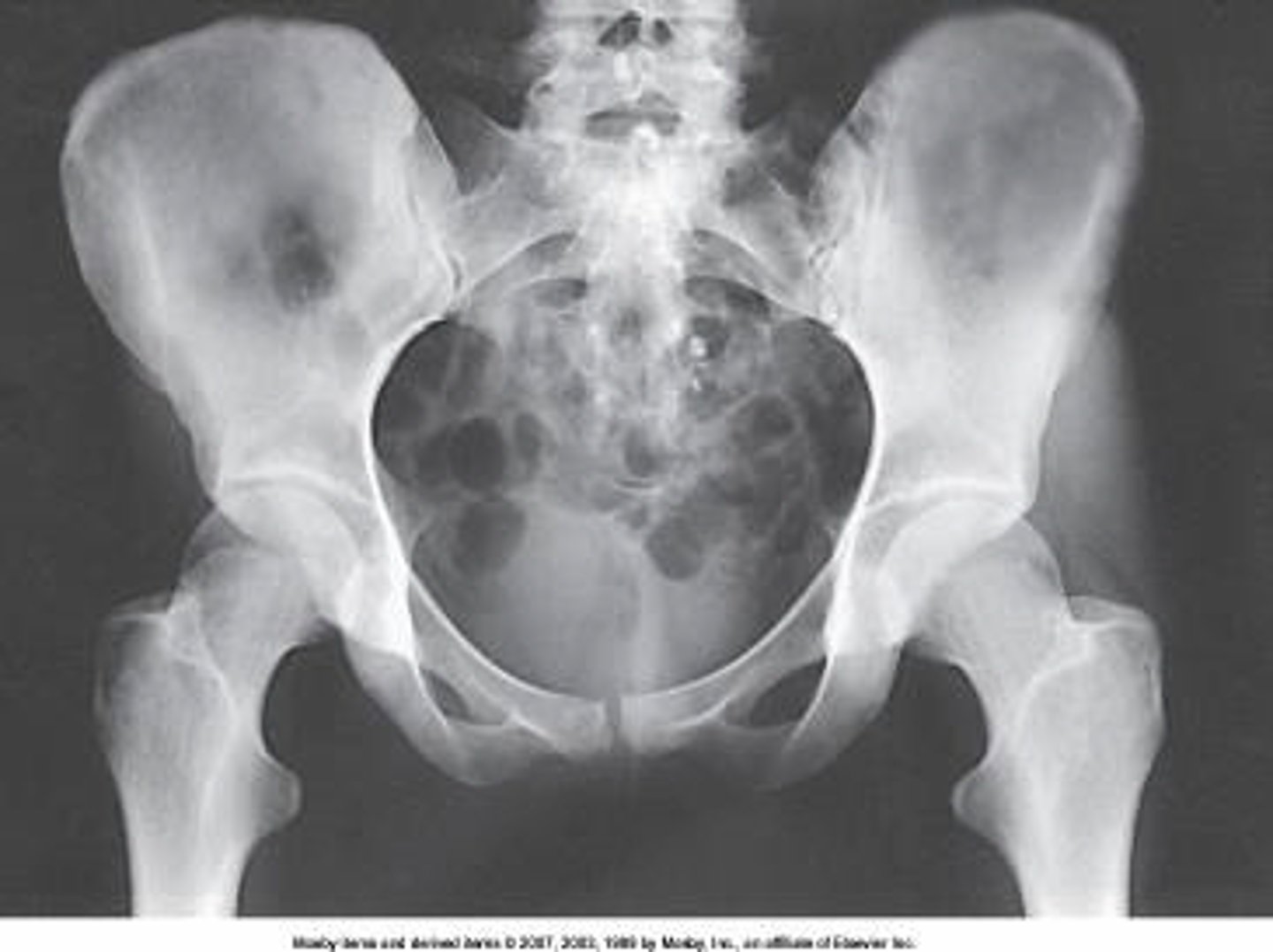
The part identified on the ilium above is the _____ iliac spine.
anterior superior
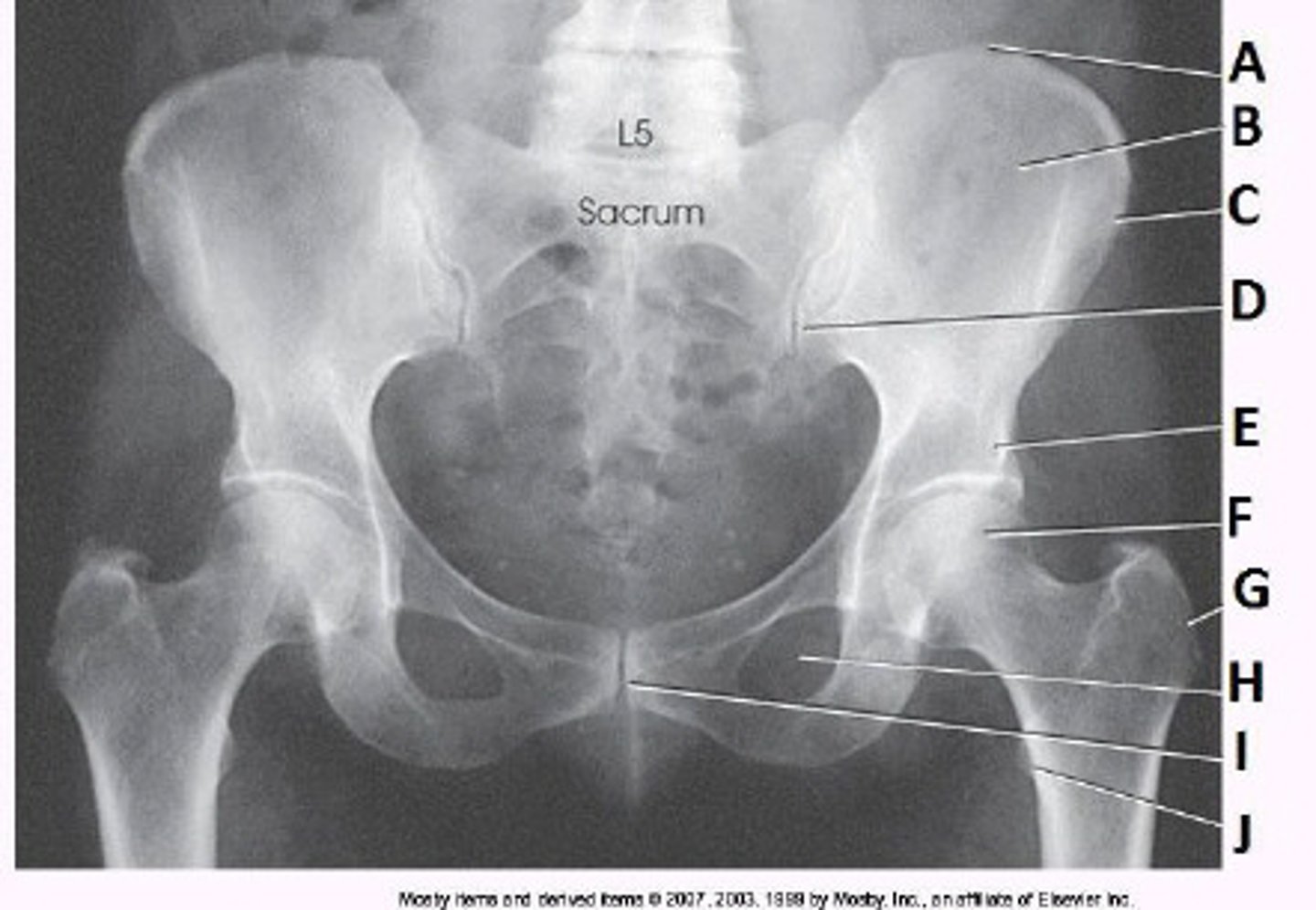
What anatomy is labeled as letter C in the image below?
ASIS
What anatomy is labeled as letter B in the image below?
Lesser trochanter
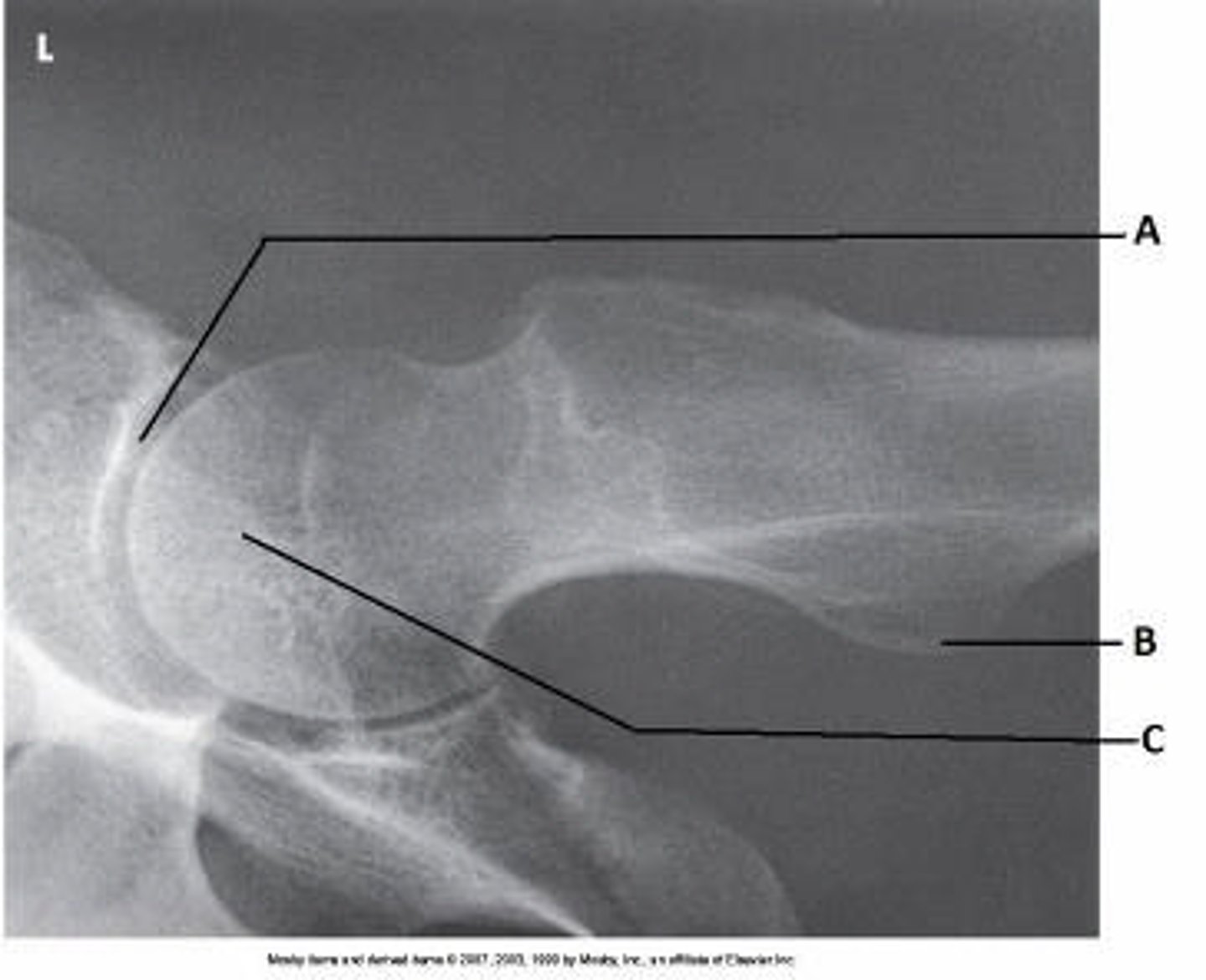
The area identified on the bone shown above is the:
intertrochanteric crest
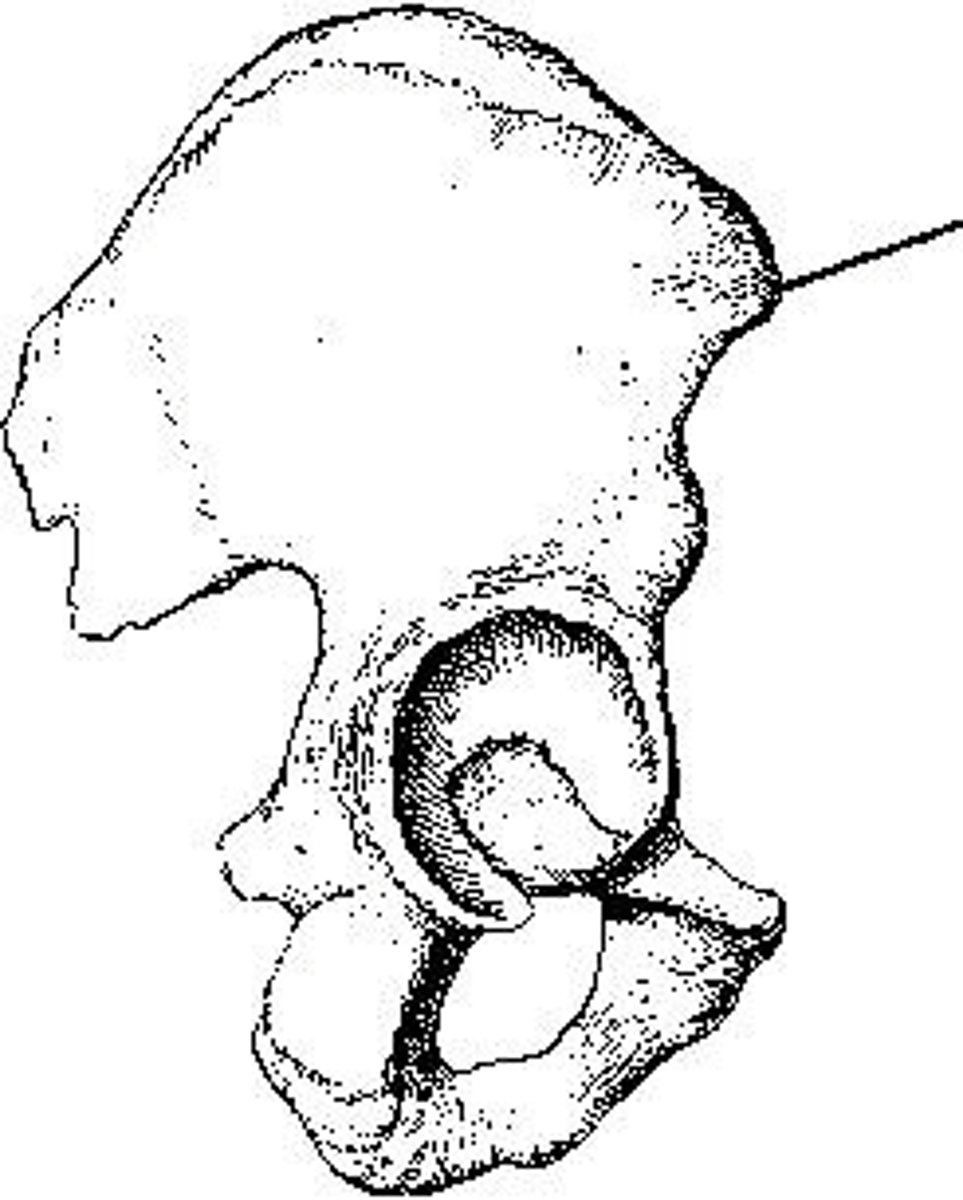
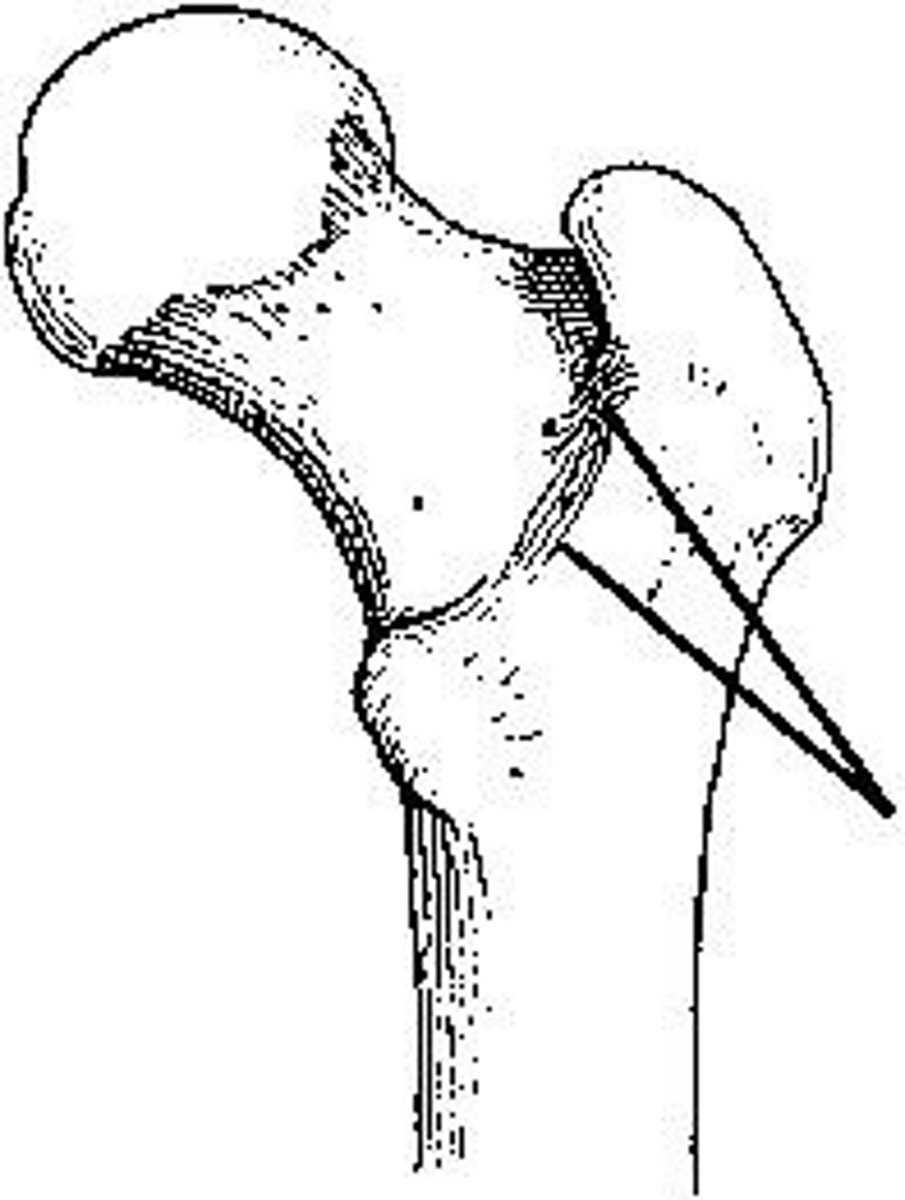
Which projection of the hip is shown in the figure above?
Axiolateral

The area of anatomy indicated on the figure above is the:
obturator foramen
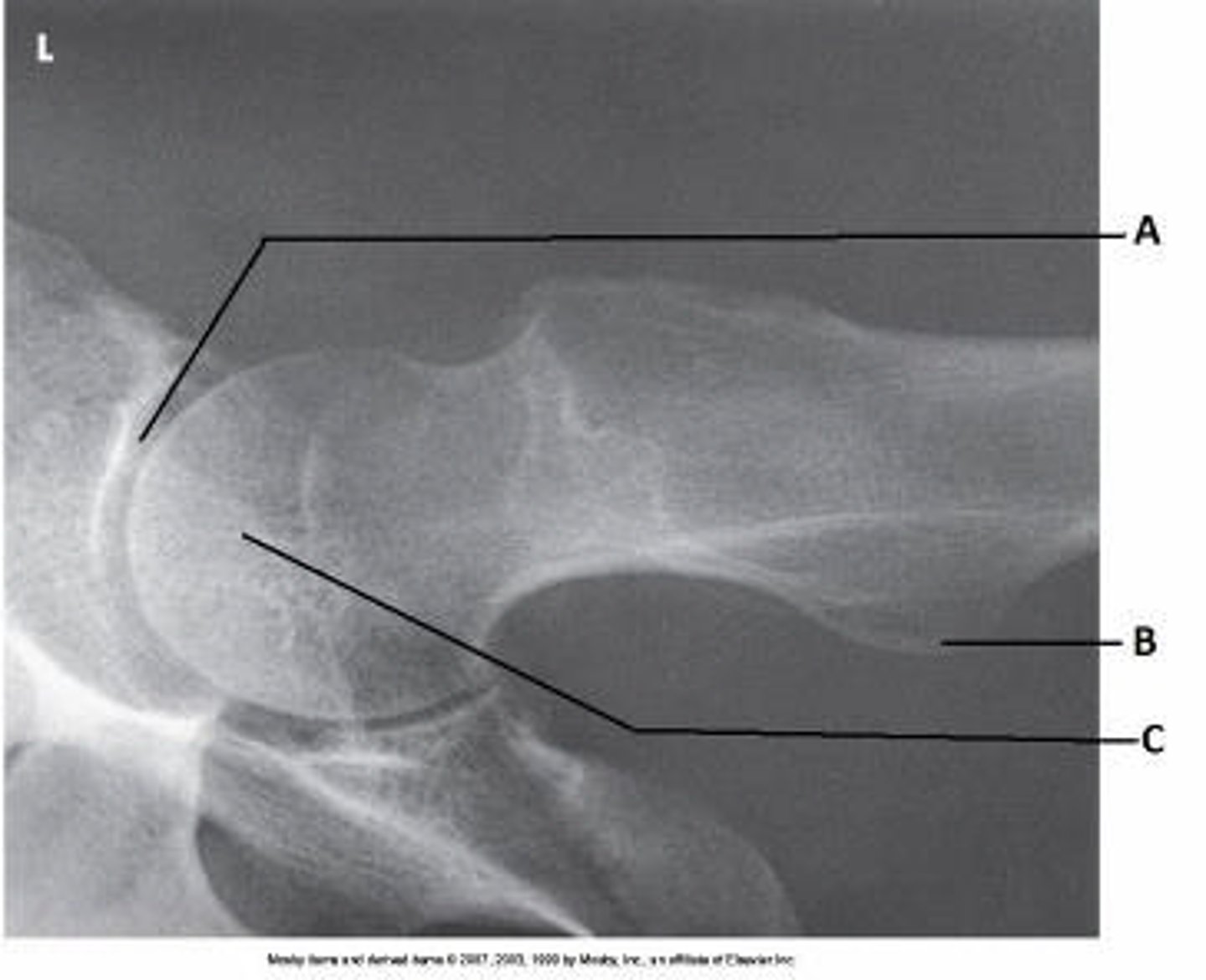
What anatomy is labeled as letter A in the image below?
Acetabulum
AOI: Axiolateral Hip (Cross Table)
- hip
- acetabulum
- head
- neck
-trochanters of femur
Foot/Leg Inversion:
- AP Femur (Proximal)
- AP Pelvis
- AP Hip
- Axiolateral Hip
No Foot/Leg Inversion:
- AP Femur (Distal)
- Lateral Femur
- AP Oblique Hip
- Lateral Hip
AOI: AP Femur (Proximal/Distal)
- femur
- both joints
AOI: Lateral Femur (Proximal/Distal)
- 3/4 of femur
- adjacent joint
AOI: AP Pelvis
- pelvis
- head
- neck
- proximal 1/3 of femur
AOI: AP Hip
- head
- neck
- trochanters
- proximal 1/3 of femur
AOI: AP Oblique Hip (Modified Cleaves)
- oblique projection of hip
- head
- neck
- trochanter
AOI: Lateral Hip (Lauenstein Method)
- lateral projection of hip
- acetabulum
- proximal femur
IA Positioning: AP Femur (Proximal)
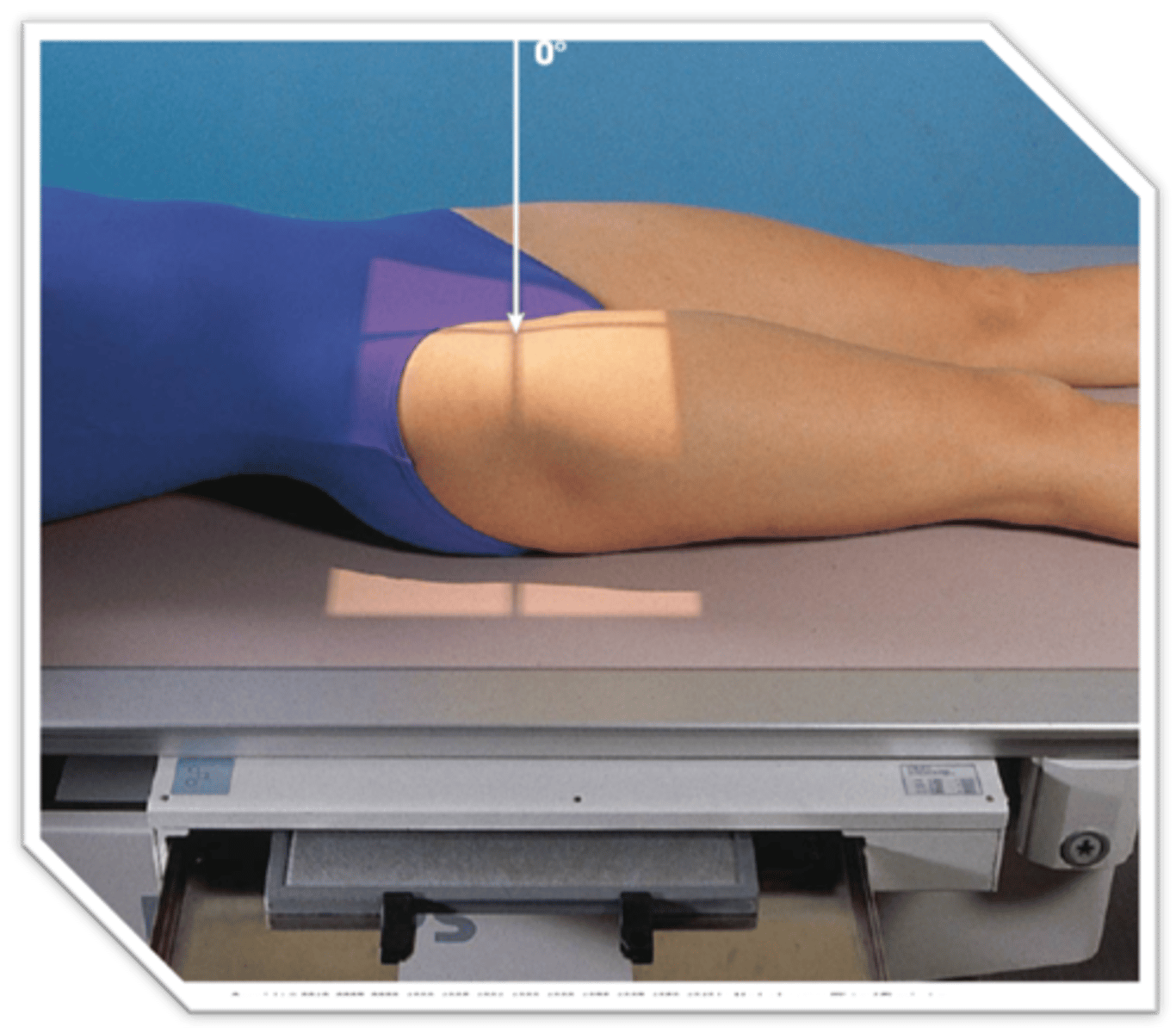
- leg internally rotated (10-15 degrees)
- femoral neck not foreshortened
- only a small amount of lesser trochanter visible beyond medial border
- greater trochanter in profile
IA Positioning: AP Femur (Distal)
- condyles are symmetrical (indicates no rotation)
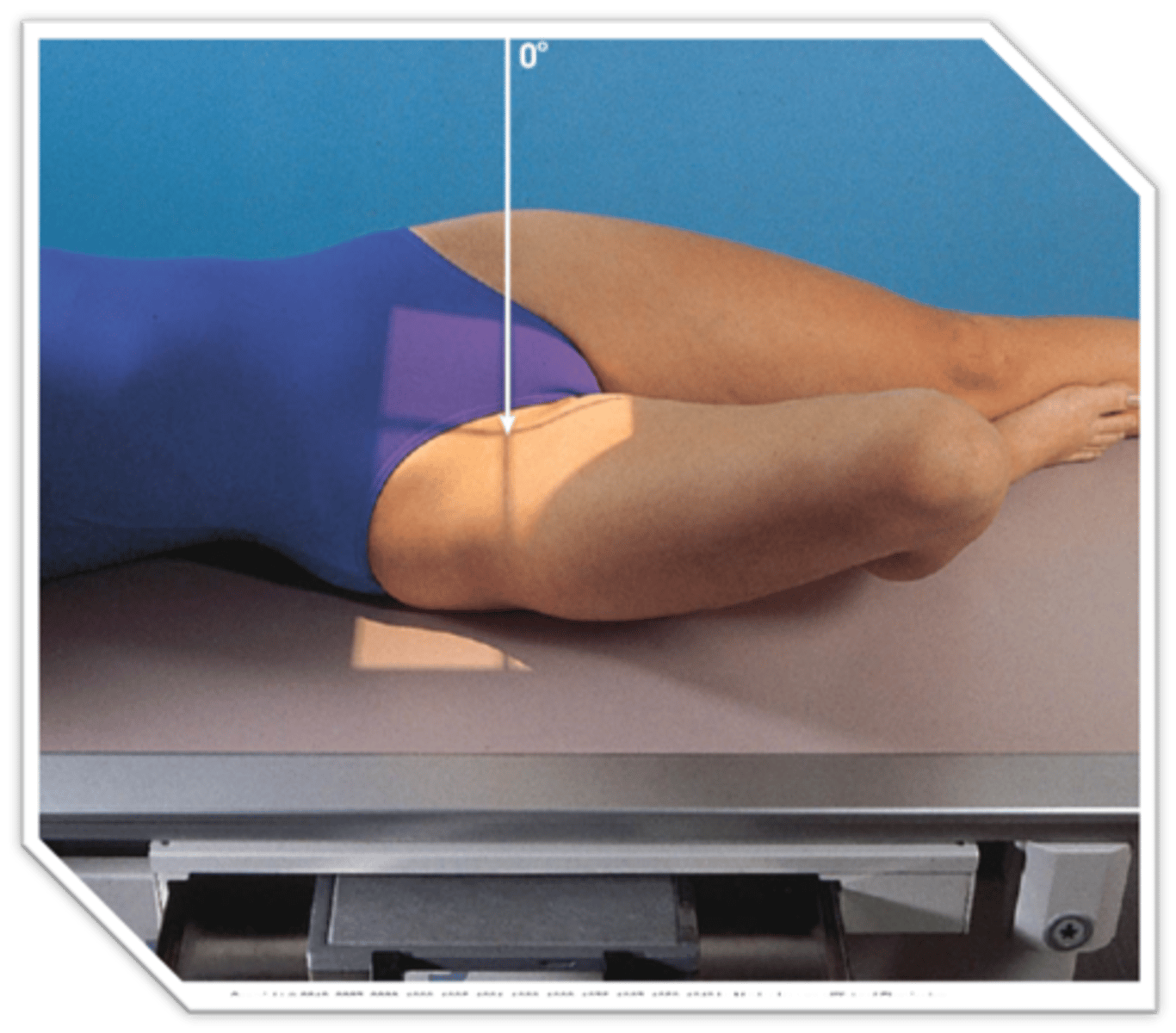
IA Positioning: Lateral Femur (Proximal)
- knee flexed 45 degrees
- greater trochanter super-imposed over femoral neck
- lesser trochanter visible beyond medial border
IA Positioning: Lateral Femur (Distal)
- knee flexed 45 degrees
- anterior/posterior condyles superimposed
- open patellofemoral space
- patella in profile
IA Positioning: AP Pelvis
- leg internally rotated (15-20 degrees)
- femoral neck not foreshortened
- only a small amount of lesser trochanter visible beyond medial border
- greater trochanter in profile
- crests on same level and symmetrical
- symmetrical obturator foramen
- ischial spine seen/not seen (equally on both sides)
- sacrum and coccyx aligned to PS
IA Positioning: AP Hip
- leg internally rotated (15-20 degrees)
- greater trochanter in profile
- femoral neck not foreshortened
- only a small amount of lesser trochanter visible beyond medial border
- 1/3 of proximal femur should be seen
IA Positioning: AP Oblique Hip (Modified Cleaves)
- no rotation of pelvis
- femur approx. 25-45 degree angle from table
- femoral neck is seen without super-imposition of greater trochanter
- lesser trochanter visible beyond medial border
IA Positioning: Lateral Hip (Lauenstein Method)
- femur is parallel to IR
- femoral neck is super-imposed by greater trochanter
IA Positioning: Axiolateral Hip
- femoral neck seen without overlap of the greater trochanter
- ischial tuberosity seen below the femoral head
- soft tissue of unaffected thigh without overlap of AOI
- small amount of lesser trochanter visible on posterior side
- small amount of greater trochanter visible on anterior and posterior portions of femur
Method Name: Axiolateral Hip
Danelius-Miller Method
Method Name: AP Oblique Hip
Modified Cleaves
Method Name: Lateral Hip
Lauenstein Method
What is the purpose of inverting the foot/feet on an AP hip or AP pelvis?
To show the head, neck and proximal femur
To place the femoral neck parallel to the IR
To place the femoral neck perpendicular to the IR
To reduce scatter and improve contrast
To place the femoral neck parallel to the IR
Where should the top of the IR be placed on an AP proximal femur?
Iliac crest
2" below the crest
ASIS
1" superior to the iliac crest
ASIS
What positioning landmark is located at the same level as the pubic symphysis?
Iliac crest
Greater trochanter
Lesser trochanter
Ischial tuberosity
Greater trochanter
What is the method name for the AP oblique hip projection (frog leg)?
Danelius-Miller
Lauenstein
Modified Cleaves
Judet
Modified Cleaves
What is the purpose of using a grid on a hip and pelvis?
To improve contrast and reduce scatter
So you will use less mAs
To increase scatter
To reduce contrast
To improve contrast and reduce scatter
What is the anatomy of interest on a Danelius-Miller?
Distal femur
Pelvis
Ischial tuberosity
Head, neck and proximal femur
Pubis bone
Head, neck and proximal femur
What is the projection on the Danelius-Miller method?
Lateral
AP oblique
Axiolateral
AP
Axiolateral
How much should the lower legs and feet be inverted on an AP pelvis or an AP hip?
10-15 degrees
15-20 degrees
20-30 degrees
25 degrees
15-20 degrees
If an AP oblique hip is contraindicated, what projection should be done instead?
Lateral hip
Modified Cleaves
Axiolateral (Danelius-Miller)
Lauenstein
Axiolateral (Danelius-Miller)
Where should you place the bottom of the IR for a distal lateral femur?
At the knee joint
2" above the popliteal line
At the popliteal line
2" below the popliteal line
2" below the popliteal line
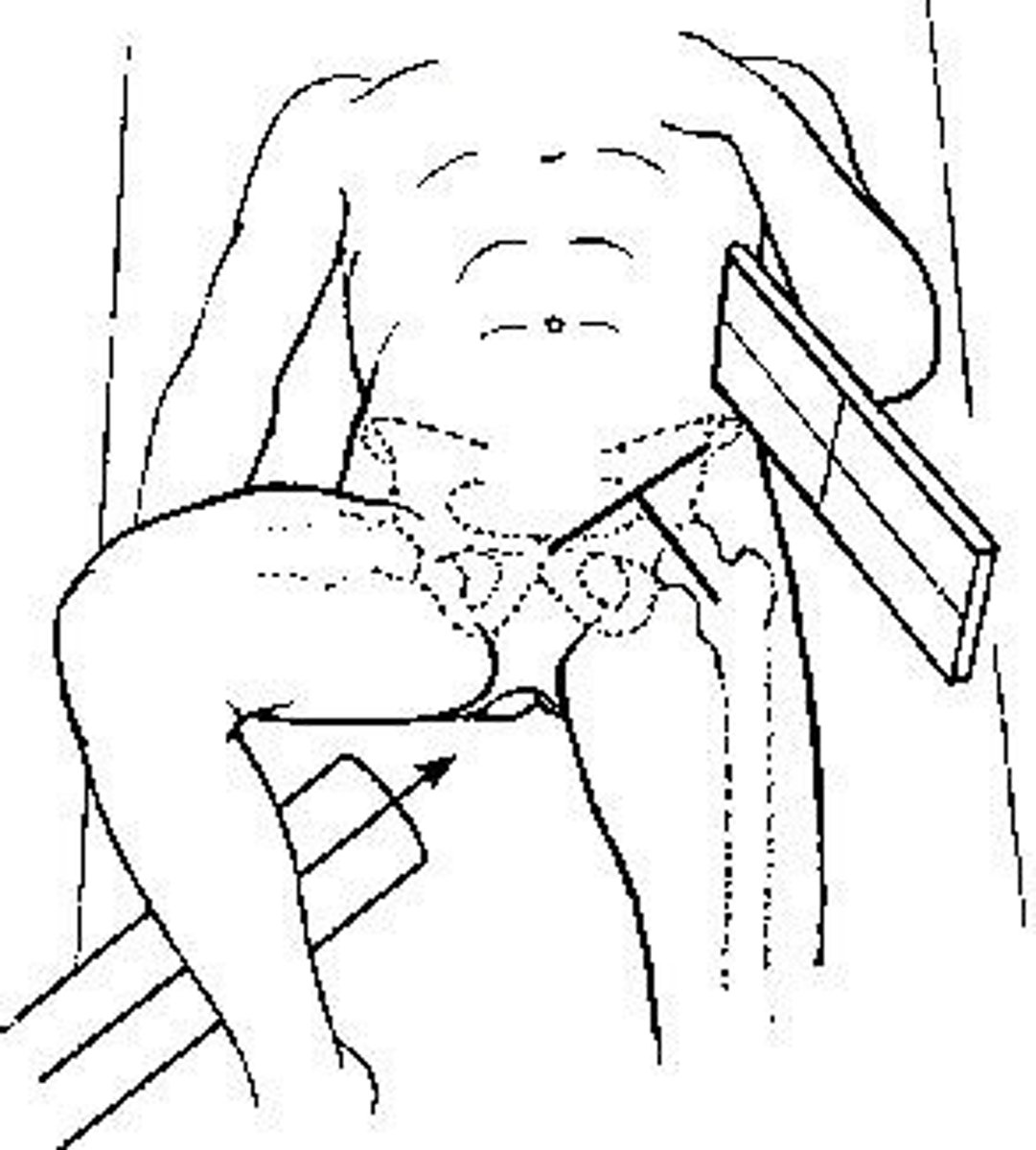
On an axiolateral "cross-table" hip, the central ray should be __________ to the IR and the neck of the femur.
Parallel
Perpendicular
15-30 degree medial angle
20-40 degree medial angle
Perpendicular
What is the projection on the Lauenstein method of the hip?
AP oblique
AP
Axiolateral
Lateral
Lateral
For the Lauenstein method, the femur should be positioned ____________ to the IR.
Perpendicular
Parallel
Obliqued
Horizontal
Parallel
Where is the top of the IR placed on an AP pelvis?
2" superior to the crest
At the pubic symphysis
1 1/2" superior to the crest
At the crest
1 1/2" superior to the crest
What is the position of the femur on a Modified Cleaves projection?
Lateral
AP
25-45 degree angle from table/IR
Obliqued 75 degrees
25-45 degree angle from table/IR
What should be included in it's entirety (in addition to the AOI) on a post-surgery hip exam?
Any hardware or prosthesis
The entire femur
Both hips for comparison
The entire pelvis
Any hardware or prosthesis
What is the routine for a trauma hip?
AP pelvis or hip and modified Cleaves
AP pelvis or hip and Lauenstein
PA pelvis or hip and modified Cleaves
AP pelvis or hip and axiolateral hip
AP pelvis or hip and axiolateral hip
In localizing the femoral neck a line is first drawn from the _________ to the superior pubic symphysis.
Top of the crest
ASIS
Greater trochanter
Lesser trochanter
ASIS
In localizing the femoral neck, the second line is drawn from 1" inferior to the _____________ to the midpoint of the first line.
Top of the crest
ASIS
Greater trochanter
Lesser trochanter
Greater trochanter
Where should the bottom of the IR be placed for an AP distal femur?
At the popliteal line
1" above the popliteal line
2" below the popliteal line
At the level of the apex of the patella
2" below the popliteal line
Using the localization method, after the first and second lines are drawn, then center ____________ below the intersection of the localization lines for the femoral neck.
1"
1 1/2"
2 1/2"
3"
2 1/2"
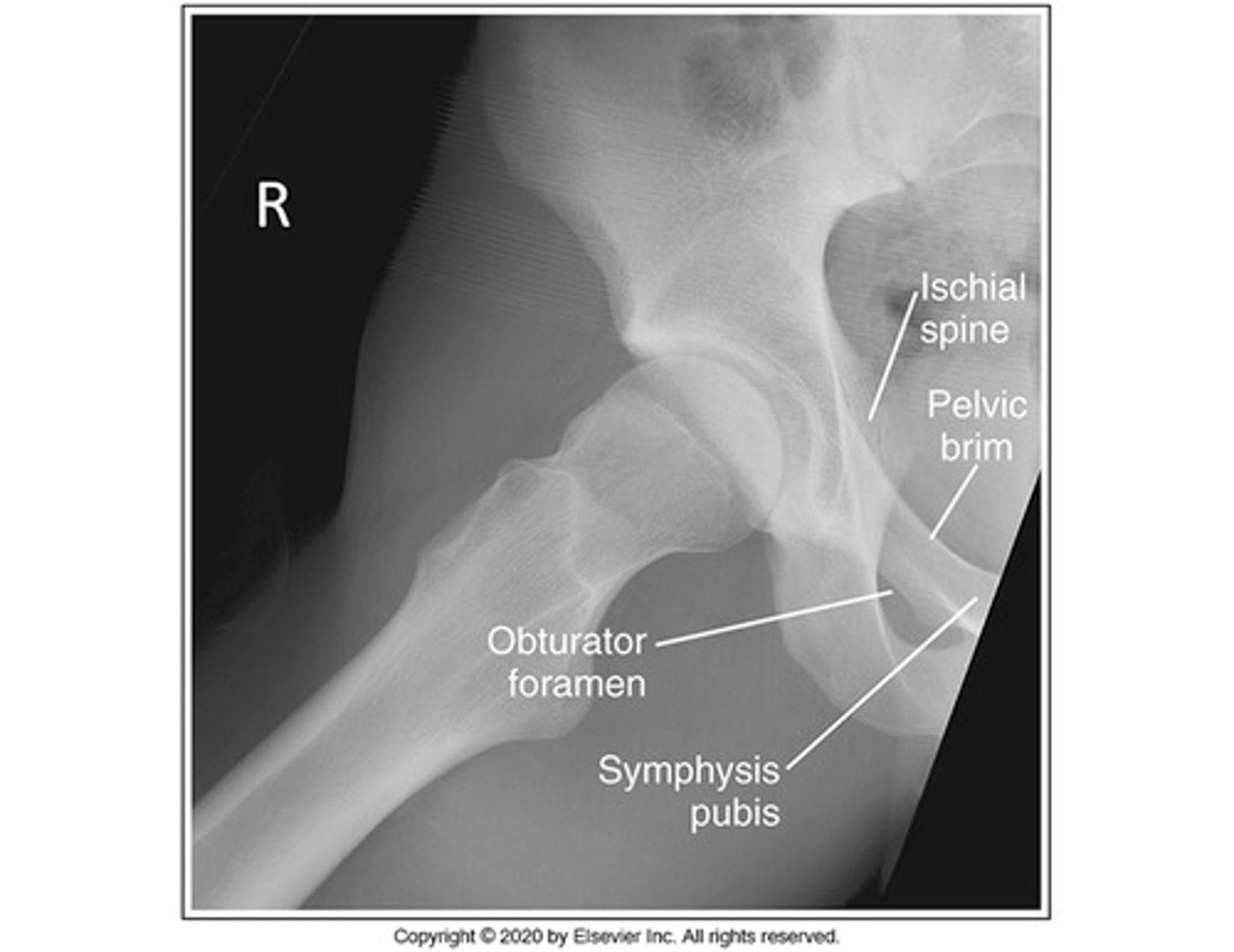
Identify the projection:
AP Hip
Axiolateral Hip (Danelius-Miller)
AP oblique hip (Modified Cleaves)
Lateral hip (Lauenstein)
AP oblique hip (Modified Cleaves)
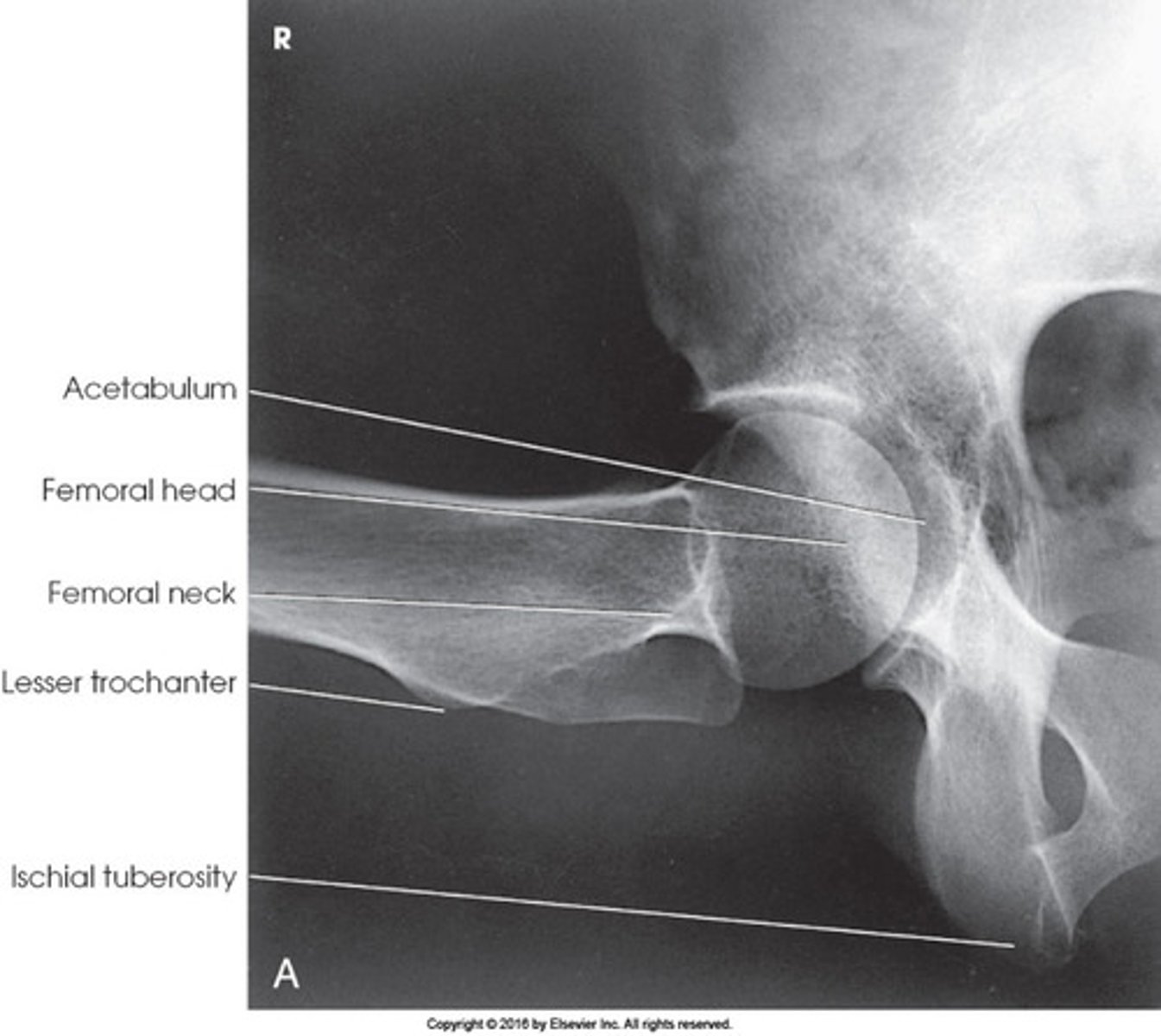
Identify the projection:
AP Hip
Axiolateral Hip (Danelius-Miller)
AP oblique hip (Modified Cleaves)
Lateral hip (Lauenstein)
Lateral Hip (Lauenstein)
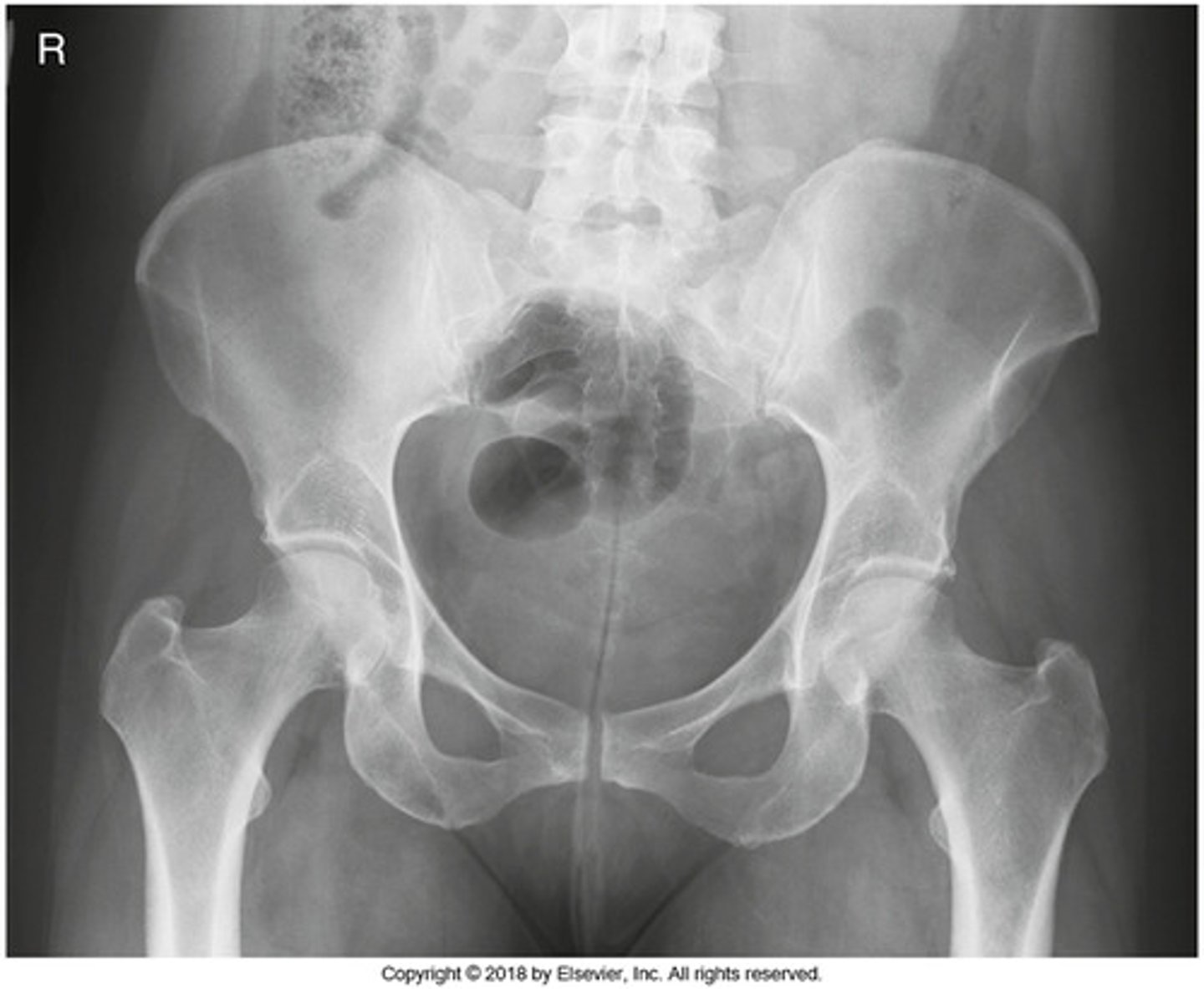
Identify the projection:
AP hip
AP oblique hip
AP pelvis
Lateral hip
AP Pelvis
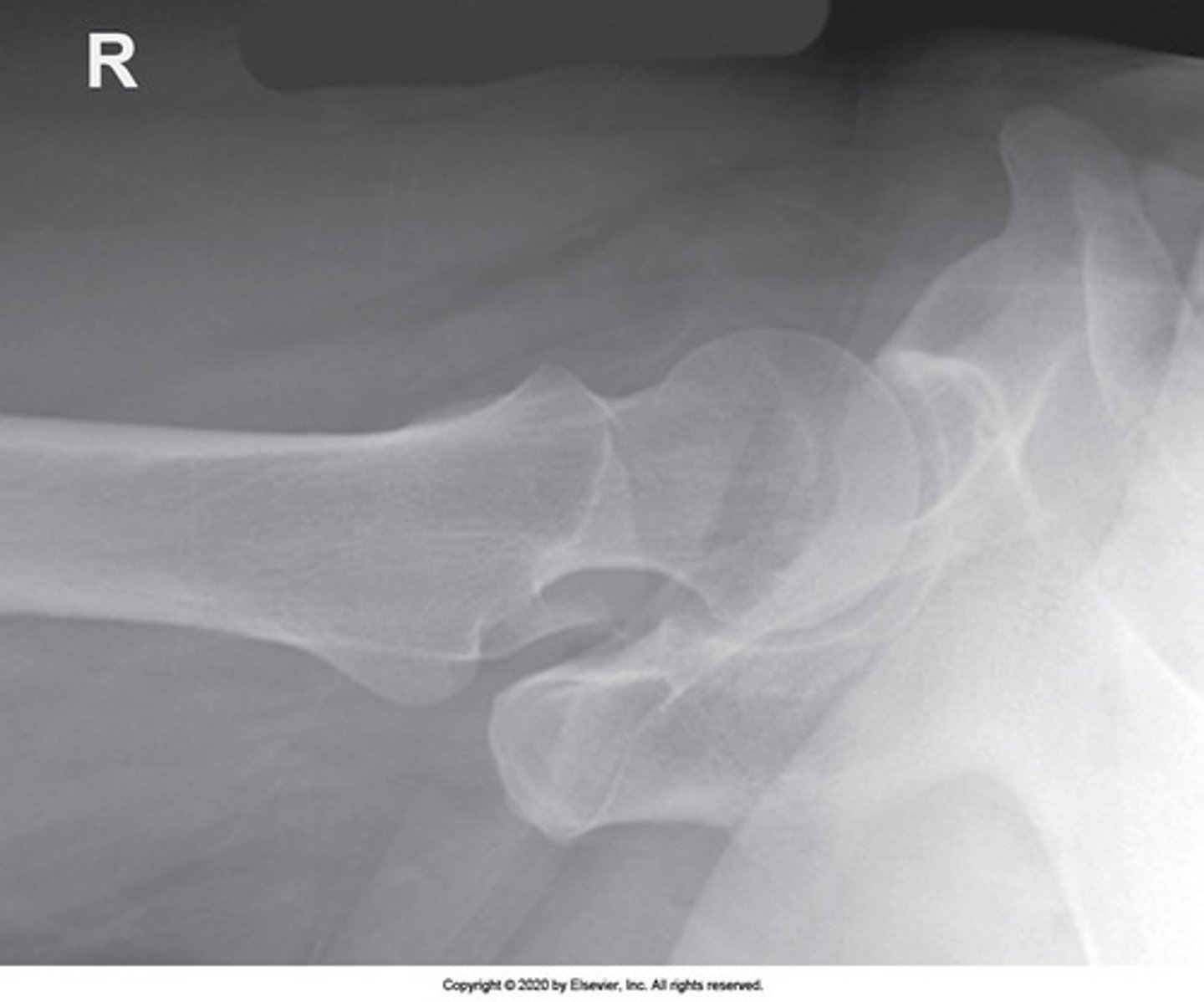
Identify the projection:
AP hip
AP oblique hip
Lateral hip
Axiolateral hip
Axiolateral Hip
For the AP oblique hip (Modified Cleaves) the CR is:
15-20 degrees cephalic
20-25 degrees caudal
Perpendicular
15 degrees caudal
Perpendicular
The ilia articulate with the sacrum posteriorly at the:
Hip joint
Pubic symphysis
Sacroiliac joints
L5-S1 area
Sacroiliac joints
How many degrees should the foot and lower limb be internally rotated for an AP femur radiograph?
5-10 degrees
15-20 degrees
20-30 degrees
10-15 degrees
10-15 degrees

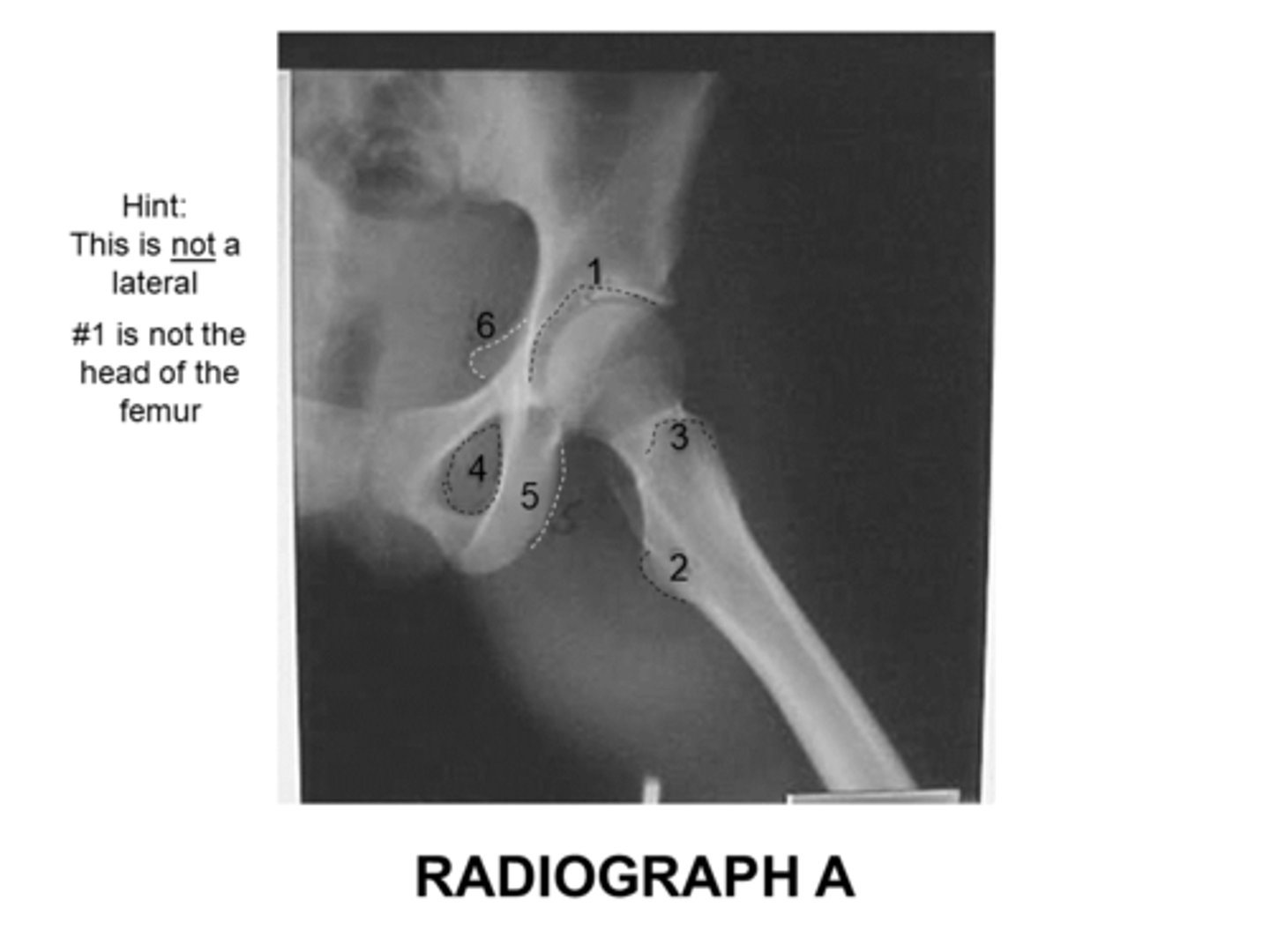
Identify the anatomy marked A:
Pubis bone
Head of the femur
Femoral neck
Ischial tuberosity
Coccyx
Ischial tuberosity
The anatomy marked with #6 is the:
Acetabulum
Lesser trochanter
Obturator foramen
Greater trochanter
Ischial spine
Ischial spine
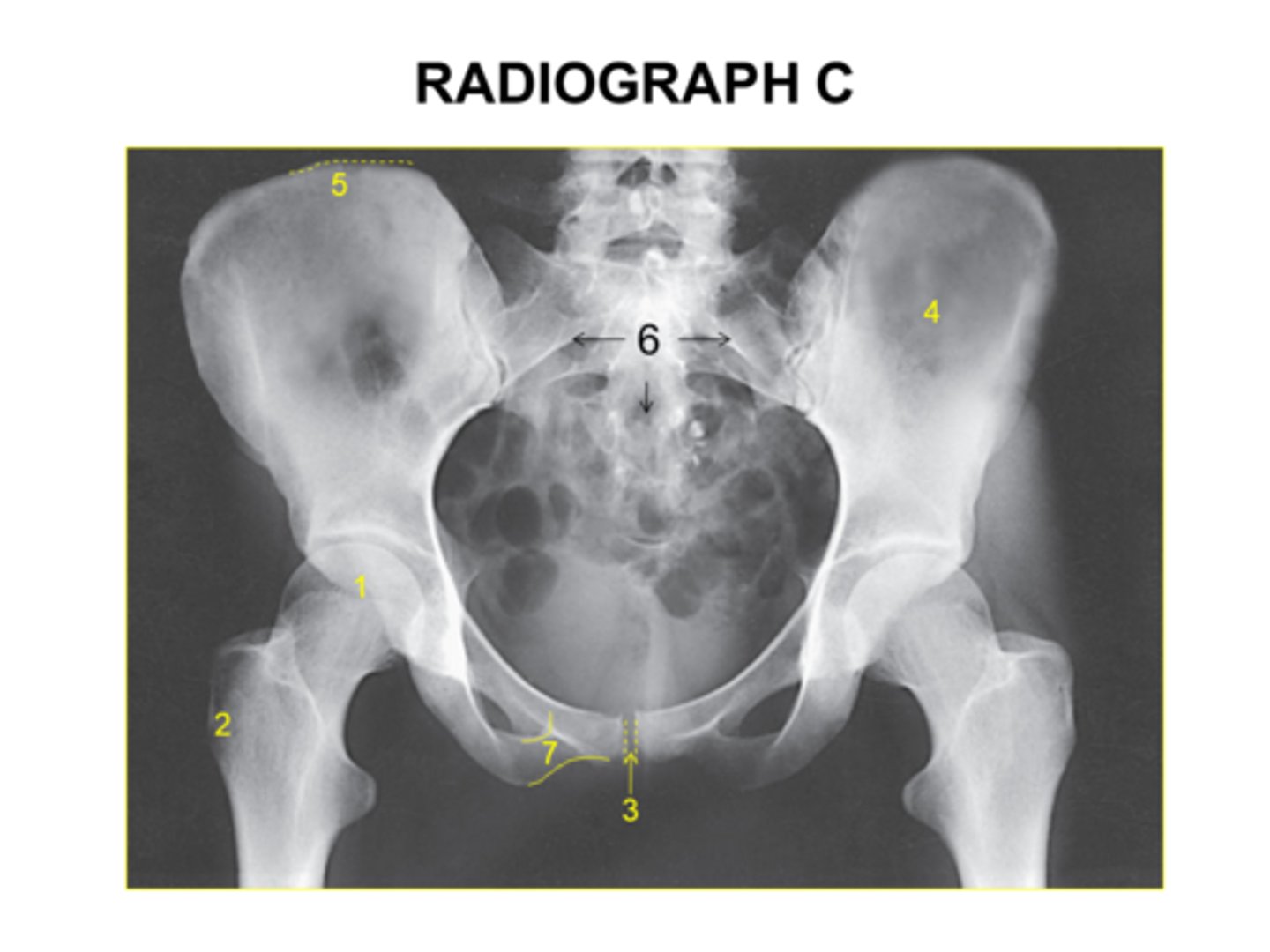
Identify the anatomy marked with #7:
Pubic symphysis
Ischial tuberosity
Pubic bone
ilium
Pubic bone
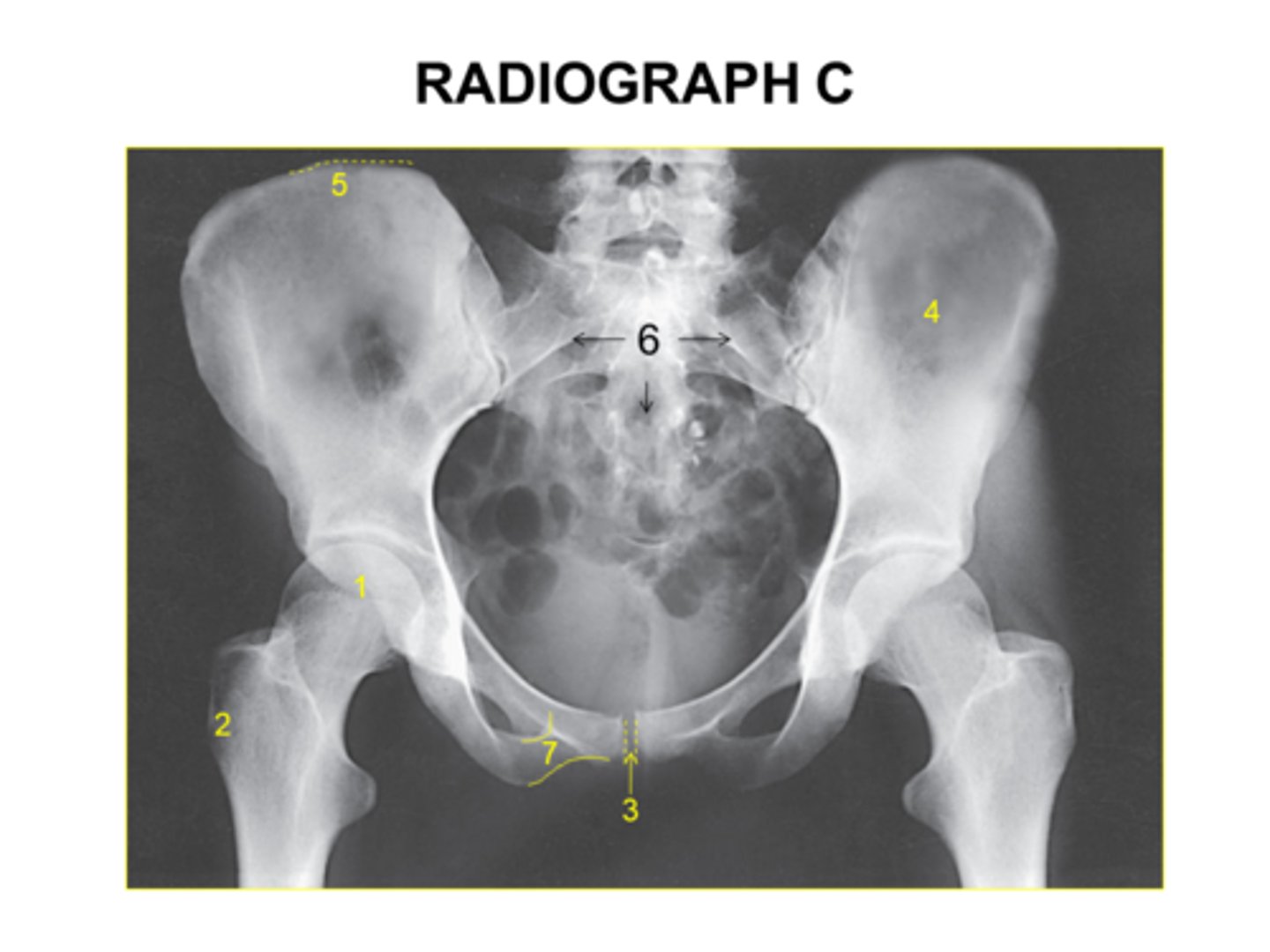
Is this pelvis rotated?
Yes
No
I'm not sure
Yes
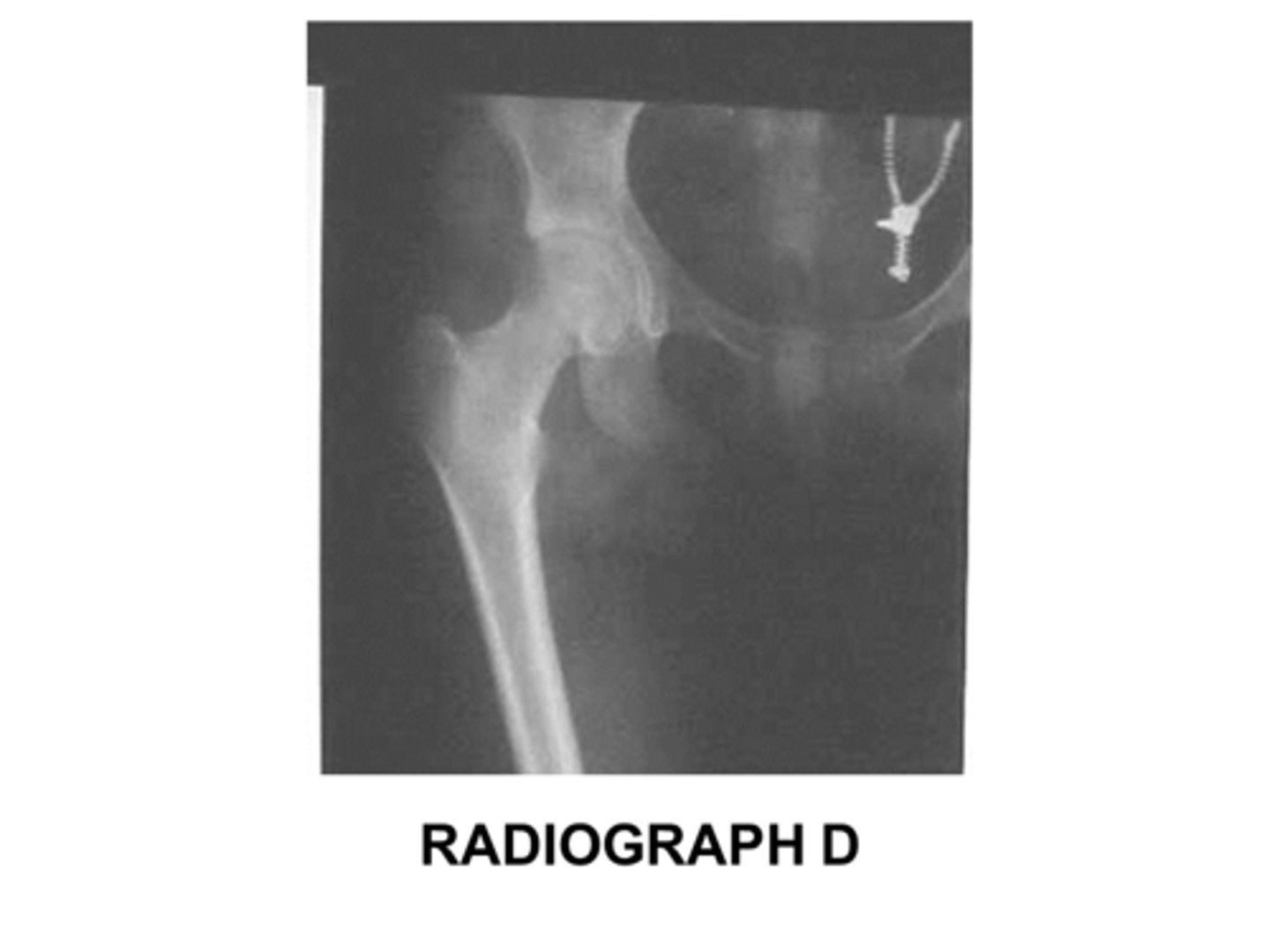
Identify this projection:
AP femur
AP pelvis
AP hip
Modified Cleaves
AP hip
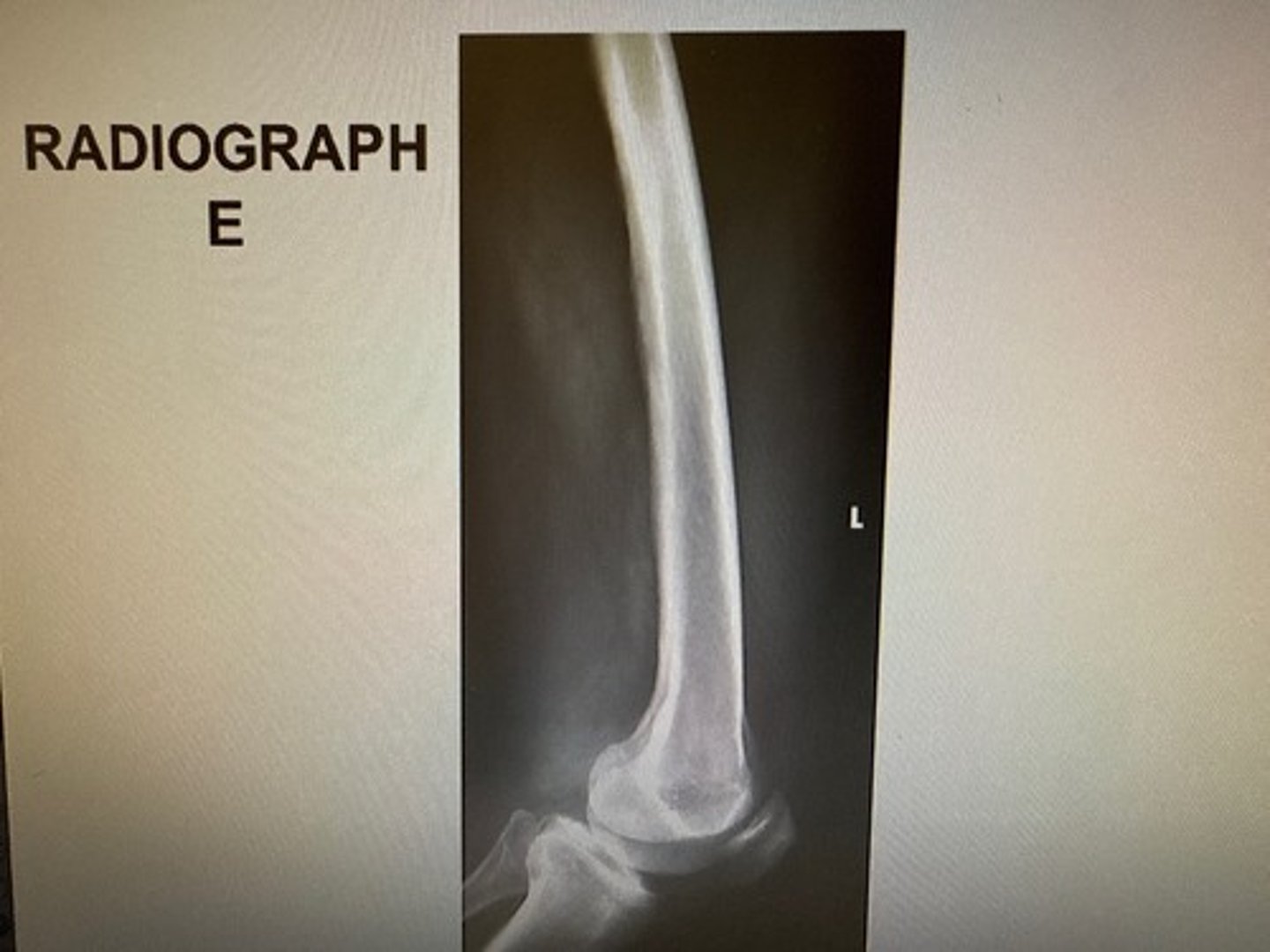
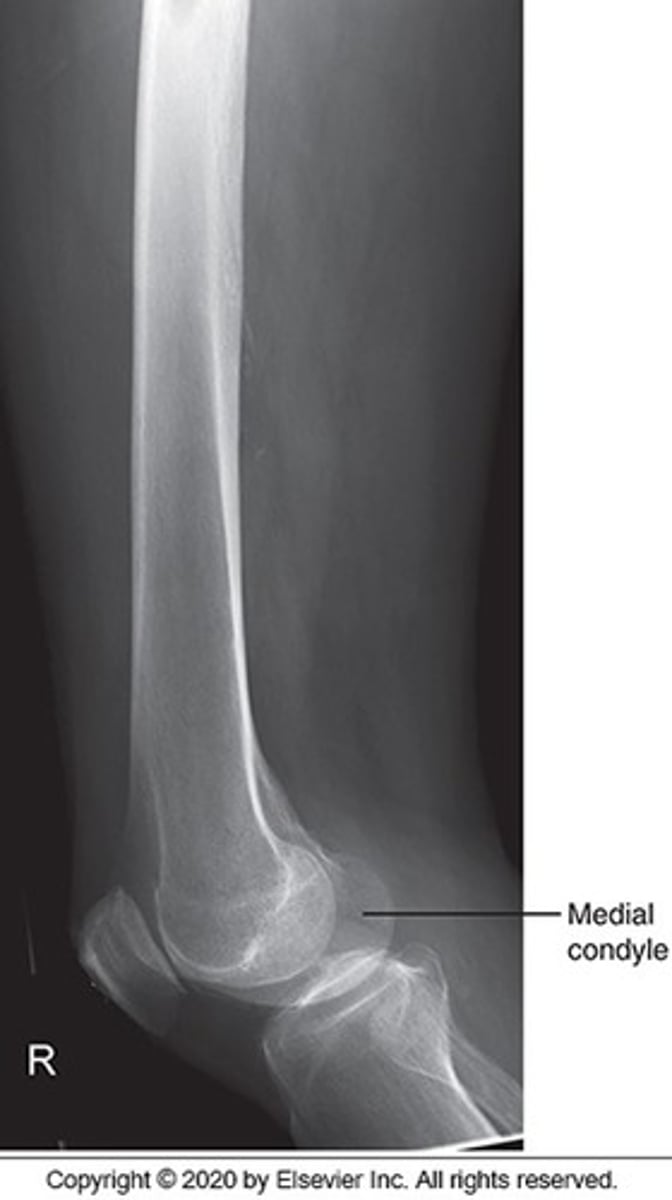
Choose three reasons why the inferior condyles are not SI on this image:
The med condyle is inferior to the lat condyle
Poor positioning
No angle on the CR
Poor centering
The divergence of the beam
The med condyle is inferior to the lat condyle
No angle on the CR
The divergence of the beam
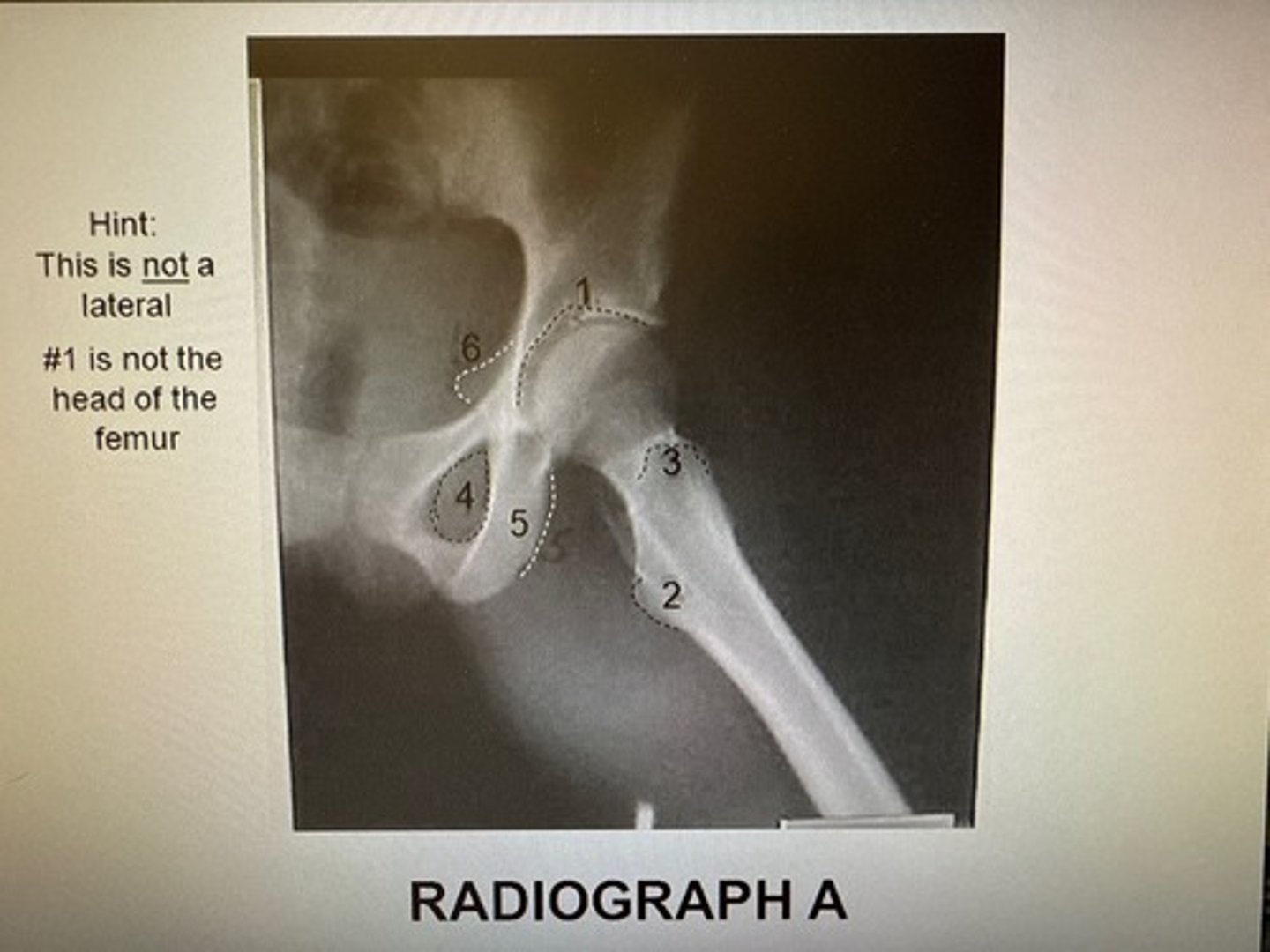
The anatomy marked with #3 is the:
Acetabulum
Lesser trochanter
Obturator foramen
Greater trochanter
Ischial spine
Greater trochanter