exam 1 - learner objectives (dr. moore)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
routes of enteral (_____) administration
in _____
in _____
by _____
by _____ _____
oral
food
water
mouth
oral gavage
routes of parental (_____ _____) administration
_____/topical
_____
_____
intra_____
_____
intra_____
intra_____
intra_____
intra_____
not oral
dermal
inhalation
injections
muscular
subcutaneous
peritoneal
venous
cardiac
nasal
steps in gavage in rodents
measure _____ of the mouth to _____ rib for proper length/depth of insertion
_____
use needle to push back on _____ _____ & rock head back so passage is _____
ensure maximum volume is not _____
corner
last
restraint
hard palate
straight
exceeded
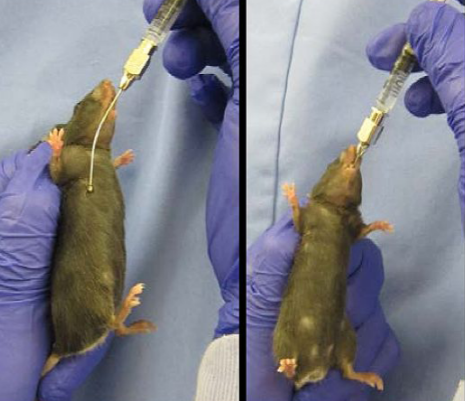
inhalant exposure: whole body vs. nose-only exposure concerns
whole body
inhalants can deposit on _____ & _____
inhalants can be _____ → _____ dose than calculated
nose-only
limits to just the _____ dose
fur
skin
ingested
greater
inhaled
luer-lock pro’s
when using _____ liquids, pressure may build when pushing plunger & needle may _____ _____
luer-lock - the needle is _____ & prevents the needle from being _____ _____
thick
shoot off
screwed
blown off

identifying needle diameter & needle size ranges
lower number = _____ gauge (diameter)
higher number = _____ gauge (diameter)
needle sizes for animals:
rodents = _____
rabbits = _____
larger
smaller
23-27
23
why to not reuse needles
tissue _____
_____
_____
trauma
contamination
pain
reasons why commercially manufactured drugs are better than non-pharmaceutical grade agents
_____
_____
_____-_____ balance
_____ storage/shelf-life
_____ of pyrogens
purity
sterility
acid-base
longer
absence
rodent injection sites
intra_____ = _____ muscles of the _____ limbs
_____ = over the _____
intra_____ = ventral _____, near the midline of the _____ portion of the _____ two quadrants
intra_____ = _____ _____ vein
muscular
thigh
hind
subcutaneous
back
peritoneal
abdomen
upper
lower
venous
lateral tail
rabbit injection sites
intra_____ = _____ muscles of the _____ limbs & _____ muscles that parallel the spine
_____ = same as rodents
intra_____ = same as rodents
intra_____ = _____ _____ vein
muscular
thick
hind
epaxial
subcutaneous
peritoneal
venous
marginal ear
when giving injections, fluids need to be _____ to near _____ temperature to prevent _____
warmed
body
hypothermia
blood collection volumes
mouse ≤ _____
rat ≤ _____
hamster ≤ _____
rabbit ≤ _____
0.3
3.0
1.0
30
using a _____ for blood collection in rodents is usually not successful due to the _____ _____, which may cause the vessel to _____, preventing blood collection
vacutainer
negative pressure
collapse
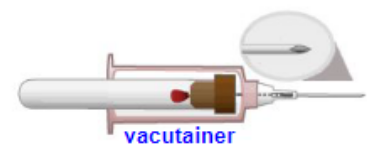
blood collection vessel locations
tail - _____ _____ vein
hind leg - lateral & medial _____ veins; guinea pigs - _____ vein
head/face - _____/_____ vein
eye - _____ orbital
heart - _____ collection
rabbit - _____ ear vein; front leg - _____ vein; hind leg - _____ _____ vein
lateral tail
saphenous
metatarsal
submandibular/facial
retro
cardiac
marginal
cephalic
lateral saphenous
promoting vasodilation
heat _____
_____ light bulb
heating _____
_____ in warm water
heated, water-filled _____ _____
lamp
incandescent
pad
immersion
exam glove
indwelling catheter maintenance
to prevent blockage from a _____
_____ formation
to prevent _____ _____
to prevent _____
clot
thrombus
bacterial contamination
embolus
surgical scrub procedure at skin incision
_____ alternating scrubs of _____ solution & alcohol
start at the _____ & spiral outward
three
betadyne
center

laparotomy: surgical procedure incising the _____
_____ site
surgical _____
_____ skin with a _____ - NOT _____; will crush the cells & _____ healing
use _____-_____ forceps to handle skin & abdominal muscles
less _____
less _____ of tissues
abdomen
clip
scrub
incise
scalpel
scissors
delay
rat-tooth
trauma
crushing

thoracotomy: surgical procedure incising the _____ cavity (heart, lungs, & other organs)
insert _____ tube
_____ site
surgical _____
use _____-_____ forceps to handle skin & abdominal muscles
less _____
less _____ of tissues
cut _____ muscles (between the _____)
** loss of _____ pressure will _____ the lungs; need to manually _____ or mechanical _____
thoracic
endotracheal
clip
scrub
rat-tooth
trauma
crushing
intercostal
ribs
negative
collapse
inflate
ventilator

instrument proper use
skin & muscle
use _____-_____ forceps to prevent excessive _____ of cells
use _____ to cut - less trauma
_____ crush cells & delay healing
hemostats
used for _____ dissection of _____ tissues & for _____ off vessels
rat-tooth
crushing
scalpel
scissors
blunt
subcutaneous
clamping
swedged needles: have the suture contained _____ the end of the needle
does not stick out _____ the cross-section of the needle
less _____
less _____ to tissues
within
beyond
drag
trauma
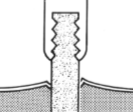
non-swedged needles: have an _____ & suture must be _____ _____ & thus a _____ diameter than the needle itself
_____/friction/_____ to the tissues - delays healing
eyelet
looped through
wider
dragging
trauma
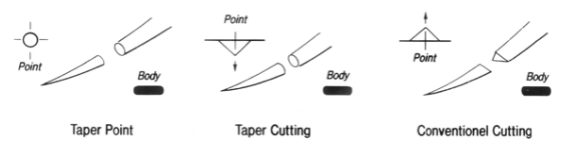
point needles
taper
used for _____ organs
cutting
used for _____
facilitate passage of the needle through _____ tissue
can tear _____ _____ tissues
hollow
skin
dense
less dense
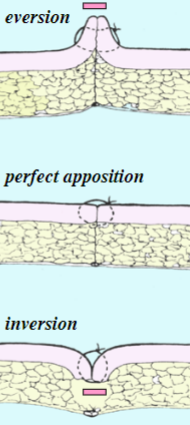
wound margin
perfect apposition
allows for _____ healing with _____ scar tissue
eversion or inversion
results in _____
_____ tissue is not as strong
faster
minimal
scarring
scar
order of tissue tensile strength
_____ > _____ fascia > _____ > _____ fat
skin
muscle
muscle
subcutaneous
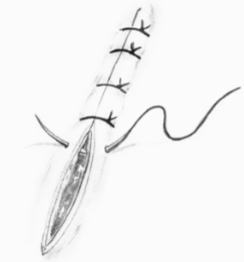
simple interrupted suture
advantages
good _____
loss of one suture has _____ effect
disadvantages
takes _____ to do
may _____ tissue if tension is present
apposition
minimal
longer
tear

horizontal mattress suture
advantages
good for high _____ areas
loss of one suture has _____ effect
disadvantages
takes _____ to do
causes _____
may _____ blood flow, effecting healing
tension
minimal
longer
eversion
strangulate
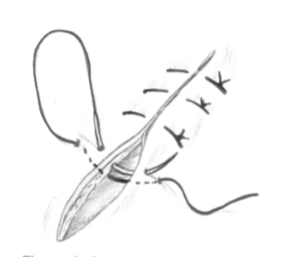
vertical mattress suture
advantages
good for high _____ areas
loss of suture has _____ effect
not as likely to restrict _____ _____
disadvantages
takes _____ to do
causes _____
tension
minimal
blood flow
longer
eversion

simple continuous suture
advantages
very _____
good _____
disadvantages
may _____ tissue if tension is present
_____ of suture allows entire wound to _____ open
fast
apposition
tear
breaking
gape
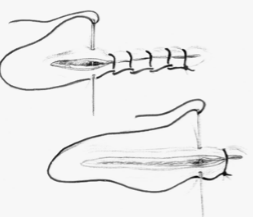
continuous interlocking suture
advantages
very _____
good for _____ relief
disadvantages
_____ of suture allows entire wound to _____ open
fast
tension
breaking
gape
suture removal
_____ suture
_____ portion that was underneath the _____, then remove
prevents entry & tracking of _____/_____ under the skin
elevate
cut
skin
bacteria/contaminants
types of anesthesia
_____ - loss of sensation in a limited body area
_____ - loss of sensation over a large area
_____ - loss of consciousness & loss of sensation
local
regional
general
factors affecting anesthesia
size
_____
gender
_____ _____
fear & activity
_____
concurrent disease (basal metabolic rate)
fever - _____ BMR
toxemia - _____ BMR
liver disease - _____ BMR
shock - _____ BMR
Vit. C deficiency in guinea pigs - _____ BMR
hyperthyroidism - _____ BMR
thyroidectomized - _____ BMR
age
recent feeding
tranquilizers
increases
decreases
decreases
decreases
decreases
increases
decreases
anesthesia delivery
_____/topical
_____ (IM, IV, IP, SC)
_____
dermal
injection
inhalant
body systems affected by anesthetic emergencies
_____
_____
cardiac
respiratory
stages & planes of anesthesia
stage I - rising _____ threshold - sensory depression
stage II - _____ phase - involuntary activity
stage III - surgical _____ - plane _____ (no reflexes - this is maintained)
stage IV - _____ paralysis - heart continues beating, can progress to death
pain
excitement
anesthesia
3
respiratory
assessing adequate anesthesia
_____ tone - easily opens
_____ reflex - tongue does not retract = adequate
_____ reflex (toe pinch) - no reaction = adequate
_____ reflex = touch corner of the eye near nose, no blink = adequate
_____ reflex - touch cornea, no blink = adequate
jaw
swallowing
withdrawal
palpebral
corneal
selecting ideal anesthesia method
_____ death without signs of _____
_____ time of loss of consciousness
reliable, reproducible
_____ of animals
_____ to personnel
_____ undesirable physiological effects
_____ environmental impact
_____, _____ to use equipment
rapid
distress
minimum
number
safety
minimum
minimum
simple, easy
easily recognized variables
_____
environmental _____
humidity
_____
_____ cycle
water
noise
diet
temperature
ventilation
light
not easily recognized variables
animal _____
_____ disease
environmental _____
_____ transmission
subtle _____ stressors
_____ reactions
genetics
latent
contaminants
microbial
behavioral
idiosyncratic
humidity effects
heat _____
low - _____ in rats & mice
low - increased _____
low - affects _____ _____ in lungs
stroke
ringtail
dust
mucociliary escalator
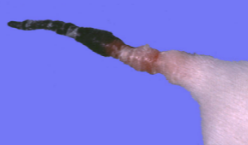
temperature effects
heat _____
_____
stroke
chilling
ventilation effects
removal of _____ gases
carbon dioxide
_____
positive pressure
protects _____ occupants from contaminants in common hallway
negative pressure
prevents escape of _____ agents from animal room into common hallway
waste
ammonia
room
disease
noise effects
induces _____
hearing _____/_____
audiogenic _____
stress
damage/deafness
seizures
light effects
retinal _____
_____ formation
altered _____ _____
damage
cataracts
circadian rhythm
intentional exposures
anesthetics
_____
tranquilizers
_____ treatments
_____
analgesics
parasite
anitbiotics
unintentional exposures
air
_____ supply
_____
bedding
_____
equipment
water
feed
caging
overt disease: clinical signs are _____ apparent
readily
latent disease: animal appears _____, but changes in _____ status, clinical signs are _____ obvious
healthy
immune
not
impact of disease in a facility
introduction of _____
_____ of animals
_____ impact
_____-wide impact
variability
loss
economic
facility