Biocore 485 Unit 1 - Endocrinology
1/176
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
177 Terms
homeostasis
internal constancy and the physiological regulatory systems that automatically make adjustments to maintain it
hyperthyroidism (grave’s disease)
disease with symptoms of high temp, perspiration, weight loss, irritability, high blood pressure, and orbitopathy
hypothyroidism (hashimoto’s disease)
disease with symptoms of weight gain, being cold, and low energy
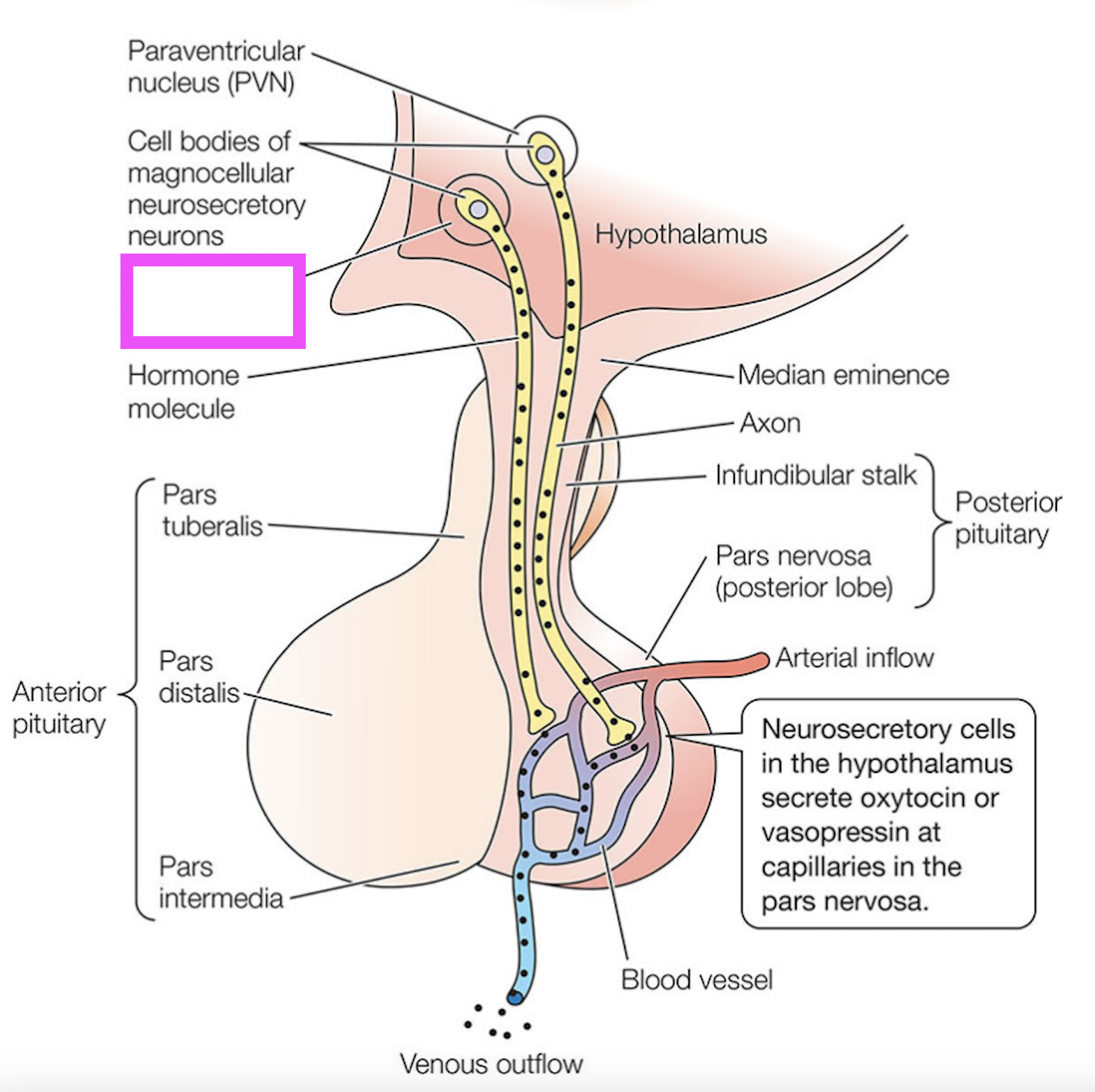
supraoptic nucleus
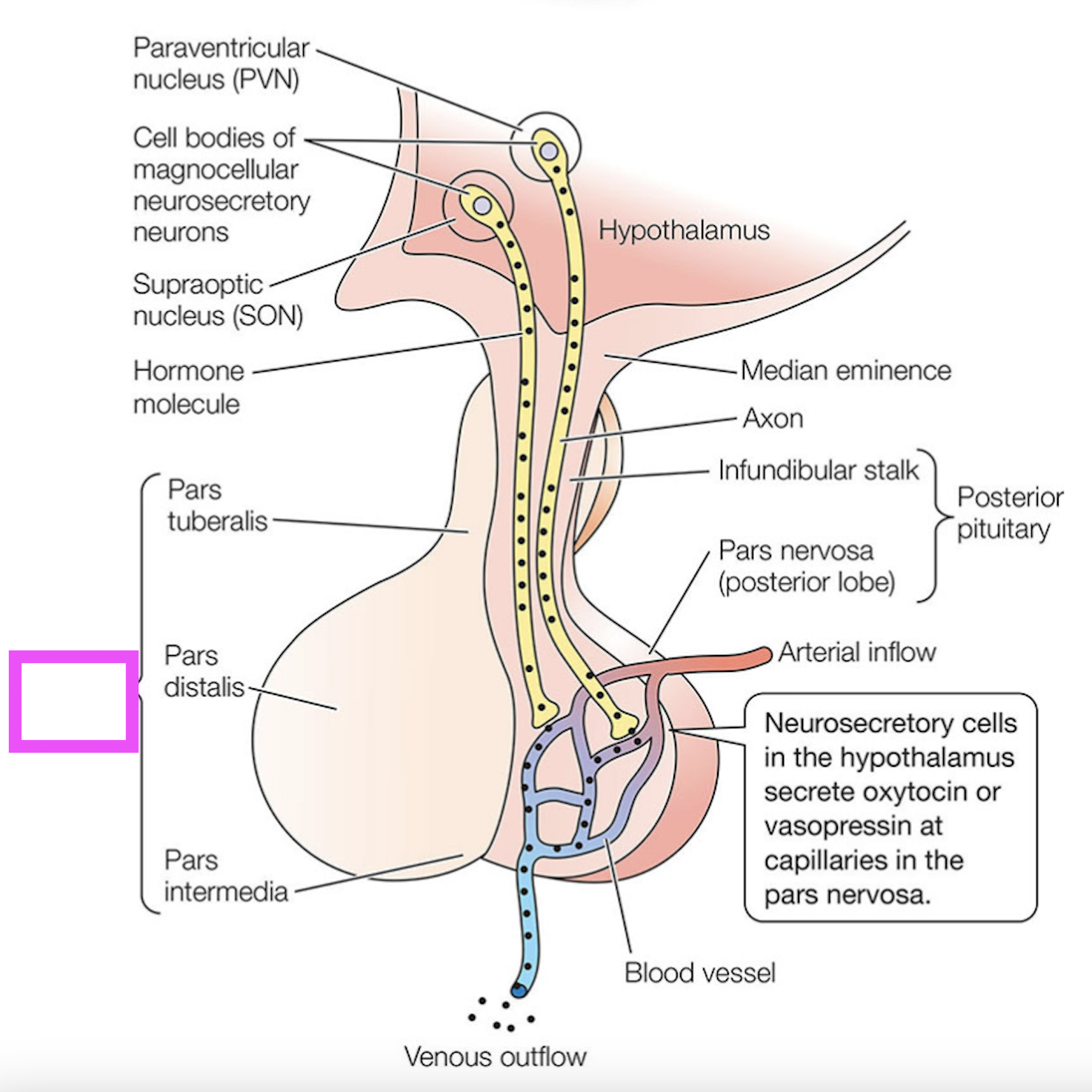
neurosecretory cell that synthesizes vasopressin for release in the posterior pituitary
paraventricular nucleus
neurosecretory cell that synthesizes oxytocin for release in the posterior pituitary
alpha cells
cells in islets of the pancreas that produce glucagon
hypoglycemic effect
a decrease in blood glucose; i.e. caused by insulin
hyperglycemic effect
an increase in blood glucose; i.e. caused by glucagon
alveoli
hollow glandular structures that produce milk
stimulates myometrium to form gap junctions and receptors for oxytocin
two roles of estrogen in pregnancy
placenta
organ that allows juxtaposition of maternal + fetal bloodstreams (but blood does not mix)
upper oviduct
fertilization occurs in the _____
implantation
entry of the early embryo in the matrix of the endometrium
nitric oxide (NO)
immediate mediator of an erection that causes dilation of blood vessels in a positive feedback loop
prostate, bulbourethral, seminal
semen contains sperm and secretions from the _____ gland, _____ gland, and _____ vesicles
GnRH
puberty starts when _____-secreting cells become active
capacitation
final maturing of sperm in the reproductive tract to make them capable of rapid forward swimming and fertilization
luteinizing hormone (LH)
secretion of testosterone by leydig cells is stimulated by _____
FSH, testosterone
production of sperm by sertoli cells is stimulated by ____ and ____
corpus luteum
without a functional _____, concentrations of progesterone, estrogen, and inhibin decrease to low levels
androgen
generally male sex hormones, like testosterone; produced by theca cells and then converted into estrogen by granulosa cells
granulosa
FSH binds to _____ cells and stimulates production of aromatase so androgens can be converted into estrogen by aromatization
early
during the _____ follicular phase, estrogen exerts negative feedback on FSH + LH
late
during ____ follicular phase, estrogen causes increased LH, FSH, and GnRH
estrogen
hormone that stimulates growth of the endometrium and stimulates endometrial cells to produce receptors for progesterone
ovulation
blood concentration of LH and FSH peak at _____
theca cells
initial target of LH in women, that stimulates them to produce androgens
atresia
when all other follicles besides the dominant one undergo programmed cell death
zona pellucida
the noncellular layer of glycoproteins the primary oocyte surrounds itself with
epinephrine, norepinephrine, CRH, vasopressin, ACTH
hormones released with stress response
glucocorticoids
during stress response, ____ inhibit the release of FSH, LH, TSH, and GH from the anterior pituitary
photoperiod
number of hours of sunlight in a 24 hour cycle; when increased it signals some animals to reproduce
primordial follicle
each primary oocyte that become enclosed in a single layer of somatic cells
folliculogenesis
when a subset of primordial follicles is recruited to mature each cycle
synergism
one hormone amplifying the effect of the other
permisiveness
when the presence of one hormone is required for the other hormone to exert its full effect on the target tissue
antagonism
when one hormone opposes the action of another; eg. epinephrine + glucagon; dopamine + prolactin
parvocellular neuron
neurons in the hypothalamus that are small and secrete releasing and inhibiting hormones that are carried in the portal to the anterior pituitary; for example releases TRH
axis
two or more hormone secreting tissues that together form a hierarchical control system
direct acting hormone
group of anterior pituitary hormones that exert their principal effects on nonendocrine tissues; eg. GH, prolactin,
tropic hormone
group of hormones secreted by the anterior pituitary that control other endocrine tissues located throughout the body; eg. TSH, ACTH, LH, FSH
peptide
all hormones synthesized and secreted by the anterior pituitary are ____ hormones
magnocellular neurons
the neurons that synthesize vasopressin and oxytocin in the hypothalamus and secrete them in the pars nervosa/posterior pituitary; the paraventricular and supraoptic neurons
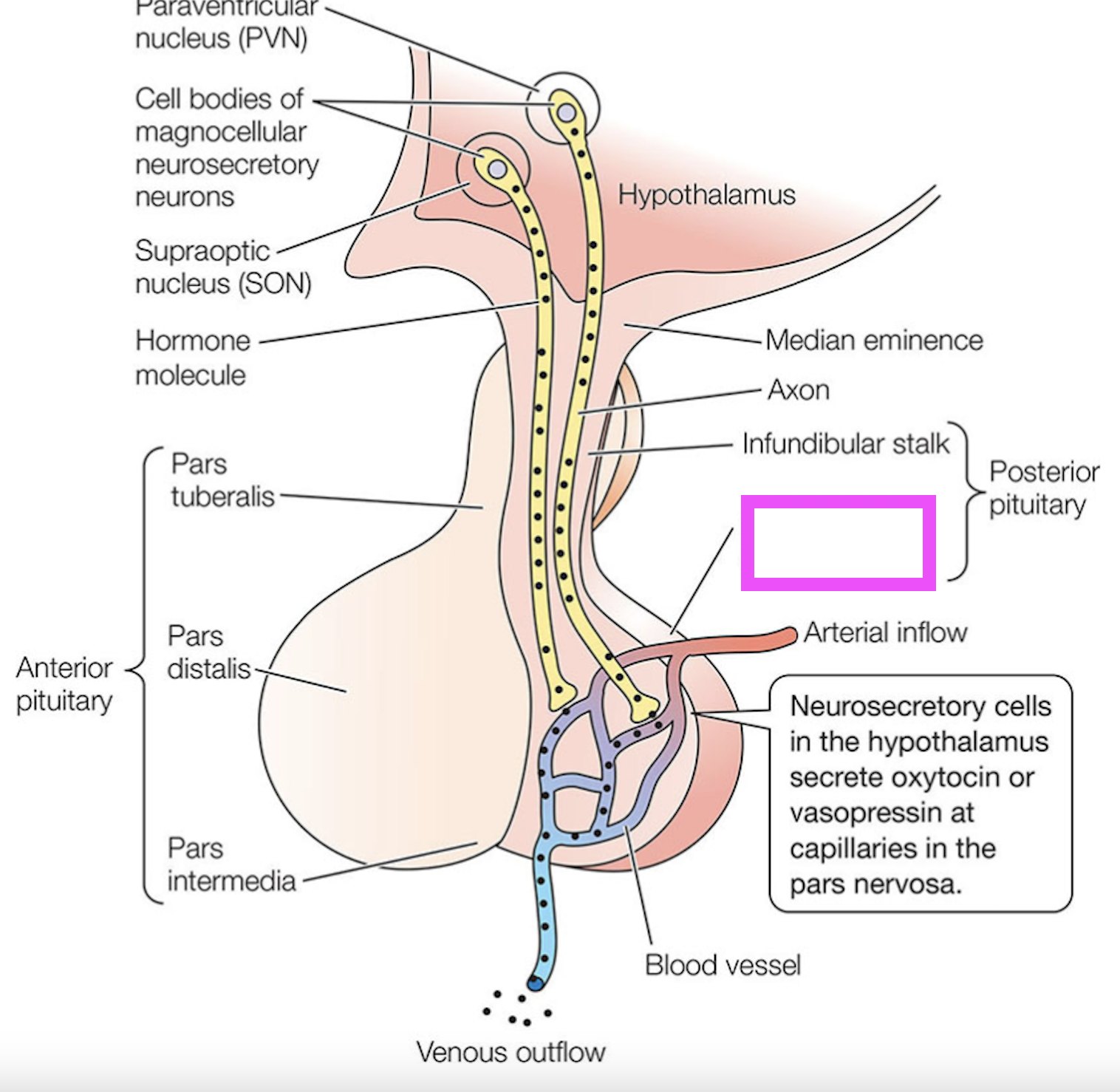
pars nervosa
pregnenolone
the six carbon side chain cleaved off of cholesterol to form several other steroid hormones; this change occurs in the mitochondria
preprohormone
large precursor molecule for a hormone, usually a peptide that needs postttranslational modifications before being the functional hormone
iodothyronine
amine hormone derived from tyrosine and synthesized in the thyroid gland; rich in iodine; thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3)
catecholamine
amine hormone derived from tyrosine that serves as neurotransmitters or hormones; eg. epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine
melatonin
amine hormone derived from tryptophan; secreted from the pineal gland, influences circadian and seasonal rhythms and promotes sleep
peripheral activation
conversion of a hormone after secretion to a more physiologically potent form
autocrine hormone
hormone that diffuses into extracellular fluid to bind to receptors on the same cell; does not enter the blood; eg. insulin or IGF-1
paracrine hormone
hormone that binds to receptors on cells in the neighborhood of the cell that released it; does not enter the blood; eg. testosterone in the testes, estrogen in the ovaries
nonneural endocrine cell
cells other than neurons that synthesize and secrete hormones; also called epithelial cells; typically stimulated by other hormones
neurohemal organ
organ made up of axon terminals of neurosecretory cells in association with well-bred capillaries in which the axon terminals store neurohormone to secrete; eg. hypothalamus
hormone
chemical substance that is produced and released by endocrine cells, carried throughout the body in blood, and exerts regulatory influence on other distant cells
conformity
when an animal permits internal and external conditions to be equal
regulation
when an animal maintains internal constancy in the face of external variability
acute response
responses exhibited during the first minutes or hours after an environmental change
chronic response
responses expressed following prolonged exposure to new environmental conditions
nervous, endocrine
____ control is fast and addressed; ____ control is slow and broadcast
exocrine gland
gland that has outflow tubes called ducts and their secretions flow out by ducts
endocrine gland
gland that secretes products directly into surrounding extracellular fluids, which can diffuse into the blood and capillaries
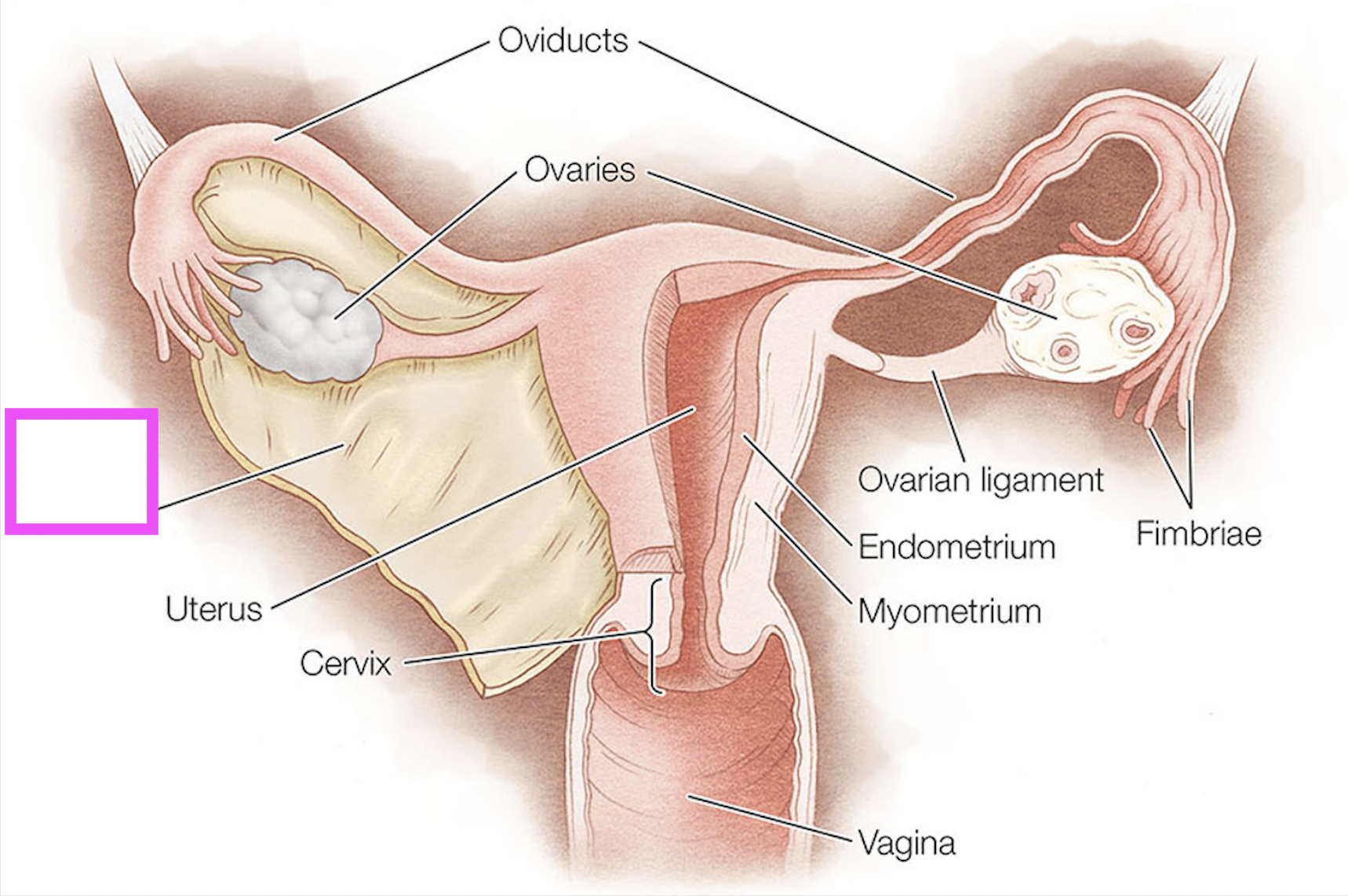
oviducts
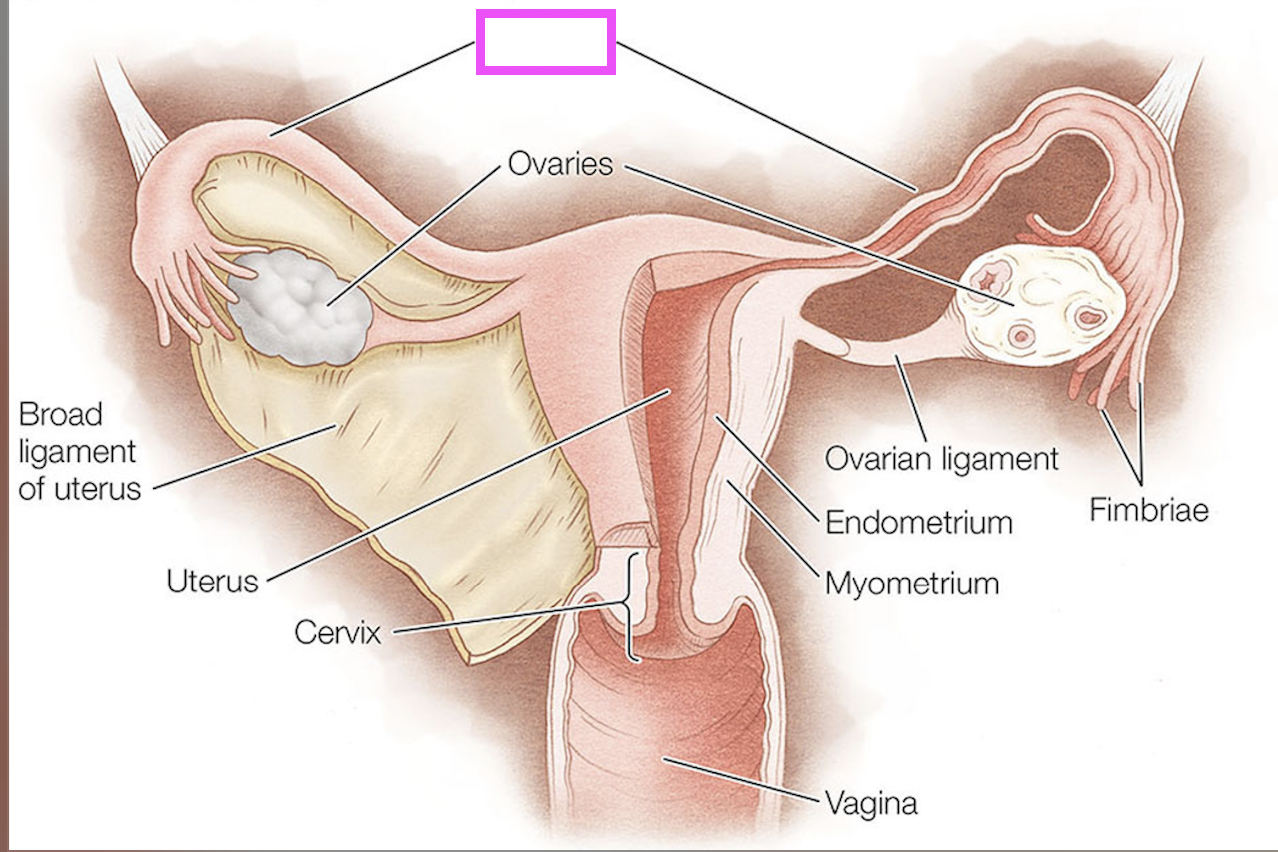
ovaries
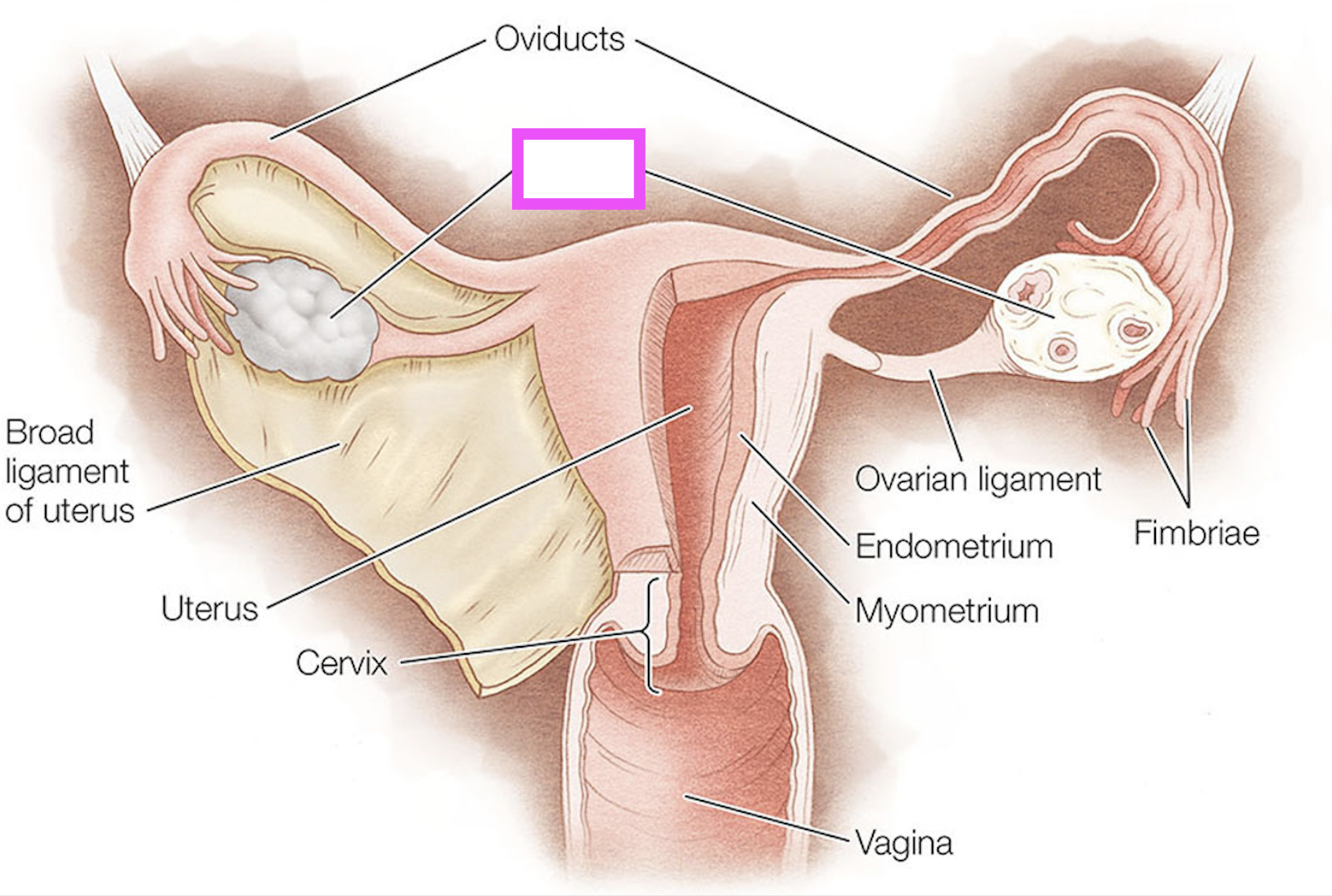
fimbriae
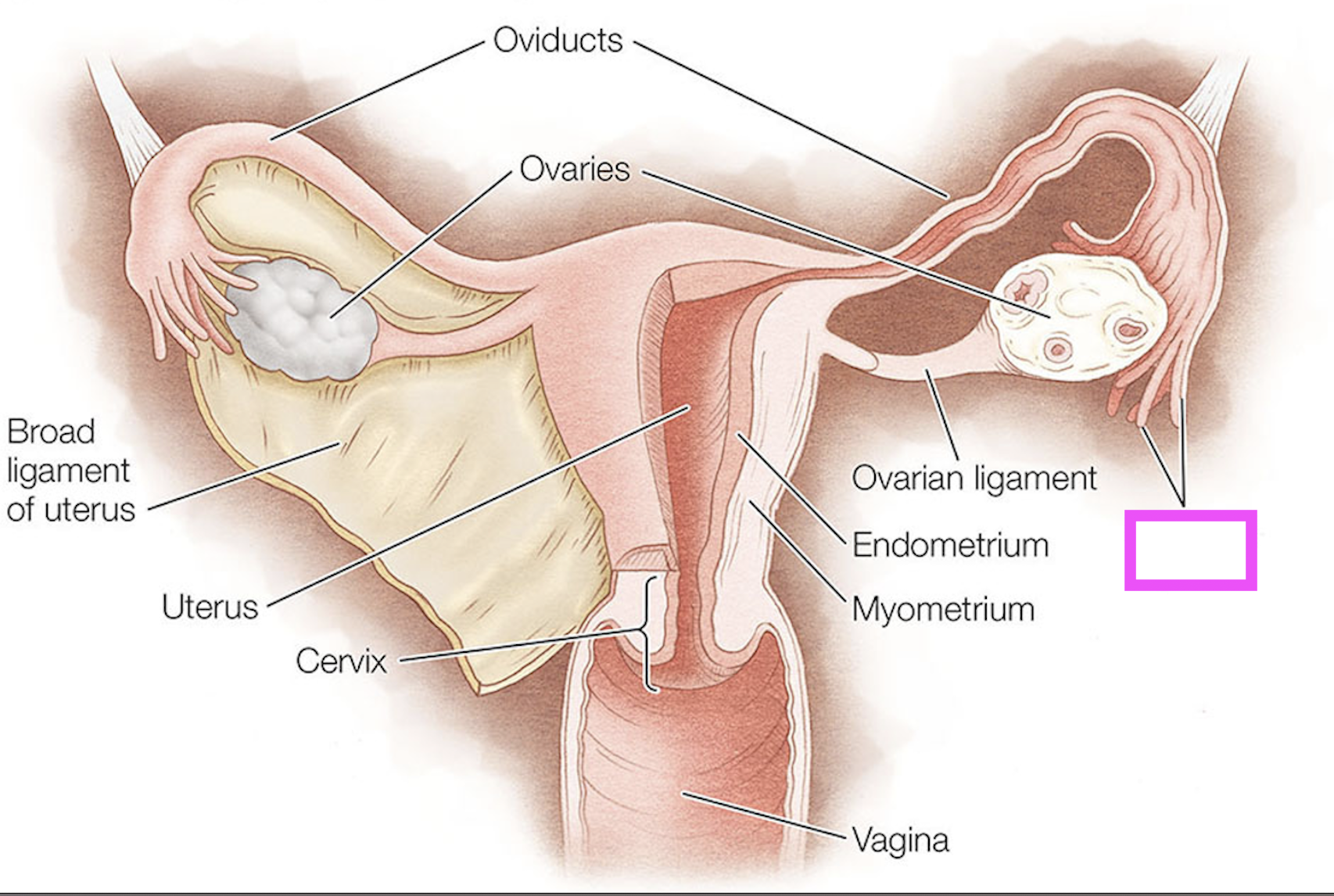
ovarian ligament
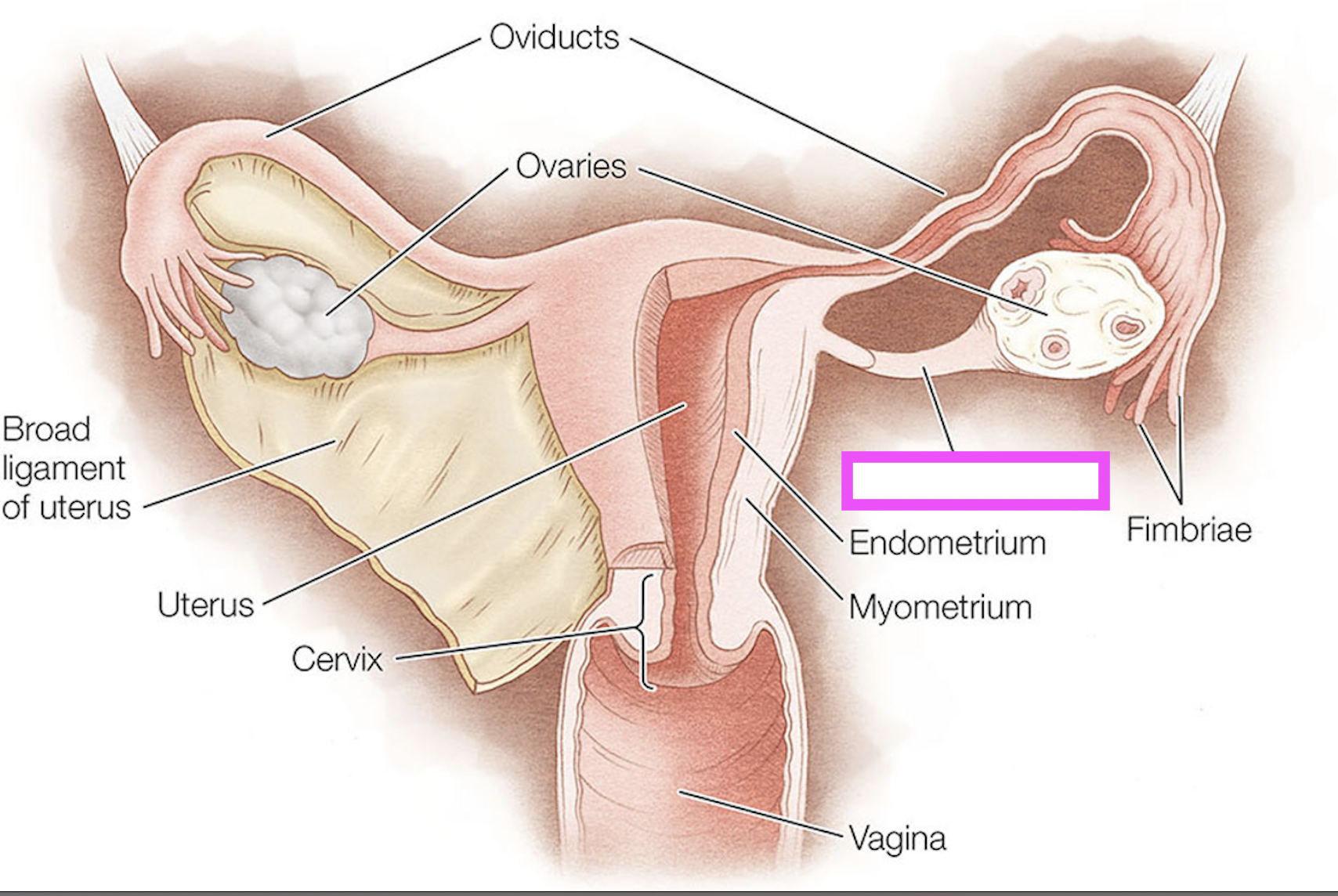
endometrium
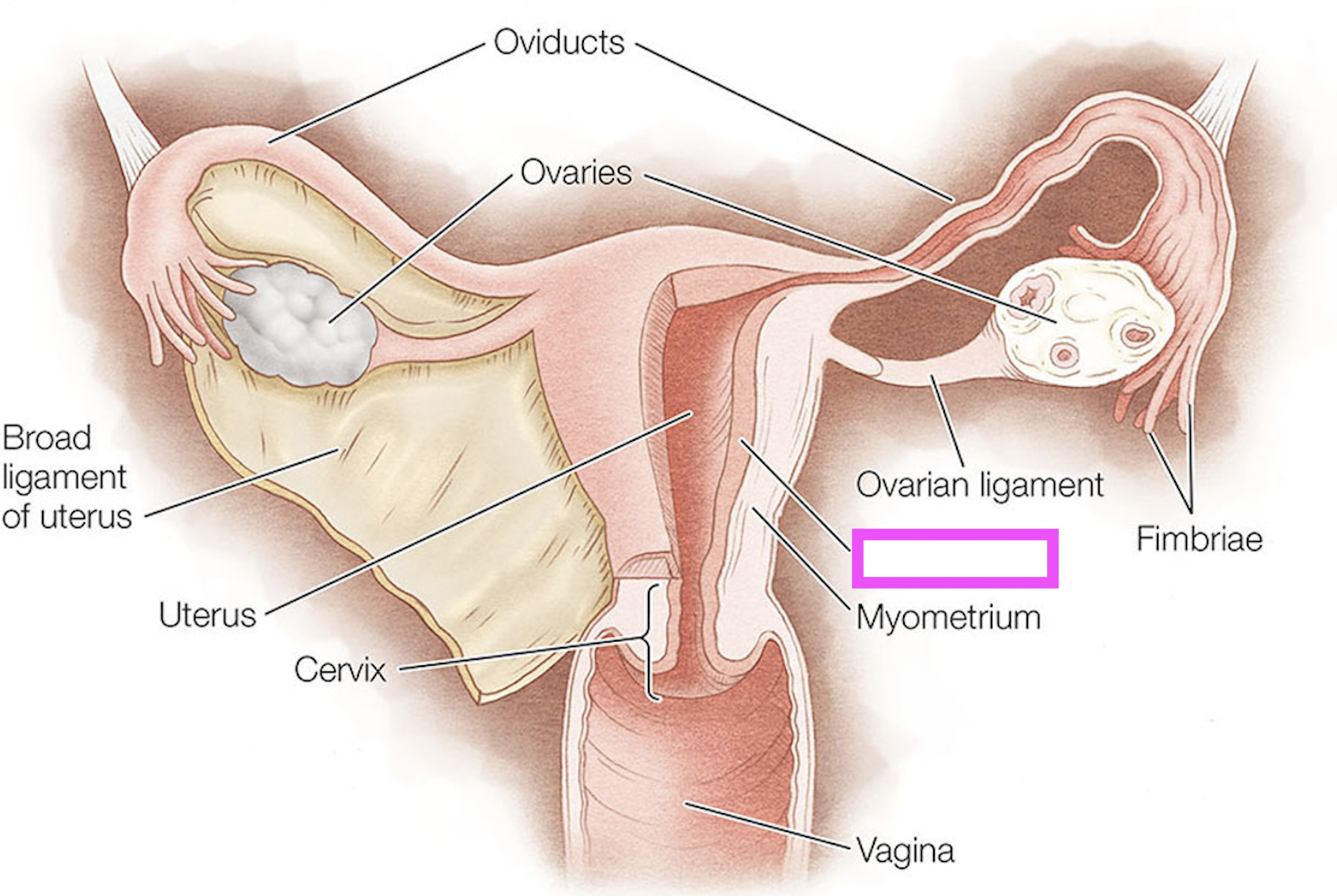
myometrium
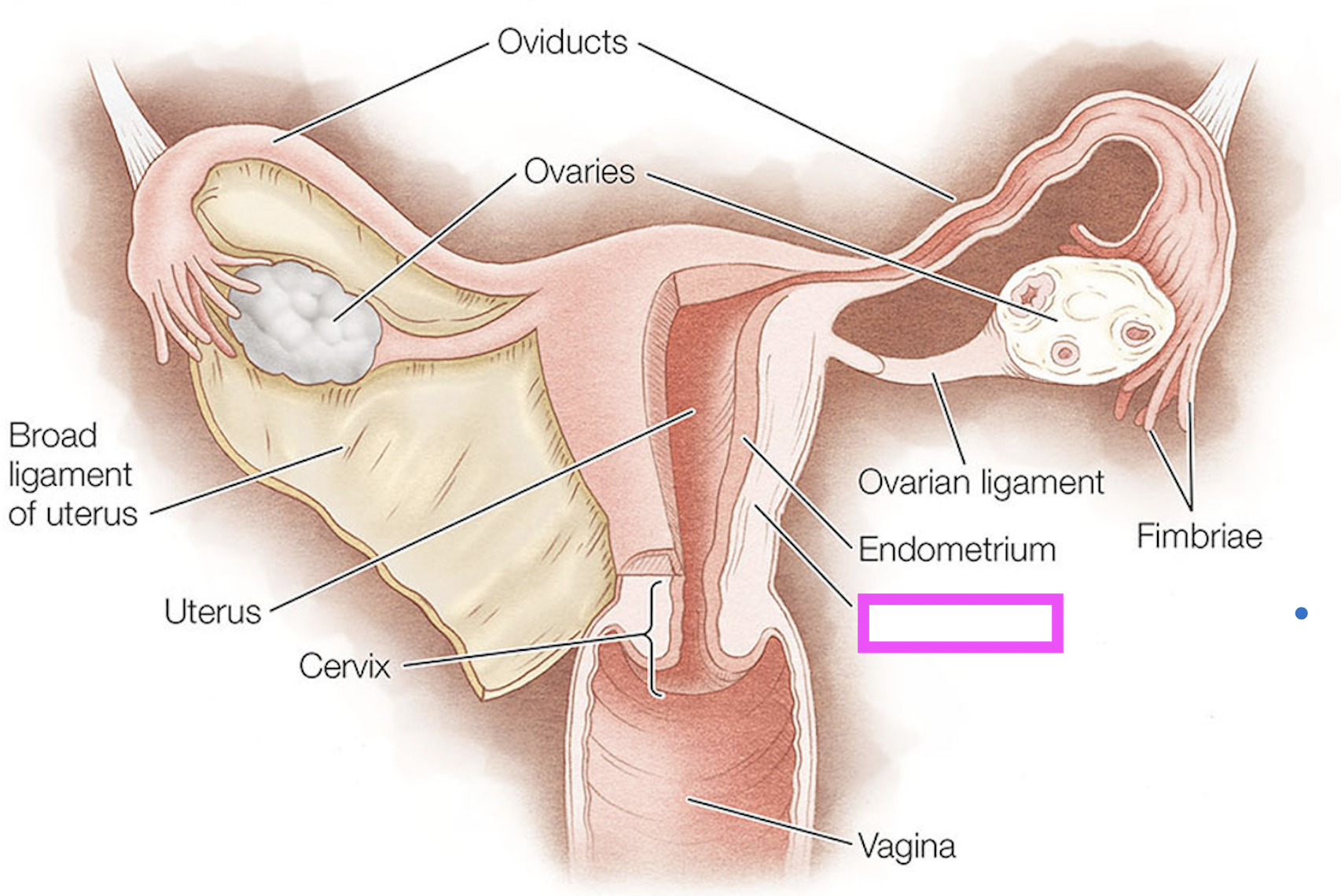
cervix
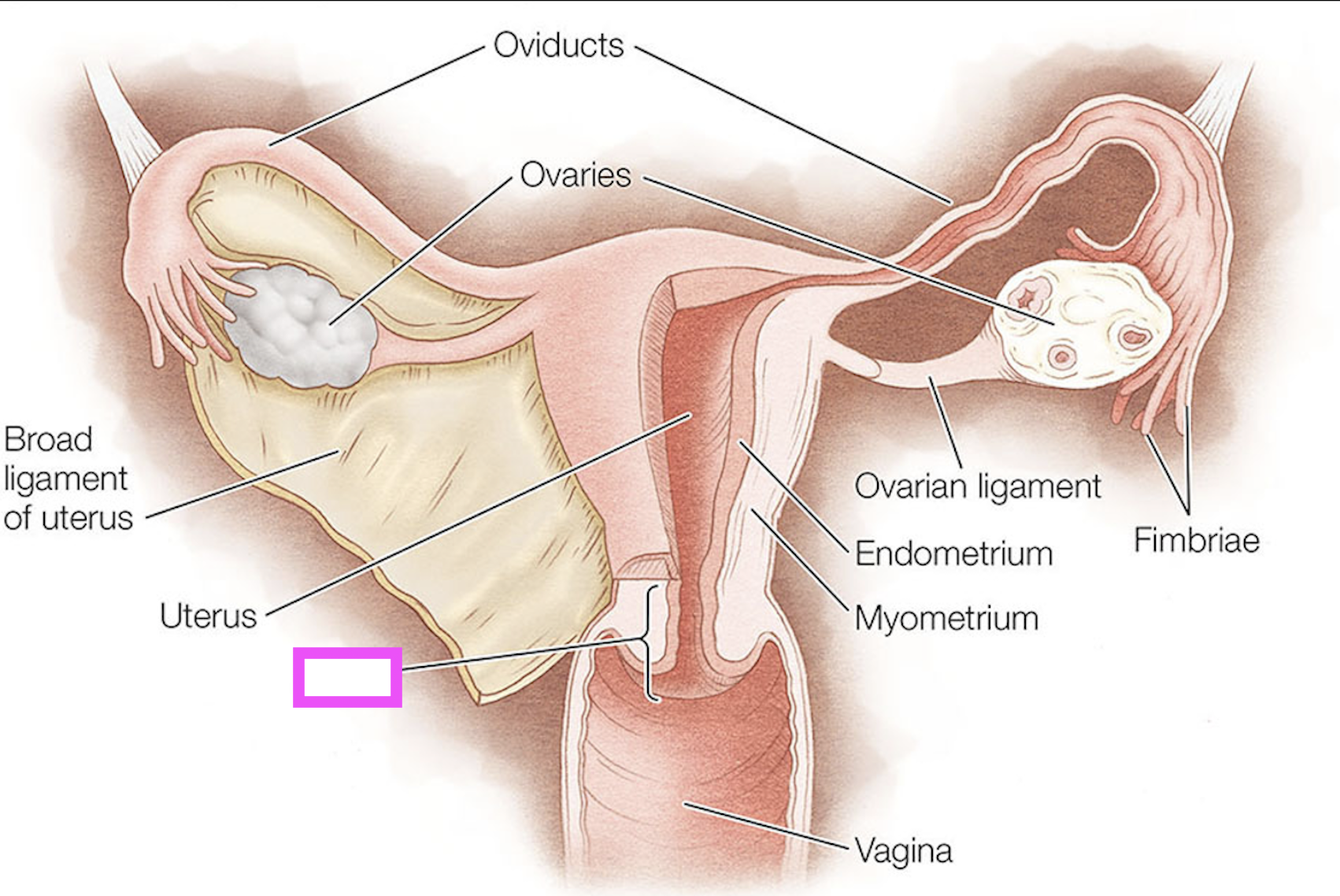
broad ligament
theca cells
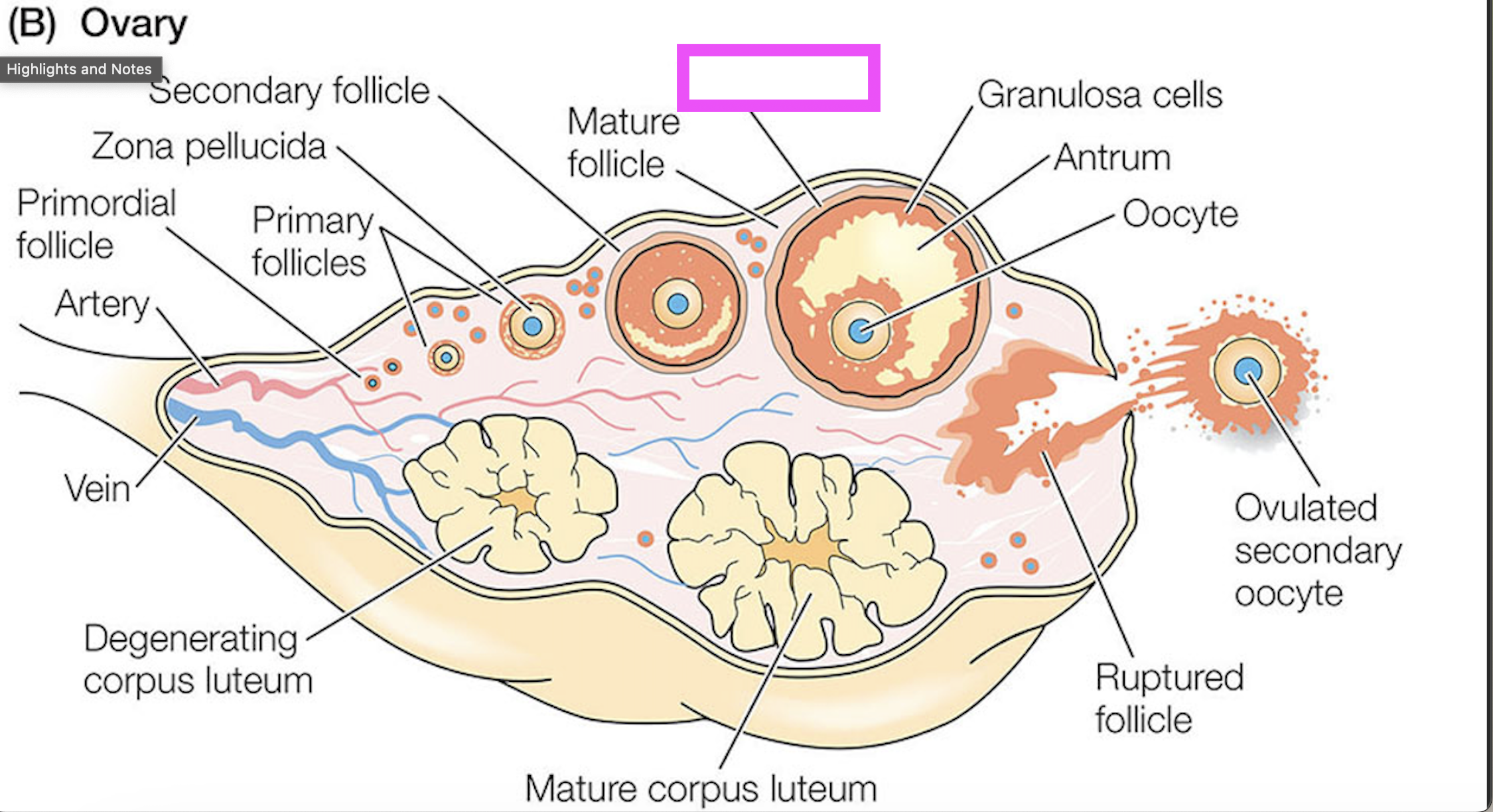
granulosa cells
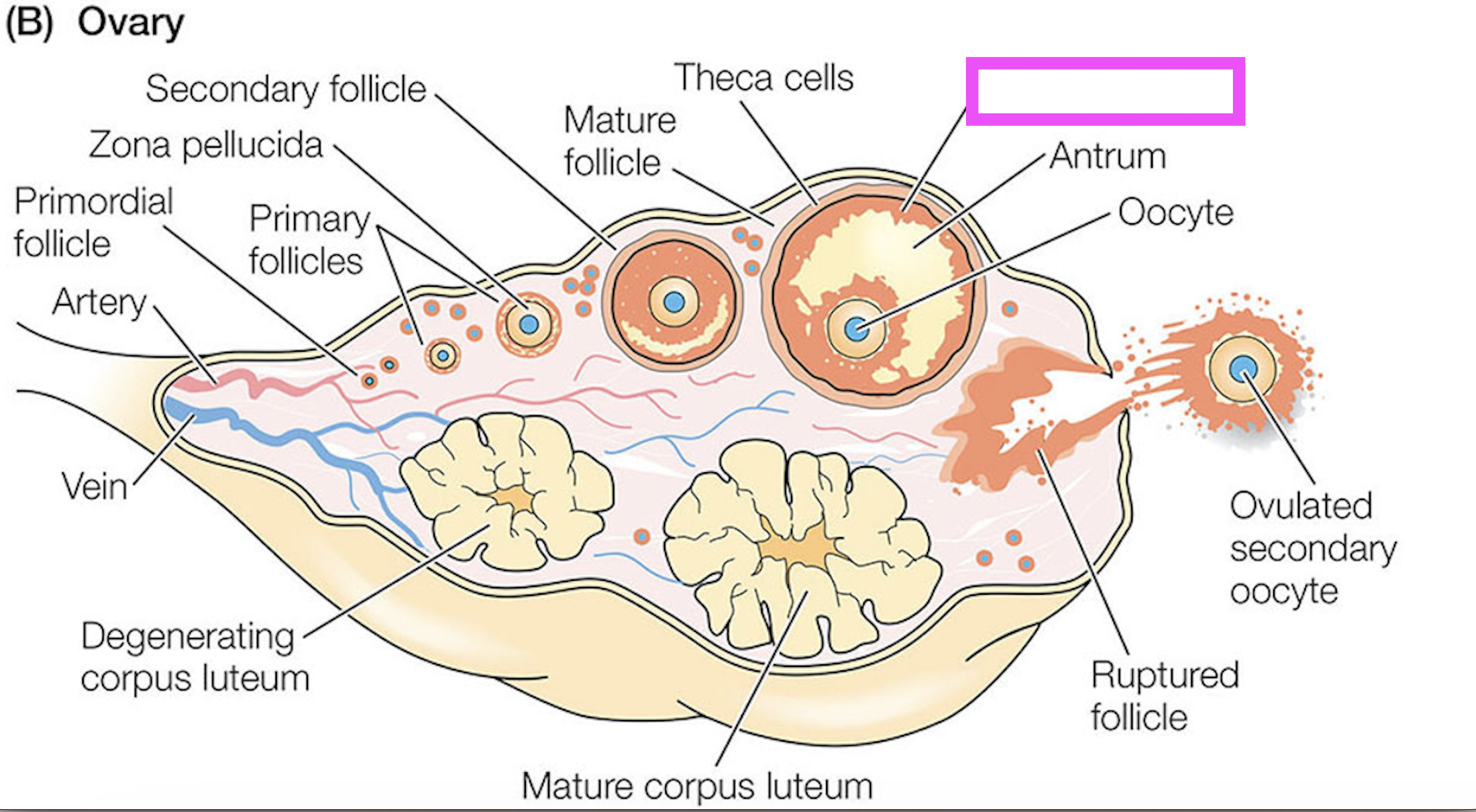
oocyte
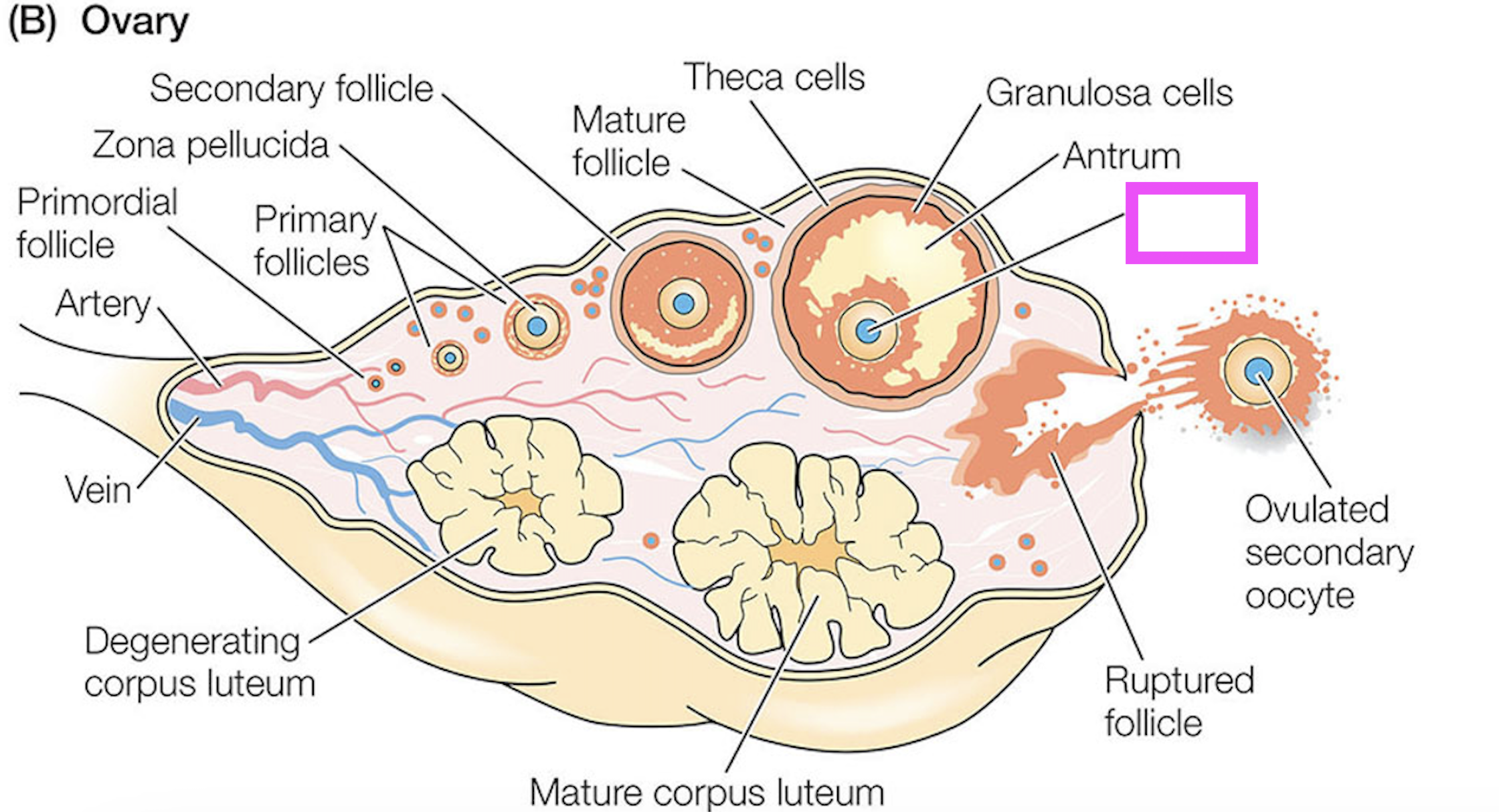
zona pellucida
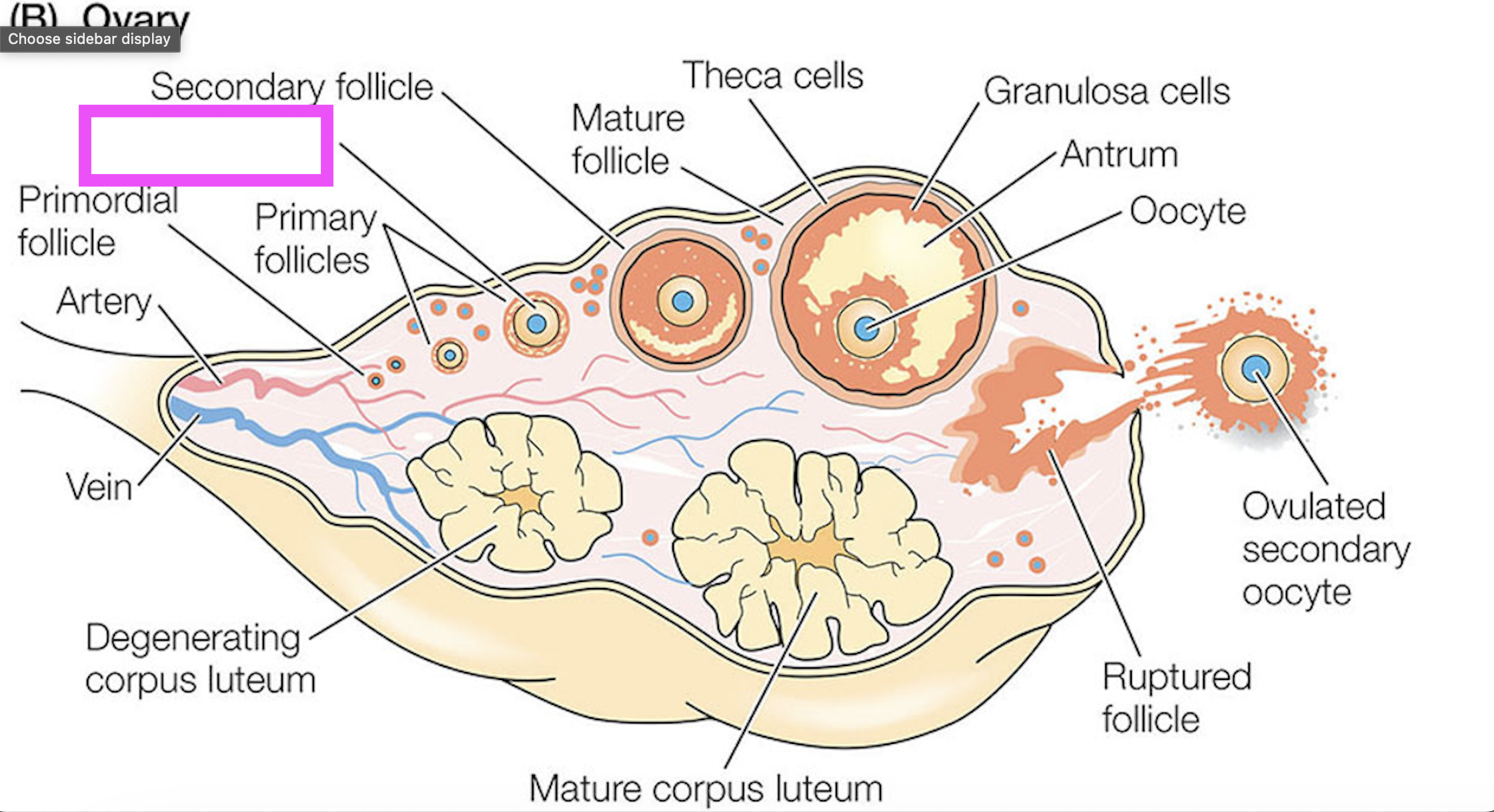
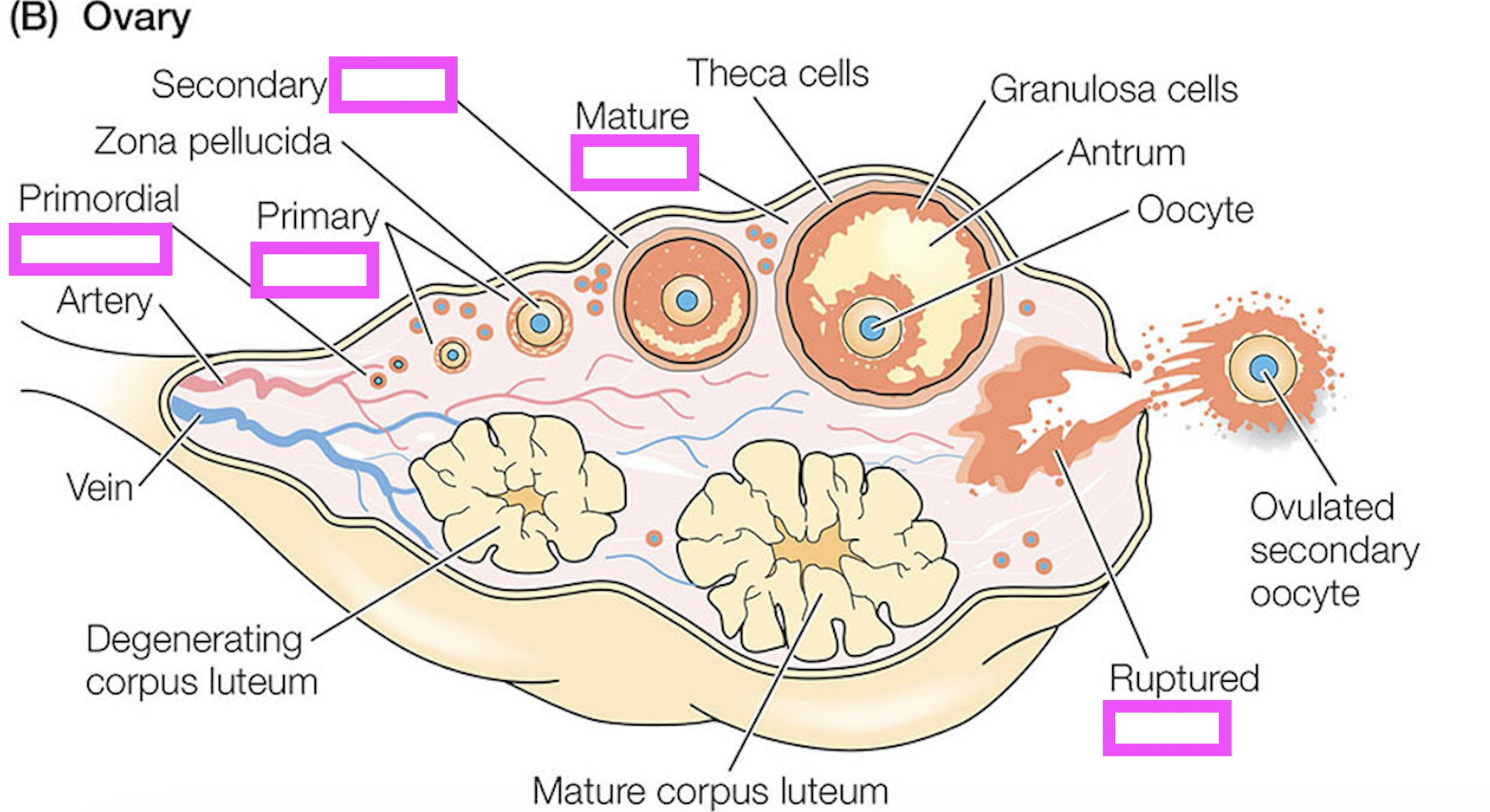
corpus luteum
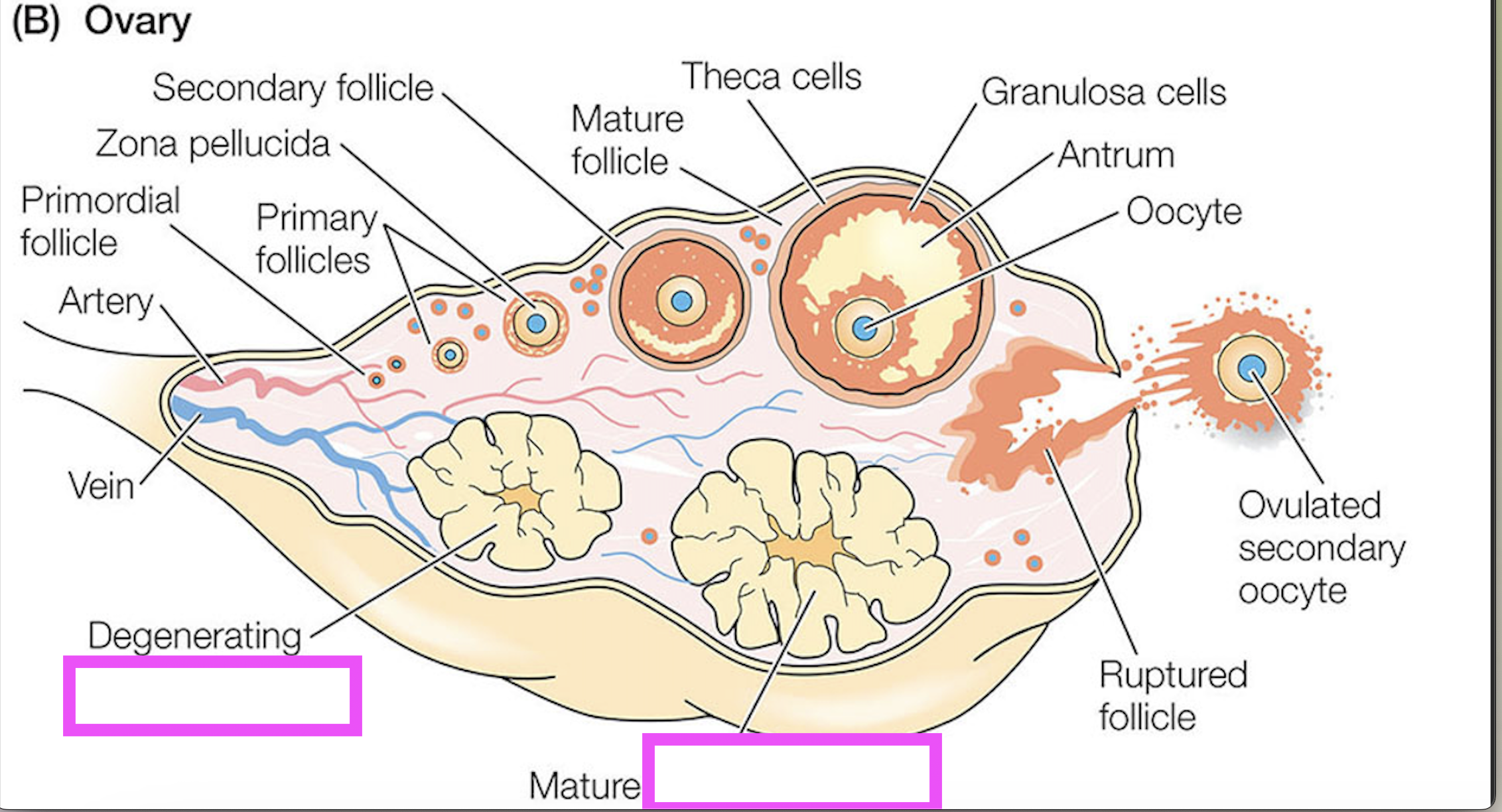
follicle
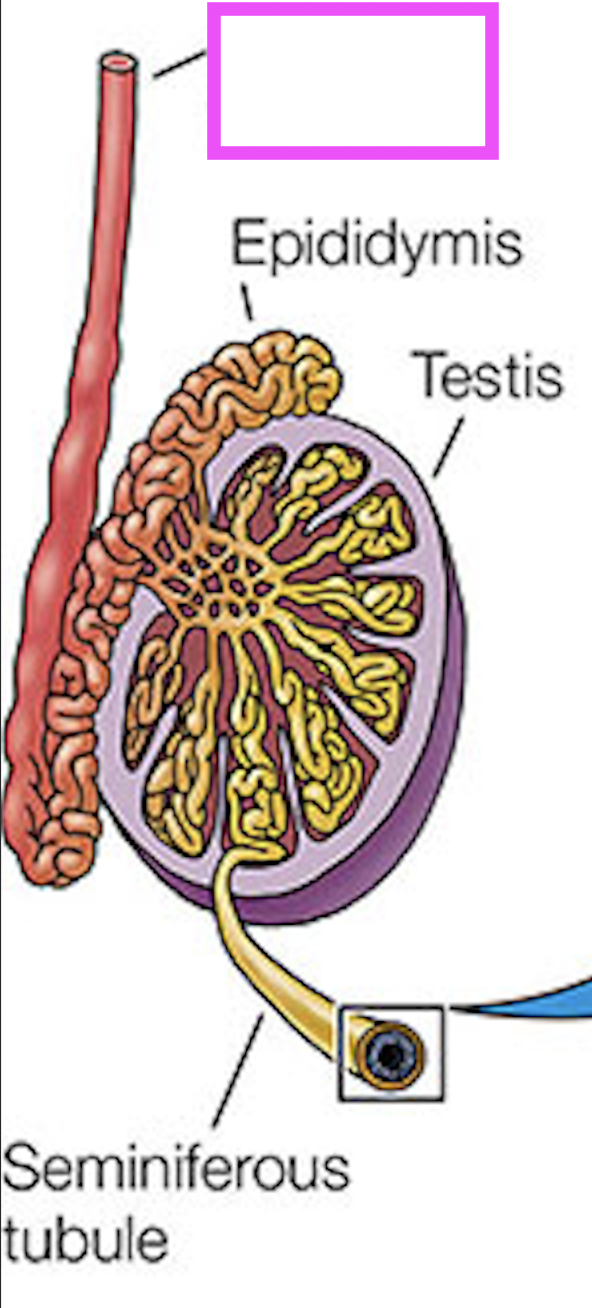
seminiferous tubules
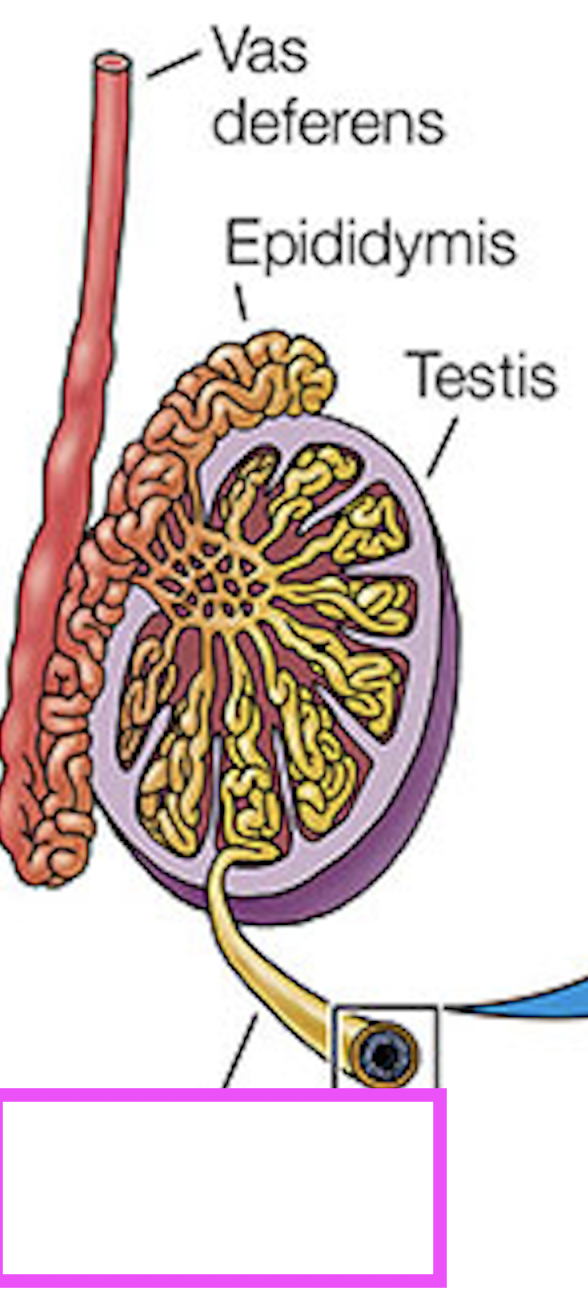
testis
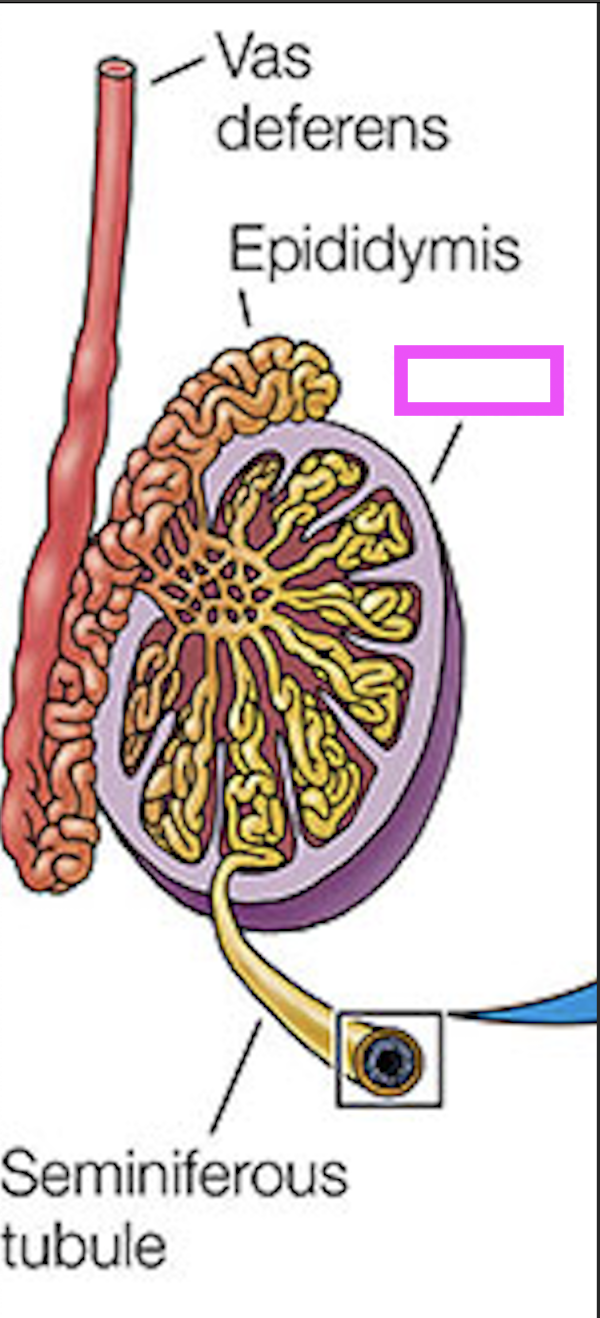
epididymus
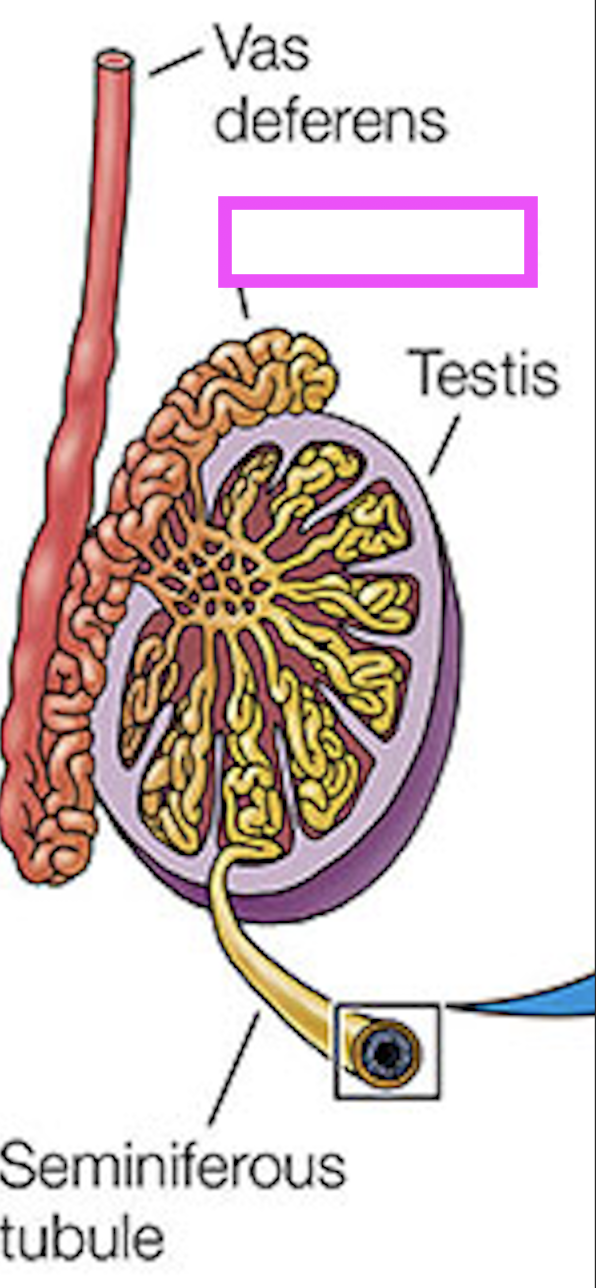
vas deferens
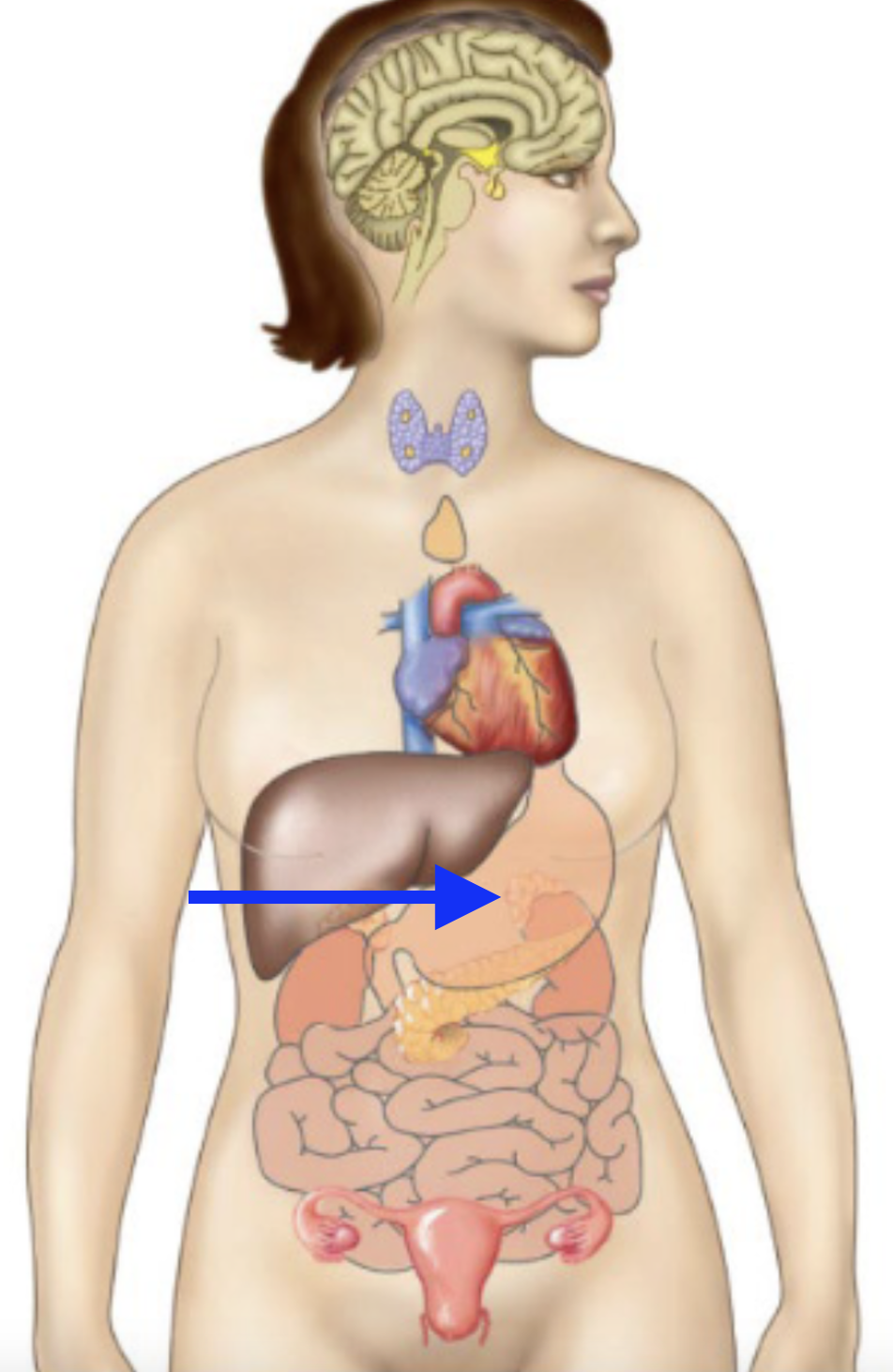
hypothalamus
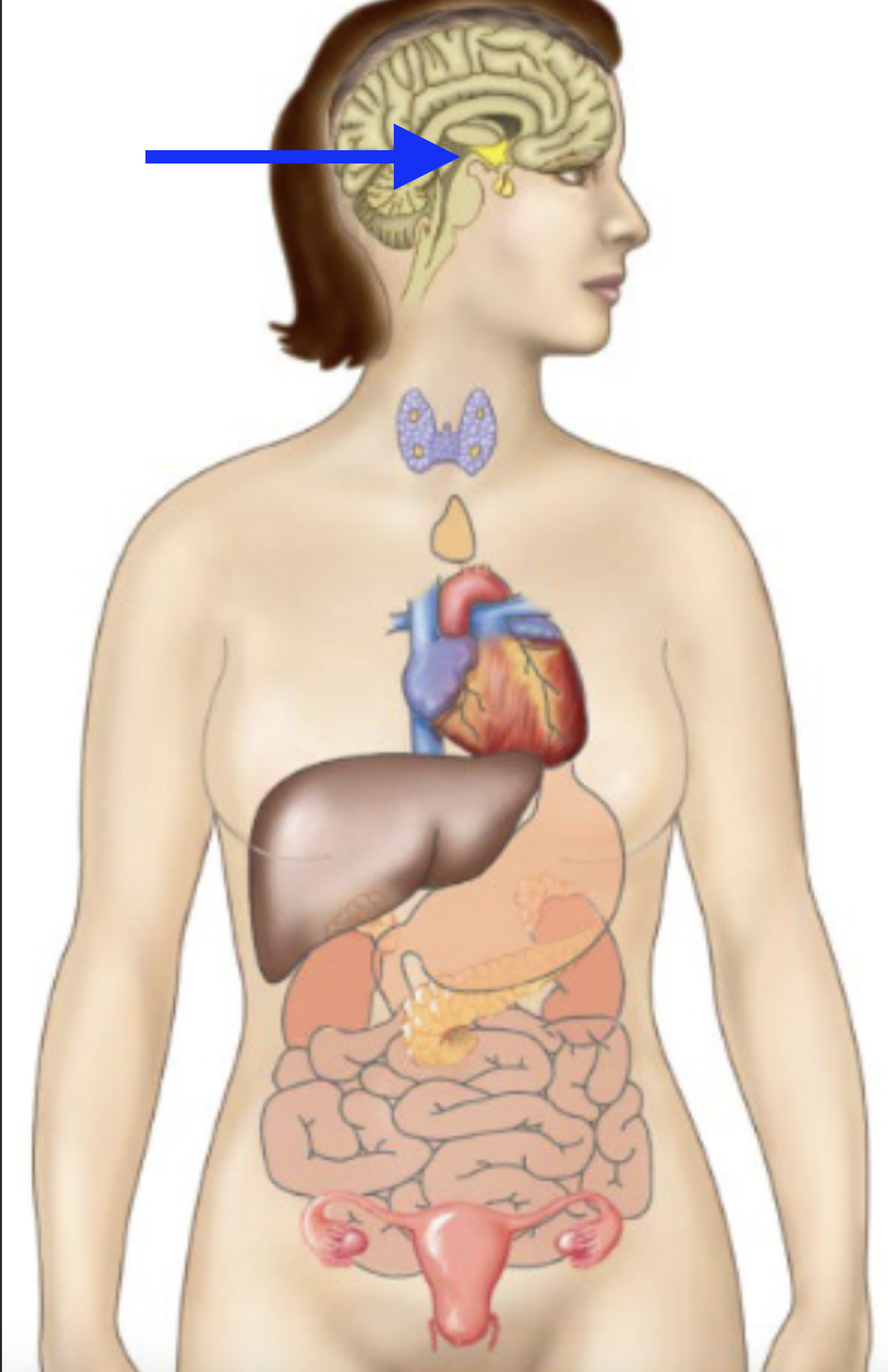
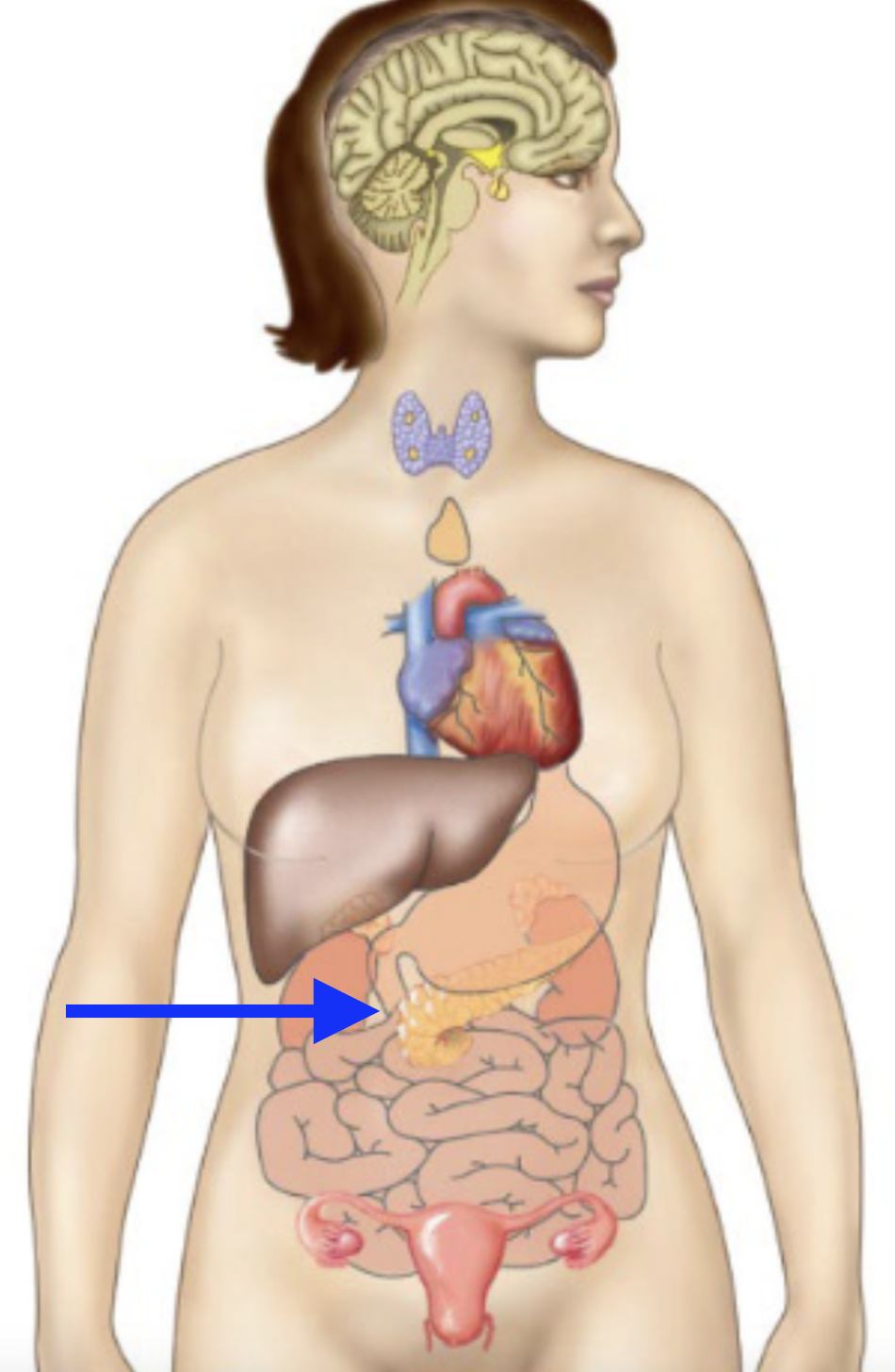
pancreas
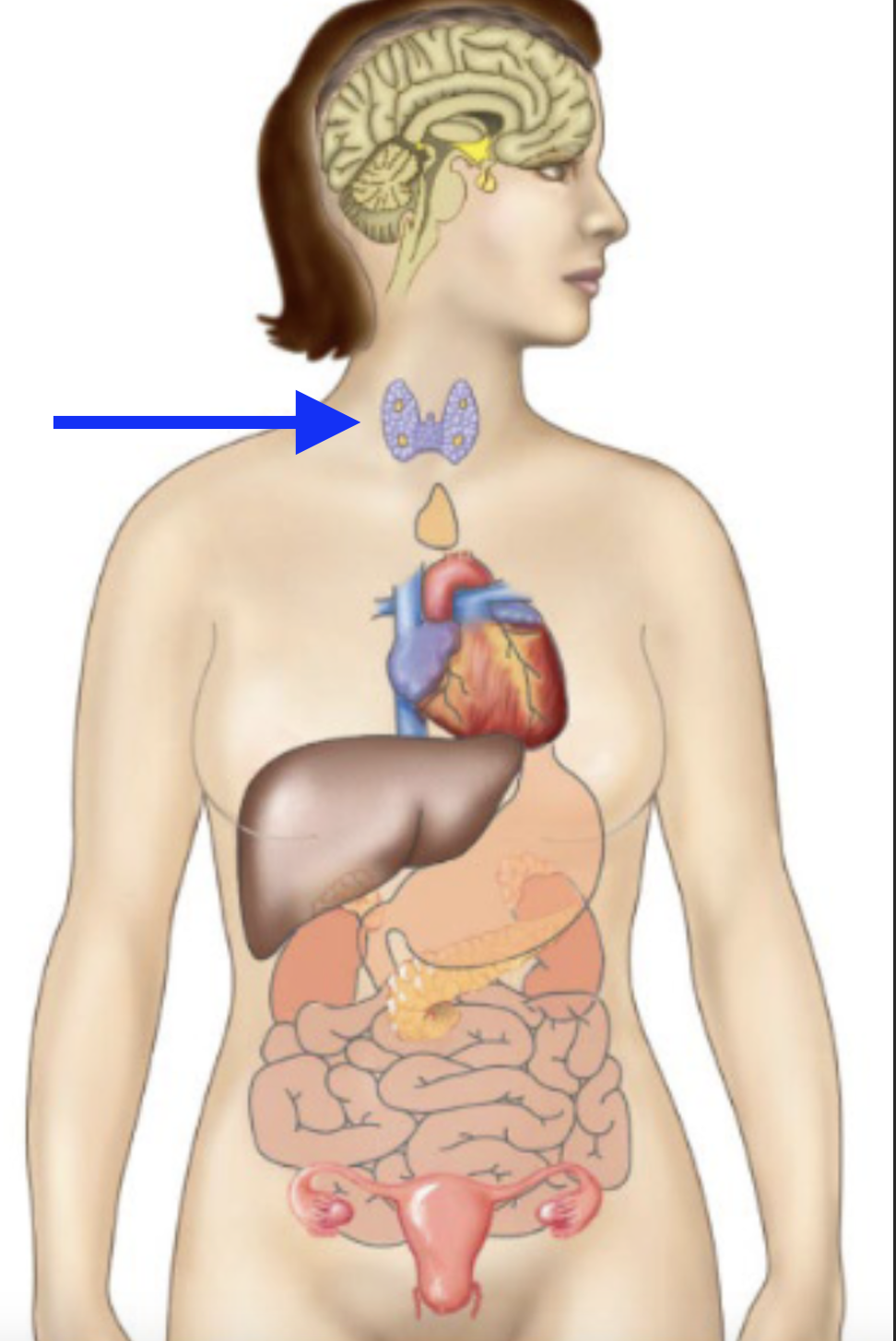
thyroid
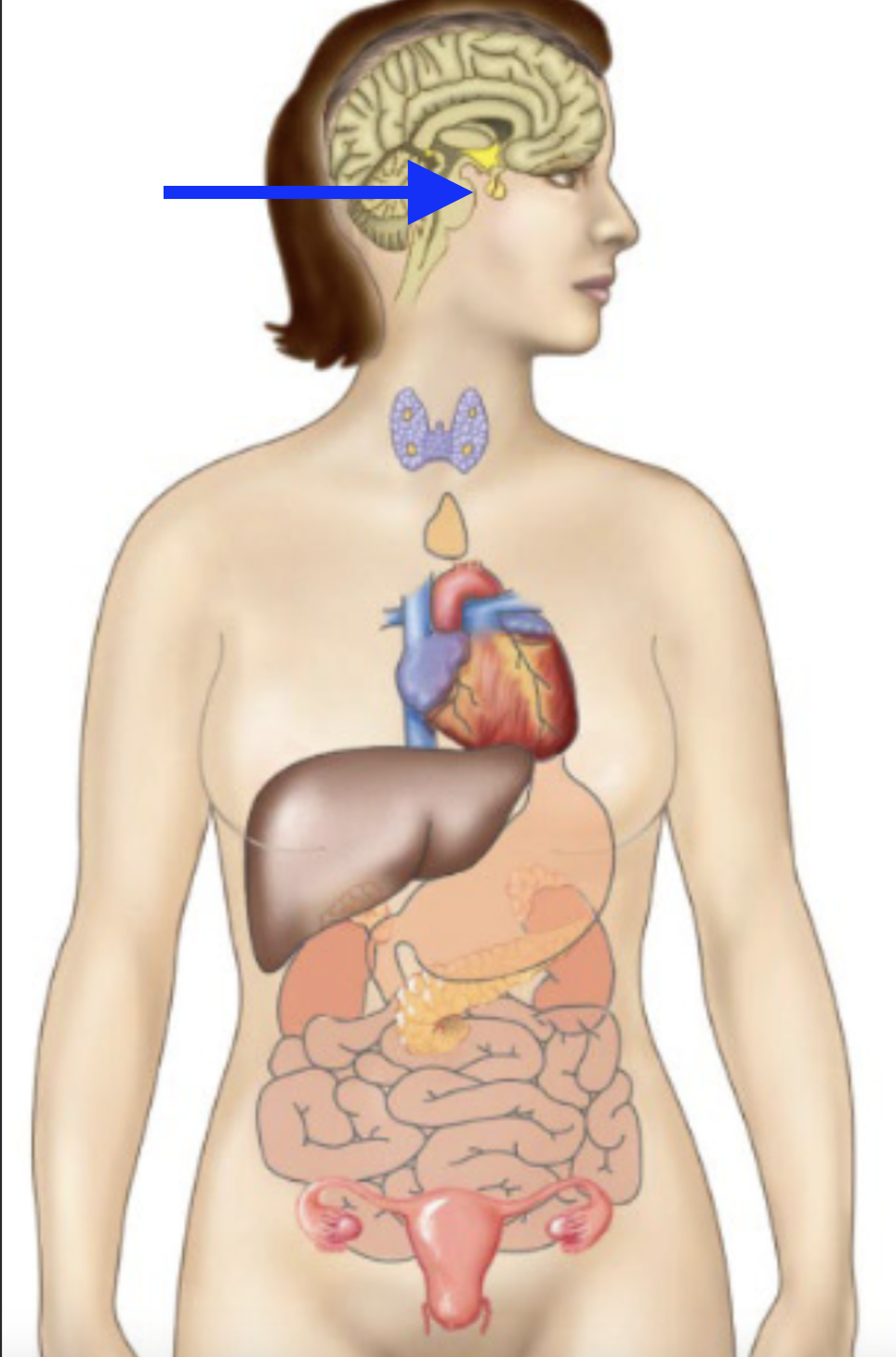
pituitary
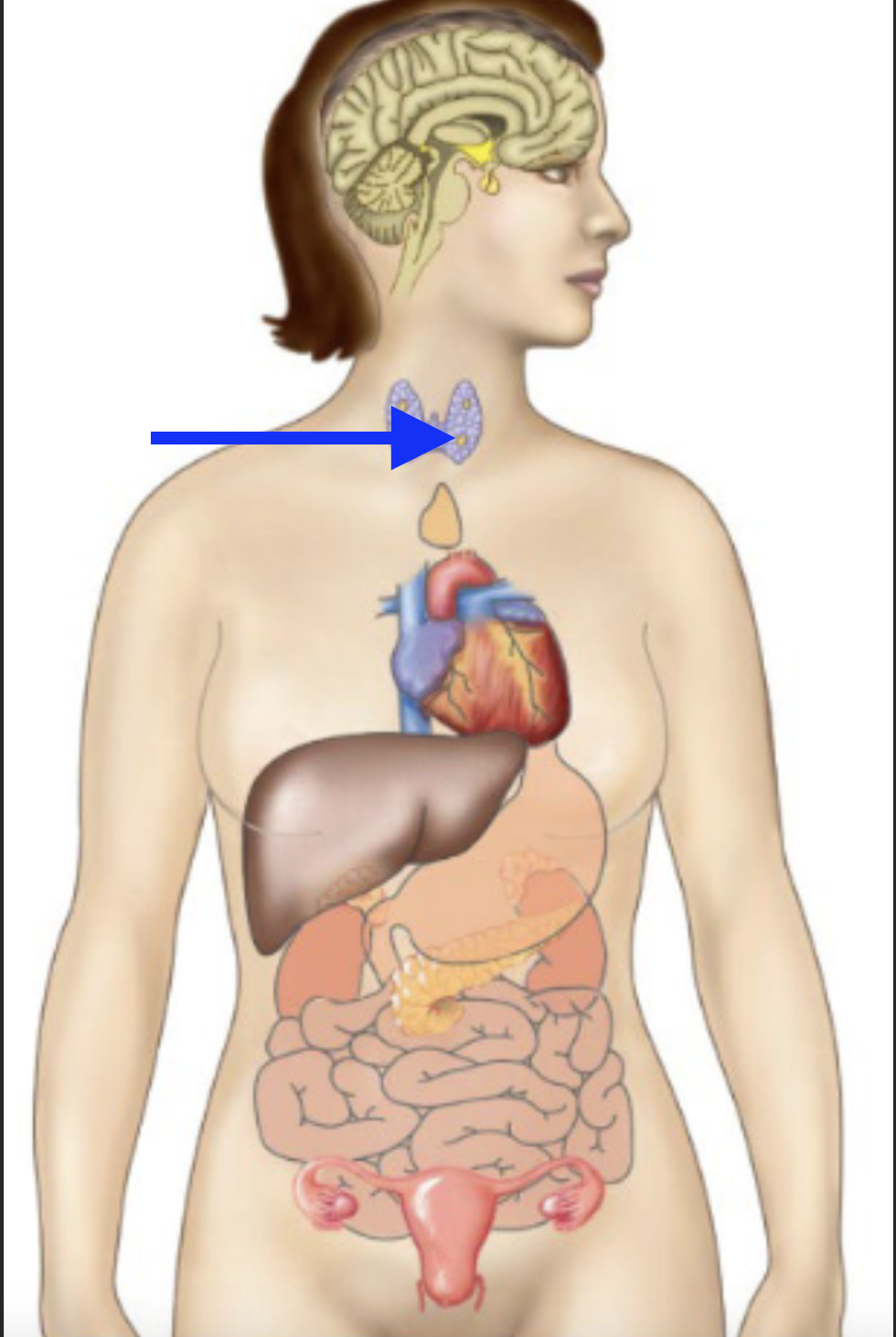
parathyroid
adrenal
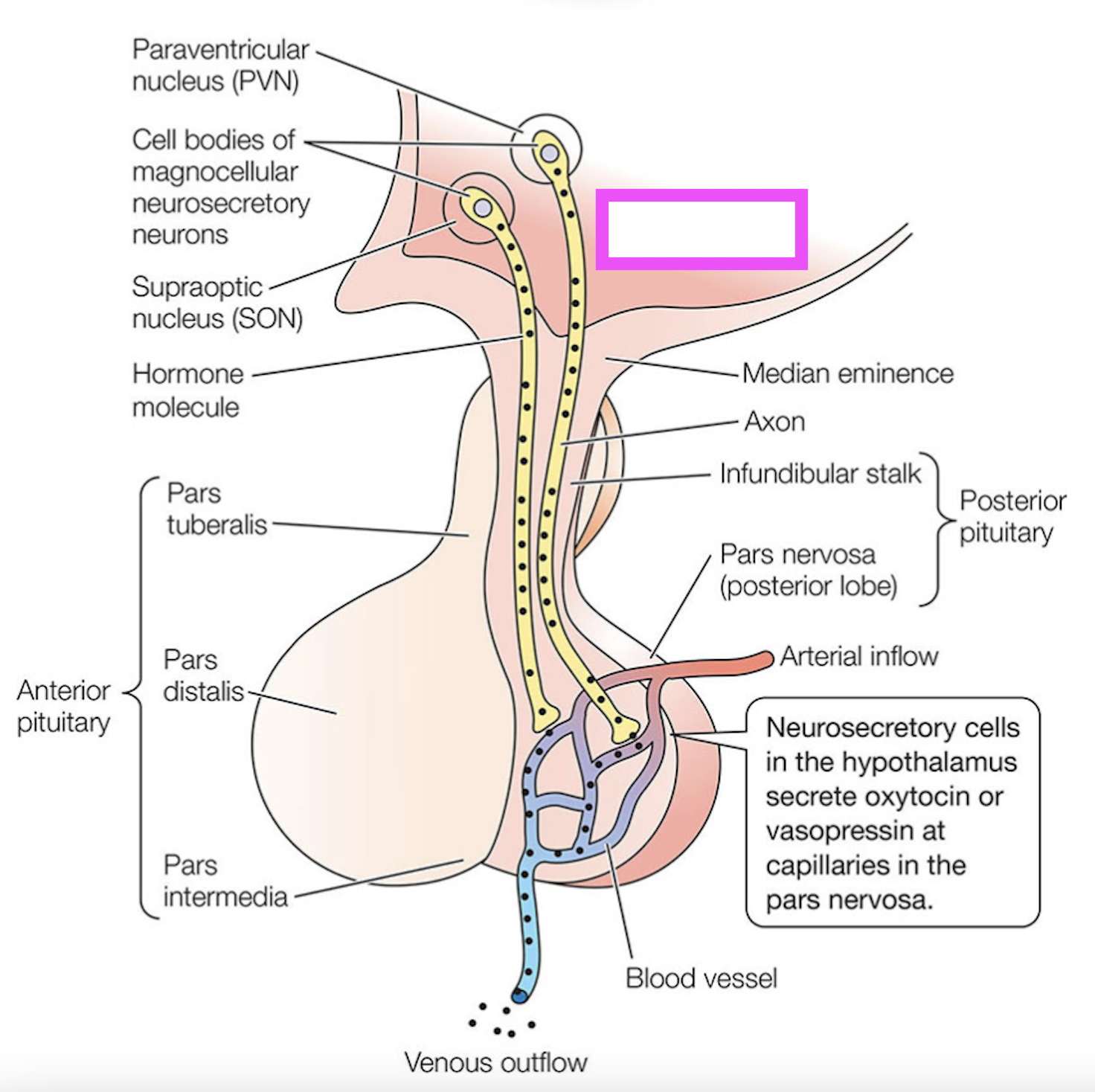
hypothalamus
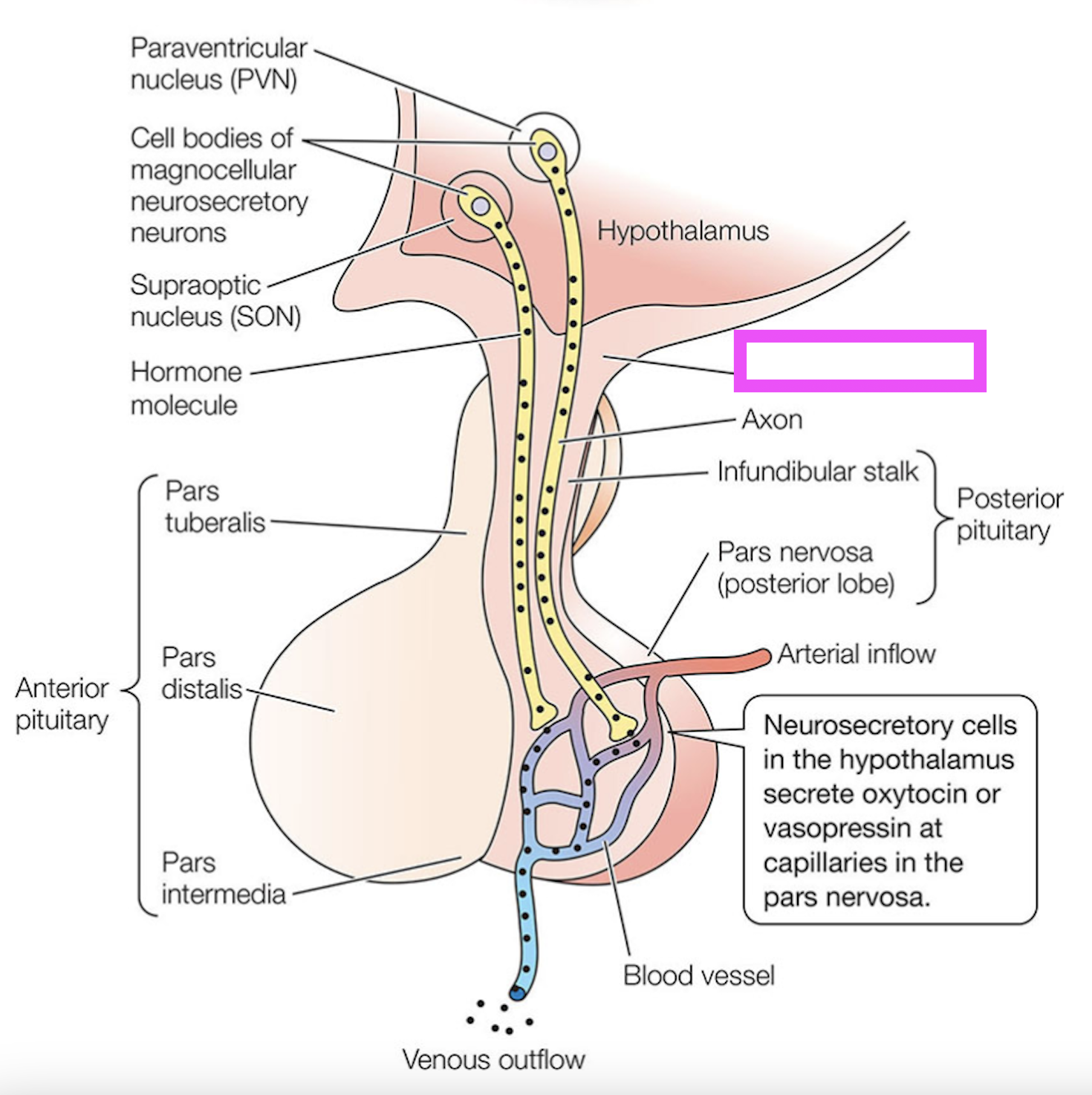
median eminence
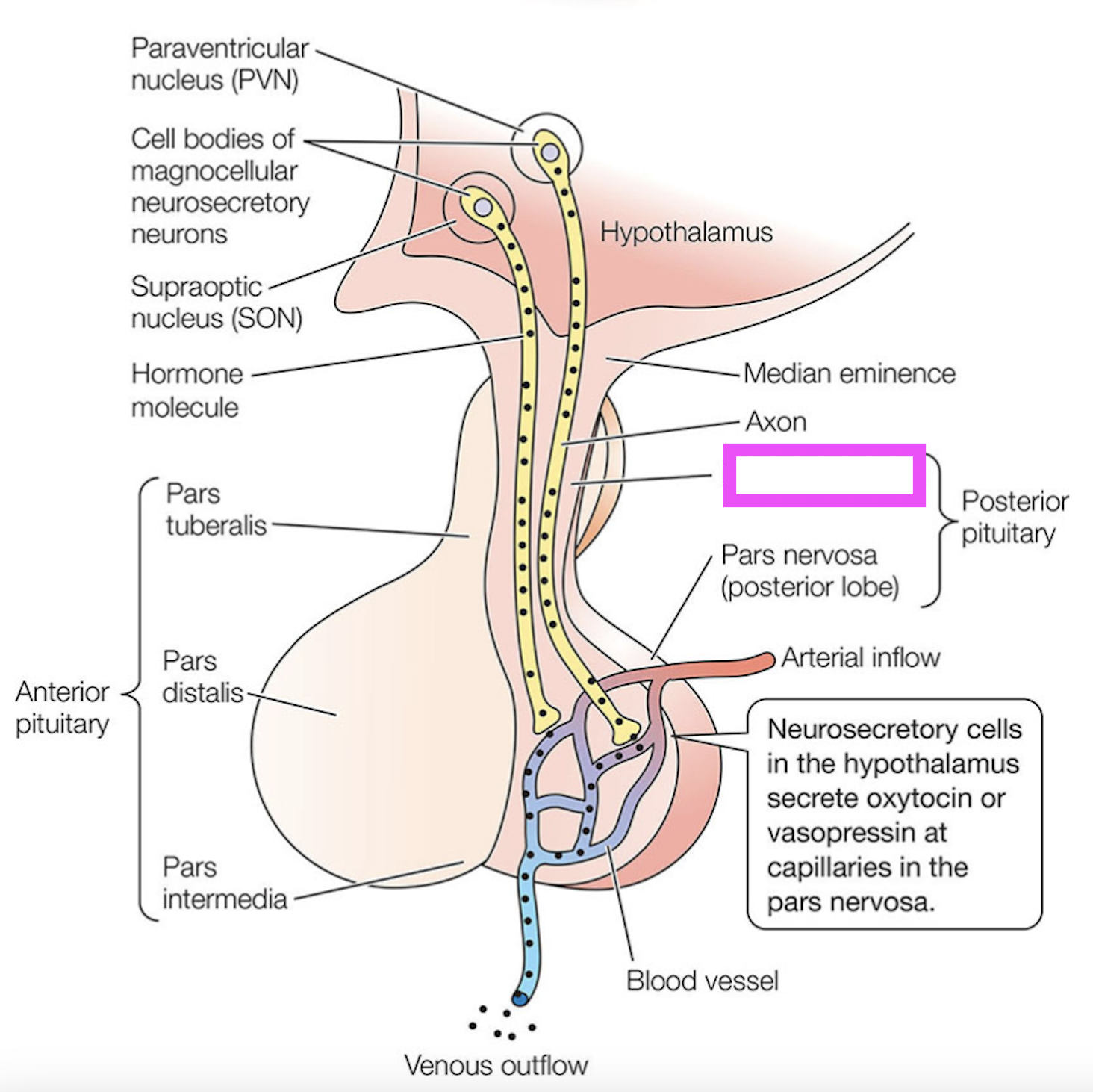
infundibular stalk
posterior pituitary
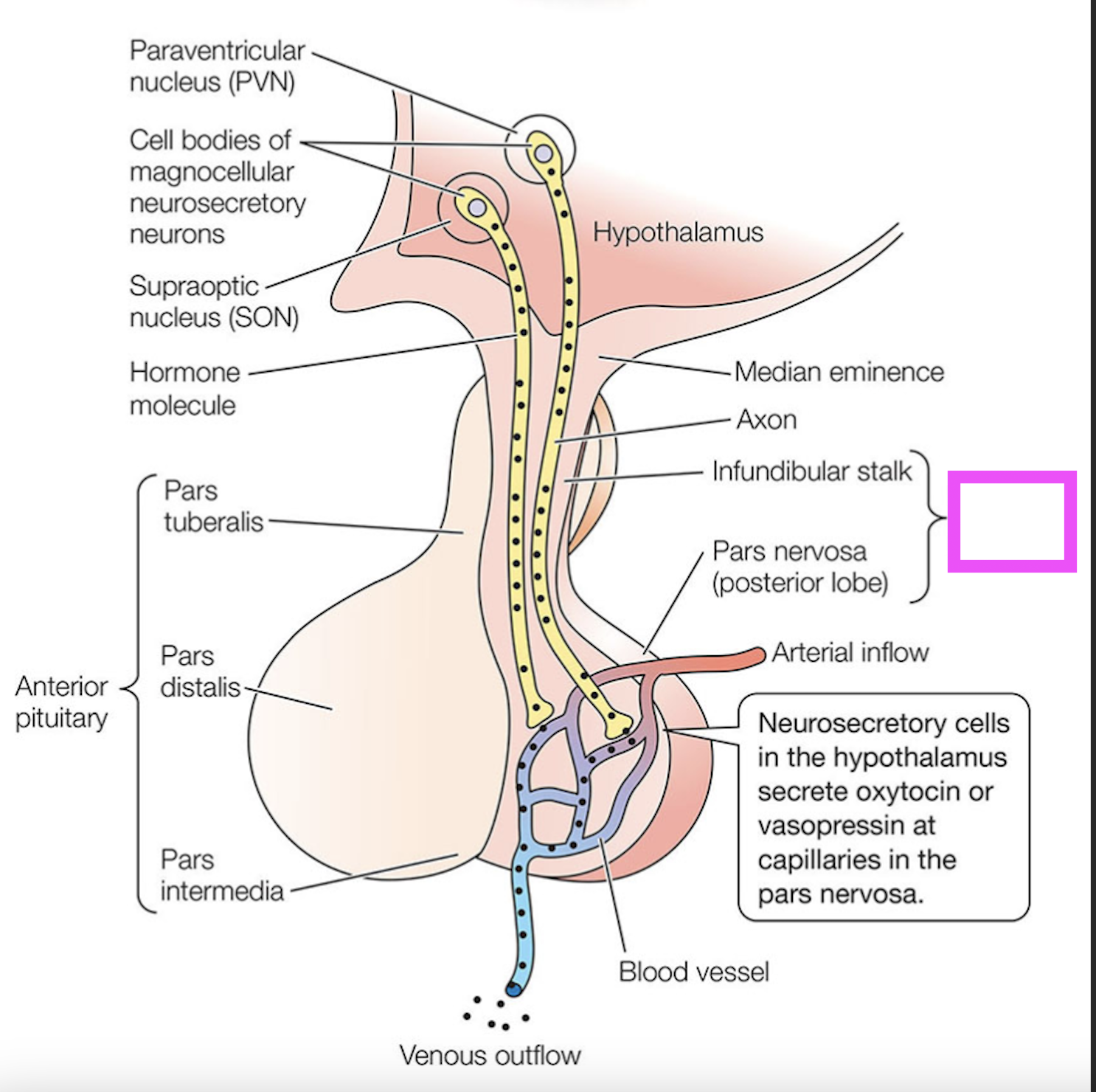
anterior pituitary
paraventricular neuron
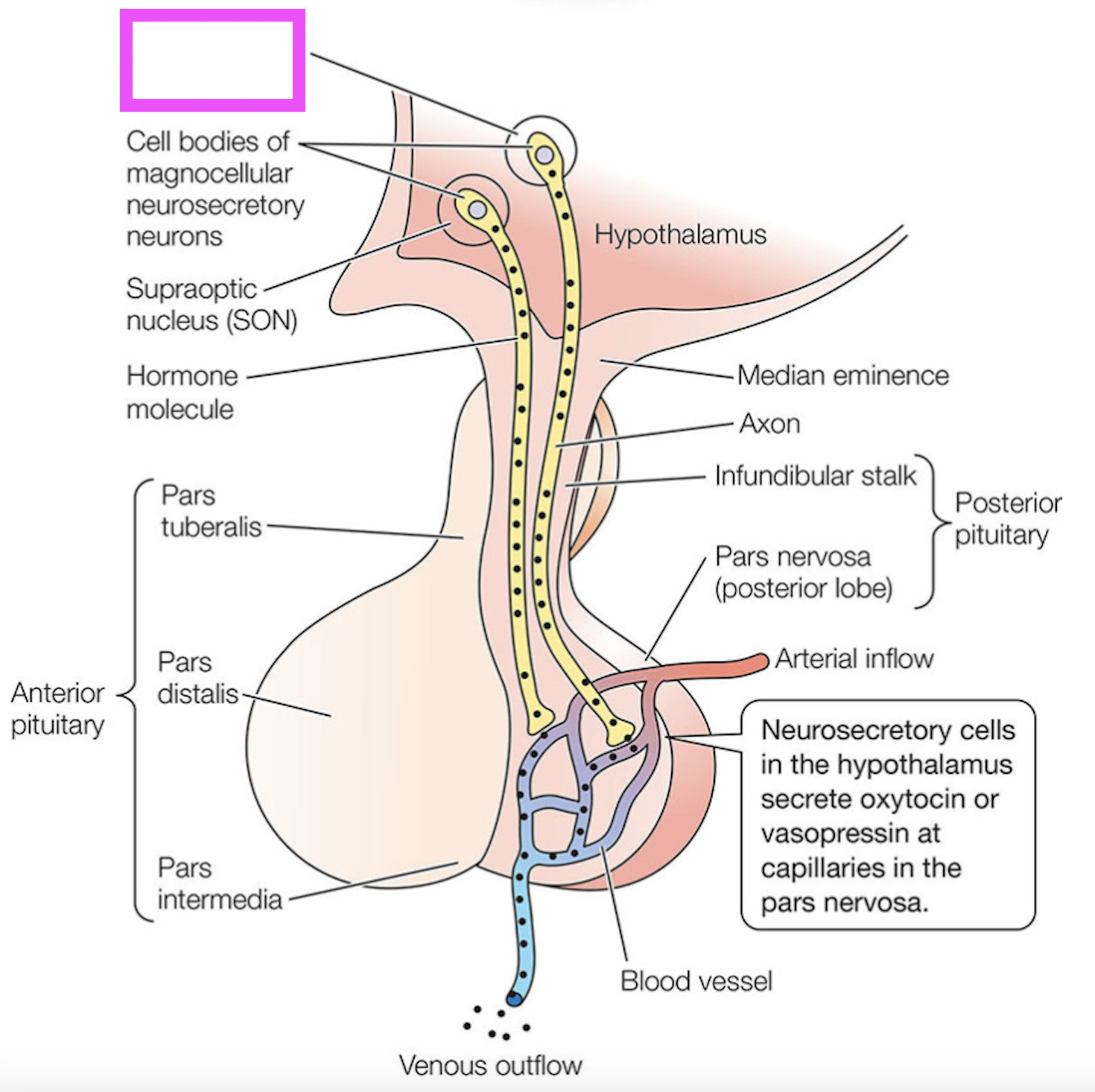
supraoptic neuron
sensor
in a negative feedback system, the part that senses a change in the variable
integrator
in a negative feedback system, the part that compares the sensed input value to the reference value (set point); also called control center
effector
a tissue, organ, or cell that carriers out functions under the direction of the nervous system or another physiological control system; in a negative feedback system, makes adjustments to the variable
steroid hormone
nonpolar hormones synthesized on demand from cholesterol, secreted by diffusion through the cell membrane and circulated in the blood bound to carrier molecules; typically bind to intracellular receptors of the target cells and exert actions through genomic means
peptide hormone
hormone made of assemblages of amino acids and soluble in water, have receptors on the cell membrane and utilize second messengers
amine hormone
chemical signals derived from the amino acids tyrosine or tyrptophan
hormone binding protein
proteins in the blood that bind to lipid-soluble hormones to transport them, prevent rapid inactivation and extend half-lives