UNC Biology 101L Pig Dissection
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Anterior or Cranial
Head
Posterior or Caudal
Tail
Dorsal
The pig's back (the side that is on the ground as the pig is being dissected)
Ventral
The side of the pig with it's belly (the side that gets cut open)
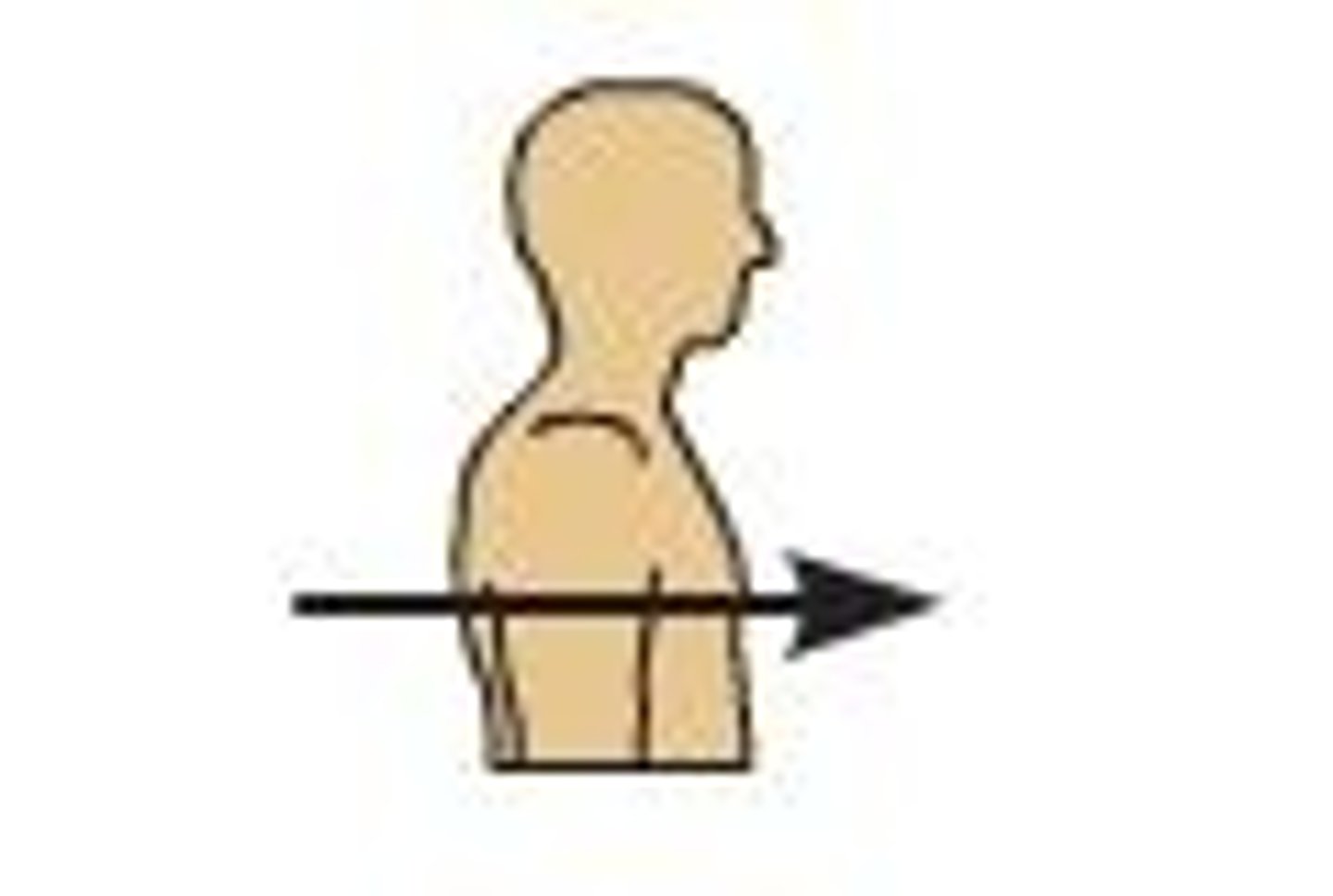
Proximal
Anything inside the pig that is more toward the middle
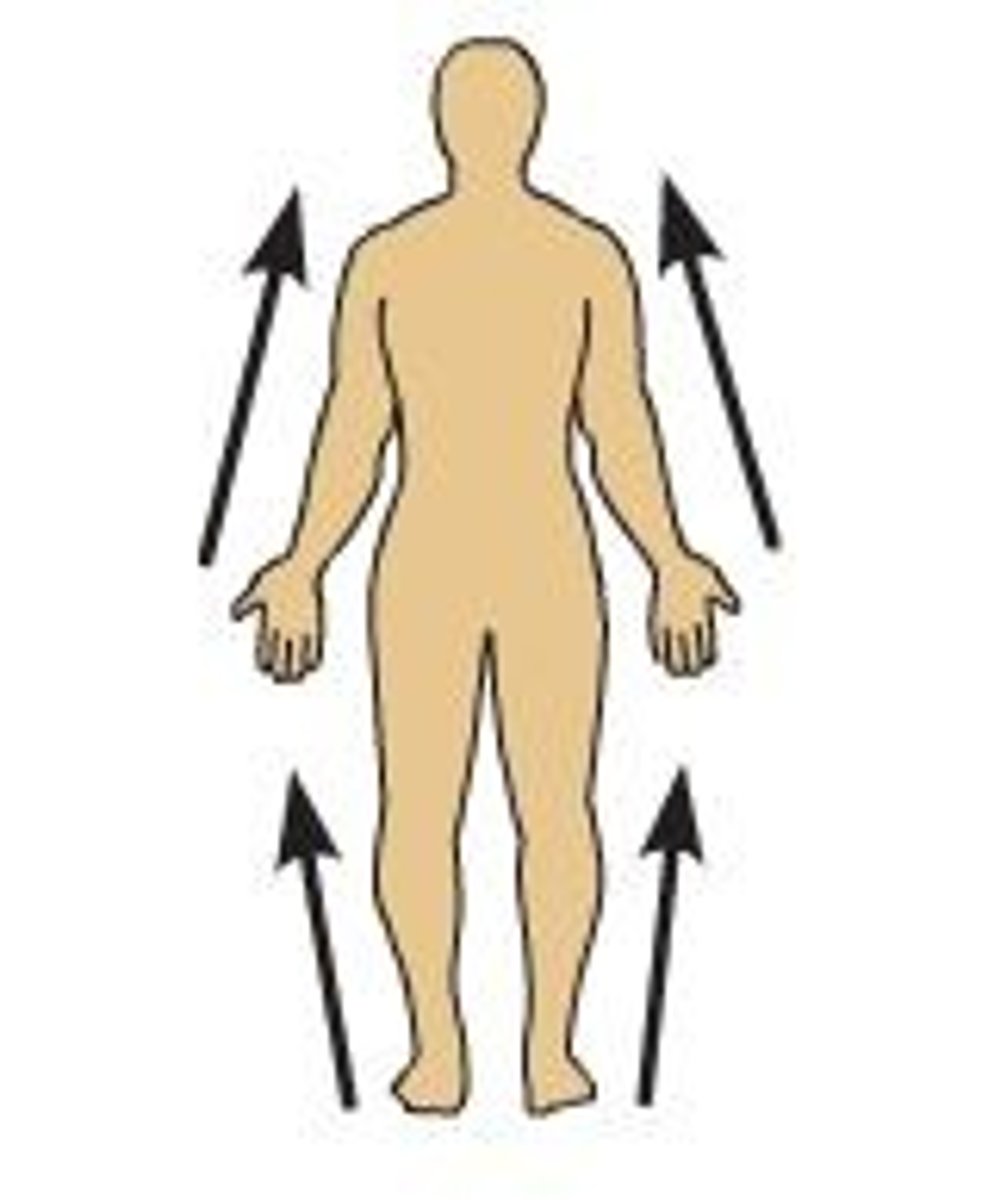
Distal
Anything more toward the outside of the pig or further away from the point of reference
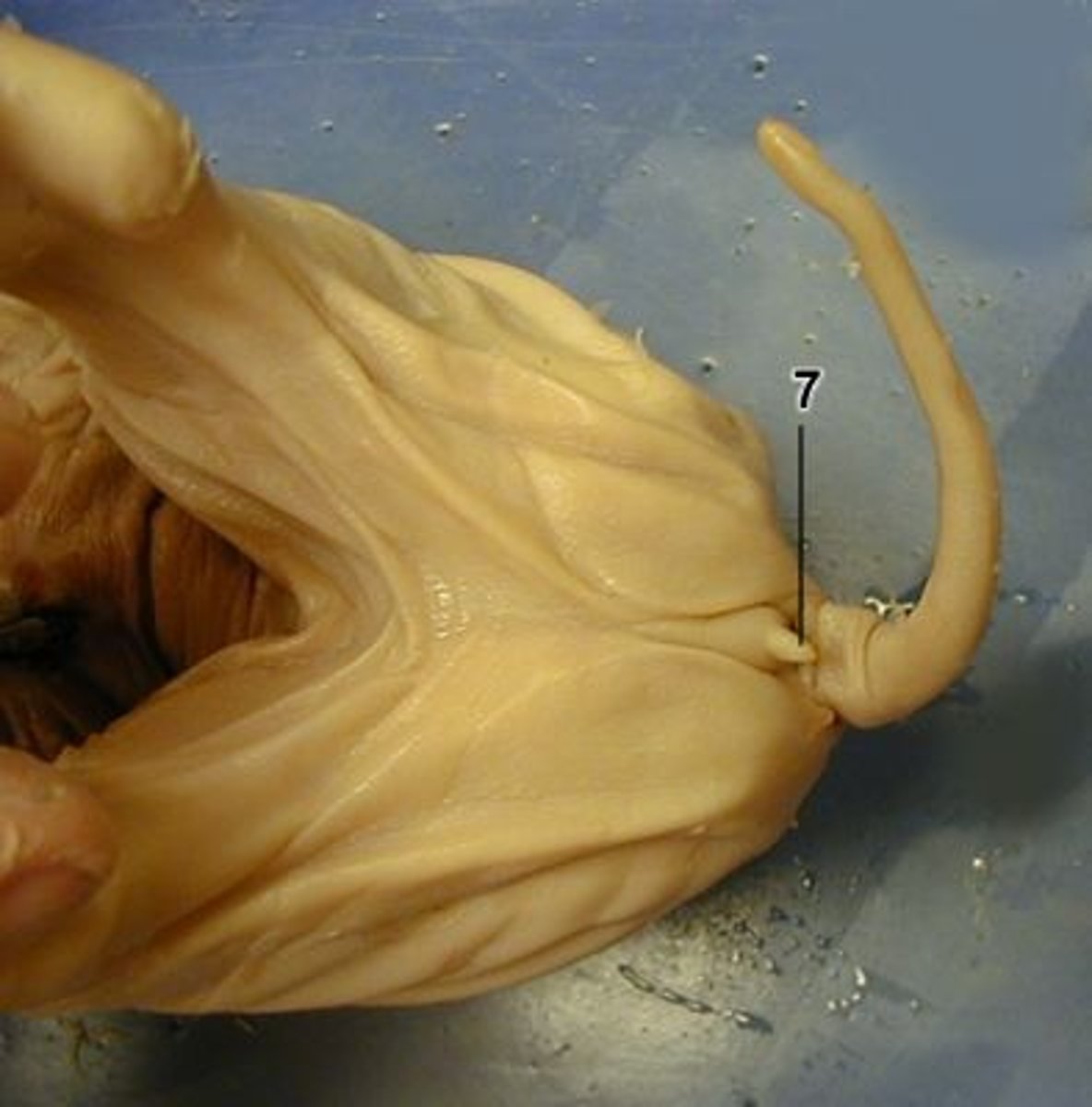
Urogenital Papilla
-A small bud-like protrusion just ventral to the anus
-If Urogenital Papilla is present, the pig is a female
-Lift the pig's tail to find the Urogenital Papilla
Scrotum
-Near the hind legs where the skin looks thin and puffy, forming two slightly rounded patches
-If Scrotum is present, the pig is male
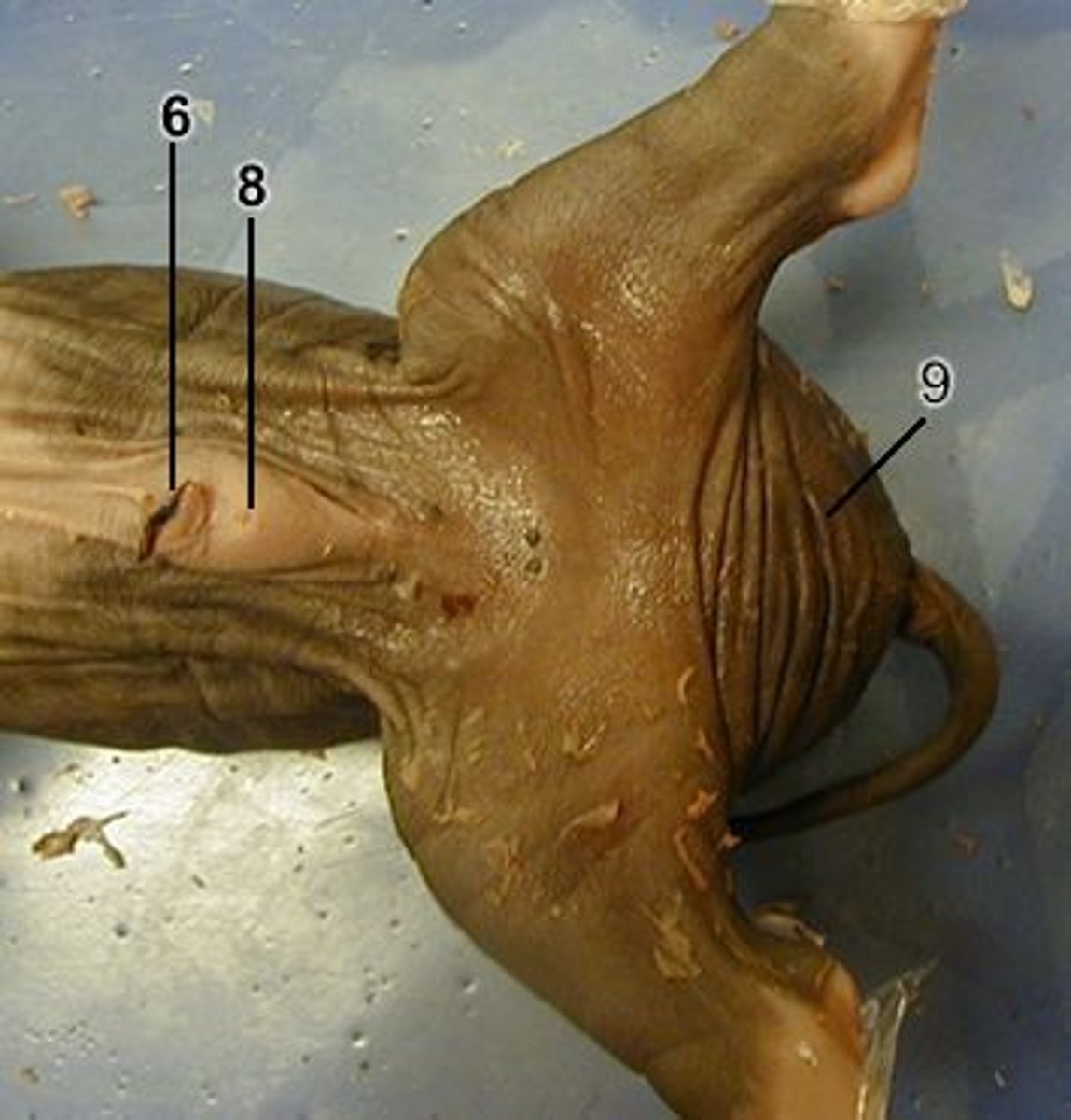
Male Urogenital Opening
A small mound just posterior to the umbilical cord on the ventral side
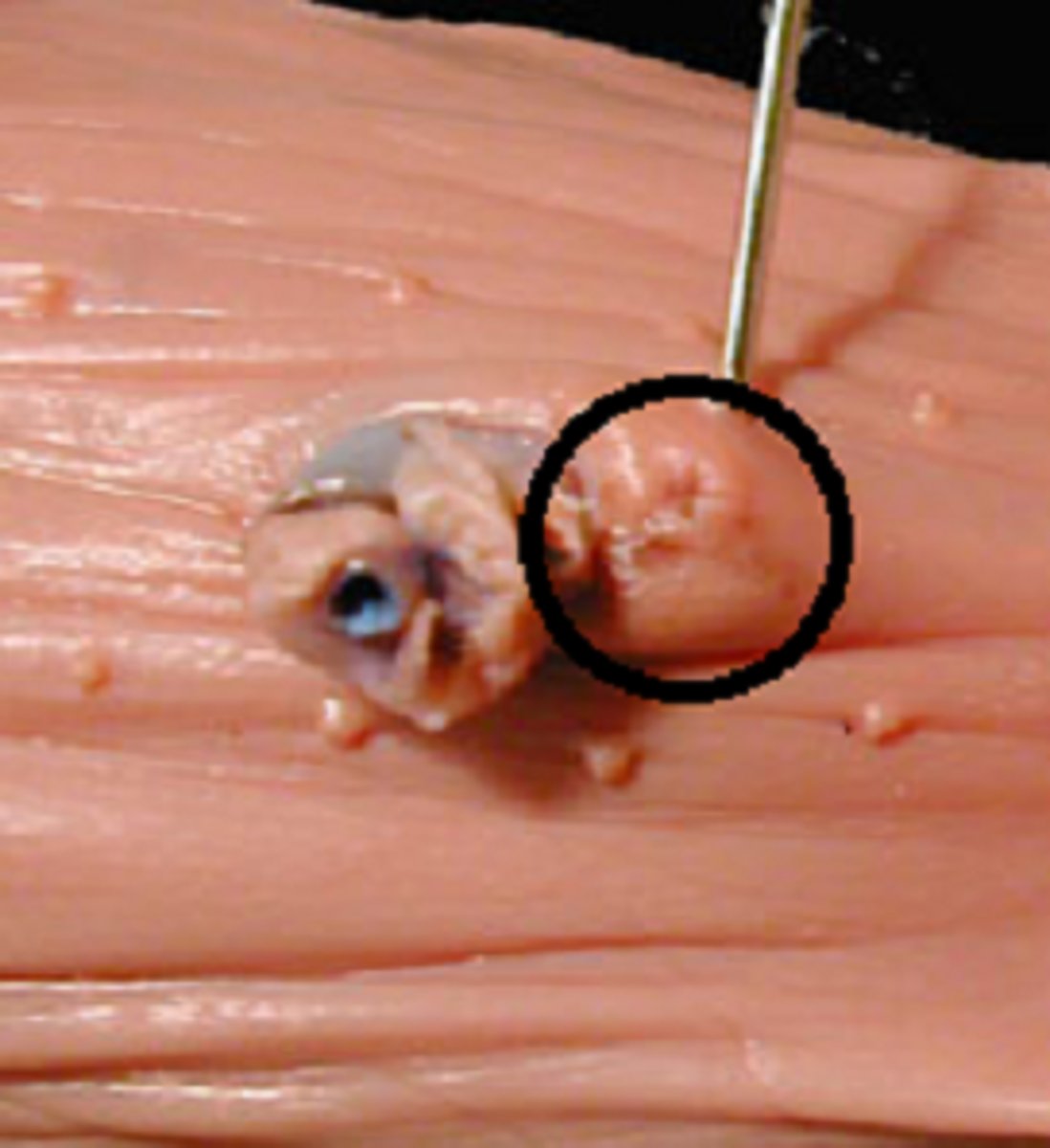
Epitrichum
-A filmy white layer of waxy material that peels off of the pig's skin
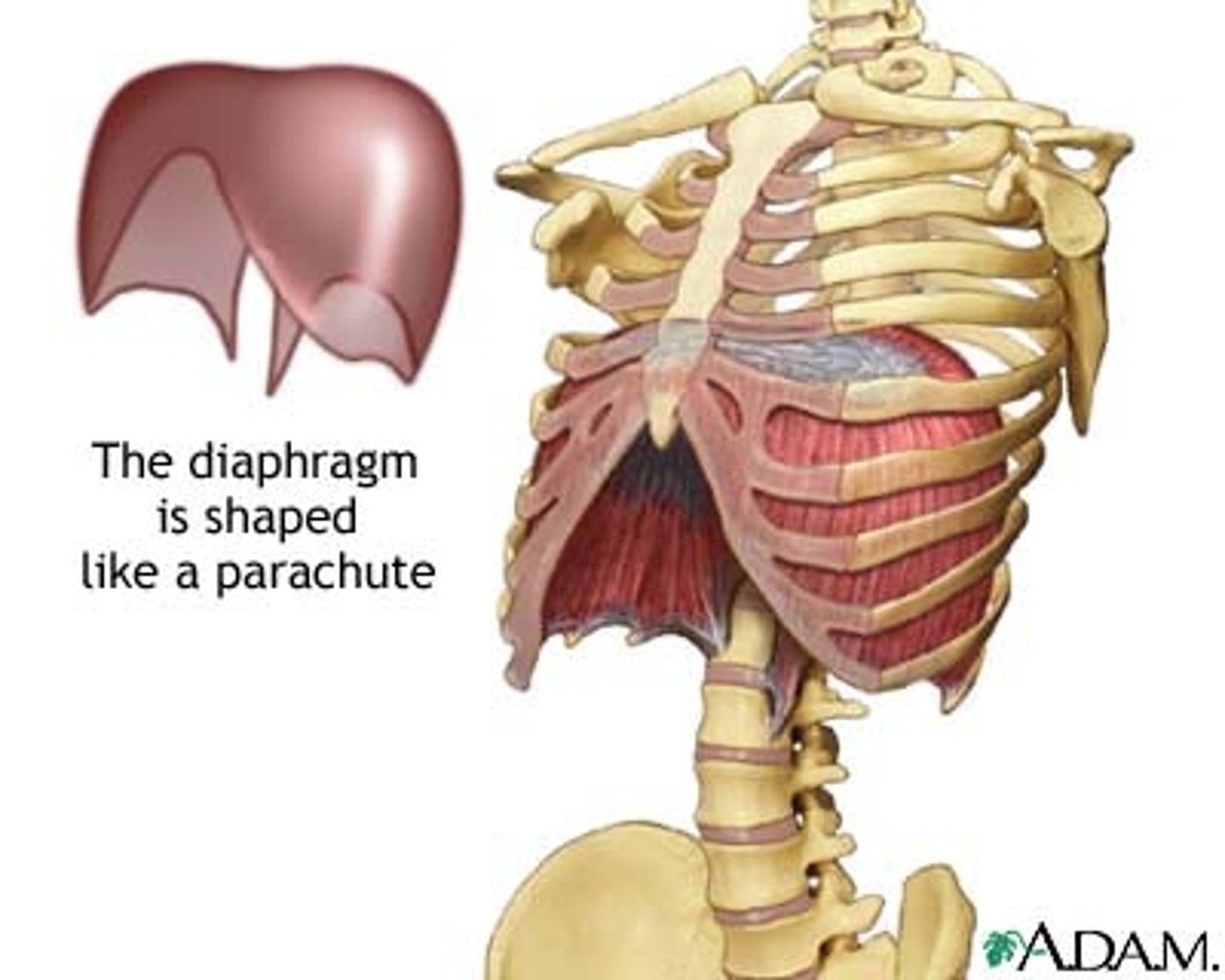
Thoracic Cavity & Abdominal Cavity are separated by the ______.
Diaphragm
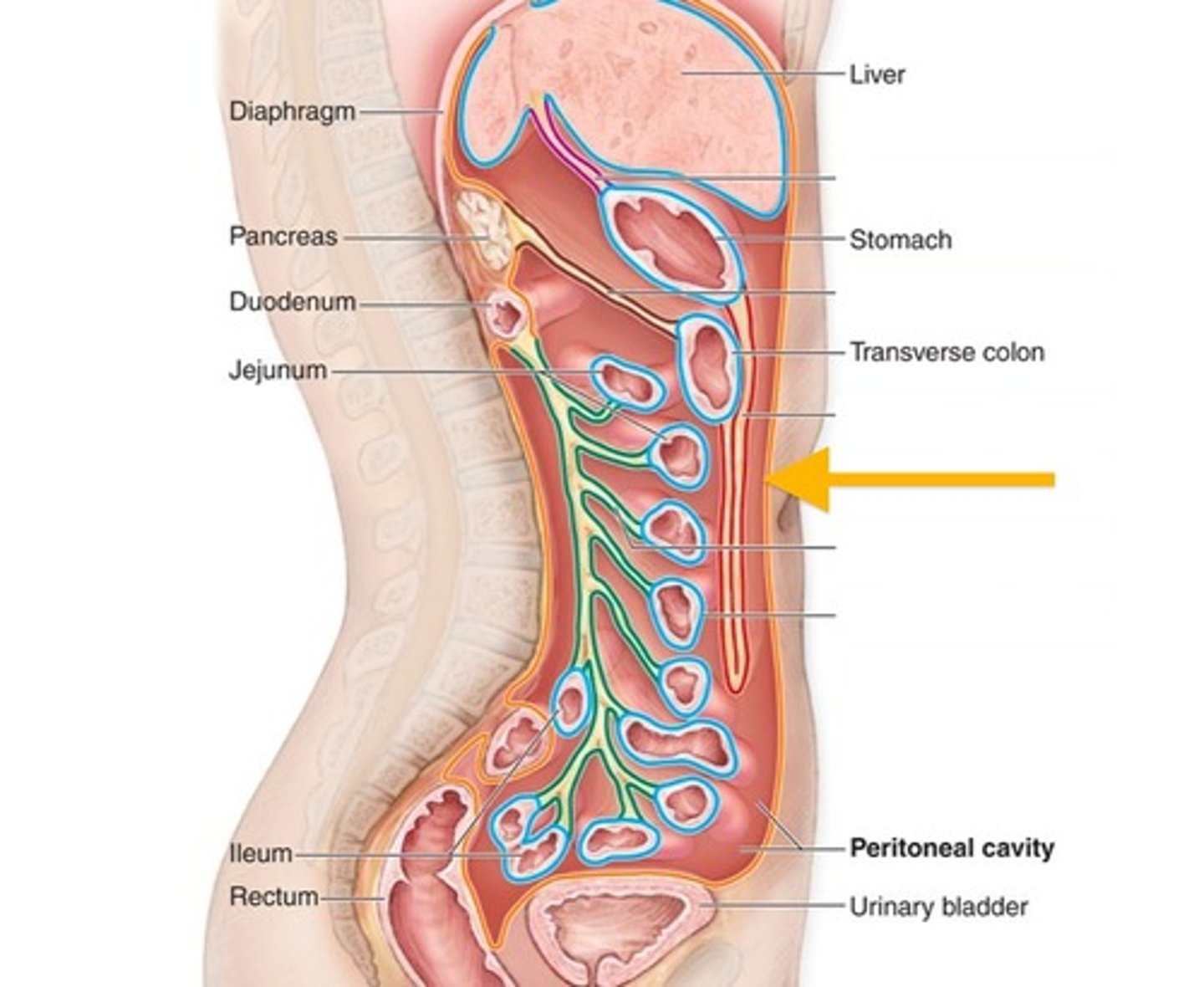
Liver
-Processes blood from the intestines, the blood that is filled with nutrients and other substances absorbed from the digestive system
-Part of the Digestive System
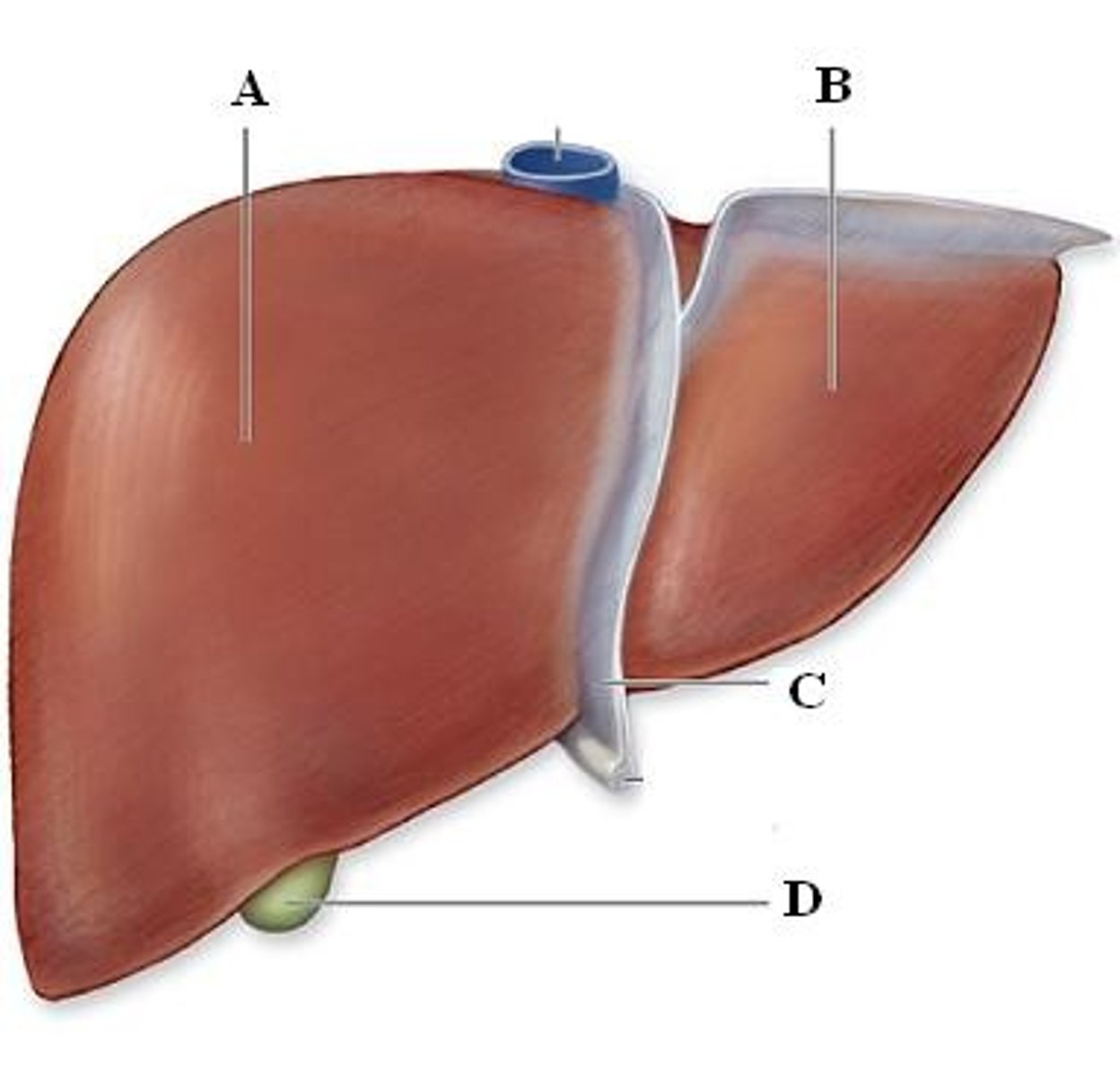
Gall Bladder
-Under the right liver lobe
-Stores bile produced in the liver
-Part of the Digestive System
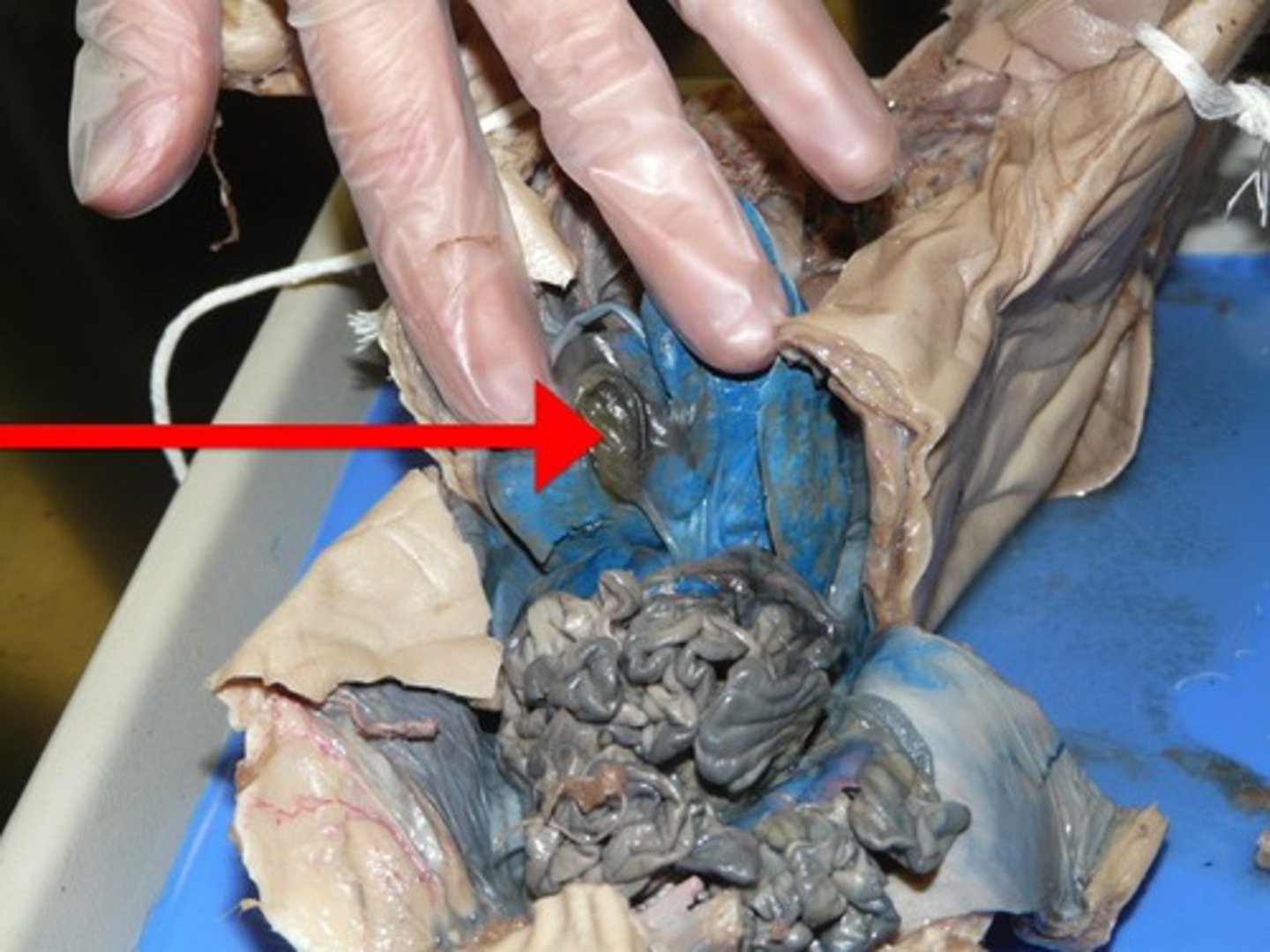
Bile
-A by-product of the breakdown of hemoglobin
-Part of the Digestive System
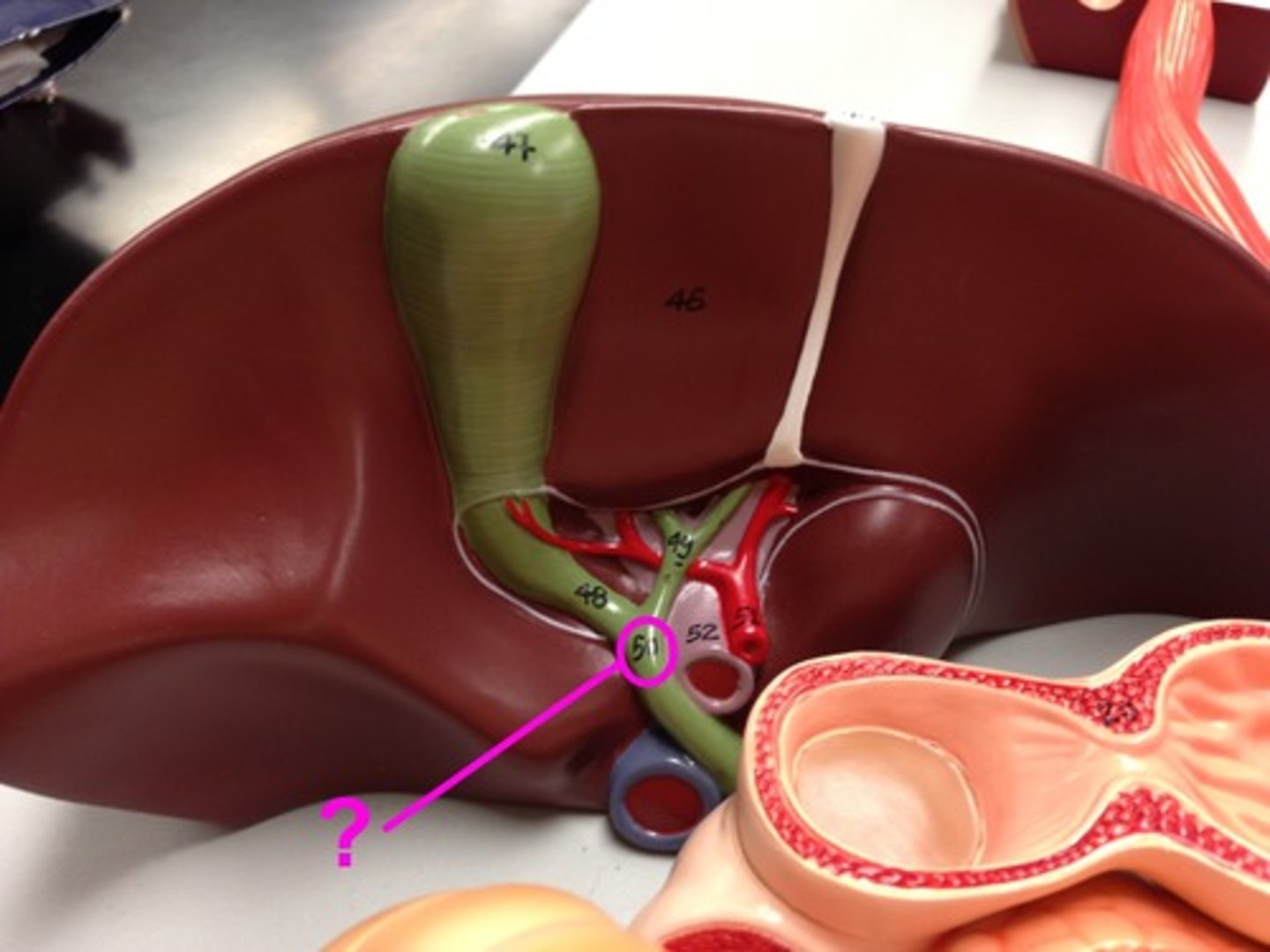
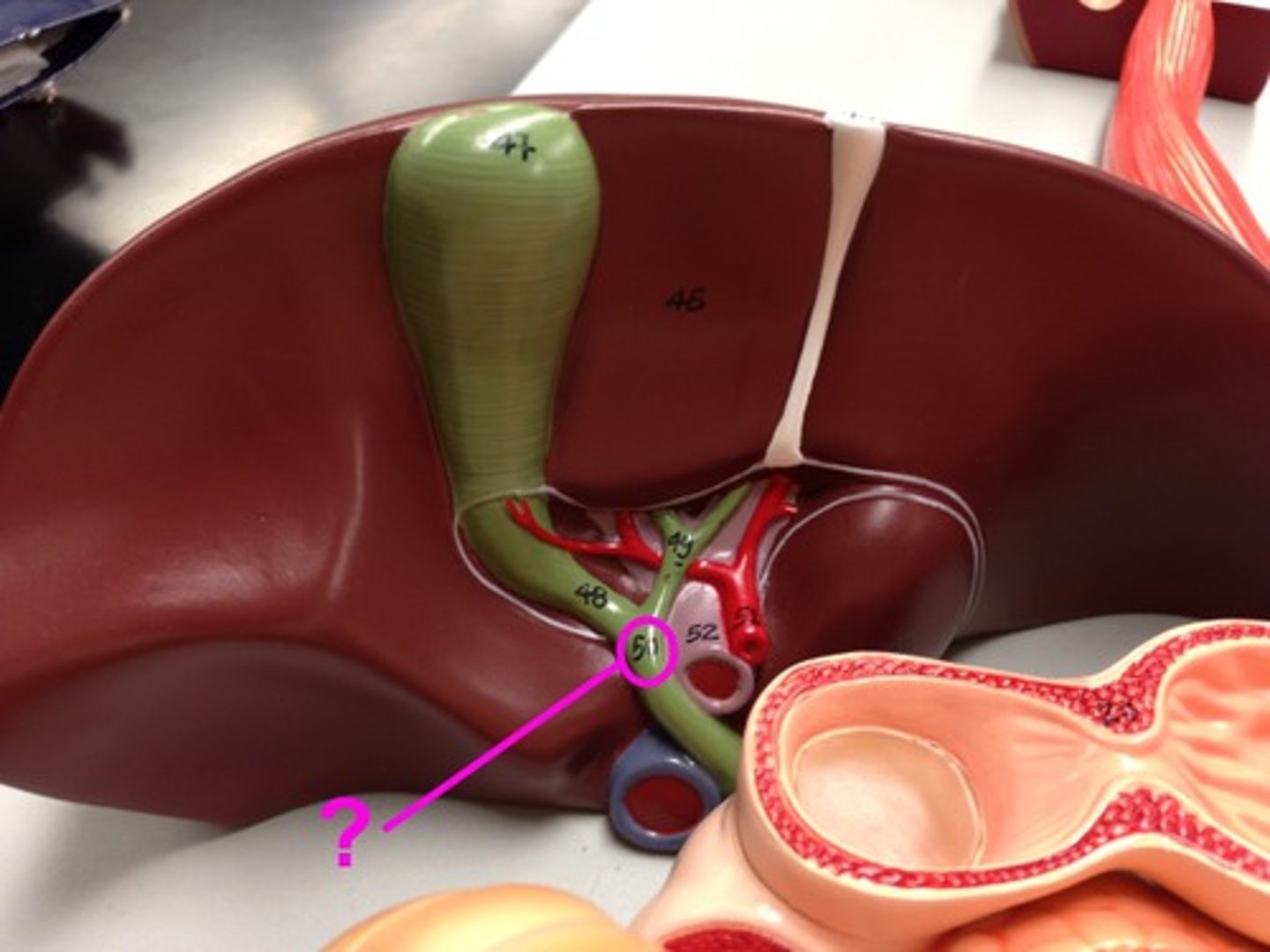
Small Intestine
-Where the gall bladder empties its contents into
-Part of the Digestive System
Bile Duct
-The duct that connects the Gall Bladder to the Small Intestine
-Part of the Digestive System
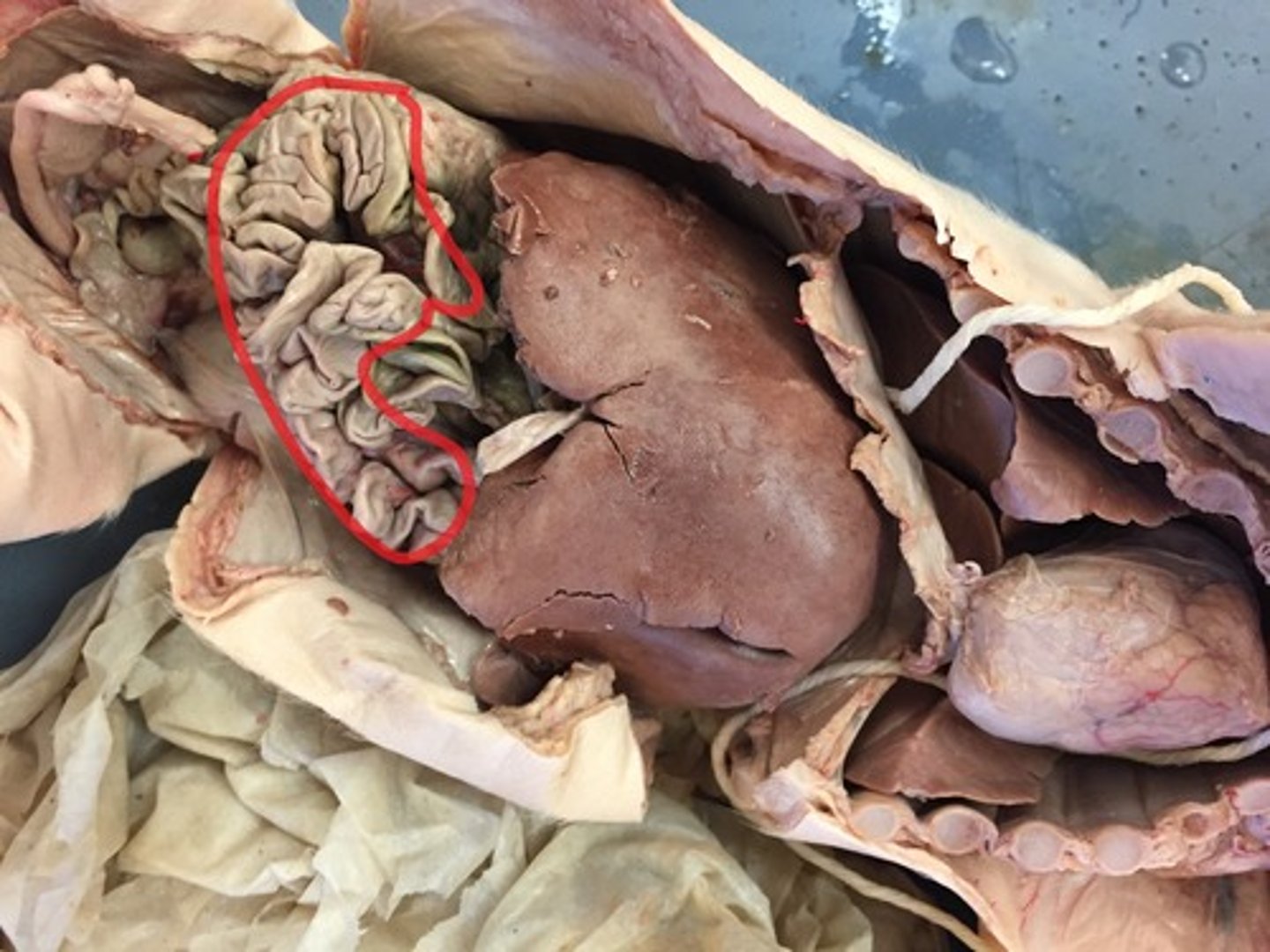
Meconium
-A Greenish-Black material formed mostly from amniotic fluid and sloughed-off cells that fills the fetal digestive system
-Part of the Digestive System

Spleen
-Located just to the left of the stomach
-A part of the immune system
-Part of the Digestive System
break down of blood cell
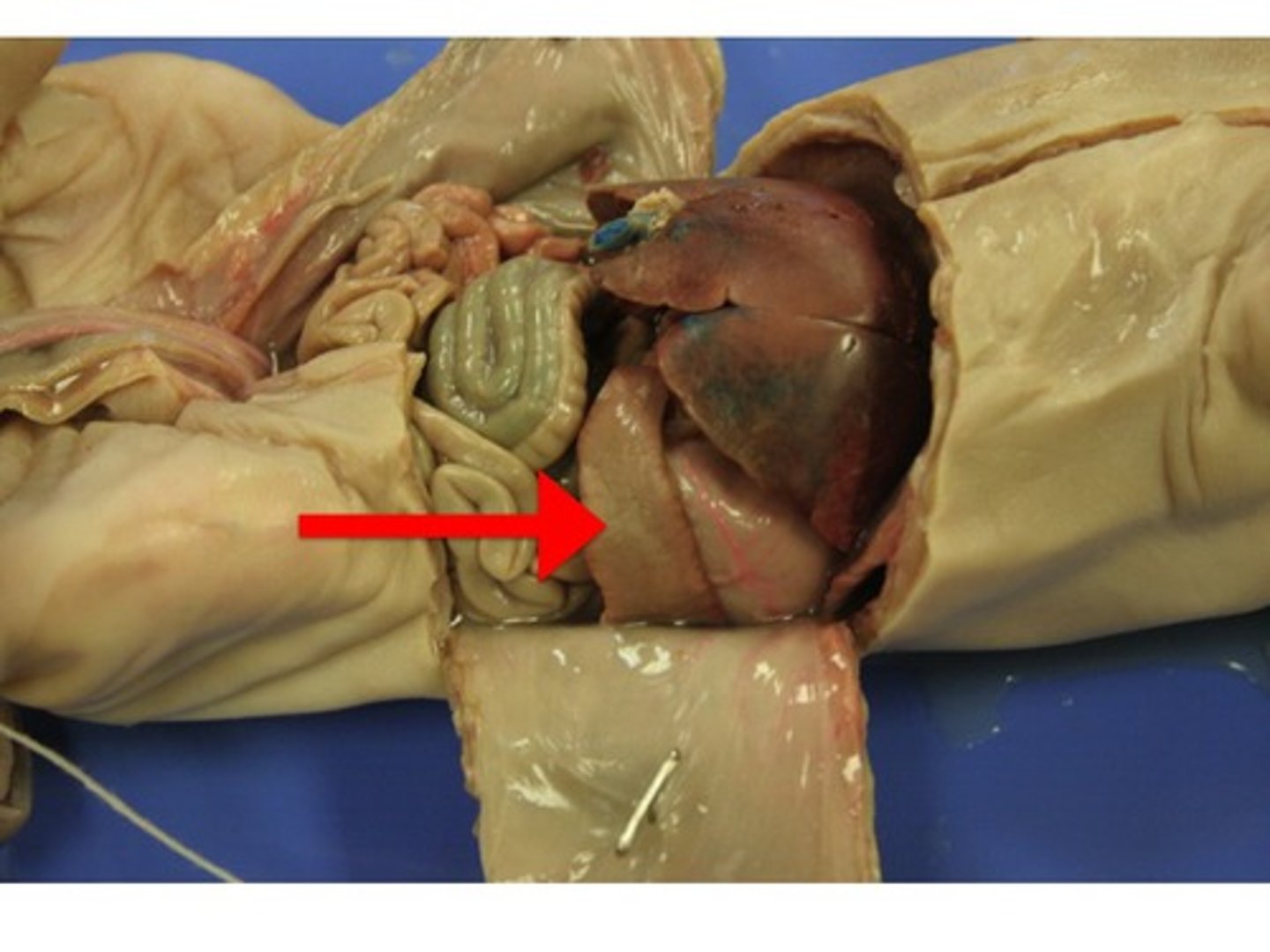
Pyloric Sphincter
-A circular muscle which prevents back flow of content
-Part of the Digestive System
the lower part of the stomach is separated from the small intestine by this.
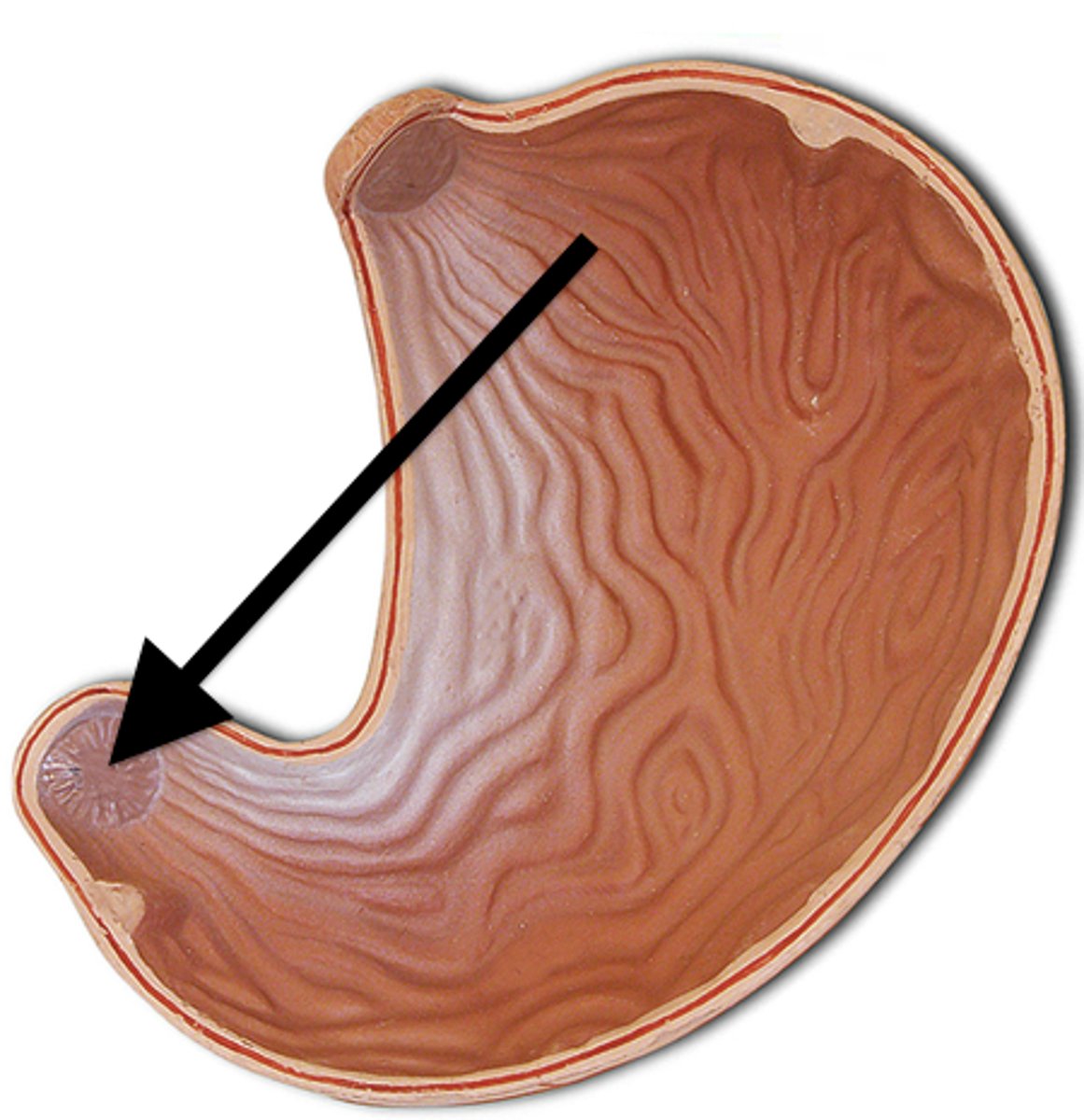
Duodenum
The first loop of the small intestine
-Part of the Digestive System
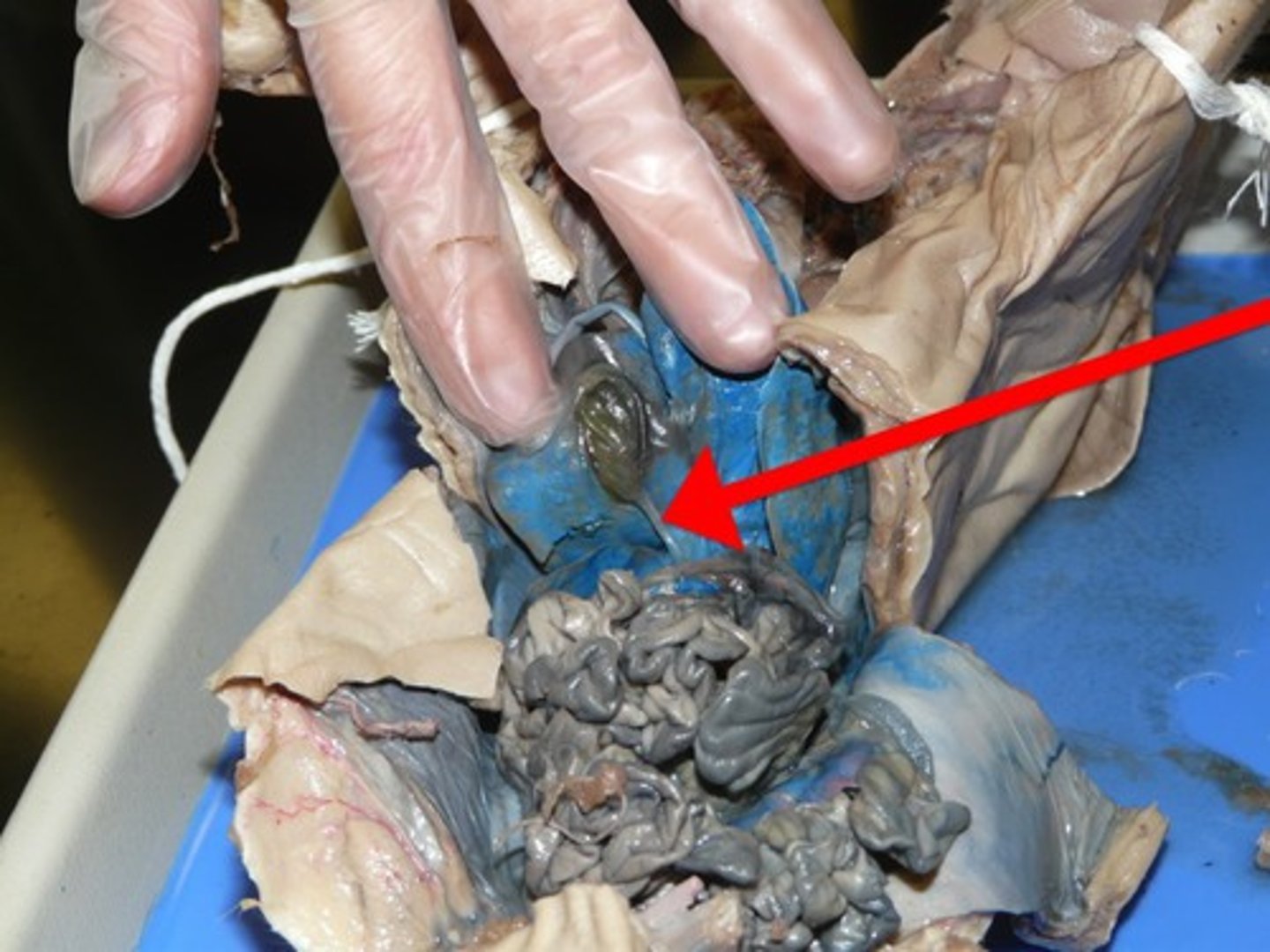
Pancreas
-An organ which has both digestive and endocrine functions
-A white granular organ between the stomach and the duodenum
-Is held in place by the mesentery membrane
-Empties through a duct into the small intestine
-Part of the Digestive System and Endocrine System
mesentery membrane
holds the pancreas in place
part of the peritoneum
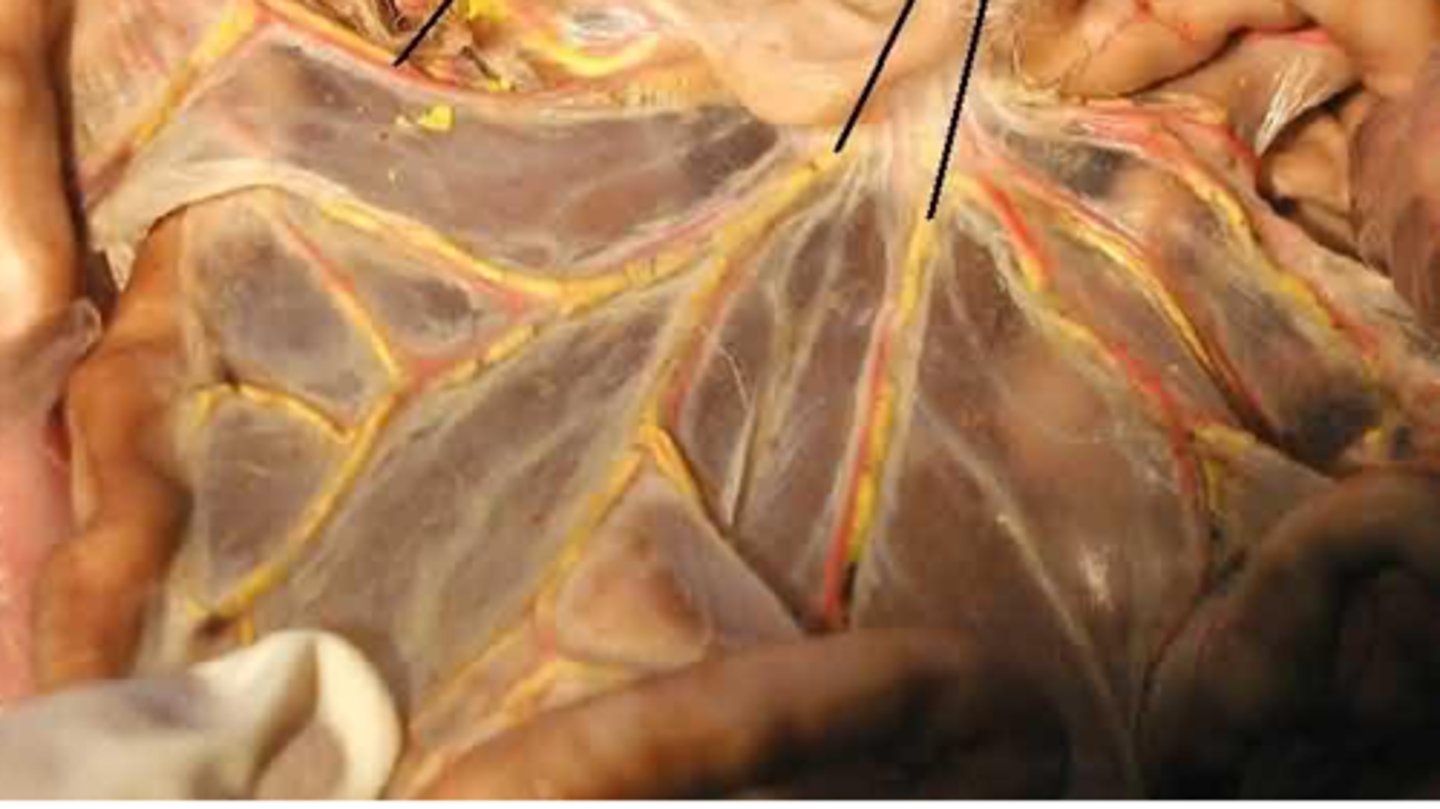
Peritoneum
-Lines the body cavity
-The mesentery membrane is part of the peritoneum
-Part of the Digestive System
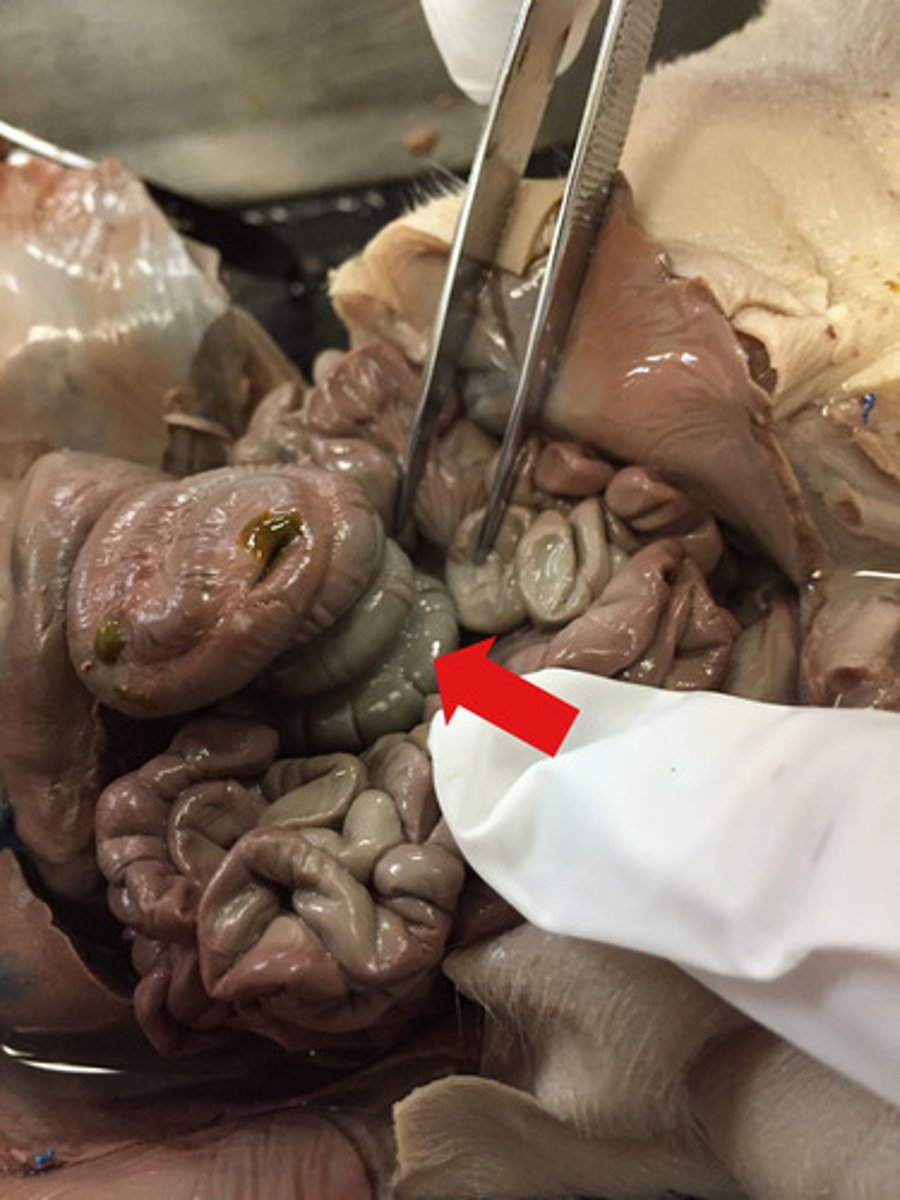
Caecum
-The small intestine toward the anus
-Located at the junction of the large intestine (colon) and the small intestine.
-Part of the Digestive System
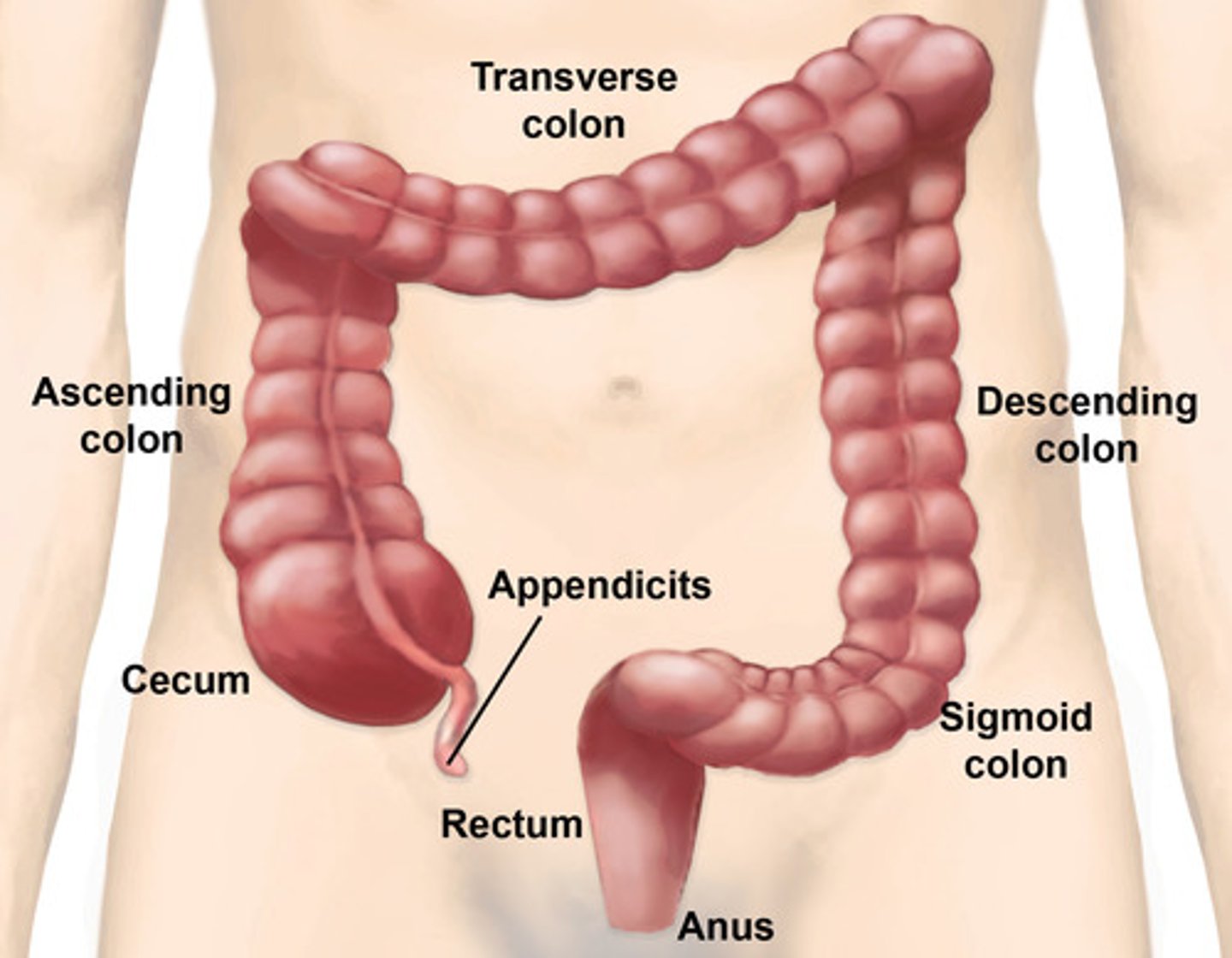
Large Intestine
-Also known as the colon
-Ends in the rectum
-Part of the Digestive System
Rectum
-Exits out at the anus
-Part of the Digestive System
Pharynx
-The cavity at the back of the mouth
-Part of the Digestive System
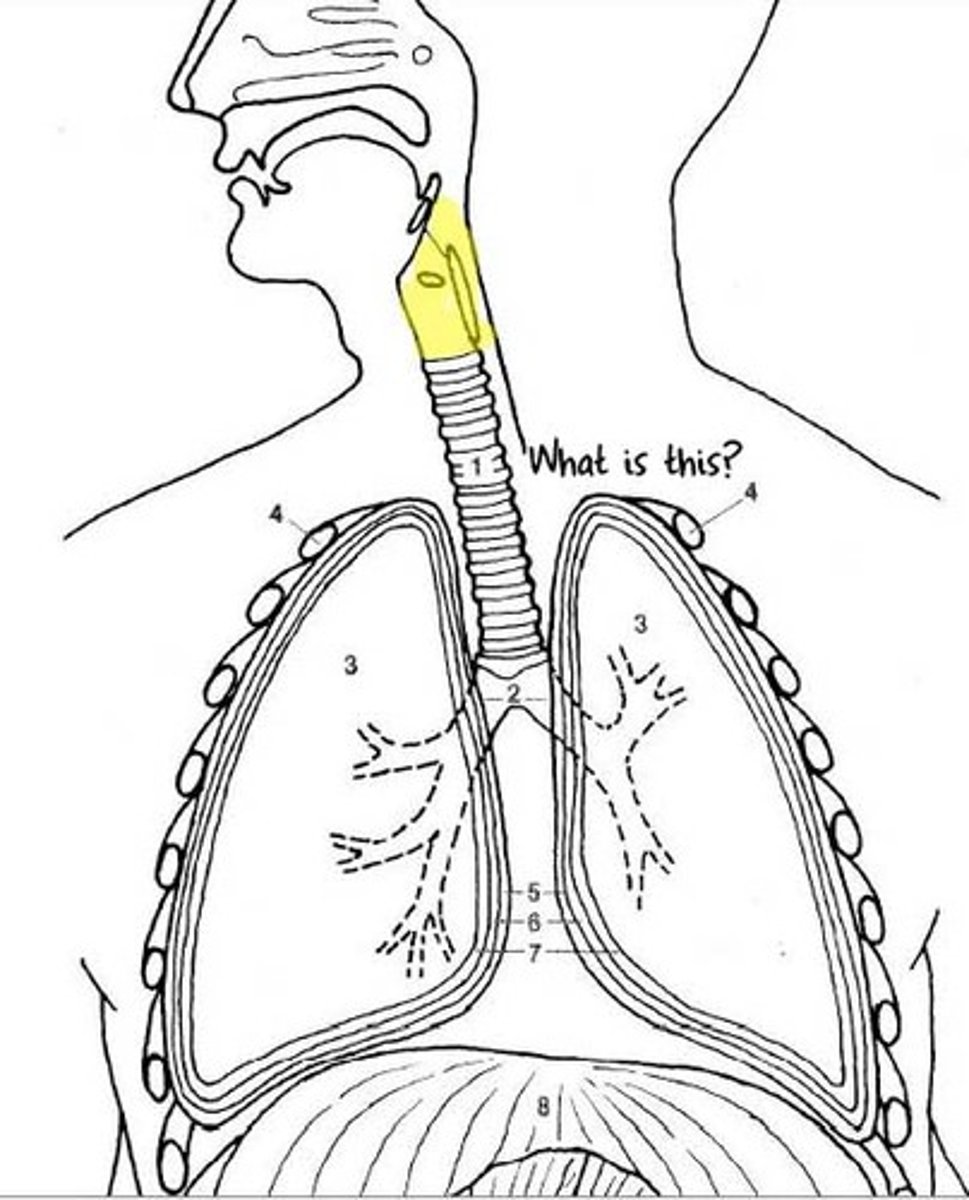
Epiglottis
-A device designed to keep the respiratory and digestive systems separate
-Located in the back of the mouth in the pharynx
-Activated during swallowing to cover the glottis (the opening into the respiratory system)
-Part of the Digestive System
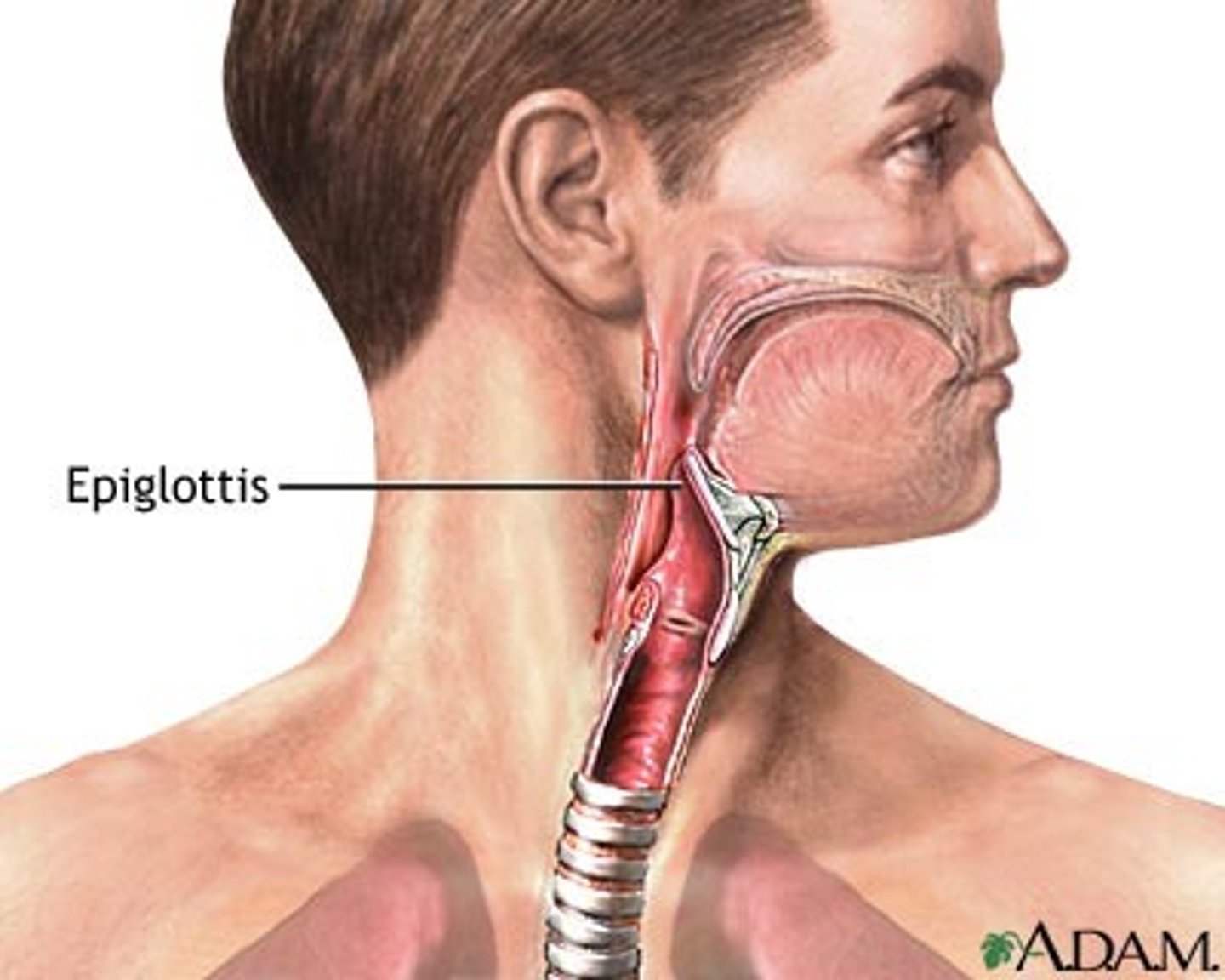
Glottis
-The opening into the respiratory system
-Part of the Respiratory system
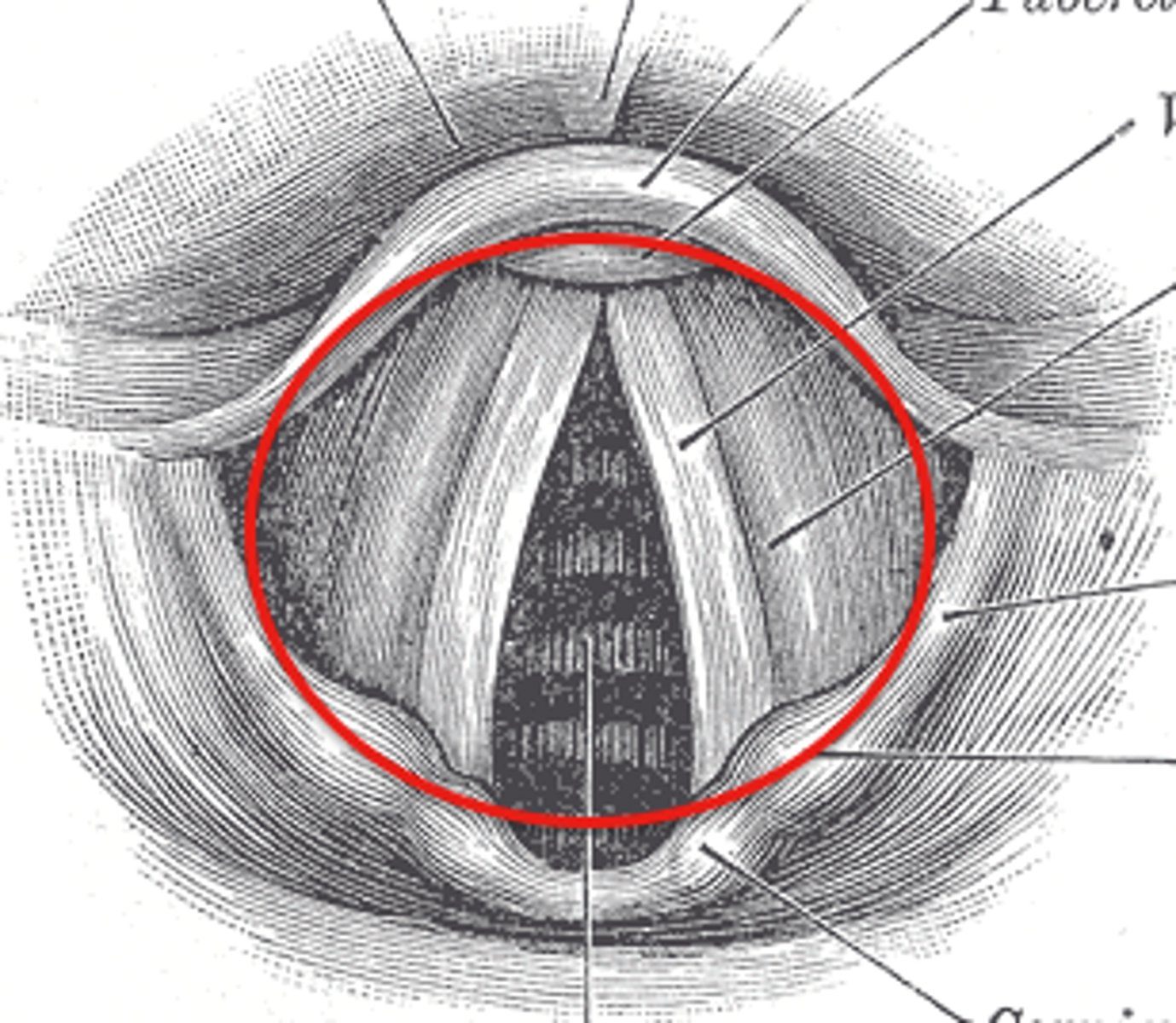
Esophagus
-The first part of the system that has solely a digestive function
-A dorsal white tube running through the diaphragm (IT IS NOT BLUE)
-If you pull on this stomach, this white tube wiggles
-Part of the Digestive System
Lungs
-The major organs of respiration
-Are found in two pleural cavities on ether side of the pericardial cavity within the thoracic cavity
-Part of the Respiratory System
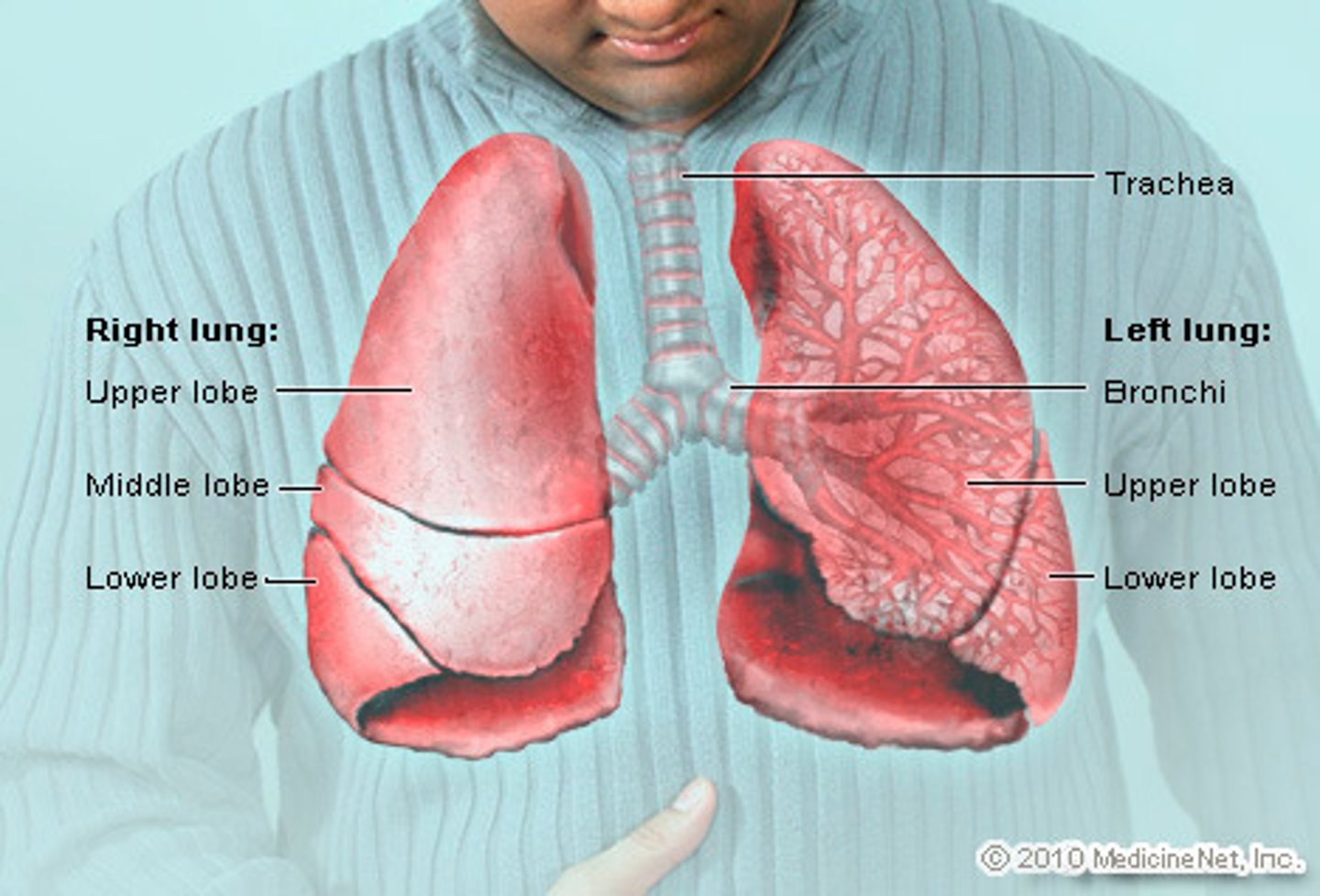
Diaphragm
Can be considered part of the Respiratory System since its contraction acts as the pull on the "bellows," bringing about the negative pressure needed to inflate the lugs.
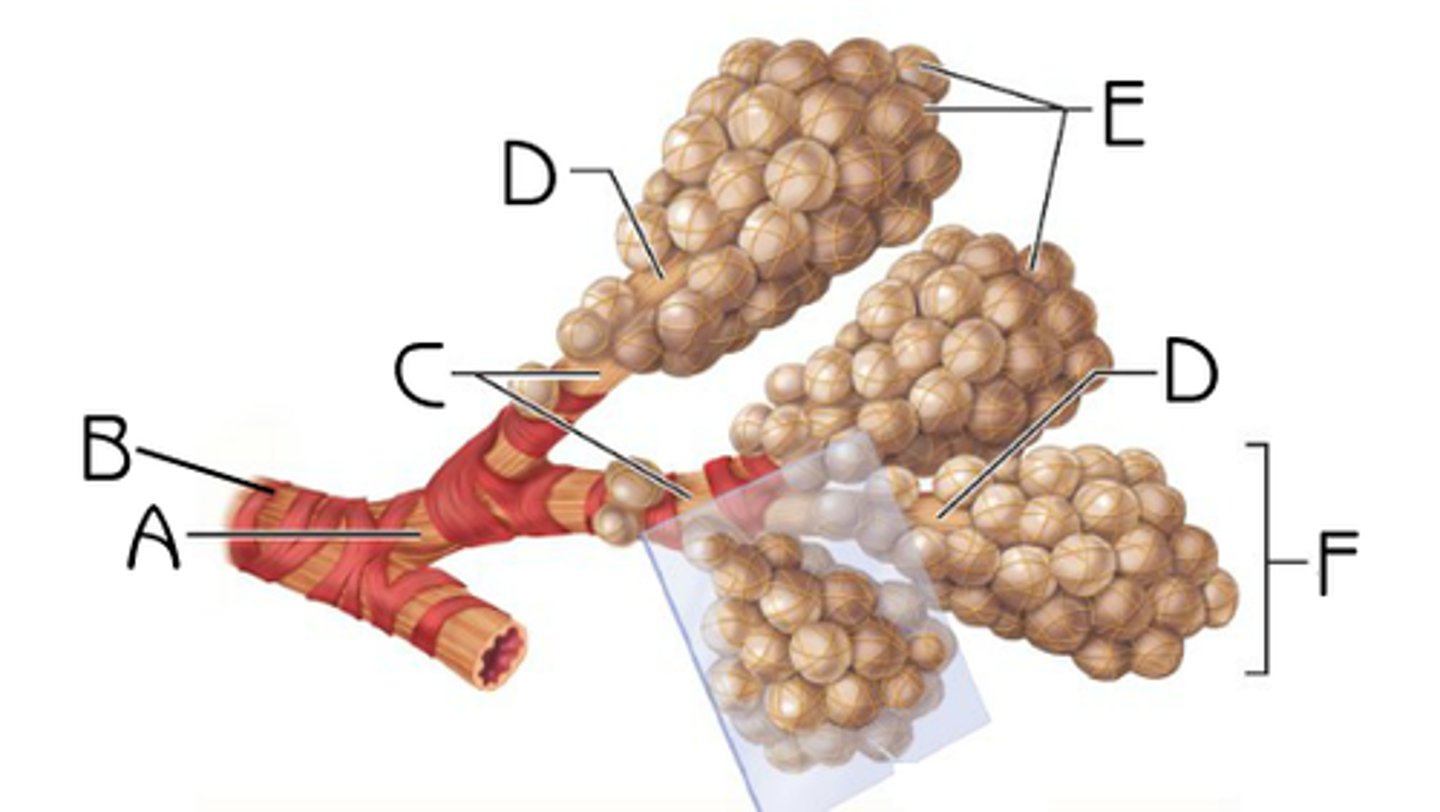
Bronchioles
-Small tubes within each lung that lead from the alveoli (or small terminal sacs) where the O2/CO2 exchange actually occurs
-Join together to form the larger bronchus which leads into each lung
-Part of the Respiratory System
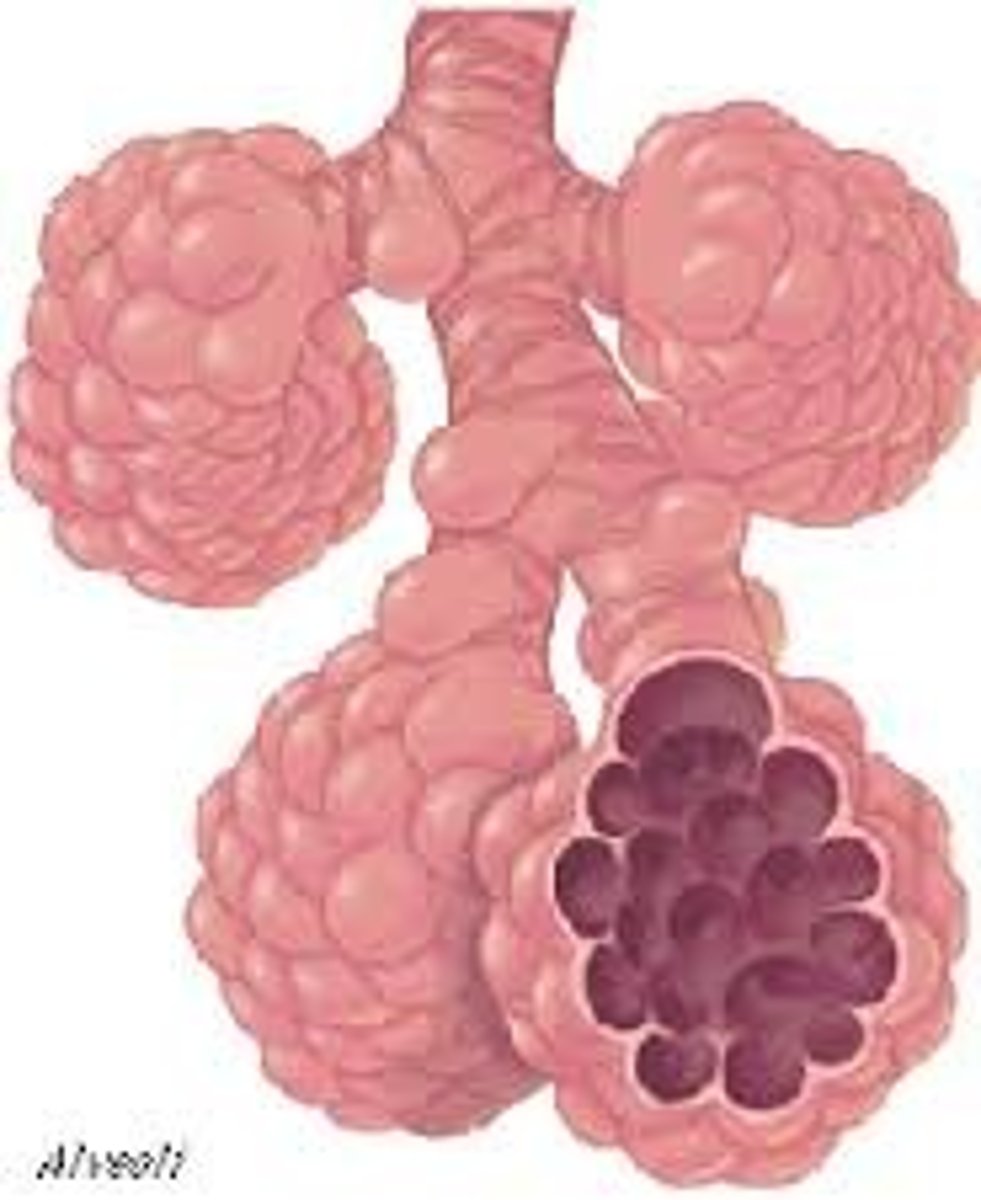
Alveoli
-Also called the Small Terminal Sacs
-Where O2/CO2 exchange actually occurs
-Part of the Respiratory System
Bronchus
-Plural = Bronchi
-Made up of Bronchioles that join together in each lung
-Joins the trachea which leads into the larynx
-Part of the Respiratory System
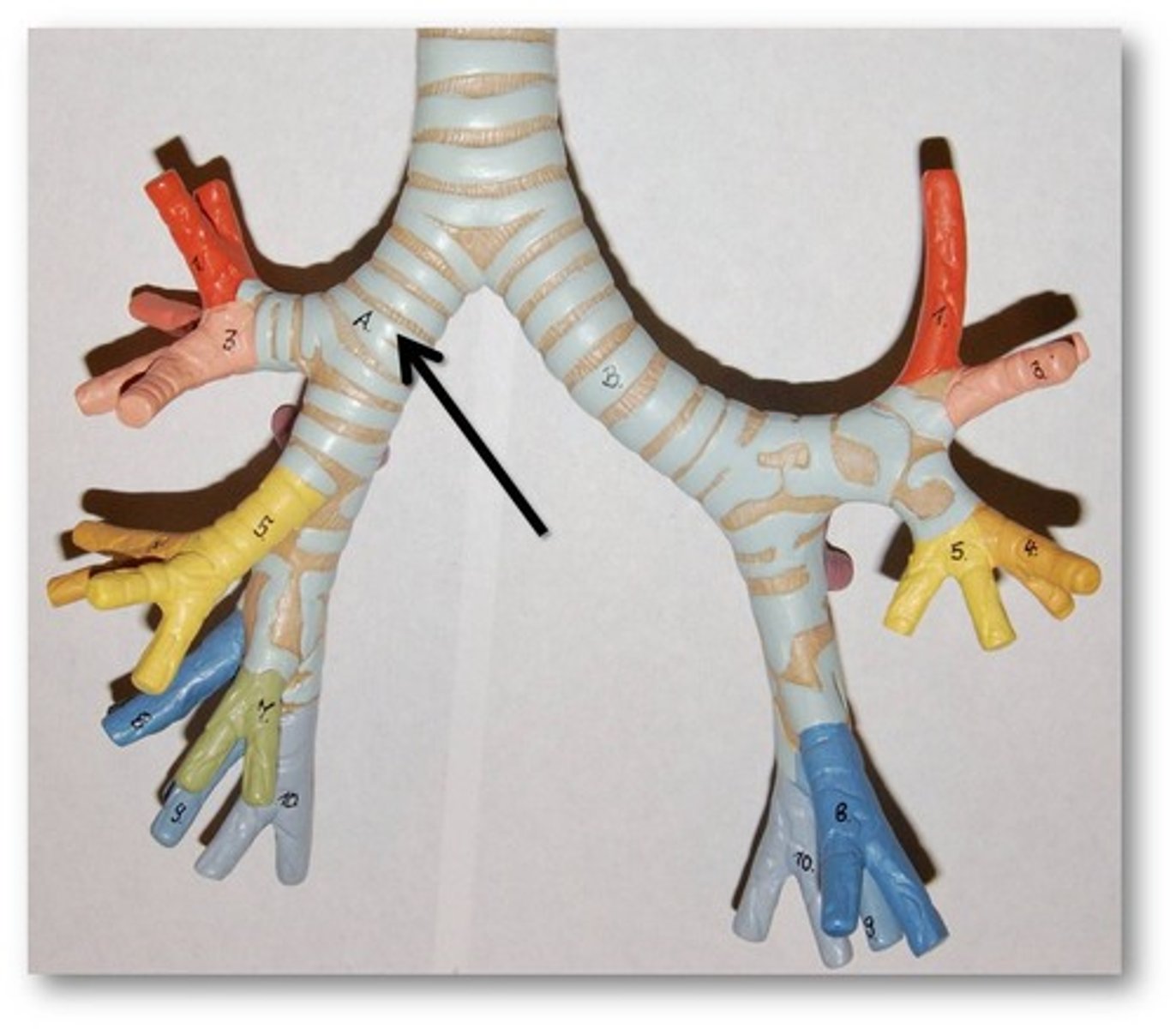
Trachea
-Leads into the larynx or voice box
-Part of the Respiratory System
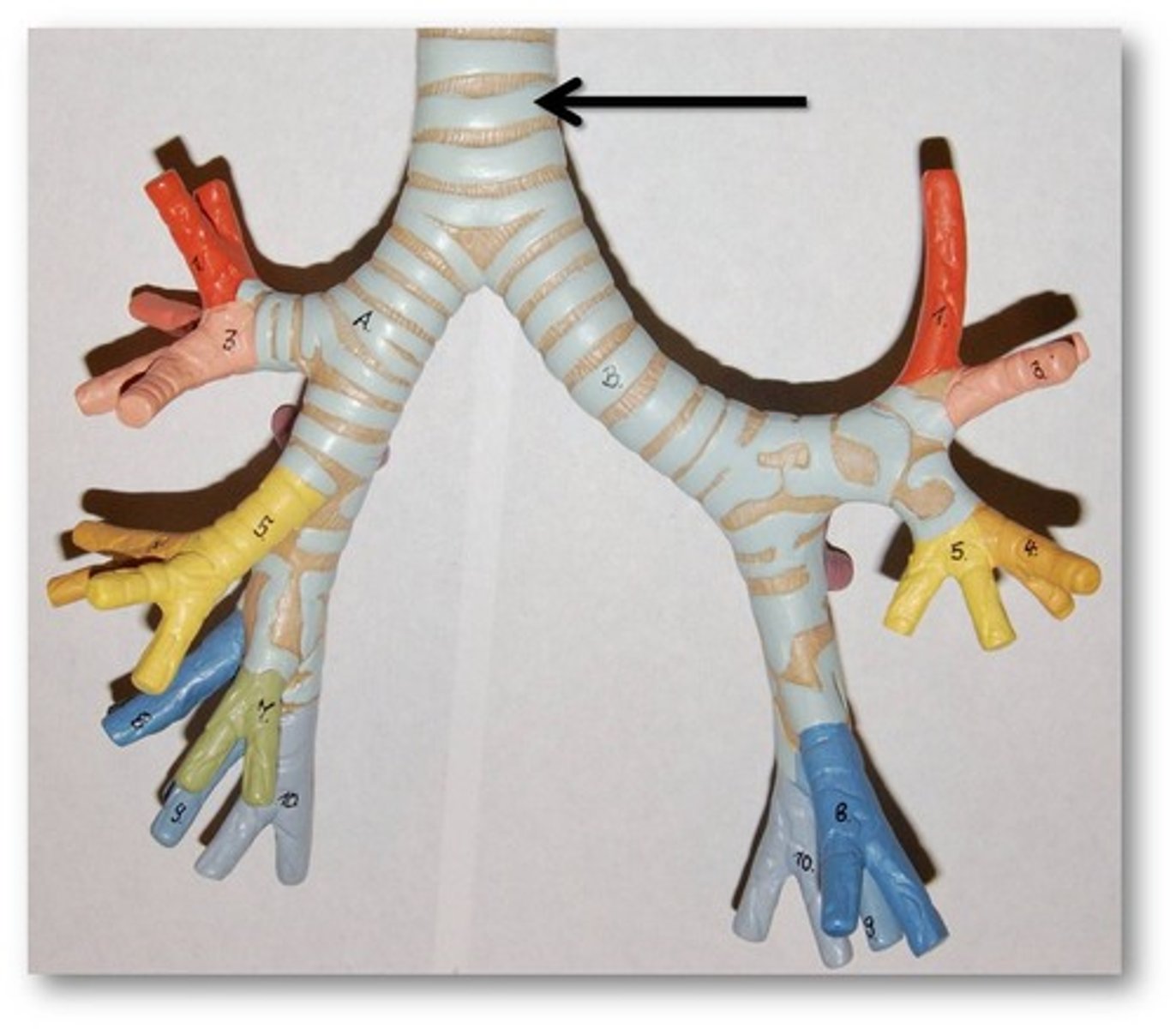
Larynx
-The Voice Box
-Part of the Respiratory System
Kidney
-Where the Excretory System Begins
-Where the blood is processed to remove its load of metabolic waste
_Looks like bumps near the spinal chord and are covered by the peritoneum which lines the abdominal cavity
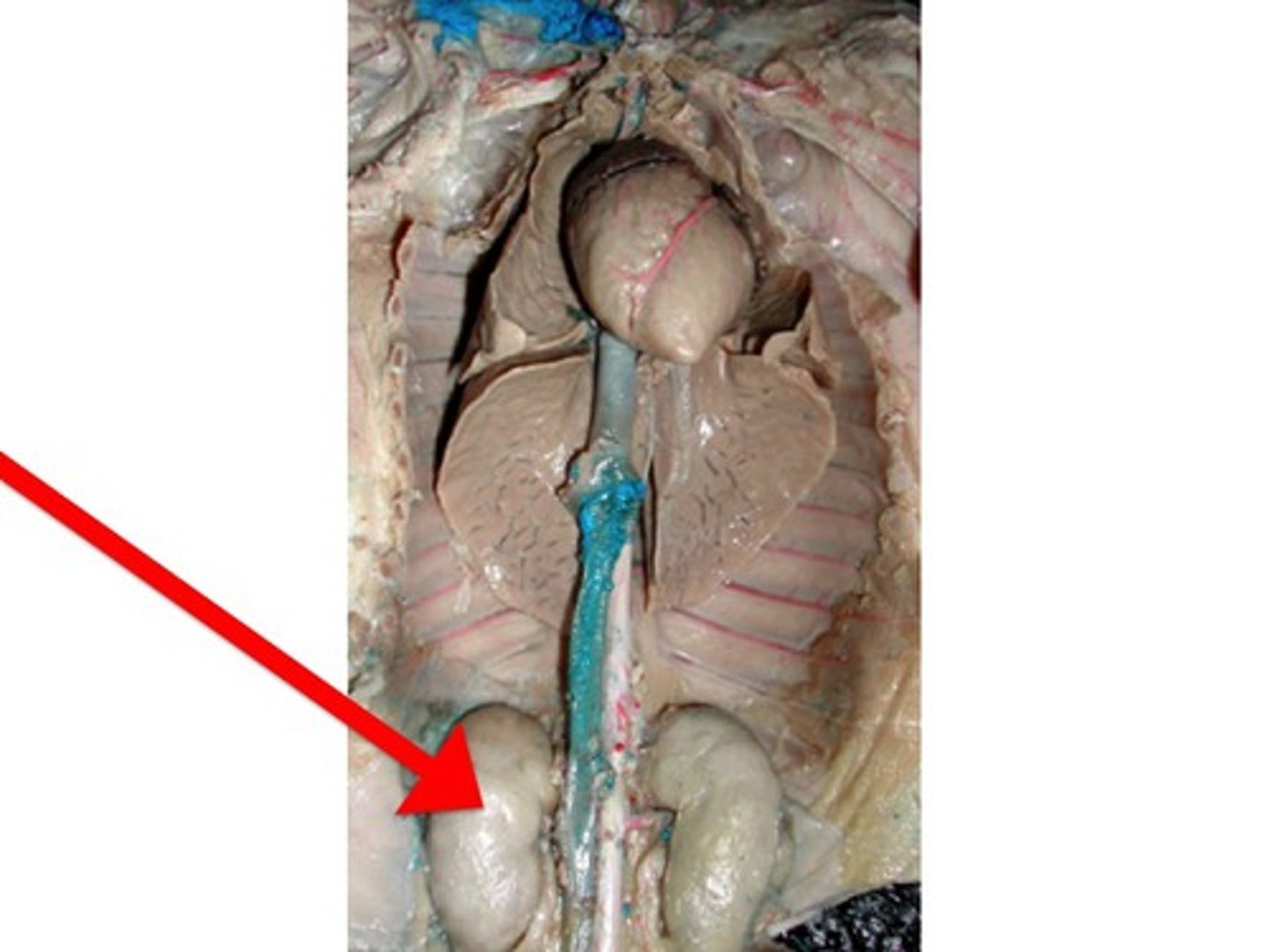
Adrenal Gland
-The spongy tissue located as a cap on the kidney
-Is part of the Excretory System
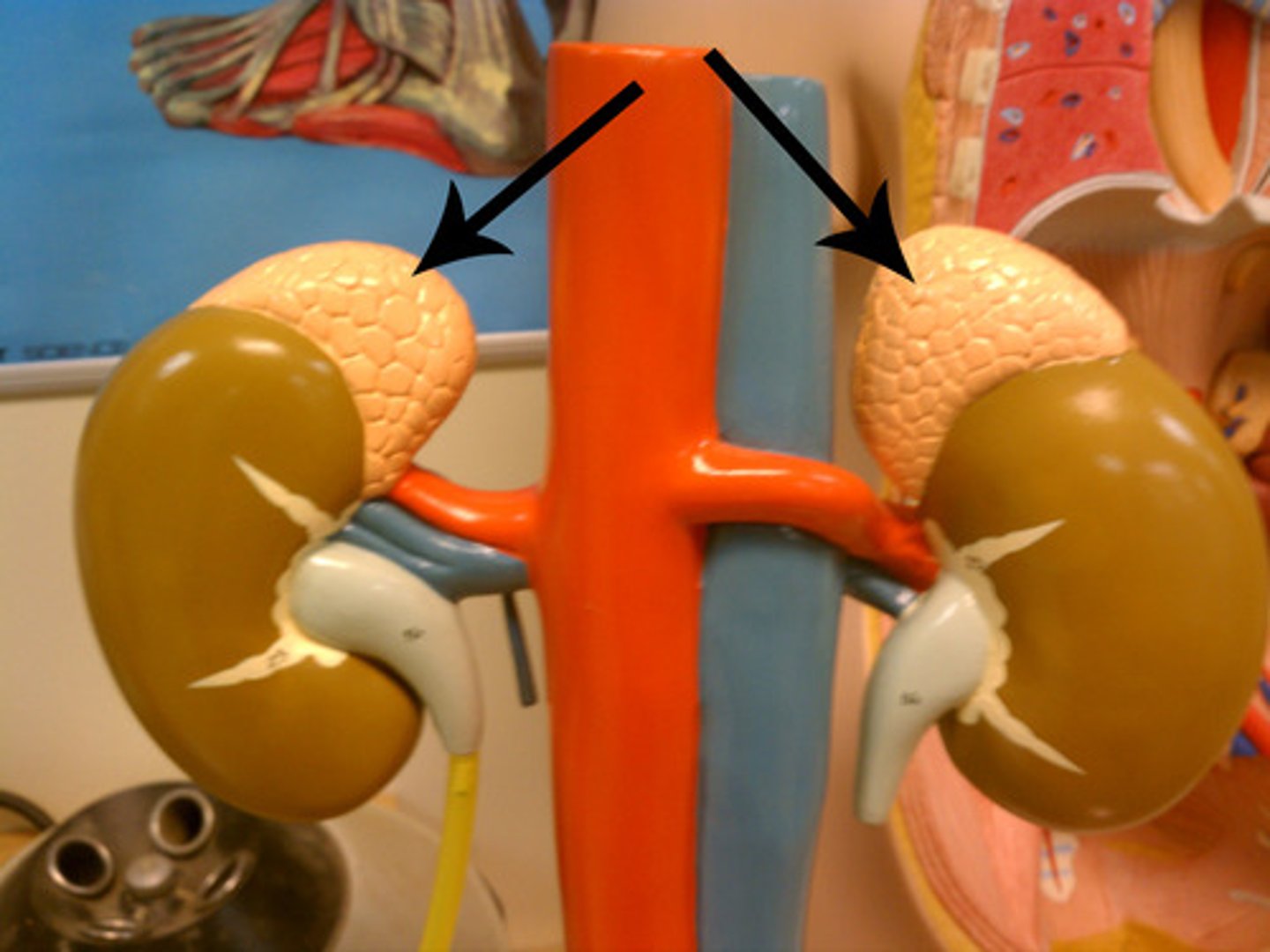
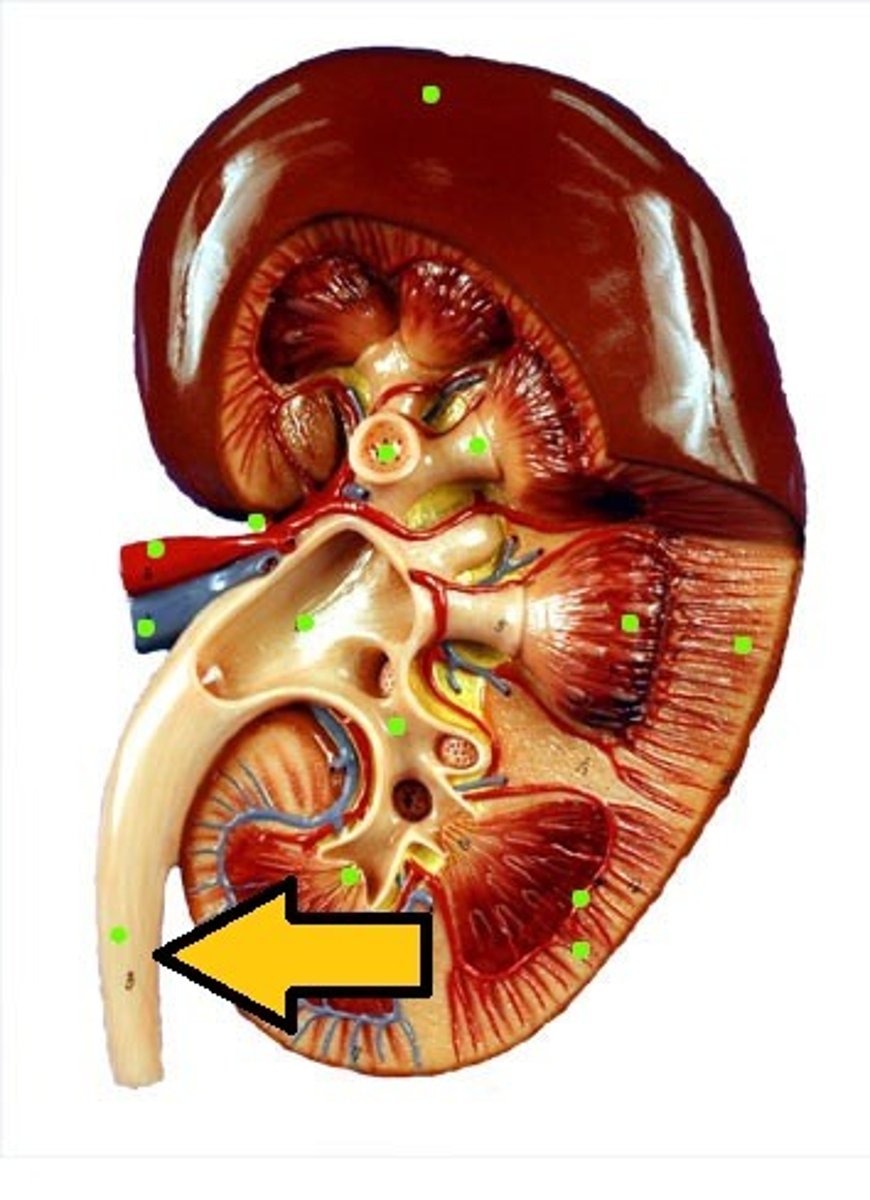
Ureter
-Leads from the kidney to the urinary bladder
-Is part of the Excretory System
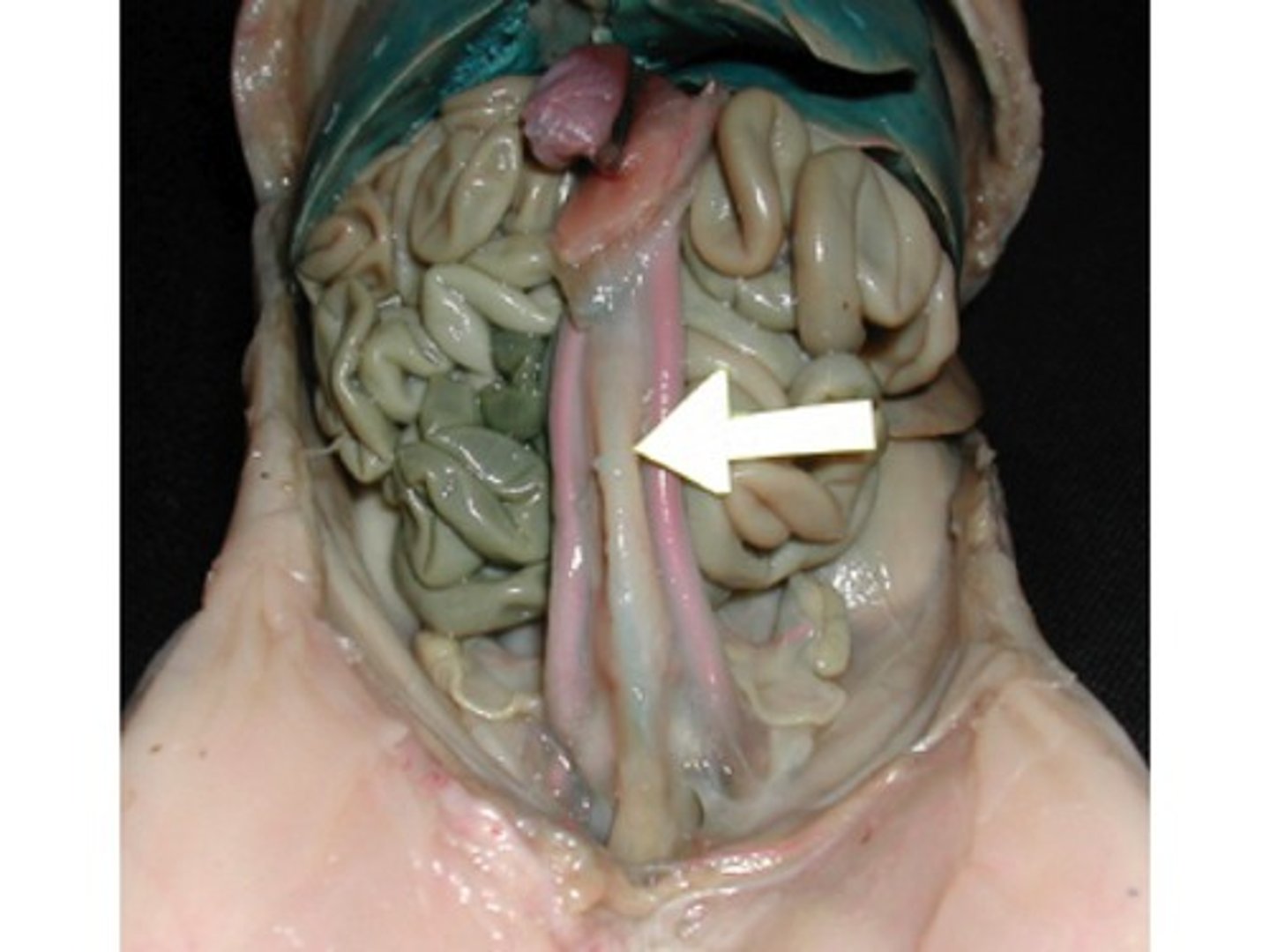
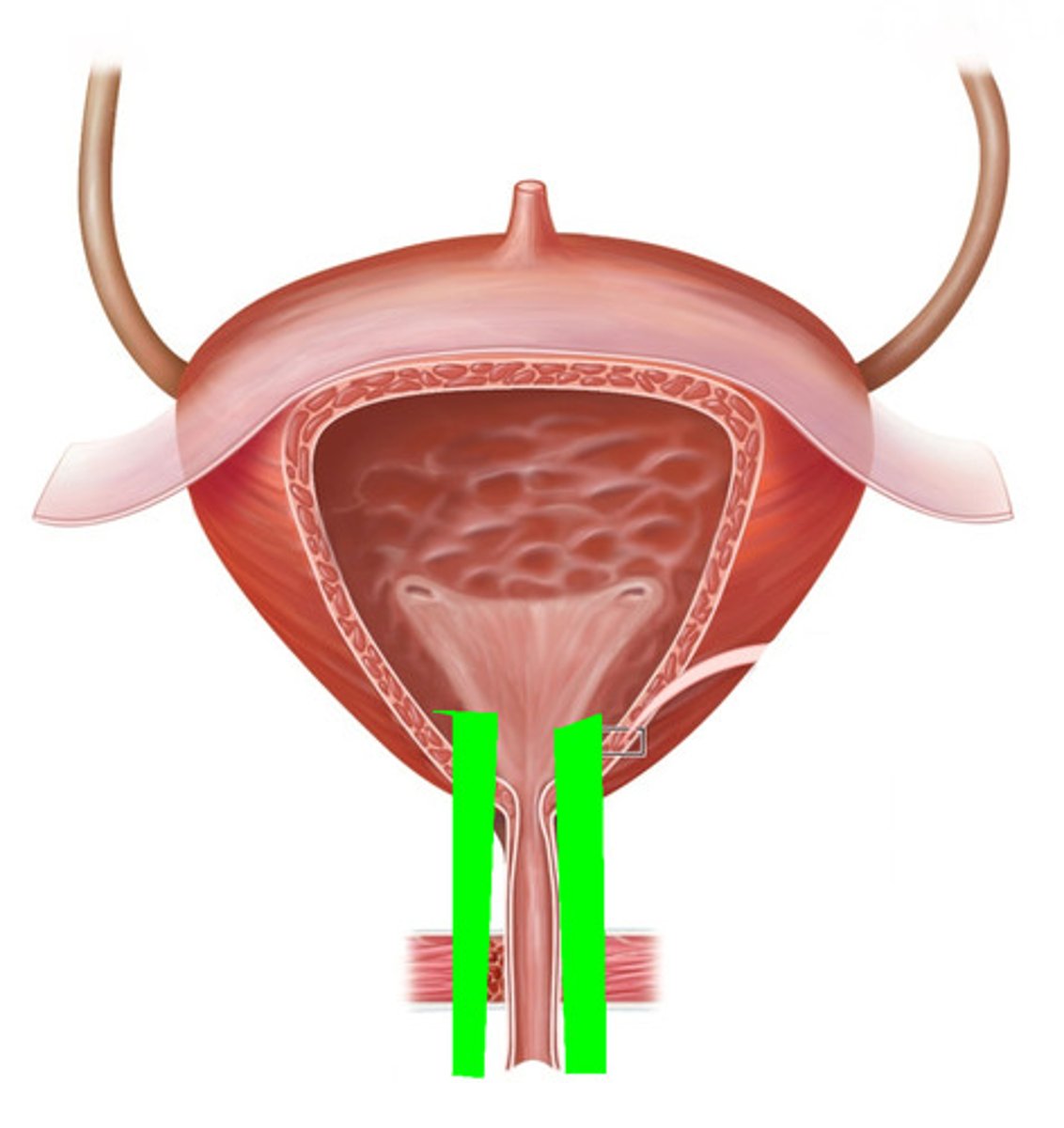
Urinary Bladder
-The bladder connected to the urethra
Urethra (Male)
The opening of the bladder
-Will be seen in detail during the dissection of the reproductive system
-Does not become functional until the allantois and allantoic stalk become non-functional as the umbilical chord shrivels up
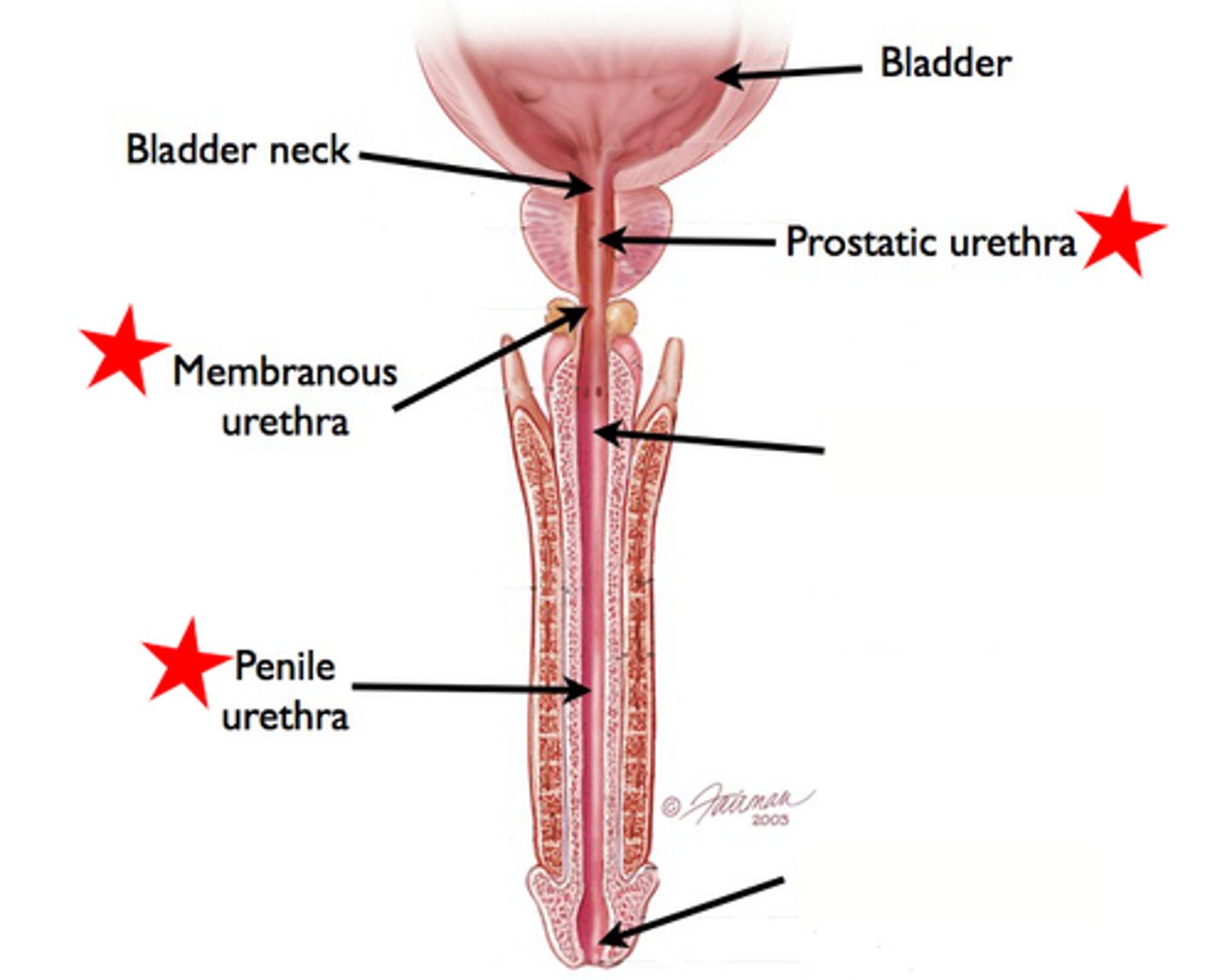
Vas Deferens
-Sperm Duct
-Originates in the Testis
-Tubes that cross the larger ureters and disappears at the base of the urinary bladder
-Part of the Male Reproduction Tract
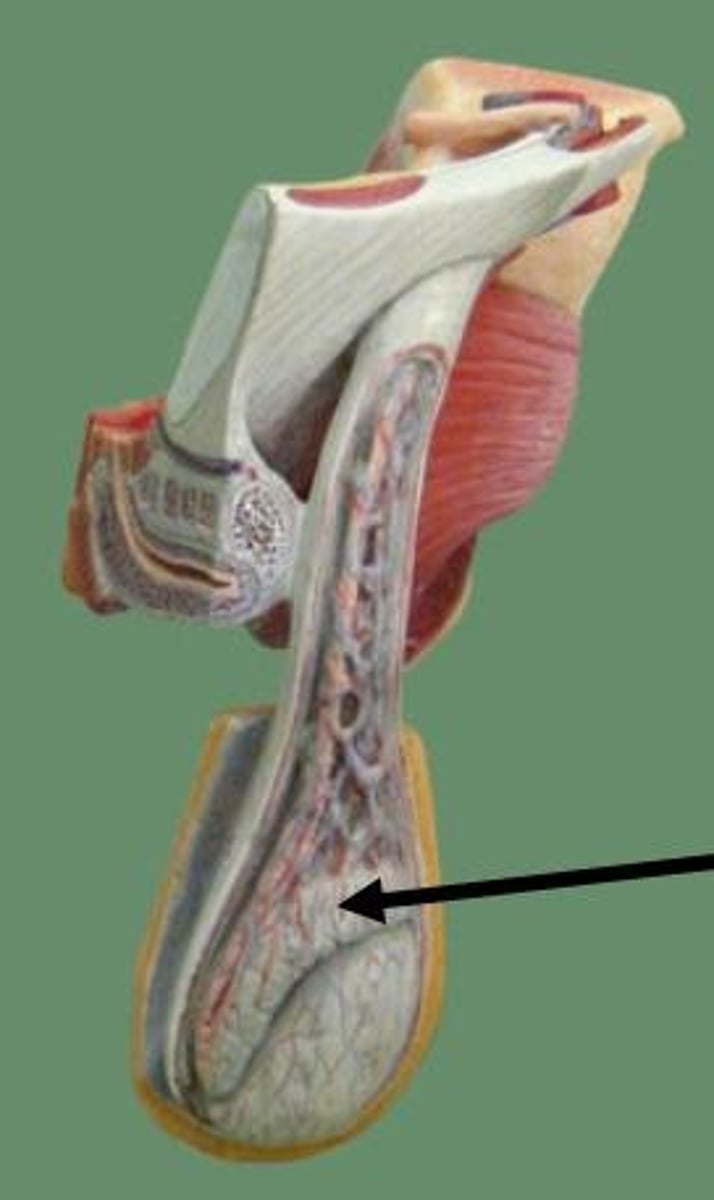
Testis
-The Testicles
-The origin of sperm
-Is joined to the scrotal sac and pilled into it by a tough ligament called the gubernaculum
-Part of the Male Reproduction Tract
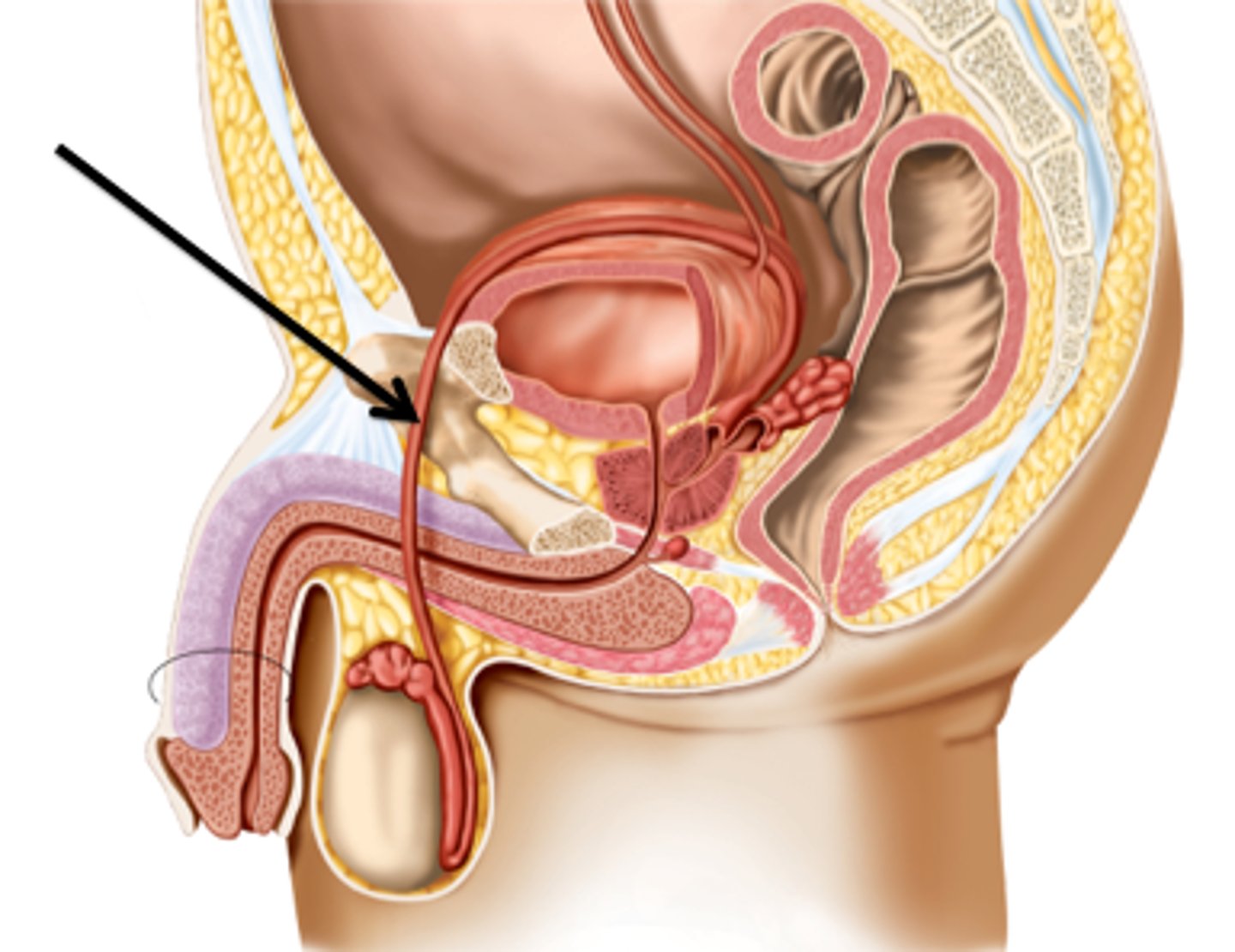
Inguinal Canal
-The opening into the abdominal wall
-Part of the Male Reproduction Tract
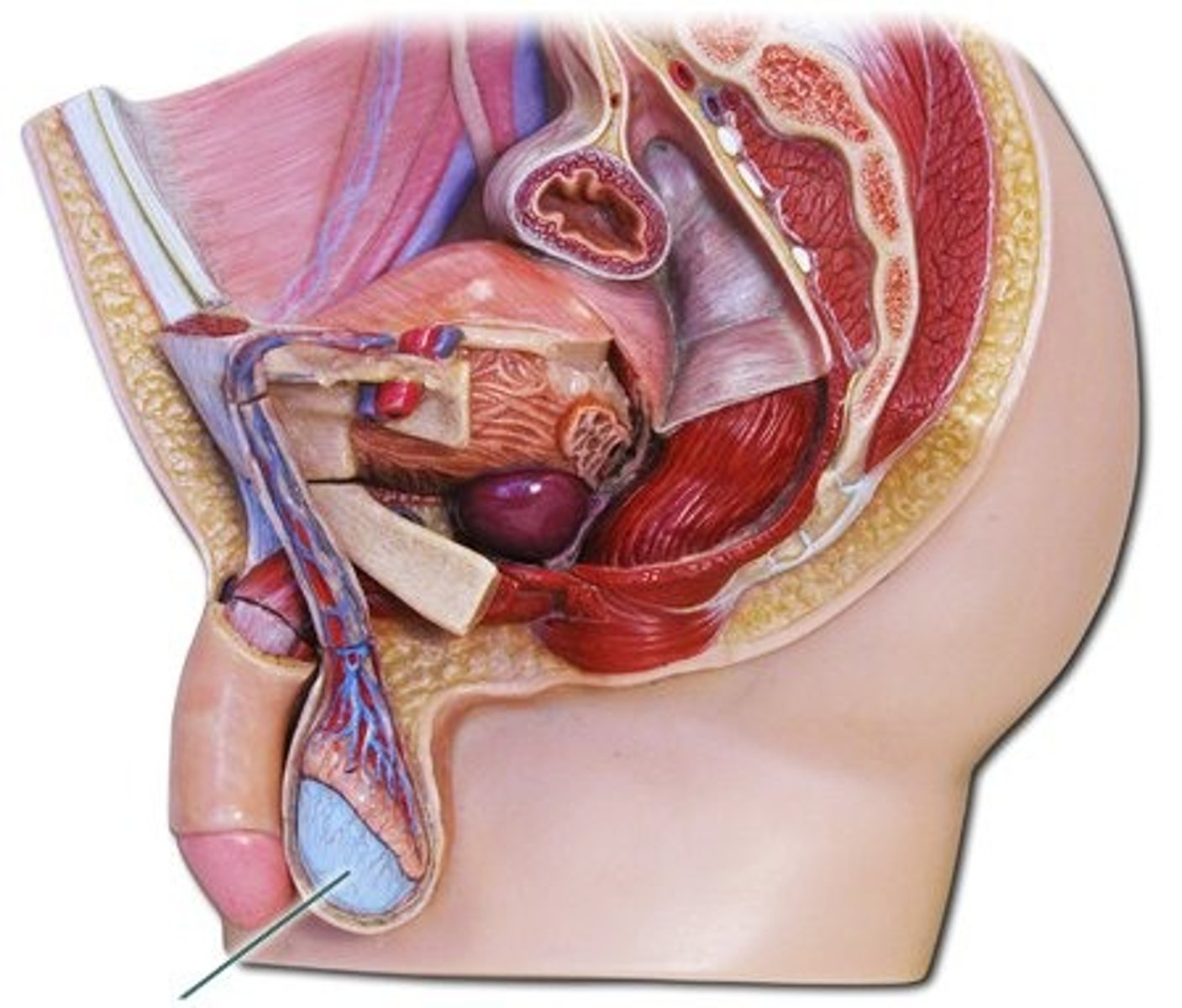
Epididymis
-A coiled set of tubules that surrounds the testis
-Part of the Male Reproduction Tract
Penis and Urethra
-Makes up the urogenital duct
-Part of the Male Reproduction Tract
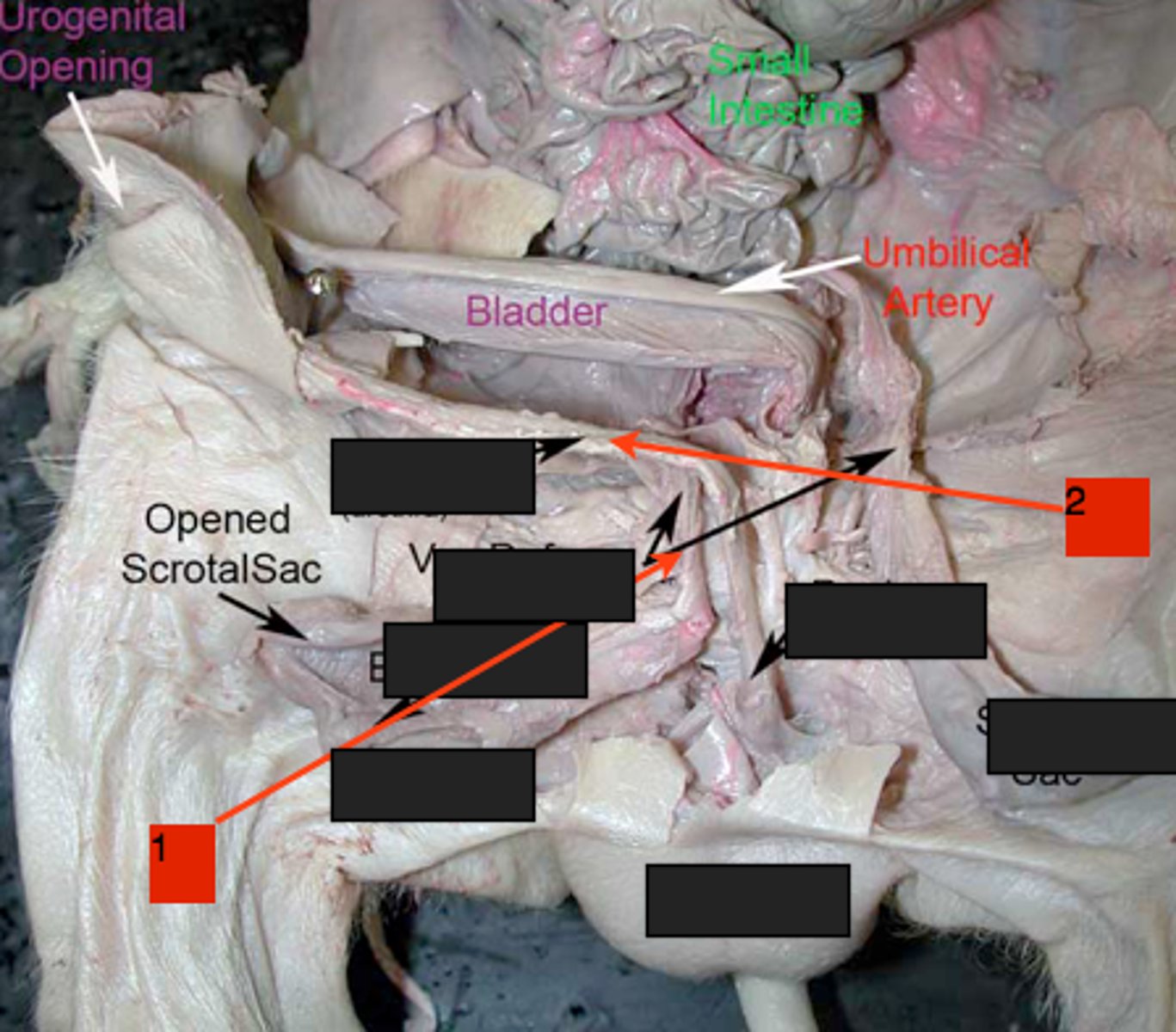
Pelvic Urethra
-The urethra which runs from the urinary bladder to the penis
-Part of the Male Reproduction Tract
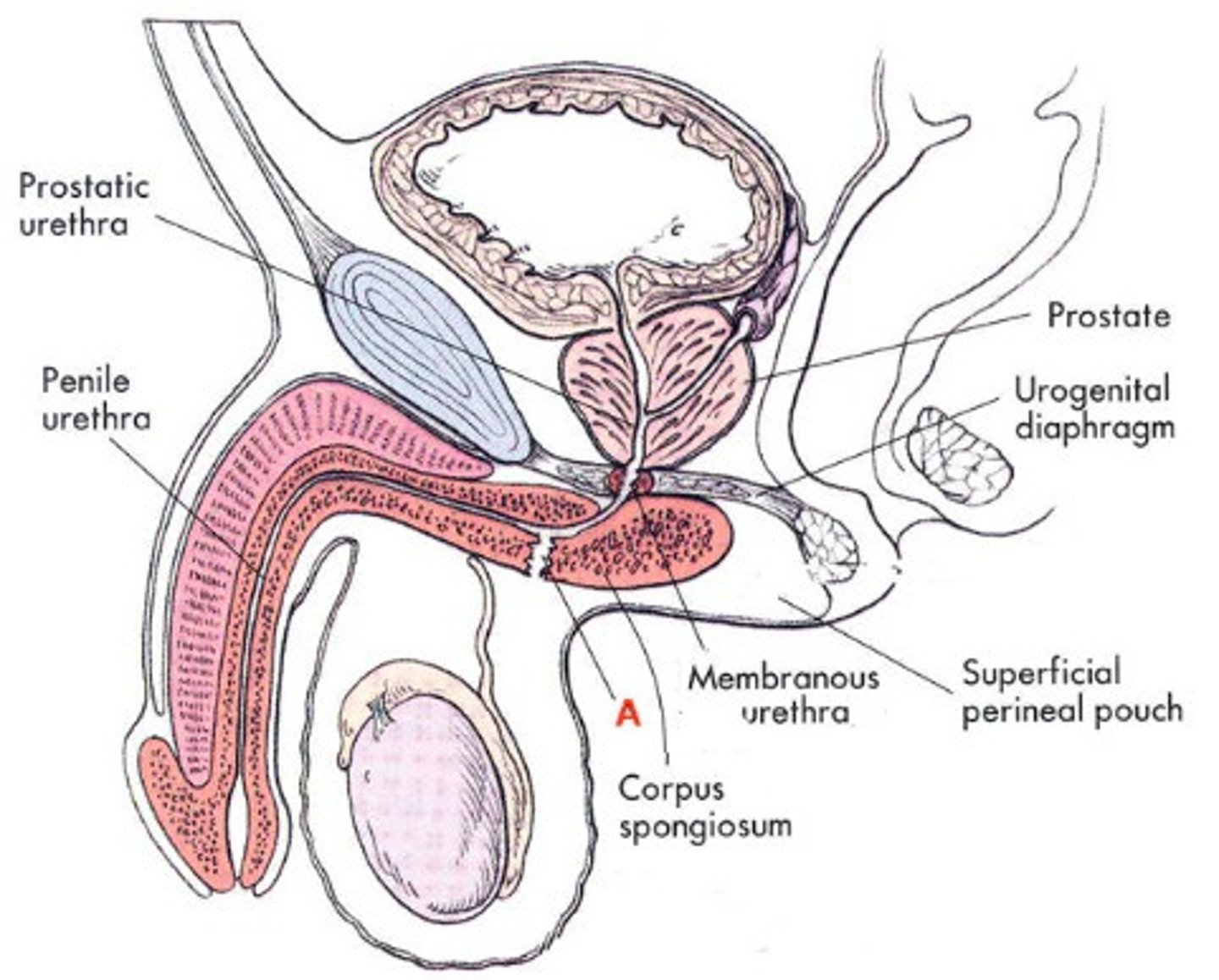
Prostate Gland
-Lies at the anterior end of the urethra surrounding the point of attachment of the vas deferens
-Part of the Male Reproduction Tract
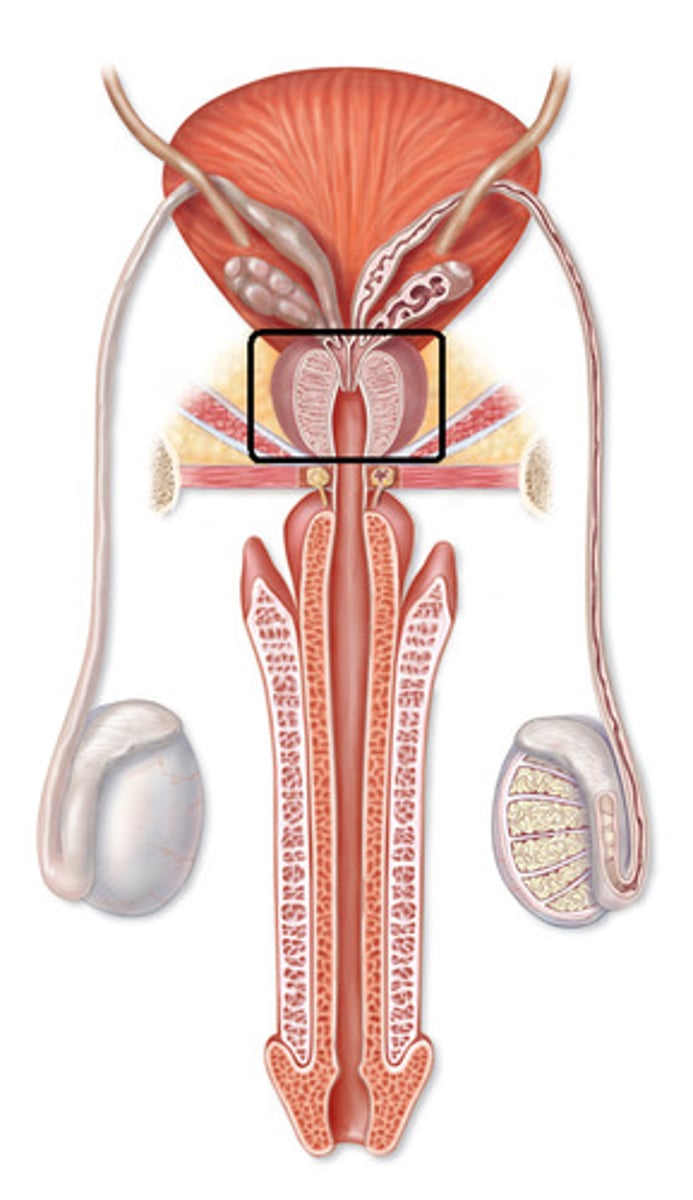
Bulbourethral (or Cowper's) Glands
-Located at the base of the pelvic urethra just before it becomes the penile urethra
-Two bulbous glands
-Produce components of the seminal fluid
-Part of the Male Reproduction Tract
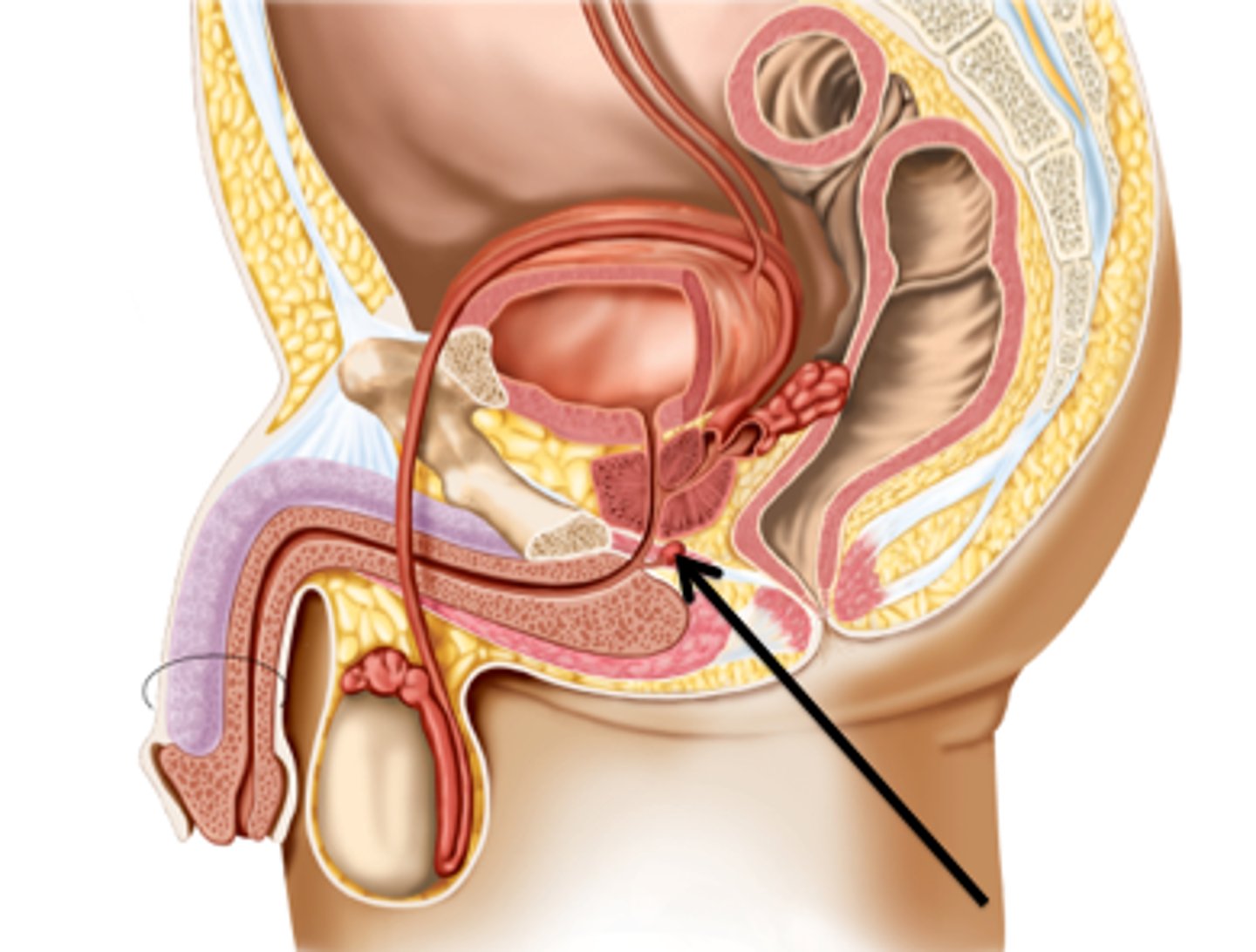
Penile Urethra
-The part of the urethra that continues through the penis to the urogenital opening
-Part of the Male Reproduction Tract
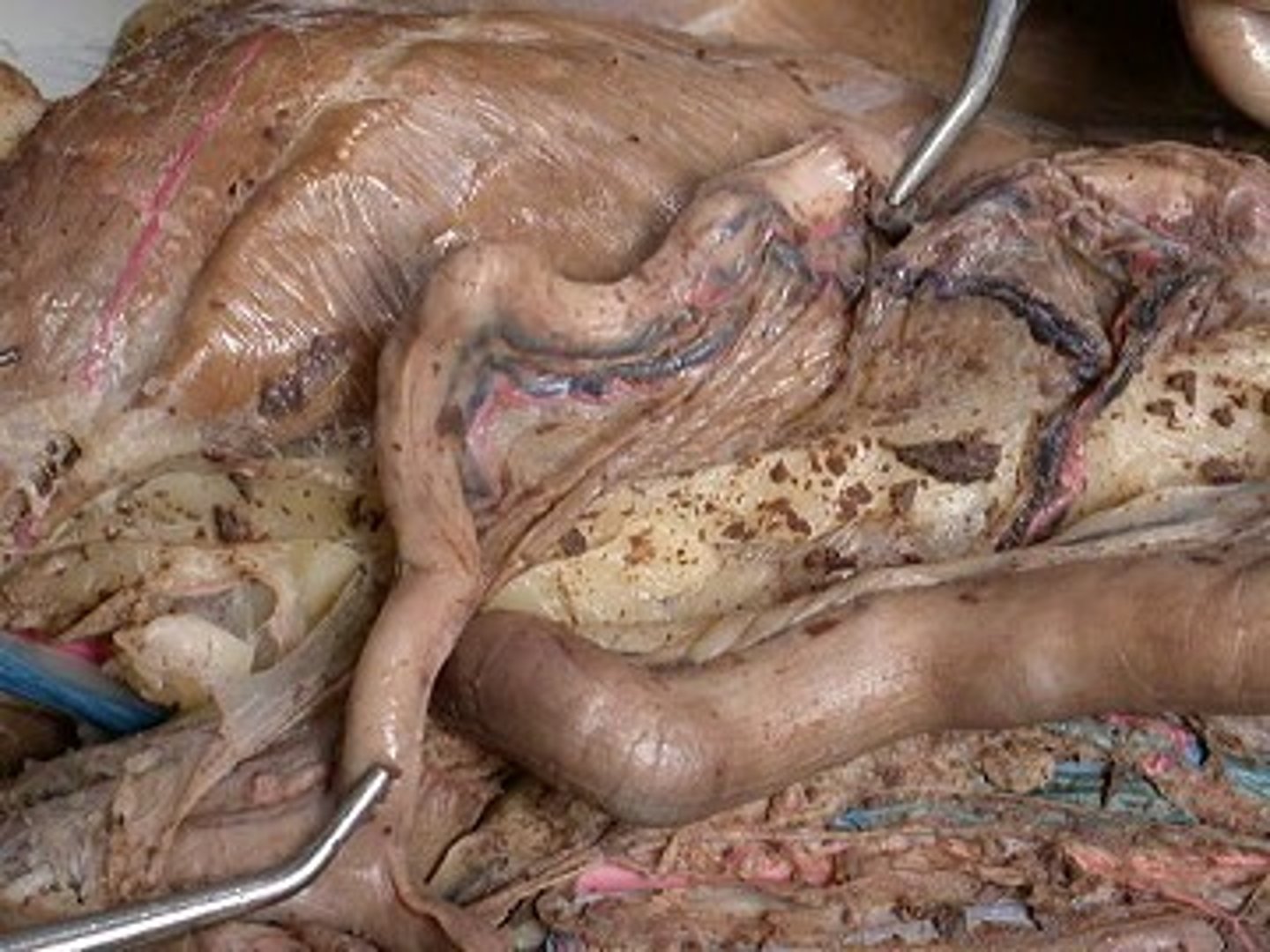
Oviduct (Fallopian Tube)
-Located in the abdominal cavity
-Part of the Female Reproduction Tract
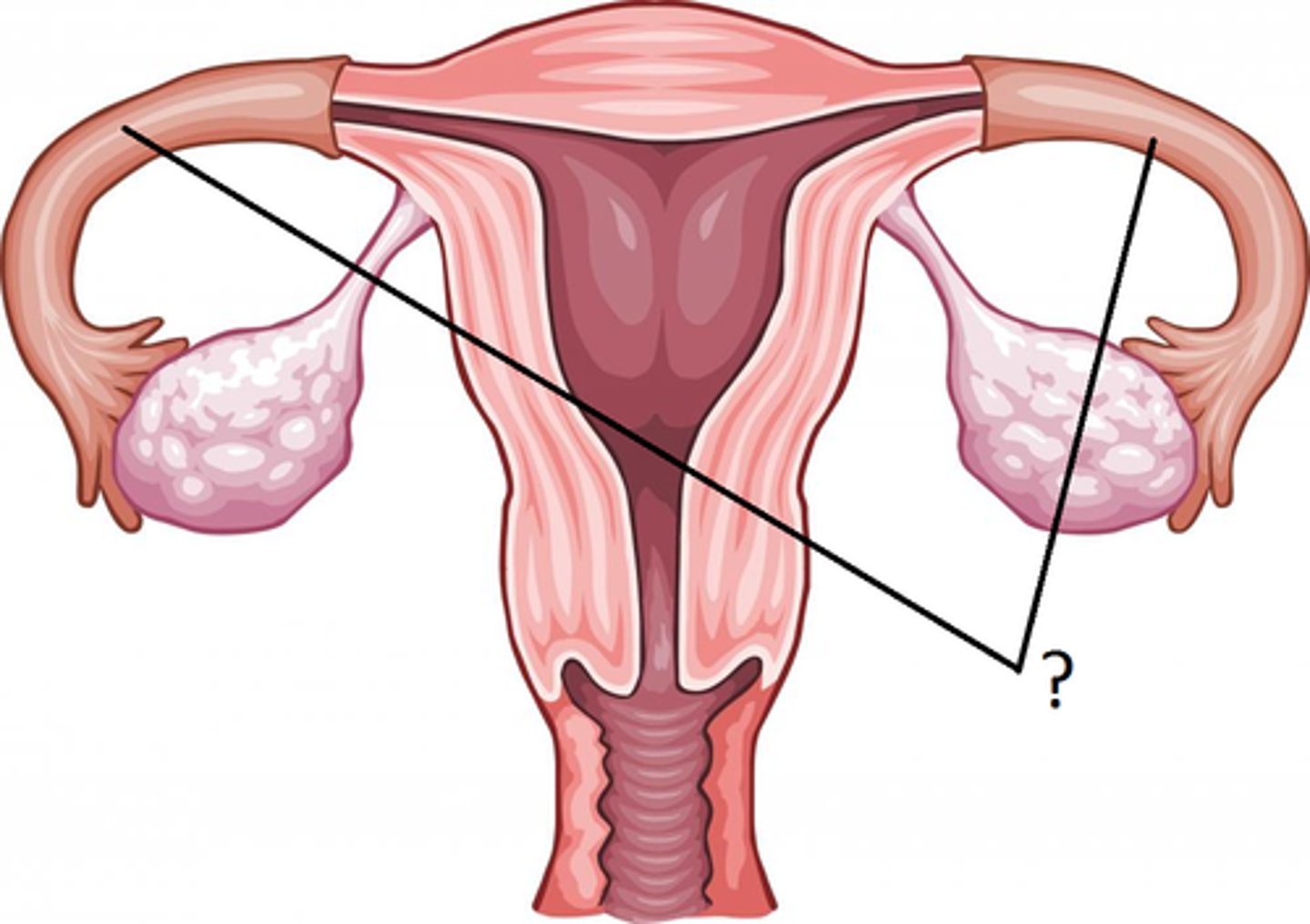
Horn of the Uterus
-Where each oviduct merges
-The right and left horns join in the midline to form the main uterine tube
-Part of the Female Reproduction Tract
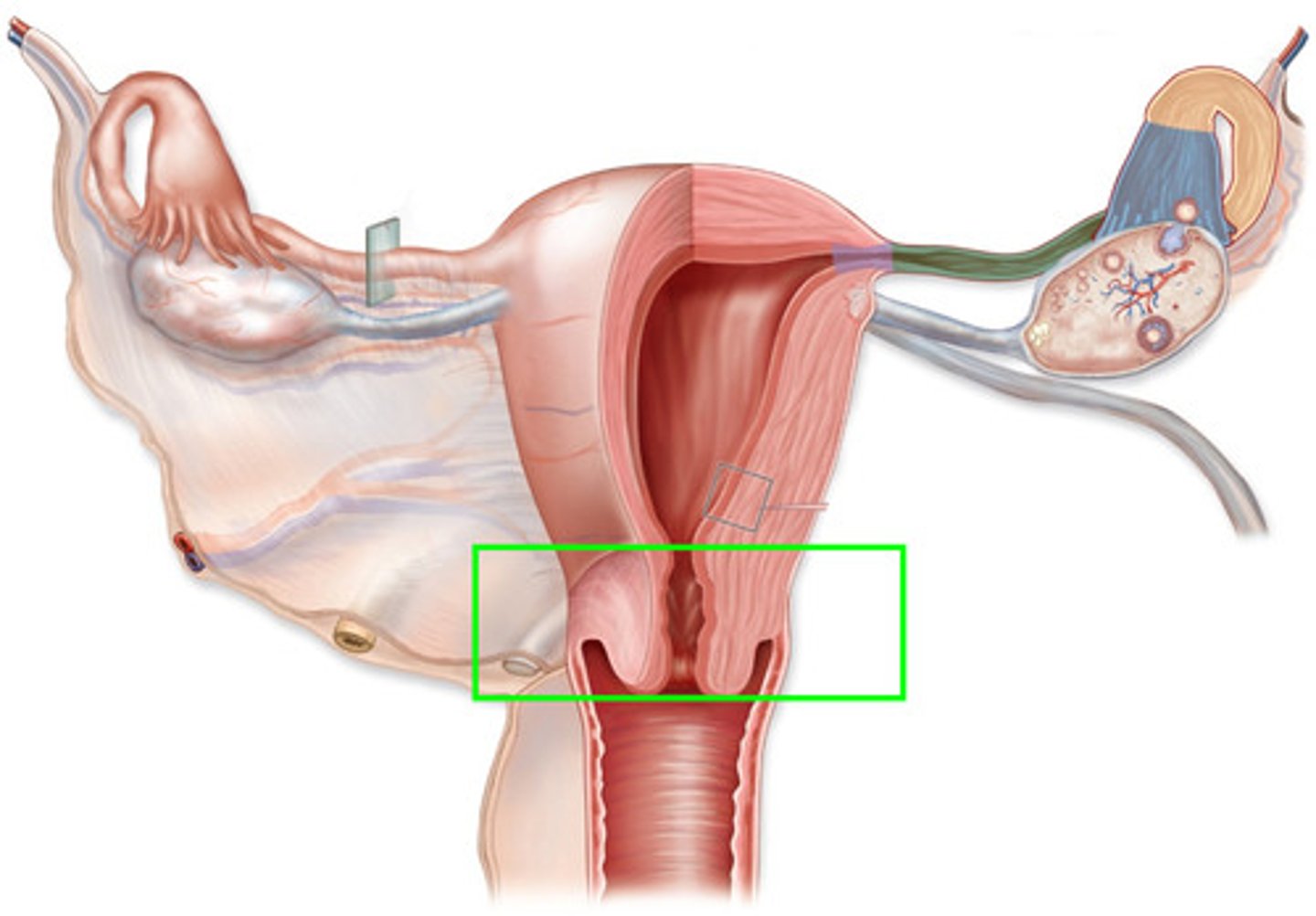
Uterus
-Created by the two oviducts converging
-Part of the Female Reproduction Tract
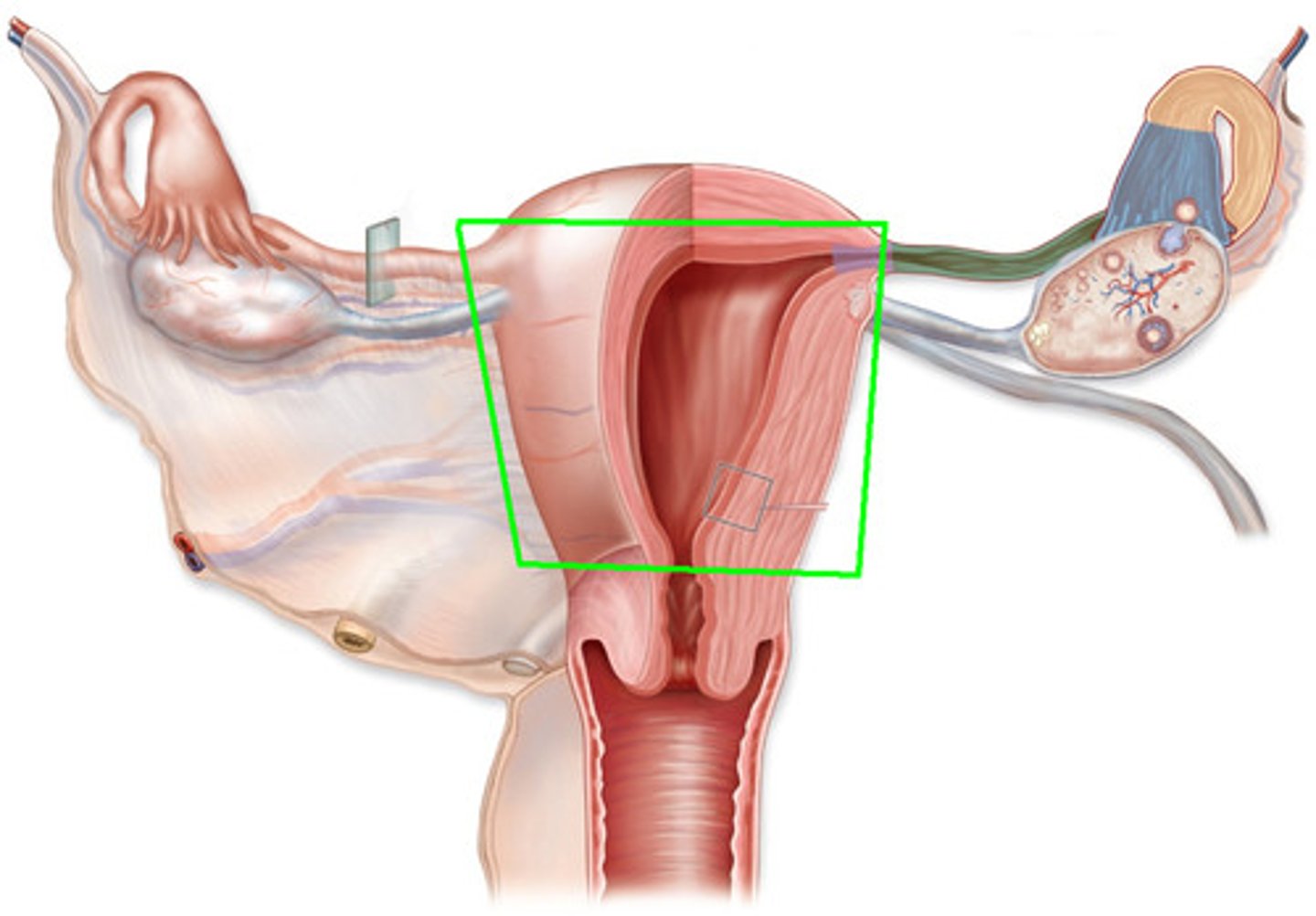
Vagina
-The tube leading to the outside of the pig
-Joins the uterus at a constriction called the cervix
-Part of the Female Reproduction Tract
Urethra (Female)
-Leads from the bladder to the outside
-Joins the vagina so that the chamber might be more appropriately called the urogenital chamber
-Part of the Female Reproduction Tract
Cervix
-The mouth of the womb
-Part of the Female Reproduction Tract
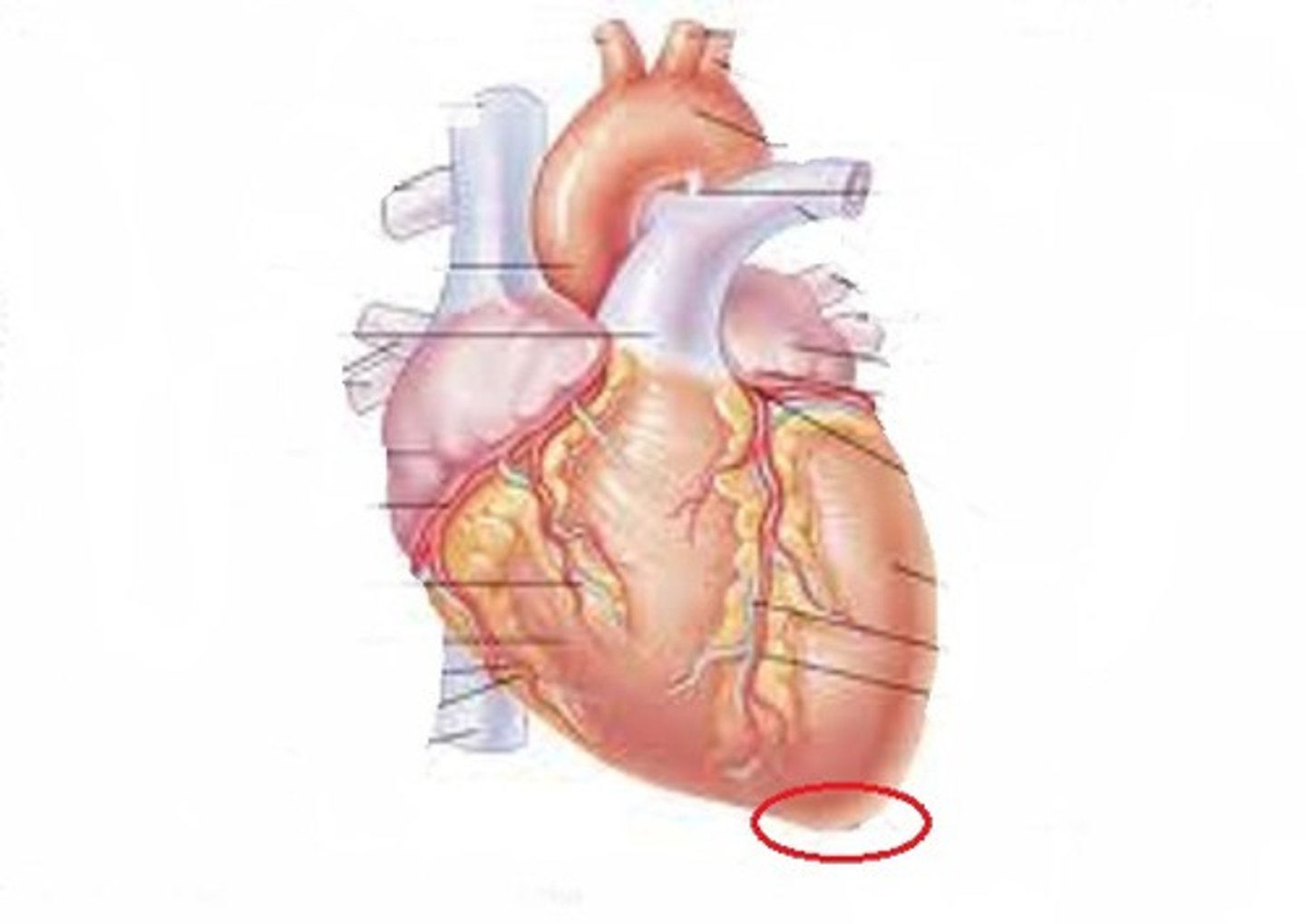
Heart
-The major organ of the circulatory system
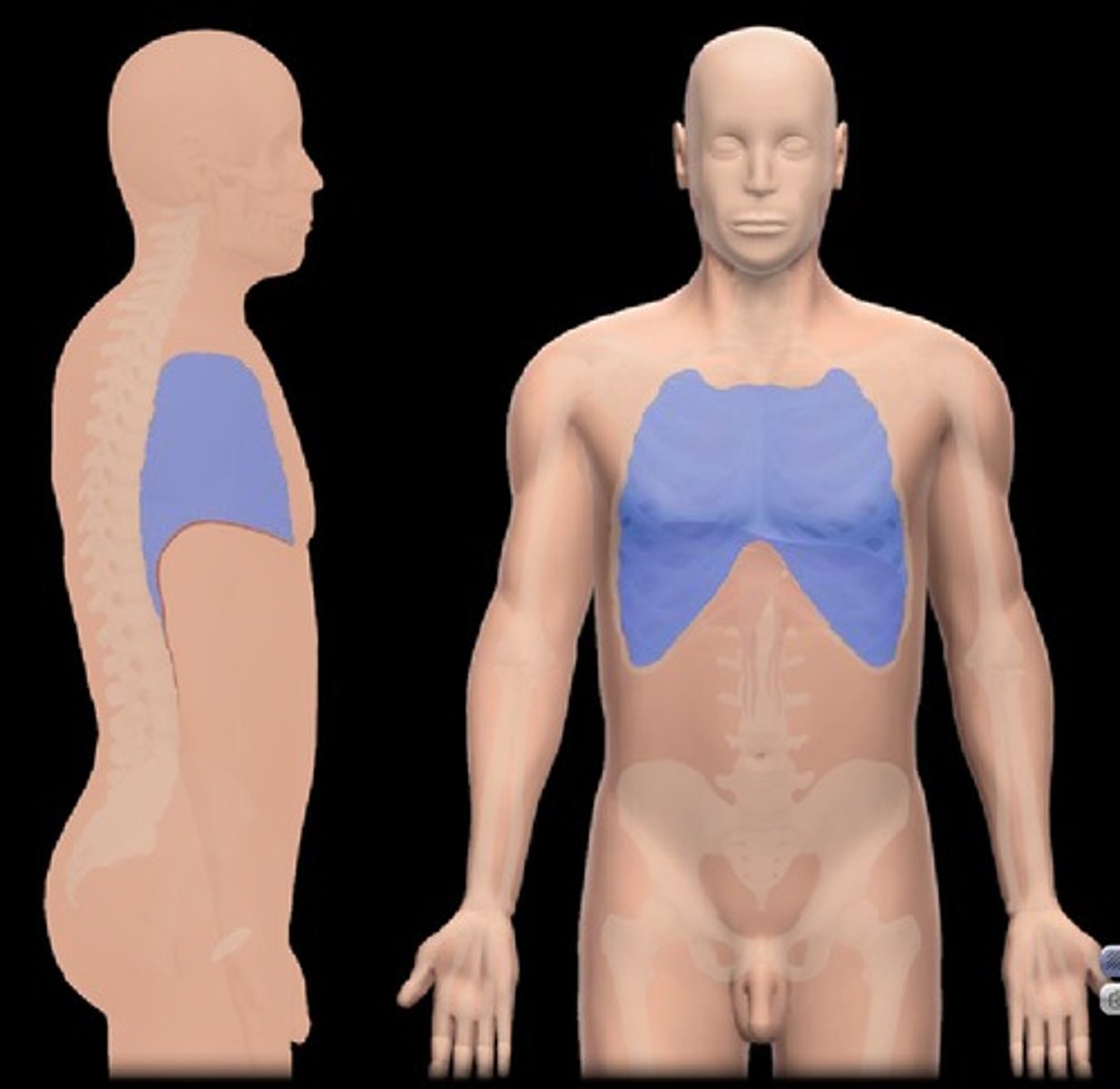
Thoracic Cavity
-Must be opened if we want to see inside the thoracic cavity
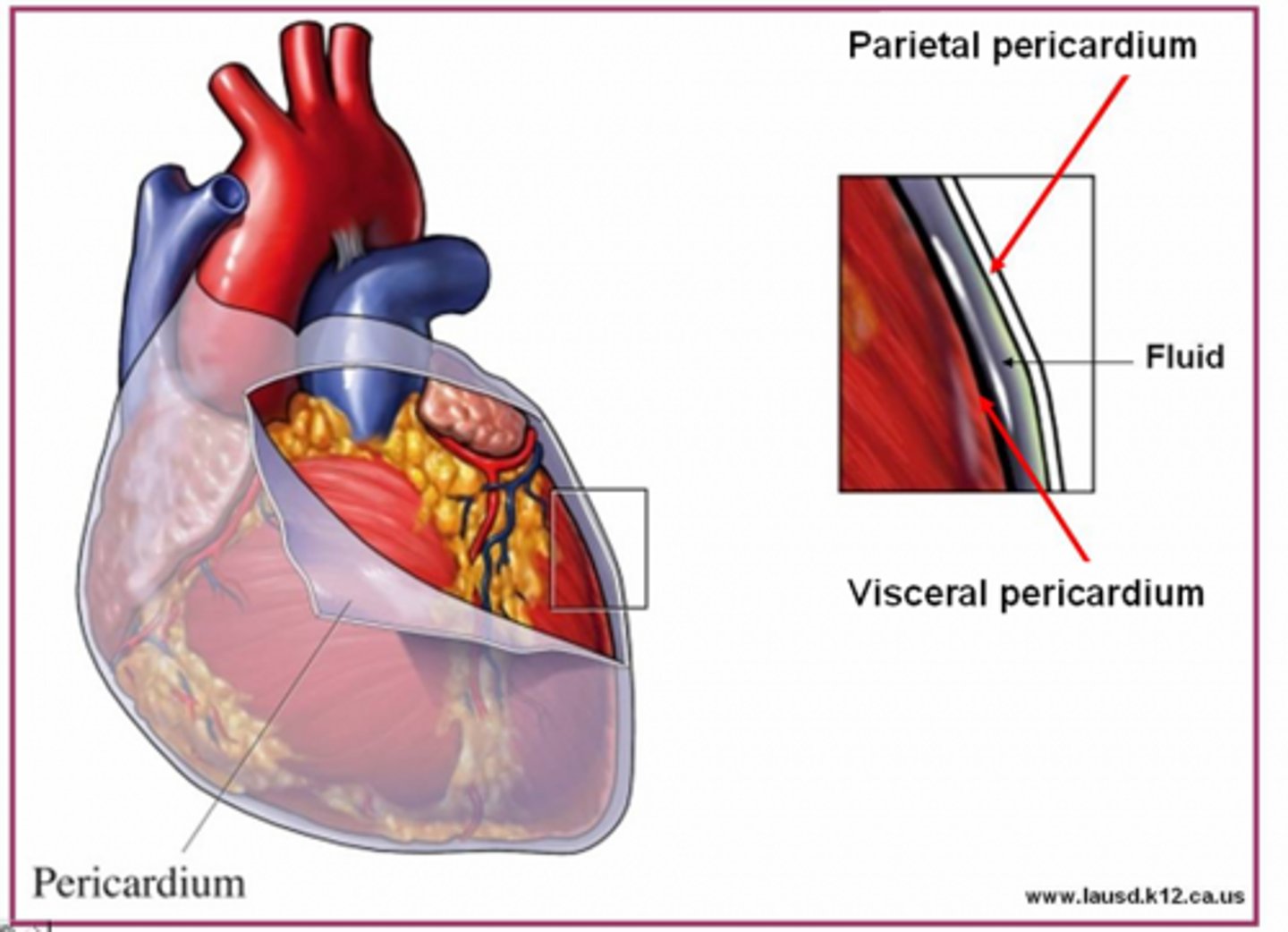
Pericardium
-The translucent membrane covering the heart
-Part of the Circulatory System
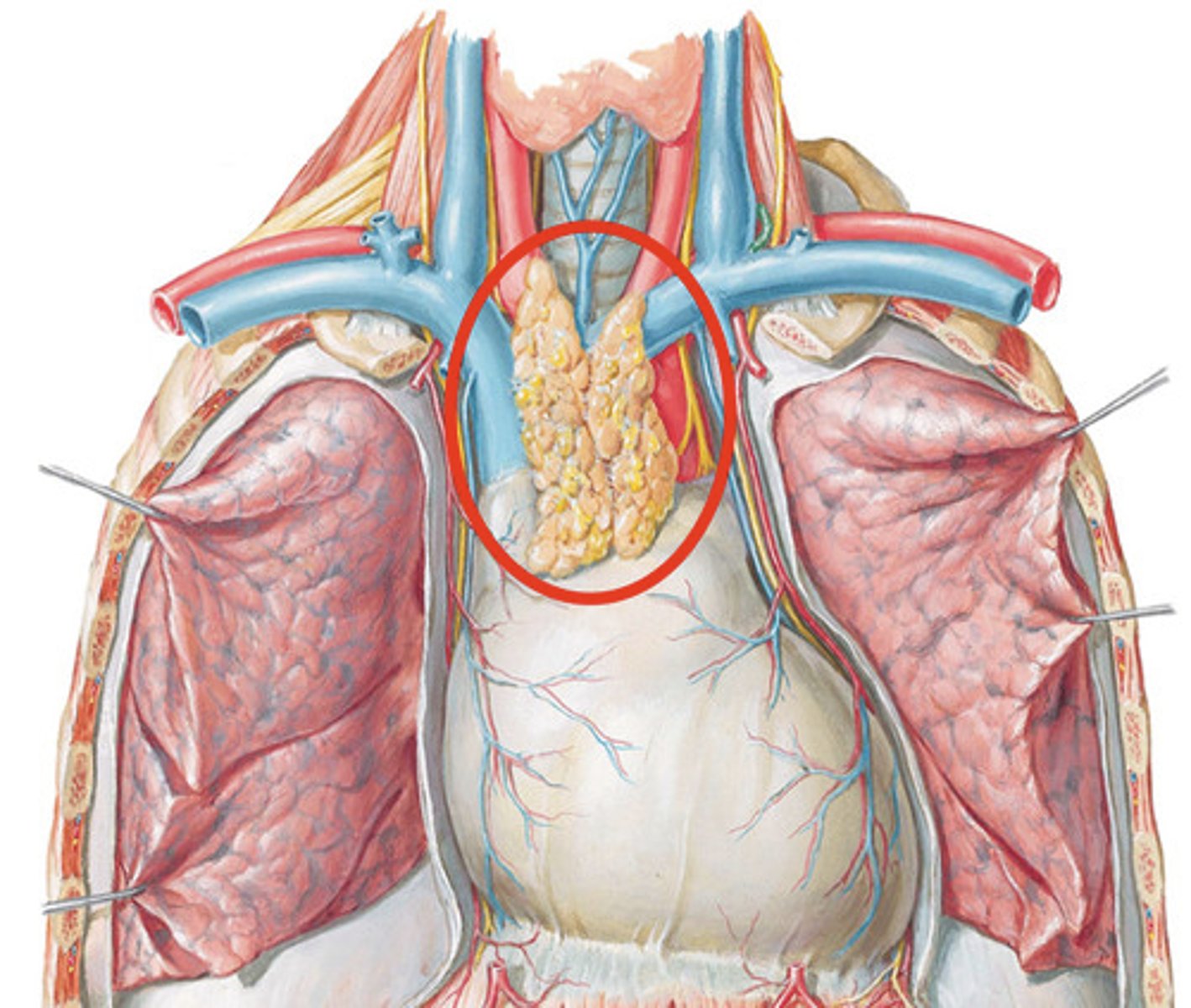
Thymus
-The spongy tissue anterior to the heart
-Is larger during early development and begins to shrink during childhood
-Is part of the immune system
-Part of the Circulatory System
Atrium (heart)
-The two upper, smaller, thin-walled receiving chambers of the heart
-Part of the Circulatory System
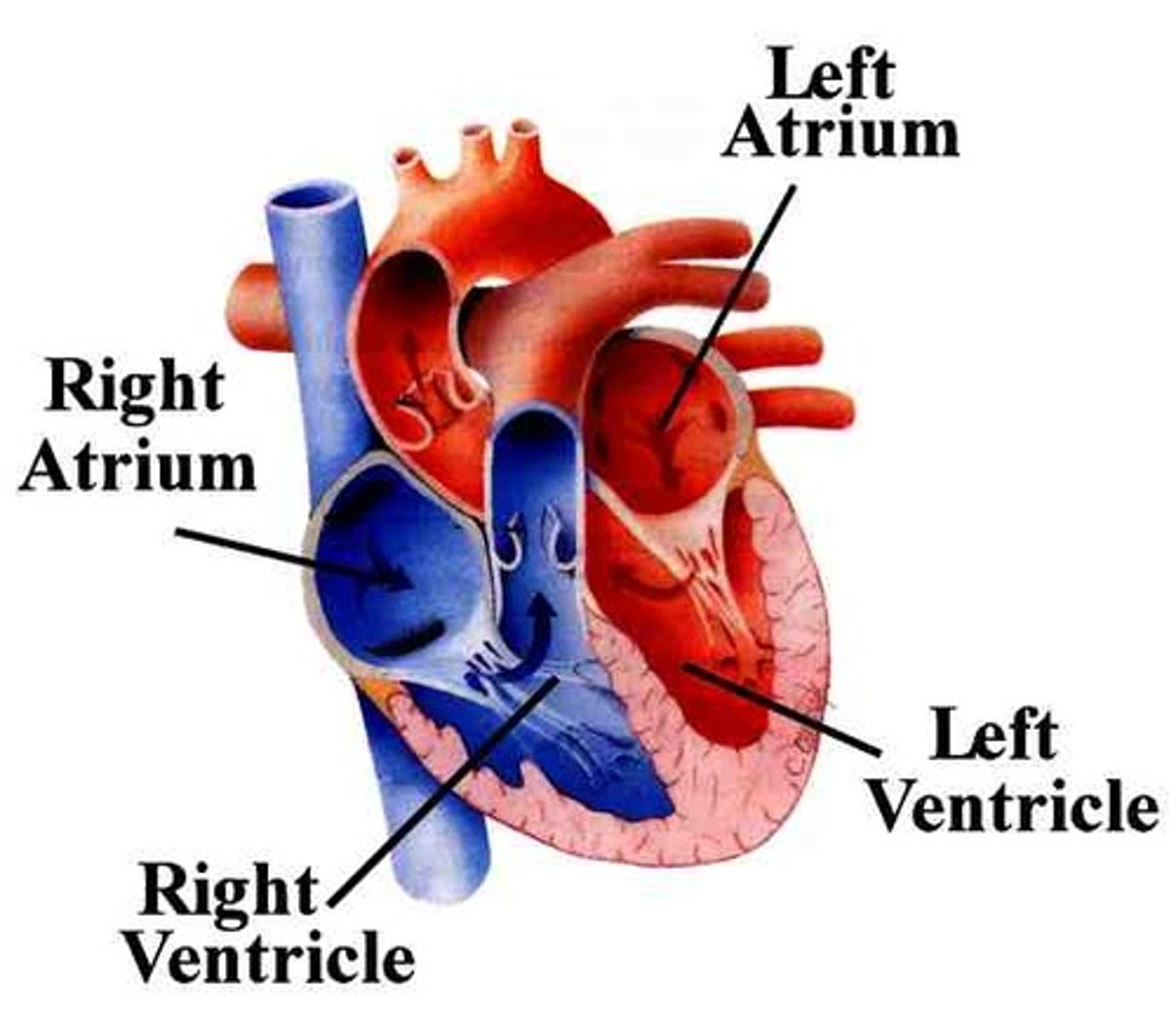
Ventricles
The two larger, more pointed pumping chambers in the heart
-Part of the Circulatory System
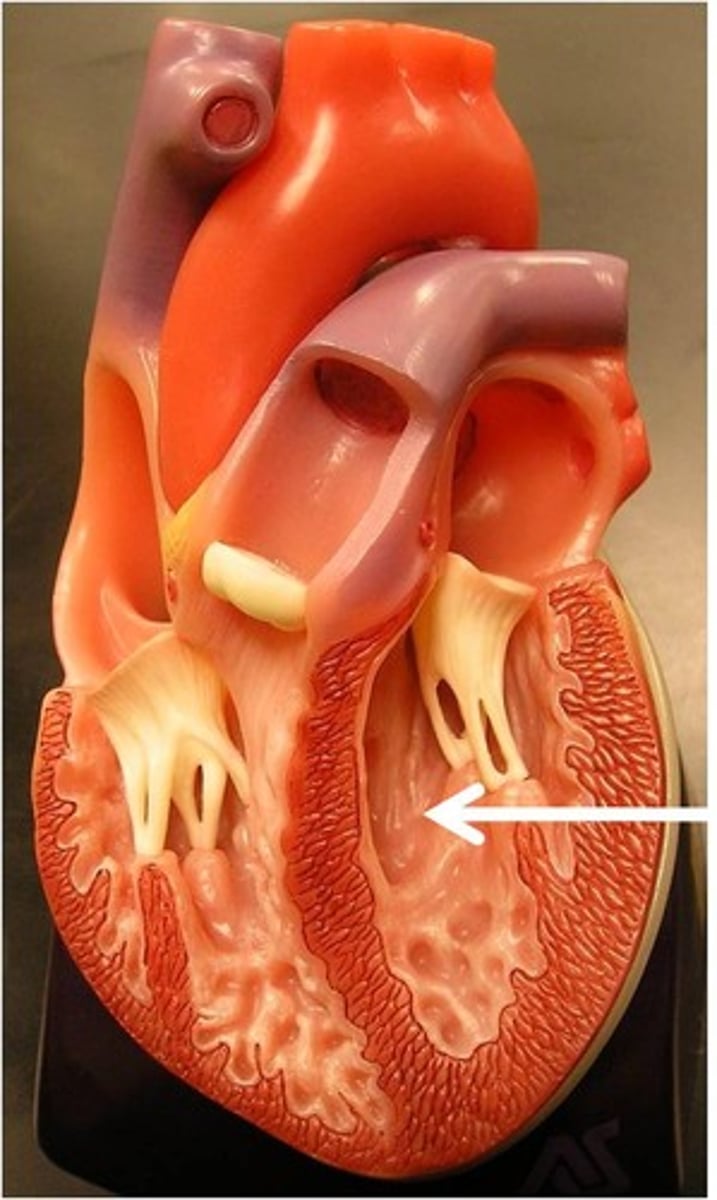
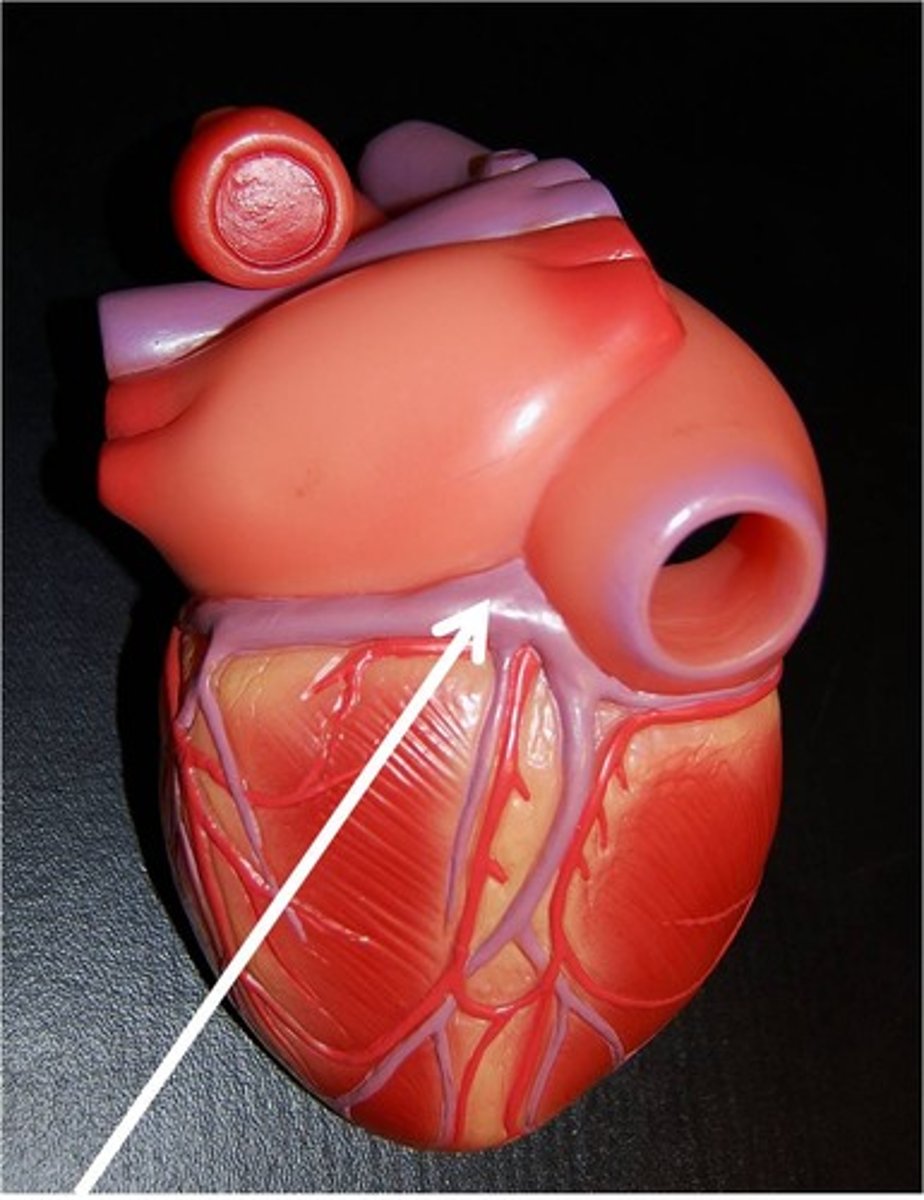
Coronary Artery and Vein
-Located in the groove which delineates the boundary between the two ventricles in the heart
-Part of the Circulatory System