Physics: Energy (Paper 1)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What is kinetic energy and the formula?
Energy stored in moving objects
Stationary objects have no kinetic energy
Ek = 0.5 x m x v2
What is elastic potential energy?
Putting energy in to stretch the spring
The stretched spring is storing the energy as ‘elastic potential energy’
Extension is directly proportional to force applied
In metres!
What is work done?
Doing work
Meachnical work: Applying a force to move an object
Energy transferred from one store to another
Electrical work: Current transferring energy
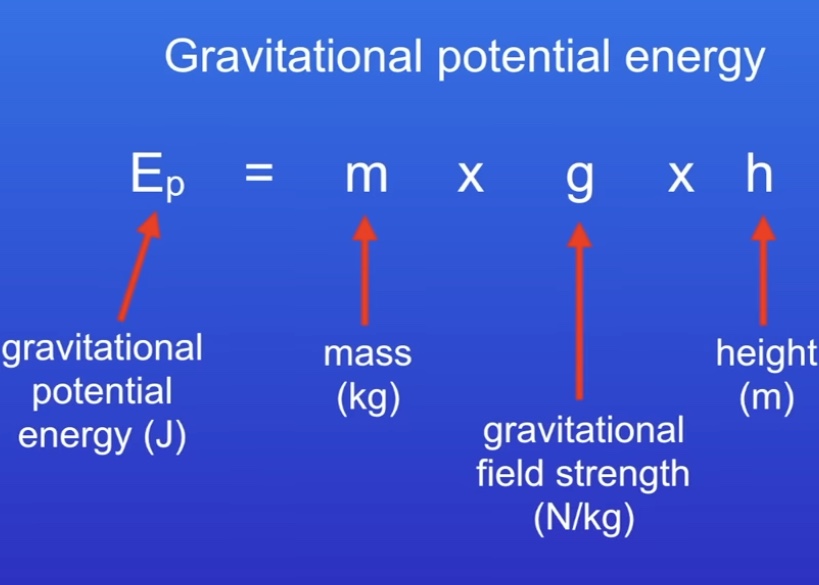
What is gravitational potential energy?
Energy stored in an object sue to its position above the earths surface
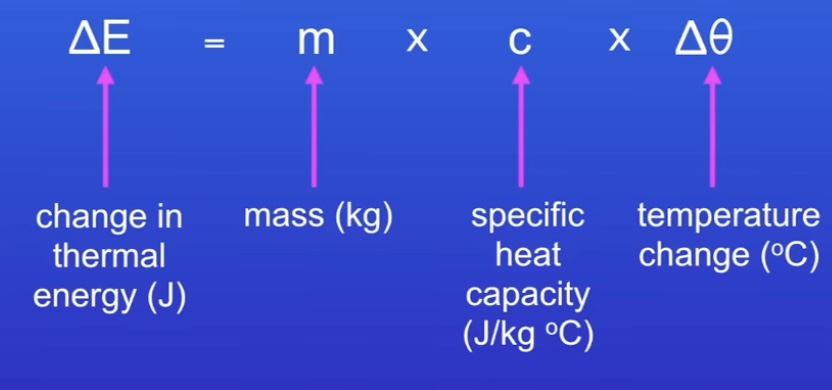
What is specific heat capacity?
The amount of energy required to raise the temp of 1kg of the substance by 1ºC
(Given formula in exam)
What is the law of conservation of energy?
Energy can be transferred usefully, stored or dissipated but it cannot be created or destroys
What is energy dissipation?
Energy wasted
e.g. friction transfers energy to thermal energy stores
How is energy transferred in a system?
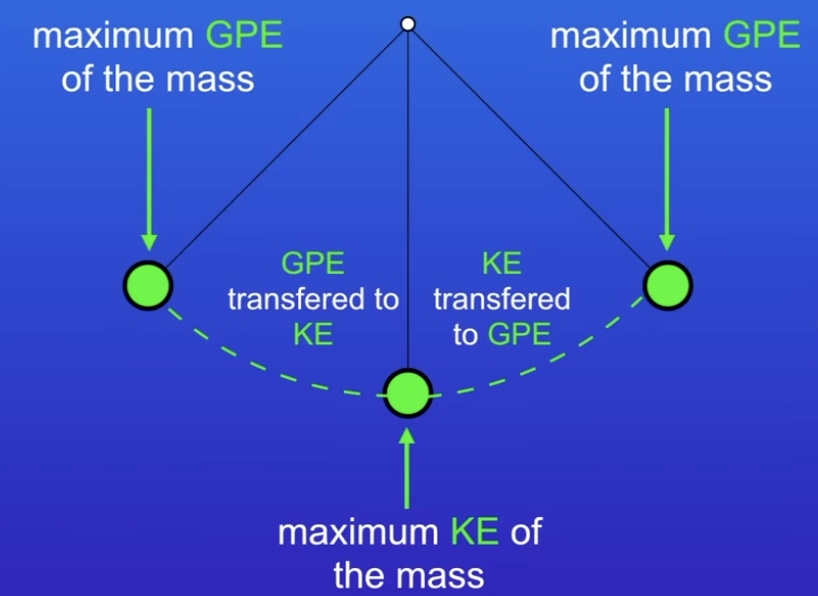
How is energy transferred in a bungee jump?
All energy is GPE
As they fall, GPE is transferred to KE
Rope tightens, KE is at its max
Fully extended, zero kinetic energy
All energy EPE
Going back up, EPE transferred to KE
KE transferred to GPE
At the top, all energy is GPE
Never return to original position. Energy is dissipated as thermal energy (friction, stretching effects in elastic)
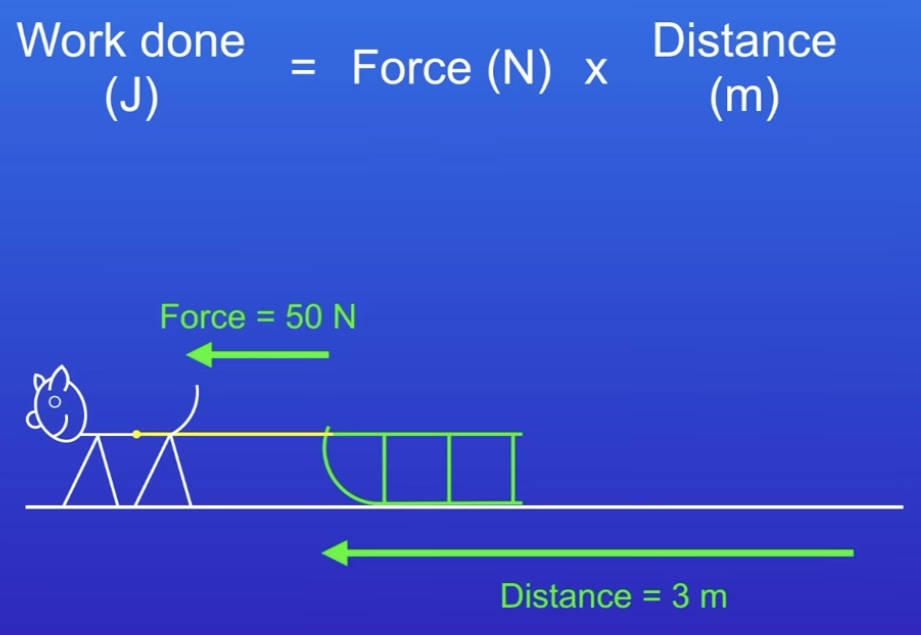
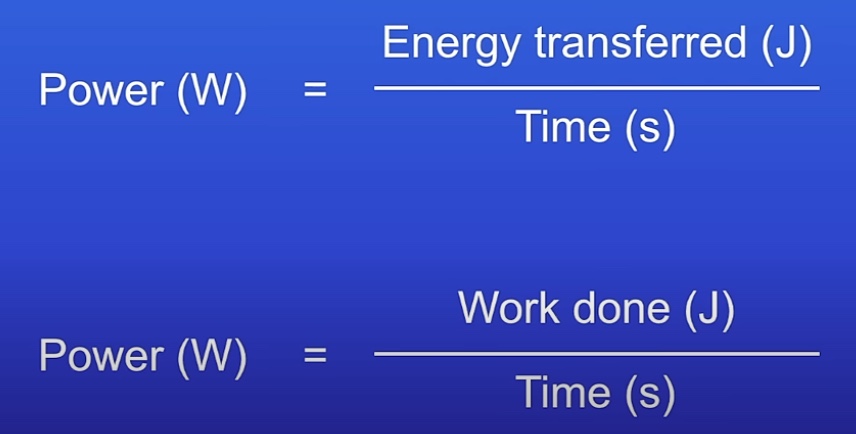
How can you calculate work done?
How can you calculate the power?
How can you calculate efficiency?
x 100 for percentage
You know you have switched the equation if your answer is more than 1

How can you increase efficiency of an energy transfer?
What factors reduce cooling of a building?
insulation
Double glazed windows
Loft insulation
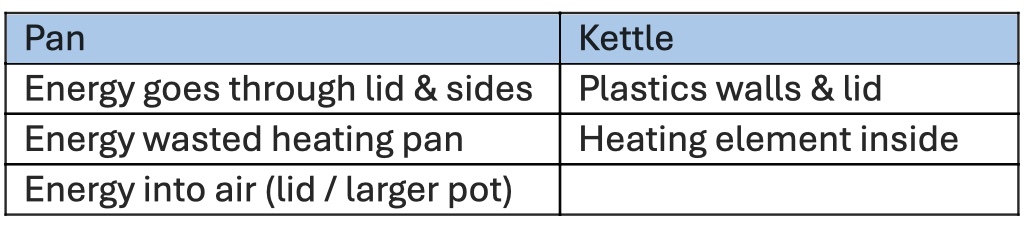
Specific Heat Capacity Required Practical
Record mass of oil in beaker
Place thermometer & emersion heater into beaker
Wrap beaker in insulating foam
Connect joule meter & power pack to emersion heater
Time for 30 mins
Read total no of joules and temperature
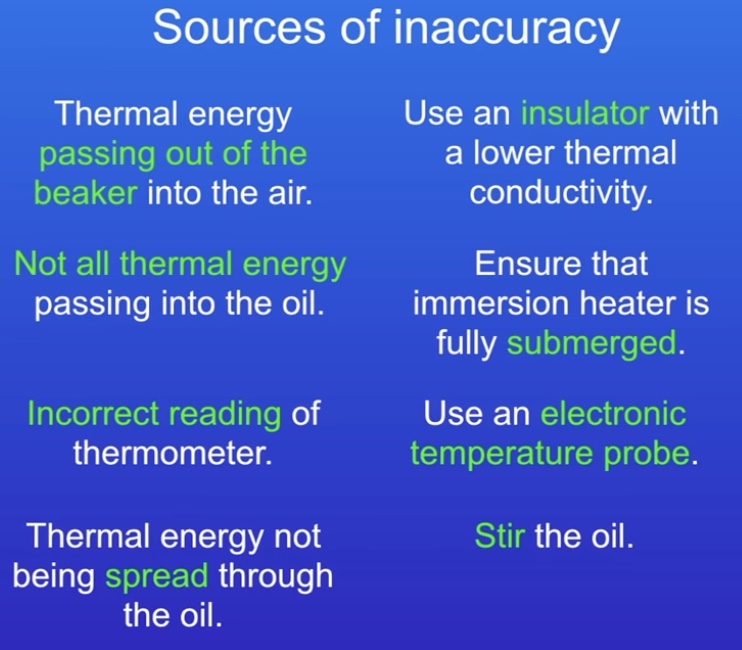
What can affect accuracy in the Specific Heat Capacity Required Practical
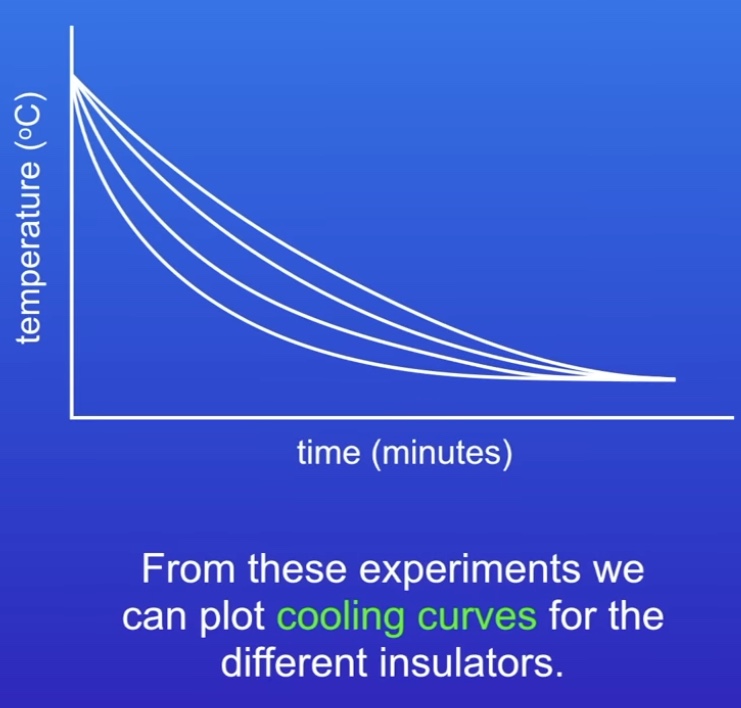
Investigating different thermal insulators required practical process & results
Small beaker in large beaker
Put boiling water into small beaker
Put thermometer through cardboard lid
Record start temp
Start timer
Record temp every 3 mins for 15 minutes
Repeat with insulating material in large beaker
Results (image)
What are the variables in the thermal insulators required practicals?
IV - Type of insulating material
DV - Temperature
CV - Vol of water, mass of material, temp of water
IV - Number of layers
DV - Temperature
CV - Start temp, vol of water
Investigating (same) thermal insulators required practical process
Fill beaker with hot water
Put on cardboard lid & Place thermometer in
Wrap in 1 layer of newspaper
Record start temp, Start timer
Record temp envy 3 mins for 15 minutes
Repeat with more layers of newspaper
What are the main fossil fuels & what do they do?
Oil
Natuaral gas
Coal
Provide: Transport, generate electricity, heating
What advantages do fossil fuels have?
Release lots of energy
Reliable
Abundant & cheap
Versatile (portable)
What disadvantages do fossil fuels have?
Releases lots of CO2
Non-renewable
Release other pollutants (health damage)

What is nuclear power advantages & disadvantages?
Non release CO2
Reliable
Dangerous radioactive materials
Extremely expensive to dismantle
Radioactive waste
Where does the UK get energy from? Why?
Coal
Got replaced by:
Nuclear power (20%)
Oil & gas (gas equal to coal use)
Burning gas generates less CO2 than burning coal
Gas-fired power stations are flexible (switched on quickly)

Why can scientist not control how energy resources are used?
Politicians didn’t worry
Fossil fuel energy is cheap
Renewable energy is not reliable
Use nuclear power & gas
What are renewable sources of energy?
Renewable energy can be replenished as it is being used
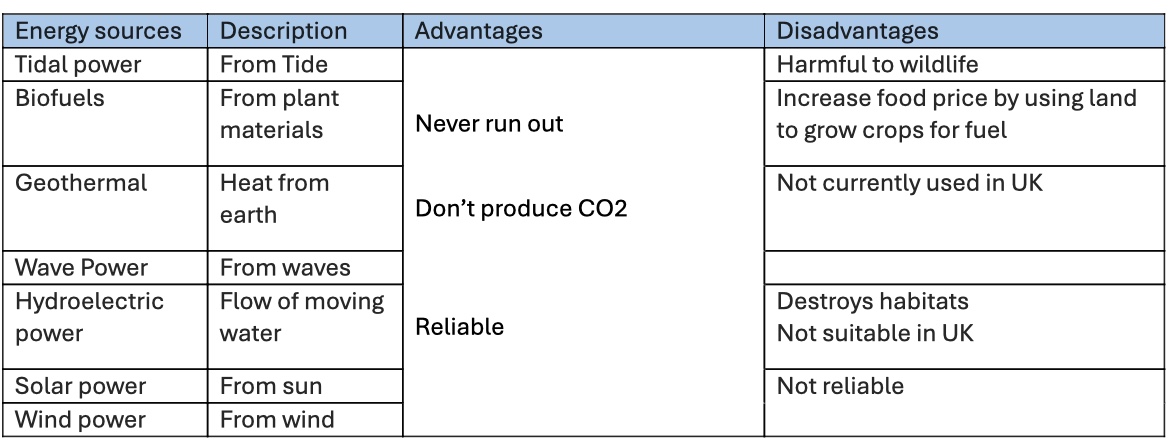
Why can solar power not generate all our electricity?
Cannot run 24/7
Would need massive amounts of land for the panels
Low useful power output
What are benefits of electric cars charging as they drive (coils of wire under motorways)
Cars dont have to stop to charge
More cars can be charged at the same time
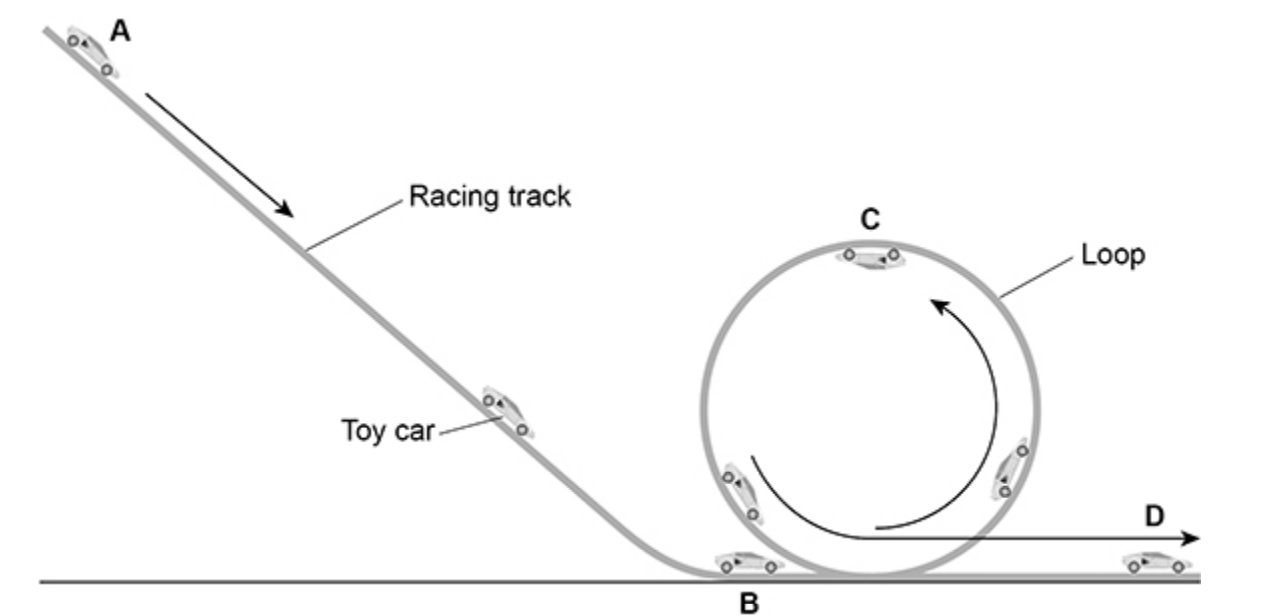
How is this a closed system?
The car has 0.20J of GPE at C how much does it need to complete the loop?
The total energy of the race track and the car is constant
More than 0.20J
Because it needs energy to be moving to complete the loop.