7. Late effects of radiation
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
def. Effects of radiation may not be seen for months or even decades
term. late effects
Late Effects Web
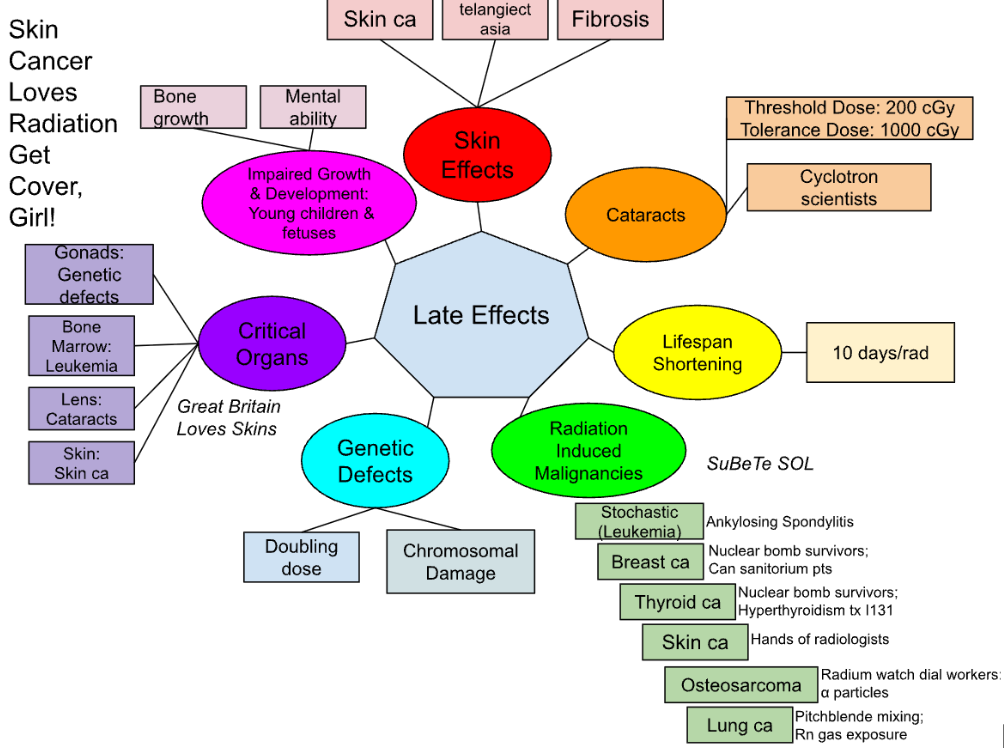
What are the 7 late effects of radiation discussed in class
Skin effects
Cataracts
Lifespan shortening (radiation-induced aging)
Radiation induced malignancy
Genetic effects
Critical organs
Growth and development
Skin
Cancer
Loves
Radiation
Get
Cover,
Girl
What are 3 late skin effects?
fibrosis
telangiectasia
skin cancer
Who developed the first cyclotron? When?
1931, university of California
By the year __ every major university had a cyclotron for research.
1940
What late effect did early cyclotron researchers get? Why?
cataracts
they’d use fluorescent screens to guide the beam without using eye protection, staring directly at the beam
What is the latent period for cataracts
5-30 years
I can’t 53E
What is the threshold dose for cataracts?
200 cGy
NOTE: Not the same as tolerance dose. Threshold dose is the minimum dose required to even see cataracts.
What is the TD 5/50 (tolerance dose) for cataracts?
1000
(where we see 5% incidence in 50% of the population)
A late effect of radiation is lifespan shortening (radiation-induced aging). Research indicates that, at worst, humans can expect a reduced lifespan of:
10 days for every rad
10 days/ rad
T/F: Lifespan shortening includes radiation induced malignancies.
False: It does not count induced malignancies, just the effects of accelerated, premature aging.
Exposures of less than ___ may actually be helpful (good for you)
1 rad/ year
What are the 6 radiation induced malignancies discussed in class:
Stochastic effect (non-threshold effect that could happen at any dose)
Thyroid cancer
Osteosarcomas
Skin cancers
Breast cancer
Lung Cancer
What is the primary stochastic effect cancer of concern?
Leukemia
Latent period for leukemia:
4-7 years
but risk for approx. 20 years
4dult Leukemia
T/F: the latent period for radiation induced leukemia is much longer than the latent period for radiation-induced solid tumors
False: other way around
____ leukemias are more prevalent in irradiated adults, while
____leukemias are more prevalent in irradiated children
adults: myeloid leukemias (AML, CML)
children: ALL
Give a historical example of radiation induced leukemias.
tx of ankylosing spondylitis patients with TSI (total spinal irradiation) in the 1940s-1950s (specially in Great Britain)
term. Ankylosing spondylitis
def. an arthritic like condition along the vertebral column that causes a painful huckaback
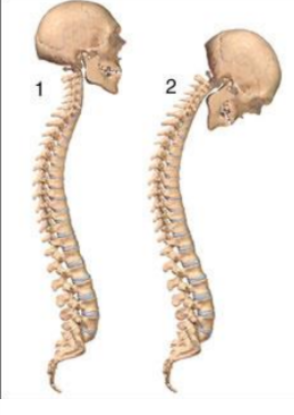
Give 2 examples of radiation induced thyroid cancers.
childhood irradiation with I131 to tx hyperthyroidism
Hiroshima/ Nagasaki survivors
Hyperthyroidism is treated by ablating the gland with ___ rad, but before the year___, the dose was___cGy
500 rad
1930s
1200-6000cGy
Give a historical example of radiation induced osteosarcomas
Radium watchdial workers
What is the main radiation that caused osteosarcomas in the radium watchdial workers?
alpha particles tend to get absorbed by bones
The first reported radiation-induced skin cancer was in the year ____, on the following body part____ of ____(person)
1902
hand
a radiologist
FYI: early radiologists made a habit of placing their hand in the path of the beam while observing their hands on early fluoro units
Give 2 historical examples of radiation induced breast cancer
Hiroshima / Nagasaki survivors
Canadian sanitorium patients in 1960s exposed to many fluoroscopies
What historical exposures causes radiation-induced lung cancer
radon gas exposure
pitchblende mixing
What area of radiation-induced malignancies is the weakest in terms of our knowledge of what radiation effects can happen?
Genetic defects
Radiation induced genetic defects can happen cuz ionizing radiation can cause
chromosomal breaks
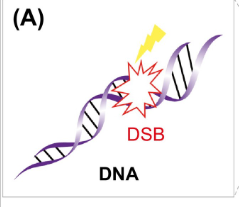
term. doubling dose
def. the dose that will produce twice the frequence of genetic mutations
as would be observed without the radiation exposure
Critical organs include the following organs, and can cause the following effects on those organs:
gonads = genetic effects
bone marrow = leukemia
lens of the eye = cataracts
skin = skin cancer
Great Britain Loves Skins
Radiation can affect the growth and development of:
What does it impair?
fetus & young children
bone growth, mental abilities and more
The dose-response relationship curves for radiation protection purposes follow the (linear/non-linear) (threshold, non-threshold) model
linear, non-threshold (even tho organs have threshold doses), this is the most conservative model