Mastering the World of Psychology Chapter 2
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
Nervous System
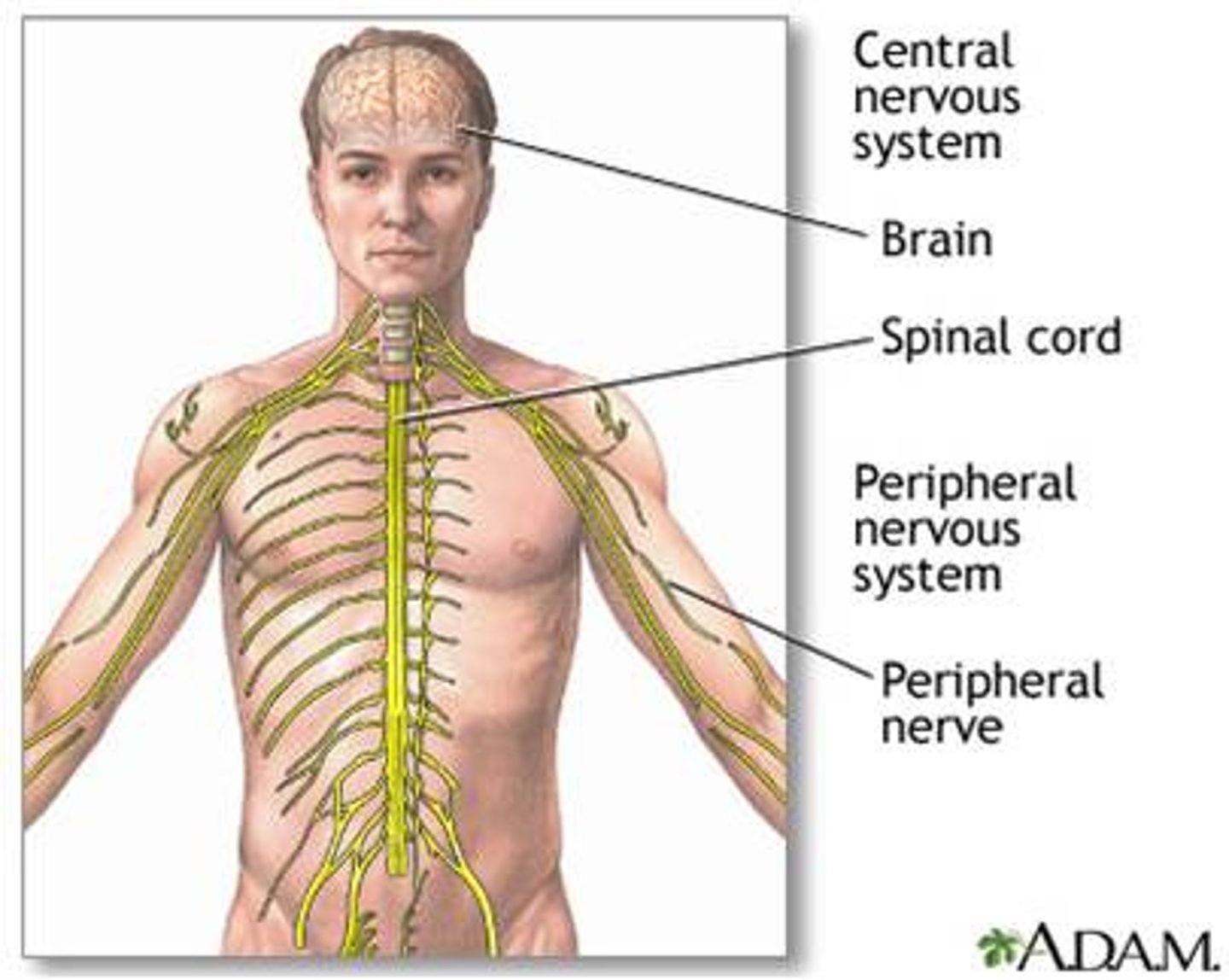
consists of the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) and the Central Nervous System ( CNS )
Central Nervous System (CNS)
-all of the neural tissues inside the skull and backbone
-made up of the spinal cord and brain
Spinal Cords
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
-Includes all of the nerves (i.e. bundles of nerves)
-not encased in bone, all neural tissue that lies outside of skull and backbone
-Carries information to and from the CNS.
- consists of the Somatic Nervous System and the Autonomic Nervous System.
Somatic Nervous System
Controls skeletal muscles and interacts with the external environment.
● consists of all sensory nerves and motor
nerves.
Autonomic Nervous System
Regulates body's internal environment:
- including organs, glands, and blood vessels.
- transmits messages between the central nervous system and glands, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscles.
- consists of the Sympathetic Nervous System and the Parasympathetic Nervous System.
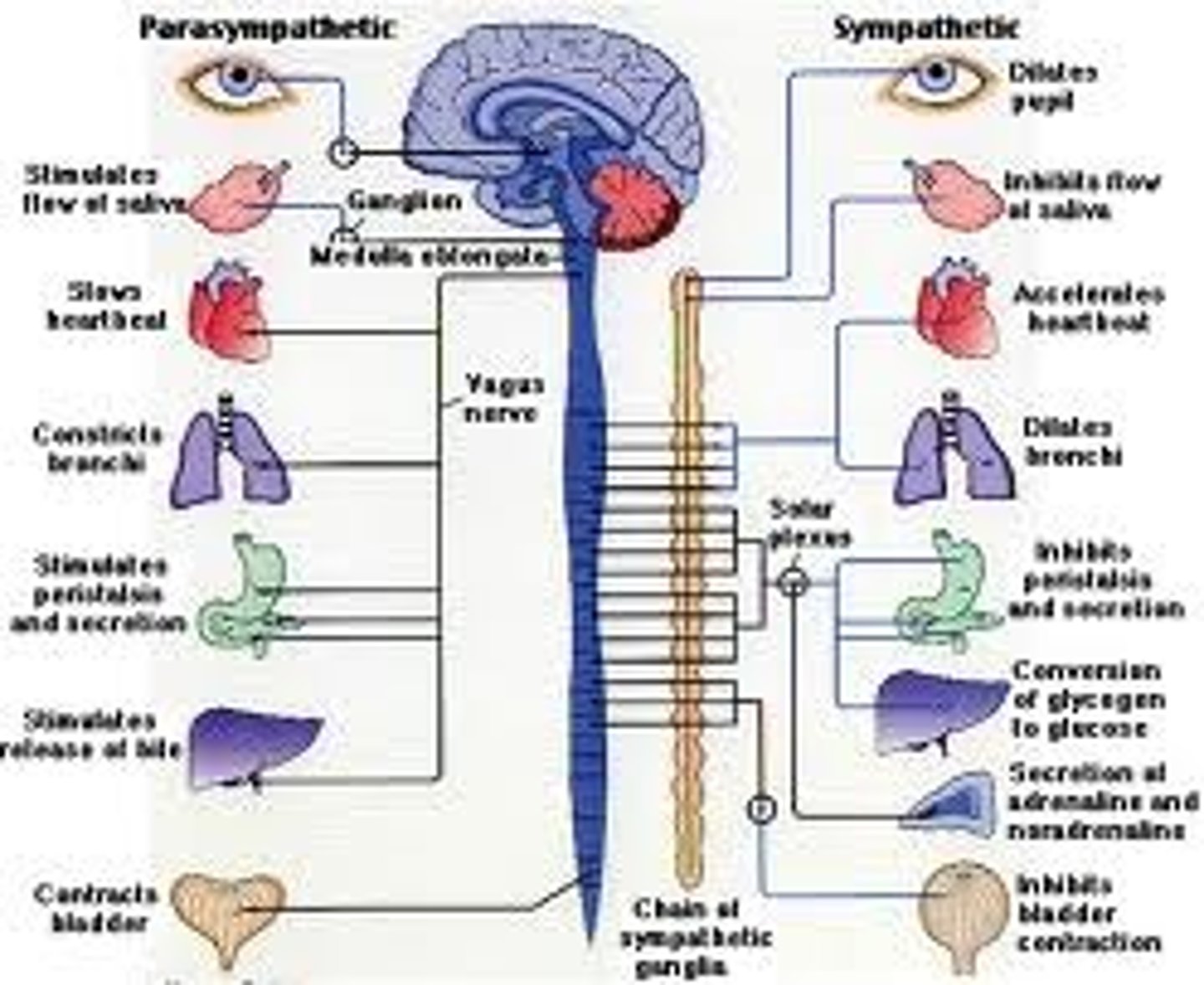
Sympathetic Nervous System
prepares the body for action and mobilizes energy resources.
It is active during fight or flight response.
( mobilizes the body's resources during
stress and emergencies. )
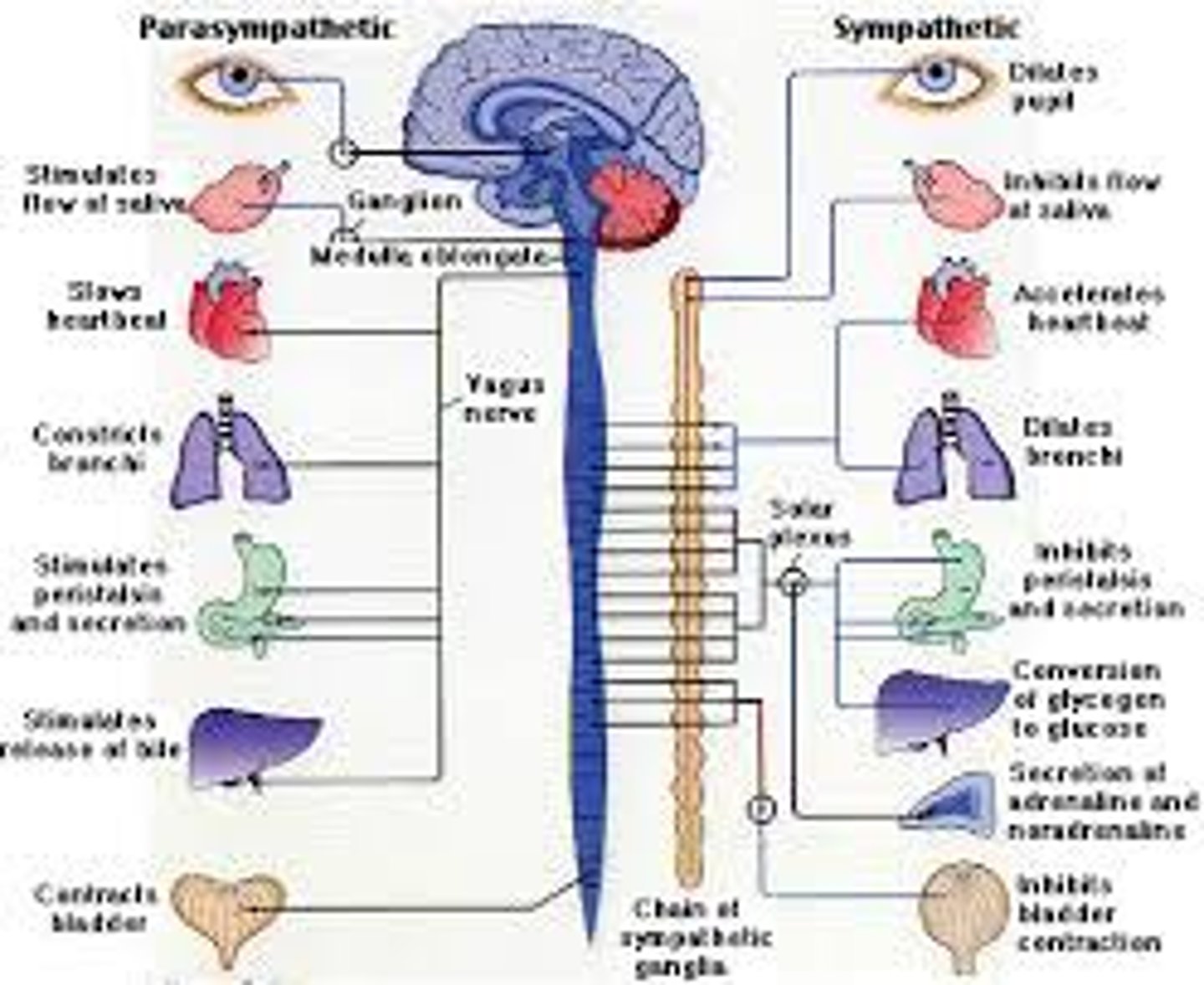
Parasympathetic Nervous System
conserves body's energy and returns the body to a normal, quiet state after an emergency.
It is active during rest and digestion.
( brings heightened bodily responses back to normal following an emergency )
Three types of neurons
-afferent, efferent, internueron
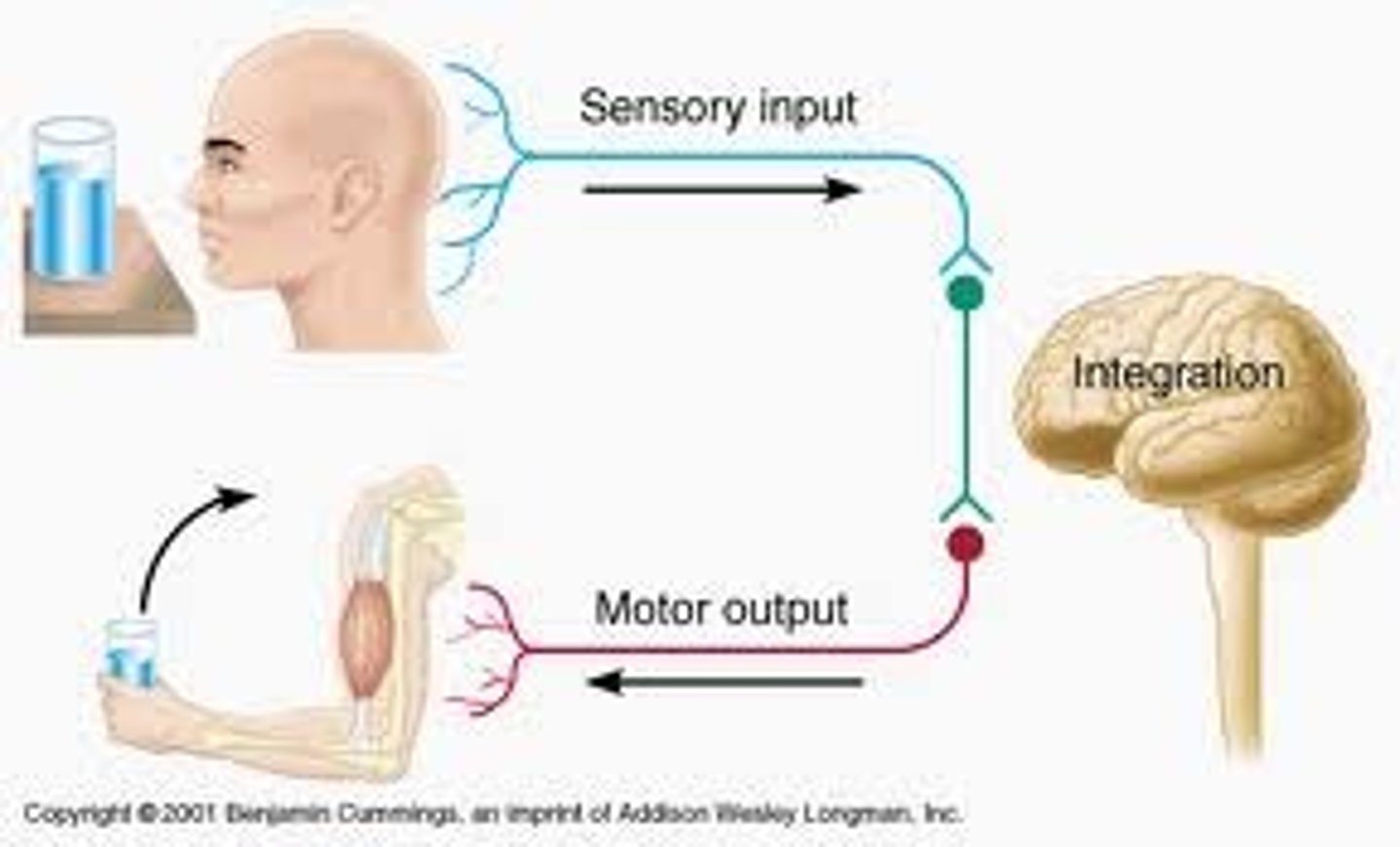
Afferent Neuron
-sensory neurons
-carries info to the brain
Efferent Neuron
-motor neurons
-send info from the brain to the skeletal muscular system
Interneuron
-interconnected excitatory or inhibitory influences
-creates inhibitory and excitatory connections between sensory and motor neurons.
Withdrawal or Spinal Reflex
● triggered by a painful stimulus.
● involves 3 types of neurons: - sensory-afferent
- motor-efferent
- interneuron

posterior hypothalamus
-lesion in this area causes to copulate until starves to death
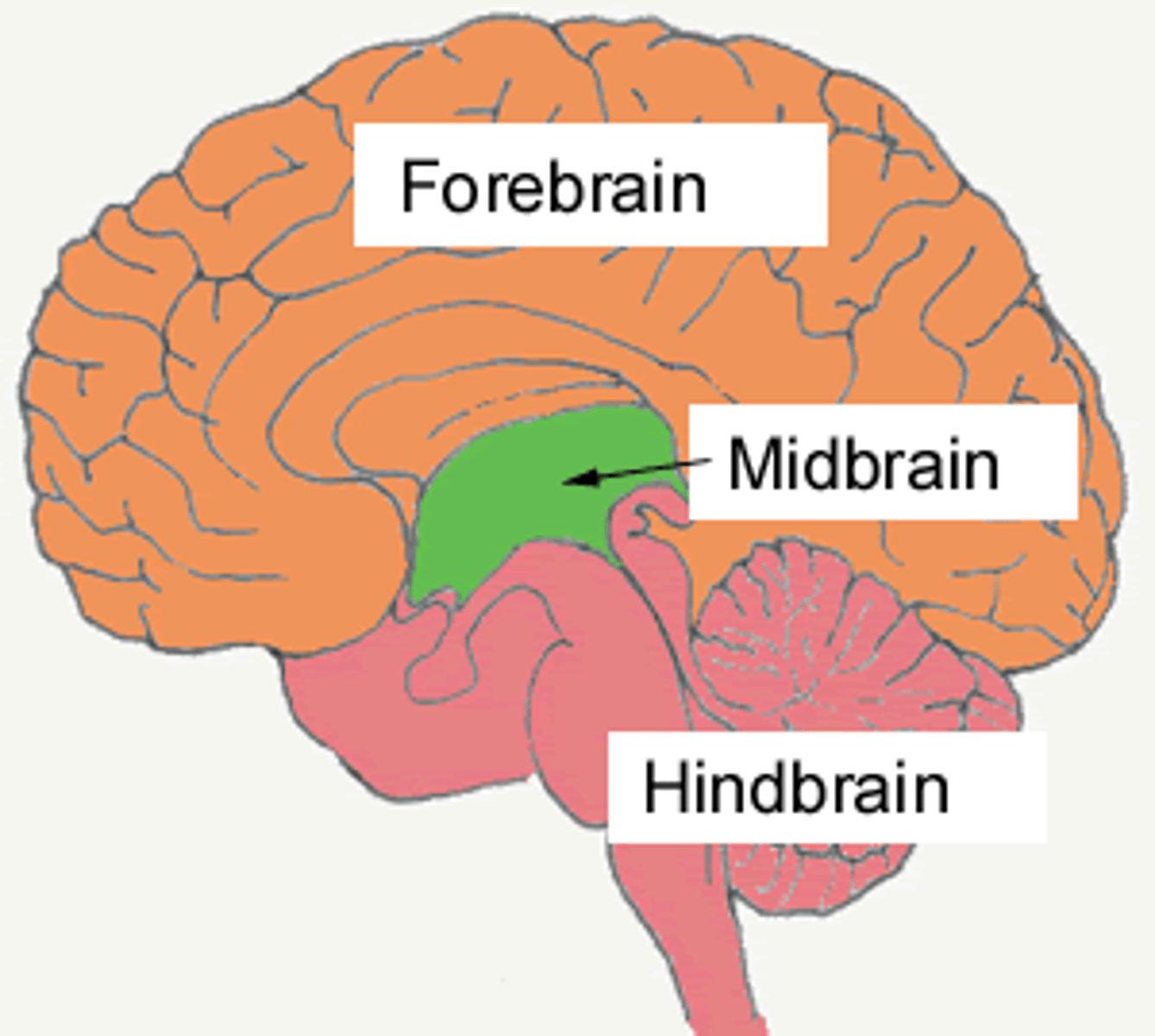
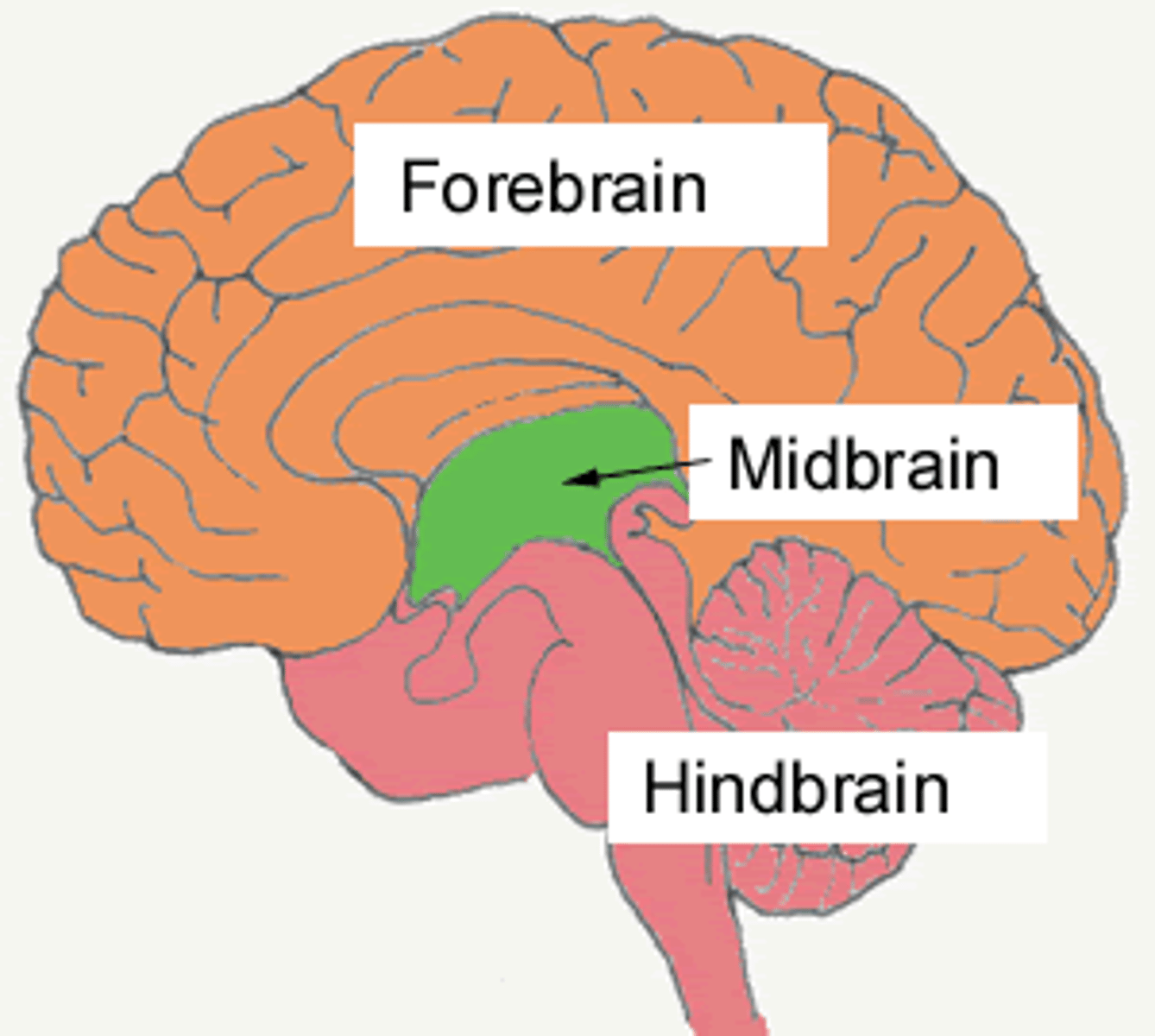
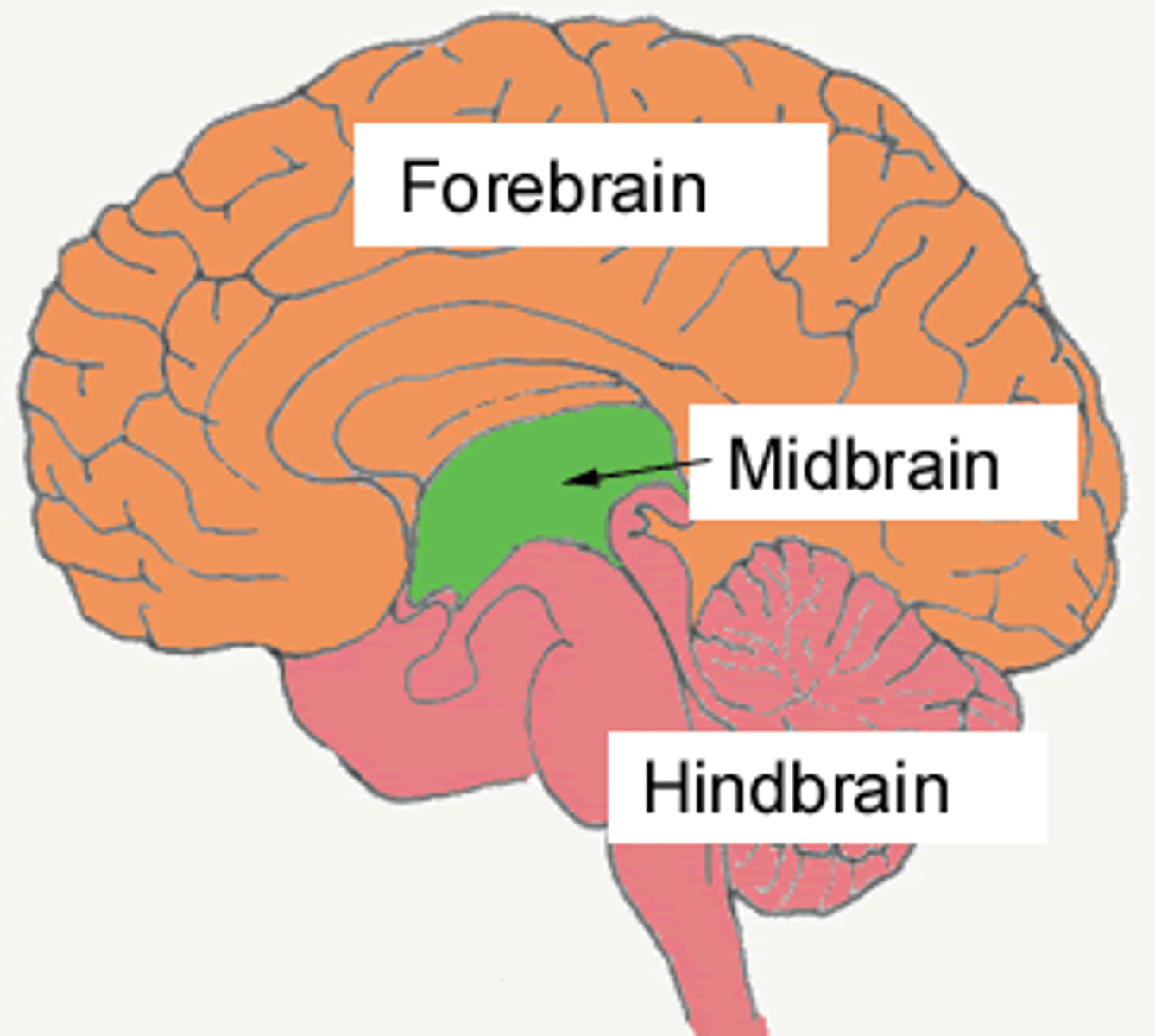
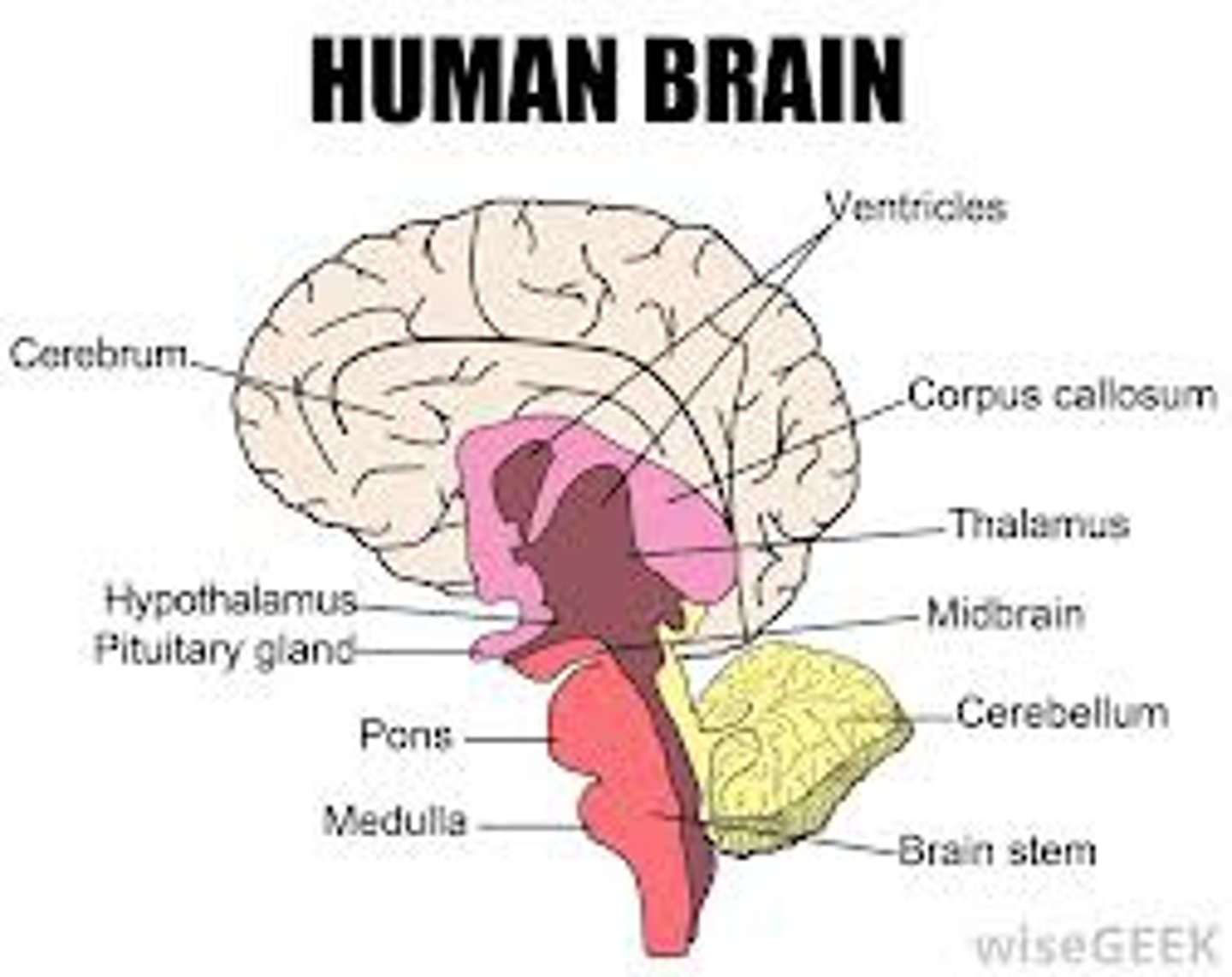
Forebrain
- the largest part of the brain where cognitive and motor functions are controlled
- functions include memory, logic, and self-awareness.
Hypothalamus
-smaller than thalamus
-the control center of a drive of motivation such as hunger, thirst, sex
-regulates body temperature;
-helps control endocrine system;
-involved in emotion
-houses the biological sleep-wake cycle
-hollow feeling in the pit of the stomach
Left lateral hypothalamus
-lesion in this area causes adipsia
right lateral hypothalamus
-damage in this area causes overeating to death
Cerebrum
The thinking part of the brain.
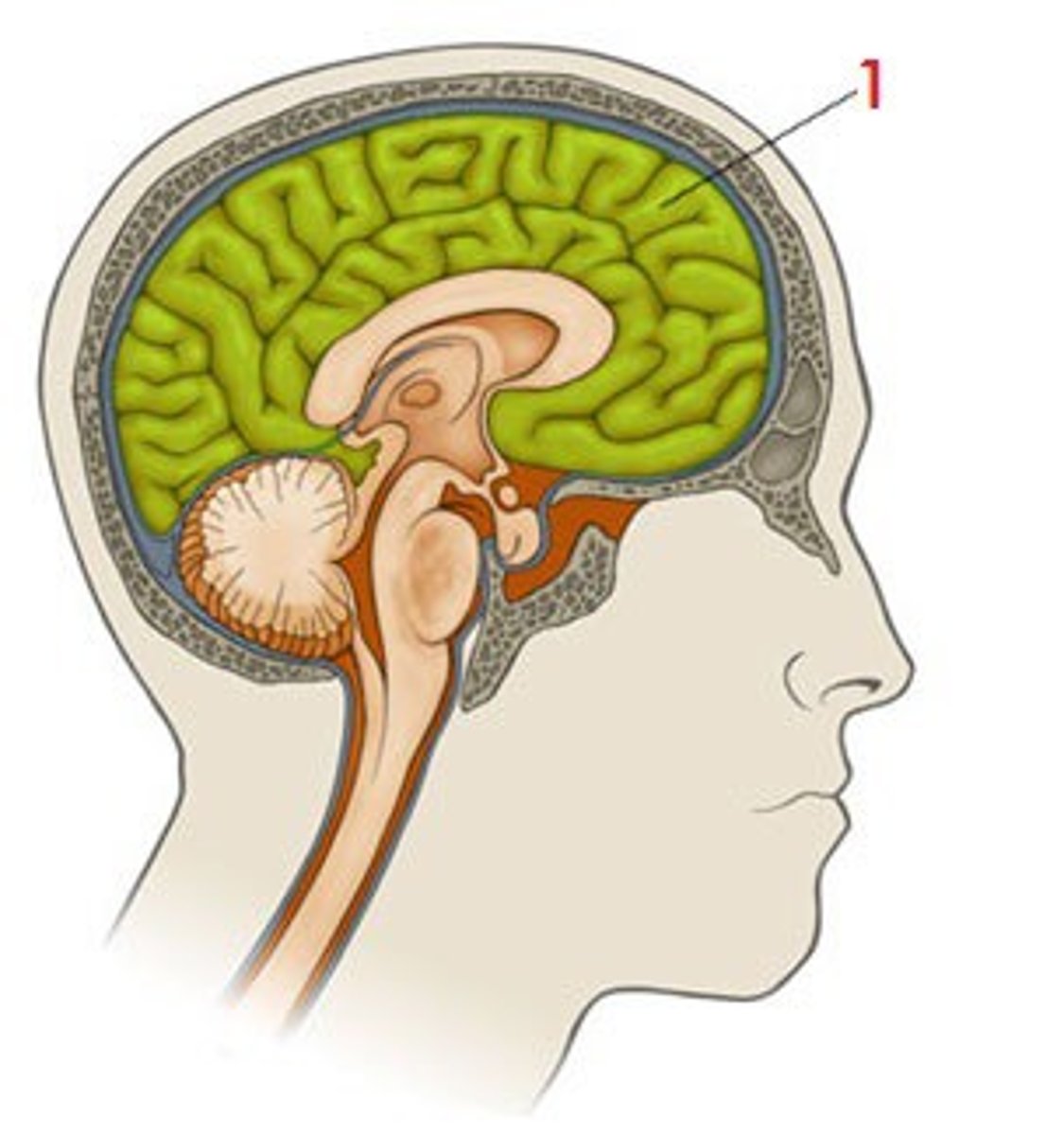
Cerebral Cortex
- wrinkle grey outer covering of cerebrum.
- responsible for higher mental processes of language, memory, and thinking.
- contains 3 areas: Sensory Input Areas, Motor Areas and Association Areas
-the convoluted covering of the cerebral hemispheres that is responsible for higher mental processes.
Corpus callosum
-band of nerve fibers that connects the two sides of the brain.
-inter-hemisphere transfer how info in our hemisphere crosses over to the other hemisphere.
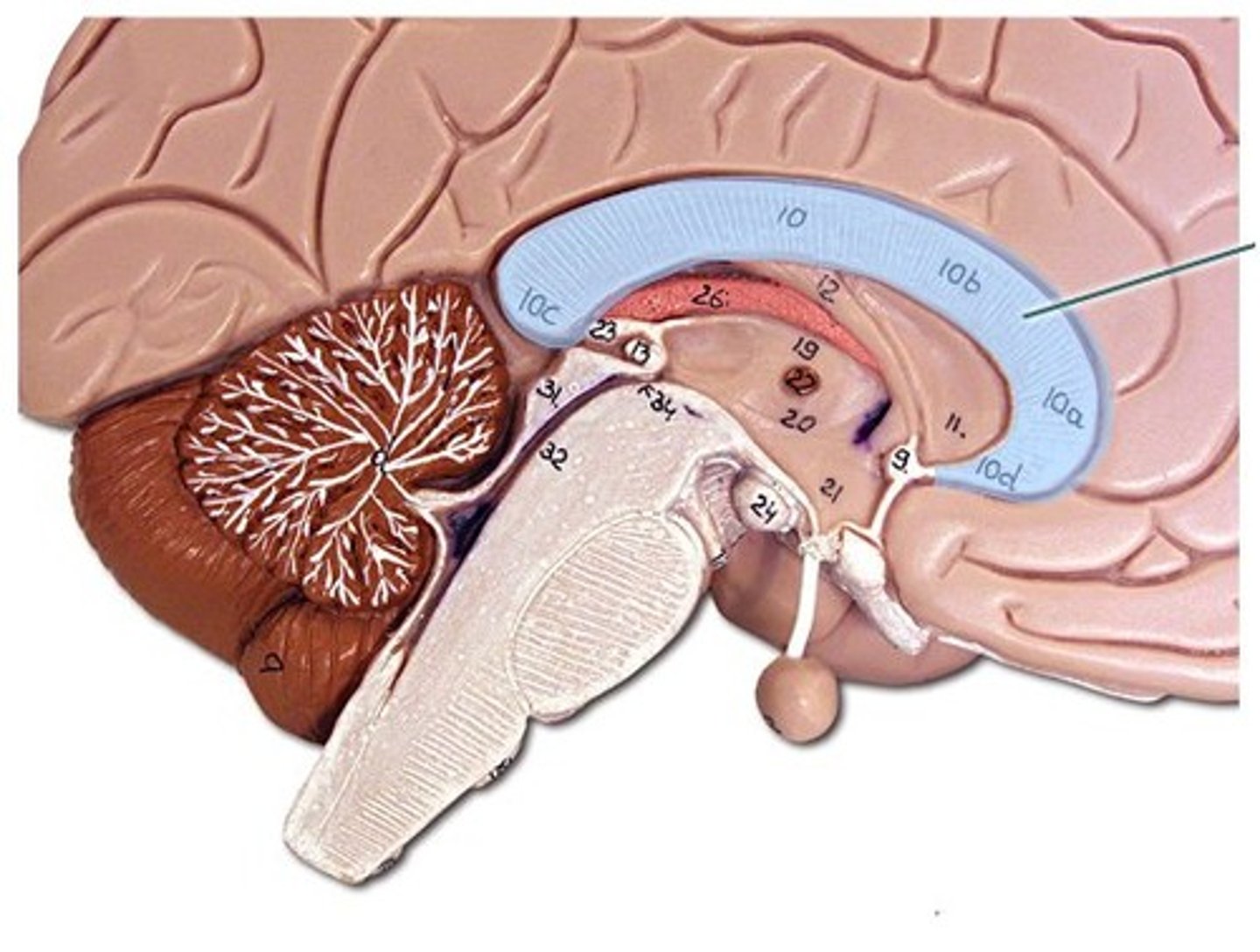
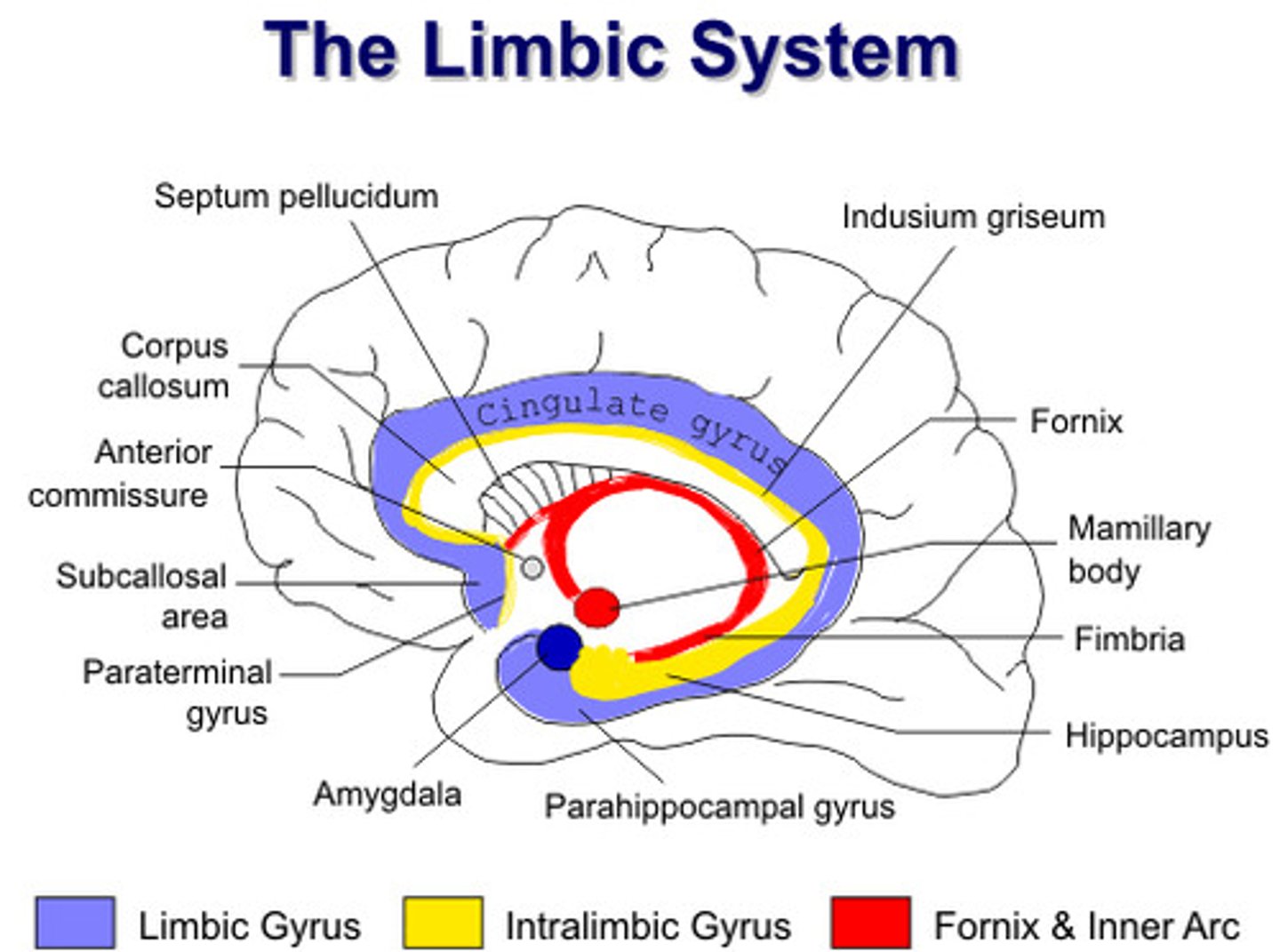
Limbic system
group structures involved in emotional expression, memory, and motivation.
- consists of Amygdala and Hippocampus
Amygdala
- part of the limbic system.
- plays important role in emotion, especially emotions associated with punishment
-involved in learning fear responses
-enables humans to form vivid memories of emotional events/helps animals avoid a dangerous situation
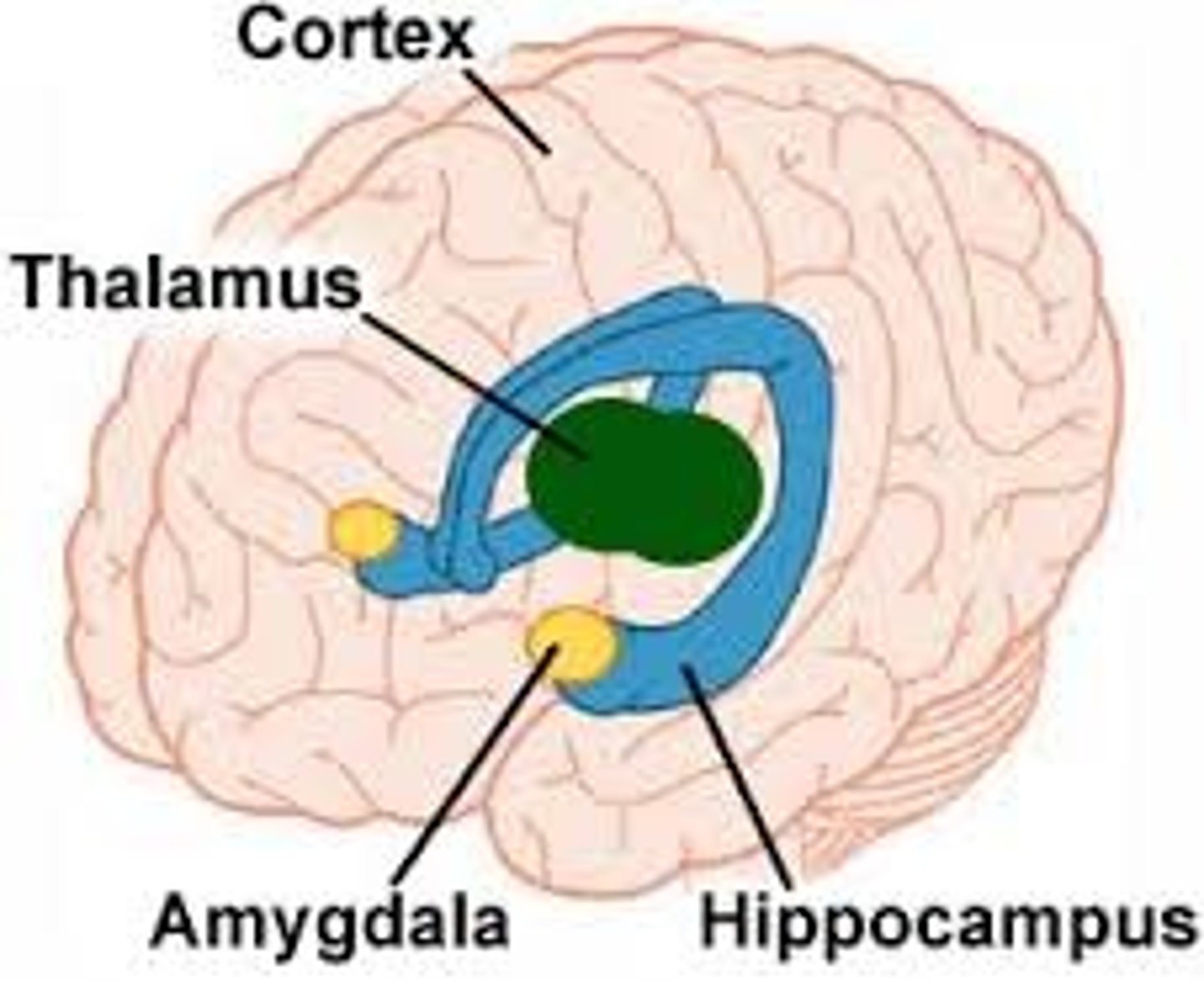
Hippocampus
- part of the limbic system.
- the central role in storing new memories, responses to new or unexpected stimuli, and navigational ability.
-the internal representation of space and can form neural maps which help us learn our way in a new environment and remembers where we have been
-if this area is damaged, new information will not be stored, but preexisting memories will be intact
-helps develop cognitive maps
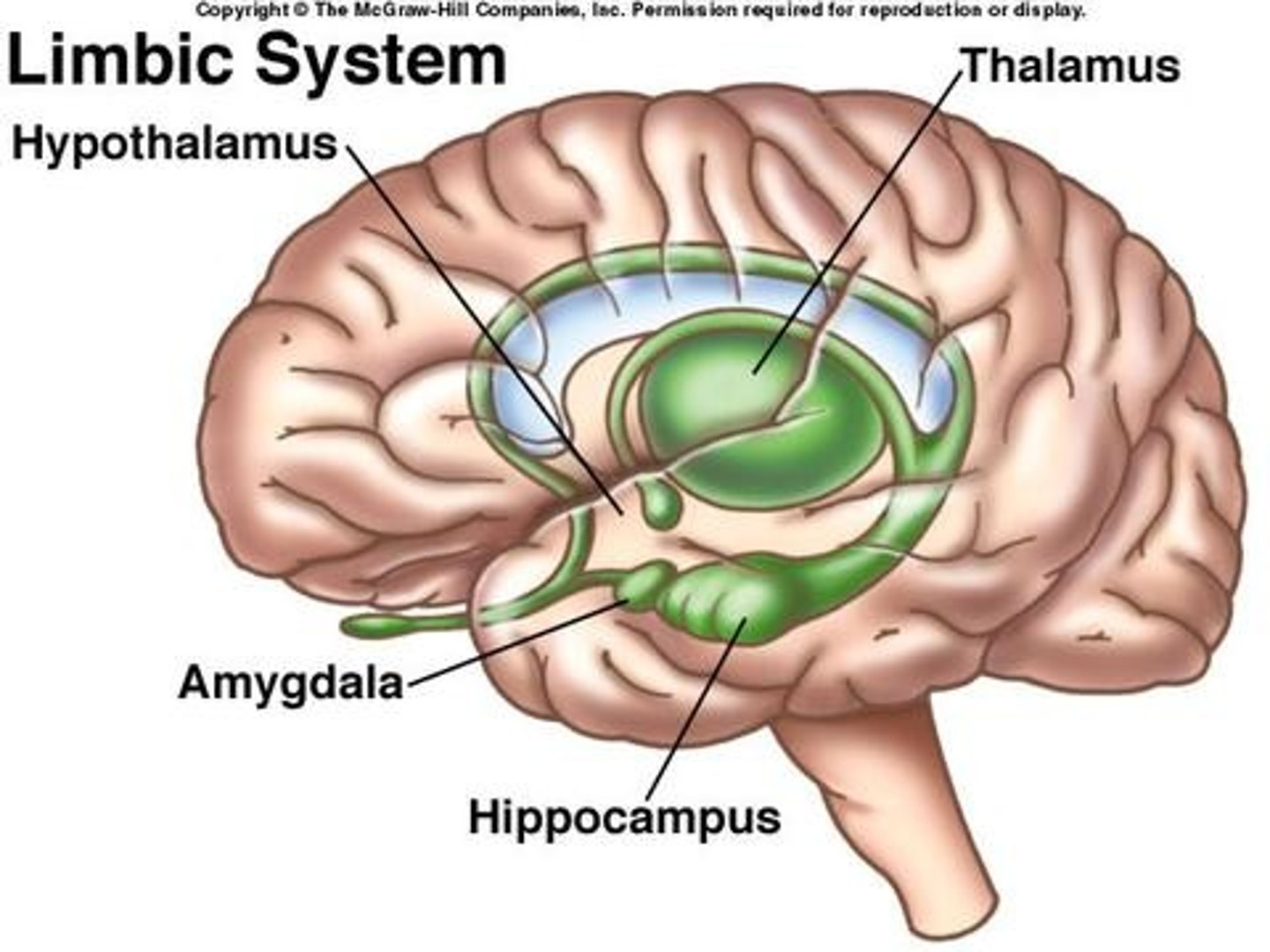
Thalamus
-relay station between cerebral cortex and lower brain centers.
-relay station for all sensory info except smell
-controls ability to learn the new verbal information
-plays a role in regulation of sleep cycle
-damage in this area will cause vegetative state, coma
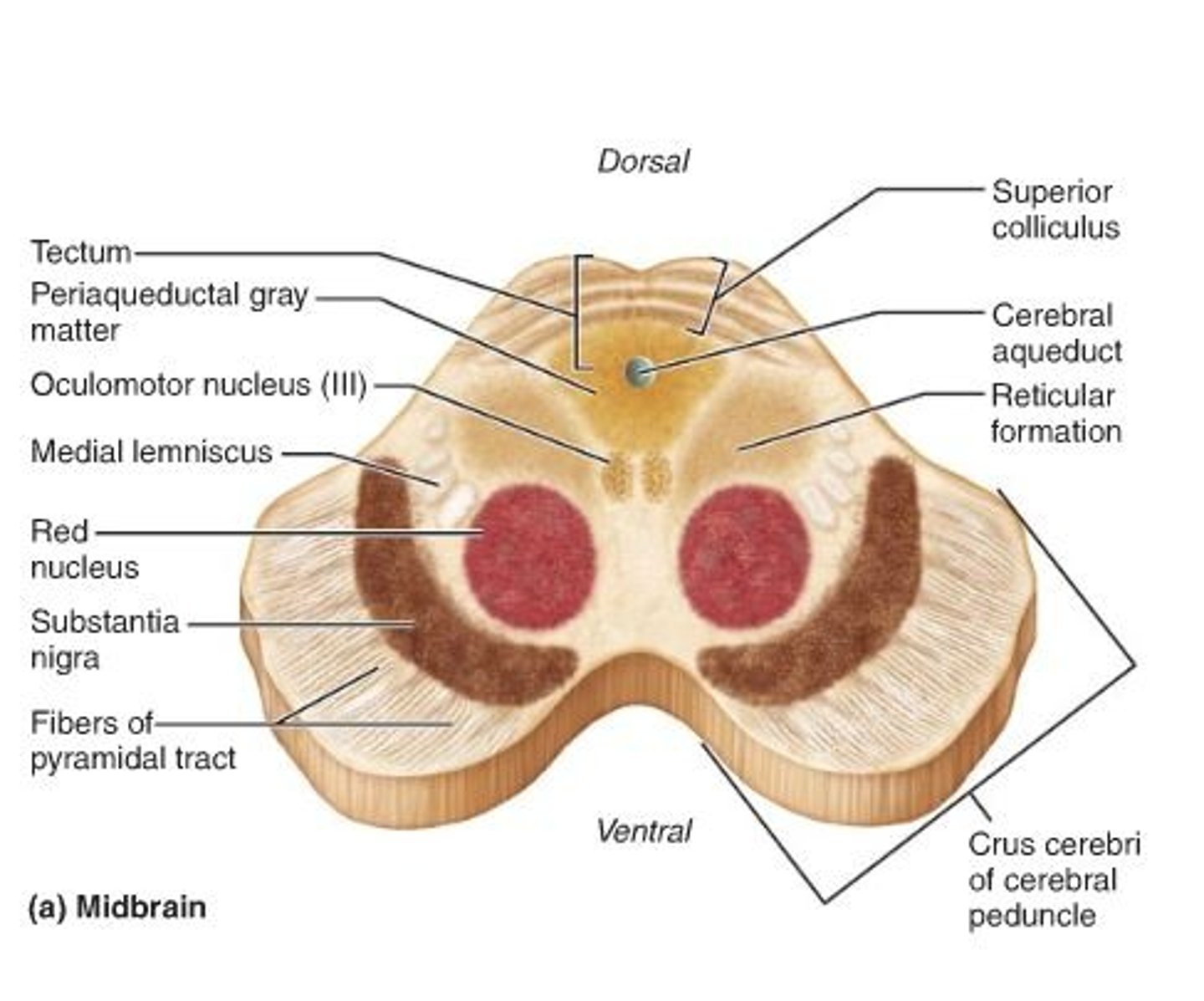
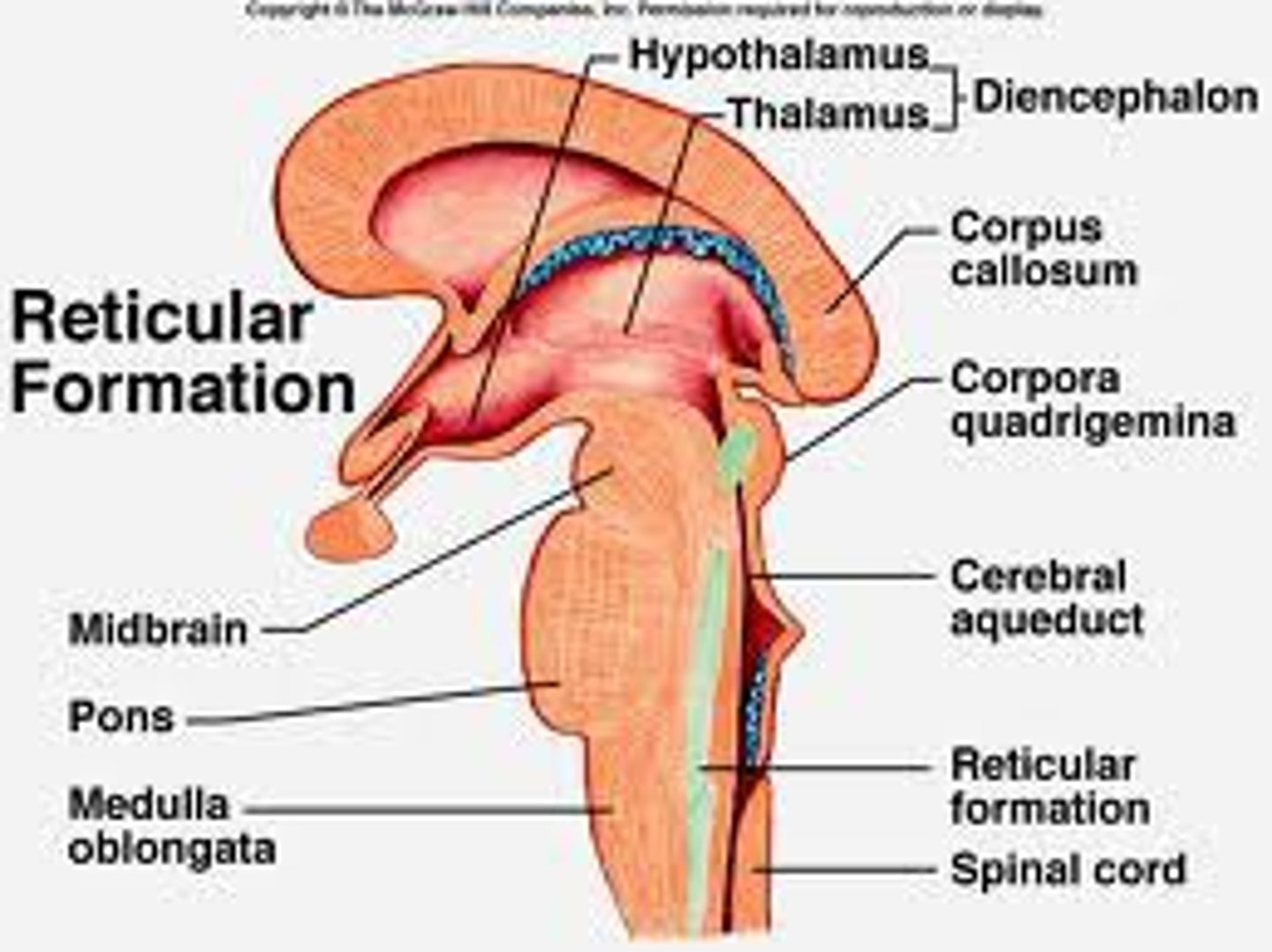
Midbrain
-links the physiological functions of the hindbrain to the cognitive functions of the forebrain.
Substantia Nigra
-controls unconscious motor movements (ex. sleepwalking)
-defect in dopaminergic neurons in this area may explain why people with Parkinson's have trouble with controlling physical movement
Hindbrain
-a link between the spinal cord and the brain that contains structures that regulate physiological functions, including heart rate, respiration, and blood pressure.
-consists of pons, medulla, spinal cord, reticular formation, cerebellum
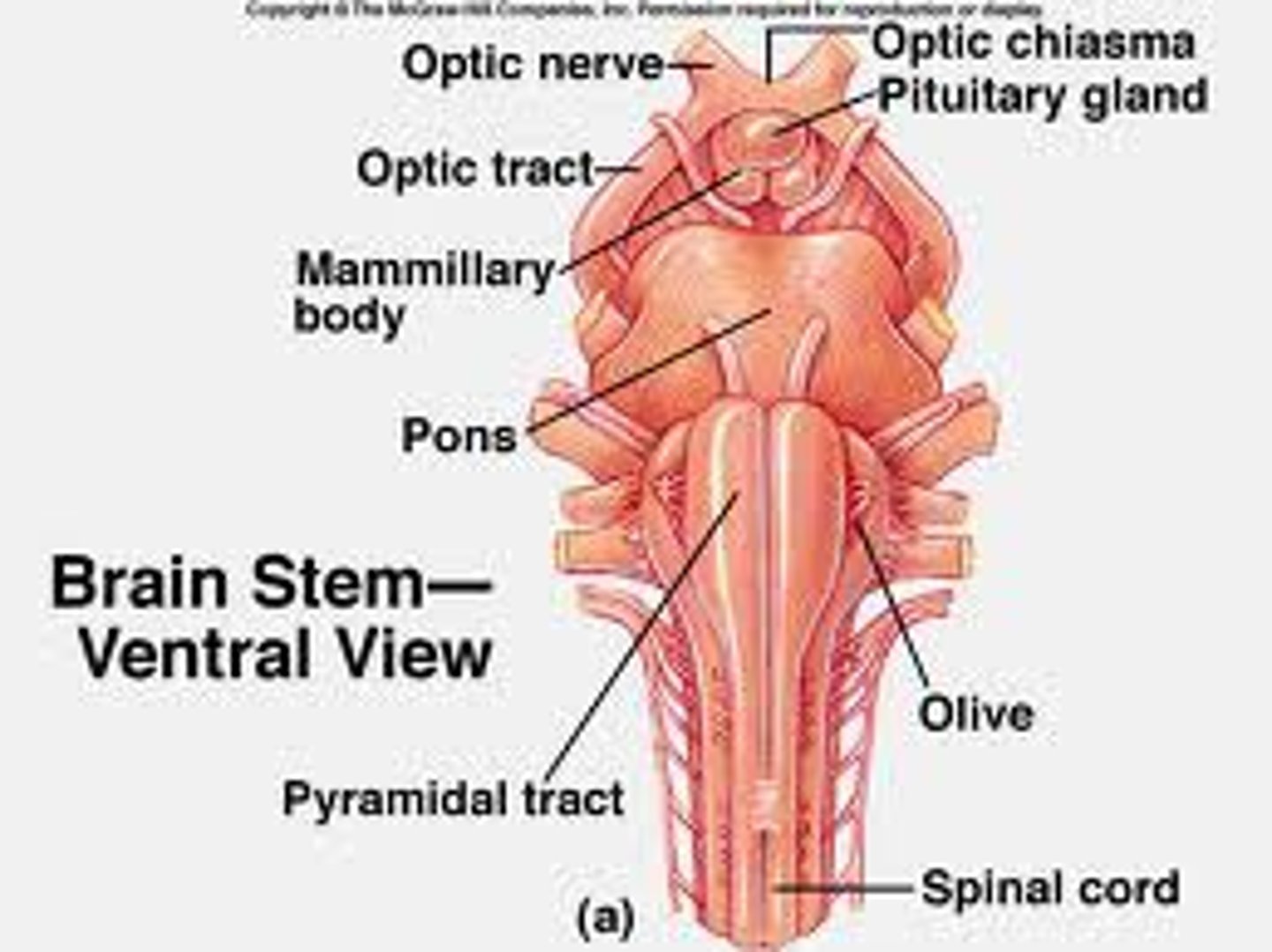
Pons
-plays role in relaying messages between cerebellum and motor cortex, exerts force on sleep and dreaming.
-controls body movement, sleeping and dreaming
-dreaming (most restorative stage, REM sleep, help maintain concentration

Medulla
control center for heartbeat, breathing blood pressure, swallowing and coughing.
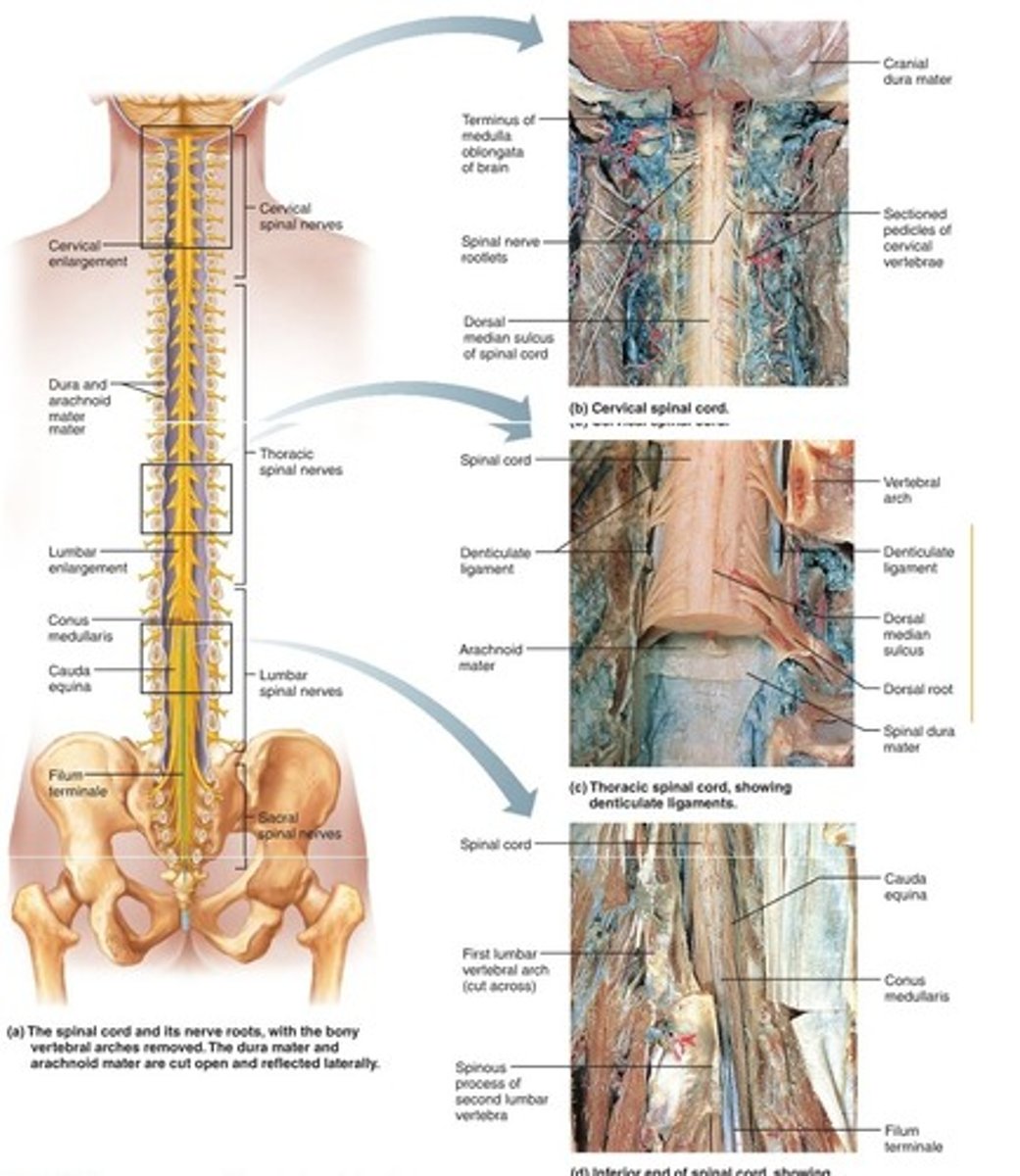
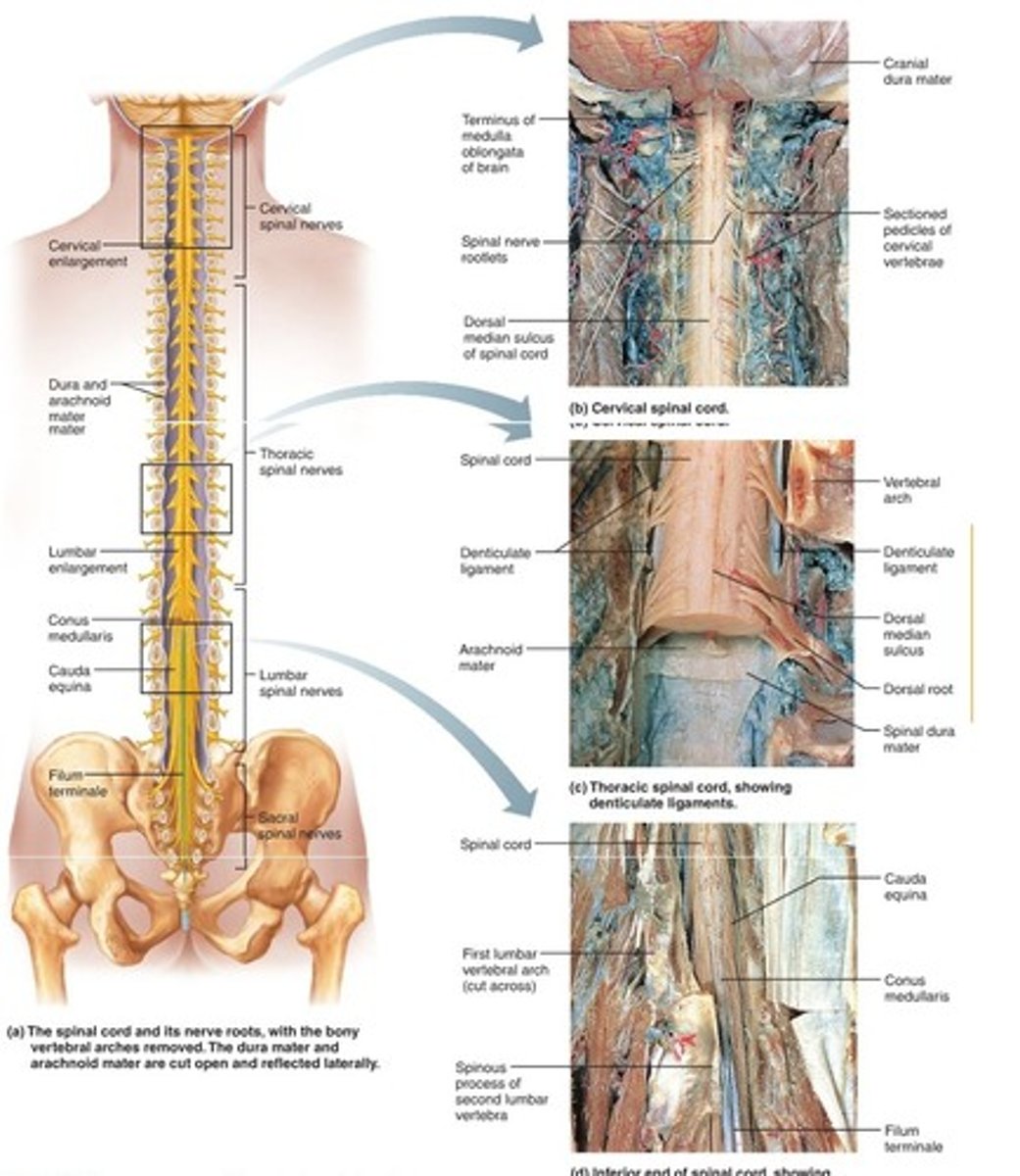
Spinal Cord
- best thought of as the extension of the
brain.
- transmits messages between the brain and the peripheral nervous system.
- can act without help from the brain to protect the body from injury.
- controls simple reflexes
-spinal cords are 1" in diameter
Brainstem
begins at the site where the spinal cord enlarges as it enters the skull.
Reticular Formation
- plays a crucial role in arousal (stationary) and attention (directive)
-determines alertness
- screens sensory messages entering the brain.
Cerebellum
-coordinates skilled movement (ex. playing piano, gymnast's performance on balance beam
-regulates muscle tone and posture.
-motor learning (ex. learn to skate and ski)
Phrenology
-studying bumps on the back of the head
localization of function
-part of the brain has different functions
Lateralization of function
-the specialization of one of the cerebral hemispheres to handle a particular function.
-function differs from left side of the brain to right side of the brain
Left Hemisphere (of the brain)
- controls the right side of the body.
- handles most language functions (ex. speaking, reading, writing, speech comprehension, writing comprehension
- specialized for mathematics and logic.
-the sense of well-being
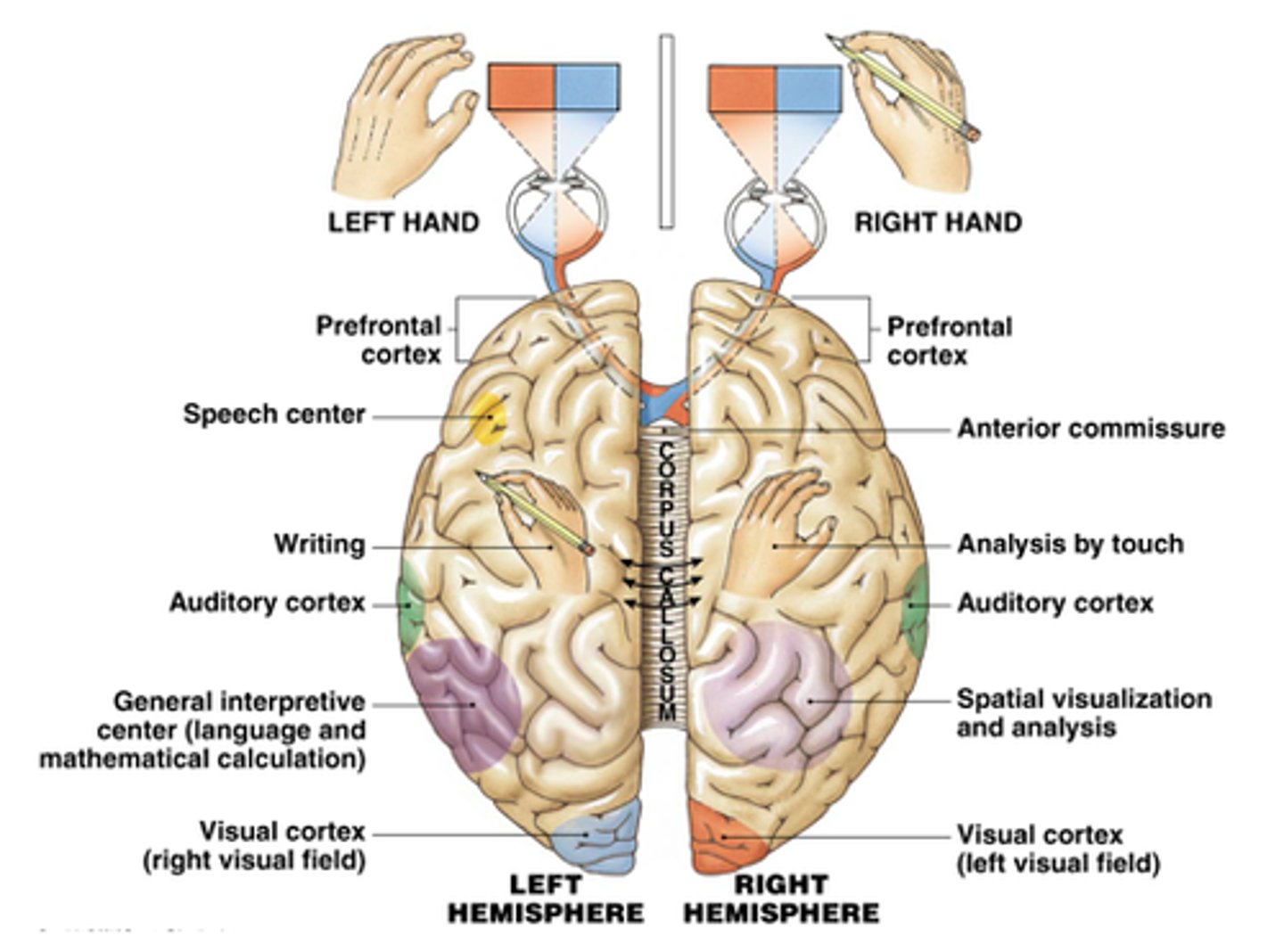
Right Hemisphere (of the brain)
Right Hemisphere
- controls left side of body.
- processes music.
- interprets emotional messages conveyed by tone of voice and gestures.
- is specialized for visual-spatial relations.
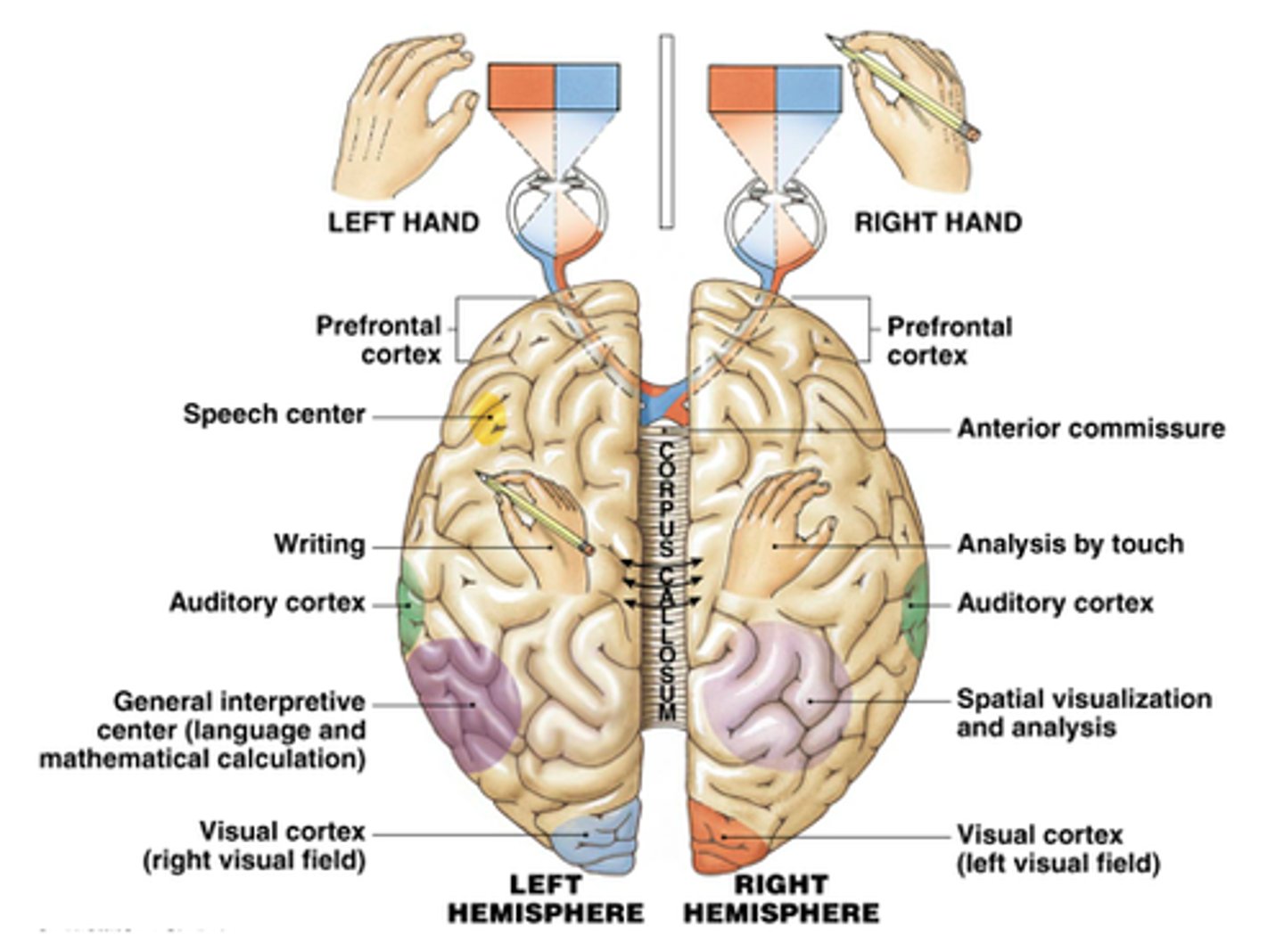
Cerebral Hemispheres
left and right halves of cerebrum.
unilateral neglect
-unaware of the objects in the left side of visual field
Sensory Input Areas
● vision, hearing, touch, pressure, and
temperature register.
seisure
-electrical activity in the brain
-electricity moves from left to right and back and forth
Motor Areas
● control voluntary movement
Association Areas
● house memories and are involved in thought, perception, and language
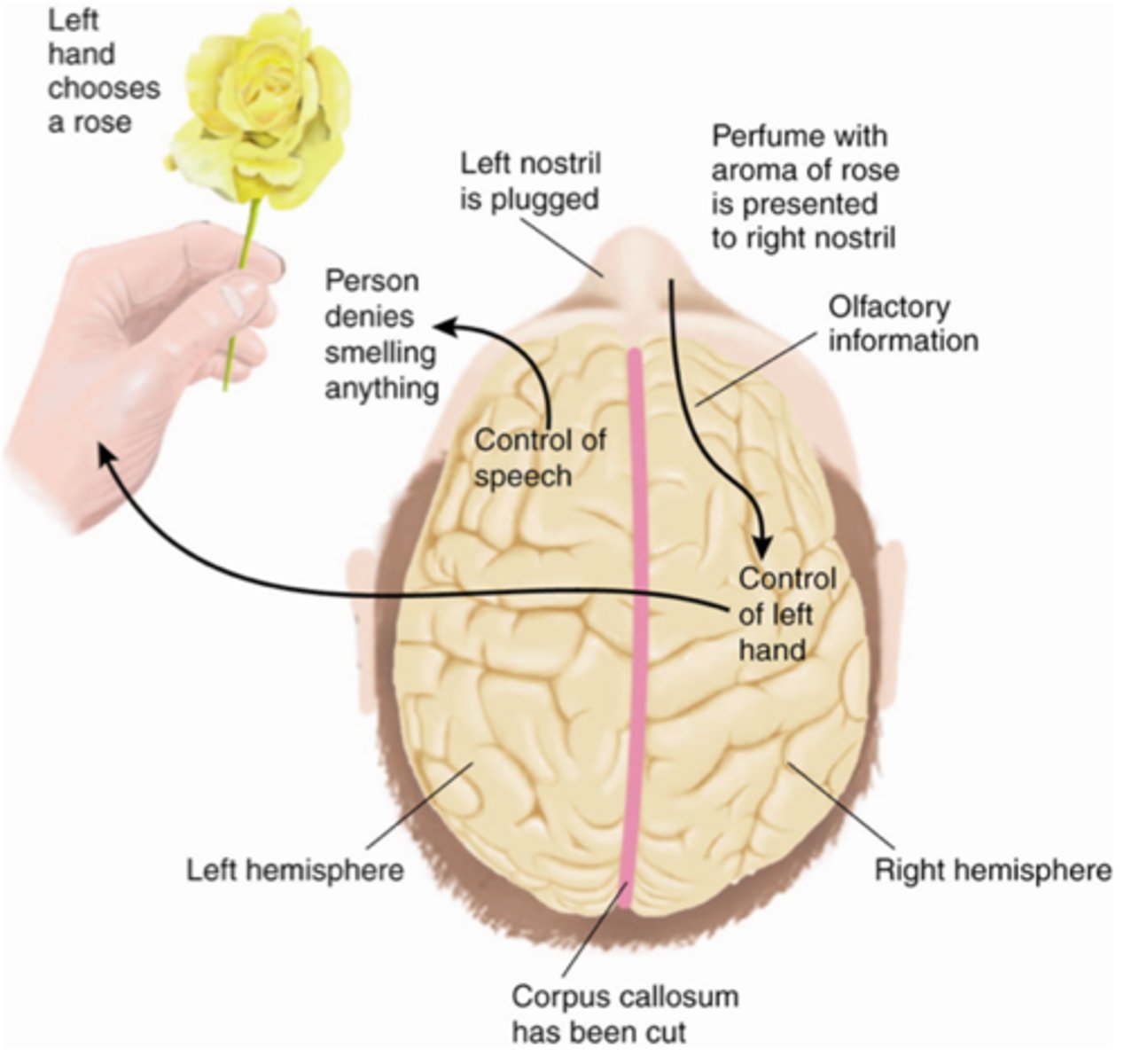
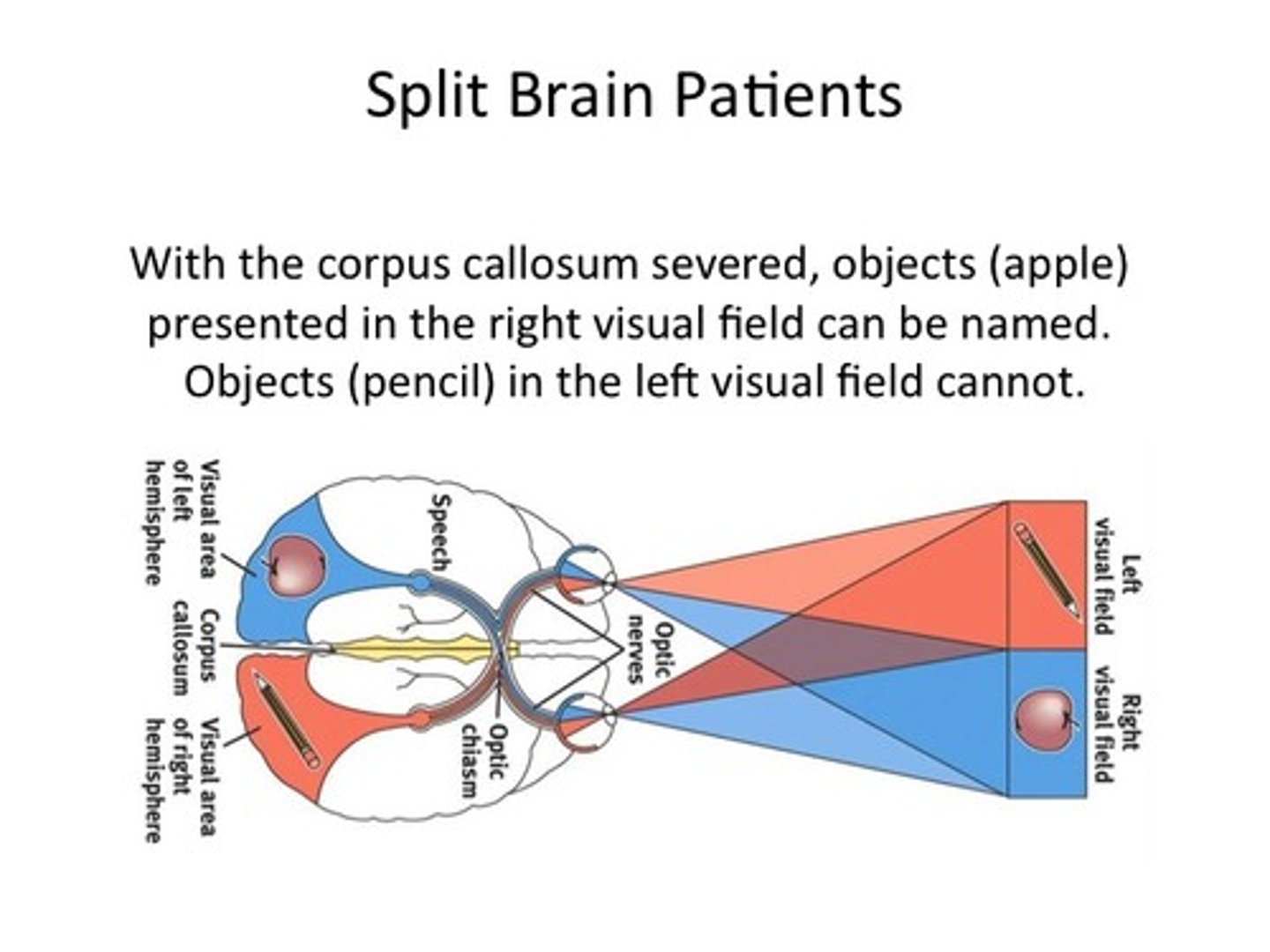
The Split Brain
• Corpus callosum is absent or has been surgically modified.
• Only the verbal left hemisphere can report what it sees.
• The left hemisphere does not see what is flashed to the right hemisphere; the right hemisphere is unable to report verbally what it has viewed.
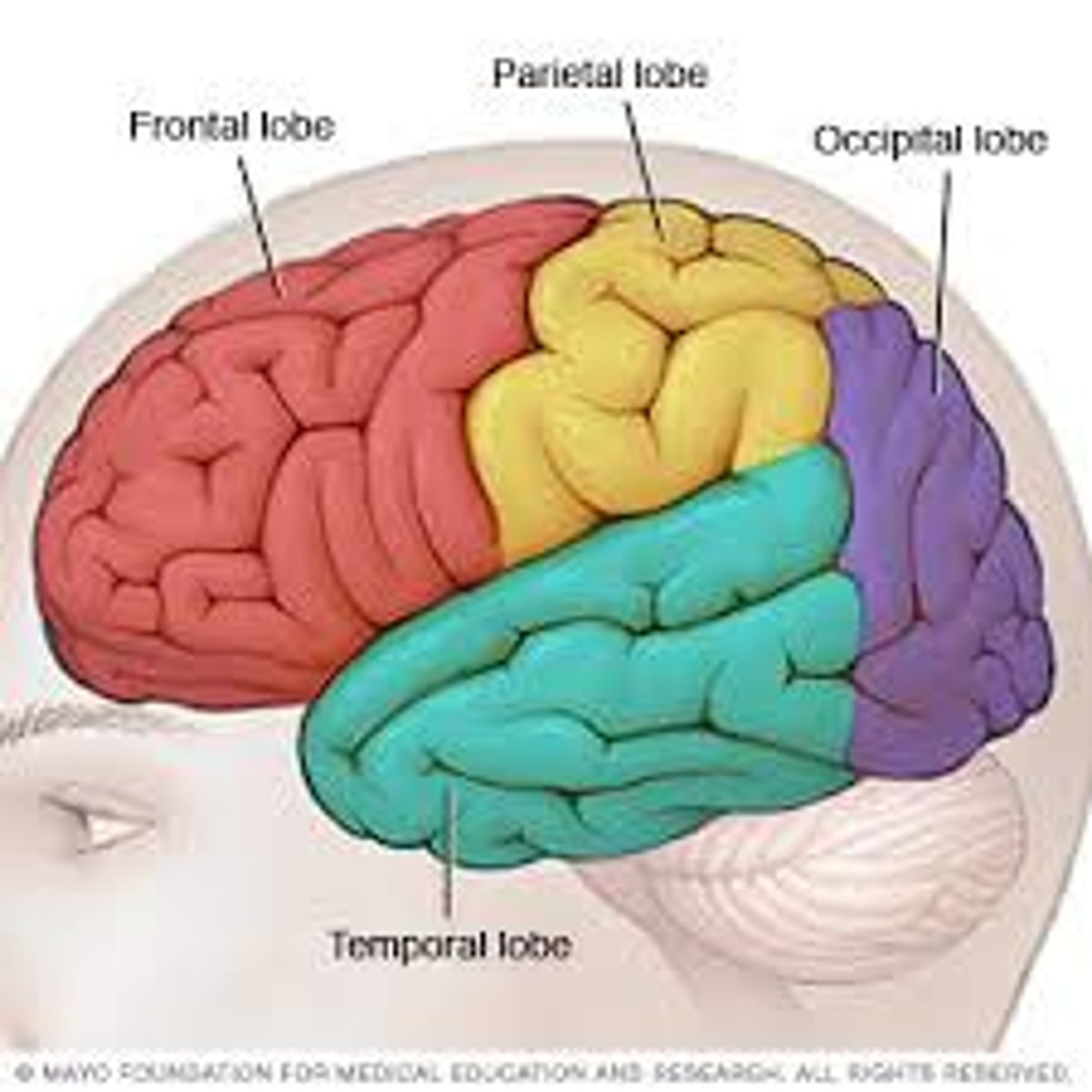
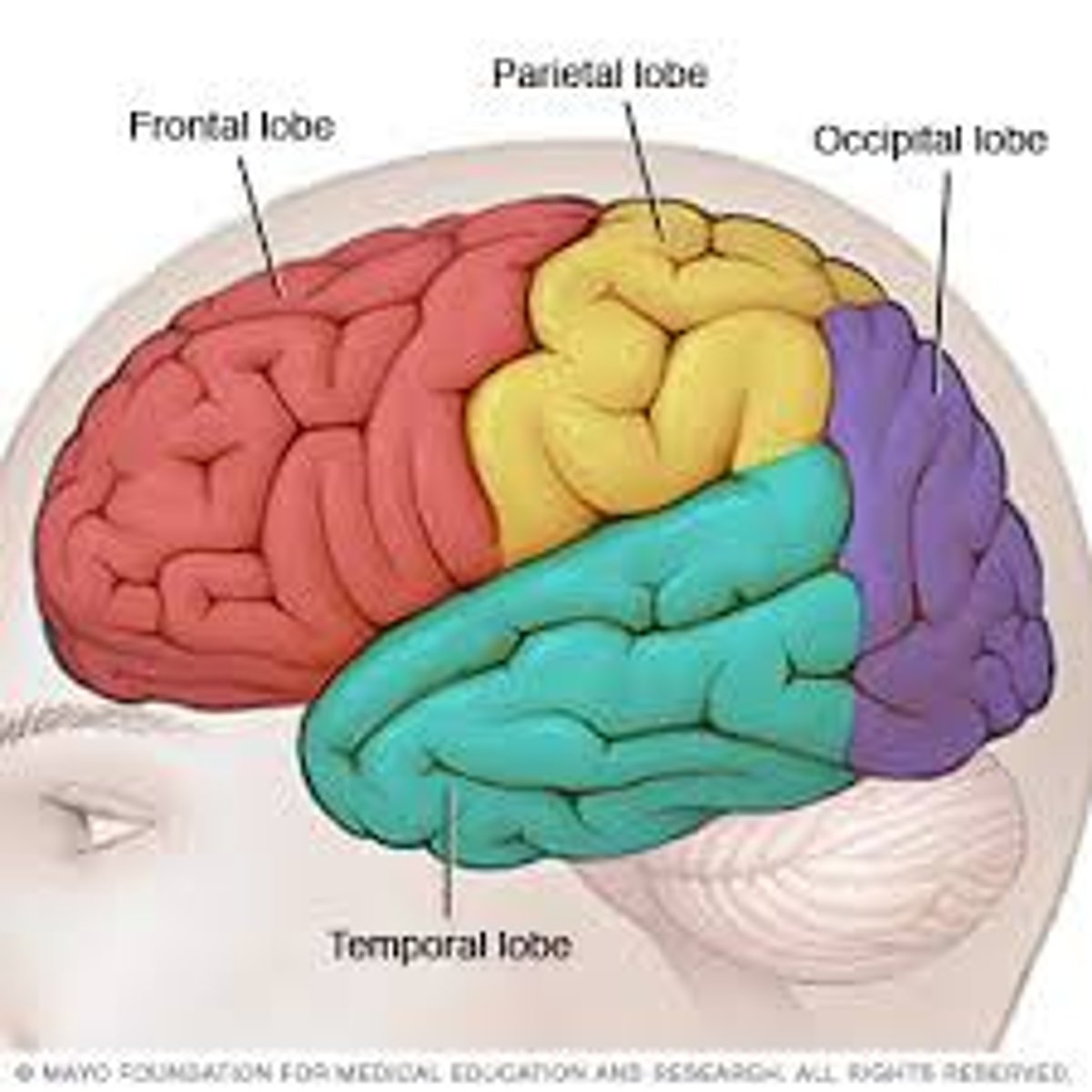
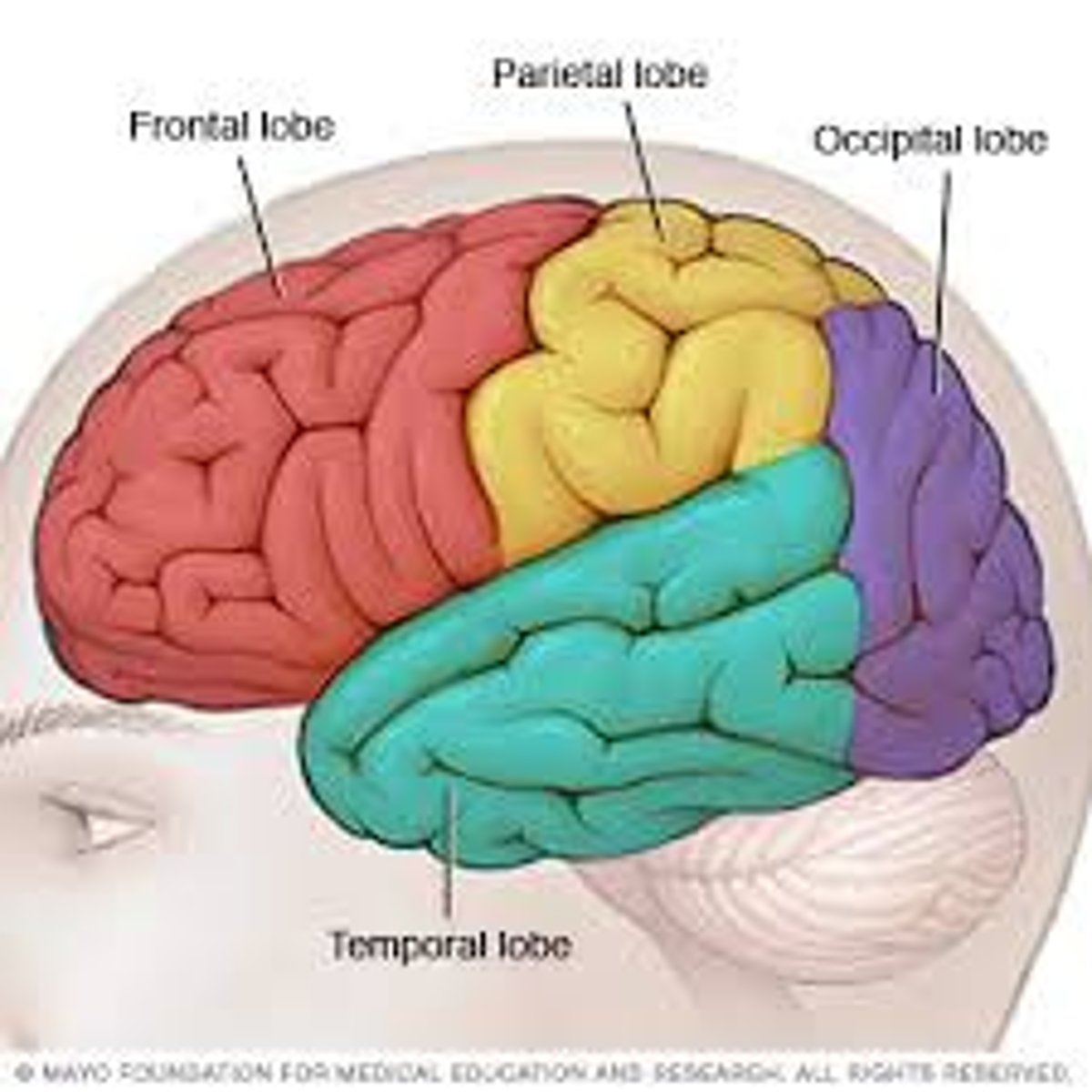
The 4 Lobes of the Brain
The frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, temporal lobe
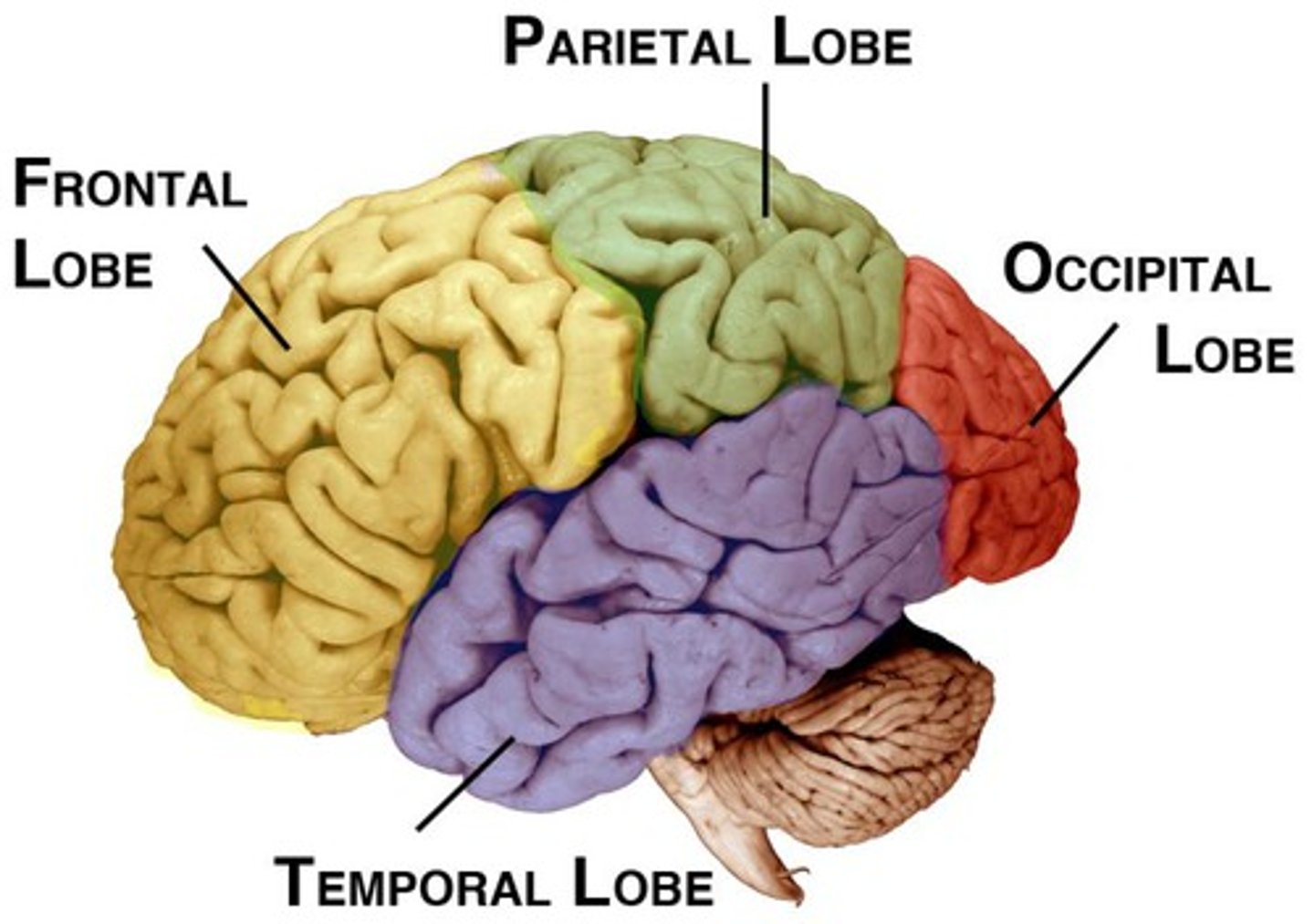
Frontal Lobe
-the largest lobe; includes the motor cortex and the Broca's area.
-act as an executor of the human anatomy & nervous system
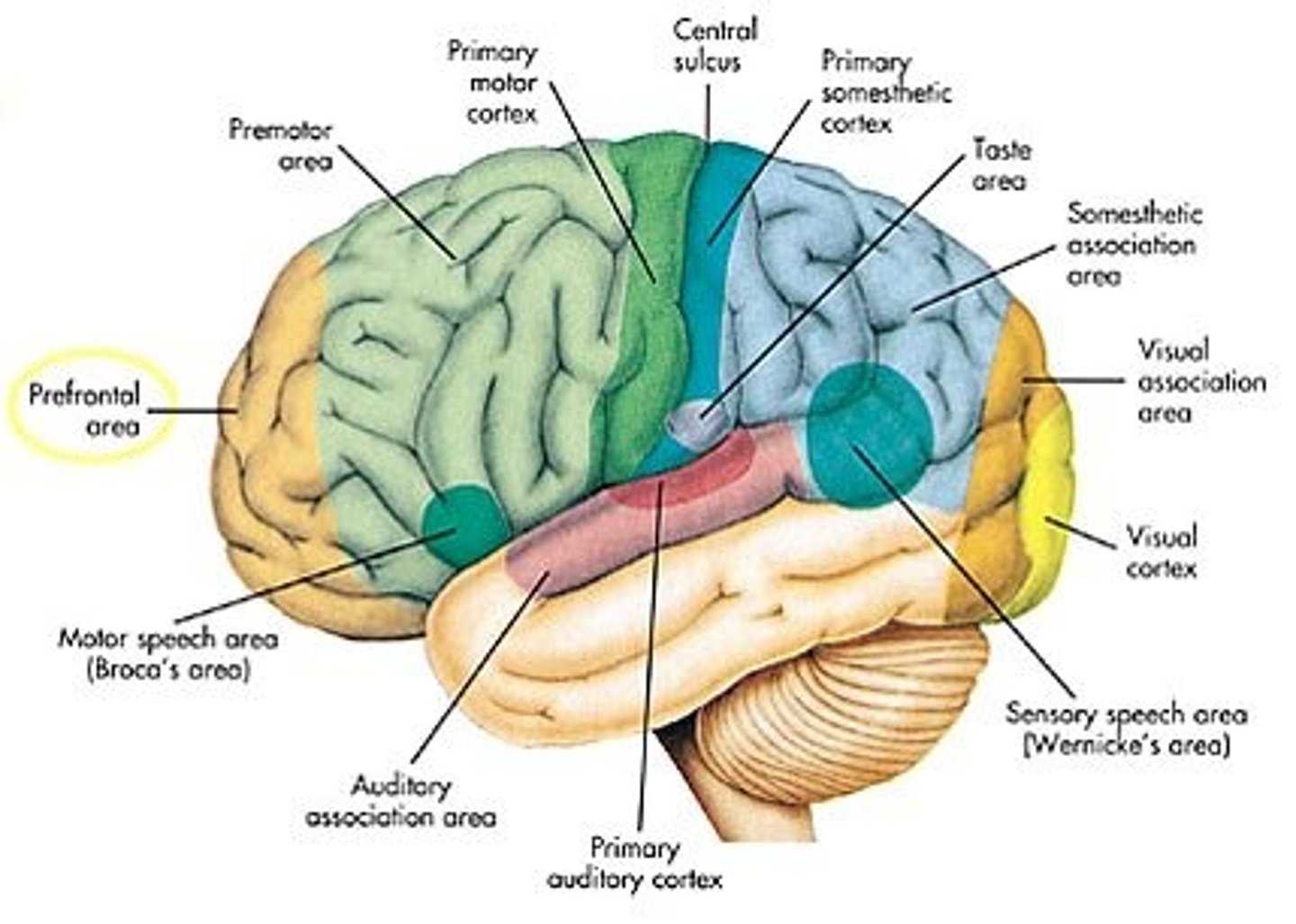
Prefrontal Cortex
-The part of the frontal lobes directly behind the forehead that controls executive processing
-the coordination of multiple brain activities in pursuit of cognitive goals.
-damage in this area causes unable to regulate emotions, preventing from modulating emotions.
-cannot regulate the impulse
-if cannot control the impulse, then cannot anticipate the consequences of their behavior
executive processing
-let you experience tasks as a whole instead of fragmentary disconnected activities
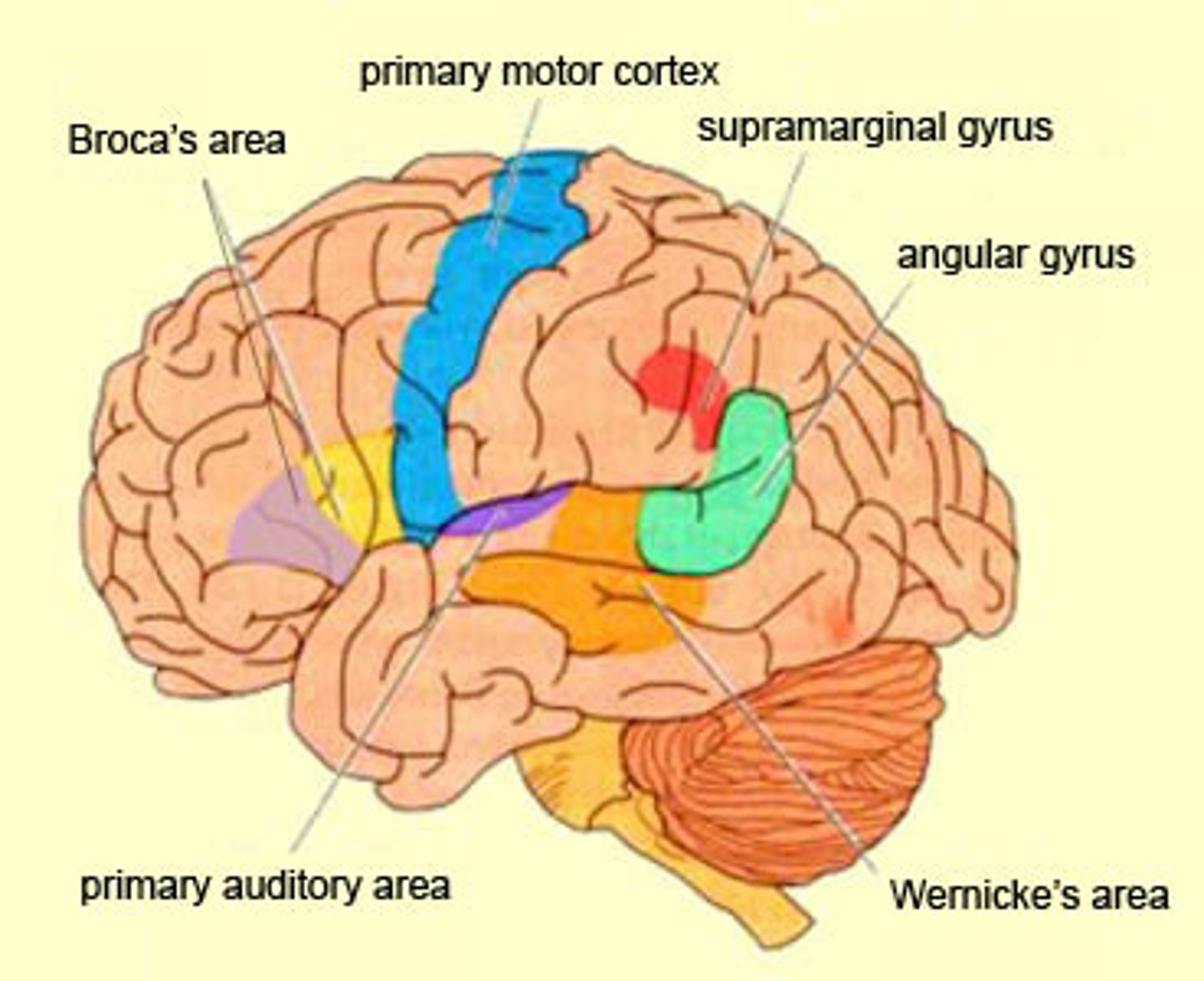
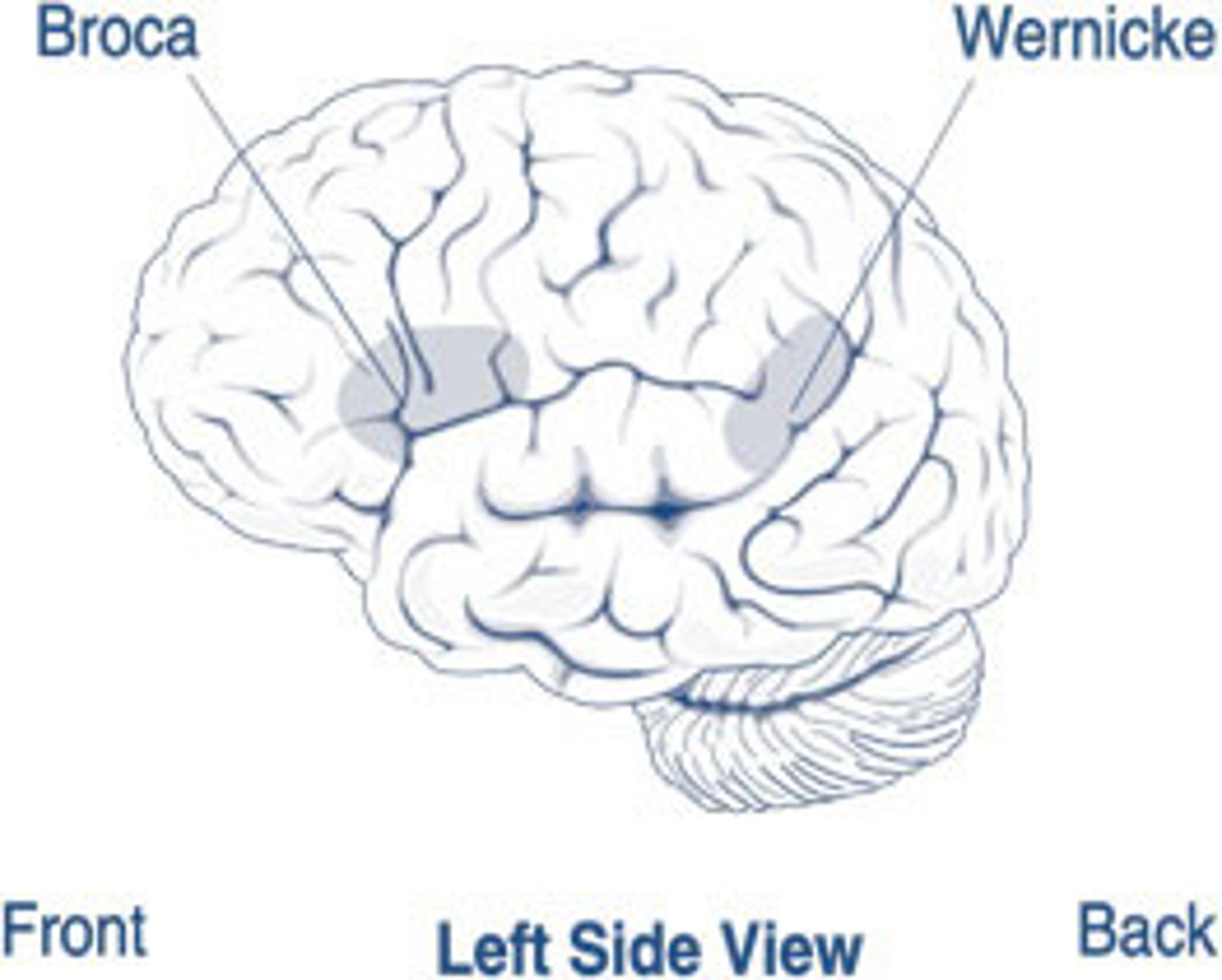
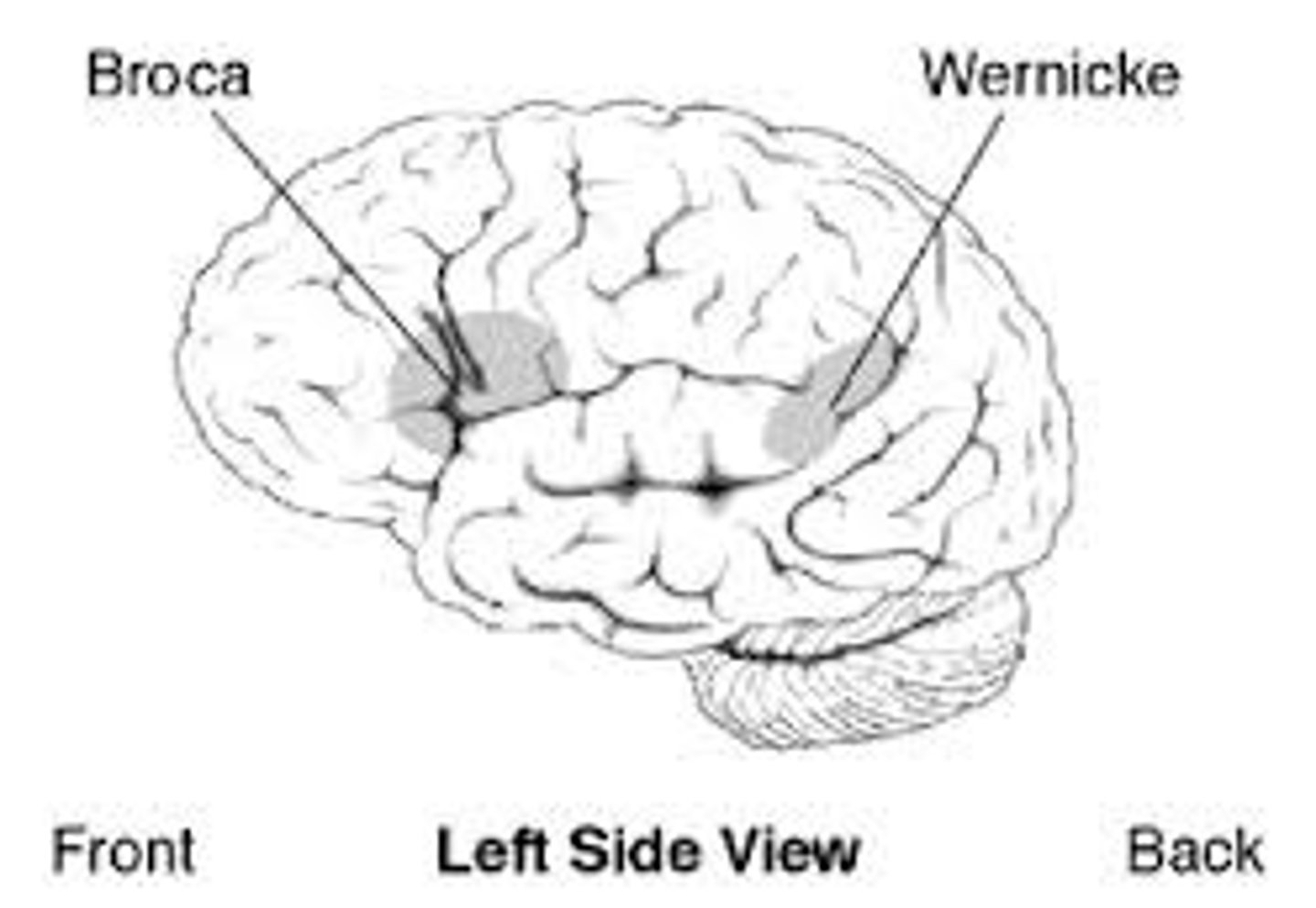
Broca's area
controls production of speech sounds.
- located in the frontal lobe
- usually in the left hemisphere
-damage in this area causes "aphasia"
Broca's Aphasia
-impairment in the physical ability to produce speech sounds or, in extreme cases, an inability to speak at all
-caused by damage to Broca's area
expressive aphasia
-know vocabularies but cannot move the lips the way person wanted to
Motor cortex
-controls all voluntary movements.
-right motor cortex controls movement on the left side of the body and left motor cortex controls right side
-the parts of the body capable of the most finely coordinated movements have a larger share of the motor cortex (fingers, lips, tongue)
-movement in the lower part of the body is controlled by neurons at the top of the motor cortex vice versa (columnar organization)
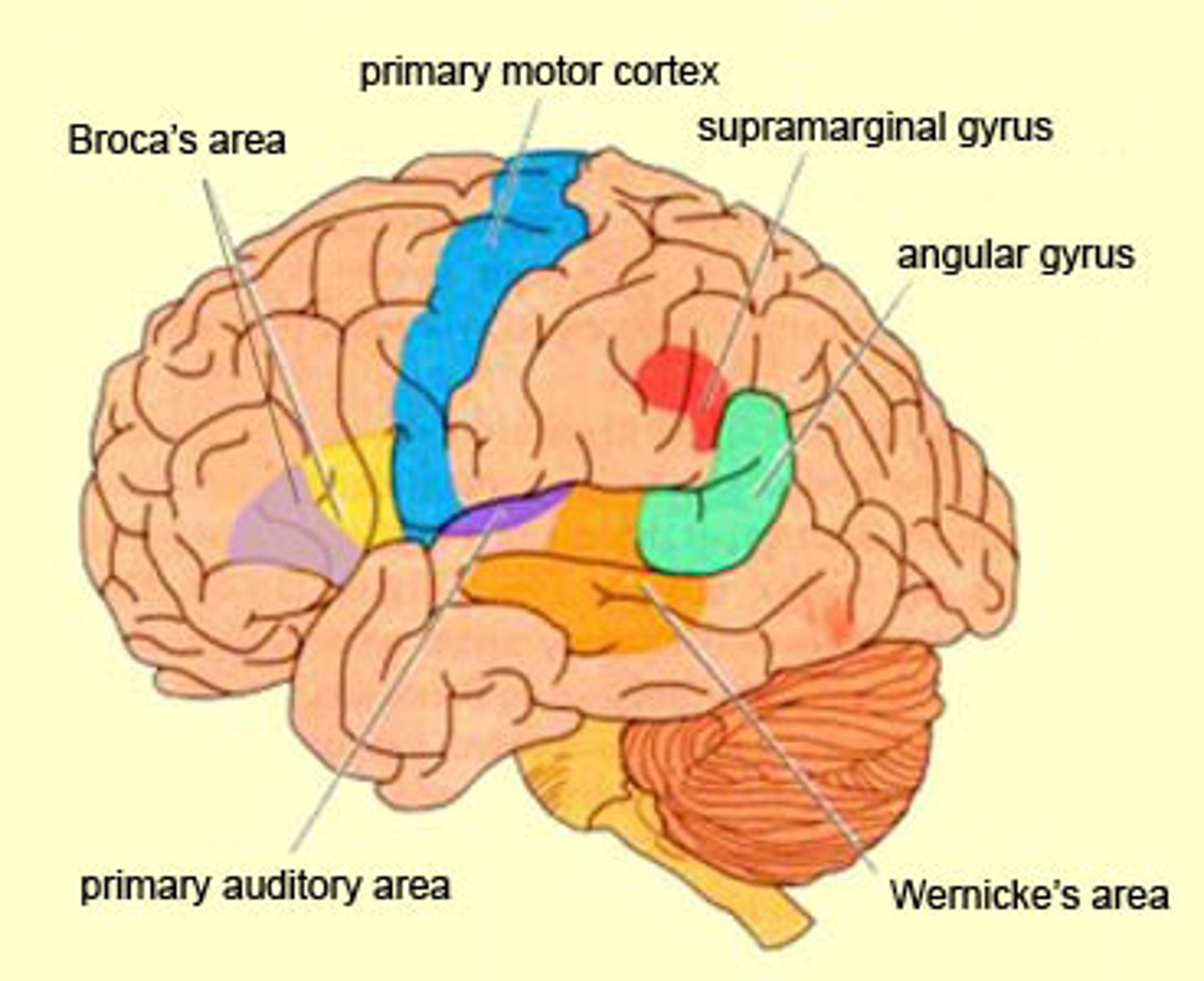
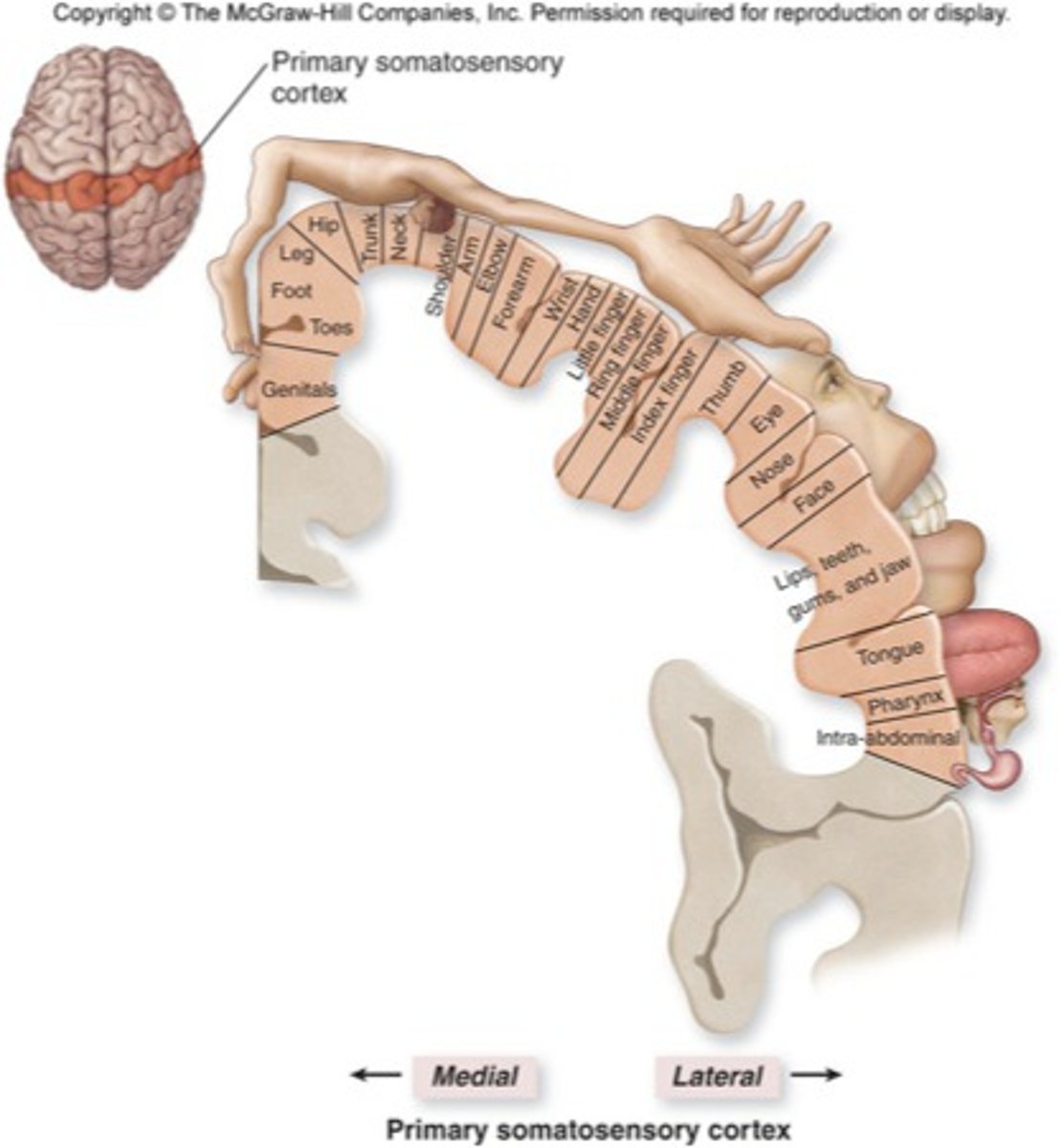
Parietal Lobe
-receives information relevant to body awareness, spatial orientation; includes the somatosensory cortex.
-involved in reception and processing of touch stimuli
Somatosensory Cortex
Interprets touch, pressure, temperature, and pain.
● located at the front of the parietal lobes.
● where touch, pressure, temperature, and pain register in the cortex.
Occipital Lobe
Receives visual information from the eyes; includes primary visual cortex.
Primary visual cortex
interprets visual input.
- area at the rear of the occipital lobes where vision registers in the cortex.
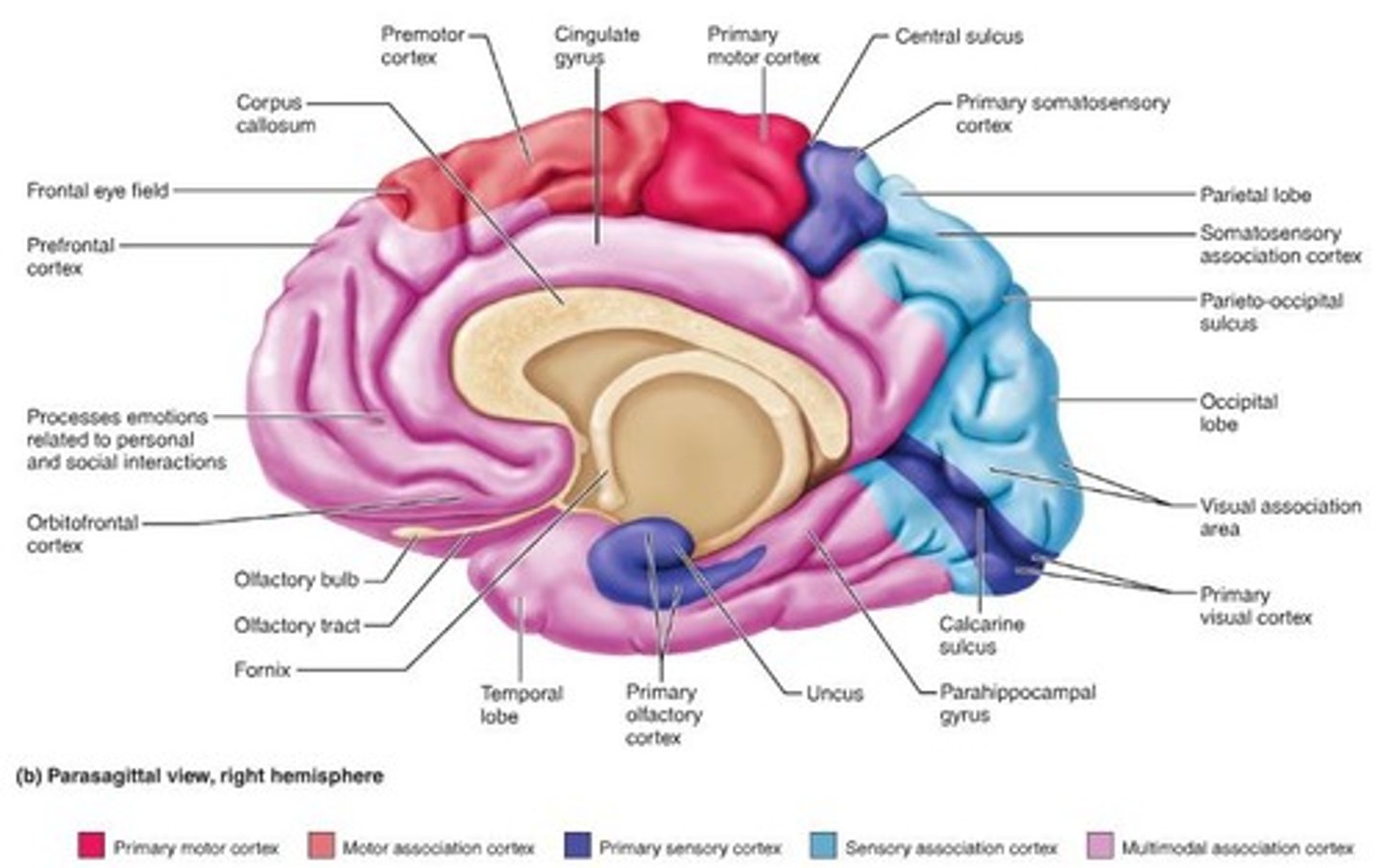
Temporal Lobe
Receives auditory information from the ears; contains primary auditory cortex and Wernicke's area.
Wernicke's area
-interprets language; controls comprehensibility of speech.
- language area in the left temporal lobe involved in comprehending spoken language and formulating coherent speech and written language
Primary auditory cortex
interprets sounds.
Aphasia
a loss or impairment of the ability to use or understand language, resulting from damage to the brain (in Broca's area).
Synaptogenesis
occurs in spurts throughout the life
span.
Pruning
process through which the developing brain eliminates unnecessary or redundant synapses follows periods of synaptogenesis.
Stroke
an event in the cardiovascular system in which a blood clot or plug of fat blocks an artery and cuts off the blood supply to a particular area of the brain.
Myelination
development of myelin sheaths around axons.
- begins prior to birth but continues well
into adulthood
Plasticity
the capacity to adapt to changes is maintained throughout life.
Women's Brains
- Equal proportions of gray and white matter in the left and right hemispheres.
- More gray matter in the area of the brain that controls emotions.
● may explain women's superior ability to perceive emotions.
Men's Brains
- Lower proportion of white matter in the
left hemisphere than in the right.
● may explain men's superior ability in spatial tasks.
- Navigational Information
● use left hippocampus.
Endocrine System
- system of ductless glands
● manufacture hormones
● secretes hormones into bloodstream
hormone
● chemical substance that is manufactured and released in one part of the body and affects other parts of the body.
Endocrine Glands
- pituitary gland
● "master gland."
● releases hormones that activate other endocrine glands
- pineal gland.
● secretes melatonin, which controls sleep/wakefulness cycle
Thyroid Gland
- located below the voice box - produces thyroxine.
● regulates rate of food metabolization.
Parathyroid Gland
- produces parathyroid hormone.
● helps the body absorb minerals from the diet.
Thymus Gland
- produces thymosin.
- regulates immune system.
Adrenal Gland
- releases hormones that prepare the body for emergencies and stressful situations.
Pancreas
- the endocrine gland responsible for regulating the amount of sugar in the bloodstream.
Gonads
- ovaries in females.
- testes in males.
- produce sex hormones.
Genes
- segments of DNA located on
chromosomes.
- transmit all heredity traits.
Chromosomes
- 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) contain
20,000 to 25,000 genes.
- 22 matching pairs called autosomes; 23rd pair are sex chromosomes.
Genotype
- An individual's genetic makeup
Phenotype
- An individual's actual characteristics
dominant
● It is only necessary that one gene be present on chromosome pair for a given trait to be expressed.
recessive
Two genes are required on the chromosome pair for trait expression.
Polygenetic Inheritance
Many genes influence a particular
characteristic.
Multifactorial inheritance
influenced by genes and environmental factors
Sex-Linked Inheritance
involves genes on the X and Y chromosomes.
● example: red-green color blindness.
Behavioral Genetics
- investigates the effects of heredity and environment on behavior
Twin Studies
- examine identical (monozygotic) and fraternal (dizygotic) twins in order to compare similarities and differences in twin pairs.