Carboxylic acids and derivatives
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What are esters?
Derivatives of carboxcylic acids
How do you name an ester?
Name right hand side of the molecule first which is the prefix e.g. Ethyl
Name left hand side of the molecule next which is the suffix e.g. ethanoate
Name is ethyl ethanoate
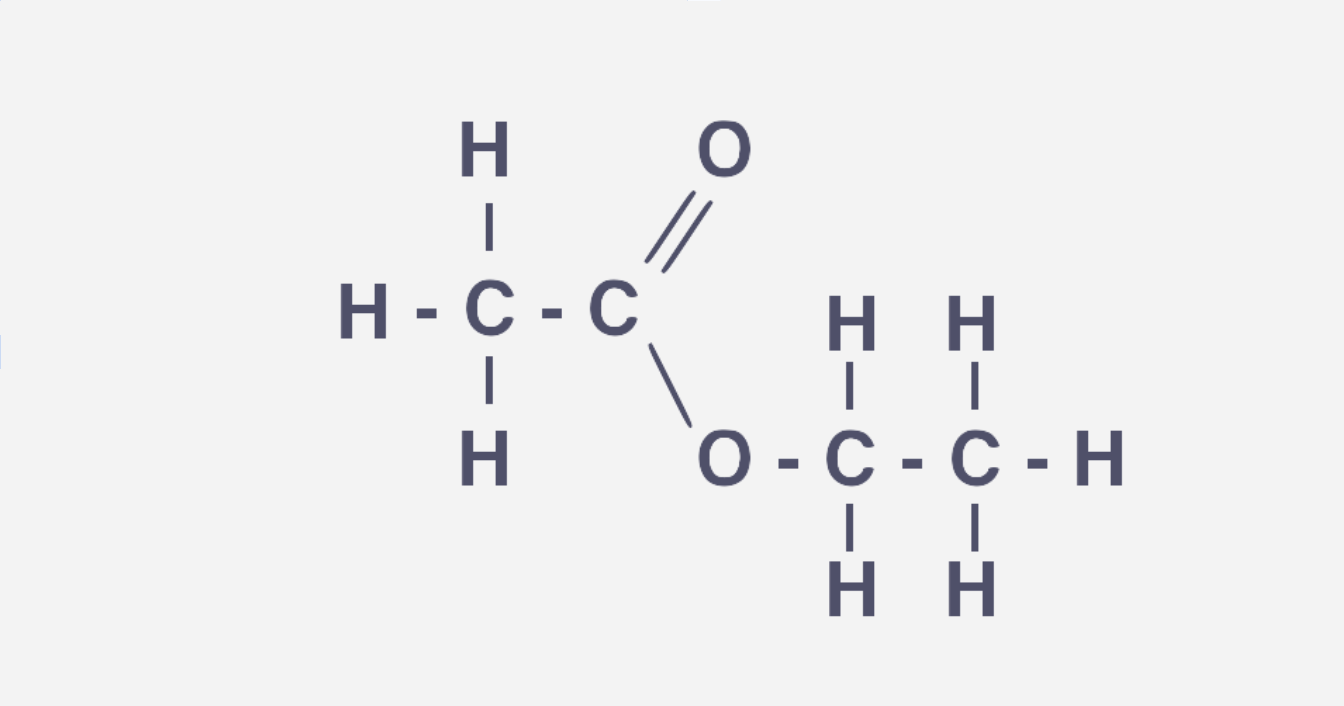
Intermolecular forces of esters
Ester have weaker IM forces so they have lower BPs than carboxcylic acids and alcohols
As they cannot form hydrogen bonds with each other as they lack a partially positive H (while alcohols and carboxcylic acids can)
Why can esters form hydrogen bonds with H2o ?
Oxygen atoms in an ester have lone pairs of electrons that attracts the partially positive H of H2o
Check notes for additional guidance.
What the name for forming ester and how are they formed ?
Esterification
Reaction between a carboxcylic acid +alcohol → ester + water
Esterification is a reversible reaction
Explain how you can get your ester from esterification
Get rid of the H from the OH of carboxcylic acid
Get rid of OH from alcohol
Add remaining structure of alcohol to the acid to get ester.
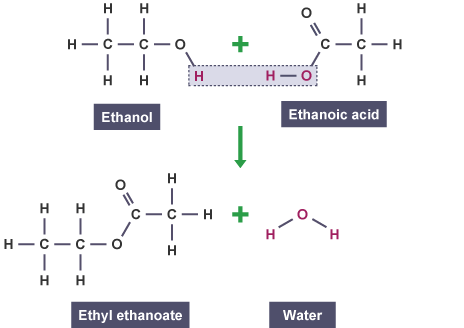
Conditions for an esterification reaction
Reaction is quite slow so an acid catalyst is used (Typically H2SO4)
And reaction is heated under reflux
Esterification also called a condensation reaction
Why is esterification reversible?
Ester can react with water to produce a carboxcylic acid and alcohols
Known as hydrolysis of esters
In what 2 conditions can esters be hydrolysed in?
Acid conditions
Alkaline conditions
Reagent needed to hydrolyse an ester in acidic conditions
Dilute HCL- (source of H+ catalyst)
Heat under reflux
Reaction is reversible
What do you get when ethyl propanoate is hydrolysed (in acidic conditions)
Propanoic acid
Ethanol
(Whatever is the ..oate becomes the acid)
How is hydrolysis of an ester in alkaline conditions different?
Not reversible
Will form a carboxylate salt (and alcohol) instead of acid
This reaction also called saponification
What are the products when ethylethanoate reacts with NaOH (hydrolysis in alkaline conditions)- How did we get the products?
CH3COO-Na+ →Sodium ethanoate (carboxylate salt)
CH3CH2OH → Ethanol
For the salt get rid of the CH2CH3 of ethyl ethanoate and replace it with Na
The CH2CH3 you got rid of becomes the alcohol
Why is saponification not a reversible reaction?
Carboxylate salt is negatively charged.
Negative charge is delocalised over the 2 oxygen atoms
Making the carbonyl carbon less positively charged
So it is resistant to attack by weak nucleophiles like alcohols
(So the products don’t react to form the reactants)
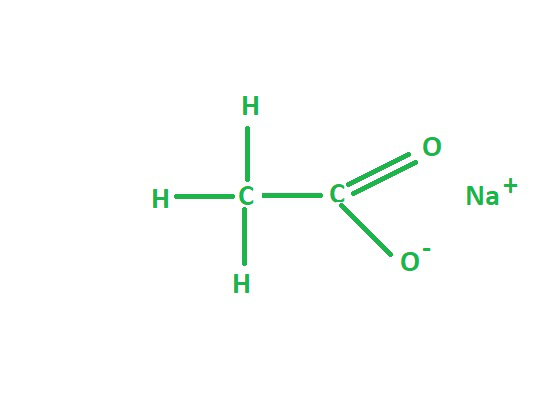
Conditions for hydrolysis in alkaline conditions
Reagent: Dilute NaOH
Heat under reflux
Excess NaOH → To ensure the seter is completely hydrolysed into its carboxylate salt and alcohol.
Uses for esters and why
Solvents - as esters are polar
Plasticisers- added to pure polymers to increase flexibility as esters reduce the IMF between the polymer chains
Perfumes and food flavouring - due to pleasant smells and taste
(Esters used in food flavouring and perfumes must be non toxic)
For esters to be used in perfumes what conditions must be met?
Esters must be soluble in alcohol
Must not react with water
And must be volatile (can turn into gas/vapour)
What happens when we react glycerol and fatty acids?
Glycerol (alcohol)
Fatty acids (long chain carboxcylic acids)
Produce fats and oils -which are naturally occurring esters (also called triglycerides)
Fatty acids can be ..
Saturated
Unsaturated
What are poly unsaturated fatty acids?
Unsaturated fatty acids with more than one double bond
Properties of vegetable oil
Have unsaturated hydrocarbon chains
That are not straight, which means the chains cannot pack closely together
Lower Vander Waals forces
So veg oils have lower melting points and are liquids at room temperature
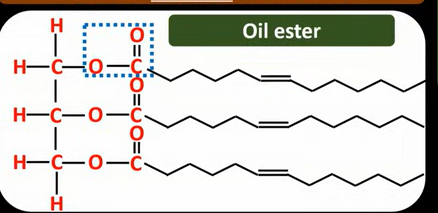
Why are the unsaturated hydrocarbon chains not straight in oils?
Have a cis double bond
Hydrogen atoms are on the same side of the double bond
Creating a kink in the chain
Kink prevents tight packing of the chains
Properties of fat
Fats (animal fat) have saturated hydrocarbon chains
That are straight and more uniform than oils
They can pack together closely
Higher Vander Waals forces
High Melting points and are solids at room temperature
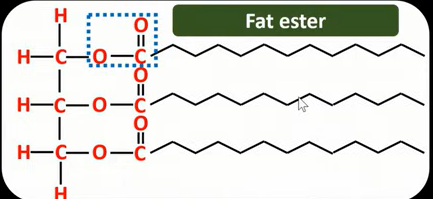
How can soap be produced?
Animal fats and vegetable oils can be hydrolysed by heating them with NaOH
Producing soap
Equation for the production of soap
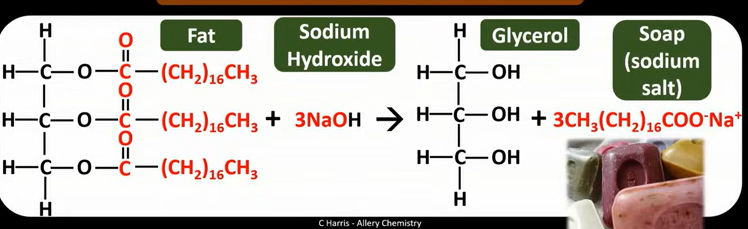
How can vegetable oils be converted into biodiesel?
Reacting oils with methanol
And KOH as a catalyst
What is biodiesel?
A mixture of fatty acid methyl esters
(Made from reacting methanol with rapeseed oil)
Equation for production of biodiesel
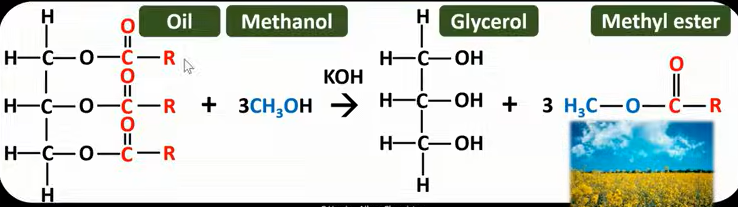
Functional group of acyl/acid chlorides
and how to name them
COCL (acyl group)
Carbon attached to acyl group is always carbon number 1 and acyl group is always on the end
Find the longest carbon chain and then add “oyl chloride” to the end
What can react with acyl chlorides?
Water
Ammonia
Alcohol
Primary amines
*In each reaction Cl is substituted for either an Oxygen or Nitrogen
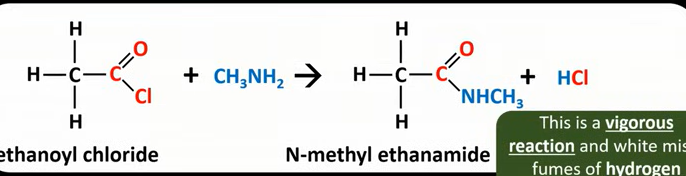
What is produced when acyl chlorides react with the 4 reactants listed and what is the nature of the reaction?
White misty fumes of hydrogen chloride gas
Vigorous reaction
Acyl chloride+ H2O → ?
Carboxcylic acid
HCL (Hydrogen chloride gas)
Acyl chloride + NH3→?
Amide (Cl of acyl chloride replaced with NH2)
HCL
Acyl chloride+ Alcohol→?
Ester
HCL
Acyl chloride+ Primary amine→?
N- substituted amide
HCL
E.g If the amine is CH3NH2
The CL group of the acyl chloride is replaced with NHCH3
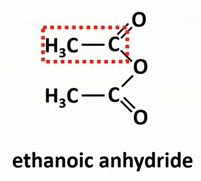
What are acid anhydrides and how do you name them?
A molecule made from 2 carboxcylic acids
Identify the carboxcylic acid and replace “acid” with “anhydride”
What do acid anhydrides react with and what’s the nature of the reaction?
H2O
NH3
Alcohols
Primary amines
Less vigorous
Acid anhydride + H2O → ?
2 carboxcylic acids
Acid anhydride+ NH3→ ?
Amide
Carboxcylic acid
BUT if NH3 is in excess a carboxylate salt is produced instead of acid
E.g instead of ethanoic acid you will get CH3COO-NH4+
Acid anhydride + alcohol→ ?
ester
Carboxcylic acid
Acid anhydride + Primary amines→?
N-substituted amide
Carboxcylic acid
E.g instead of ethanoic acid you get CH3COO-CH3NH3+ (methylammonium ethanoate)
What do both acid chlorides and acid anhydrides have, that allow them to go through nucleophilic addition elimination?
A strong partial positive charge on carbon atom(s) in the carbonyl group(s)
Which is susceptible to attack from nucleophiles
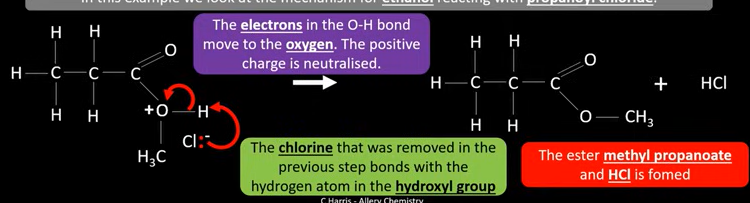
Nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism for propanol chloride reacting with ethanol: part 1
Ethanol is a nucleophile and attacks partially positive carbon
Pair of electrons from double bond is then transferred to oxygen -double bond breaks
Lone pair of electrons on the oxygen move to remake double bond
Electrons from c-cl bond move to cl→ bond breaks

Nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism for propanol chloride reacting with ethanol: part 2
Chlorine that was removed in the previous step bonds with hydrogen atom in the hydroxyl group -HCL breaks off
Electrons in the OH bond move to the positive O →Neutralising the charge
Producing methyl propanoate and HCL
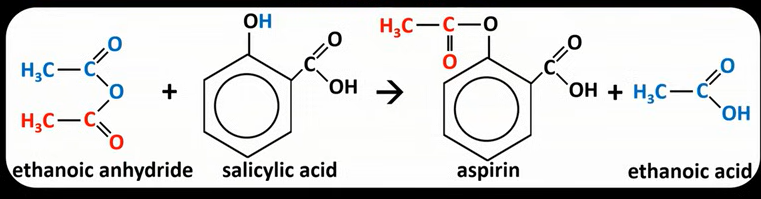
What is aspirin?
An ester made by reacting ethanoic anhydride or ethanoyl chloride with salicylic acid
Why is ethanoic anhydride used instead of ethanoyl chloride in the production of aspirin?
Ethanoic anhydride is less corrosive
Does not produce harmful HCL gas
Also cheaper and don’t react vigorously with water
Equation for ethanoic anhydride + salicylic acid to produce aspirin?
What is reflux/refluxing
Technique used to heat a mixture of volatile liquids
Reflux allows strong heating without losing volatile reactants and products
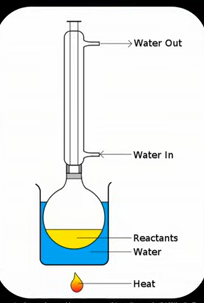
Reflux apparatus
Liebig condenser has cold water running through the walls
When hot evaporating substances hit the condenser they turn back into a liquid and return back to round bottomed flask to react further
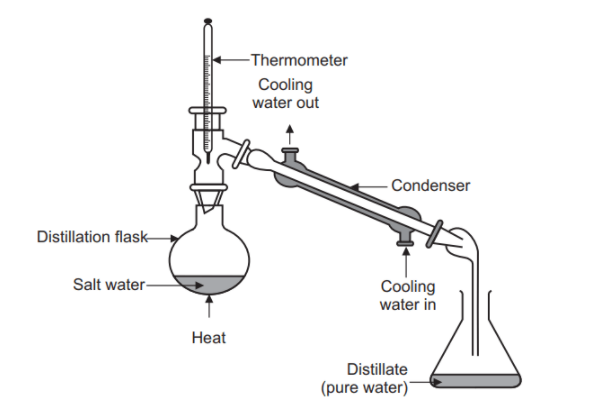
When is distillation used
To separate substances with different boiling points
Gently heating the mixture will result in compounds separating out in order of boiling points
Why may a sample be re-distilled?
In order to further purify it
As it can still contain other substances if boiling points of those substances are very close to BP of desired compound
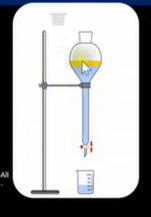
Why may a separation funnel be used?
Separate immiscible liquids (liquids that don’t mix together)
Purify an organic product
How a separation funnel works?
Add sample into separating funnel→ add water to dissolve soluble impurities
2 layers will form → Top layer is impure product, bottom layer is aqueous containing water soluble impurities
Drain aqueous layer by removing stopper
Remove impure product from funnel and add into round bottomed flask
Add anhydrous cacl2 (solid) →dehydrating agent and will remove aqueous substances still remaining
Invert the flask and leave for 20/30 minutes
Filter the solid drying agent
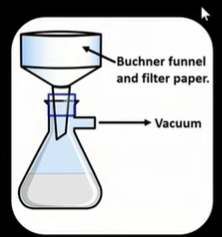
What is Buchner funnel used for
Vacuum used to help separate liquid and solid components thoroughly.
How do you use Buchner funnel?
Place filter paper disc in funnel and dampen slightly to make a seal
pour reaction mixture into funnel and ensure vacuum source is on
Vacuum creates a reduced pressure in flask and pulls the liquid through
Solid will be left in Buchner funnel
(In the case of aspirin the solid component is what we are after)
Why is recrystallisation used?
To purify an impure solid
Steps for recrystallisation
Dissolve impure solid in a minimum volume of hot solvent → Minimum volume maximises the amount that will recrystalise
Hot filtration to remove insoluble impurities
Allow solution to cool and crystalise → Can put in ice bath to maximise crystal formation. (soluble impurities stay dissolved)
Use a vacuum (Buchner funnel) to filter the crystals
Wash crystals with cold solvent to remove remaining soluble impurities stuck to the surface of crystals
Dry crystals
How can you determine the purity of a liquid ?
Measuring its BP via distillation
Gently heat the sample and ,measure the temperature at which it distils using a thermometer → which will give you its BP
How do you know if a liquid contains impurities?
Measured BP is higher than data book value
If it boils over a range of temperatures instead of just 1
*Various organic products have the same BP→ so other techniques like mass spectrometry may need to be used
How do you determine the purity of a solid?
Measuring its melting point
Add sample of solid product into a capillary tube and place into the heating element of the MP apparatus
Slowly increase temp until sample begins to melt
There will be a temp range from when solid just starts to melt to when it fully melts
Compare values to data book value.
How do you know if a solid contains impurities?
Temp range the substance melts at is larger then data book range
If MP is lower than data book value→ as pure solids have a regular ordered crystal lattice, impurities fit irregularly into the lattice and weaken IMF so MP is lower