ACh transmission modulators
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
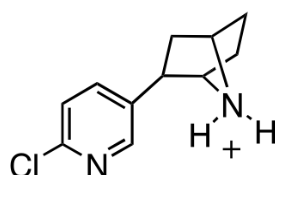
Nicotine
agonist
binds to neuronal nAChR, activating it
releases dopamine
similar structure to ACh
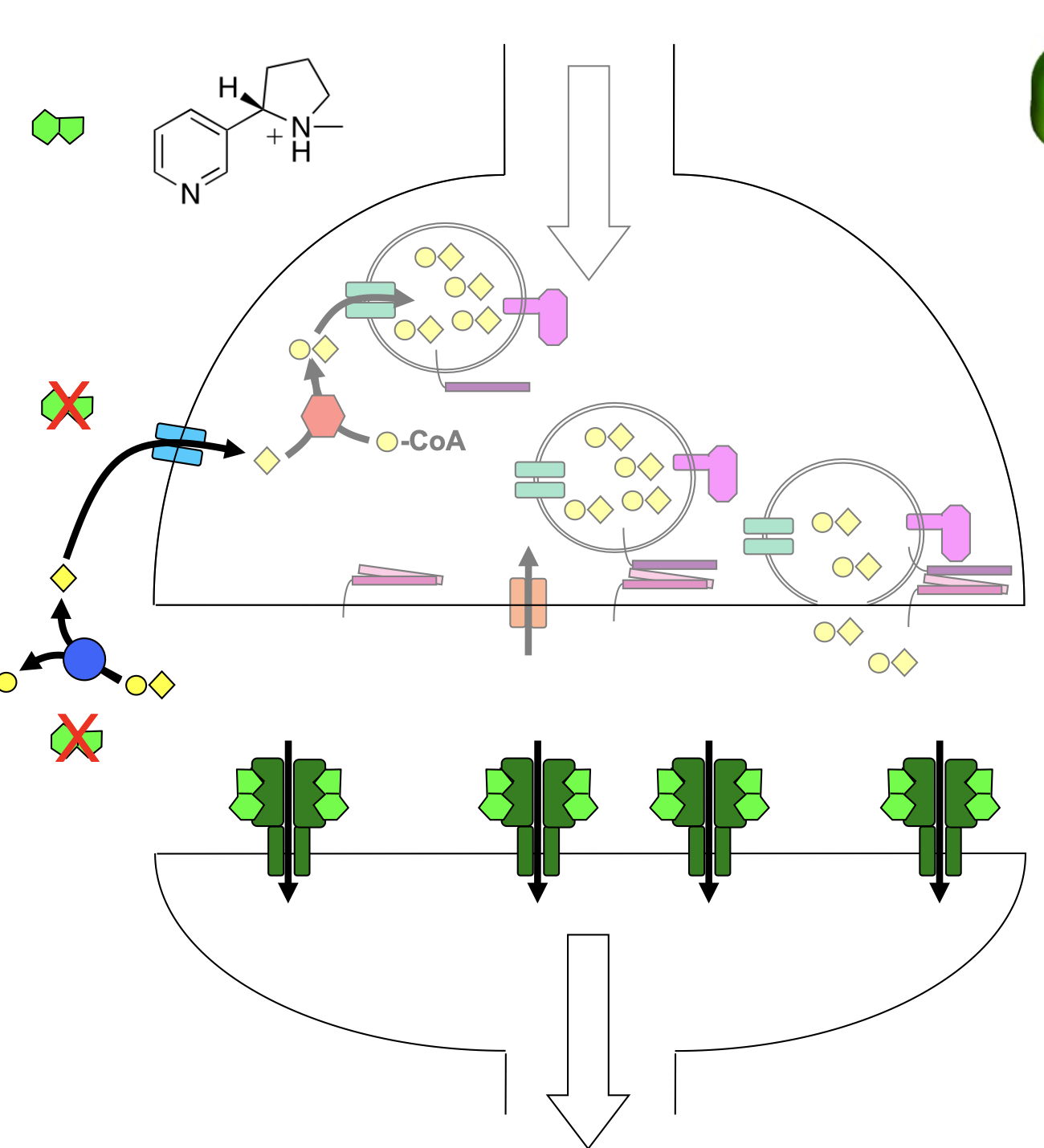
chantix (varenicline)
partial agonist: competitive modulator
binds more tightly to nAChR than nicotine but does not cause receptor to open as much
partial mimicry of ACh structure: ring system instead
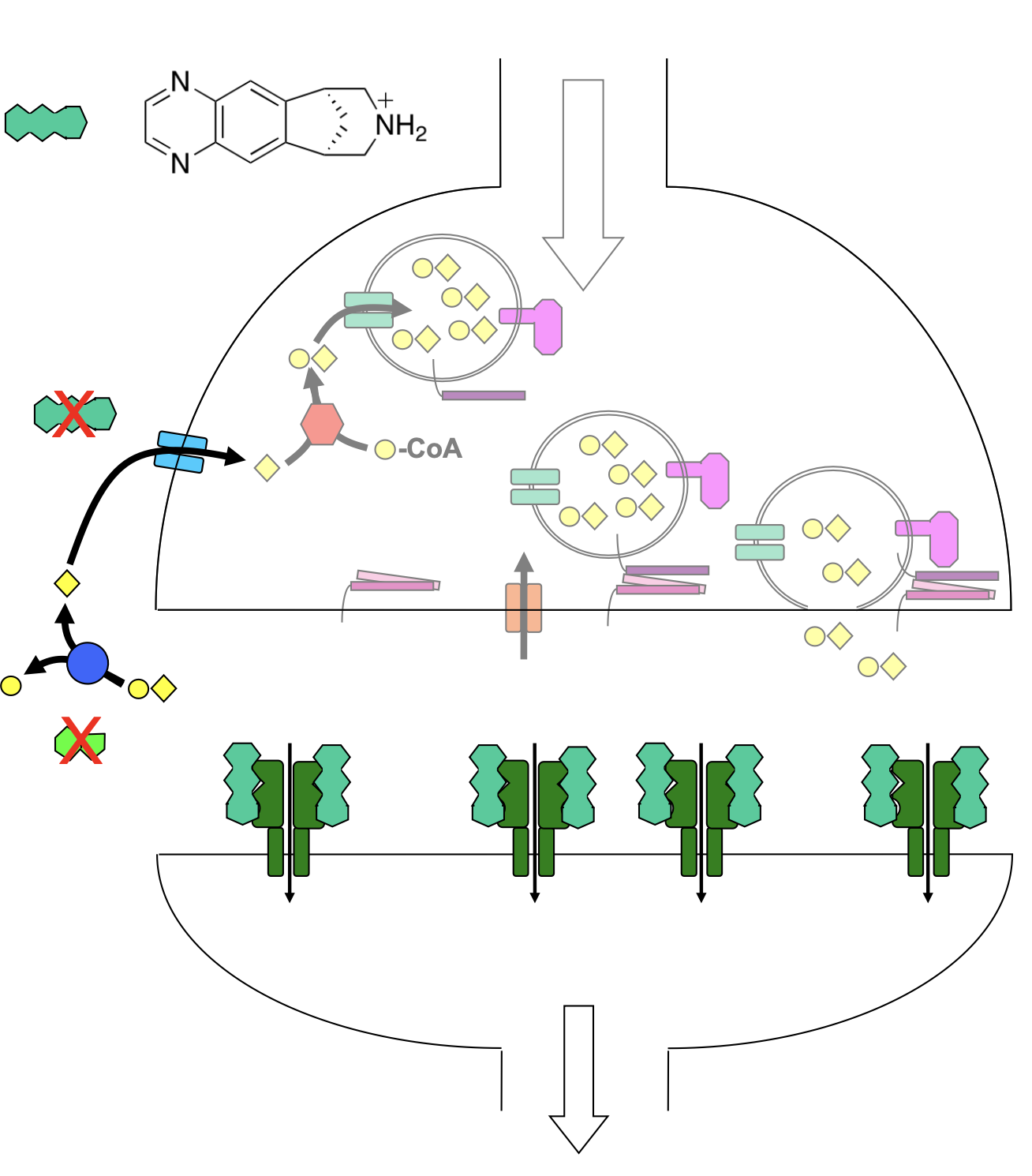
Conotoxin (snail venom)
antagonist, binds to muscle nAChR
prevents channel from open (cys loop pushed out)
no muscle activation
structure: surface is rigid and structured
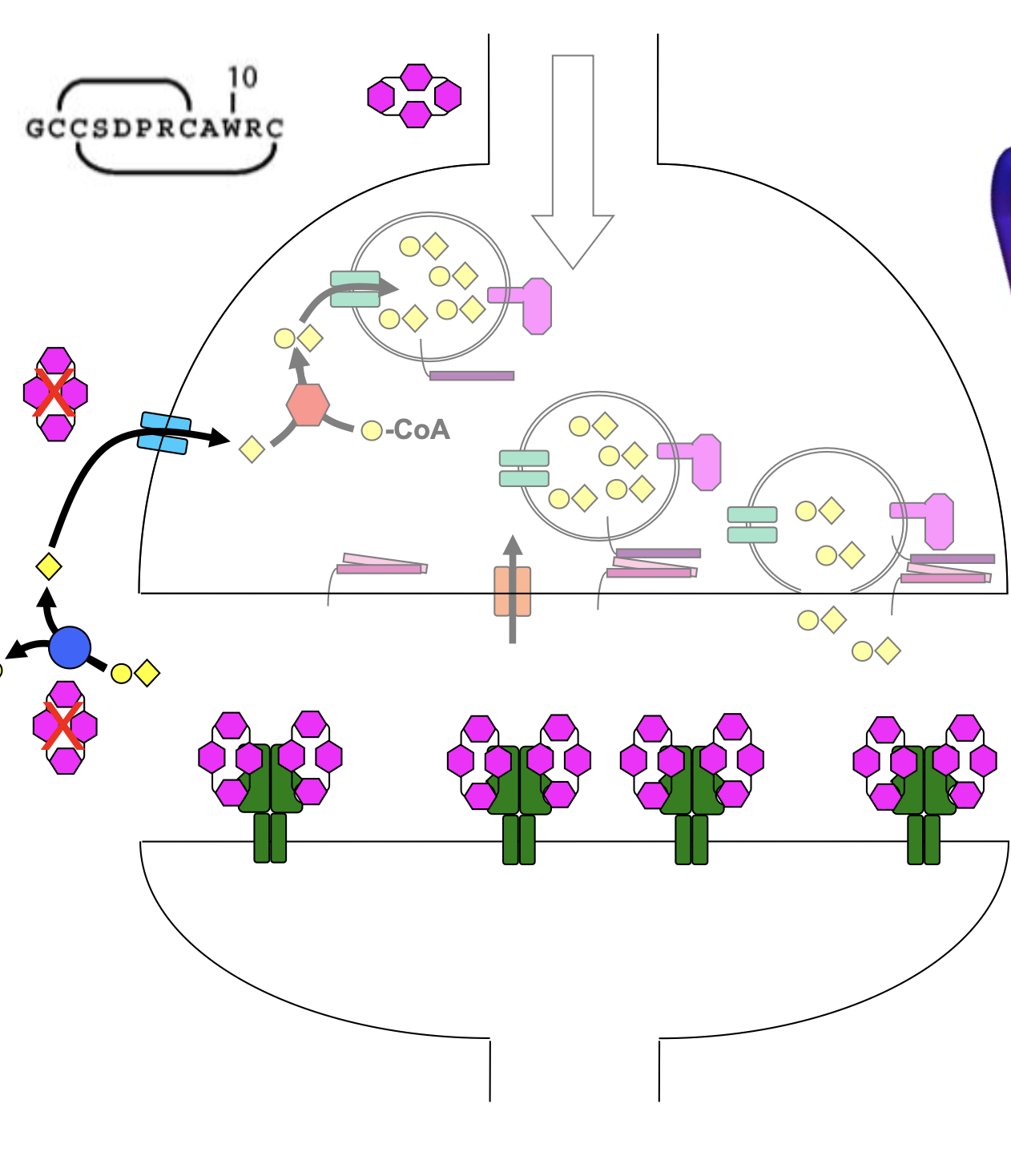
galantamine
noncompetitive inhibitor, binds to allosteric sites on nAChRs in prescence/absence of ACh
decreases activation of the nAChR
competitive reversible inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
binding prevents hydrolysis of ACh in neurons
slows cognitive decline in AD patients
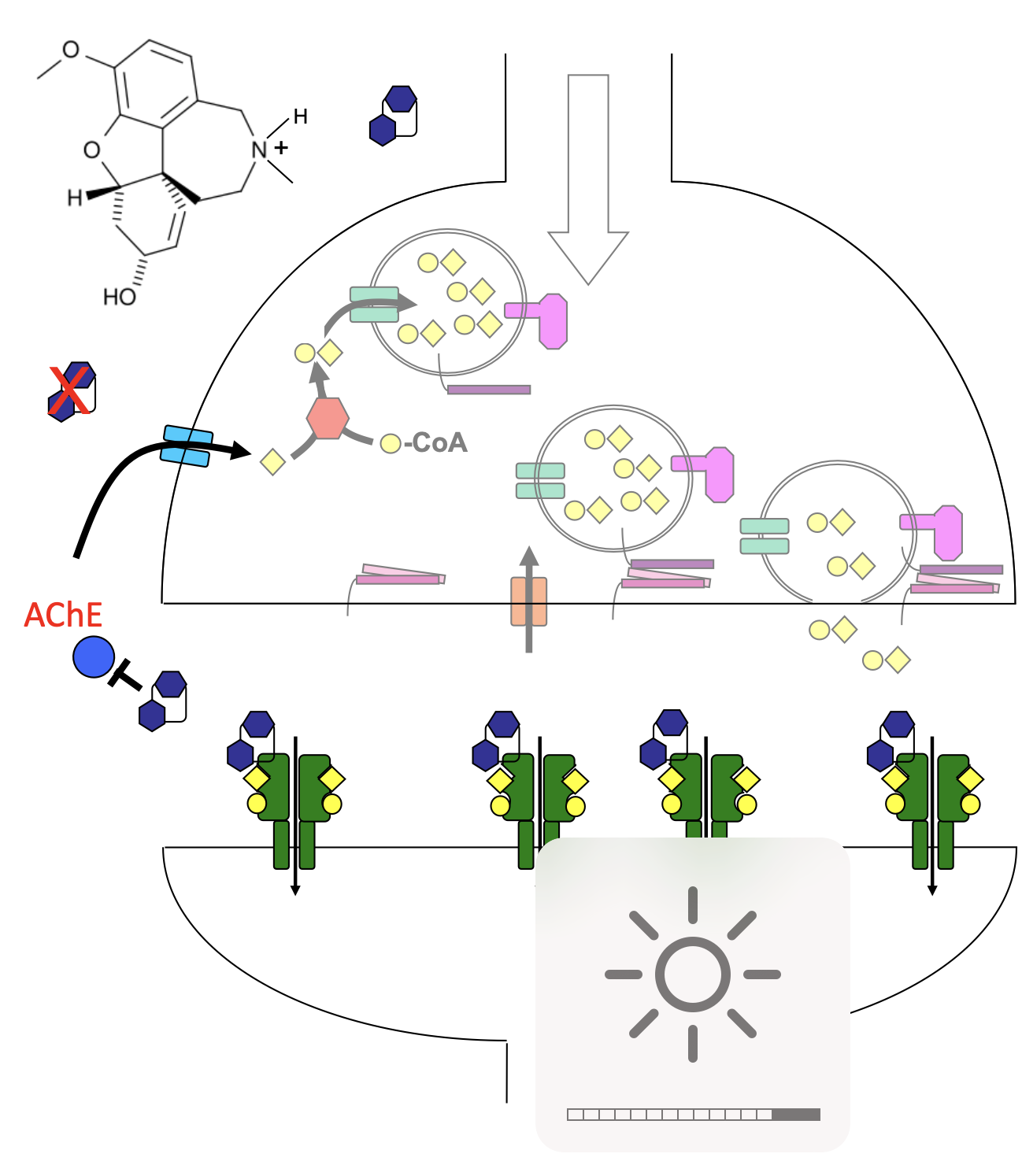
hemicholinium
mimics Choline, binds in cleft of choline transporter but too large to pass through
slows ACh synthesis
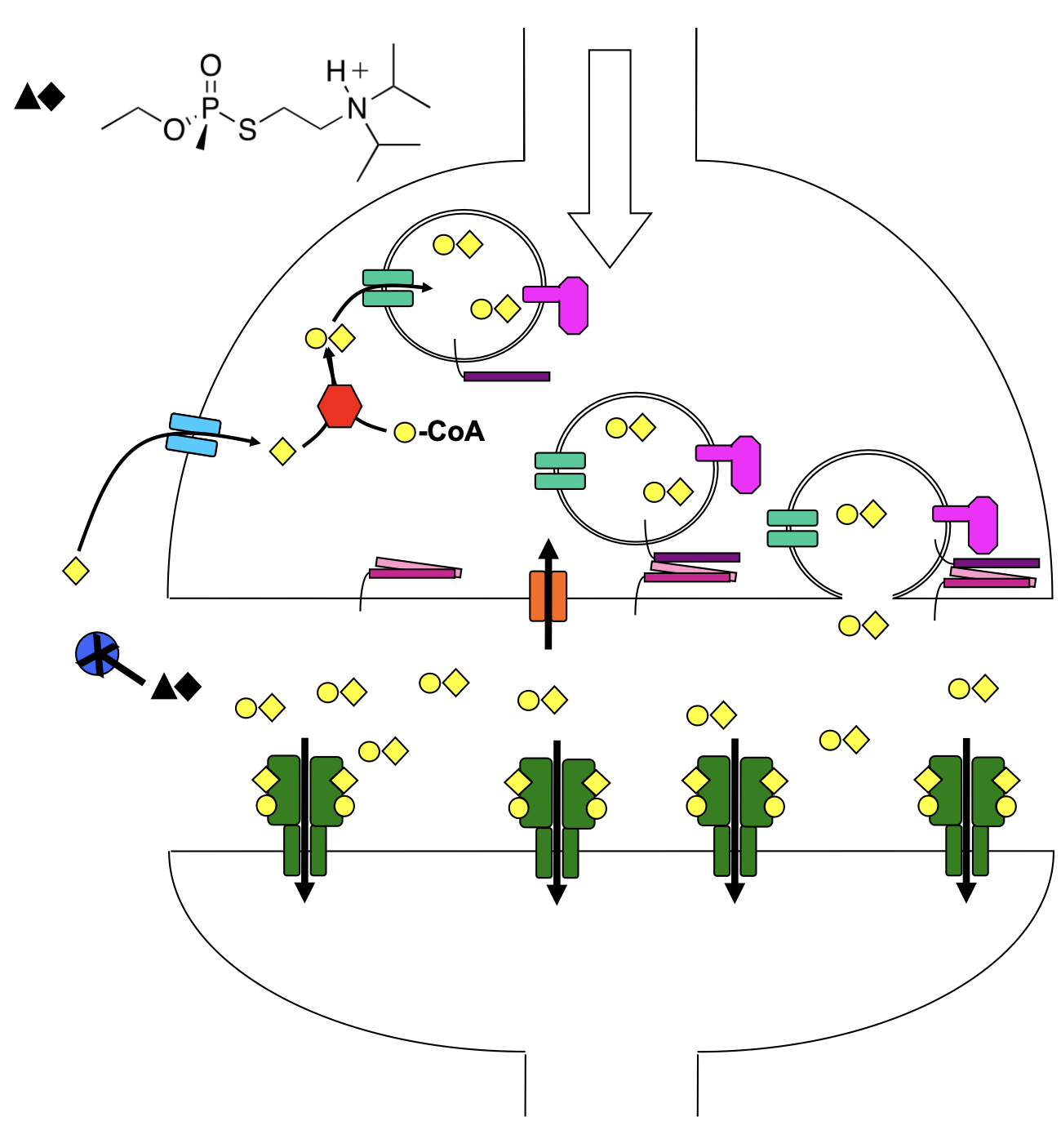
can offset ACh accumulation by VX
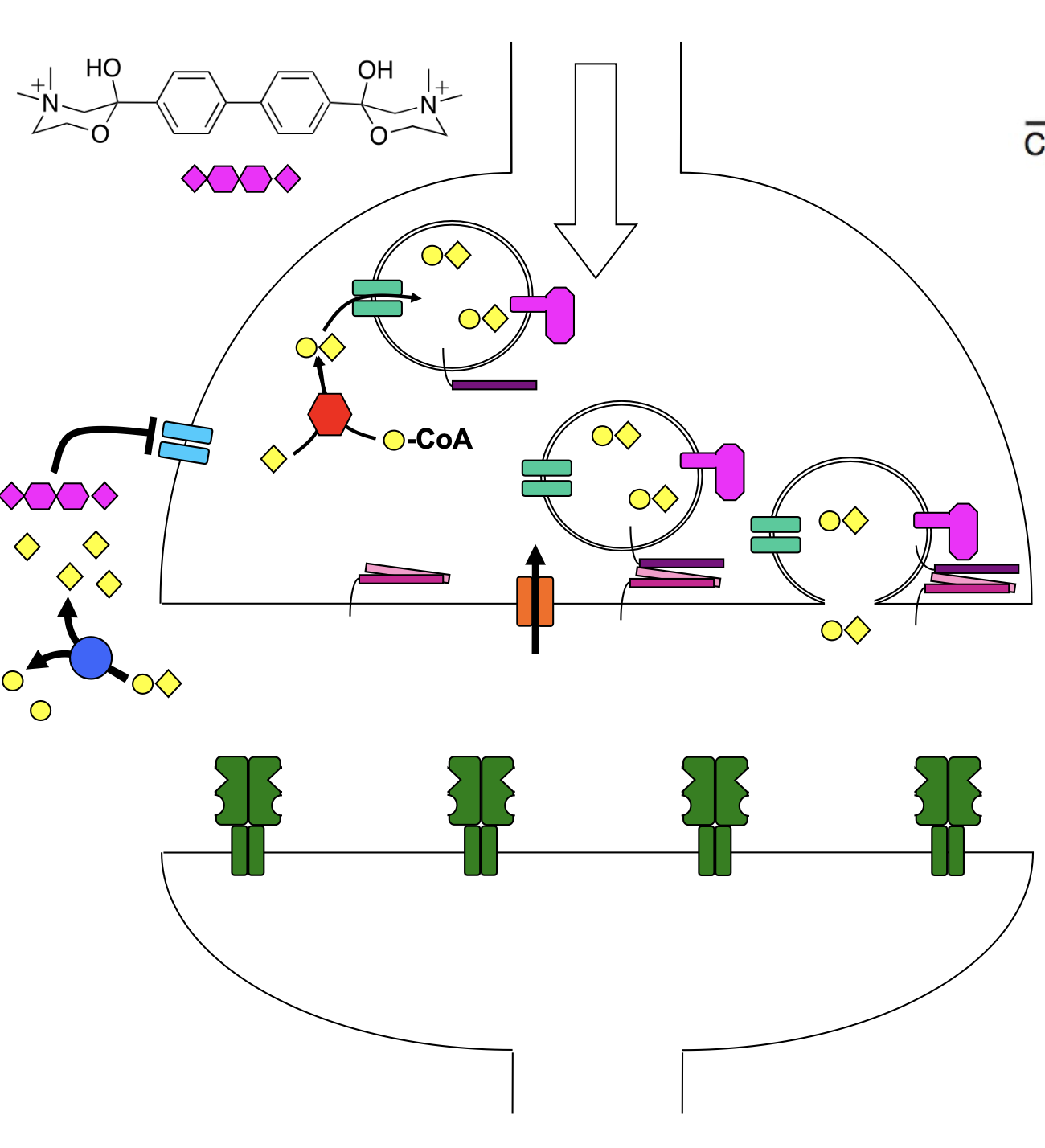
VX Gas
irreversibly inhibits AChE: its phosphonate not hydrolyzed; highly reactive
active site serine of AChE attacks phosphorus instead of breaking down ACh using the Ser-His-Glu triad
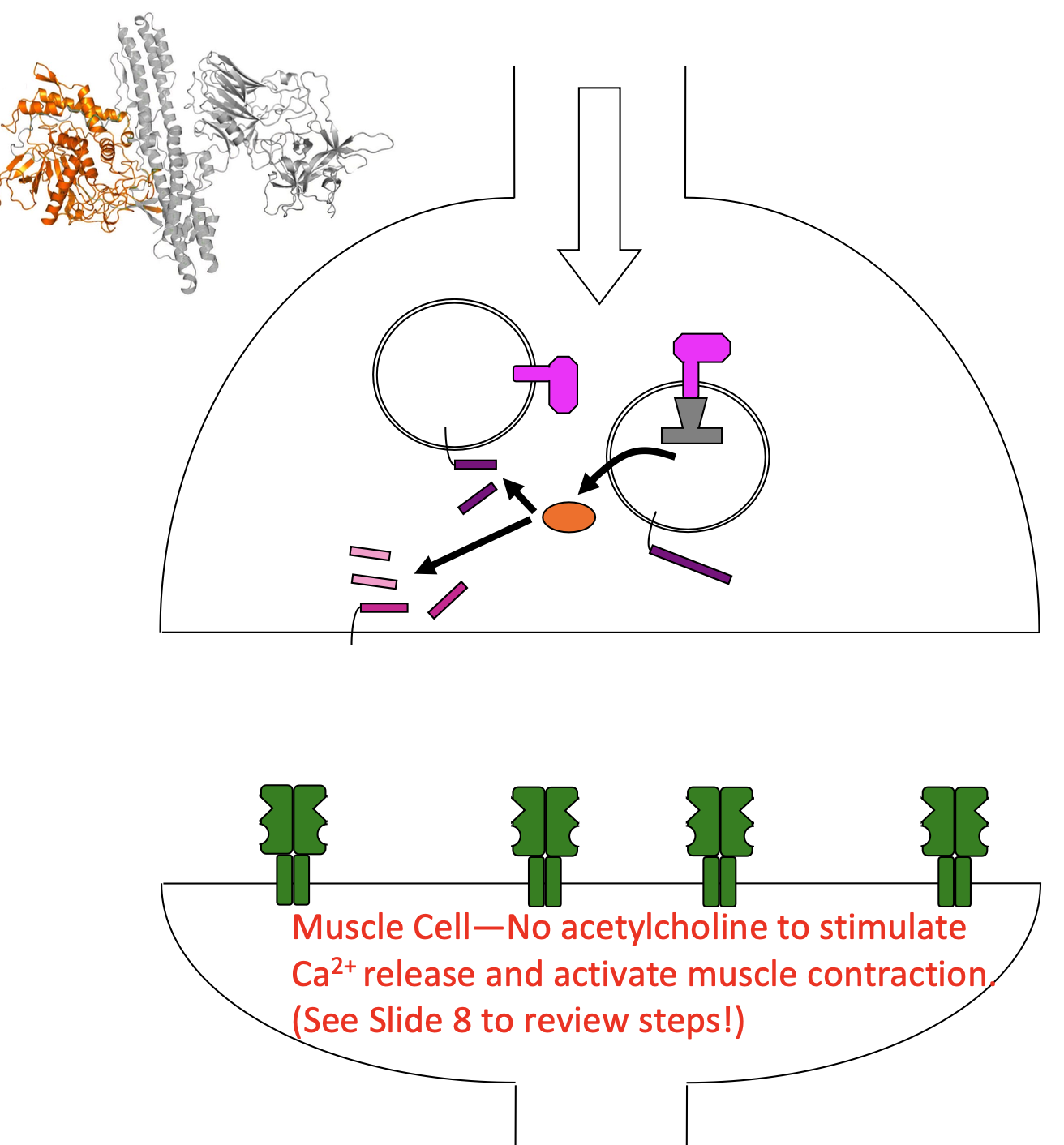
Botox
heavy chain binds to synaptotagmin
gets imported with recycled empty vesicles
light chain released into cytosol
cleaves SNARE proteins
ACh release into synaptic cleft inhibited
no muscle contraction
epibatidine
agonist of ACh
very high binding affinity, very potent
blocks pain receptors without being an opioid but very toxic